Please set your exam date
Immunological System
Study Questions
Role of nurses in immunology counselling
Explanation
Explanation: The nurse's counseling role includes providing education about the benefits of immunizations, potential risks, and addressing any concerns or questions the client may have. This helps the client make informed decisions and feel more comfortable with the process.
Incorrect choices:
a. Providing the client with detailed medical terminology about each vaccine. This choice is incorrect because using medical jargon can confuse and overwhelm the client. The nurse should use clear and simple language to explain the vaccines.
b. Offering a distraction during the vaccine administration. While distractions can help ease discomfort, the primary role of counseling is to provide education and address the client's concerns.
d. Administering the vaccines quickly without explanation. This choice is incorrect because the nurse should always provide explanations and information to the client before any medical procedure.
Explanation
Explanation: The nurse's role in counseling includes providing accurate and evidence-based information to address the parent's concerns. Providing information about the safety and effectiveness of vaccines can help alleviate fears and promote informed decision-making.
Incorrect choices:
a. Assure the parent that vaccines are optional and can be skipped. This choice is incorrect because vaccines are recommended for public health and skipping vaccines can put the child and others at risk.
c. Tell the parent that their concerns are not valid and they should trust medical recommendations. This choice is incorrect because dismissing the parent's concerns is not respectful or helpful in addressing their worries.
d. Avoid discussing the topic and quickly move on to other subjects. This choice is incorrect because the nurse should actively engage in discussions and provide information to address the parent's concerns.
Explanation
Explanation: The nurse's counseling role involves validating the client's concerns and providing accurate information to address any misconceptions. This helps the client make an informed decision based on reliable sources.
Incorrect choices:
a. Ignore the misinformation and proceed with the vaccine administration. This choice is incorrect because ignoring the client's concerns and proceeding without addressing them can undermine trust and cooperation.
b. Provide additional misinformation to counteract what the client read online. This choice is incorrect because providing misinformation is unethical and can further confuse the client.
d. Tell the client that vaccines are mandatory and non-negotiable. While some vaccines may be required for certain situations, the nurse should prioritize communication and education rather than using a confrontational approach.
Explanation
Explanation: The primary role of the nurse in immunology counseling is to provide education and guidance to clients about managing and avoiding allergens. This empowers the client to make informed decisions and take proactive measures to prevent allergic reactions.
Incorrect choices:
a. Administering allergy medications to the client. While administering medications may be part of the client's overall care plan, the primary focus in counseling is on education and prevention.
b. Teaching the client to self-administer allergy injections. While teaching self-administration of injections may be important for some clients, it is not the primary role of the nurse in immunology counseling.
d. Monitoring the client's vital signs for signs of an allergic reaction. Monitoring for allergic reactions is important, but the primary role of the nurse in counseling is to provide education and support for allergen avoidance.
Explanation
Explanation: The primary purpose of counseling in immunology is to provide clients with accurate and relevant information about vaccines, allowing them to make informed decisions about their healthcare. Educating the client about the benefits and potential side effects of vaccination is essential for promoting optimal health outcomes.
Incorrect choices:
a. To assess the client's health history and immunization status. While assessment is important, the primary focus of counseling is on providing education and information to the client.
b. To administer the vaccine and monitor for adverse reactions. Administering the vaccine and monitoring for reactions are nursing actions, but counseling involves educating the client.
d. To provide emotional support and reassurance to the client. Emotional support is valuable, but the primary purpose of counseling in immunology is to provide information and education.
Explanation
Explanation: The primary goal of counseling in immunology is to provide education and information to the client, ensuring that they have a clear understanding of their treatment plan, including its duration and frequency. This empowers the client to actively participate in their own care.
Incorrect choices:
a. To administer allergy medications to manage symptoms. While medication administration may be part of the treatment plan, the primary focus of counseling is on education and empowerment.
b. To prepare the client for a potential allergic reaction during treatment. While preparing for potential reactions is important, the primary goal of counseling is to provide comprehensive education about the treatment.
d. To monitor the client's vital signs for signs of anaphylaxis. Monitoring for adverse reactions is a nursing responsibility, but counseling is focused on education and information sharing.
Explanation
Explanation: The primary aim of counseling in immunology is to provide clients with accurate information about the benefits of immunizations and their role in public health, including concepts like herd immunity. This education helps clients make informed decisions about vaccinations.
Incorrect choices:
a. To administer childhood immunizations to the client. While administering vaccines is important, the primary focus of counseling is on providing information and education.
b. To assess the client's understanding of immunization schedules. Assessment is important, but counseling involves providing information and education about immunizations.
d. To monitor the client's vital signs after immunization. Monitoring for adverse reactions is a nursing responsibility, but counseling is focused on education and information sharing.
Explanation
Explanation: The primary goal of counseling in immunology is to provide clients with information and education about vaccines, including their characteristics and potential risks. This helps clients make informed decisions about vaccination.
Incorrect choices:
a. To administer the live attenuated vaccine to the client. While administering vaccines is part of nursing care, the focus of counseling is on education and information sharing.
b. To assess the client's overall health status and immunization history. Assessment is important, but counseling involves providing information about the vaccine.
d. To monitor the client's vital signs for signs of an allergic reaction. Monitoring for adverse reactions is a nursing responsibility, but counseling focuses on education and informed decision-making.
Explanation
Explanation: The nurse's counseling role involves providing emotional support and practical strategies to help clients manage their anxiety related to immunizations. Discussing coping strategies, such as deep breathing techniques or distraction techniques, can empower the client to better cope with the fear of needles.
Incorrect choices:
a. The nurse explaining the vaccine's components in detail may not directly address the client's fear of needles and anxiety.
b. Providing instructions for self-administering the vaccine may not be appropriate for all clients and may not address the underlying anxiety.
d. Prescribing medication is not within the nurse's scope of practice, and it may not be necessary for managing needle-related anxiety.
Explanation
Explanation: The nurse's counseling role includes providing evidence-based information to help parents make informed decisions about vaccinations. Addressing concerns and sharing accurate information about the benefits and potential risks of vaccines can help alleviate fears and promote informed decision-making.
Incorrect choices:
a. Administering the vaccine without discussing potential side effects does not address the parent's concerns and may not promote informed decision-making.
c. Offering a financial incentive may not address the parent's concerns about potential side effects and may raise ethical considerations.
d. Assuring the parent that vaccines are never associated with any risks is not accurate and may undermine the parent's trust in the healthcare provider.
Explanation
Explanation: The nurse's counseling role involves providing education on the importance of vaccines in preventing serious and potentially life-threatening infections. Discussing the impact of vaccines on public health and individual protection can help the client understand their significance.
Incorrect choices:
a. Advising the client to avoid all vaccines until fully recovered may not be appropriate, especially if the client is at risk for preventable infections.
b. Stating that vaccines only prevent minor illnesses is inaccurate and does not convey the full scope of their protective effects.
d. Encouraging the client to rely solely on natural immunity may not provide adequate protection against preventable diseases and may not address the client's concerns.
Explanation
Explanation: The nurse's counseling role involves tailoring information to the client's specific health condition. Providing information on vaccines that are safe and recommended for individuals with autoimmune conditions can address the client's concerns and promote informed decision-making.
Incorrect choices:
a. Insisting that the client receive all recommended vaccines may not address the client's concerns and may not promote collaborative decision-making.
b. Stating that vaccines have no impact on autoimmune conditions is not accurate and may not address the client's specific concerns.
d. Discouraging the client from seeking further information about vaccines is not aligned with the nurse's role in promoting informed decision-making and client education.
A pregnant client is unsure about receiving vaccines during pregnancy. How can the nurse's counseling role help the client make an informed decision?
Explanation
Explanation: The nurse's counseling role includes providing accurate and evidence-based information to help pregnant clients make informed decisions about vaccines. Discussing which vaccines are safe and recommended, as well as those that are contraindicated during pregnancy, can help the client make an informed choice.
Incorrect choices:
a. Stating that all vaccines are safe during pregnancy is not accurate and may not provide the client with the necessary information to make an informed decision.
b. Explaining potential risks without providing a balanced view of the benefits and risks may not promote informed decision-making.
d. Discouraging the client from discussing vaccine concerns with their healthcare provider is not aligned with the nurse's role in promoting communication and collaborative decision-making.
Immunity
Explanation
Explanation: The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to identify and respond to foreign substances in the body, including bacteria, viruses, parasites, and toxins. Its primary function is to protect the body from infections and other harmful substances.
Incorrect choices:
a. The regulation of body temperature and blood pressure is primarily controlled by the nervous and endocrine systems, not the immune system.
b. Digestion and absorption of nutrients from food are processes mainly controlled by the digestive system, not the immune system.
d. The production of hormones that control bodily functions is primarily the responsibility of the endocrine system, not the immune system.
Explanation
Explanation: Hormones are chemical messengers produced by the endocrine system to regulate various physiological processes in the body. While the endocrine system and immune system can influence each other's activities, hormones are not considered a direct component of the immune system.
Incorrect choices:
a. Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell and a critical component of the immune system. They include B cells, T cells, and natural killer cells, which play essential roles in immune responses.
b. Antigens are molecules or substances that can trigger an immune response in the body. They are recognized by the immune system as foreign or non-self and can elicit the production of antibodies.
d. Antibodies are proteins produced by B cells in response to the presence of antigens. They play a vital role in recognizing and neutralizing foreign substances in the body.
Explanation
Explanation: Active immunity is acquired when the body's immune system is exposed to a specific pathogen or antigen, either through vaccination or natural infection. In response, the immune system produces its antibodies to protect against future encounters with the same pathogen.
Incorrect choices:
a. Innate immunity is the first line of defense against infections and is present at birth. It includes physical barriers, such as the skin and mucous membranes, and non-specific immune responses that do not require prior exposure to a specific pathogen.
c. Passive immunity is the transfer of pre-formed antibodies from one individual to another, providing immediate, temporary protection. This can occur naturally, such as the transfer of antibodies from a mother to her baby during breastfeeding, or through the administration of pre-formed antibodies, as in certain medical treatments.
d. Natural immunity refers to the immunity that is acquired through natural exposure to a pathogen and the subsequent development of an immune response. This includes both active immunity from natural infection and passive immunity from maternal antibodies passed to the baby during childbirth or breastfeeding.
Which of the following cells is responsible for the production of antibodies in response to infection or vaccination?
Explanation
Explanation: B cells are a type of lymphocyte that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response. When activated by the presence of specific antigens, B cells differentiate into plasma cells, which are responsible for producing large quantities of antibodies that can target and neutralize the invading pathogen.
Incorrect choices:
a. T cells are another type of lymphocyte that is involved in cell-mediated immunity, where they directly attack infected or abnormal cells. They do not produce antibodies.
b. Natural killer cells are part of the innate immune system and are responsible for killing infected or cancerous cells. They are not involved in antibody production.
d. Macrophages are phagocytic cells that engulf and destroy pathogens and debris in the body. While they play a crucial role in immune responses, they do not produce antibodies.
Explanation
Explanation: T cells are a type of lymphocyte that plays a crucial role in cell-mediated immunity. They are responsible for recognizing and directly attacking infected or abnormal cells in the body. There are two main types of T cells: cytotoxic T cells, which directly kill infected cells, and helper T cells, which assist in coordinating the immune response.
Incorrect choices:
a. B cells are responsible for the production of antibodies and are involved in the humoral immune response, which targets pathogens outside of cells. They do not directly recognize and destroy infected cells.
c. Macrophages are antigen-presenting cells that engulf and process pathogens to present their antigens to other immune cells. While they are involved in immune recognition, they do not primarily recognize and destroy infected cells.
d. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell involved in the innate immune response. They primarily target and destroy bacteria and other foreign invaders in the body, but they do not have the specific recognition capabilities of T cells.
Explanation
Explanation: B cells are a type of lymphocyte that produces antibodies against specific antigens. When a B cell encounters an antigen that matches its specific receptor, it becomes activated and differentiates into plasma cells, which are responsible for producing large quantities of antibodies that can target and neutralize the antigen.
Incorrect choices:
b. T cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity and do not produce antibodies. They recognize and directly attack infected or abnormal cells in the body.
c. Macrophages are antigen-presenting cells that engulf and process pathogens to present their antigens to other immune cells. They do not produce antibodies themselves but play a role in initiating the immune response.
d. Natural killer cells are a type of lymphocyte involved in the innate immune response. They do not produce antibodies but can directly kill infected or abnormal cells.
Explanation
Explanation: Macrophages are a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the innate immune response. They are phagocytes, meaning they engulf and destroy pathogens, cellular debris, and foreign substances in the body. Macrophages are also antigen-presenting cells, as they process and present antigens to other immune cells to initiate an adaptive immune response.
Incorrect choices:
a. B cells produce antibodies against specific antigens but do not directly engulf and destroy pathogens.
b. T cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity and directly attack infected or abnormal cells but do not have phagocytic capabilities like macrophages.
d. Natural killer cells are a type of lymphocyte involved in the innate immune response and can directly kill infected or abnormal cells, but they do not primarily function as phagocytes like macrophages.
Which of the following components of the immune system is involved in both innate and adaptive immunity?
Explanation
Explanation: Macrophages play a dual role in both innate and adaptive immunity. As part of the innate immune response, macrophages act as phagocytes, engulfing and destroying pathogens and debris in the body. They are also antigen-presenting cells, presenting processed antigens to other immune cells to initiate the adaptive immune response.
Incorrect choices:
a. B cells are part of the adaptive immune response and produce antibodies against specific antigens. They are not involved in the innate immune response.
b. T cells are primarily involved in the adaptive immune response and directly attack infected or abnormal cells. They are not part of the innate immune response.
d. Natural killer cells are part of the innate immune response and can directly kill infected or abnormal cells. They do not participate in the adaptive immune response.
Explanation
Explanation: The immune response is a complex system of defense mechanisms that aim to protect the body from pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances. It involves the activation of various immune cells, production of antibodies, and other immune components to recognize and eliminate the invading pathogens.
Incorrect choices:
a. Directly attacking and killing infected cells is the role of cytotoxic T cells during cell-mediated immunity, but it is not the primary purpose of the overall immune response.
b. Antigens are foreign substances that trigger the immune response. They are not produced by the immune response itself but rather recognized by immune cells and antibodies.
c. The immune response is not involved in regulating the body's metabolism. Metabolism regulation is primarily controlled by other systems in the body, such as the endocrine system.
Explanation
Explanation: B cells are a type of lymphocyte that plays a crucial role in the immune response by recognizing and binding to specific antigens. When a B cell encounters an antigen that matches its specific receptor, it becomes activated and differentiates into plasma cells, which produce antibodies against the antigen.
Incorrect choices:
b. Cytotoxic T cells are responsible for directly attacking and killing infected or abnormal cells during cell-mediated immunity. They do not primarily recognize antigens during the immune response.
c. Macrophages are antigen-presenting cells that engulf and process pathogens to present their antigens to other immune cells, such as T cells and B cells. While they are involved in antigen recognition, they are not the primary cells responsible for this function.
d. Red blood cells do not have a direct role in antigen recognition or the immune response. Their primary function is to transport oxygen throughout the body.
Explanation
Explanation: B cells recognize antigens by producing specific receptors on their cell surface, known as antibodies or immunoglobulins. When a B cell encounters an antigen that matches its specific antibody, it binds to the antigen, marking it for destruction or neutralization by other immune cells.
Incorrect choices:
a. Engulfing and processing pathogens is the role of antigen-presenting cells like macrophages and dendritic cells. These cells present processed antigens to other immune cells, including B cells, to trigger an immune response.
b. Cytokines are small proteins that serve as signaling molecules in the immune system. They are produced by various immune cells to regulate immune responses, but they are not directly involved in antigen recognition by B cells.
d. Directly attacking and killing infected cells is the role of cytotoxic T cells during cell-mediated immunity, not B cells during the humoral immune response.
Which of the following is an essential step in antigen recognition during the immune response?
Explanation
Explanation: Antigen recognition during the immune response occurs when antigens bind to specific receptors on immune cells, such as B cell receptors, T cell receptors, or antibodies. This binding is a critical step that triggers the activation of the immune response against the invading pathogen or foreign substance.
Incorrect choices:
a. Activation of regulatory T cells is important for controlling and regulating the immune response but is not directly related to the antigen recognition process.
b. Production of histamines by mast cells is involved in the inflammatory response, but it is not a direct step in the antigen recognition process.
d. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell involved in the innate immune response. They do not release antibodies, as that function is primarily carried out by B cells and plasma cells.
Explanation
Explanation: B cells are part of the adaptive immune system and are responsible for antibody-mediated immunity. They do not directly attack and kill infected cells. Instead, B cells produce antibodies that can recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances.
Incorrect choices:
b. B cells are involved in antibody-mediated immunity, not cell-mediated immunity. They produce antibodies that circulate in the bloodstream and bind to antigens on pathogens, marking them for destruction by other immune cells.
c. Helper T cells, not B cells, primarily recognize antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells like macrophages and dendritic cells.
d. Phagocytosis of pathogens is mainly carried out by macrophages and neutrophils, not B cells.
Explanation
Explanation: B cells are specialized in producing antibodies against specific antigens. When B cells encounter a pathogen or foreign substance with a matching antigen, they become activated and differentiate into plasma cells. Plasma cells then secrete large amounts of antibodies, which can recognize and neutralize the pathogen.
Incorrect choices:
a. B cells do not directly attack and kill infected cells. That role is primarily performed by cytotoxic T cells during cell-mediated immunity.
c. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are responsible for regulating the immune response to prevent excessive inflammation and maintain immune homeostasis.
d. B cells recognize antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells like macrophages, but their primary function is to produce antibodies, not to recognize antigens directly.
Explanation
Explanation: During antibody-mediated immunity, B cells produce antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins. Antibodies are Y-shaped proteins that specifically recognize and bind to antigens on the surface of pathogens or foreign substances. This binding marks the pathogens for destruction by other immune cells or neutralizes their harmful effects.
Incorrect choices:
a. Cytokines are small proteins that serve as signaling molecules in the immune system, regulating the behavior and activity of immune cells. B cells can secrete cytokines, but their primary function is antibody production.
b. Cytotoxic granules contain substances like perforin and granzymes and are released by cytotoxic T cells to induce apoptosis in infected or abnormal cells. B cells do not produce cytotoxic granules.
d. Perforin is a protein released by cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells to create pores in the membrane of infected cells, leading to cell death. B cells do not produce perforin.
Which of the following is the primary role of B cells during the humoral immune response?
Explanation
Explanation: The primary role of B cells during the humoral immune response is to produce antibodies against specific antigens on pathogens. When B cells encounter an antigen that matches their specific receptor, they become activated and differentiate into plasma cells, which then secrete large amounts of antibodies into the bloodstream.
Incorrect choices:
a. Antigen presentation to B cells is carried out by antigen-presenting cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells, not by B cells themselves.
c. Directly attacking and killing infected cells is the role of cytotoxic T cells during cell-mediated immunity, not B cells during the humoral immune response.
d. The regulation of the immune response is mainly the function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and other immune regulatory mechanisms, not the primary role of B cells.
Which of the following statements about T cells is correct?
Explanation
Explanation: T cells, specifically cytotoxic T cells (CD8+ T cells), are responsible for cell-mediated immunity. They directly recognize and attack infected or abnormal cells, leading to their destruction. This process is crucial in controlling viral infections and cancer cells.
Incorrect choices:
a. B cells, not T cells, are responsible for the production of antibodies during the humoral immune response.
c. Phagocytosis of pathogens is mainly carried out by macrophages and neutrophils, not T cells.
d. Allergic reactions are primarily mediated by a different type of T cells called helper T cells (CD4+ T cells), not cytotoxic T cells.
During cell-mediated immunity, T cells recognize antigens presented by:
Explanation
Explanation: During cell-mediated immunity, T cells recognize antigens that are presented by antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as macrophages. Macrophages engulf and process pathogens, and then they display fragments of the pathogens' antigens on their cell surface using major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. T cells, specifically helper T cells, interact with these antigen-presenting macrophages and become activated to initiate immune responses.
Incorrect choices:
b. B cells present antigens to helper T cells during the humoral immune response, not during cell-mediated immunity.
c. Plasma cells are not involved in antigen presentation; they are terminally differentiated B cells that produce antibodies during the humoral immune response.
d. Memory cells are formed after the immune system encounters an antigen and are not directly involved in antigen presentation.
Explanation
Explanation: Helper T cells (CD4+ T cells) play a critical role in the immune response by enhancing the activity of other immune cells. They secrete cytokines that stimulate B cells to produce antibodies, activate cytotoxic T cells to kill infected cells, and promote the function of macrophages in phagocytosis. Helper T cells are essential for coordinating and regulating the immune response.
Incorrect choices:
a. Cytotoxic T cells (CD8+ T cells) are responsible for directly attacking and killing infected cells, not enhancing the activity of other immune cells.
b. Memory T cells are formed after the immune system encounters an antigen and are not directly involved in enhancing immune cell activity.
d. Suppressor T cells (regulatory T cells) are involved in down-regulating the immune response to prevent excessive inflammation and tissue damage, not in enhancing immune cell activity.
What is the primary role of cytotoxic T cells during cell-mediated immunity?
Explanation
Explanation: Cytotoxic T cells (CD8+ T cells) are the effector cells of cell-mediated immunity. Their primary role is to directly recognize and kill infected or abnormal cells, such as virus-infected cells or cancer cells. Cytotoxic T cells release cytotoxic granules containing perforin and granzymes, which induce apoptosis (cell death) in the target cells.
Incorrect choices:
a. Helper T cells, not cytotoxic T cells, recognize antigens presented by macrophages and play a crucial role in activating other immune cells.
b. B cells are responsible for producing antibodies against pathogens during the humoral immune response, not cytotoxic T cells.
d. Regulatory T cells (suppressor T cells) are involved in regulating the immune response to prevent excessive inflammation and tissue damage, not cytotoxic T cells.
Memory in the context of the immune system refers to:
Explanation
Explanation: Memory in the immune system refers to the ability of immune cells, particularly memory B cells and memory T cells, to recognize and respond more quickly and effectively to specific antigens upon subsequent exposure. This leads to a faster and stronger secondary immune response.
Incorrect choices:
b. The ability of immune cells to differentiate between self and non-self antigens refers to the concept of immune tolerance, which helps prevent the immune system from attacking the body's own cells and tissues.
c. The process of phagocytosis by macrophages is a mechanism by which immune cells engulf and destroy pathogens and cellular debris, but it is not directly related to memory in the immune system.
d. The ability of B cells to produce antibodies is an essential part of the primary immune response, but it is not specific to memory in the immune system.
The secondary immune response is characterized by:
Explanation
Explanation: The secondary immune response is faster and more potent than the primary immune response due to the presence of memory B cells and memory T cells. These memory cells "remember" the specific antigen from a previous encounter, allowing for a quicker and more effective immune response upon re-exposure to the same antigen.
Incorrect choices:
a. The secondary immune response is faster and stronger compared to the primary immune response, not delayed and weaker.
b. The secondary immune response involves the activation of memory B cells and memory T cells, not naive B cells and T cells.
d. The primary immune response is characterized by the production of IgM antibodies initially, but during the secondary immune response, the production of IgG antibodies predominates, which are more effective in neutralizing antigens.
Memory B cells are responsible for:
Explanation
xplanation: Memory B cells are formed during the primary immune response and play a critical role in the secondary immune response. When re-exposed to the same antigen, memory B cells quickly differentiate into plasma cells that produce large quantities of specific antibodies, leading to a rapid and robust immune response.
Incorrect choices:
a. The production of antibodies during the primary immune response is primarily carried out by plasma cells, not memory B cells.
b. The activation of helper T cells is essential for coordinating the immune response, but memory B cells are not directly responsible for this process.
c. The initiation of the complement cascade is a separate component of the immune response involving complement proteins, and memory B cells are not directly involved in this process.
Explanation
Explanation: The secondary immune response provides long-lasting immunity because of the presence of memory B cells and memory T cells. These memory cells "remember" the specific antigen and can quickly mount a strong and effective immune response upon re-exposure to the same antigen, providing long-term protection.
Incorrect choices:
a. The primary immune response is primarily mediated by IgM antibodies, while the secondary immune response involves the predominance of IgG antibodies, which are more effective and provide long-lasting immunity.
b. The secondary immune response occurs after the primary immune response and is faster, not slower, due to the presence of memory cells.
c. Memory cells are a key component of the secondary immune response, playing a central role in providing rapid and robust immunity.
VI. Immune Disorders and Clinical Considerations:
Explanation
Explanation: Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium (lining of the membranes that surround the joints), causing inflammation, pain, and joint damage.
Incorrect choices:
a. Allergic rhinitis is an allergic response to airborne allergens, such as pollen or pet dander, not an autoimmune disorder.
c. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder triggered by the ingestion of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, and it primarily affects the small intestine.
d. Type 1 diabetes mellitus is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
Explanation
Explanation: Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain disorder characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, and tender points in specific areas of the body, such as the neck, shoulders, back, and hips.
Incorrect choices:
a. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disorder that can affect multiple organs and systems, including the skin, joints, kidneys, and nervous system.
c. Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disorder that affects the central nervous system, causing symptoms such as fatigue, muscle weakness, and coordination problems.
d. Sjögren's syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the salivary and lacrimal glands, leading to dry eyes and dry mouth.
True or False: Immune disorders can be caused by both genetic and environmental factors.
Explanation: Immune disorders can result from a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers. Some individuals may have a genetic susceptibility to developing certain immune disorders, and exposure to certain environmental factors, such as infections or certain substances, can trigger the immune response leading to the development of the disorder.
Explanation
Explanation: Sjögren's syndrome is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks and damages the salivary and lacrimal glands, resulting in dry eyes and dry mouth.
Incorrect choices:
a. Rheumatoid arthritis primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation and joint damage.
c. Crohn's disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the gastrointestinal tract, leading to inflammation and ulcers.
d. Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin, and it is not related to the salivary and lacrimal glands.
Explanation
Explanation: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks the myelin sheath, the protective covering of nerve fibers in the central nervous system, leading to communication problems between the brain and the rest of the body.
Incorrect choices:
a. Rheumatoid arthritis primarily affects the joints, not the central nervous system.
b. Sjögren's syndrome primarily affects the salivary and lacrimal glands, not the central nervous system.
d. Crohn's disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the gastrointestinal tract, not the central nervous system.
Which of the following immune disorders is characterized by the immune system attacking and damaging the small intestine in response to gluten consumption?
Explanation
Explanation: Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks and damages the lining of the small intestine in response to the ingestion of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye.
Incorrect choices:
a. Rheumatoid arthritis primarily affects the joints, not the small intestine.
b. Sjögren's syndrome primarily affects the salivary and lacrimal glands, not the small intestine.
d. Type 1 diabetes mellitus is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, not the small intestine.
True or False: Immune disorders are always associated with an overactive immune system.
Explanation
Explanation: Immune disorders can result from either an overactive immune system (autoimmune disorders) or an underactive immune system (immunodeficiency disorders). In autoimmune disorders, the immune system attacks the body's own tissues, while in immunodeficiency disorders, the immune system is weakened, making the individual more susceptible to infections.
Explanation
Explanation: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disorder that can affect multiple organs and systems, including the skin, joints, kidneys, and nervous system. The presence of a "butterfly rash" on the face, joint pain, and skin lesions are common manifestations of SLE.
Incorrect choices:
b. Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain disorder characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, and tender points in specific areas of the body, but it does not typically present with a "butterfly rash" or skin lesions.
c. Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disorder that affects the central nervous system, causing symptoms such as fatigue, muscle weakness, and coordination problems, but it does not typically present with a "butterfly rash" or joint pain.
d. Sjögren's syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the salivary and lacrimal glands, leading to dry eyes and dry mouth, but it does not typically present with a "butterfly rash" or skin lesions.
VII. Vaccination and Immunization:
Which of the following vaccines is recommended for infants at 2 months of age to protect against whooping cough (pertussis)?
Explanation
Explanation: At 2 months of age, infants are recommended to receive the DTaP vaccine, which protects against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (whooping cough). The MMR vaccine protects against measles, mumps, and rubella and is usually administered at a later age. The hepatitis B vaccine is given shortly after birth, and the varicella vaccine is typically administered at 12 months of age.
Incorrect choices:
a. The MMR vaccine protects against measles, mumps, and rubella, not whooping cough (pertussis).
b. The hepatitis B vaccine is typically given shortly after birth, not at 2 months of age.
d. The varicella vaccine is usually administered at 12 months of age, not at 2 months.
True or False: Vaccinations can cause the diseases they are designed to prevent.
Explanation
Explanation: Vaccinations are made from either weakened or killed pathogens or parts of pathogens, which cannot cause the disease they are meant to protect against. However, they stimulate the body's immune system to produce a protective response, providing immunity against the specific disease.
Explanation
Explanation: Live attenuated vaccines use a weakened form of the pathogen that is still capable of replicating but does not cause severe illness in healthy individuals. This type of vaccine can provide long-lasting immunity with a single dose.
Incorrect choices:
a. Inactivated vaccines use killed pathogens, not weakened forms.
b. Subunit vaccines use only specific parts of the pathogen, not weakened forms.
d. Toxoid vaccines use inactivated toxins produced by the pathogen, not weakened forms of the pathogen itself.
Explanation
Explanation: Booster doses of vaccines are recommended to reinforce and extend the duration of immunity provided by the initial vaccination. They help the immune system to maintain a higher level of protection against the disease over time.
Incorrect choices:
a. The number of antibodies in the blood is not increased by booster doses; rather, the immune system's memory is reinforced.
b. Booster doses do not decrease the risk of adverse reactions; they are given to maintain immunity.
d. Booster doses do not reduce the number of required vaccine doses; they are additional doses given to maintain immunity over time.
Explanation
Explanation: The pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine is recommended for older adults to protect against pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria. The influenza vaccine is recommended annually for people of all ages to prevent the flu.
Incorrect choices:
a. The hepatitis B vaccine is not specifically recommended for older adults to prevent pneumonia.
b. The influenza vaccine protects against the flu, not pneumonia.
d. The HPV vaccine is recommended for adolescents and young adults, not older adults, and does not protect against pneumonia.
Which type of immunity is acquired when an individual's immune system is exposed to a pathogen through vaccination or natural infection?
Explanation
Explanation: Active immunity is acquired when the body's immune system is exposed to a pathogen through vaccination or natural infection and produces an immune response to provide protection against future infections.
Incorrect choices:
b. Passive immunity is acquired when preformed antibodies are transferred to an individual, providing immediate but temporary protection against a specific pathogen.
c. Natural immunity refers to immunity that is acquired through natural exposure to a pathogen, either through infection or vaccination.
d. Herd immunity is the indirect protection that occurs when a large percentage of a population becomes immune to a disease, either through vaccination or previous infection, reducing the likelihood of transmission to susceptible individuals.
Explanation
Explanation: Healthcare workers are recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccine to protect against hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, which can be transmitted through contact with infected blood or body fluids.
Incorrect choices:
a. The influenza vaccine is recommended annually for healthcare workers to protect against seasonal flu, not hepatitis B.
b. The tetanus toxoid vaccine protects against tetanus, not hepatitis B.
d. The pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine protects against pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria, not hepatitis B.
Explanation
Explanation: Passive immunity is acquired when preformed antibodies are transferred to an individual, providing immediate but temporary protection against a specific pathogen. This can occur naturally from a mother to her newborn or artificially through administration of specific antibodies.
Incorrect choices:
a. Active immunity is acquired when the body's immune system is exposed to a pathogen and produces an immune response to provide protection against future infections.
c. Natural immunity refers to immunity that is acquired through natural exposure to a pathogen, either through infection or vaccination.
d. Herd immunity is the indirect protection that occurs when a large percentage of a population becomes immune to a disease, either through vaccination or previous infection, reducing the likelihood of transmission to susceptible individuals.
Explanation
Explanation: The human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine is recommended for adolescents to protect against certain types of HPV infections, which can lead to cervical, vaginal, vulvar, penile, anal, and throat cancers.
Incorrect choices:
a. The hepatitis B vaccine is typically given in infancy and does not protect against certain types of cancer.
b. The influenza vaccine is recommended annually for people of all ages to prevent the flu, not certain types of cancer.
d. The meningococcal vaccine protects against meningococcal infections, not certain types of cancer.
Conclusion xx
Explanation
Explanation: Passive immunity is the temporary immunity that is acquired from an external source, such as the transfer of antibodies from a mother to her baby through the placenta during pregnancy or through breastfeeding. This type of immunity provides immediate protection but does not result in the production of memory cells.
Incorrect choices:
a. The body's response to a vaccine is an example of active immunity, where the body produces its own antibodies in response to exposure to a weakened or inactive form of a pathogen.
c. The activation of T cells in response to an infection is part of the body's adaptive immune response, contributing to active immunity.
d. The production of memory cells after exposure to a pathogen is also a characteristic of active immunity, as it allows the body to recognize and respond more quickly to future infections with the same pathogen.
True or False: Vaccines can cause autism in children.
Explanation
Explanation: Numerous scientific studies have found no link between vaccines and autism. The notion that vaccines cause autism was based on a discredited and fraudulent study, and subsequent research has shown no evidence of such a link.
Explanation
Explanation: Memory cells are a type of immune cell that are formed during the body's initial encounter with a pathogen. They "remember" the specific antigen of the pathogen and allow the immune system to respond more rapidly and effectively if the same pathogen is encountered again in the future. Memory cells are responsible for providing long-term immunity.
Incorrect choices:
a. Engulfing pathogens and foreign invaders is the role of phagocytes, such as macrophages and neutrophils.
b. Initiating the inflammatory response is carried out by various immune cells, including mast cells and basophils, as part of the innate immune response.
c. Producing antibodies in response to infection is the primary role of B cells in the immune system.
Explanation
Explanation: Antigens are unique molecules or proteins present on the surface of cells, including pathogens. The immune system can recognize these antigens as "non-self" and mount an immune response to eliminate them while sparing the body's own cells, which display different antigens that are recognized as "self."
Incorrect choices:
b. Recognizing different blood types is relevant for blood transfusions but not a primary mechanism of distinguishing self from non-self by the immune system.
c. Monitoring hormone levels in the body is not directly related to the immune system's ability to distinguish between self and non-self.
d. Cytokines are signaling molecules released by immune cells to regulate the immune response but are not the primary means of distinguishing self from non-self.
Which of the following best describes the concept of immunity?
Explanation
Explanation:The body's ability to produce antibodies against specific pathogens. Immunity refers to the body's ability to recognize and respond to specific pathogens, such as bacteria or viruses, by producing antibodies that target and neutralize these invaders.
Incorrect choices:
a. The body's ability to tolerate foreign substances without a response is not immunity but rather the concept of immunological tolerance, which prevents the immune system from attacking the body's own cells and tissues.
c. Immunity does not guarantee the prevention of infections, but it provides protection and reduces the severity of infections upon subsequent exposures to the same pathogen.
d. While the immune system is designed to fight off infections, it is not capable of fighting off all types of infections equally. The immune response is specific to the type of pathogen encountered.
Which type of immunity is acquired through vaccination or exposure to a specific pathogen?
Explanation
Explanation: Active immunity. Active immunity is acquired when the immune system is exposed to a pathogen, either through natural infection or vaccination. It results in the production of memory cells that provide long-term protection against future exposures to the same pathogen.
Incorrect choices:
a. Passive immunity is acquired when preformed antibodies are transferred from one individual to another. It provides immediate but temporary protection and does not involve the production of memory cells.
b. Innate immunity is the body's first line of defense against infections and provides immediate, non-specific protection, but it does not involve the production of antibodies specific to a particular pathogen.
d. Acquired immunity is a general term that includes both active and passive immunity, but it does not specifically describe the type of immunity acquired through vaccination or exposure to a specific pathogen.
What is the primary role of antibodies in the immune response?
Explanation
Explanation: Todirectly destroy pathogens and infected cells. Antibodies are Y-shaped proteins produced by B cells in response to a specific pathogen. They bind to the surface of the pathogen and mark it for destruction by other components of the immune system or directly neutralize the pathogen.
Incorrect choices:
b. While antibodies can attract white blood cells to the site of infection, their primary role is not to do so but rather to directly target and neutralize pathogens.
c. Antibodies do not produce hormones but are part of the humoral immune response, which involves the production of antibodies to fight off infections.
d. Antibodies do not play a role in maintaining body temperature during infections; instead, fever is a response triggered by the release of certain chemicals called pyrogens during infections.
Which of the following best describes the function of T cells in the immune response?
Explanation
Explanation: Recognizing and responding to specific antigens. T cells are a type of lymphocyte that plays a central role in cell-mediated immunity. They recognize and respond to specific antigens presented by infected or abnormal cells, leading to their destruction.
Incorrect choices:
a. T cells are not responsible for the production of antibodies, but that is the role of B cells in the humoral immune response.
b. While T cells are involved in directly attacking and destroying infected cells, their main function is to recognize specific antigens rather than directly attacking pathogens.
c. Marking pathogens for destruction by phagocytes is primarily a function of antibodies and complement proteins, not T cells.
Which type of immunity is transferred from a mother to her baby through breast milk?
Explanation
Explanation: Passive immunity. Passive immunity is acquired when preformed antibodies are transferred from one individual to another. In this case, the mother's antibodies are transferred to her baby through breast milk, providing temporary protection against certain infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. Active immunity is acquired when the immune system is exposed to a pathogen or vaccination, leading to the production of memory cells and long-term protection.
b. Innate immunity is the body's first line of defense against infections and is not transferred from the mother to the baby but rather present from birth.
c. Adaptive immunity is another term for acquired immunity and involves the production of memory cells after exposure to a specific pathogen or vaccination. It is not transferred through breast milk.
Which of the following is an example of passive immunity?
Explanation
Explanation: Receiving antibodies through placenta during pregnancy. Passive immunity is acquired when preformed antibodies are transferred from one individual to another, providing immediate but temporary protection. This can occur naturally through breastfeeding or artificially through administration of preformed antibodies, as in the case of placental transfer of antibodies from a mother to her baby.
Incorrect choices:
a. Receiving a flu vaccine involves active immunity, where the body is exposed to an attenuated or inactivated pathogen to stimulate the production of antibodies and memory cells for long-term protection.
b. Developing immunity after recovering from a viral infection is an example of active immunity, where the body mounts an immune response and produces memory cells to provide long-lasting protection against the pathogen.
d. Producing memory cells after exposure to a pathogen is part of the adaptive immune response and contributes to long-term immunity, not passive immunity.
Which type of immune response is the body's first line of defense against infections?
Explanation
Explanation:Innate immunity. Innate immunity is the body's first line of defense and provides immediate protection against infections without prior exposure to the pathogen. It includes physical barriers, such as the skin, and various cellular and chemical components.
Incorrect choices:
a. Adaptive immunity is the acquired immunity that develops after exposure to a specific pathogen or vaccination. It takes some time to mount a response and produce antibodies or memory cells.
b. Humoral immunity is a component of adaptive immunity that involves the production of antibodies by B cells to neutralize pathogens.
d. Cell-mediated immunity is another component of adaptive immunity, where T cells directly attack infected or abnormal cells.
What is the role of antibodies in the immune response?
Explanation
Explanation:Destroying infected cells. Antibodies are produced by B cells in response to a specific pathogen and play a crucial role in identifying and neutralizing the invading pathogens, including infected cells.
Incorrect choices:
b. Attracting white blood cells to the site of infection is not the primary role of antibodies. White blood cells are attracted to the site of infection by chemical signals released by damaged tissues or pathogens.
c. Antibodies do not produce hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands to regulate various bodily functions.
d. Antibodies do not regulate body temperature. Body temperature regulation is mainly controlled by the hypothalamus in the brain.
Which of the following components of the immune system is responsible for recognizing and attacking cancer cells?
Explanation
Explanation: T cells are a type of lymphocyte that plays a central role in cell-mediated immunity. They can recognize and destroy abnormal cells, including cancer cells, through direct cell-to-cell interactions.
Incorrect choices:
b. B cells produce antibodies in response to specific pathogens, but they do not directly attack cancer cells.
c. Antibodies are protein molecules that can bind to specific antigens on pathogens, but they do not have a direct role in attacking cancer cells.
d. Macrophages are phagocytic cells that engulf and destroy foreign substances, including pathogens, but they are not the primary cells responsible for recognizing and attacking cancer cells.
How do memory cells contribute to long-term immunity?
Explanation
Explanation: Memory cells recognize and respond rapidly to previously encountered pathogens. Memory cells are a type of immune cell that are formed after an initial infection or vaccination. They "remember" the specific pathogen and allow the immune system to mount a faster and stronger response upon subsequent exposures to the same pathogen, providing long-term immunity.
Incorrect choices:
a. Memory cells do not directly attack pathogens in the body. They serve as a form of immune "memory" to help the body respond more effectively to future infections.
b. Memory cells do not produce antibodies upon initial pathogen exposure. B cells are responsible for producing antibodies in response to the pathogen.
d. Memory cells do not regulate the body's temperature during an infection. Temperature regulation is mainly controlled by the hypothalamus in the brain in response to infection or other stimuli.
Infection Prevention and Control (IPC)
Which type of transmission-based precaution is used for a client with a diagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection?
Explanation
Explanation: Contact precautions are used for clients with infections that can be transmitted through direct or indirect contact with the client or their environment. Clostridium difficile infection is primarily transmitted through contact with contaminated surfaces, requiring the use of gloves and gowns.
Incorrect choices: a. Airborne precautions are used for diseases that are transmitted through small airborne particles.
b. Droplet precautions are used for diseases that are transmitted through large droplets produced by an infected individual.
d. Standard precautions should always be followed, but additional precautions specific to the mode of transmission (in this case, contact precautions) are necessary for effective infection control.
Which precaution is appropriate for a client with pulmonary tuberculosis?
Explanation
Explanation: Pulmonary tuberculosis is primarily transmitted through airborne particles containing the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. Airborne precautions, including the use of specialized respiratory protection and negative pressure isolation rooms, are necessary to prevent its transmission.
Incorrect choices:
b. Droplet precautions are not sufficient for tuberculosis as it can be transmitted through smaller airborne particles.
c. Contact precautions are not necessary unless there are additional skin lesions or draining wounds associated with tuberculosis.
d. Standard precautions should always be followed, but additional precautions specific to the mode of transmission (in this case, airborne precautions) are required for effective infection control.
Which type of transmission-based precaution is used for a client with influenza?
Explanation
b. Droplet precautions Explanation: Influenza is primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets generated when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. Droplet precautions, including the use of masks and maintaining a safe distance, are necessary to prevent its spread.
Incorrect choices:
a. Airborne precautions are not necessary for influenza, as it is primarily transmitted through larger respiratory droplets rather than small airborne particles.
c. Contact precautions are not required for influenza unless the client has additional conditions or infections that warrant contact precautions.
d. Standard precautions should always be followed, but additional precautions specific to the mode of transmission (in this case, droplet precautions) are required for effective infection control.
Which precaution is used for a client with chickenpox (varicella)?
Explanation
Chickenpox is highly contagious and primarily transmitted through airborne particles containing the varicella-zoster virus. Airborne precautions, including the use of specialized respiratory protection and negative pressure isolation rooms, are necessary to prevent its transmission.
Incorrect choices:
b. Droplet precautions are not sufficient for chickenpox as it can be transmitted through smaller airborne particles.
c. Contact precautions are not necessary unless there are additional skin lesions or the client has conditions that warrant contact precautions.
d. Standard precautions should always be followed, but additional precautions specific to the mode of transmission (in this case, airborne precautions) are required for effective infection control.
True or False: Standard precautions are sufficient for all clients, regardless of their infectious status.
Explanation
Standard precautions are the foundation of infection prevention and control and should be followed for all clients. They include hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment, safe injection practices, respiratory hygiene, and environmental controls. Standard precautions are designed to prevent the transmission of common infectious agents and should be followed in addition to any specific transmission-based precautions that may be required.
Which type of transmission-based precaution is used for a client with tuberculosis?
Explanation
Airborne precautions are used for clients with infectious diseases that are spread through small airborne particles, such as tuberculosis. It involves the use of specialized respiratory protection and negative pressure isolation rooms.
Incorrect choices:
a. Contact precautions are used for diseases that can be transmitted through direct or indirect contact with the client or their environment.
b. Droplet precautions are used for diseases that are transmitted through large droplets produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks.
d. Standard precautions are the basic level of infection prevention and control measures that should be followed for all clients, regardless of their specific infectious status.
Which of the following is an example of a condition requiring contact precautions?
Explanation
MRSA is a multidrug-resistant bacterium that can be spread through direct contact with an infected individual or contaminated objects. Contact precautions, including the use of gloves and gowns, are necessary to prevent its transmission.
Incorrect choices:
a. Influenza is primarily spread through respiratory droplets and requires droplet precautions.
c. Pertussis (whooping cough) is also spread through respiratory droplets and requires droplet precautions.
d. Tuberculosis requires airborne precautions due to the risk of transmission through airborne particles.
Which precaution is appropriate for a client with a respiratory infection caused by the influenza virus?
Explanation
Influenza is primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets generated when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. Droplet precautions, including wearing a mask and maintaining a safe distance, are necessary to prevent its spread.
Incorrect choices:
a. Contact precautions are not required for influenza unless the client also has additional conditions or infections that warrant contact precautions.
c. Airborne precautions are not necessary for influenza, as it is primarily transmitted through droplets rather than airborne particles.
d. Standard precautions should always be followed, but additional precautions specific to the mode of transmission (in this case, droplet precautions) are required for effective infection control.
Which precaution is used for a client with a draining wound infection?
Explanation
Contact precautions are used for clients with infections or conditions that are transmitted through direct or indirect contact with the client or their environment. A draining wound infection can potentially spread infectious material to others, requiring contact precautions, including the use of gloves and gowns.
Incorrect choices:
b. Droplet precautions are not necessary for a draining wound infection unless there is evidence of concurrent respiratory infection or the wound is contaminated with respiratory secretions.
c. Airborne precautions are not needed for a draining wound infection unless there is evidence of airborne pathogens present in the wound.
d. Standard precautions should always be followed, but additional precautions specific to the mode of transmission (in this case, contact precautions) are necessary when dealing with infectious wounds.
Which precaution is used for a client with a draining wound infection?
Explanation
Contact precautions are used for clients with infections or conditions that are transmitted through direct or indirect contact with the client or their environment. A draining wound infection can potentially spread infectious material to others, requiring contact precautions, including the use of gloves and gowns.
Incorrect choices:
b. Droplet precautions are not necessary for a draining wound infection unless there is evidence of concurrent respiratory infection or the wound is contaminated with respiratory secretions.
c. Airborne precautions are not needed for a draining wound infection unless there is evidence of airborne pathogens present in the wound.
d. Standard precautions should always be followed, but additional precautions specific to the mode of transmission (in this case, contact precautions) are necessary when dealing with infectious wounds.
True or False: Standard precautions are sufficient for all clients, regardless of their infectious status.
Explanation
Standard precautions are the foundation of infection prevention and control and should be followed for all clients. They include hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), safe injection practices, respiratory hygiene, and environmental controls. Standard precautions are designed to prevent the transmission of common infectious agents and should be followed in addition to any specific transmission-based precautions that may be required.
When should healthcare providers perform hand hygiene?
Explanation
Before and after every patient contact or care activity Explanation: Hand hygiene should be performed before and after every patient contact or care activity to prevent the transmission of microorganisms.
Incorrect choices:
a. Hand hygiene should be performed before and after every patient contact or care activity, not limited to direct contact with bodily fluids.
b. Hand hygiene should be performed both before and after patient care tasks, not only after completing all tasks.
d. Hand hygiene should be performed regardless of visible dirt or contamination, as microorganisms may be present even if not visible.
What is the recommended duration for performing hand hygiene using an alcohol-based hand rub?
Explanation
The recommended duration for using an alcohol-based hand rub is approximately 15 seconds, ensuring all surfaces of the hands are thoroughly covered and rubbed until dry.
Incorrect choices:
a. 5 seconds is insufficient for proper hand hygiene using an alcohol-based hand rub.
c. 30 seconds and
d. 60 seconds are longer than necessary for using an alcohol-based hand rub and can lead to wastage of the product.
Which of the following is true regarding hand hygiene with soap and water?
Explanation
If alcohol-based hand rubs are not readily available, hand hygiene with soap and water can be used as an effective alternative.
Incorrect choices:
b. Hand hygiene with soap and water is equally effective as using hand rubs, as long as proper technique and sufficient duration are followed.
c. Hand hygiene with soap and water requires friction and rubbing to effectively remove microorganisms.
d. Hand hygiene with soap and water should be performed even if gloves were worn during patient care, as gloves may have microscopic defects or contamination.
Which of the following is an appropriate method for drying hands after hand hygiene?
Explanation
Using a paper towel for drying hands and turning off the faucet is an appropriate method to maintain hand hygiene after the handwashing process.
Incorrect choices:
b. Shaking hands vigorously can increase the risk of cross-contamination and should be avoided.
c. Wiping hands on a disposable gown or apron can lead to contamination of the gown and should not be done.
d. Using a shared hand towel with other healthcare providers can promote the spread of microorganisms and is not recommended.
True or False: Hand hygiene should be performed even if gloves are worn during patient care.
Explanation
Hand hygiene should be performed before donning gloves, after removing gloves, and whenever there is a risk of cross-contamination or transmission of microorganisms. Gloves are not a substitute for hand hygiene.
Which of the following is an example of appropriate use of personal protective equipment (PPE)?
Explanation
Answer: c. Wearing a surgical mask in place of a respirator when caring for a patient with tuberculosis Explanation: When caring for a patient with tuberculosis, the appropriate use of PPE includes wearing a respirator to protect against airborne transmission of the infectious agent.
Incorrect choices:
a. Wearing gloves when handling non-infectious materials is unnecessary and does not align with appropriate PPE use.
b. Reusing a disposable gown after disinfection is not recommended as disposable gowns are meant for single-use to prevent cross-contamination.
d. Wearing goggles only when there is a risk of splashing does not provide adequate eye protection in all situations where eye exposure may occur.
Which of the following is true regarding the order of donning and removing PPE?
Explanation
Answer: c. The gown should be removed before the gloves. Explanation: When removing PPE, the gown should be removed before the gloves to prevent contamination of the hands during the process.
Incorrect choices: a. Gloves should be removed last after removing the gown to minimize the risk of contaminating the hands.
b. The mask should be donned before wearing gloves to ensure proper respiratory protection.
d. The mask should be removed after removing the goggles or face shield to maintain a barrier against respiratory droplets.
Which of the following is an example of appropriate glove use?
Explanation
Answer: b. Touching clean surfaces with gloved hands
Explanation: Gloves should not be considered a substitute for hand hygiene. Touching clean surfaces with gloved hands can contaminate those surfaces, and proper hand hygiene should be performed after glove removal.
Incorrect choices: a. Wearing the same pair of gloves for multiple patient care tasks increases the risk of cross-contamination and is not recommended.
c. Gloves should be removed after completing all necessary patient care tasks and hand hygiene should be performed immediately.
d. Gloves should be removed and hand hygiene performed before touching clean surfaces.
When should a healthcare provider wear a gown as part of their PPE?
Explanation
Answer: b. When providing oral care to an unconscious patient
Explanation: When providing oral care to an unconscious patient, a gown should be worn to protect against potential contact with bodily fluids or contaminants.
Incorrect choices:
a. Wearing a gown during routine hand hygiene is unnecessary and not recommended.
c. Wearing a gown while transporting a stable patient within the facility is unnecessary unless there is a risk of contact with potentially infectious materials.
d. Wearing a gown when administering oral medication to a non-isolated patient is not typically required unless there is a risk of splashing or exposure to bodily fluids.
Which of the following is true regarding the use of N95 respirators?
Explanation
Answer: c. N95 respirators should be fit-tested to ensure proper seal and protection.
Explanation: N95 respirators should be fit-tested to ensure a proper seal and provide adequate respiratory protection.
Incorrect choices:
a. N95 respirators should only be used when there is a risk of airborne transmission, such as caring for patients with airborne infections.
b. N95 respirators are not designed for multiple reuse and should be disposed of properly after use to prevent contamination and maintain effectiveness.
Which of the following actions is recommended as part of respiratory hygiene practices?
Explanation
Answer: b. Using a tissue to cover the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
Explanation: Using a tissue to cover the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing helps contain respiratory droplets and reduces the risk of spreading infectious respiratory illnesses.
Incorrect choices:
a. Coughing or sneezing into hands can lead to the spread of germs through direct contact with surfaces or other individuals.
c. Blowing the nose without using a tissue can result in the release of respiratory droplets and should be avoided.
d. Discarding used tissues on the floor is unsanitary and can contribute to the transmission of infections.
Explanation
Explanation: Healthcare providers should perform hand hygiene before and after each patient contact, including after assisting with respiratory procedures. This helps prevent the spread of pathogens to other patients and healthcare personnel.
Incorrect choices:
a. Performing hand hygiene only if visible soiling is present is insufficient, as pathogens may be present even when hands appear clean.
b. Performing hand hygiene every hour may not be frequent enough to maintain proper infection prevention and control.
d. Performing hand hygiene only once at the end of the shift does not ensure continuous protection throughout patient care interactions.
Explanation
Explanation: Providing masks to patients who are coughing or sneezing helps contain respiratory droplets and reduce the risk of spreading infections within the healthcare setting.
Incorrect choices:
a. Encouraging visitors to wear masks only if they have symptoms does not account for asymptomatic individuals who may be carriers of respiratory infections.
c. Allowing healthcare personnel to cough or sneeze freely in patient care areas is unhygienic and can contribute to the spread of infections.
d. Reusing masks throughout the day to conserve supplies increases the risk of contamination and compromises respiratory hygiene practices.
Explanation
Explanation: Maintaining a distance of 6 feet (2 meters) from someone who is coughing or sneezing helps reduce the risk of inhaling respiratory droplets and potential pathogen transmission.
Incorrect choices:
a. 1 foot (30 centimeters) may not provide sufficient distance to minimize the risk of inhaling respiratory droplets.
b. 3 feet (1 meter) is closer than the recommended distance and may not effectively reduce exposure to respiratory droplets.
d. 10 feet (3 meters) is farther than necessary for routine respiratory etiquette and may not be practical in most healthcare settings.
What is the appropriate method for disposing of used masks or tissues contaminated with respiratory secretions?
Explanation
Explanation: Used masks or tissues contaminated with respiratory secretions should be disposed of in a biohazard container to minimize the risk of exposure to infectious agents.
Incorrect choices:
a. Placing them in a regular waste bin increases the risk of contamination and potential spread of infections.
b. Flushing them down the toilet can cause plumbing issues and is not an appropriate method of disposal.
d. Leaving them on a clean surface for someone else to handle is unhygienic and may lead to cross-contamination.
Explanation
Explanation: Using single-use syringes and needles for each injection is an essential component of safe injection practices. It helps prevent the transmission of infectious agents between patients.
Incorrect choices:
a. Reusing needles on the same patient is not a safe practice as it can lead to contamination and infection.
b. Recapitulating needles increases the risk of accidental needlestick injuries and should be avoided.
c. Administering medication from a multidose vial to multiple patients can introduce contamination and increase the risk of infection.
Explanation
Explanation: Disposing of used needles and syringes in a biohazard sharps container is the recommended method. It ensures safe containment and proper disposal of sharps to minimize the risk of needlestick injuries and transmission of infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. Placing used needles and syringes in a regular trash bin is unsafe and can lead to accidental injuries for waste handlers.
b. Recapitulating needles is not recommended due to the increased risk of needlestick injuries.
d. Leaving used needles and syringes on the patient's bedside table is unsafe and can pose a risk to the patient and healthcare providers.
Explanation
Explanation: If a needlestick injury occurs during an injection, the healthcare provider should follow the facility's protocol for reporting the incident and receiving appropriate post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) to minimize the risk of infection transmission.
Incorrect choices:
a. Continuing with the injection procedure without reporting the needlestick injury is unsafe and can lead to further complications.
b. Washing the affected area with soap and water is a general first aid measure, but it is not sufficient in the case of a needlestick injury.
c. Discarding the used needle in a regular trash bin is inappropriate as it does not ensure proper handling and disposal of the contaminated needle.
Explanation
Explanation: It is unnecessary to clean the rubber stopper on a medication vial before withdrawing medication, as long as proper aseptic technique is used during the preparation process.
Incorrect choices:
a. Sharing medication vials among multiple patients, even with needle changes, can lead to contamination and should be avoided.
b. Drawing medication from a vial using the same syringe for multiple injections increases the risk of contamination and infection.
d. Ampules should be broken open using a sterile device or ampule breaker to ensure a clean break and prevent injuries.
What is the recommended duration for hand hygiene before and after administering injections?
Explanation
Explanation: The recommended duration for hand hygiene before and after administering injections is typically 15 seconds. This allows sufficient time to effectively clean the hands and reduce the risk of infection transmission.
Incorrect choices:
a. 5 seconds may not be enough to adequately clean the hands and remove potential pathogens.
c. 30 seconds and d. 60 seconds are longer than necessary for routine hand hygiene before and after administering injections.
Explanation
Explanation: The primary goal of environmental control in infection prevention is to minimize the risk of infection transmission by implementing strategies to eliminate or reduce the presence of infectious agents in the healthcare environment.
Incorrect choices:
a. Enhancing the aesthetic appeal of the healthcare facility is not the primary goal of environmental control in infection prevention, although it may be considered as part of overall facility management.
b. While environmental control measures can help reduce healthcare costs indirectly by preventing healthcare-associated infections, cost reduction is not the primary goal.
d. Increasing patient satisfaction scores is important but not the primary goal of environmental control in infection prevention.
Explanation
Explanation: Isolation gowns are an example of a physical barrier used for environmental control in infection prevention. They create a barrier between healthcare workers and patients, preventing the transfer of microorganisms.
Incorrect choices:
a. Hand hygiene stations are not physical barriers but rather a measure to promote hand hygiene.
b. Antimicrobial cleaners are chemical agents used for cleaning and disinfection, not physical barriers.
d. Air filtration systems are designed to control airborne contaminants but do not act as physical barriers themselves.
Explanation
Explanation: Proper ventilation is important in environmental control to minimize the concentration of airborne pathogens and maintain air quality within healthcare facilities.
Incorrect choices:
a. Maintaining a pleasant odor is a secondary consideration compared to infection prevention.
b. While energy conservation is important, it is not the primary purpose of proper ventilation in infection prevention.
c. Controlling temperature and humidity levels contribute to comfort but are not directly related to infection prevention through ventilation.
Explanation
Explanation: Disinfection of high-touch surfaces is an example of routine cleaning in environmental control. It involves regularly cleaning and disinfecting surfaces that are frequently touched by healthcare workers, patients, and visitors.
Incorrect choices:
a. Terminal disinfection after patient discharge is not considered routine cleaning but rather a more thorough cleaning process.
c. Sterilization of surgical instruments is a specialized process for eliminating all microorganisms, not routine cleaning.
d. Fumigation of patient rooms is a more extreme measure typically used for specific situations, such as outbreaks, and is not part of routine cleaning.
What is the purpose of implementing aseptic techniques in environmental control?
Explanation
Explanation: Aseptic techniques are used in environmental control to prevent the spread of infections in sterile areas, such as operating rooms or invasive procedure areas.
Incorrect choices:
a. Reducing energy consumption is not the primary purpose of implementing aseptic techniques.
b. While patient comfort is important, it is not the primary goal of aseptic techniques.
d. Maintaining a pleasant scent is not the primary purpose of aseptic techniques but can be achieved through other means unrelated to infection prevention.
Explanation
Explanation: Regular hand hygiene practices are essential for staff health and infection prevention. It helps reduce the risk of transmitting pathogens and maintaining a safe working environment.
Incorrect choices:
a. Compliance with personal phone usage policies is unrelated to staff health and immunization.
b. Adequate supply of office stationery is important for daily operations but not directly related to staff health and immunization.
d. Attending team-building activities is beneficial for team dynamics but not directly related to staff health and immunization.
Explanation
Explanation: Healthcare staff receiving immunizations helps prevent the transmission of infectious diseases to vulnerable patients and also protects themselves from contracting vaccine-preventable infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. Reducing the cost of healthcare services is not the primary reason for healthcare staff to receive immunizations.
b. Enhancing physical fitness levels is unrelated to the purpose of immunizations for infection prevention.
c. Compliance with organizational dress code policies does not address the importance of immunizations.
Explanation
Explanation: If a healthcare staff member has a known contraindication to a specific vaccine, it is important to refer them to occupational health services for further assessment and guidance regarding alternative options or accommodations.
Incorrect choices:
a. Ignoring the contraindication and administering the vaccine can jeopardize the staff member's health and well-being.
b. Consulting a coworker may not provide the appropriate expertise to address contraindications.
d. Delaying vaccination until the contraindication resolves may not be appropriate, as some contraindications may be permanent.
Explanation
Explanation: The influenza vaccine is a common vaccine recommended for healthcare staff to protect themselves and prevent the spread of influenza to patients and coworkers.
Incorrect choices:
a. Meningococcal vaccine is typically recommended for individuals at high risk or traveling to certain areas but may not be a common recommendation for healthcare staff.
b. Varicella vaccine is typically recommended for individuals who are not immune to chickenpox but may not be a primary recommendation for healthcare staff.
c. Pneumococcal vaccine is typically recommended for individuals at high risk or older adults but may not be a primary recommendation for all healthcare staff.
What is the purpose of staff health programs in infection prevention and control?
Explanation
Explanation: Staff health programs aim to promote and maintain the health and well-being of staff members, including measures such as immunizations, health screenings, and education on infection prevention and control.
Incorrect choices:
a. Providing extra breaks and time off is not the primary purpose of staff health programs.
b. Increasing the workload is counterproductive to promoting staff health and well-being.
d. Enforcing strict dress code policies is unrelated to the primary purpose of staff health programs.
Explanation
Explanation: Surveillance in infection prevention and control is performed to identify and control the spread of infections within healthcare settings.
Incorrect choices:
a. Tracking the movement of healthcare providers is not the primary purpose of surveillance.
b. Monitoring patient satisfaction is important but not the primary purpose of surveillance in infection prevention and control.
d. Ensuring compliance with documentation requirements is important but not the primary purpose of surveillance.
Explanation
Explanation: Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) that occur within healthcare facilities, such as surgical site infections, should be reported for surveillance and appropriate management.
Incorrect choices:
a. Common colds acquired outside the healthcare facility are not considered HAIs and do not require reporting.
c. Self-limiting gastrointestinal infections are not typically considered HAIs and may not require reporting.
d. Mild respiratory infections in healthcare providers may not necessarily be considered HAIs and may not require reporting.
Explanation
Explanation: Reporting infections in healthcare facilities allows for the monitoring of trends and patterns, which helps in the identification of potential outbreaks and implementation of appropriate preventive measures.
Incorrect choices:
a. Identifying the responsible healthcare provider is not the primary purpose of infection reporting.
b. Allocating additional funding for infection control may be a potential outcome of infection reporting but is not the primary purpose.
d. Assigning blame for the occurrence of infections is not the primary purpose of infection reporting.
Explanation
Explanation: Effective infection surveillance requires the collection and analysis of accurate and timely data to identify trends, patterns, and potential areas for improvement.
Incorrect choices:
a. Conducting patient satisfaction surveys is important but is not directly related to infection surveillance.
b. Inspecting the physical environment is important for infection control but is not the primary component of infection surveillance.
c. Implementing staff disciplinary actions is not directly related to infection surveillance and may be more focused on individual incidents rather than overall surveillance.
Explanation
Explanation: Central line-associated bloodstream infections are considered serious healthcare-associated infections and should be reported to the appropriate regulatory agencies for surveillance and intervention.
Incorrect choices:
a. Minor skin abrasions are not typically considered reportable healthcare-associated infections.
b. Asymptomatic urinary tract infections in non-catheterized patients may not necessarily require reporting.
d. Self-limiting viral upper respiratory infections are not typically considered reportable healthcare-associated infections.
Explanation
Explanation: Analyzing infection surveillance data allows for the identification of trends and patterns, which can help in the implementation of targeted interventions and preventive measures.
Incorrect choices:
a. Identifying the individual responsible for the infection is not the primary purpose of analyzing surveillance data.
b. Determining the cost of treating infections may be a potential outcome of data analysis but is not the primary purpose.
d. Assigning blame for the occurrence of infections is not the primary purpose of analyzing surveillance data.
Explanation
Explanation: Submitting electronic reports to public health agencies is a common method used for reporting infections in healthcare facilities, ensuring appropriate surveillance and monitoring.
Incorrect choices:
a. Posting infection-related data on social media platforms is not a recommended method for reporting infections in healthcare facilities.
b. Sending individual emails may not be practical for reporting infections on a larger scale.
d. Publishing infection reports in local newspapers is not a standard method for reporting infections in healthcare facilities.
More Questions
Explanation
Explanation: Healthcare-associated infections are infections that occur as a result of receiving healthcare, such as in hospitals or other healthcare settings.
Incorrect choices:
a. A cold contracted from a family member is not an example of a healthcare-associated infection.
c. Food poisoning from contaminated food is not an example of a healthcare-associated infection.
d. Athlete's foot from a public swimming pool is not an example of a healthcare-associated infection.
Explanation
Explanation: Hand hygiene is considered the most effective way to prevent the transmission of healthcare-associated infections. It includes washing hands with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizers.
Incorrect choices:
a. Wearing gloves during patient care is important but not as effective as hand hygiene in preventing infection transmission.
c. Disinfecting surfaces regularly is important for infection control, but hand hygiene is the most effective measure.
d. Administering prophylactic antibiotics is not a preventive measure for healthcare-associated infections but rather a treatment option in certain cases.
Explanation
Explanation: Respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette is a standard precaution that involves covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing and using tissues or elbow to prevent the spread of respiratory droplets.
Incorrect choices:
a. Wearing a gown and gloves during a sterile procedure is an example of contact precautions, not standard precautions.
c. Placing a patient in airborne isolation is an example of airborne precautions, not standard precautions.
d. Using dedicated equipment for each patient is an example of transmission-based precautions, not standard precautions.
Explanation
Explanation: The recommended duration for performing hand hygiene with alcohol-based hand sanitizers is approximately 15 seconds, ensuring all surfaces of the hands are covered and allowed to dry.
Incorrect choices:
a. 5 seconds is not a sufficient duration for effective hand hygiene with alcohol-based hand sanitizers.
c. 30 seconds and d. 60 seconds are longer durations than necessary for alcohol-based hand sanitizers.
Explanation
Explanation: When entering the room of a patient with tuberculosis, healthcare workers should wear a fitted N95 respirator mask to protect against airborne transmission.
Incorrect choices:
a. Gloves and gown are necessary for contact precautions, but the primary concern with tuberculosis is airborne transmission.
b. Mask and goggles are not sufficient for protecting against airborne transmission of tuberculosis.
d. Face shield and gloves are not the recommended combination of PPE for tuberculosis precautions.
Explanation
Explanation: The appropriate technique for removing PPE after caring for a patient with a highly contagious infection is to remove the gown first, followed by the gloves, mask, and goggles, in order to minimize the risk of self-contamination.
Incorrect choices:
a. Removing gloves first can lead to contamination of the hands when removing the gown. The correct order is to remove the gown first.
c. Removing the goggles first can potentially expose the eyes to contamination. The correct order is to remove the gown first.
d. Removing the mask first can potentially expose the face to contamination. The correct order is to remove the gown first.
Explanation
Explanation: Sterile gloves should be worn when performing invasive procedures, such as administering intravenous medication, to maintain a sterile field and prevent infection.
Incorrect choices:
a. Oral hygiene does not require sterile gloves. Non-sterile gloves should be used.
b. Emptying a urinary drainage bag does not require sterile gloves. Non-sterile gloves should be used.
d. Assisting a patient with ambulation does not require sterile gloves. Non-sterile gloves should be used.
Explanation
Explanation: The appropriate technique for cleaning a contaminated surface is to use a detergent or disinfectant to effectively remove or kill microorganisms present on the surface.
Incorrect choices:
a. Wiping the surface with a dry cloth does not effectively remove microorganisms. Cleaning agents should be used.
b. Spraying the surface with water alone does not effectively kill microorganisms. Detergent or disinfectant is required.
d. Blowing air over the surface does not effectively clean or disinfect it. Cleaning agents should be used.
Explanation
Explanation: Practicing proper hand hygiene is an important infection prevention measure in healthcare settings and can help reduce the risk of healthcare-associated infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. Using sterile technique during surgical procedures is a specific practice for maintaining a sterile field but does not address overall infection prevention.
c. Administering prophylactic antibiotics before surgery is a strategy to prevent surgical site infections but does not encompass all healthcare-associated infections.
d. Performing routine maintenance of medical equipment is important for preventing equipment-related infections but is not the only infection prevention measure.
What is the primary purpose of using isolation precautions in healthcare settings?
Explanation
Explanation: The primary purpose of using isolation precautions is to protect patients from getting infections and to prevent the spread of infectious agents within healthcare settings.
Incorrect choices:
a. Protecting healthcare providers from getting infections is important but not the primary purpose of isolation precautions.
c. Restricting visitors' access to healthcare facilities may be a component of infection control but is not the primary purpose of isolation precautions.
d. Reducing healthcare costs associated with infections is a potential benefit of effective infection prevention and control, but it is not the primary purpose of isolation precautions.
Immunodefeciency disorders
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Immunodeficiency disorders can lead to an increased susceptibility to infections. Immunodeficiency disorders are characterized by a weakened or impaired immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, both common and opportunistic.
Incorrect choices:
a. Immunodeficiency disorders result from a weakened immune system, not an overactive one. In overactive immune responses, autoimmune disorders may occur.
b. While some immunodeficiency disorders have a genetic basis, not all cases are caused by genetic factors. Some immunodeficiency disorders can be acquired later in life due to infections, medications, or other factors.
d. Immunodeficiency disorders are not typically treated with anti-inflammatory medications. Treatment may involve immunoglobulin replacement therapy, antiviral medications, or stem cell transplantation, depending on the specific disorder and its underlying cause.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Allergic reactions and skin rashes are not typically associated with immunodeficiency disorders. Immunodeficiency disorders primarily result in an increased susceptibility to infections and recurrent, severe infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. Frequent, severe infections are a common symptom of immunodeficiency disorders due to the weakened immune response, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
b. Fatigue and weakness can occur in individuals with immunodeficiency disorders due to the impact of chronic infections on the body's energy reserves.
d. Delayed wound healing may occur in individuals with immunodeficiency disorders due to the impaired immune response and decreased ability to fight infections at the site of a wound.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is b. Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID). CVID is an example of a primary immunodeficiency disorder, which is typically caused by genetic mutations affecting the immune system's development and function.
Incorrect choices:
a. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection is an example of a secondary immunodeficiency disorder, which occurs due to an external factor, such as a viral infection, damaging the immune system.
c. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that affects the joints and is not classified as an immunodeficiency disorder.
d. Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder involving insulin production and does not directly affect the immune system's function.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Immunodeficiency disorders involve a deficiency in the body's ability to fight infections. These disorders are characterized by a weakened or impaired immune system, leading to an increased susceptibility to infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. Immunodeficiency disorders are not characterized by an overactive immune system. Instead, they are characterized by an underactive or weakened immune system.
b. Immunodeficiency disorders do not result from excessive production of antibodies. Instead, they involve a deficiency in the production or function of immune cells or antibodies.
d. Immunodeficiency disorders primarily affect the immune system, not the nervous system.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is b. Primary immunodeficiency disorders result from a genetic or inherited defect, while secondary immunodeficiency disorders are caused by external factors, such as infections or medications.
Incorrect choices:
a. Primary immunodeficiency disorders are present from birth and are usually genetic or inherited, while secondary immunodeficiency disorders can be acquired later in life due to external factors.
c. The manifestations and systems affected by primary and secondary immunodeficiency disorders can vary widely and are not limited to specific areas of the body.
d. Secondary immunodeficiency disorders are more common than primary immunodeficiency disorders, as they can be caused by various factors and are often associated with other medical conditions.
What is the primary cause of immunodeficiency disorders?
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is b. Genetic or inherited defects. Immunodeficiency disorders are primarily caused by genetic mutations or defects that result in a weakened or impaired immune system.
Incorrect choices:
a. While environmental factors can contribute to the development of secondary immunodeficiency disorders, they are not the primary cause of most immunodeficiency disorders.
c. Autoimmune reactions are not the primary cause of immunodeficiency disorders. Autoimmune disorders involve the immune system attacking the body's own tissues, not a deficiency in the immune system.
d. Excessive production of white blood cells is not the primary cause of immunodeficiency disorders. In fact, immunodeficiency disorders are characterized by a deficiency or impairment of white blood cells, which are essential components of the immune system.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is b. Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID). CVID is a primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by a reduced level of immunoglobulins, particularly IgA, leading to an increased susceptibility to infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is a more severe immunodeficiency disorder that affects multiple components of the immune system, not specifically IgA levels.
c. DiGeorge syndrome is caused by a genetic abnormality and is characterized by a defect in the development of certain organs, including the thymus and parathyroid glands. It may result in immune system abnormalities but does not primarily involve IgA deficiency.
d. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is a rare X-linked genetic disorder that affects platelet function and immune system regulation but is not specifically associated with IgA deficiency.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is a. Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). SCID is a severe and rare primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by the absence or severe impairment of both T and B cells, leading to a profound deficiency in cellular and humoral immunity.
Incorrect choices:
b. X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) primarily affects B-cell function, resulting in a lack of mature B cells and low levels of immunoglobulins, but does not typically involve T-cell deficiency.
c. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome affects platelet function and immune system regulation, but it is not characterized by a deficiency of both T and B cells.
d. Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is characterized by reduced levels of immunoglobulins, particularly IgG and IgA, but it does not typically lead to a complete deficiency of both T and B cells.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is d. Selective IgA deficiency. This disorder is characterized by a lack of immunoglobulin A, which can lead to an increased susceptibility to infections, particularly in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts.
Incorrect choices:
a. Selective IgM deficiency is a rare immunodeficiency disorder characterized by a lack of immunoglobulin M (IgM), not IgA.
b. X-linked agammaglobulinemia is a primary immunodeficiency disorder caused by a mutation in the BTK gene, resulting in a deficiency of B cells and immunoglobulins.
c. Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by decreased levels of immunoglobulins, including IgA, IgG, and IgM.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is b. DiGeorge syndrome. This disorder is caused by a deletion in chromosome 22, resulting in the underdevelopment of the thymus and parathyroid glands. It leads to impaired T cell function and is associated with developmental delays, chronic infections, and autoimmune problems.
Incorrect choices:
a. X-linked agammaglobulinemia is a primary immunodeficiency disorder that primarily affects B cell function, leading to a deficiency of immunoglobulins (antibodies).
c. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is an X-linked recessive disorder characterized by a triad of symptoms: eczema, thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), and immunodeficiency.
d. Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is a group of rare disorders characterized by a severe deficiency of T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells.
Which type of immunodeficiency disorder is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern and primarily affects males, leading to the absence of mature B cells and immunoglobulins?
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. X-linked agammaglobulinemia. This disorder primarily affects males and is caused by mutations in the BTK gene, resulting in a lack of mature B cells and immunoglobulins.
Incorrect choices:
a. Selective IgA deficiency is a primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by a deficiency of immunoglobulin A (IgA), and it can affect both males and females.
b. DiGeorge syndrome is caused by a chromosome 22 deletion and is not inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern.
d. Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is a group of disorders that can be inherited in various patterns, including autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant, or X-linked recessive. SCID affects both males and females and results in a severe deficiency of T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is b. Persistent fever and night sweats. Fever and night sweats are common clinical manifestations of immunodeficiency disorders. The immune system's inability to fight off infections can lead to recurrent fevers and night sweats as the body tries to combat pathogens.
Incorrect choices:
a. Hyperactivity and restlessness are not typical clinical manifestations of immunodeficiency disorders. These symptoms are more commonly associated with conditions affecting the central nervous system.
c. Weight gain and increased appetite are not typical clinical manifestations of immunodeficiency disorders. They may be seen in conditions like hypothyroidism or hormonal imbalances.
d. Elevated blood pressure is not a common clinical manifestation of immunodeficiency disorders. It may be seen in conditions like hypertension or cardiovascular disorders.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is d. Abdominal pain and diarrhea. Abdominal pain and diarrhea are common clinical manifestations of immunodeficiency disorders. The weakened immune system makes the child more susceptible to gastrointestinal infections, leading to these symptoms.
Incorrect choices:
a. Rash and hives are more common clinical manifestations of allergic reactions or immune hypersensitivity disorders, not immunodeficiency disorders.
b. Rapid weight loss may be seen in conditions like malnutrition or metabolic disorders but is not a typical clinical manifestation of immunodeficiency disorders.
c. Excessive thirst and frequent urination are clinical manifestations of diabetes or other endocrine disorders, not immunodeficiency disorders.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is b. Recurrent skin infections. Recurrent skin infections are common clinical manifestations of immunodeficiency disorders in the elderly. The weakened immune system makes the skin more susceptible to infections and delays wound healing.
Incorrect choices:
a. Impaired balance and coordination are more commonly associated with neurological disorders or conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system, not immunodeficiency disorders.
c. Vision changes and blindness may be seen in conditions affecting the eyes or the visual system but are not typical clinical manifestations of immunodeficiency disorders.
d. Hearing loss is more commonly associated with conditions affecting the ears or the auditory system and is not a typical clinical manifestation of immunodeficiency disorders.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Frequent and severe infections. Immunodeficiency disorders impair the body's ability to fight infections, leading to recurrent and severe infections. This is a hallmark sign of immunodeficiency.
Incorrect choices:
a. Hyperactivity and restlessness are not typical clinical manifestations of immunodeficiency disorders. These symptoms are more commonly associated with conditions like attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
b. Increased appetite and weight gain are not specific to immunodeficiency disorders. They may be seen in conditions like hypothyroidism or certain eating disorders.
d. Hypertension and tachycardia are not characteristic clinical manifestations of immunodeficiency disorders. These symptoms may be associated with cardiovascular issues.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Chronic diarrhea. Primary immunodeficiency disorders can affect the gastrointestinal system, leading to chronic diarrhea due to frequent infections and inflammation.
Incorrect choices:
a. Unexplained weight loss is not a specific symptom of primary immunodeficiency disorders. It may be seen in various other medical conditions, such as cancer or metabolic disorders.
b. Recurrent skin rashes are not a characteristic symptom of primary immunodeficiency disorders. Skin rashes may be caused by allergic reactions or dermatological conditions.
d. Difficulty falling asleep is not typically associated with primary immunodeficiency disorders. It may be related to sleep disorders or anxiety.
Which of the following clinical manifestations is often observed in individuals with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)?
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Failure to thrive. SCID is a severe form of immunodeficiency that affects multiple components of the immune system, leading to recurrent and severe infections and failure to thrive in affected infants.
Incorrect choices:
a. Recurrent ear infections are more commonly seen in other types of immunodeficiency disorders, such as selective IgA deficiency.
b. Chronic fatigue and lethargy may be seen in various medical conditions but are not specific to SCID.
d. Persistent joint pain is not a characteristic symptom of SCID. It may be associated with other autoimmune or inflammatory conditions.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is d. Flow cytometry for lymphocyte subsets. Flow cytometry is a diagnostic test used to analyze the quantity and types of lymphocytes in the blood, which helps identify abnormalities in the immune system and diagnose immunodeficiency disorders.
Incorrect choices:
a. A complete blood count (CBC) provides general information about the client's overall blood cell counts, but it does not specifically diagnose immunodeficiency disorders.
b. Urinalysis is used to assess kidney function and identify urinary tract infections but is not a specific test for diagnosing immunodeficiency disorders.
c. Skin testing for allergies is performed to identify allergic reactions to specific allergens and is not used to diagnose immunodeficiency disorders.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is d. Absence or significantly reduced T cell levels. Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is characterized by a severe deficiency or absence of T cells, which are essential for cell-mediated immunity.
Incorrect choices:
a. Increased levels of circulating B cells are not characteristic of SCID. In SCID, both T and B cell immunity are affected, and the client may have reduced levels of both.
b. Elevated immunoglobulin M (IgM) levels may occur in certain types of immunodeficiency disorders, but it is not a specific finding for SCID.
c. Abnormal antibody response to vaccinations can be observed in various immunodeficiency disorders, but it does not specifically indicate SCID.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is a. The procedure will assess the function of the client's immune system. A bone marrow aspiration is a diagnostic procedure that involves extracting a sample of bone marrow to evaluate the production and function of blood cells, including immune cells.
Incorrect choices:
b. A bone marrow aspiration does not involve removing lymph nodes. It is a procedure specifically focused on obtaining a bone marrow sample.
c. General anesthesia is not typically used for a bone marrow aspiration. Instead, local anesthesia is administered to numb the area around the bone marrow site.
d. A bone marrow aspiration is not a blood test to measure circulating antibodies. It is used to evaluate the bone marrow's cellular components, not circulating antibodies.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is a. Complete blood count (CBC) with differential. A CBC with differential is a standard diagnostic test used to assess the levels of different blood cells, including white blood cells, which are crucial for the immune system. Abnormalities in the white blood cell count and differential can indicate potential immunodeficiency.
Incorrect choices:
b. A chest X-ray is not a specific diagnostic test for immunodeficiency disorders. It is typically used to assess the condition of the lungs and chest organs.
c. An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test used to assess the electrical activity of the heart and is not related to the diagnosis of immunodeficiency disorders.
d. A urinalysis is a test used to assess the urine for various abnormalities and is not specific to diagnosing immunodeficiency disorders.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Serum immunoglobulin levels. A primary immunodeficiency disorder often results in abnormal levels of immunoglobulins (antibodies) in the blood. Measuring serum immunoglobulin levels can help identify potential deficiencies and guide the diagnosis of primary immunodeficiency disorders.
Incorrect choices:
a. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a test used to detect specific antibodies or antigens in the blood, but it is not specific to diagnosing primary immunodeficiency disorders.
b. A chest X-ray is not a specific test for diagnosing primary immunodeficiency disorders. It is typically used to assess the condition of the lungs and chest organs.
d. A complete blood count (CBC) is a general blood test that may reveal abnormalities in white blood cell count but does not specifically assess immunoglobulin levels.
The nurse is caring for an infant suspected of having severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). Which diagnostic test should the nurse anticipate being prescribed for the infant?
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Flow cytometry. Flow cytometry is a specialized test used to analyze the different cell types in a blood sample. In the case of SCID, flow cytometry can help identify the absence or severe deficiency of T cells and B cells, which are essential components of the immune system.
Incorrect choices:
a. A tuberculin skin test (TST) is used to detect exposure to tuberculosis (TB) and is not specific to diagnosing SCID.
b. A Western blot test is a type of immunoassay used to detect specific antibodies or antigens in the blood but is not specific to diagnosing SCID.
d. Liver function tests are used to assess the health of the liver and are not specific to diagnosing SCID.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Administer intramuscular immunoglobulins (IG) as ordered. For clients with immunodeficiency disorders, intramuscular immunoglobulins can be prescribed to provide passive immunity and help prevent infections. Immunoglobulins contain antibodies that the client's immune system may be lacking, offering protection against various pathogens.
Incorrect choices:
a. Encouraging the client to receive live vaccines is not appropriate for clients with immunodeficiency disorders. Live vaccines contain live, attenuated viruses or bacteria, which can cause severe infections in individuals with compromised immune systems.
b. Prescribing broad-spectrum antibiotics prophylactically may be used in some cases, but it is not the first-line treatment for immunodeficiency disorders. It is essential to identify the specific pathogens causing infections before initiating antibiotic therapy to avoid antimicrobial resistance.
d. Initiating high-dose corticosteroid therapy is not appropriate for the management of immunodeficiency disorders. Corticosteroids can suppress the immune system further and increase the risk of infections in these clients.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is a. "Practice proper hand hygiene and infection prevention measures." Proper hand hygiene, including regular handwashing with soap and water, is essential for clients with immunodeficiency disorders to reduce the risk of acquiring infections. It is one of the most effective ways to prevent the transmission of pathogens.
Incorrect choices:
b. Engaging in intense physical activities is not recommended for clients with immunodeficiency disorders, as it can put additional stress on the immune system. Moderate, regular exercise is beneficial for overall health, but extreme physical activities may be harmful to the immune system.
c. There is no need for clients with immunodeficiency disorders to limit their fluid intake unless they have a medical condition that requires fluid restriction. Adequate fluid intake is essential for overall health and immune function.
d. Consuming a diet rich in raw and undercooked meat is not recommended for clients with immunodeficiency disorders, as it can increase the risk of foodborne infections. It is important for these clients to follow food safety guidelines and avoid consuming raw or undercooked meat.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is a. Complete blood count (CBC) with differential. A CBC with differential is essential for monitoring the client's immune status and treatment response. It provides information about the client's white blood cell count, including different types of white blood cells, such as lymphocytes, which play a crucial role in the immune response.
Incorrect choices:
b. Blood glucose level is not specifically related to monitoring the immune status or treatment response in clients with immunodeficiency disorders.
c. Liver function tests (LFTs) are important for monitoring liver health but are not directly related to the immune status or treatment response in clients with immunodeficiency disorders.
d. An electrolyte panel is used to assess the balance of electrolytes in the body and is not specifically related to monitoring the immune status or treatment response in clients with immunodeficiency disorders.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is d. Ensuring the client receives prophylactic antibiotics as prescribed. Prophylactic antibiotics are commonly prescribed for clients with immunodeficiency disorders to prevent bacterial infections. It is essential to adhere to the prescribed antibiotic regimen to minimize the risk of infections in these clients.
Incorrect choices:
a. Administering live vaccines is contraindicated in clients with immunodeficiency disorders, as live vaccines can cause severe infections in this population. Only inactivated vaccines are recommended for these clients.
b. Regular physical exercise is beneficial for overall health, but it is not a specific intervention for managing immunodeficiency disorders.
c. Strict isolation precautions may be necessary for clients with severe immunodeficiency or during periods of increased infection risk, but it is not the priority intervention for all clients with immunodeficiency disorders.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. "It's essential for me to receive all recommended vaccines, including live vaccines." Clients with primary immunodeficiency disorders should not receive live vaccines, as they can cause severe infections in this population. Only inactivated vaccines are recommended to avoid the risk of vaccine-associated infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. Avoiding contact with sick individuals is crucial for clients with primary immunodeficiency disorders to minimize the risk of acquiring infections.
b. Taking prescribed immunoglobulin therapy as scheduled is an important treatment for clients with primary immunodeficiency disorders to boost their immune response and prevent infections.
d. Reporting any signs of infection or illness promptly to the healthcare provider is essential for early detection and treatment of infections in clients with primary immunodeficiency disorders.
The nurse is caring for a client with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Which intervention should the nurse include in the client's plan of care?
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Ensuring the client receives antiretroviral therapy (ART) as prescribed. ART is the mainstay of treatment for HIV infection and is essential for suppressing viral replication, improving immune function, and preventing disease progression.
Incorrect choices:
a. Encouraging strenuous physical activities is not recommended for clients with HIV infection, as it may place additional stress on the immune system and exacerbate symptoms.
b. While a balanced diet is essential for overall health, there is no specific evidence that a diet high in raw fruits and vegetables alone can boost the immune system sufficiently to manage HIV infection.
d. Clients with HIV infection should follow infection control precautions to prevent the transmission of the virus to others. Interacting freely with other clients may put them and others at risk of infection transmission.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is b. "I will make sure to get all the live vaccines recommended for my age." Clients with immunodeficiency disorders should not receive live vaccines, as they can cause severe infections in this population. Only inactivated vaccines are recommended to avoid the risk of vaccine-associated infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. Avoiding contact with individuals who have colds or other infections is essential for clients with immunodeficiency disorders, as they are at a higher risk of acquiring infections.
c. Practicing good hand hygiene and washing hands frequently are essential infection prevention measures for clients with immunodeficiency disorders.
d. Informing the healthcare provider if any signs of infection develop is crucial for early detection and treatment of infections in clients with immunodeficiency disorders.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. "I need to limit my fluid intake to prevent fluid overload." There is no specific recommendation to limit fluid intake for clients with immunodeficiency disorders unless they have a medical condition that requires fluid restriction. Adequate fluid intake is essential for overall health, including immune function.
Incorrect choices:
a. Eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables is important for overall well-being, including supporting the immune system in clients with immunodeficiency disorders.
b. Avoiding raw or undercooked meat and eggs is recommended to prevent foodborne infections in all individuals, including those with immunodeficiency disorders.
d. Avoiding unpasteurized dairy products is important to reduce the risk of infections caused by foodborne pathogens in all individuals, including those with immunodeficiency disorders.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. "I should avoid close contact with pets to reduce the risk of infections." While it is essential to practice good hygiene when handling pets, avoiding close contact with pets is not typically necessary for clients with immunodeficiency disorders unless they have a specific allergy or pet-related infection.
Incorrect choices:
a. Avoiding crowded places and large gatherings is important for clients with immunodeficiency disorders, as it helps reduce the risk of exposure to infections.
b. Cleaning and disinfecting frequently touched surfaces in the home regularly can help prevent the transmission of infections in clients with immunodeficiency disorders.
d. Wearing a mask when visiting the hospital or healthcare settings is a standard infection prevention measure for clients with immunodeficiency disorders to reduce the risk of acquiring infections from others.
VI. Nursing Considerations:
.
Questions
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Implement strict infection control measures. Clients with immunodeficiency disorders have a weakened immune system and are more susceptible to infections. Implementing strict infection control measures, such as hand hygiene, using personal protective equipment, and limiting exposure to potential sources of infection, can help prevent the spread of pathogens and protect the client from infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. Encouraging the client to participate in crowded social gatherings can put the client at risk of exposure to infectious agents, which is not appropriate for someone with immunodeficiency.
b. Live vaccines contain weakened pathogens and are contraindicated for clients with immunodeficiency disorders, as they can cause serious infections in this population.
d. While a diet high in fresh fruits and vegetables is generally beneficial for overall health, it does not specifically address the increased risk of infections in clients with immunodeficiency disorders. Strict infection control measures are more relevant to preventing infections in these clients.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Limit visitors to family members only. Clients with immunodeficiency disorders are at increased risk of infections, and limiting visitors to family members only can help reduce the risk of exposure to infectious agents. It is essential to create a controlled and safe environment for these clients.
Incorrect choices:
a. Encouraging the client to interact with other clients in the unit can increase the risk of exposure to infections and is not appropriate for someone with immunodeficiency.
b. Live vaccines contain weakened pathogens and are contraindicated for clients with immunodeficiency disorders, as they can cause serious infections in this population.
d. Providing the client with a private room with negative pressure is not necessary for every client with immunodeficiency disorder. Negative pressure rooms are used for clients with specific airborne infectious diseases, and the decision to use such rooms is based on the specific circumstances of each client.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is d. Educating the client on proper hand hygiene. Educating the client on proper hand hygiene is essential to reduce the risk of infections in individuals with immunodeficiency disorders. Frequent handwashing is a simple yet effective way to prevent the transmission of infectious agents.
Incorrect choices:
a. Administering live vaccines is contraindicated for clients with immunodeficiency disorders, as live vaccines contain weakened pathogens that can cause serious infections in this population.
b. Encouraging the client to perform strenuous physical activities is not appropriate for someone with immunodeficiency, as strenuous activities can put additional strain on the immune system and increase the risk of infections.
c. Limiting the client's intake of fluids is not a necessary intervention for immunodeficiency disorders. Adequate fluid intake is generally important for overall health, but it is not directly related to managing immunodeficiency disorders.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is b. Limit the client's exposure to visitors and restrict contact with other clients in the healthcare setting. Clients with immunodeficiency disorders are at a higher risk of infections due to their weakened immune system. Restricting exposure to potential sources of infection, such as visitors and other sick clients, can help minimize the risk of acquiring infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. Engaging in vigorous physical activities may not be appropriate for clients with immunodeficiency disorders, as it can lead to an increased risk of infections and may not strengthen the immune system in these individuals.
c. Live vaccines are contraindicated for clients with immunodeficiency disorders, as they can cause severe infections in this population. Only inactivated vaccines are recommended to avoid the risk of vaccine-associated infections.
d. While a healthy diet is essential for overall well-being, there is no specific evidence to suggest that a diet high in fresh fruits and vegetables will improve immune function in clients with immunodeficiency disorders. Dietary considerations for these clients may include avoiding certain high-risk foods, but it should be discussed with the healthcare provider based on the specific immunodeficiency disorder.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is d. Maintain strict hand hygiene and utilize protective equipment when providing care. Children with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) have a severely compromised immune system, making them highly susceptible to infections. Strict hand hygiene and the use of protective equipment, such as gloves and masks, are essential in preventing the transmission of infections to the child.
Incorrect choices:
a. Placing the child on contact precautions may not be sufficient to protect them from infections due to their high susceptibility. Additional precautions, such as strict hand hygiene and protective equipment, should be implemented.
b. Encouraging the child to play with other children may increase the risk of exposure to infections. Children with SCID should be protected from contact with potential sources of infection.
c. Live attenuated vaccines are contraindicated for children with SCID, as they can cause severe infections. Only inactivated vaccines are recommended to avoid the risk of vaccine-associated infections.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is d. Teach the client about the importance of hand hygiene and infection control measures. For clients with immunodeficiency disorders, preventing infections is of utmost importance. Hand hygiene and infection control measures, such as proper handwashing techniques and avoiding contact with sick individuals, can help reduce the risk of acquiring infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. While consuming a diet rich in probiotics may be beneficial for gut health, there is no specific evidence to suggest that it will prevent infections in clients with immunodeficiency disorders.
b. Engaging in regular exercise may have various health benefits, but it may not necessarily boost the immune system in clients with immunodeficiency disorders. In fact, excessive exercise can even increase the risk of infections in these individuals.
c. Live vaccines are contraindicated for clients with immunodeficiency disorders, as they can cause severe infections. Only inactivated vaccines are recommended to avoid the risk of vaccine-associated infections.
The nurse is caring for a client with an immunodeficiency disorder. Which precaution should the nurse take when caring for the client?
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is a. Wear a mask when entering the client's room. Wearing a mask when entering the client's room is a standard precaution that can help prevent the transmission of infectious agents, especially for clients with immunodeficiency disorders who are at a higher risk of infections.
Incorrect choices:
b. Using a sterile dressing change technique for all wound care may not be necessary for all clients with immunodeficiency disorders. It is essential to assess the client's specific condition and wound characteristics to determine the appropriate dressing change technique.
c. Encouraging the client to wear a mask at all times may not be feasible or necessary, as masks are typically used to prevent the transmission of infections from the client to others, not the other way around.
d. Placing the client on strict isolation precautions may not be necessary for all clients with immunodeficiency disorders. The appropriate level of isolation precautions should be determined based on the client's specific condition and risk factors for infections.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Primary immunodeficiency disorders are typically present at birth or during early childhood and are caused by genetic defects that affect the function of the immune system. They are not acquired later in life due to environmental factors.
Incorrect choices:
a. Primary immunodeficiency disorders are not acquired later in life; they are usually genetic and present from birth.
b. Primary immunodeficiency disorders are characterized by a weakened or deficient immune response, not an overactive immune response.
d. Primary immunodeficiency disorders are often not easily treatable with antibiotics and antiviral medications because they result from genetic defects in the immune system.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Frequent and severe infections are common clinical manifestations of immunodeficiency disorders. The weakened immune system is unable to effectively defend against infections, leading to recurrent and severe infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. Severe allergic reactions are more characteristic of allergies or hypersensitivity disorders, not immunodeficiency disorders.
b. Chronic inflammation can be seen in various conditions, but it is not a specific clinical manifestation of immunodeficiency disorders.
d. Autoimmune diseases result from an overactive immune response attacking the body's own tissues, which is the opposite of immunodeficiency disorders where the immune system is weakened and unable to adequately protect against infections.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is characterized by a deficiency or absence of B cells, leading to a reduced ability to produce antibodies and an increased susceptibility to infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. DiGeorge syndrome is a disorder caused by a genetic defect resulting in the underdevelopment of the thymus and parathyroid glands, leading to T cell deficiency.
b. Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is a severe form of immunodeficiency that affects both B and T cells, leading to a complete absence or dysfunction of the immune system.
d. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is a rare X-linked genetic disorder characterized by a triad of symptoms, including eczema, low platelet count, and immunodeficiency. It primarily affects T cells and platelets, not B cells.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is d. Immunoglobulin replacement therapy is a common treatment option for patients with primary immunodeficiency disorders. It involves infusing patients with immunoglobulins (antibodies) to help boost their immune response and protect against infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. Allergy shots are used to desensitize the immune system to specific allergens in individuals with allergies, not to treat primary immunodeficiency disorders.
b. Immunosuppressive medications are used to suppress the immune response in conditions such as autoimmune diseases or after organ transplantation, but they are not typically used to treat primary immunodeficiency disorders.
c. Blood transfusions may be used to treat anemia or certain blood disorders, but they are not a specific treatment for primary immunodeficiency disorders.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Autoimmune diseases are a potential complication of primary immunodeficiency disorders. When the immune system is deficient or dysfunctional, it may fail to distinguish between self and non-self antigens, leading to the development of autoimmune diseases.
Incorrect choices:
a. Hypertension is a condition characterized by high blood pressure and is not directly related to primary immunodeficiency disorders.
b. Chronic fatigue syndrome is a complex disorder with unknown causes and is not directly related to primary immunodeficiency disorders.
d. Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder caused by insufficient insulin production or insulin resistance and is not directly related to primary immunodeficiency disorders.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is d. Immunodeficiency disorders can be caused by medications or medical treatments. Immunodeficiency disorders are conditions in which the immune system is weakened or dysfunctional, leading to an increased susceptibility to infections. They can be primary (genetic) or secondary (acquired). Secondary immunodeficiency disorders can be caused by various factors, including medications (e.g., immunosuppressive drugs used after organ transplants), medical treatments (e.g., chemotherapy for cancer), and certain diseases (e.g., HIV/AIDS).
Incorrect choices:
a. Immunodeficiency disorders are characterized by a weakened immune system, not an overactive one. Overactive immune responses are seen in autoimmune disorders.
b. Immunodeficiency disorders can be both primary (genetic) and secondary (acquired) in nature. While some immunodeficiencies are genetic, others can be acquired later in life due to various factors.
c. Immunodeficiency disorders result in a decreased ability to fight infections, not an increased one. Individuals with immunodeficiencies are more susceptible to infections and may experience recurrent or severe infections.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is b. X-linked agammaglobulinemia. X-linked agammaglobulinemia is a primary immunodeficiency disorder caused by a genetic mutation that leads to the absence of mature B cells, resulting in an inability to produce antibodies (immunoglobulins). As a result, individuals with this disorder are highly susceptible to infections, especially bacterial infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. DiGeorge syndrome is a primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by abnormalities in the development of certain organs, including the thymus, leading to impaired T cell function.
c. Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is a group of rare genetic disorders that affect both T cells and B cells, resulting in a severe impairment of the immune system.
d. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a secondary immunodeficiency disorder caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, which specifically targets and destroys CD4+ T cells, weakening the immune system's ability to fight infections.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Frequent and severe infections. One of the hallmark features of immunodeficiency disorders is an increased susceptibility to infections. Individuals with immunodeficiencies may experience frequent and severe infections, including bacterial, viral, and fungal infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. Excessive inflammation at the site of infection is not a common clinical manifestation of immunodeficiency disorders. Immunodeficiencies are characterized by a weakened immune response, which may result in a reduced inflammatory response to infections.
b. Hyperactive immune response to allergens is seen in allergies and autoimmune disorders, not immunodeficiency disorders.
d. Immunodeficiency disorders are characterized by a lack or dysfunction of specific immune components, such as B cells or T cells, leading to a decreased production of antibodies, not increased.
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is d. Immunoglobulin levels. Immunoglobulin levels, specifically IgG, IgM, and IgA, are commonly measured to assess immune function and identify deficiencies in immunoglobulin production. Abnormalities in immunoglobulin levels can indicate the presence of an immunodeficiency disorder.
Incorrect choices:
a. A complete blood count (CBC) provides information about various blood components, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, but it does not specifically assess immune function.
b. A chest X-ray may be used to evaluate the condition of the lungs and detect infections, but it is not a specific test for immunodeficiency disorders.
c. Allergy skin testing is used to diagnose allergies and assess the body's response to allergens, but it is not a diagnostic test for immunodeficiency disorders.
Which type of immunodeficiency disorder is characterized by a lack of T cell function and is often referred to as "bubble boy disease"?
Explanation
Explanation: The correct answer is c. Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). SCID is a group of rare genetic disorders that affect both T cells and B cells, resulting in a severe impairment of the immune system. Individuals with SCID are highly susceptible to infections and may need to live in a protected environment to avoid exposure to pathogens, hence the term "bubble boy disease."
Incorrect choices:
a. DiGeorge syndrome is a primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by abnormalities in the development of certain organs, including the thymus, leading to impaired T cell function, but it does not affect B cell function.
b. X-linked agammaglobulinemia is a primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by a lack of mature B cells and an inability to produce antibodies, but it does not affect T cell function.
d. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a secondary immunodeficiency disorder caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, which specifically targets and destroys CD4+ T cells, but it does not affect B cell function.
Which of the following immunodeficiency disorders is characterized by defective T-cell function and is often diagnosed in infancy or early childhood?
Explanation
The correct answer is c. Ataxia-telangiectasia. Ataxia-telangiectasia is a rare genetic disorder that affects the cerebellum, causing poor muscle coordination (ataxia) and small, dilated blood vessels (telangiectasias). It also leads to defective T-cell function, making affected individuals more susceptible to infections.
Incorrect choices:
a. X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) is a primary immunodeficiency disorder that primarily affects B-cell function, leading to a lack of mature B cells and low levels of immunoglobulins, but does not involve defective T-cell function.
b. Selective immunoglobulin A (IgA) deficiency is characterized by a deficiency of IgA, but it does not typically lead to defective T-cell function.
d. DiGeorge syndrome is caused by a deletion on chromosome 22 and primarily affects the development of certain organs, including the thymus and parathyroid glands, resulting in T-cell deficiency. While it may lead to some B-cell abnormalities, defective T-cell function is the hallmark of this disorder.
Exams on Immunological System
Custom Exams
Login to Create a Quiz
Click here to loginLessons
 Nursingprepexams
Just Now
Nursingprepexams
Just Now
Notes Highlighting is available once you sign in. Login Here.
Role of nurses in immunology counselling
Objectives
- By the end of this module, learners should be able to explain basic immunology concepts to patients in a clear and understandable manner.
- After completing this topic, participants should be capable of discussing vaccine basics, schedules, and benefits with patients and families.
- At the conclusion of this learning experience, learners should be able to engage respectfully and sensitively with patients from diverse cultural backgrounds when discussing immunology.
- Upon engagement with this content, participants should be able to assist patients in making informed decisions about immunization and healthy practices.
- After this module, learners should be able to offer guidance and support to patients managing chronic immune-related conditions.
Introduction
- Immunology, the study of the immune system and its response to various threats plays a pivotal role in maintaining health and preventing diseases.
- Nurses, as frontline healthcare providers, have a vital role in counseling patients about immunology-related topics to promote understanding, adherence, and proactive health management
Patient Education
- Nurses provide clear and concise explanations of immunological concepts, such as immune responses, antibodies, antigens, and vaccines.
- Education empowers patients to make informed decisions about immunizations, preventive measures, and health behaviors.
Vaccine Counseling
- Nurses counsel patients and families about the importance of vaccines, vaccine schedules, and potential side effects.
- Addressing concerns and misconceptions promotes vaccine acceptance and enhances public health.
Disease Prevention
- Nurses educate patients about immunization schedules, highlighting vaccines for preventable diseases like influenza, measles, and COVID-19.
- Promoting immunization contributes to disease prevention and herd immunity.
Immune Disorders
- Nurses explain autoimmune disorders, allergies, and immunodeficiencies to patients and their families.
- Providing information about symptoms, triggers, and management strategies enhances patients' ability to recognize and manage these conditions.
Chronic Conditions and Immunity
- Nurses counsel patients with chronic illnesses on how their condition may impact their immune system's function.
- Empowering patients to manage their health optimally helps prevent complications and improve overall well-being.
Medication Adherence
- Nurses emphasize the importance of medication adherence for patients with immunosuppressive therapies, organ transplants, or chronic diseases.
- Educating patients about potential interactions and side effects ensures safe and effective treatment.
Infection Prevention
- Nurses counsel patients on infection prevention strategies, including proper hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and lifestyle adjustments.
- Proactive measures reduce the risk of infections and support overall immune health.
Health Promotion
- Nurses advocate for healthy lifestyle choices that support a robust immune system, such as balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and stress management.
- Empowering patients to adopt healthy habits contributes to overall immune resilience.
Cultural Sensitivity
- Nurses consider cultural beliefs and practices related to immunology and health, adapting counseling approaches accordingly.
- Respecting cultural diversity fosters effective communication and patient engagement.
Informed Decision-Making
- Nurses facilitate shared decision-making, ensuring patients understand the benefits, risks, and alternatives related to immunological interventions.
- Collaborative decision-making enhances patient autonomy and satisfaction.
Counseling During Outbreaks
- Nurses provide timely and accurate information during disease outbreaks, addressing concerns, dispelling myths, and promoting evidence-based practices.
- Clear communication helps mitigate panic and supports effective public health responses.
Conclusion
- In conclusion, nurses play a crucial role in counseling patients about immunology-related topics, fostering understanding, empowerment, and proactive health management.
- Through patient education, vaccine counseling, and disease prevention initiatives, nurses contribute to promoting optimal immune health and preventing immunology-related complications.
- Their role as educators and advocates significantly impacts patients' ability to make informed decisions and actively participate in their healthcare journey.
Immunity
Objectives
- Define the key components of the immune system:
- Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity:
- Understand the mechanisms of immune response:
- Identify factors that influence immune function:
- Recognize the significance of vaccination and immunization:
Introduction
- Immunity is a complex and intricate defense mechanism of the body that protects against infections, diseases, and harmful substances.
- The immune system is a network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to recognize and eliminate foreign invaders while maintaining tolerance to the body's own cells and tissues.
- Understanding the principles of immunity is essential for healthcare professionals as it plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and preventing various illnesses.
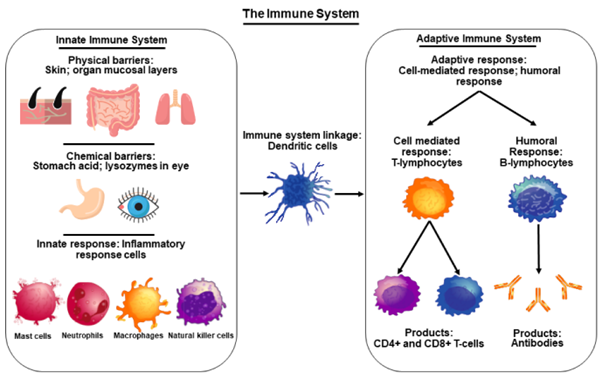
Components of the Immune System:
A. Innate Immunity:
1. Physical and Chemical Barriers: The first line of defense includes physical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes, along with chemical barriers such as enzymes and antimicrobial proteins that prevent the entry and growth of pathogens.
2. Inflammatory Response: When tissues are injured or invaded by pathogens, innate immune cells release chemical signals, leading to inflammation, which helps to destroy invaders and promote healing.
B. Adaptive Immunity:
1. Humoral Immunity: Mediated by B lymphocytes (B cells), humoral immunity produces antibodies that recognize and neutralize specific pathogens or foreign substances.
2. Cell-Mediated Immunity: Involves T lymphocytes (T cells) that directly attack infected or abnormal cells and modulate the immune response.
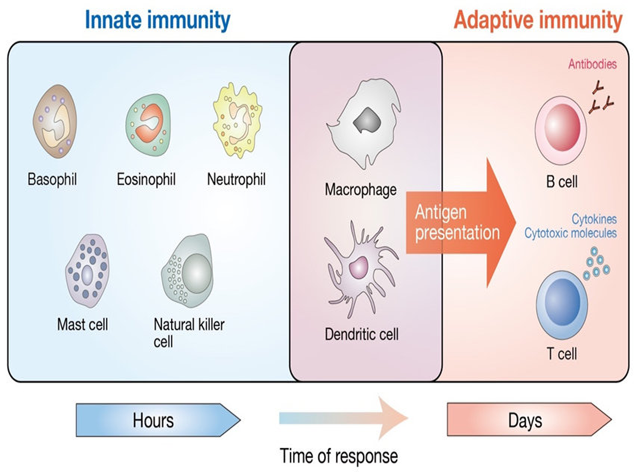
Immune Response and Antigen Recognition
A. Antigens: Antigens are foreign substances, such as proteins on the surface of pathogens or non-self cells, that trigger an immune response.
B. Antigen-Presenting Cells (APCs): Dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells are APCs that capture and process antigens to present them to T cells, initiating an adaptive immune response.
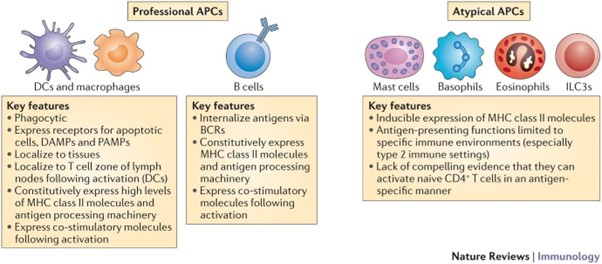
B Lymphocytes (B Cells) and Antibody-Mediated Immunity
A. B Cell Activation: When a B cell encounters its specific antigen, it becomes activated, undergoes clonal expansion, and differentiates into plasma cells and memory cells.
B. Antibody Production: Plasma cells secrete antibodies (immunoglobulins) that bind to antigens, marking them for destruction by other immune cells or neutralizing their harmful effects.
C. Types of Antibodies: There are five classes of antibodies (IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, and IgE), each with unique functions in the immune response.
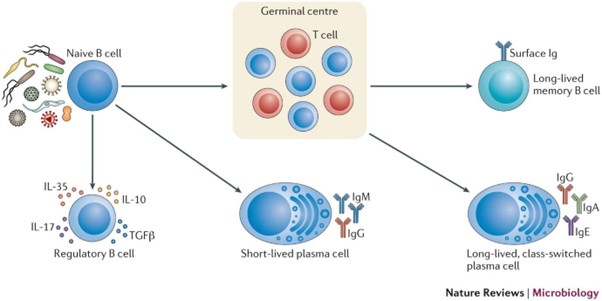
T Lymphocytes (T Cells) and Cell-Mediated Immunity
A. T Cell Activation: T cells are activated when they recognize antigen fragments presented on APCs through their T cell receptors (TCRs).
B. Types of T Cells:
1. Cytotoxic T Cells (CD8+): Destroy infected or abnormal cells directly by inducing apoptosis (programmed cell death).
2. Helper T Cells (CD4+): Assist B cells and cytotoxic T cells by secreting cytokines that enhance the immune response.
3. Regulatory T Cells (Tregs): Suppress the immune response to prevent excessive reactions and maintain self-tolerance.
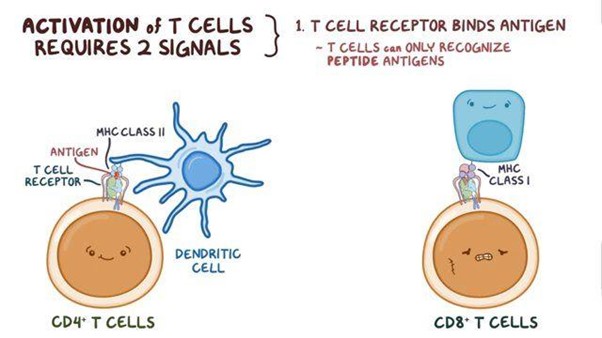
Memory and Secondary Immune Response
A. Memory Cells: Both B cells and T cells can form memory cells, which "remember" previous encounters with specific antigens and mount a faster and stronger response upon re-exposure.
B. Secondary Immune Response: If the body encounters the same antigen again, memory cells rapidly differentiate into effector cells, leading to a more robust and rapid immune response.
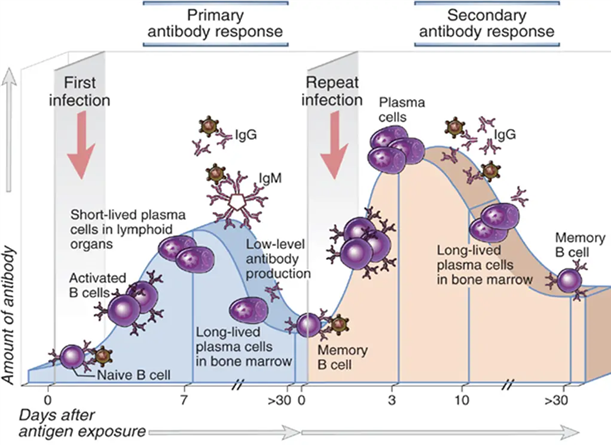
Immune Disorders and Clinical Considerations
A. Immunodeficiencies: Primary immunodeficiencies result from genetic defects in the immune system, leading to increased susceptibility to infections. Secondary immunodeficiencies can occur due to medical treatments or certain conditions (e.g., HIV).
B. Autoimmune Disorders: Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own cells and tissues, causing chronic inflammation and tissue damage.
C. Hypersensitivity Reactions: Allergies and hypersensitivity reactions occur when the immune system overreacts to harmless substances, leading to an exaggerated immune response.
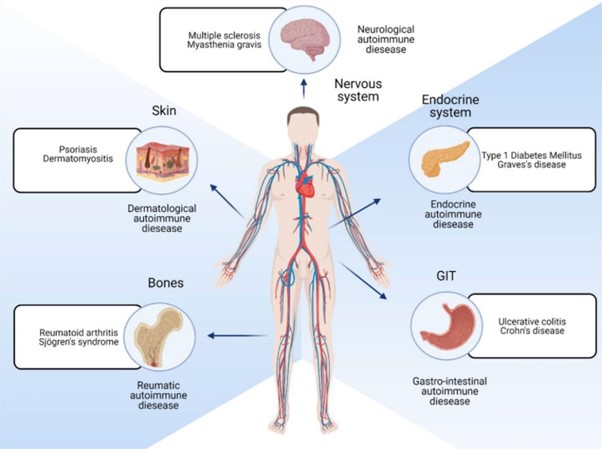
Vaccination and Immunization
A. Vaccines: Vaccines contain weakened or inactivated antigens that stimulate the immune system to produce a protective response without causing the disease.
B. Herd Immunity: Vaccination of a significant portion of the population can create herd immunity, protecting those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons.
Conclusion
- In conclusion, immunity is a sophisticated defense system that protects the body against infections and harmful substances. It involves both innate and adaptive immune responses, with B cells and T cells playing essential roles in antibody-mediated and cell-mediated immunity, respectively.
- The immune system can be affected by various disorders, leading to immunodeficiencies, autoimmune diseases, and hypersensitivity reactions.
- Vaccination and immunization play a critical role in preventing infectious diseases and promoting population health.
- Understanding the principles of immunity allows healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care, support immunization efforts, and promote optimal health outcomes for patients.
Infection Prevention and Control (IPC)
Objectives
- Demonstrate proper hand hygiene techniques and explain the rationale for its importance in preventing the transmission of infections.
- Identify and apply appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) based on the type of anticipated exposure or isolation precautions.
- Describe the principles and techniques of safe injection practices to minimize the risk of infection transmission.
- Explain the importance of environmental control measures, such as maintaining cleanliness and implementing proper disinfection protocols, in preventing the spread of infections.
- Differentiate between standard precautions and transmission-based precautions, and apply the appropriate precautions based on the specific infectious agent or mode of transmission.
Introduction
Infection prevention and control play a crucial role in healthcare settings to minimize the transmission of infectious diseases and ensure the safety of patients, healthcare professionals, and visitors. The ATI/HESI curriculum emphasizes the importance of infection control practices, which are based on evidence-based guidelines and regulations established by healthcare organizations such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
Standard Precautions
- Standard precautions are the foundation of infection prevention and control and should be applied to all patients regardless of their diagnosis or infection status.
- They include hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette, safe injection practices, safe handling of potentially contaminated equipment or surfaces, and safe handling of linen.
- Hand hygiene is the single most important measure for preventing the transmission of healthcare-associated infections. It can be performed using soap and water or an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- PPE includes gloves, gowns, masks, and eye protection, and should be worn when there is a risk of exposure to blood, bodily fluids, secretions, or excretions.
Transmission-Based Precautions
- Transmission-based precautions are used in addition to standard precautions for patients with known or suspected infections that are spread through specific routes, including contact, droplet, or airborne transmission.
- Contact precautions: Used for infections spread through direct or indirect contact with the patient or their environment. Examples include methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Clostridium difficile (C. diff), and vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE).
- Droplet precautions: Used for infections spread through respiratory droplets generated by coughing, sneezing, or talking. Examples include influenza, pertussis, and meningococcal meningitis.
- Airborne precautions: Used for infections spread through small droplet nuclei that remain suspended in the air for long periods. Examples include tuberculosis (TB), measles, and varicella (chickenpox).
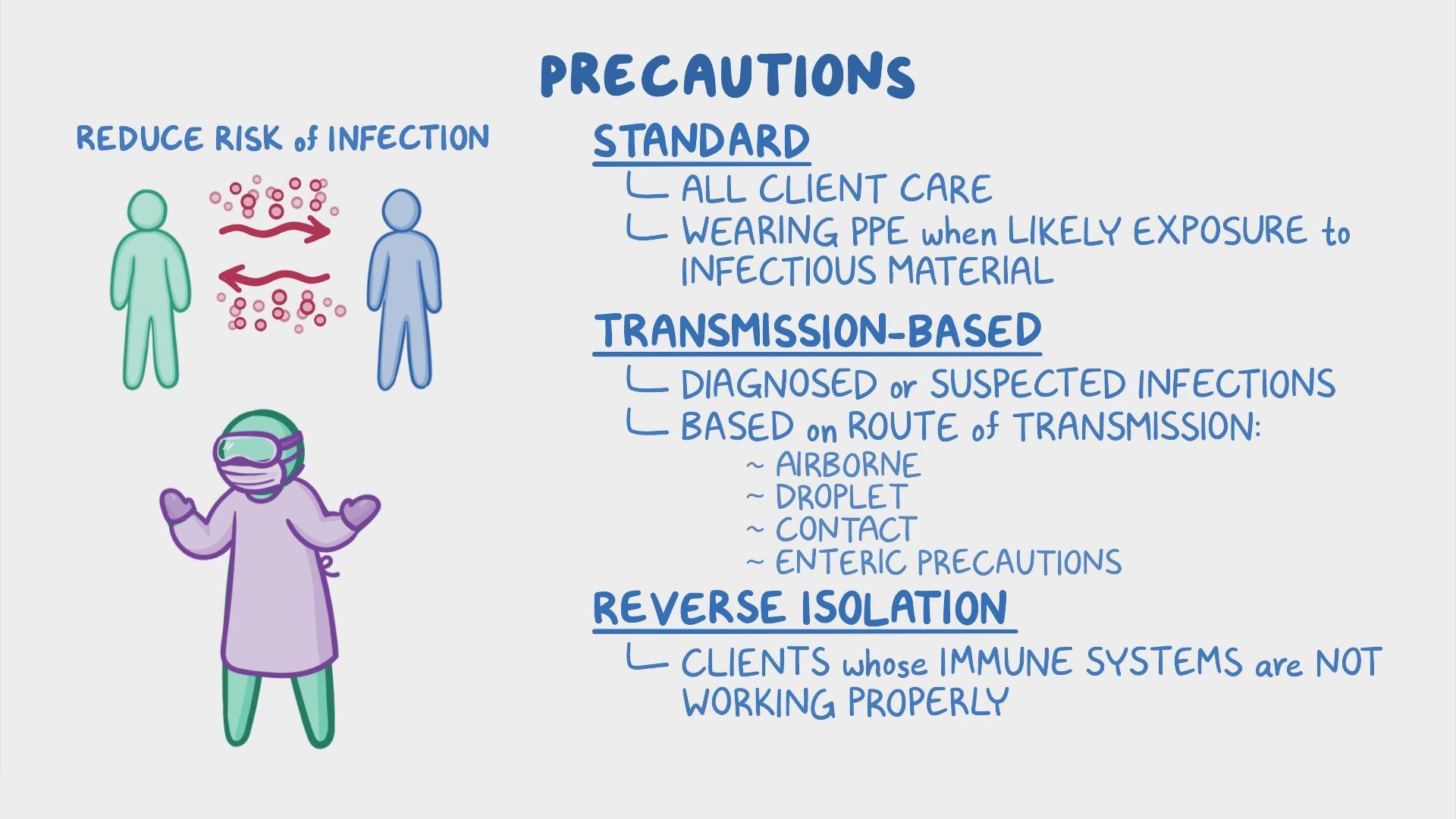
Hand Hygiene
- Hand hygiene is a critical component of infection prevention and control.
- Hands should be washed with soap and water for at least 20 seconds when they are visibly soiled or contaminated with blood or body fluids.
- Alcohol-based hand sanitizers containing at least 60% alcohol can be used when hands are not visibly soiled.
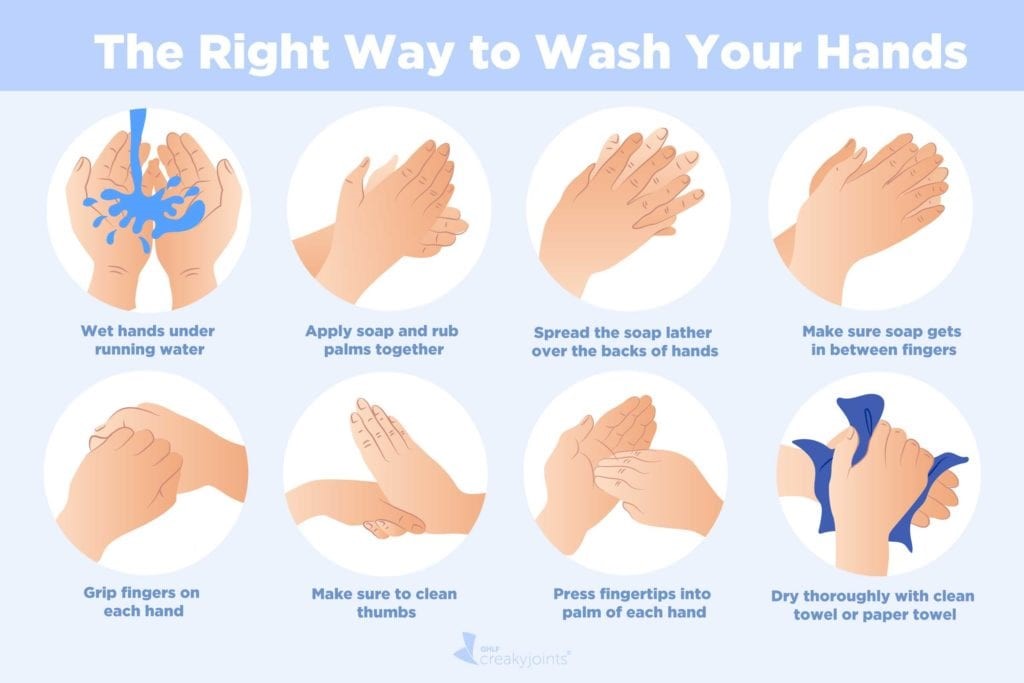
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- PPE should be used based on the anticipated exposure to blood, bodily fluids, secretions, or excretions.
- Gloves should be worn when touching blood, body fluids, or contaminated surfaces, and they should be changed between patient contacts.
- Gowns should be worn during procedures and patient care activities that may generate splashes or sprays of blood, body fluids, secretions, or excretions.
- Masks and eye protection should be used when there is a risk of droplet or airborne transmission.
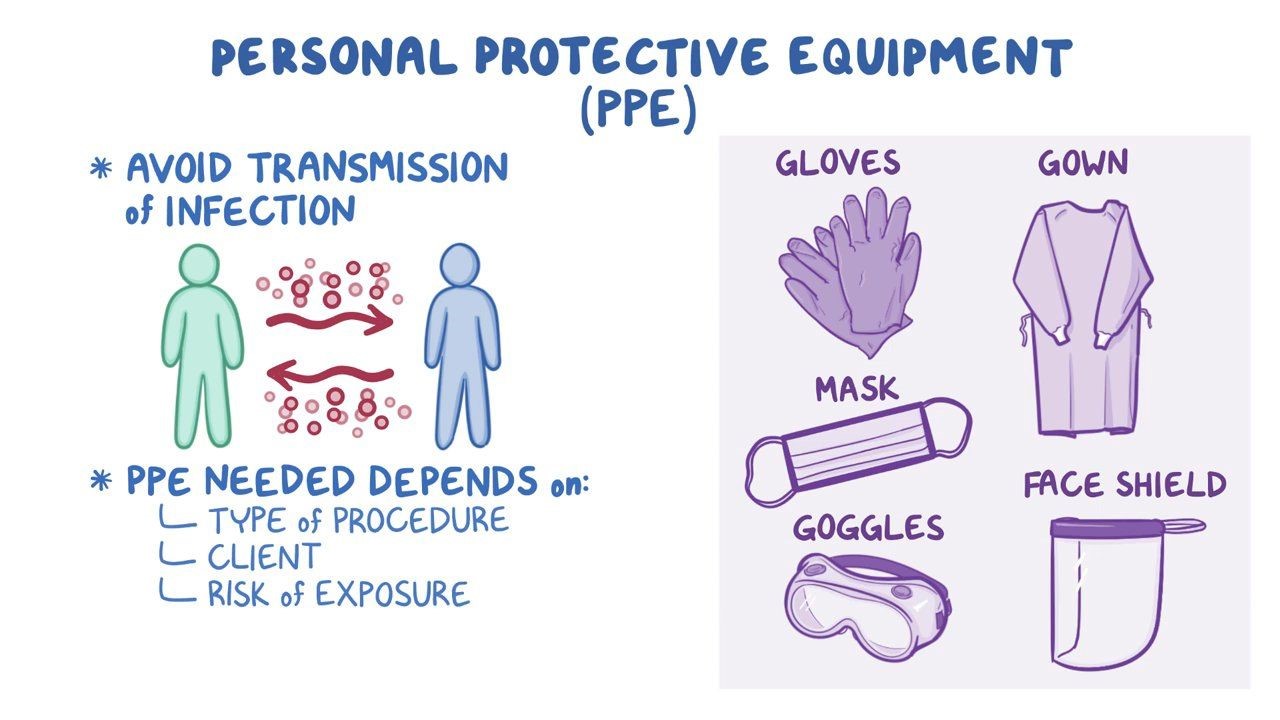
Respiratory Hygiene/Cough Etiquette
- Respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette aim to prevent the transmission of respiratory infections.
- Patients and visitors with respiratory symptoms should be provided with tissues and instructed to cover their mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
- They should be encouraged to perform hand hygiene after coughing, sneezing, or using tissues.

Safe Injection Practices
- Safe injection practices are essential to prevent the transmission of bloodborne infections.
- Needles, syringes, and other injection equipment should be used for a single patient and should not be reused.
- Multi-dose vials should be dedicated to a single patient whenever possible, and if used for multiple patients, they should be accessed with a new needle and new syringe.
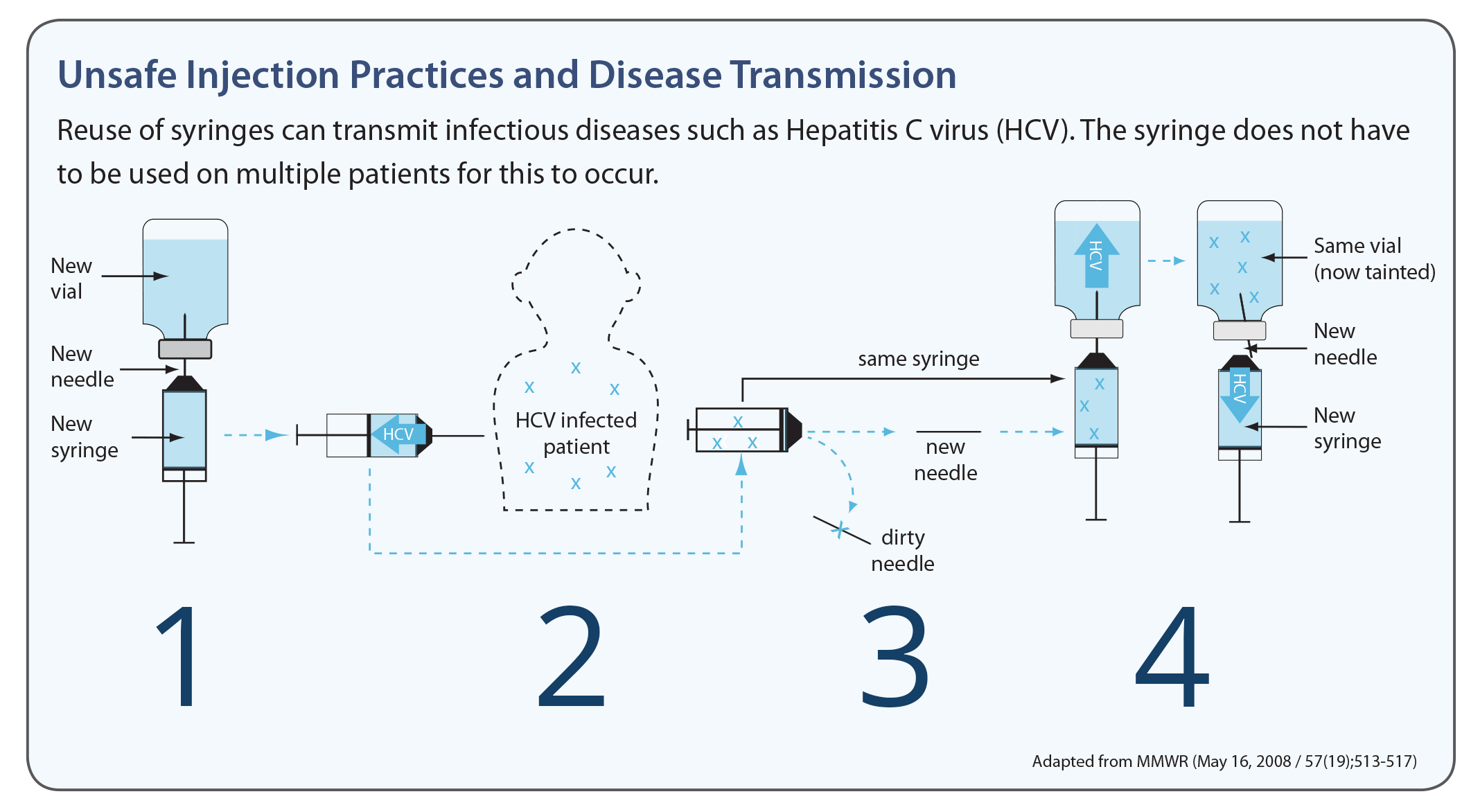
Environmental Control
- Proper cleaning and disinfection of patient care equipment and the healthcare environment are crucial to prevent healthcare-associated infections.
- Surfaces should be cleaned regularly with appropriate disinfectants, paying particular attention to high-touch surfaces.
- Single-use items should be properly disposed of, and reusable items should be appropriately cleaned and sterilized or high-level disinfected.
Staff Health and Immunizations
- Healthcare professionals should comply with immunization requirements to prevent the transmission of vaccine-preventable diseases.
- Routine immunizations recommended for healthcare professionals include influenza, hepatitis B, measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR).
- Healthcare professionals should monitor their health and report any signs or symptoms of infectious diseases. They should not work when they are ill and potentially infectious.
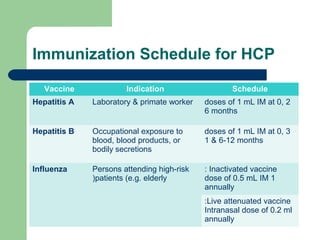
Education and Training
- Ongoing education and training programs should be implemented to ensure that healthcare professionals are knowledgeable about infection prevention and control practices.
- Training should cover topics such as hand hygiene, proper use of PPE, respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette, safe injection practices, and environmental control measures.
- Healthcare professionals should stay updated with the latest evidence-based guidelines and recommendations related to infection prevention and control.
Surveillance and Reporting
- Surveillance systems should be in place to monitor healthcare-associated infections and identify trends or outbreaks.
- Infections should be reported to the appropriate authorities and infection prevention and control committee or department.
- Timely reporting of infections allows for prompt investigation, implementation of control measures, and prevention of further transmission.
Immunodefeciency disorders
Objectives
- Differentiate between primary and secondary immunodeficiency disorders:
- Identify the key components of the immune system affected by different immunodeficiency disorders:
- Understand the clinical manifestations and diagnostic criteria of immunodeficiency disorders:
- Discuss the management and treatment of immunodeficiency disorders:
- Promote patient and family education regarding immunodeficiency disorders:
Introduction
- Immunodeficiency disorders, also known as primary immunodeficiencies (PIDs), are a group of genetic disorders characterized by defects in the immune system, leading to increased susceptibility to infections and a reduced ability to fight off pathogens.
- These conditions can affect different components of the immune system, including B cells, T cells, phagocytes, and complement proteins.
- Understanding immunodeficiency disorders is crucial for healthcare professionals to recognize and manage these conditions effectively.
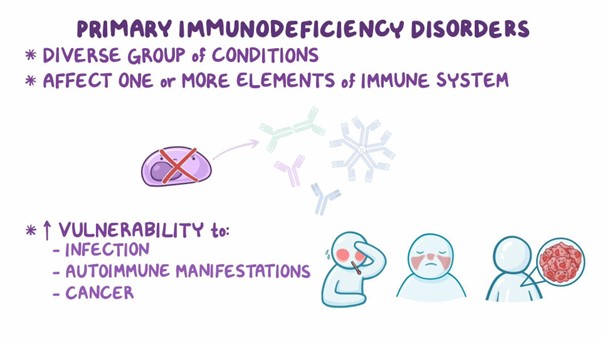
Types of Immunodeficiency Disorders
A. Antibody Deficiencies:
1. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID): CVID is one of the most common PIDs, characterized by reduced antibody production, leading to recurrent bacterial infections, particularly of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts.
2. Selective IgA Deficiency: This condition involves a deficiency or absence of IgA antibodies, making affected individuals prone to respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary infections.
B. T Cell Deficiencies:
1. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID): SCID is a severe form of PID characterized by impaired T cell function, leading to a lack of both cellular and humoral immunity. SCID is life-threatening and requires early diagnosis and intervention, such as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
2. DiGeorge Syndrome: DiGeorge syndrome results from incomplete development of the thymus and parathyroid glands, leading to T cell deficiencies and calcium metabolism disorders.
C. Phagocyte Deficiencies:
1. Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD): CGD is a PID characterized by impaired phagocyte function, particularly neutrophils, leading to recurrent bacterial and fungal infections. CGD is due to defects in the NADPH oxidase enzyme complex.
2. Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency (LAD): LAD is a group of disorders caused by defects in leukocyte adhesion molecules, resulting in impaired migration of immune cells to sites of infection and delayed wound healing.
D. Complement Deficiencies:
1. Hereditary Angioedema (HAE): HAE is caused by deficiencies or dysfunctions in complement proteins, leading to episodes of severe swelling of various body parts.
2. Complement Component Deficiencies: Deficiencies in various complement proteins can lead to increased susceptibility to certain infections, particularly encapsulated bacteria.
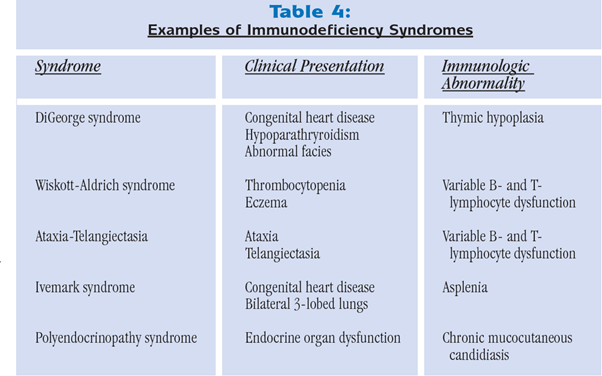
Clinical Manifestations
- The signs and symptoms of immunodeficiency disorders vary depending on the specific defect but may include:
- Recurrent Infections: Frequent or severe infections, such as respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and gastrointestinal infections.
- Failure to Thrive: Infants and children may exhibit growth failure and developmental delays due to chronic infections.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Some immunodeficiencies can result in autoimmunity, where the immune system attacks the body's own cells and tissues.
Diagnostic Evaluation
- Diagnosis of immunodeficiency disorders involves a comprehensive evaluation, including:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Assessing the patient's medical history, family history, and signs of recurrent or severe infections.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests to measure immunoglobulin levels, complete blood count, and immune cell counts, as well as functional tests to assess immune responses.
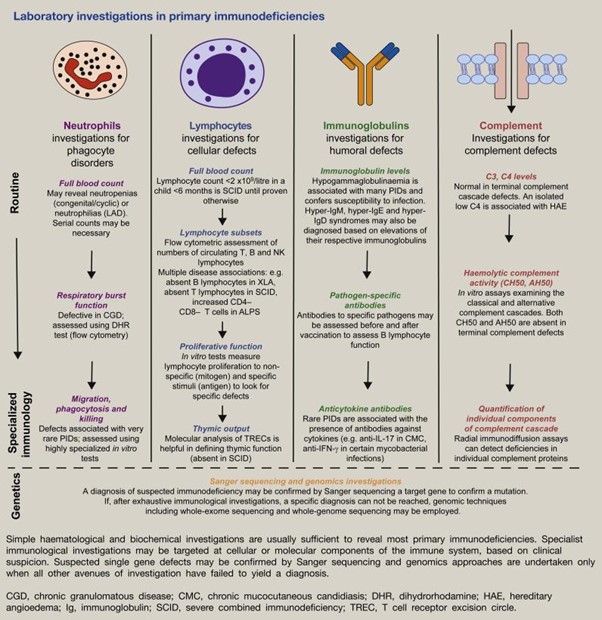
Management and Treatment
- The management of immunodeficiency disorders may include:
- Immunoglobulin Replacement Therapy: Administering intravenous or subcutaneous immunoglobulins to boost antibody levels in individuals with antibody deficiencies.
- Prophylactic Antibiotics: Long-term antibiotic therapy to prevent infections in certain types of immunodeficiency disorders.
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: For severe immunodeficiencies like SCID, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation can be curative.
- Avoidance of Live Vaccines: Individuals with certain PIDs should avoid live vaccines due to their weakened immune system.
- Supportive Care: Providing supportive care and addressing complications or infections promptly.
Patient Education
- Education for patients and their families with immunodeficiency disorders includes:
- Infection Prevention: Promoting good hygiene practices and avoiding exposure to sick individuals or crowded places.
- Medication Management: Ensuring adherence to prescribed medications and understanding potential side effects.
- Recognizing Warning Signs: Educating patients about signs of infection or complications that require immediate medical attention.
Nursing Considerations
- Nurses play a critical role in the care of patients with immunodeficiency disorders, including:
- Early Detection: Recognizing early signs of immunodeficiency and ensuring timely referral to specialists for further evaluation and management.
- Infection Control: Implementing infection prevention measures in healthcare settings to protect patients from potential infections.
- Patient Support: Providing emotional support and patient education to help individuals and their families cope with the challenges of living with a PID.
Conclusion
- In conclusion, immunodeficiency disorders encompass a group of genetic conditions that lead to impaired immune system function, increasing the risk of infections and other complications.
- Different types of PIDs affect various components of the immune system, and early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial for improving patient outcomes.
- By understanding the clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluation, treatment options, and nursing considerations associated with immunodeficiency disorders, healthcare professionals can deliver comprehensive care, promote infection prevention, and support patients and their families throughout their journey with these conditions.
Nursingprepexams
Videos
Login to View Video
Click here to loginTake Notes on Immunological System
This filled cannot be empty

