ATI Custom 23 WN 250 Exam
Total Questions : 50
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is monitoring a client who is receiving packed RBCs. The nurse identifies which of the following as an expected finding?
Explanation
A. The drip chamber should not be filled completely with blood, as this can cause clotting and occlusion.
B. The blood should not be infused for more than 4 hr, as this increases the risk of bacterial contamination and transfusion reactions.
C. Medications are usually administered separately from blood products to avoid incompatibility.
D. The packed RBCs should be connected by Y tubing to normal saline to prevent hemolysis and maintain fluid balance. This is an expected finding because it allows the nurse to flush the line with normal saline before and after the blood transfusion, and to switch to normal saline in case of a transfusion reaction.
A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving an IV infusion of dextrose 10% in water. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following adverse effects?
Explanation
A: Dextrose 10% in water does not contain calcium, so hypercalcemia is not a concern.
B: Dextrose 10% in water provides hydration and is not associated with hypovolemia.
C: Dextrose is a form of sugar, and its infusion can lead to increased blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia).
D: Dextrose 10% in water does not affect potassium levels, so hypokalemia is not a concern.
A nurse is applying knowledge to analyze a clinical situation. Which of the following roles is the nurse taking?
Explanation
A: Educator involves providing information and teaching, which is not explicitly related to analyzing a clinical situation.
B: Advocate involves supporting and defending the client's rights but doesn't necessarily imply analyzing a clinical situation.
C: Mentor involves guiding and advising, but it's not directly related to analyzing a clinical situation.
D: Critical thinker involves using knowledge and experience to analyze and solve complex problems in clinical situations.
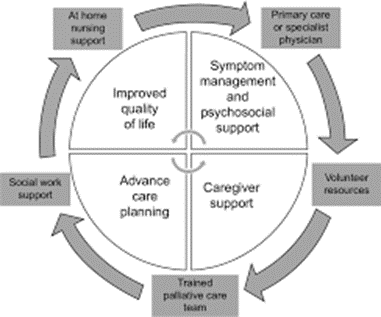
A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a terminal illness and is considering palliative care services. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
A: Palliative care includes holistic care, but it's not primarily focused on managing meals.
B: Palliative care can be provided at various locations, including the client's home, not necessarily a skilled facility.
C: While palliative care may support caregivers, its primary focus is on the comfort and well-being of the client.
D: Palliative care aims to make the client comfortable physically, emotionally, and spiritually during a terminal illness.
A nurse is assessing a client who is experiencing hypervolemia. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
A: Hypervolemia is often associated with increased fluid volume, which typically results in an increased heart rate (tachycardia), not bradycardia.
B: Peripheral edema is a common manifestation of hypervolemia due to the excess fluid in the extracellular space.
C: Hypervolemia is more likely to cause increased blood pressure (hypertension), not hypotension.
D: Oliguria (decreased urine output) is associated with hypovolemia, not hypervolemia.
A nurse is assessing a client who has hypokalemia as a result of nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
A: Hypokalemia is associated with hypoactive reflexes, not hyperactive reflexes.
B: Hyperactive bowel sounds are more indicative of hyperkalemia, not hypokalemia.
C: Weak, irregular pulse is a common manifestation of hypokalemia and reflects the impact of potassium on cardiac function.
D: Extreme thirst is not a typical symptom of hypokalemia.
A nurse is caring for four hospitalized clients. Which of the following clients should the nurse identify as being at risk for fluid volume deficit?
Explanation
A: End-stage renal failure is associated with fluid retention, making this client less likely to be at risk for fluid volume deficit.
B: Left-sided heart failure with an elevated BNP level suggests fluid overload, not deficit.
C: The client who has been NPO since midnight for endoscopy is not at risk for fluid volume deficit because the duration of fasting is not long enough to cause significant dehydration.
D: The client who has gastroenteritis and is febrile is at risk for fluid volume deficit because of the loss of fluids and electrolytes from vomiting and diarrhea, as well as the increased insensible water loss from fever.
A nurse is instructing a group of clients regarding calcium rich foods. Which of the following foods should the nurse include in the teaching as the best source of calcium?
Explanation
A. While cheese contains calcium, the serving size is small, and it may be higher in fat. Milk is generally a better source.
B. Ice cream contains calcium, but it is also high in sugar and fat. Additionally, the serving size is small, so it may not be the most efficient way to get calcium.
C. Milk is a rich source of calcium and is easily absorbed by the body. It is a staple in promoting bone health.
D. Cottage cheese does contain calcium, but the amount may not be as high as in milk. Also, some people may not prefer cottage cheese.

A nurse is caring for a client who had total thyroidectomy and a serum calcium level of 7.6 mg/dL. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
A: Hypocalcemia (low calcium) is associated with increased bowel motility, leading to diarrhea rather than constipation.
B: Hypocalcemia is more likely to cause prolonged, not shortened, QT intervals on an electrocardiogram.
C: Hypocalcemia is associated with hyperactive, not hypoactive, deep tendon reflexes.
D: Tingling of the extremities (paresthesia) is a common neurological manifestation of hypocalcemia.

A nurse is caring for a client.
Nurses' Notes History and Physical Nurses' Notes
0800:
Client is admitted following cerebrovascular accident (CVA) Client is alert and oriented. Heart rate regular. Respirations rapid and non-labored. Wheezing auscultated in upper lobes of the lungs. Client is receiving 2 L/min of oxygen via nasal cannula. Right upper and lower extremities flaccid with decreased muscle tone and strength.
1200:
Client sitting up in a chair for lunch. Client states they are right-handed and are having difficulty feeding themselves.
For which of the following interprofessional team members should the nurse anticipate a provider's referral? Select all that apply.
Explanation
A. Case manager may be involved in coordinating overall care, but based on the current assessment findings, there is a more immediate need for rehabilitation services.
B. A respiratory therapist can help manage the client's oxygen therapy and monitor their lung function.
C. Diabetes nurse educator is not directly relevant to the client's current condition as described.
D. The client's flaccid right upper and lower extremities with decreased muscle tone and strength indicate a need for rehabilitation and physical therapy.
E. The client's difficulty feeding themselves suggests a need for occupational therapy to address activities of daily living (ADLs) and improve independence.
F. Enterostomal therapy nurse is not indicated based on the information provided. The client's issues are primarily related to mobility and activities of daily living.
A nurse is assisting with teaching a class about expected physiological changes in older adult clients. Which of the following changes should the nurse include?
Explanation
A. This is more related to psychological changes rather than physiological changes in older adults.
B. Bedwetting is not a typical physiological change in older adults. It is more commonly associated with children.
C. Older adult clients might experience changes in their appetite and metabolism that can lead to overeating and obesity. This can increase the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular problems.
D. While emotional changes may occur, the term "feelings" is too broad. Physiological changes are more specific to bodily functions.
A nurse is caring for a client who is unconscious and has a living will. The client's family asks if they can make changes to lifesaving measures now that the client is unconscious. Which of the following statements should the nurse make?
Explanation
A. While this act supports a patient's right to make decisions about their medical care, it doesn't grant the family the right to change the living will.
B. Changes to a living will should be discussed with the person who created it or someone legally designated to make those decisions, such as a durable power of attorney.
C. The living will is a legal document that outlines the client's wishes regarding medical treatment in specific situations.
D. This document designates someone to make healthcare decisions if the client is unable to do so but doesn't grant the authority to cancel the living will.
A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving total parenteral nutrition via a peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC). When assessing the client, the nurse notes swelling of the client's arm above the PICC insertion site. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
A. While cold packs might be used for certain conditions, measuring the circumference of both upper arms is the priority in this situation.
B. Swelling of the arm above the PICC insertion site can indicate a complication such as thrombophlebitis, which is inflammation and clotting of the vein. The nurse should measure the circumference of both upper arms and compare them to detect any difference in size, which can indicate edema due to impaired venous return. This is the first action the nurse should take because it is an assessment step that can provide objective data to guide further interventions.
C. Swelling above the PICC insertion site could indicate complications such as infiltration, and the provider needs to be informed promptly. However, the nurse should first measure the circumference of both upper arms first.
D. Removing the PICC line should be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider, and it is not the first action to take.
A nurse is assessing an older adult client who is experiencing age-related changes. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
A. In older adults, bones tend to lose calcium, becoming less dense, and more prone to fractures.
B. Generally, older adults may experience a decrease in muscle mass due to factors such as decreased physical activity and hormonal changes.
C. This is the correct answer. Joint stiffness is a common age-related change due to wear and tear on the cartilage.
D. Balance tends to decline with age due to factors such as changes in vision, muscle strength, and joint flexibility.
A nurse is organizing interprofessional team members to meet the needs of a client. Which of the following roles is the nurse taking?
Explanation
A. The nurse is organizing team members to ensure the comprehensive needs of the client are met.
B. A researcher focuses on gathering and analyzing data to contribute to evidence- based practice.
C. An educator provides information and teaching to clients, families, and other healthcare professionals.
D. A counselor offers emotional support and guidance to clients and their families.
A nurse is preparing to administer potassium chloride (KCL) to a client who is receiving diuretic therapy. The nurse reviews the client's serum potassium level results and discovers the client's potassium level is 3.2 mEq/L. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. The nurse should not withhold the dose without consulting the provider, especially with a low potassium level.
B. A client who is receiving diuretic therapy may lose potassium through urine and develop hypokalemia, which is a low level of potassium in the blood. Hypokalemia can cause cardiac arrhythmias, muscle weakness, and fatigue. The normal range of serum potassium is 3.5 to 5.0 mEq/L. A serum potassium level of 3.2 mEq/L indicates mild hypokalemia and requires potassium supplementation
C. While it's important to verify lab results, the nurse should first administer the prescribed dose of KCL since the patient has mild hypokalemia.
D. This is important but it may delay the treatment of hypokalemia and increase the risk of complications.
A client is admitted to the emergency room with a respiratory rate of 7/min. Arterial blood gases (ABG) reveal the following values. Which of the following is an appropriate analysis of the ABGS?
pH 7.22
PaCO2 68 mm Hg
Base excess-2
PaO2 78 mm Hg
Saturation 80%
Bicarbonate 26 mEq/L
Explanation
A. The base excess, PaO2, saturation, and bicarbonate values are within normal ranges and do not indicate metabolic acidosis.
B. A client who has a respiratory rate of 7/min may have hypoventilation, which is a decreased rate or depth of breathing that causes carbon dioxide retention and decreased oxygenation. Hypoventilation can result in respiratory acidosis, which is a condition characterized by a low pH (less than 7.35) and a high PaCO2 (greater than 45 mm Hg).
C. The base excess, PaO2, saturation, and bicarbonate values are within normal ranges and do not indicate metabolic alkalosis.
D. The base excess, PaO2, saturation, and bicarbonate values are within normal ranges and do not indicate respiratory alkalosis.
A nurse is assessing a client who has diarrhea. Which of the following findings is a manifestation of hypokalemia?
Explanation
A. Hyperactive bowel sounds are associated with hyperkalemia, not hypokalemia.
B. Hypertension is not typically associated with hypokalemia. In fact, hypokalemia is more likely to be associated with hypotension.
C. Cerebral edema is not a common manifestation of hypokalemia; it is more commonly associated with conditions like hyponatremia.
D. Muscle weakness is a classic manifestation of hypokalemia. Potassium is crucial for proper muscle function, and a deficiency can lead to weakness.

A nurse is caring for an older adult client. The client has an increased risk for dehydration due to which of the following physiological changes that can occur with aging?
Explanation
A. A decrease in systolic blood pressure is not directly related to dehydration.
Dehydration is more associated with fluid balance.
B. With aging, there is a natural decline in kidney function, including a decrease in the ability to concentrate urine. This can contribute to an increased risk of dehydration.
C. An increase in saliva production is not typically associated with dehydration.
D. With aging, there is actually a decrease in the percentage of body water, making older adults more susceptible to dehydration.
A nurse is caring for a client who is experiencing severe nausea and vomiting after a course of chemotherapy. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following clinical manifestations?
Explanation
A. Severe vomiting can lead to a loss of gastric acid, resulting in metabolic alkalosis and not acidosis.
B. A client who is experiencing severe nausea and vomiting may lose gastric acid through vomitus and develop metabolic alkalosis, which is a condition characterized by a high pH (greater than 7.45) and a high bicarbonate (greater than 26 mEq/L). Metabolic alkalosis can cause confusion, tremors, tetany, and hypokalemia.
C. Respiratory alkalosis is not typically associated with vomiting; it is more often seen in conditions with hyperventilation.
D. Respiratory acidosis is not the primary acid-base imbalance associated with vomiting; it is more commonly associated with conditions affecting lung function.
A nurse is preparing to administer 0.45% sodium chloride (NaCl) 1000 mL IV to infuse over 8 hr. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero)
Explanation
To calculate the infusion rate, the nurse should divide the total volume of fluid by the total time of infusion. In this case, the nurse should divide 1000 mL by 8 hr, which equals 125 mL/hr. Therefore, the nurse should set the IV pump to deliver 125 mL/hr of 0.45% sodium chloride (NaCl) solution.
A nurse is assessing an older adult client who is receiving IV therapy. The nurse should recognize that which of the following findings indicates fluid volume excess? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
A. Urine-specific gravity greater than 1.030 is indicative of concentrated urine and is more associated with dehydration, not fluid volume excess.
B. Pitting edema is a classic sign of fluid volume excess, indicating an accumulation of fluid in the interstitial spaces.
C. Swelling at the IV site may be related to local inflammation or extravasation of fluids but is not specific to fluid volume excess.
D. Crackles upon auscultation suggest fluid accumulation in the lungs, which is a common finding in fluid volume excess.
E. A bounding pulse is often associated with increased stroke volume and can be a sign of fluid volume excess.
A nurse is assessing a client who has had diarrhea for several days. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
A. Diarrhea can lead to significant fluid loss, causing dehydration.
B. Hypothermia is not a typical finding associated with diarrhea; instead, clients may experience fever or an elevated body temperature.
C. Diarrhea is more likely to be associated with increased bowel sounds rather than decreased bowel sounds.
D. A rigid abdomen is not a common finding in diarrhea; it may suggest more serious conditions such as peritonitis.
A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving IV fluids to correct dehydration. Which of the following laboratory values should indicate to the nurse that the client is effectively responding to treatment?
Explanation
A. A urine specific gravity of 1.020 indicates a concentration within the normal range, suggesting that the kidneys are effectively conserving water and concentrating urine, which is a positive response to fluid therapy.
B. A sodium level of 165 mEq/L is elevated and may indicate hypernatremia, which could be a sign of inadequate water intake or excess sodium.
C. Hct (hematocrit) of 62% may indicate hemoconcentration and is not a specific marker for fluid status.
D. A potassium level of 5.2 mEq/L is within the normal range and is not a specific indicator of the effectiveness of fluid resuscitation.
A nurse is caring for a client.
Vital Signs Nurses Notes 1000:
T38.2° C (100.8°F), oral.
BP 114/56 mm Hg, supine HR 99/min
R 32/min
Pulse oximetry 85% on room air (95% to 100%)
1100:
T38.6° C (101.5°F), oral.
BP 112/54 mm Hg, supine Apical HR 108/min
Click to highlight the findings at 1100, that require follow-up. To deselect a finding, click on the finding again.
Explanation
A. Elevated oral temperature may indicate a fever and requires further assessment.
B. This blood pressure value is within the normal range.
C. An elevated heart rate (108/min) suggests tachycardia, and it requires further investigation to determine the cause.
D. A respiratory rate of 22/min is not a finding that raises concern.
E. A pulse oximetry reading of 90% on supplemental oxygen (40% O2) is below the expected range, indicating potential respiratory distress and requiring immediate attention.
F. Pink mucous membrane is a normal finding.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 50 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

