Please set your exam date
Pathophysiology of the renal system
Study Questions
Acute Kidney Failure
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Acute renal failure is not a chronic condition; it is an acute condition that develops rapidly and is typically reversible with prompt treatment.
B) Incorrect. While long-term uncontrolled diabetes can lead to chronic kidney disease, acute renal failure is not caused by chronic kidney damage related to diabetes.
C) Correct. Acute renal failure, also known as acute kidney injury (AKI), is characterized by a sudden and temporary loss of kidney function. It is often caused by factors such as decreased blood flow to the kidneys, kidney damage, or obstruction of the urinary tract.
D) Incorrect. While the statement is partially true, it does not capture the acute and sudden nature of acute renal failure. The inability of the kidneys to filter waste products from the blood is one of the manifestations of AKI.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Elevated blood pressure is not typically an initial assessment finding in acute renal failure. In fact, it is more common to see low blood pressure (hypotension) due to decreased blood flow to the kidneys.
B) Correct. One of the hallmark manifestations of acute renal failure is decreased urine output (oliguria) or even no urine output (anuria). This is often accompanied by low blood pressure as a result of decreased kidney function.
C) Incorrect. Acute renal failure usually leads to changes in blood pressure and urine output. Stable blood pressure and urine output are not typical initial assessment findings in this condition.
D) Incorrect. High blood sugar levels and frequent urination are not directly related to acute renal failure. These symptoms are more characteristic of diabetes mellitus.
Explanation
A) Correct. Hypertension (high blood pressure) is a significant risk factor for the development of acute renal failure. Elevated blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys and impair kidney function.
B) Incorrect. Osteoporosis is not directly related to the development of acute renal failure. Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones.
C) Incorrect. While type 2 diabetes is a risk factor for chronic kidney disease, it is not a common risk factor for the development of acute renal failure.
D) Incorrect. Seasonal allergies are not associated with an increased risk of acute renal failure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hypotension and tachycardia are more commonly associated with fluid depletion, not fluid overload.
B) Incorrect. Dry mucous membranes and decreased skin turgor are signs of dehydration, which is not indicative of fluid overload.
C) Correct. Fluid overload in acute renal failure can lead to pulmonary congestion and edema in the extremities. Crackles in the lungs (rales) are auscultated when there is fluid accumulation in the lung tissue, and edema in the extremities is visible swelling caused by excessive fluid retention.
D) Incorrect. Hypoactive bowel sounds and constipation are not directly related to fluid overload in acute renal failure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While protein intake may need to be adjusted in acute renal failure, increasing protein intake is not typically recommended during the acute phase, as it may place additional stress on the kidneys.
B) Correct. Limiting potassium-rich foods is essential for clients with acute renal failure, as impaired kidney function can lead to hyperkalemia (high potassium levels), which can be life-threatening.
C) Incorrect. A high-sodium diet is not recommended in acute renal failure, as it can exacerbate fluid retention and fluid overload.
D) Incorrect. Fluid restriction is not typically recommended in acute renal failure, especially if the client is experiencing fluid depletion and dehydration.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Loop diuretics are used to increase urine output, not decrease it. They help reduce fluid overload and prevent dehydration.
B) Incorrect. Loop diuretics typically lead to a decrease in blood pressure, not an increase. They are often prescribed to address hypertension in acute renal failure.
C) Incorrect. Loop diuretics promote the excretion of sodium and water from the kidneys, not their reabsorption.
D) Correct. Loop diuretics are prescribed in acute renal failure to increase urine output and promote fluid excretion. This helps reduce fluid overload and decrease edema.
Explanation
A) Correct. In acute renal failure, when the kidneys are unable to excrete acids properly, metabolic acidosis can occur. Administering bicarbonate intravenously helps raise the pH levels and correct the acid-base imbalance.
B) Incorrect. Encouraging the client to consume more acidic foods would worsen metabolic acidosis and is not a suitable intervention.
C) Incorrect. Increasing fluid intake is not a specific intervention for correcting metabolic acidosis. The focus should be on addressing the underlying acid-base imbalance.
D) Incorrect. Promoting shallow breathing to retain carbon dioxide is not a recommended intervention for correcting metabolic acidosis. Respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis are different types of acid-base imbalances with distinct causes and treatments.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While administering prescribed medications is important, the priority in acute renal failure is to closely monitor the client's intake and output to assess kidney function and fluid balance.
B) Correct. Monitoring intake and output is a priority nursing intervention in acute renal failure. Accurate assessment of urine output helps determine the client's kidney function and the effectiveness of treatment.
C) Incorrect. Providing emotional support is essential, but it is not the priority over monitoring kidney function and fluid balance.
D) Incorrect. Preventing infection and complications is important, but it is not the priority over assessing kidney function in acute renal failure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Acute renal failure is characterized by a rapid onset of symptoms over a short period of time, not a gradual onset.
B) Incorrect. Unlike chronic renal failure, acute renal failure is often reversible with timely intervention and does not result in irreversible loss of kidney function.
C) Correct. Acute renal failure is defined by a sudden and rapid decline in kidney function, typically occurring within hours to days.
D) Incorrect. Genetic factors are not the primary cause of acute renal failure; it is more commonly triggered by various factors such as ischemia, nephrotoxic agents, or obstructive conditions.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. In acute renal failure, there is impaired filtration and excretion of waste products by the kidneys, not enhanced filtration.
B) Correct. Elevated BUN and creatinine levels in acute renal failure result from the kidneys' reduced ability to filter and excrete waste products, leading to their accumulation in the blood.
C) Incorrect. The liver produces waste products like ammonia, but elevated BUN and creatinine levels are primarily related to kidney dysfunction, not increased production by the liver.
D) Incorrect. Decreased reabsorption of waste products by the renal tubules can contribute to elevated levels, but the primary issue in acute renal failure is impaired filtration and excretion.
Explanation
A) Correct. Hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) is a common electrolyte imbalance in acute renal failure. Elevated potassium levels can lead to cardiac arrhythmias and other serious complications.
B) Incorrect. While electrolyte imbalances such as hyponatremia can occur in acute renal failure, hyperkalemia is more commonly associated with severe consequences.
C) Incorrect. Hypocalcemia (low calcium levels) can occur but is not the primary electrolyte imbalance associated with cardiac arrhythmias in acute renal failure.
D) Incorrect. Hyperphosphatemia (high phosphate levels) can occur in acute renal failure, but it is not the primary electrolyte imbalance leading to cardiac arrhythmias.
Explanation
A) Correct. Pre-renal causes of acute renal failure involve reduced blood flow to the kidneys, often due to factors like dehydration or hypovolemia.
B) Incorrect. Intrinsic renal causes involve direct damage to the renal parenchyma, which is not the primary issue in cases of dehydration.
C) Incorrect. Post-renal causes result from urinary tract obstructions, which do not apply to this scenario.
D) Incorrect. "Metabolic renal" is not a recognized category of acute renal failure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hyperglycemia is an increase in blood glucose levels and is not a typical complication of untreated acute renal failure.
B) Incorrect. Anemia can occur in acute renal failure but is not a direct consequence of the accumulation of waste products.
C) Incorrect. Metabolic alkalosis is not a typical complication of acute renal failure; metabolic acidosis is more common.
D) Correct. Uremia is a syndrome that results from the accumulation of waste products in the body due to impaired kidney function. It can lead to a wide range of symptoms and complications, including nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and neurological disturbances.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While long-term use of NSAIDs can contribute to kidney damage and chronic kidney disease, it is not the primary cause of acute renal failure.
B) Incorrect. Acute renal failure is a sudden and abrupt loss of kidney function, and it is distinct from chronic kidney disease, which develops gradually over time.
C) Correct. Acute renal failure is characterized by a rapid and sudden decline in kidney function, often caused by a sudden decrease in blood flow to the kidneys (prerenal), kidney injury (intrinsic), or obstruction of the urinary tract (postrenal).
D) Incorrect. While UTIs and kidney stones can cause kidney injury, they are not the exclusive causes of acute renal failure, which can have various underlying etiologies.
Explanation
A) Correct. Dehydration is a significant risk factor for prerenal acute renal failure. Insufficient fluid intake or excessive fluid loss (e.g., vomiting, diarrhea) can lead to decreased blood volume and decreased blood flow to the kidneys, impairing kidney function.
B) Incorrect. A UTI can cause kidney injury but is not specifically associated with prerenal acute renal failure.
C) Incorrect. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a risk factor for the development of intrinsic acute renal failure, but it is not directly related to prerenal causes.
D) Incorrect. Diabetes mellitus is a risk factor for chronic kidney disease, but it is not a specific risk factor for prerenal acute renal failure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hypovolemia is associated with prerenal acute renal failure, not intrinsic acute renal failure.
B) Correct. Glomerulonephritis is one of the common causes of intrinsic acute renal failure. It is characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli in the kidneys, which can lead to kidney damage and impaired function.
C) Incorrect. Prostate enlargement is associated with postrenal acute renal failure due to urinary tract obstruction, not intrinsic causes.
D) Incorrect. Urinary tract obstruction is also associated with postrenal acute renal failure, not intrinsic causes.
Explanation
A) Correct. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including ibuprofen, are known to cause kidney damage and are a common cause of intrinsic acute renal failure, especially when used in high doses or for extended periods.
B) Incorrect. Loop diuretics, such as furosemide, are not typically associated with intrinsic acute renal failure.
C) Incorrect. Metformin is not a common cause of intrinsic acute renal failure. However, it is contraindicated in individuals with severe kidney impairment.
D) Incorrect. While ciprofloxacin and other antibiotics may have renal-related side effects, they are not a common cause of intrinsic acute renal failure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hypertension is a risk factor for prerenal acute renal failure, not postrenal.
B) Incorrect. While a UTI can cause kidney injury, it is not directly related to postrenal acute renal failure.
C) Correct. An enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), can cause obstruction of the urinary tract and lead to postrenal acute renal failure. The obstruction prevents urine flow, causing pressure buildup in the kidneys and impairing kidney function.
D) Incorrect. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a risk factor for intrinsic acute renal failure, not postrenal.
Explanation
A) Correct. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a significant risk factor for the development of acute renal failure. Chronic hypertension can lead to kidney damage and impaired kidney function over time.
B) Incorrect. Seasonal allergies, osteoarthritis, and anemia are not direct risk factors for acute renal failure.
C) Incorrect. Osteoarthritis is not directly related to acute renal failure.
D) Incorrect. While anemia can be associated with chronic kidney disease, it is not a specific risk factor for acute renal failure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Kidney stones are not a common cause of prerenal acute renal failure. They may cause postrenal acute renal failure if they
obstruct the urinary tract.
B) Incorrect. Bladder infection (cystitis) is not directly related to prerenal acute renal failure.
C) Correct. Severe dehydration, often caused by decreased fluid intake or excessive fluid loss (e.g., vomiting, diarrhea), is a common cause of prerenal acute renal failure. Dehydration leads to decreased blood volume and decreased blood flow to the kidneys, resulting in impaired kidney function.
D) Incorrect. Kidney infection (pyelonephritis) is associated with intrinsic acute renal failure due to kidney inflammation and damage.
Explanation
A) Correct. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors can contribute to prerenal acute renal failure, especially in clients with preexisting cardiovascular disease. These medications may cause vasodilation and decrease blood flow to the kidneys, leading to impaired kidney function.
B) Incorrect. Beta-blockers are not directly associated with prerenal acute renal failure.
C) Incorrect. Calcium channel blockers are not typically associated with prerenal acute renal failure.
D) Incorrect. Thiazide diuretics may cause electrolyte imbalances and metabolic disturbances, but they are not a common cause of prerenal acute renal failure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Increased glomerular filtration rate (GFR) would lead to increased urine output, not decreased urine output.
B) Incorrect. Obstruction of the urethra would cause postrenal acute renal failure and may lead to urinary retention, but it would not cause decreased urine output in prerenal or intrinsic acute renal failure.
C) Correct. In prerenal and intrinsic acute renal failure, impaired blood flow to the kidneys reduces the perfusion of nephrons, leading to decreased urine output.
D) Incorrect. Excessive fluid intake may contribute to fluid overload and decreased urine output in prerenal acute renal failure, but it is not the primary pathophysiological process that leads to decreased urine output.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Constipation and abdominal pain are not typical manifestations of the fluid and electrolyte imbalance seen in acute renal failure.
B) Correct. Acute renal failure can lead to imbalances in electrolytes, particularly potassium and sodium. Muscle weakness and fatigue are common manifestations of these electrolyte imbalances.
C) Incorrect. Decreased heart rate and blood pressure are more commonly associated with fluid volume depletion in prerenal acute renal failure, rather than electrolyte imbalances.
D) Incorrect. Increased respiratory rate and depth are not typically associated with acute renal failure or its fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Elevated creatinine levels are not specific to dehydration and fluid deficit, although dehydration can contribute to prerenal acute renal failure.
B) Incorrect. Elevated creatinine levels do not suggest normal kidney function. Instead, they indicate impaired kidney function and acute kidney injury.
C) Correct. Creatinine is a waste product produced by muscles and excreted by the kidneys. Elevated creatinine levels are a reliable indicator of acute kidney injury and impaired kidney function.
D) Incorrect. Elevated creatinine levels can be seen in both acute and chronic kidney diseases, but they are not exclusively seen in chronic kidney disease.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Increased heart rate and blood pressure are more commonly associated with metabolic alkalosis, not metabolic acidosis.
B) Correct. Muscle twitching and irritability are common clinical manifestations of metabolic acidosis. Acidosis can lead to an increase in excitability of nerve cells, causing muscle twitching and irritability.
C) Incorrect. Excessive thirst and frequent urination are not typically associated with metabolic acidosis.
D) Incorrect. Warm, flushed skin and headache are not directly related to metabolic acidosis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Muscle weakness and fatigue are manifestations of hyperkalemia, but they are not the most critical indicators of severe hyperkalemia.
B) Incorrect. Tingling sensations in the extremities are not the most critical indicator of severe hyperkalemia.
C) Correct. The most critical manifestation of severe hyperkalemia is an irregular heart rhythm (dysrhythmia), which can be life-threatening.
D) Incorrect. Excessive thirst and dry mucous membranes are not specific to hyperkalemia and are not the most critical indicators of severe hyperkalemia.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Increased urine output and polyuria are not associated with uremia. In fact, acute renal failure often leads to decreased urine output (oliguria or anuria).
B) Incorrect. Hypertension and bradycardia are not typical manifestations of uremia.
C) Correct. Uremia is a condition characterized by the buildup of waste products and toxins in the blood due to impaired kidney function. Clinical manifestations of uremia include confusion (encephalopathy), nausea and vomiting, and pericarditis (inflammation of the pericardium, the sac surrounding the heart).
D) Incorrect. Decreased respiratory rate and shallow breathing are not directly associated with uremia.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Decreased blood volume and hypovolemia may contribute to prerenal acute renal failure, but they are not the primary pathophysiological processes that lead to edema in acute renal failure.
B) Incorrect. Increased vascular permeability and leakage of fluid into tissues are not the primary mechanisms of edema in acute renal failure.
C) Correct. In acute renal failure, the impaired filtration and reduced excretion of fluid by the kidneys lead to fluid retention and edema in various parts of the body.
D) Incorrect. Excessive fluid intake and fluid overload may contribute to fluid retention and edema in prerenal acute renal failure, but they are not the primary pathophysiological process in acute renal failure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Bradypnea (slow respiratory rate) is not typically associated with acute renal failure.
B) Correct. Kussmaul respirations are rapid and deep respirations seen in metabolic acidosis, a common complication of acute renal failure. The body tries to compensate for the acidosis by increasing the elimination of carbon dioxide through rapid and deep breathing.
C) Incorrect. Dyspnea and crackles in the lungs are not directly related to acute renal failure.
D) Incorrect. Increased respiratory rate and shallow breathing are not typical respiratory manifestations of acute renal failure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. A complete blood count (CBC) provides information about the number and types of blood cells but does not assess kidney function.
B) Correct. Serum creatinine level is a commonly used blood test to assess kidney function. Elevated levels of creatinine in the blood indicate impaired glomerular filtration and decreased kidney function.
C) Incorrect. Urinalysis provides information about the presence of substances such as protein, blood, and glucose in the urine but does not directly assess GFR.
D) Incorrect. Renal ultrasound is an imaging test that provides information about the structure of the kidneys but does not directly measure GFR.
Explanation
A) Correct. A renal ultrasound is an imaging test that uses sound waves to create images of the kidneys. It can help identify kidney stones, obstructions, and other structural abnormalities in the urinary tract.
B) Incorrect. The renal ultrasound does not directly measure the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which is typically assessed through blood tests.
C) Incorrect. A renal ultrasound does not provide information about the number and types of blood cells in the bloodstream.
D) Incorrect. While a renal ultrasound can visualize the blood vessels in the kidneys, its primary purpose is to assess kidney structure, not blood flow.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Fasting is not typically required before a renal biopsy.
B) Incorrect. The renal biopsy does not directly measure the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which is usually assessed through blood tests.
C) Correct. A renal biopsy is a procedure in which a needle is inserted through the skin and into the kidneys to obtain a small tissue sample for examination. This allows for a direct assessment of kidney tissue and helps identify the cause of kidney dysfunction.
D) Incorrect. While a renal biopsy can provide information about the kidney's structure, its primary purpose is to obtain a tissue sample for histological examination, not to assess blood flow.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Withholding food and drink for 24 hours is not necessary for a CT scan with contrast dye.
B) Correct. Before a CT scan with contrast dye, it is essential to assess the client for allergies, especially to iodine and shellfish. Contrast dyes used in CT scans contain iodine, and clients with allergies to iodine or shellfish may have an allergic reaction to the contrast dye.
C) Incorrect. While administering intravenous fluids may be beneficial in certain situations, it is not a specific precaution for a CT scan with contrast dye.
D) Incorrect. Removing jewelry and metallic objects is a standard precaution for all imaging procedures, but it is not specific to a CT scan with contrast dye.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Unlike computed tomography (CT) scans, MRI scans do not typically require the ingestion of a contrast solution.
B) Incorrect. The MRI scan does not directly measure the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which is typically assessed through blood tests.
C) Incorrect. A renal biopsy involves inserting a needle through the back to obtain a tissue sample from the kidneys, not an MRI scan.
D) Correct. Before an MRI scan, clients need to remove all metal objects and devices, including jewelry, piercings, hearing aids, and certain medical implants. Metal can interfere with the MRI's magnetic field and cause safety concerns during the procedure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Fasting is not typically required before a renal nuclear scan.
B) Incorrect. The renal nuclear scan does not directly measure the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which is typically assessed through blood tests.
C) Incorrect. A renal nuclear scan does not involve inserting a catheter into the bladder to obtain a urine sample.
D) Correct. A renal nuclear scan, also known as a renal scintigraphy, involves injecting a small amount of radioactive material intravenously. The radioactive material is taken up by the kidneys, and the scan creates images that assess kidney function and blood flow.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While fluid restriction may be necessary in certain cases of acute renal failure, it should be prescribed and monitored by the healthcare provider based on the client's specific needs.
B) Incorrect. A high-protein diet can put additional strain on the kidneys, and it is not recommended for clients with acute renal failure.
C) Incorrect. Over-the-counter diuretics may not be safe for clients with acute renal failure and can lead to further electrolyte imbalances.
D) Correct. The nurse's best response is to encourage the client to follow their healthcare provider's instructions and avoid medications that may harm the kidneys. Compliance with prescribed treatment plans and avoiding nephrotoxic medications are essential to support kidney function and prevent further damage.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hemodialysis is not a procedure for kidney transplantation.
B) Correct. Hemodialysis is a treatment that helps remove waste products, toxins, and excess fluids from the blood when the kidneys are not functioning properly. It helps maintain the body's internal environment and prevent complications of acute renal failure.
C) Incorrect. While hemodialysis can improve kidney function temporarily, its primary purpose is to provide kidney support and replace some of the kidney's functions.
D) Incorrect. The description provided refers to the insertion of a urinary catheter for bladder drainage, not hemodialysis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) provides gradual and continuous removal of waste products and excess fluids from the blood, but it may not be as rapid as intermittent hemodialysis.
B) Incorrect. CRRT typically requires continuous sessions, which may last 24 hours or more. Intermittent hemodialysis involves shorter but more frequent sessions.
C) Correct. One of the primary advantages of CRRT is that it does not require the use of anticoagulants to prevent blood clotting in the machine. This reduces the risk of bleeding and other complications associated with anticoagulant use during hemodialysis.
D) Incorrect. The cost of CRRT and intermittent hemodialysis can vary based on the healthcare setting and the client's needs. The cost-effectiveness depends on individual factors and resource availability.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Cloudy dialysis fluid may indicate infection or peritonitis, which requires immediate attention and intervention.
B) Correct. Cloudy dialysis fluid may indicate infection or peritonitis, which can be a severe complication of peritoneal dialysis. The nurse should stop the procedure immediately and notify the healthcare provider for further assessment and management.
C) Incorrect. Administering antibiotics without a proper diagnosis and healthcare provider's order is not appropriate.
D) Incorrect. Increasing the dwell time would not address the issue of cloudy dialysis fluid and potential infection.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Increasing the rate of dialysis may further lower the client's blood pressure and worsen the situation.
B) Incorrect. Administering an antihypertensive medication during a hypotensive episode could exacerbate the client's low blood pressure.
C) Correct. The nurse's priority action is to stop the dialysis procedure immediately and notify the healthcare provider of the significant drop in blood pressure. The client may be experiencing a hypotensive episode, which requires prompt evaluation and intervention.
D) Incorrect. Increasing the client's
fluid intake is not appropriate during a hypotensive episode, as it may not rapidly improve blood pressure and could lead to fluid overload.
Explanation
A) Correct. Loop diuretics can cause potassium loss and potentially lead to hypokalemia. The nurse should monitor the client's serum potassium levels frequently to assess for any imbalances.
B) Incorrect. While loop diuretics can be given intravenously for rapid action, the administration route depends on the client's condition and the healthcare provider's order.
C) Incorrect. Loop diuretics are used to promote diuresis and fluid removal from the body. Encouraging fluid restriction while on diuretic therapy may exacerbate dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
D) Incorrect. The timing of loop diuretic administration is determined by the healthcare provider's order and the client's specific needs. Taking diuretics at bedtime may result in increased nighttime urination and sleep disruption.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Increasing sodium intake would exacerbate fluid retention and worsen the client's fluid overload.
B) Correct. Limiting fluid intake to the prescribed amount helps manage fluid balance in clients with acute renal failure, especially those experiencing fluid overload.
C) Incorrect. Rapid administration of intravenous fluids may worsen fluid overload and increase the risk of edema and hypertension.
D) Incorrect. Encouraging the client to drink water freely would exacerbate fluid overload and impair the body's ability to eliminate excess fluids.
Explanation
A) Correct. Bananas and oranges are high-potassium fruits that the client should avoid on a potassium-restricted diet.
B) Incorrect. Bread and pasta are not typically high in potassium and are usually acceptable in a potassium-restricted diet.
C) Incorrect. Eggs and cheese are not significant sources of potassium and are usually allowed in a potassium-restricted diet.
D) Incorrect. Chicken and fish are sources of protein and do not have high potassium content that would require restriction in most cases.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Encouraging the client to sit up in a chair for extended periods can increase pressure on certain areas and contribute to skin breakdown.
B) Incorrect. Applying a heating pad to areas at risk for skin breakdown can lead to thermal injury and exacerbate skin issues.
C) Correct. Regular repositioning and skin assessments are essential in preventing pressure ulcers and maintaining skin integrity in clients with acute renal failure who may be bedridden or have limited mobility.
D) Incorrect. Adhesive tape can cause skin irritation and damage when removed, especially in clients at risk for impaired skin integrity.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Encouraging a low-carbohydrate diet is not the appropriate intervention for correcting metabolic acidosis.
B) Correct. Sodium bicarbonate is an alkalizing agent that can help correct metabolic acidosis by increasing the body's bicarbonate levels, which buffers excess acids.
C) Incorrect. Fluid restriction would not directly correct metabolic acidosis and may be detrimental to the client's overall fluid balance.
D) Incorrect. Deep breathing exercises are not specific interventions for correcting metabolic acidosis.
Explanation
A) Correct. Encouraging the client to perform active range-of-motion exercises can help prevent complications of immobility, such as muscle wasting and joint contractures.
B) Incorrect. Elevating the head of the bed primarily benefits respiratory function and does not directly address the complications of immobility.
C) Incorrect. Limiting fluid intake would not prevent complications of immobility and may lead to dehydration.
D) Incorrect. Administering pain medication before passive range-of-motion exercises is not a standard practice and does not directly prevent complications of immobility.
Explanation
:
A) Incorrect. Cheese and yogurt are high in phosphate and should be avoided in a low-phosphate diet.
B) Incorrect. Beans and lentils are also high in phosphate and are not suitable for a low-phosphate diet.
C) Incorrect. Eggs and poultry are significant sources of phosphate and are not recommended in a low-phosphate diet.
D) Correct. Fresh fruits and vegetables are generally low in phosphate and are suitable for a low-phosphate diet. These foods can help meet the client's nutritional needs while adhering to the dietary restriction.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Muscle cramps in acute renal failure are often related to electrolyte imbalances, including high potassium levels. Encouraging the consumption of potassium-rich foods would exacerbate the issue.
B) Incorrect. Muscle relaxants may not be appropriate for all clients, and the underlying cause of the muscle cramps should be addressed first.
C) Correct. Applying warm compresses to the affected muscles can help relax muscle tension and provide relief from muscle cramps.
D) Incorrect. Gentle stretching exercises may not be appropriate for a client experiencing muscle cramps, as stretching could exacerbate the discomfort.
Explanation
A) Correct. Erythropoietin-stimulating agents (ESAs) are commonly used to treat anemia in clients with renal failure. These medications stimulate the production of red blood cells and help manage anemia associated with kidney dysfunction.
B) Incorrect. Anticoagulants such as heparin are not used to treat anemia; they are prescribed to prevent blood clotting and thrombosis.
C) Incorrect. Loop diuretics are used to promote diuresis and manage fluid overload in clients with acute renal failure; they do not treat anemia.
D) Incorrect. Antihypertensive agents are prescribed to manage hypertension and do not treat anemia in clients with renal failure.
Chronic Renal Failure
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Being physically active and maintaining a healthy weight can actually reduce the risk of chronic renal failure, as it helps to control blood pressure and blood sugar levels, which are risk factors for kidney disease.
B) Incorrect. Having a family history of kidney disease can increase the risk of chronic renal failure, as genetics can play a role in the development of kidney problems.
C) Incorrect. Consuming a high-sodium diet can actually be harmful to the kidneys, as it can lead to hypertension and contribute to kidney damage.
D) Correct. Conditions such as hypertension and diabetes are well-established risk factors for chronic renal failure. These conditions can cause damage to the blood vessels and filtering units of the kidneys over time, leading to kidney dysfunction.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. The volume of urine produced in 24 hours is measured through a different test called the 24-hour urine collection, not the GFR test.
B) Incorrect. The GFR test does not assess blood glucose levels; it is primarily used to evaluate kidney function.
C) Correct. The GFR test measures how well the kidneys are filtering waste and fluids from the blood. It is an important indicator of kidney function and is commonly used to stage chronic renal failure.
D) Incorrect. The GFR test does not specifically measure the excretion of potassium and sodium in the urine; instead, it focuses on overall kidney function and filtration rate.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While chronic renal failure is often irreversible, the rate of decline in kidney function can vary depending on the underlying cause and the effectiveness of treatment and management.
B) Incorrect. While appropriate lifestyle changes and medications can improve the client's quality of life and slow the progression of the disease, chronic renal failure is a chronic condition that may require ongoing management.
C) Incorrect. Chronic renal failure is generally not curable, but proper management can help stabilize the condition and slow the progression of kidney damage.
D) Correct. The prognosis for chronic renal failure can vary widely depending on factors such as the cause of kidney disease, the stage of kidney damage, and the client's response to treatment. Early intervention, such as controlling blood pressure and blood sugar levels, can help slow the progression of kidney damage and improve long-term outcomes.
Explanation
A) Correct. An increase in blood pressure readings can be an early indication of fluid retention in a client with chronic renal failure. Fluid overload can lead to hypertension as the kidneys struggle to excrete excess fluids.
B) Incorrect. Shortness of breath and crackles in the lungs are signs of fluid overload but are considered more advanced symptoms. These indicate that fluid has accumulated in the lungs, leading to pulmonary edema.
C) Incorrect. Decreased serum potassium levels (hypokalemia) are not typically associated with fluid overload. Instead, chronic renal failure often leads to hyperkalemia due to impaired potassium excretion.
D) Incorrect. Rapid weight loss over a few days is not indicative of fluid retention; rather, it may suggest dehydration or inadequate caloric intake.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While assessing vital signs and blood pressure is important, it is not the first action when the client reports cloudy dialysate effluent during an exchange.
B) Correct. Cloudy dialysate effluent may indicate peritonitis, an infection of the peritoneal cavity. Obtaining a sample of the effluent for testing is the first action to determine if an infection is present and requires immediate treatment.
C) Incorrect. Instructing the client to stop the exchange immediately may be necessary if there are signs of infection or other complications, but obtaining a sample of the effluent should be done first to determine the cause.
D) Incorrect. Providing the client with an analgesic is not the priority when the client reports cloudy dialysate effluent; the focus is on identifying the cause of the cloudiness.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Reducing protein intake can lead to calcium loss and bone fractures in clients with chronic renal failure, as it may affect
bone health.
B) Correct. Limiting protein intake is a common dietary recommendation for clients with chronic renal failure to reduce the workload on the kidneys and slow the progression of kidney damage. Protein metabolism produces waste products that the kidneys must filter and excrete, and reducing protein intake can help alleviate this burden on the already compromised kidneys.
C) Incorrect. Decreasing protein intake may not necessarily improve appetite or overall nutritional status, as protein is essential for maintaining body functions and tissue repair.
D) Incorrect. While reducing protein intake can result in fewer waste products being generated, the primary reason for limiting protein intake in chronic renal failure is to reduce the strain on the kidneys, not solely to decrease waste production.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Chronic renal failure often leads to hypertension (high blood pressure), not decreased blood pressure.
B) Incorrect. Chronic renal failure typically results in decreased urine production due to impaired kidney function.
C) Incorrect. Chronic renal failure is more likely to cause hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) rather than hypokalemia.
D) Correct. Anemia is a common complication of chronic renal failure because the kidneys play a crucial role in producing erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production. When the kidneys are damaged, erythropoietin production decreases, leading to anemia.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Limiting protein intake can help manage nitrogenous waste products, but it is not the primary reason for a low-protein diet.
B) Incorrect. Fluid overload is managed by restricting fluid intake, not protein intake.
C) Incorrect. The primary treatment for metabolic acidosis in chronic renal failure is bicarbonate supplementation, not a low-protein diet.
D) Correct. A low-protein diet is prescribed to reduce the production of nitrogenous waste products, such as urea and creatinine, which the damaged kidneys are unable to efficiently excrete. This helps prevent the buildup of waste products in the body.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hyponatremia (low sodium levels) is not typically associated with chronic renal failure.
B) Incorrect. Hypocalcemia (low calcium levels) can occur in chronic renal failure, but hyperkalemia is more common.
C) Correct. Hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) is a common electrolyte imbalance in chronic renal failure because the kidneys are responsible for excreting excess potassium from the body, and impaired kidney function can lead to potassium retention.
D) Incorrect. Hypophosphatemia (low phosphate levels) is not a typical electrolyte imbalance in chronic renal failure.
Explanation
A) Correct. Metabolic bone disease, such as renal osteodystrophy, is primarily due to the imbalances of calcium and parathyroid hormone (PTH) in chronic renal failure. Kidney dysfunction can lead to impaired calcium regulation and increased PTH secretion.
B) Incorrect. Hypokalemia and decreased thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) are not typically associated with metabolic bone disease in chronic renal failure.
C) Incorrect. Hypernatremia and elevated insulin levels are not directly related to metabolic bone disease.
D) Incorrect. Hypermagnesemia and decreased cortisol production are not the primary factors contributing to metabolic bone disease in chronic renal failure.
Explanation
A) Correct. Hemodialysis is a treatment modality that uses a machine (dialyzer) to filter waste products and excess fluid from the blood, compensating for the impaired kidney function in chronic renal failure.
B) Incorrect. Peritoneal dialysis uses the peritoneal membrane within the abdomen to remove waste products and excess fluid, rather than a machine.
C) Incorrect. Kidney transplant involves replacing a damaged kidney with a healthy one from a donor and is not a form of dialysis.
D) Incorrect. Pharmacological therapy may be part of the treatment plan for chronic renal failure, but it does not focus on removing waste products and excess fluid from the blood like dialysis does.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Chronic renal failure is characterized by a gradual and progressive loss of kidney function, not a sudden and rapid decline.
B) Incorrect. While infections can lead to kidney damage, they are not the primary cause of chronic renal failure.
C) Correct. Chronic renal failure is marked by a slow, continuous decline in kidney function that is typically irreversible.
D) Incorrect. Chronic renal failure is not a result of temporary stress on the kidneys; it is a chronic condition with irreversible kidney damage.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Reabsorption of filtered waste products occurs primarily in the renal tubules, not the glomerulus.
B) Correct. The glomerulus is a key component of the nephron and functions to filter blood, removing waste products and excess substances to form urine.
C) Incorrect. The release of renin is primarily regulated by specialized cells in the kidney called juxtaglomerular cells, not the glomerulus itself.
D) Incorrect. Urine storage occurs in the bladder, not the glomerulus
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Smoking and tobacco use are harmful to the kidneys and can increase the risk of chronic renal failure.
B) Incorrect. While genetic factors may play a role in some cases of chronic renal failure, lifestyle changes can significantly impact the risk and progression of kidney disease.
C) Incorrect. While a history of kidney stones may be associated with an increased risk of kidney damage, it is not a primary risk factor for chronic renal failure.
D) Correct. Conditions such as hypertension and diabetes are two of the leading causes of chronic renal failure. Uncontrolled high blood pressure and elevated blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and filtering units of the kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease over time.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Age is a non-modifiable risk factor for chronic renal failure. While the risk of kidney disease may increase with age, it is not something that individuals can control or change.
B) Incorrect. Gender is also a non-modifiable risk factor, as both males and females can develop chronic renal failure. It does not impact an individual's ability to modify their risk.
C) Correct. Smoking is a modifiable risk factor for chronic renal failure. Smoking can damage blood vessels, leading to reduced blood flow to the kidneys and an increased risk of kidney disease.
D) Incorrect. Family history of kidney disease is a non-modifiable risk factor. While individuals cannot change their family history, they can modify other lifestyle factors, such as smoking, to reduce their overall risk of kidney disease.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hyperthyroidism is not a known risk factor for chronic renal failure. However, uncontrolled thyroid disease may contribute to cardiovascular issues that can impact kidney health.
B) Incorrect. Peptic ulcer disease is not a risk factor for chronic renal failure.
C) Incorrect. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is not directly associated with an increased risk of chronic renal failure. However, chronic illnesses can place additional stress on the kidneys over time.
D) Correct. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a significant risk factor for chronic renal failure. Long-term uncontrolled hypertension can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Diabetes is strongly associated with an increased risk of chronic renal failure. Chronic kidney disease related to diabetes is known as diabetic nephropathy.
B) Correct. Diabetes is a leading cause of chronic renal failure. Uncontrolled high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys over time, leading to kidney disease.
C) Incorrect. Both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes are associated with an increased risk of chronic renal failure. It is essential for individuals with either type of diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels to reduce the risk of kidney complications.
D) Incorrect. Chronic renal failure can be caused by various factors, but diabetes is a significant and common cause of kidney disease, especially in individuals with uncontrolled diabetes.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Antibiotics are generally safe and are not known to be a risk factor for chronic renal failure.
B) Incorrect. Antihypertensive medications are essential for managing high blood pressure and reducing the risk of kidney damage in individuals with hypertension. They are not considered a risk factor for chronic renal failure.
C) Correct. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are commonly used to treat conditions such as acid reflux and peptic ulcers. Prolonged and high-dose use of PPIs has been associated with an increased risk of kidney disease, including acute interstitial nephritis and chronic kidney disease.
D) Incorrect. Antipyretics such as acetaminophen are generally safe when used appropriately and are not considered a risk factor for chronic renal failure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Cardiovascular disease can impact kidney health. The heart and kidneys are closely connected, and conditions that affect the heart can also have implications for kidney function.
B) Incorrect. High cholesterol levels can contribute to cardiovascular disease, and cardiovascular disease is a significant risk factor for chronic renal failure. Therefore, high cholesterol indirectly impacts kidney health.
C) Correct. Cardiovascular disease, including conditions like heart failure or atherosclerosis, can lead to decreased blood flow to the kidneys, impairing kidney function and contributing to chronic renal failure.
D) Incorrect. High blood pressure is a well-established risk factor for chronic renal failure. Uncontrolled hypertension can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to kidney dysfunction over time.
Explanation
A) Correct. Fatigue and weakness are early clinical manifestations of chronic renal failure, often due to anemia and the accumulation of waste products in the blood.
B) Incorrect. Hematuria may be present in some cases of kidney dysfunction, but it is not typically an early symptom of chronic renal failure.
C) Incorrect. Shortness of breath and chest pain are more likely to be associated with fluid overload or cardiac issues, which may occur in advanced stages of chronic renal failure.
D) Incorrect. Hyperkalemia is a complication of chronic renal failure but may not be an early clinical manifestation. It is more likely to occur as kidney function declines and potassium excretion becomes impaired.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Pruritus (itching) is a common symptom of chronic renal failure and is related to the buildup of waste products and toxins in the blood, leading to skin irritation.
B) Correct. Pruritus is a common and distressing symptom of chronic renal failure, caused by the retention of uremic toxins in the blood. These toxins can irritate the skin and lead to itching.
C) Incorrect. While medications can sometimes cause pruritus as a side effect, it is not the primary cause of itching in clients with chronic renal failure.
D) Incorrect. Persistent pruritus in a client with chronic renal failure is not necessarily indicative of an allergic reaction to medications. It is more likely related to the buildup of waste products in the blood.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Administering an antiemetic medication may help relieve nausea, but it is not the priority action in a client with chronic renal failure experiencing anorexia and nausea.
B) Incorrect. Encouraging the client to increase protein intake is not appropriate if they are experiencing anorexia and nausea. Protein intake may need to be adjusted based on the client's symptoms and kidney function.
C) Incorrect. While assessing serum electrolyte levels is important in chronic renal failure, it is not the priority action in this situation. The client's anorexia and nausea require immediate attention.
D) Correct. Monitoring the client's weight and fluid intake is the priority action when the client is experiencing anorexia and nausea. These symptoms may indicate fluid and electrolyte imbalances that need to be addressed promptly.
Explanation
A) Correct. Increased blood pressure readings can be an early clinical manifestation of fluid overload in clients with chronic renal failure. Fluid retention can lead to hypertension as the kidneys struggle to excrete excess fluids.
B) Incorrect. Hyperkalemia may occur in chronic renal failure, but it is not an early clinical manifestation of fluid overload.
C) Incorrect. Dry and cracked skin is more commonly associated with dehydration rather than fluid overload.
D) Incorrect. Polyuria is not typically associated with fluid overload. Instead, it may be present in early stages of chronic renal failure due to the inability of the kidneys to concentrate urine properly.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Applying compression stockings may help reduce swelling but does not address the underlying cause. Additionally, compression stockings should not be used if the client has arterial insufficiency.
B) Incorrect. Elevation may provide temporary relief from swelling, but it does not address the underlying cause of fluid retention
in chronic renal failure.
C) Correct. The nurse should measure the client's blood pressure and pulse rate to assess for fluid overload and possible hypertension, which can be associated with chronic renal failure.
D) Incorrect. Assessing the client's daily protein intake is not the priority when the client presents with swelling in the ankles and legs. Fluid retention is a more immediate concern that requires assessment and intervention.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Applying a heating pad may provide temporary relief for muscle cramps, but it does not address the underlying cause.
B) Correct. Muscle cramps in clients with chronic renal failure can be caused by dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Encouraging the client to increase fluid intake can help alleviate muscle cramps and maintain adequate hydration.
C) Incorrect. While calcium supplements may be prescribed in certain situations, they are not the first-line intervention for muscle cramps in chronic renal failure.
D) Incorrect. Educating the client about potassium-rich foods is important for managing potassium levels, but it is not the priority in this situation. Muscle cramps are more likely related to fluid and electrolyte imbalances rather than potassium intake.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Peripheral edema and weight gain are more commonly associated with fluid retention in later stages of chronic renal failure when the kidneys are unable to effectively remove excess fluids from the body.
B) Incorrect. Frothy urine and increased urination may indicate proteinuria, a condition where excessive protein is excreted in the urine. While proteinuria can be a symptom of kidney dysfunction, it is not an early symptom.
C) Incorrect. Hypertension and headache can be associated with chronic renal failure, but they are not specific to early stages of kidney dysfunction.
D) Correct. Fatigue and decreased appetite are early clinical manifestations of kidney dysfunction in chronic renal failure. The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste products and toxins from the blood, and when kidney function is compromised, it can lead to a buildup of waste products in the body, causing fatigue and decreased appetite.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Excess production of calcium in the body is not a typical cause of bone pain in chronic renal failure.
B) Correct. Chronic renal failure can lead to impaired phosphorus excretion, resulting in elevated levels of phosphorus in the blood. High phosphorus levels can lead to bone demineralization, weakening the bones and causing bone pain.
C) Incorrect. While some medications used in the management of chronic renal failure may have side effects, frequent bone pain is not commonly associated with these medications.
D) Incorrect. Kidney dysfunction in chronic renal failure does not typically lead to low levels of calcium in the bones. Instead, it can lead to abnormalities in phosphorus levels, which affect bone health.
Explanation
A) Correct. Peripheral neuropathy, characterized by tingling sensations or "pins and needles" in the hands and feet, is a common neurological complication of chronic renal failure. Uremic toxins build up in the blood when the kidneys are unable to adequately filter waste products, leading to nerve damage and peripheral neuropathy.
B) Incorrect. Increased blood flow to the extremities is not typically associated with the "pins and needles" sensation described by the client.
C) Incorrect. Adequate nerve conduction related to calcium levels would not cause the "pins and needles" sensation; instead, disturbances in calcium levels can lead to other neurological symptoms.
D) Incorrect. Hypokalemia, or low potassium levels, can cause muscle weakness or cramps but is not typically associated with peripheral neuropathy.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hyperkalemia, or high potassium levels, can cause muscle weakness and potentially cardiac arrhythmias, but it is not typically associated with difficulty concentrating or irritability.
B) Incorrect. Hyponatremia, or low sodium levels, can cause neurological symptoms such as confusion and headache, but it is not typically associated with muscle cramps.
C) Incorrect. Hypocalcemia, or low calcium levels, can cause muscle cramps and neurological symptoms, but it is not specifically associated with difficulty concentrating and irritability.
D) Correct. Hyperphosphatemia, or high phosphorus levels, is common in chronic renal failure due to impaired kidney function. Elevated phosphorus levels can lead to the binding of calcium, resulting in decreased ionized calcium in the blood. This can cause neuromuscular irritability, difficulty concentrating, and muscle cramps.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Proteinuria, or the presence of excessive protein in the urine, may be a symptom of kidney dysfunction, but it is not directly related to periorbital edema and swelling of the ankles and feet.
B) Incorrect. Hypokalemia, or low potassium levels, may cause muscle weakness and other symptoms but is not associated with the specific edema described.
C) Incorrect. Hypernatremia, or high sodium levels, may lead to symptoms such as thirst and confusion but does not typically cause peripheral edema.
D) Correct. Periorbital edema (swelling around the eyes) and edema in the ankles and feet are classic signs of fluid overload in chronic renal failure. The impaired kidney function in chronic renal failure leads to the retention of fluid and sodium in the body, resulting in edema.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Increasing the intake of potassium-rich foods may not be appropriate, especially if the client's potassium levels are already elevated due to chronic renal failure. High potassium levels can lead to muscle cramps.
B) Incorrect. While regular weight-bearing exercises are beneficial for overall health, they may not specifically address or alleviate muscle cramps in chronic renal failure.
C) Correct. Engaging in stretching exercises before bedtime can help reduce the frequency of muscle cramps in clients with chronic renal failure. Stretching can help relax and lengthen muscles, reducing the risk of cramping.
D) Incorrect. Taking over-the-counter calcium supplements without proper evaluation of calcium levels can be dangerous and may contribute to other imbalances in chronic renal failure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Severe anemia in chronic renal failure is characterized by low hemoglobin levels, not elevated levels.
B) Incorrect. Chronic renal failure can lead to decreased red blood cell production, resulting in a reduced red blood cell count.
C) Correct. Chronic renal failure often leads to decreased production of erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production. This deficiency results in low hematocrit levels and severe anemia.
D) Incorrect. Chronic renal failure is not typically associated with elevated platelet counts; in fact, it can lead to platelet dysfunction and an increased risk of bleeding.
Explanation
A) Correct. The GFR test measures how well the kidneys are filtering waste and fluids from the blood. It is an essential indicator of kidney function and is commonly used to diagnose and stage chronic renal failure.
B) Incorrect. The volume of urine produced in 24 hours is measured through a different test called the 24-hour urine collection, not the GFR test.
C) Incorrect. While the GFR test is used to assess kidney function, it is not specific to diagnosing particular kidney diseases like glomerulonephritis.
D) Incorrect. The GFR test does not specifically assess the excretion of potassium and sodium in the urine; instead, it focuses on overall kidney function and filtration rate.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. A GFR value of 50 mL/min/1.73m² indicates some level of kidney dysfunction, not normal kidney function.
B) Incorrect. A GFR value of 50 mL/min/1.73m² indicates moderate kidney dysfunction, not mild impairment.
C) Correct. A GFR value of 50 mL/min/1.73m² is considered to represent moderate kidney dysfunction. This level of GFR indicates that the kidneys are not effectively filtering waste and fluids from the blood.
D) Incorrect. While a GFR value of 50 mL/min/1.73m² indicates kidney dysfunction, it does not represent severe kidney damage. Severe kidney dysfunction would have a much lower GFR value.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Converting the creatinine level to micromoles per liter is not necessary for the GFR calculation.
B) Incorrect. While a 24-hour urine sample can be used to measure creatinine clearance, it is not required for the GFR calculation, which can be estimated using formulas.
C) Incorrect. Calculating the body surface area is not necessary for the GFR calculation.
D) Correct. The GFR can be estimated using formulas that include the serum creatinine level, such as the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula or the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Fasting is not required for a GFR test.
B) Incorrect. While staying hydrated is essential for overall health, there are no specific hydration requirements before a GFR test.
C) Incorrect. While dietary changes may be necessary for other tests, such as creatinine clearance, there are no specific dietary restrictions for the GFR test.
D) Correct. There are no special preparations needed for a GFR test. The test can be done at any time, regardless of food intake or hydration status.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. A GFR value of 10 mL/min/1.73m² indicates severe kidney dysfunction, not mild impairment.
B) Correct. A GFR value of 10 mL/min/1.73m² is considered very low and indicates severe kidney dysfunction. At this level, the kidneys are severely damaged and unable to effectively filter waste and fluids from the blood.
C) Incorrect. A GFR value of 10 mL/min/1.73m² is much lower than the threshold for moderate kidney dysfunction.
D) Incorrect. A GFR value of 10 mL/min/1.73m² is far below the normal range and indicates significant kidney dysfunction, not normal kidney function.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While a GFR value of 60 mL/min/1.73m² is within the normal range for some populations, it is considered below the normal range for adults and indicates some level of kidney dysfunction.
B) Correct. A GFR value of 60 mL/min/1.73m² indicates mild kidney impairment. While it may not be severely compromised, it still represents some level of kidney dysfunction.
C) Incorrect. A GFR value of 60 mL/min/1.73m² is not considered moderate kidney dysfunction. It is within the mild impairment range.
D) Incorrect. A GFR value of 60 mL/min/1.73m² is not indicative of severely damaged kidneys. Severe kidney dysfunction would have a much lower GFR value.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Pain medication is not typically administered for a GFR test as the test itself is not painful.
B) Correct. The GFR test is painless and non-invasive. It involves a blood test to measure creatinine levels and does not cause discomfort.
C) Incorrect. While relaxation techniques can be helpful for other procedures, they are not necessary for the GFR test as it does not cause discomfort.
D) Incorrect. Reassuring the client about the brief and tolerable nature of discomfort would be misleading, as the GFR test does not cause discomfort.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. In chronic renal failure, the kidneys may have difficulty processing excess protein, so protein intake should be limited to reduce the workload on the kidneys.
B) Correct. Limiting fluid intake is crucial in managing chronic renal failure. The kidneys' reduced ability to filter waste products can lead to fluid retention and electrolyte imbalances, so restricting fluid intake helps prevent overload and complications.
C) Incorrect. In chronic renal failure, high-potassium foods should be limited to prevent hyperkalemia, a condition in which potassium levels in the blood become too high.
D) Incorrect. Foods high in phosphorus should be restricted in chronic renal failure because the kidneys may have difficulty excreting excess phosphorus, leading to hyperphosphatemia, which can contribute to bone and mineral disorders.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Phosphate binders are not used to reduce calcium absorption. They are specifically prescribed to control phosphate levels in the blood.
B) Correct. Phosphate binders are medications that bind to dietary phosphorus in the digestive tract, preventing its absorption and reducing phosphate levels in the blood. This helps manage hyperphosphatemia, a common complication in chronic renal failure.
C) Incorrect. Phosphate binders do not improve iron absorption or manage anemia. They are not related to iron metabolism.
D) Incorrect. Phosphate binders do not affect potassium excretion. They are specific to phosphate control in the body and do not impact potassium levels.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While proper medication adherence can help prevent drug interactions, it is not the primary reason for advising clients to take medications as prescribed in chronic renal failure.
B) Incorrect. Medication adherence may or may not directly impact the cost of treatment, but the main reason for consistent use is to manage the condition effectively.
C) Correct. Adhering to medication regimens in chronic renal failure is crucial for slowing the progression of kidney damage. Medications are prescribed to control blood pressure, manage complications, and reduce the strain on the kidneys.
D) Incorrect. Medication adherence is essential, but it does not eliminate the need for dietary restrictions in chronic renal failure. Dietary modifications are also a vital part of managing the condition effectively.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. ESA therapy is not directly related to dehydration or thirst. It is used to manage anemia by stimulating red blood cell production.
B) Correct. ESA therapy can increase red blood cell production, which may elevate blood pressure. Regular blood pressure monitoring is essential to ensure it remains within a safe range.
C) Incorrect. Increased appetite and weight gain are not typical side effects of ESA therapy.
D) Incorrect. ESA therapy is not associated with an increased risk of bleeding or restrictions on engaging in strenuous activities. It is used to manage anemia and improve overall blood cell counts.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Encouraging the client to drink 3 liters of fluid daily may be excessive and can contribute to fluid overload in individuals on hemodialysis. Fluid intake needs to be limited and closely monitored.
B) Correct. Monitoring the vascular access site is crucial to detect early signs of infection or clotting, which can lead to serious complications such as sepsis or thrombosis.
C) Incorrect. Phosphate binders are used to control phosphate levels in the blood and are generally taken with meals, not specifically before hemodialysis sessions.
D) Incorrect. Promoting a high-potassium diet is not appropriate for individuals on hemodialysis, as it can lead to hyperkalemia. Clients on hemodialysis typically need to restrict potassium intake.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Encouraging the client to drink more fluids may not immediately resolve the cloudy dialysate drainage. The nurse needs to assess the client's dialysis technique and the potential cause of the cloudiness.
B) Incorrect. Administering intravenous antibiotics is not the initial intervention for cloudy dialysate drainage. First, the nurse should assess the client's technique and position during dialysis.
C) Correct. Cloudy dialysate drainage may indicate improper dialysate exchange, infection, or other complications. The nurse should first assess the client's dialysis technique and ensure proper positioning to identify the cause.
D) Incorrect. Discontinuing peritoneal dialysis should be considered if there is clear evidence of infection or other serious complications, but it is not the initial intervention for cloudy drainage without further assessment.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Calcitriol is not given to enhance appetite or improve nutrition. Its primary role is in regulating calcium and phosphate levels.
B) Incorrect. Calcitriol does not directly impact urine output or prevent kidney stones.
C) Incorrect. While some medications may be prescribed to manage blood pressure in chronic renal failure, calcitriol is not one of them.
D) Correct. Calcitriol is the active form of vitamin D and plays a crucial role in regulating calcium and phosphate levels in the body. It helps maintain bone health by promoting the absorption of calcium from the digestive tract and preventing bone demineralization.
Explanation
A) Correct. ACE inhibitors are commonly prescribed to manage hypertension and fluid overload in clients with chronic renal failure. These medications help relax blood vessels, reduce fluid retention, and lower blood pressure.
B) Incorrect. Phosphate binders are prescribed to control phosphate levels, but they do not directly address fluid overload and hypertension.
C) Incorrect. Erythropoietin-stimulating agents (ESA) are used to manage anemia in chronic renal failure and do not specifically address hypertension or fluid overload.
D) Incorrect. Potassium-sparing diuretics may not be the first choice for managing fluid overload and hypertension in chronic renal failure, especially if the client has elevated potassium levels. ACE inhibitors are a more suitable option in this scenario.
Explanation
A) Correct. Touching the dialysis catheter site increases the risk of infection, and clients receiving peritoneal dialysis must practice meticulous catheter care to minimize this risk.
B) Incorrect. While daily weight monitoring is essential for clients on peritoneal dialysis, it is not specifically related to peritoneal dialysis care.
C) Incorrect. Peritoneal dialysis is a home-based treatment, and the client performs the dialysis exchanges themselves. There is no need for frequent visits to the dialysis center.
D) Incorrect. Pain medication is not typically needed before starting a peritoneal dialysis exchange, as the procedure itself is not painful. Proper technique and sterile care are the main focus of peritoneal dialysis education.
Explanation
A) Correct. In chronic renal failure, limiting protein intake is essential to reduce the workload on the kidneys and slow the progression of kidney damage.
B) Incorrect. Increasing sodium intake is not recommended in chronic renal failure, as it can lead to fluid retention and hypertension.
C) Incorrect. While potassium intake may need to be adjusted based on blood levels, there is no indication to consume potassium-rich foods to prevent deficiency.
D) Incorrect. Fluid restrictions are typically necessary in chronic renal failure to prevent fluid overload and related complications.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While physical activity is essential for overall health, the client's fatigue may be related to anemia, not lack of physical activity.
B) Correct. Fatigue and lethargy are common symptoms of anemia, which is a common complication of chronic renal failure. Iron supplements can help address anemia-related fatigue.
C) Incorrect. Increasing protein intake may not directly address the underlying cause of the client's fatigue, which is likely anemia.
D) Incorrect. Caffeine-containing beverages can contribute to fluid overload and hypertension in chronic renal failure and are not a suitable intervention for addressing fatigue.
Explanation
A) Correct. Phosphate binders are most effective when taken with meals because they bind to dietary phosphorus, preventing its absorption in the digestive tract.
B) Incorrect. While constipation can be a side effect of some phosphate binders, drinking plenty of fluids is not directly related to this issue.
C) Incorrect. Phosphate binders should be taken with meals, and calcium supplements should be taken separately to prevent interactions between the two medications.
D) Incorrect. Phosphate binders do not typically lower potassium levels, and monitoring potassium intake is not specifically related to their use.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Dairy products are high in potassium and should be limited in clients at risk for hyperkalemia.
B) Incorrect. Fruits and vegetables are also high in potassium and should be limited in clients with chronic renal failure and hyperkalemia risk.
C) Correct. Nuts and seeds are rich sources of potassium and should be restricted in the diet of clients at risk for hyperkalemia.
D) Incorrect. Poultry is a good protein source, but the type of protein is not the main concern for clients at risk for hyperkalemia; it is the overall potassium content of the diet that needs to be reduced.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While dietary modifications are often necessary in chronic renal failure, this response does not address the client's concerns about lifestyle impact.
B) Correct. Hemodialysis requires a significant time commitment, and clients must plan their activities around the dialysis schedule. It is important for the client to understand the need for regular dialysis sessions to manage their condition effectively.
C) Incorrect. While hemodialysis does require regular sessions, it should not necessarily limit a client's ability to travel or participate in social events. Many individuals on hemodialysis can adjust their activities and still engage in meaningful experiences.
D) Incorrect.
Physical activity is generally encouraged in clients with chronic renal failure, as it contributes to overall well-being. Hemodialysis may increase energy levels and improve the client's ability to engage in physical activity.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Calcium-based phosphate binders should not be taken with milk or calcium-rich foods, as this can lead to an excessive calcium load and increase the risk of hypercalcemia.
B) Incorrect. Calcium-based phosphate binders are most effective when taken with meals to bind to dietary phosphorus.
C) Incorrect. While vitamin D plays a role in calcium metabolism, its supplementation is not directly related to the use of calcium-based phosphate binders.
D) Correct. Constipation is a common side effect of calcium-based phosphate binders. Increasing fluid intake can help alleviate constipation and promote bowel regularity.
Nephrotic Syndrome
Explanation
A) Correct. Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by increased protein loss in the urine, leading to hypoalbuminemia and a weakened immune system. Clients with nephrotic syndrome are at a higher risk of infection, so the priority nursing intervention is to assess for signs of infection and initiate appropriate treatment promptly.
B) Incorrect. While monitoring blood glucose levels is essential in some conditions, it is not the priority for a client with nephrotic syndrome.
C) Incorrect. Dietary education may be necessary, but increasing protein intake is not appropriate for clients with nephrotic syndrome due to the increased protein loss in the urine.
D) Incorrect. Diuretics may be used to manage edema in nephrotic syndrome, but the priority intervention is to assess for infection, as it poses a more immediate threat to the client's health.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Corticosteroids should be taken with food to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
B) Incorrect. While corticosteroids may improve proteinuria over time, it is unlikely to see an immediate improvement after starting the medication.
C) Correct. Corticosteroids can suppress the immune system and increase the risk of infection, so the client should avoid crowded places and contact with individuals who are sick to minimize the risk of infections.
D) Incorrect. Corticosteroids do not specifically affect potassium levels, so there is no need for a diet high in potassium to offset potential electrolyte imbalances.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Restricting fluid intake may not be appropriate for clients with nephrotic syndrome, as they may already have reduced fluid intake due to decreased glomerular filtration.
B) Incorrect. Elevating the client's legs can help reduce edema, but a low-sodium diet is a more direct and essential intervention for managing fluid retention in nephrotic syndrome.
C) Correct. A low-sodium diet is crucial in managing edema in nephrotic syndrome. Sodium intake can lead to fluid retention, and reducing sodium intake helps decrease edema.
D) Incorrect. Monitoring blood glucose levels is important for clients with diabetes, but it is not directly related to managing edema in nephrotic syndrome.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Frothy, foamy urine is not characteristic of increased glucose levels in the urine.
B) Incorrect. While blood in the urine may cause changes in urine color, it does not result in frothy, foamy appearance.
C) Correct. Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by increased protein excretion in the urine (proteinuria). The presence of protein in the urine can cause it to appear frothy and foamy.
D) Incorrect. Creatinine levels reflect kidney function, but they do not cause changes in urine appearance.
Explanation
A) Correct. ACE inhibitors are commonly prescribed in nephrotic syndrome to reduce proteinuria by dilating blood vessels and decreasing pressure in the glomerulus. This helps preserve kidney function and slow the progression of kidney damage.
B) Incorrect. ACE inhibitors are not primarily used to manage blood glucose levels in diabetes, although they may have some impact on blood pressure control in clients with both diabetes and nephrotic syndrome.
C) Incorrect. ACE inhibitors do not directly impact calcium absorption or bone health in nephrotic syndrome.
D) Incorrect. ACE inhibitors do not specifically increase potassium excretion. In fact, they may lead to potassium retention, so clients may need to be cautious about potassium intake while on ACE inhibitors.
Explanation
A) Correct. Diuretics can lead to potassium loss, potentially causing hypokalemia. Monitoring serum potassium levels is essential to prevent complications related to potassium imbalances.
B) Incorrect. Diuretics may affect blood glucose levels indirectly, but their primary impact is not related to glucose control.
C) Incorrect. Diuretics do not directly impact calcium levels
in nephrotic syndrome.
D) Incorrect. While monitoring blood pressure is important in nephrotic syndrome, it is not the primary focus when clients are on diuretic therapy.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While increased proteinuria can increase the risk of clot formation in the urinary tract, anticoagulant therapy is not typically prescribed for this reason in nephrotic syndrome.
B) Incorrect. Anticoagulants are not primarily used to reduce inflammation and pain associated with kidney damage.
C) Incorrect. Anticoagulants do not directly impact the risk of infection related to hypoalbuminemia.
D) Correct. Nephrotic syndrome can cause damage to the glomerular capillaries, leading to clot formation. Anticoagulant therapy is prescribed to prevent clot formation in the kidneys and reduce the risk of complications such as renal vein thrombosis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by increased proteinuria, indicating the loss of proteins from the bloodstream, not increased filtration of proteins into the urine.
B) Incorrect. Thickening of the glomerular basement membrane is a feature of some kidney diseases but is not the primary abnormality in nephrotic syndrome.
C) Incorrect. Nephrotic syndrome is associated with increased permeability of the glomerular capillaries, allowing proteins to pass through into the urinary space.
D) Correct. Disruption of the glomerular filtration barrier, which includes the glomerular endothelium, basement membrane, and podocytes, leads to the key features of nephrotic syndrome, such as proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hyperlipidemia in nephrotic syndrome results from increased hepatic synthesis of lipoproteins and is not directly related to decreased serum albumin levels.
B) Correct. Hypoalbuminemia reduces the colloid osmotic pressure in the blood vessels, causing fluid to leak into the interstitial spaces, leading to edema formation, a hallmark of nephrotic syndrome.
C) Incorrect. Hypertension may occur in nephrotic syndrome due to sodium and water retention, but it is not directly related to decreased serum albumin levels.
D) Incorrect. Hematuria (blood in the urine) is not a direct consequence of hypoalbuminemia but may be present in some cases of nephrotic syndrome due to underlying glomerular damage.
Explanation
A) Correct. Nephrotic syndrome is associated with the loss of antithrombin III in the urine, which impairs its anticoagulant function, contributing to a hypercoagulable state.
B) Incorrect. Elevated fibrinogen levels are not a primary factor contributing to the hypercoagulability in nephrotic syndrome.
C) Incorrect. While platelet count can be altered in various medical conditions, it is not the primary factor leading to hypercoagulability in nephrotic syndrome.
D) Incorrect. Reduced prothrombin time is not a characteristic feature of nephrotic syndrome but rather a measure of blood clotting.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Increased sodium reabsorption in the renal tubules contributes to sodium and water retention but is not the primary cause of generalized edema in nephrotic syndrome.
B) Incorrect. Elevated blood pressure may contribute to capillary leakage, but it is not the primary cause of edema in nephrotic syndrome.
C) Correct. Decreased colloid osmotic pressure in the blood vessels, resulting from hypoalbuminemia due to proteinuria, leads to fluid shifting from the blood vessels into the interstitial spaces, causing generalized edema.
D) Incorrect. Hyperfiltration of glomerular capillaries is not a mechanism directly related to the development of edema in nephrotic syndrome.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. The glomerular endothelium is part of the glomerular filtration barrier, but it primarily restricts the passage of blood cells and large molecules.
B) Correct. The glomerular basement membrane acts as a selective barrier that prevents the loss of proteins, including albumin, into the urine.
C) Incorrect. Podocytes play a role in maintaining the integrity of the filtration barrier, but they are not the primary component responsible for preventing protein loss.
D) Incorrect. Bowman's capsule is involved in the initial filtration of blood components but does not play a direct role in preventing protein loss.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hematuria (blood in the urine) and dysuria (painful urination) are not characteristic manifestations of nephrotic syndrome. Instead, they may indicate other kidney conditions or infections.
B) Incorrect. While clients with nephrotic syndrome may experience increased urine output (polyuria) and nighttime urination (nocturia) due to fluid imbalances, these are not the primary clinical manifestations.
C) Correct. Frothy, foamy urine output is a classic sign of nephrotic syndrome due to the presence of excessive protein (proteinuria) in the urine. This foamy appearance is caused by the high levels of protein, mainly albumin, in the urine.
D) Incorrect. Suprapubic tenderness and urgency are not typical manifestations of nephrotic syndrome and may indicate other urinary tract or bladder issues.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Increased renal blood flow and fluid overload would lead to excessive urine output and reduced edema, which is not consistent with nephrotic syndrome.
B) Incorrect. Excessive sodium excretion and dehydration would lead to reduced fluid retention and edema, which is not consistent with nephrotic syndrome.
C) Correct. Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by glomerular damage, leading to increased permeability of the glomerular capillaries and loss of protein (mainly albumin) in the urine. This results in decreased oncotic pressure in the blood vessels, leading to edema in various parts of the body.
D) Incorrect. Elevated blood pressure and vascular leakage would lead to a different set of clinical manifestations, not characteristic of nephrotic syndrome.
Explanation
A) Correct. Periorbital edema is a common manifestation of nephrotic syndrome, especially in the morning after fluid accumulation overnight. Elevated blood pressure and headache may accompany this edema, indicating fluid retention and hypertension, which are frequently associated with nephrotic syndrome.
B) Incorrect. Yellowish discoloration of the skin and sclera (jaundice) is not a typical manifestation of nephrotic syndrome and is more indicative of liver dysfunction or bile flow obstruction.
C) Incorrect. Pain and tenderness over the lower back are not directly related to periorbital edema and may suggest a separate issue, such as musculoskeletal pain.
D) Incorrect. Shortness of breath and crackles in the lungs are not specific to nephrotic syndrome and may suggest other respiratory or cardiac issues.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Elevated blood pressure and fluid overload are more indicative of fluid retention and hypertension in nephrotic syndrome, not hypoalbuminemia.
B) Correct. Hypoalbuminemia, a common feature of nephrotic syndrome, results from the loss of albumin (a protein) in the urine. Low albumin levels can lead to muscle weakness and fatigue due to decreased oncotic pressure in the blood vessels, resulting in fluid shifting from the blood vessels to the interstitial spaces.
C) Incorrect. Hyperactivity and restlessness are not typical manifestations of hypoalbuminemia and nephrotic syndrome.
D) Incorrect. Pallor and cold extremities are not directly related to hypoalbuminemia and are not specific to nephrotic syndrome.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Elevated platelet count and clotting factors are not characteristic of nephrotic syndrome. Clients with nephrotic syndrome tend to have normal platelet counts.
B) Incorrect. Decreased blood viscosity and enhanced blood flow would not directly lead to an increased risk of thromboembolic events in nephrotic syndrome.
C) Incorrect. While impaired liver function may impact clotting factors, it is not a common manifestation of nephrotic
syndrome.
D) Correct. Nephrotic syndrome is associated with a loss of anticoagulant proteins, particularly antithrombin III, in the urine. This loss of anticoagulant proteins contributes to a state of hypercoagulability, increasing the risk of thromboembolic events, such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Abdominal distension and discomfort are not typical manifestations of a urinary tract infection, even in the presence of proteinuria.
B) Correct. Nephrotic syndrome often results in hypoalbuminemia due to significant protein loss in the urine. Hypoalbuminemia leads to decreased oncotic pressure in the blood vessels, causing fluid to leak into the peritoneal cavity and resulting in abdominal distension and discomfort, known as ascites.
C) Incorrect. Hyperkalemia may occur in chronic kidney disease, including nephrotic syndrome, but it is not directly related to abdominal distension and discomfort.
D) Incorrect. Renal vein thrombosis is a complication of nephrotic syndrome but is not typically associated with acute abdominal distension and discomfort.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While increased cholesterol synthesis in the liver can contribute to hyperlipidemia, it is not the primary reason for elevated lipid levels in nephrotic syndrome.
B) Incorrect. Impaired fat absorption in the small intestine is not a significant factor contributing to hyperlipidemia in nephrotic syndrome.
C) Correct. Nephrotic syndrome results in increased protein loss, including proteins involved in lipid transport and metabolism. Reduced clearance of lipids by the kidneys leads to elevated lipid levels in the bloodstream.
D) Incorrect. Elevated blood glucose levels and insulin resistance are not directly related to hyperlipidemia in nephrotic syndrome.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While a renal biopsy may provide information about kidney function and glomerular filtration rate, its primary purpose in diagnosing nephrotic syndrome is to identify the specific histopathological changes in the kidney, which can help confirm the diagnosis and guide treatment decisions.
B) Incorrect. The response to diuretic therapy can be monitored through other means, such as assessing urine output and fluid balance. A renal biopsy is not performed primarily to evaluate the response to diuretics.
C) Incorrect. Renal biopsy is not typically used to evaluate the extent of renal inflammation and infection. Other imaging or laboratory tests are more suitable for assessing renal inflammation and infection.
D) Correct. A renal biopsy is the definitive diagnostic procedure for nephrotic syndrome. It allows the pathologist to examine a small tissue sample from the kidney and identify the specific histopathological changes, such as glomerular changes, that confirm the diagnosis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Decreased serum albumin levels may contribute to fluid overload and hypertension in nephrotic syndrome, but they are not the primary indicators of these complications.
B) Incorrect. A decreased serum albumin level alone does not confirm the presence of proteinuria, which requires additional tests, such as a 24-hour urine collection for protein quantification.
C) Incorrect. Decreased serum albumin levels are not directly related to the presence of renal vein thrombosis, although nephrotic syndrome can increase the risk of thromboembolic events.
D) Correct. In nephrotic syndrome, the glomerular damage results in significant proteinuria, leading to decreased serum albumin levels. The loss of albumin in the urine contributes to hypoalbuminemia, a hallmark feature of nephrotic syndrome.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Glomerular filtration rate and kidney function are typically assessed through blood tests, such as serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels. A 24-hour urine collection is not used to assess these parameters.
B) Incorrect. The presence of glucose and ketones in the urine is typically assessed using a urinalysis or dipstick test. A 24-hour urine collection is not used to determine glucose and ketone levels.
C) Correct. A 24-hour urine collection measures the amount of protein excreted in the urine over a 24-hour period. This test is essential in diagnosing and monitoring nephrotic syndrome, as significant proteinuria is a hallmark feature of the condition.
D) Incorrect. The concentration of electrolytes in the urine is not typically assessed through a 24-hour urine collection. Urinary electrolyte levels are more commonly evaluated through spot urine samples or blood tests.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Monitoring lipid levels is not primarily aimed at identifying liver dysfunction in clients with nephrotic syndrome.
B) Incorrect. While nephrotic syndrome can lead to secondary diabetes mellitus in some cases, monitoring lipid levels is not a direct indicator of diabetes.
C) Correct. Nephrotic syndrome is associated with increased levels of lipids, including cholesterol and triglycerides, in the blood (hyperlipidemia). Monitoring lipid levels helps detect this common complication of nephrotic syndrome and informs treatment decisions.
D) Incorrect. Monitoring lipid levels is not directly related to evaluating electrolyte imbalances in clients with nephrotic syndrome. Electrolyte imbalances are typically assessed through separate blood tests.
Explanation
A) Correct. Diuretics are commonly used to manage edema in clients with nephrotic syndrome. They help increase urine output and reduce fluid retention, which can alleviate severe edema and fluid overload.
B) Incorrect. Restricting fluid intake is not typically recommended for clients with nephrotic syndrome, as it may lead to dehydration and worsen the hypoalbuminemia.
C) Incorrect. While adequate protein intake is essential, a high-protein diet may not be appropriate for clients with nephrotic syndrome due to increased protein loss in the urine.
D) Incorrect. Monitoring blood glucose levels is important, but it is not directly related to managing edema and hypoalbuminemia in nephrotic syndrome.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Corticosteroids should be taken with food to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
B) Incorrect. While corticosteroids may improve proteinuria over time, it is unlikely to see an immediate improvement after starting the medication.
C) Correct. Corticosteroids can suppress the immune system and increase the risk of infection, so the client should avoid crowded places and contact with individuals who are sick to minimize the risk of infections.
D) Incorrect. Corticosteroids do not specifically affect potassium levels, so there is no need for a diet high in potassium to offset potential electrolyte imbalances.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Increasing sodium intake would worsen edema and fluid retention in clients with nephrotic syndrome, as sodium contributes to fluid retention.
B) Incorrect. While protein intake may need to be adjusted in nephrotic syndrome, a low-protein diet is not typically indicated, as clients may already have protein loss in the urine.
C) Incorrect. Encouraging fluid restriction is not recommended in nephrotic syndrome, as it may lead to dehydration and worsen edema due to hypoalbuminemia.
D) Correct. A low-sodium diet is crucial in managing edema in nephrotic syndrome. Sodium intake can lead to fluid retention, and reducing sodium intake helps decrease edema.
Explanation
A) Correct. ACE inhibitors are commonly prescribed in nephrotic syndrome to reduce proteinuria by dilating blood vessels and decreasing pressure in the glomerulus. This helps preserve kidney function and slow the progression of kidney damage.
B) Incorrect. ACE inhibitors are not primarily used to manage blood glucose levels in diabetes, although they may have some impact on blood pressure control in clients with both diabetes and nephrotic syndrome.
C) Incorrect. ACE inhibitors do not directly impact calcium absorption or bone health in nephrotic syndrome.
D) Incorrect. ACE inhibitors do not specifically increase potassium excretion. In fact, they may lead to potassium retention, so clients may need to be cautious about potassium intake while on ACE inhibitors.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Elevated platelet count and clotting factors are not characteristic of nephrotic syndrome. Clients with nephrotic syndrome tend to have normal platelet counts.
B) Incorrect. Decreased blood viscosity and enhanced blood flow would not directly lead to an increased risk of thromboembolic events in nephrotic syndrome.
C) Incorrect. While impaired liver function may impact clotting factors, it is not a common manifestation of nephrotic syndrome.
D) Correct. Nephrotic syndrome is associated with a loss of anticoagulant proteins, particularly antithrombin III, in the urine. This loss of anticoagulant proteins contributes to a state of hypercoagulability, increasing the risk of thromboembolic events, such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While increased cholesterol synthesis in the liver can contribute to hyperlipidemia, it is not the primary reason for elevated lipid levels in nephrotic syndrome.
B) Incorrect. Impaired fat absorption in the small intestine is not a significant factor contributing to hyperlipidemia in nephrotic syndrome.
C) Correct. Nephrotic syndrome results in increased protein loss, including proteins involved in lipid transport and metabolism. Reduced clearance of lipids by the kidneys leads to elevated lipid levels in the bloodstream.
D) Incorrect. Elevated blood glucose levels and insulin resistance are not directly related to hyperlipidemia in nephrotic syndrome.
Explanation
A) Correct. Monitoring blood pressure regularly is essential for clients with nephrotic syndrome, as they are at risk of hypertension due to fluid retention.
B) Incorrect. Restricting fluid intake is not typically recommended for clients with nephrotic syndrome, as it may lead to dehydration and worsen edema due to hypoalbuminemia.
C) Correct. Clients with nephrotic syndrome are at increased risk of infections due to immunosuppression from protein loss in the urine. Reporting any signs of infection is crucial to ensure timely intervention.
D) Correct. Daily weight monitoring is essential for clients with nephrotic syndrome to assess for fluid retention. Sudden weight changes can indicate worsening edema and fluid overload.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Increased urine output and dehydration are not common side effects of corticosteroid therapy. Instead, clients may experience fluid retention and edema due to the medication's effects.
B) Correct. Corticosteroids can cause increased appetite, leading to weight gain, which is a common side effect that clients should be aware of.
C) Incorrect. Frequent bruising and prolonged bleeding are not typical side effects of corticosteroids. Instead, clients on corticosteroid therapy may experience increased susceptibility to infections and impaired wound healing.
D) Incorrect. Corticosteroids are more likely to cause fluid retention and increased blood pressure, leading to potential hypertension, rather than low blood pressure and dizziness.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While protein intake may need to be adjusted in nephrotic syndrome, increasing protein intake is not typically recommended, as clients may already have significant protein loss in the urine.
B) Incorrect. Limiting potassium-rich foods is not a primary dietary concern in nephrotic syndrome. Clients should consume a balanced diet unless instructed otherwise by their healthcare provider.
C) Correct. A low-sodium diet is crucial in managing fluid retention and edema in clients with nephrotic syndrome. Sodium intake contributes to fluid retention, so reducing sodium intake helps decrease edema.
D) Incorrect. Restricting fluid intake is not typically recommended in nephrotic syndrome, as it may lead to dehydration and worsen fluid imbalances due to hypoalbuminemia.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While some clients on ACE inhibitors may need to be cautious about potassium intake, this instruction is not universally applicable to all clients with nephrotic syndrome on this medication.
B) Incorrect. ACE inhibitors should be taken with food to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
C) Incorrect. Monitoring blood glucose levels is important, but it is not directly related to ACE inhibitor use in nephrotic syndrome.
D) Correct. ACE inhibitors can cause a drop in blood pressure, leading to dizziness, especially when changing positions (orthostatic hypotension). Clients should be instructed to change positions slowly to prevent falls and injuries.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While some clients may be at increased risk of certain infections, avoiding close contact with family members is not practical and not recommended in general.
B) Correct. Good hand hygiene is essential in reducing the risk of infections in clients with nephrotic syndrome, as they are immunocompromised due to protein loss in the urine. Regular handwashing with soap and water, especially before meals and after using the bathroom, can help prevent the spread of pathogens.
C) Incorrect. Avoiding outdoor activities and crowded places is not necessary for all clients with nephrotic syndrome and may negatively impact their quality of life.
D) Incorrect. While physical activity is generally beneficial for overall health, it is not directly related to enhancing the immune system's response in clients with nephrotic syndrome.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While monitoring urine output and kidney function is important in nephrotic syndrome, it is not directly related to addressing skin breakdown.
B) Correct. Skin breakdown in clients with nephrotic syndrome can lead to an increased risk of infection. The nurse should assess the affected skin areas for signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, swelling, and drainage.
C) Incorrect. Providing pain medication may be necessary for managing discomfort, but the priority is to prevent infection and promote wound healing.
D) Incorrect. While reducing edema is important, it is not the immediate priority in managing skin breakdown and preventing infection.
Explanation
A) Correct. Immunosuppressive medications are prescribed in nephrotic syndrome to reduce inflammation in the kidneys and prevent further damage, including kidney scarring. They help slow the progression of the disease and preserve kidney function.
B) Incorrect. Immunosuppressive medications are not primarily used to address fluid overload or improve urinary output in nephrotic syndrome.
C) Incorrect. While some immunosuppressive medications may have an impact on blood glucose levels, they are not typically used to manage diabetes in nephrotic syndrome.
D) Incorrect. Immunosuppressive medications do not directly alleviate pain and discomfort associated with edema in nephrotic syndrome. Other interventions, such as diuretics, are used for managing edema.
Renal Calculus
Explanation
A) This is not the correct answer. Renal calculi are not bacterial infections but rather solid masses that form from mineral and acid salts in the kidneys.
B) This is the correct answer. Renal calculi, commonly known as kidney stones, are solid masses formed from mineral and acid salts that accumulate in the kidneys.
C) Renal calculi are not benign tumors. They are distinct from tumors and do not have the same characteristics.
D) Renal calculi are not blood clots. Blood clots can block the urinary tract, but they are not the same as kidney stones.
Explanation
A) Excessive water intake is not a risk factor for kidney stones. In fact, adequate hydration is encouraged to prevent kidney stone formation.
B) Low dietary calcium intake is not a common risk factor for kidney stones. In some cases, excessive calcium supplementation may be a risk factor, but dietary calcium is generally not a concern.
C) This is the correct answer. Family history, a diet high in protein and salt, and dehydration are common risk factors for kidney stones.
D) Kidney stones are not mostly caused by consuming too many fruits and vegetables. Fruits and vegetables are generally considered beneficial for kidney health.
Explanation
A) Citrus fruits are generally not a concern for calcium oxalate stones. They are a good source of citrate, which may actually help prevent stone formation.
B) Dairy products are not specifically associated with calcium oxalate stones. However, high-calcium supplements might increase the risk, not dietary calcium from dairy products.
C) Red meat is not a significant concern for calcium oxalate stones. It is more associated with uric acid stones.
D) This is the correct answer. Leafy green vegetables are high in oxalates, which can contribute to calcium oxalate stone formation. Clients with calcium oxalate stones should limit their intake of these vegetables.
Explanation
A) Severe back pain can be a symptom of kidney stones, but it is not the most common one.
B) This is the correct answer. Hematuria, or blood in the urine, is the most common symptom of kidney stones. The blood may be visible or microscopic.
C) Frequent urination can be a symptom of kidney stones, but it is not the most common one.
D) Sudden weight loss is not a symptom commonly associated with kidney stones.
A nurse is assessing a client with suspected renal calculi. The client reports experiencing sudden and severe pain in the right flank area that radiates to the groin. The nurse notes that the client is restless and unable to find a comfortable position. What type of renal calculi is most likely causing the client's symptoms?
Explanation
A) Calcium oxalate stones may cause pain, but they do not typically radiate to the groin. They are more likely to cause localized pain in the back or side.
B) This is the correct answer. Uric acid stones can cause sudden and severe pain that radiates from the back to the groin. The pain is often described as colicky and is associated with restlessness.
C) Struvite stones are typically associated with urinary tract infections and may not cause the sudden and severe pain described in the question.
D) Cystine stones are rare and are more likely to cause chronic, dull pain rather than sudden and severe pain.
Explanation
A) Avoiding all dairy products is not a recommended prevention strategy for kidney stones. In fact, adequate dietary calcium may be beneficial for reducing the risk of certain types of stones.
B) Increasing dietary calcium intake, especially from food sources, may help prevent certain types of kidney stones, such as calcium oxalate stones.
C) Reducing fluid intake is not a recommended prevention strategy for kidney stones. Inadequate hydration can actually increase the risk of stone formation.
D) This is the correct answer. Drinking plenty of water and staying hydrated is one of the most effective ways to prevent kidney stones. Adequate hydration helps dilute urine and reduce the concentration of minerals that can lead to stone formation.
Explanation
A) ESWL is a non-invasive procedure, and it does not require a hospital stay. It is typically performed on an outpatient basis.
B) This is not entirely accurate. ESWL is a non-invasive procedure that does not require general anesthesia. Instead, the client may be given sedation or local anesthesia.
C) It is essential to maintain adequate hydration after ESWL to help pass the broken-up stone fragments. Avoiding all fluids for 24 hours is not recommended and may lead to dehydration.
D) This is the correct answer. ESWL uses shock waves to break up kidney stones, and the client will need to remain still during the procedure to ensure precise targeting of the stones. The procedure is usually painless, but some discomfort may be experienced during the process.
Explanation
A) Excessive consumption of fruits and vegetables is not a primary cause of kidney stones. Some specific types of fruits and vegetables may contribute to stone formation, but it is not a general cause.
B) While genetic factors and family history can play a role in kidney stone formation, they are not the primary cause. The presence of minerals and salts in the urine is the main contributing factor.
C) An overactive bladder and frequent urination are not direct causes of kidney stone formation. They may be related to other urinary conditions but not to the formation of kidney stones.
D) This is the correct answer. Kidney stones are formed when certain minerals and salts in the urine form solid crystals that can clump together and grow into stones.
Explanation
A) This is the correct answer. High dietary calcium intake is a common risk factor for certain types of kidney stones, particularly calcium oxalate stones. However, dietary calcium intake from food sources is not typically associated with an increased risk of kidney stones. Calcium supplements, on the other hand, may contribute to stone formation.
B) A low protein diet is not a significant risk factor for kidney stones. High-protein diets may be associated with an increased risk, but low protein intake is not a concern.
C) Adequate water consumption is essential to prevent kidney stones. Dehydration is a risk factor for stone formation, but excessive water consumption alone is not a significant risk factor.
D) While a sedentary lifestyle may be associated with other health risks, it is not a primary risk factor for kidney stones.
Explanation
A) This is the correct answer. Calcium oxalate stones are common, and limiting the intake of foods high in oxalate, such as spinach, nuts, and certain other vegetables and fruits, can help reduce the risk of stone recurrence.
B) Increasing the intake of red meat and fish is not recommended to prevent calcium oxalate stones. In fact, high intake of animal protein may increase the risk of certain types of stones, such as uric acid stones.
C) Consuming carbonated beverages is not recommended to improve kidney function or prevent kidney stones. Some carbonated beverages may contain phosphoric acid, which can contribute to stone formation.
D) Avoiding dairy products is not recommended to prevent calcium oxalate stone formation. In fact, adequate dietary calcium intake from food sources may help reduce the risk of these stones.
Explanation
A) This is not entirely accurate. While family history can be a risk factor for kidney stones, there are still preventive measures that individuals can take to reduce their risk.
B) Avoiding all calcium-rich foods and beverages is not recommended for preventing kidney stones. In fact, adequate dietary calcium from food sources is generally beneficial for kidney health and may help reduce the risk of certain types of stones.
C) This is the correct answer. Maintaining a healthy weight and drinking plenty of water are important lifestyle factors that can help reduce the risk of kidney stones. Adequate hydration helps prevent the concentration of minerals in the urine, reducing the likelihood of stone formation.
D) Surgery is not the only treatment option for kidney stones. Depending on the size and type of stone, other treatment options, such as lithotripsy or medication, may be considered.
Explanation
A) Uric acid stones may cause pain, but they do not typically present with costovertebral angle tenderness. Uric acid stones are more likely to be associated with gout and hyperuricemia.
B) Calcium oxalate stones are common and can cause pain, but they do not typically cause costovertebral angle tenderness. They are more likely to cause localized pain in the back or side.
C) This is the correct answer. Struvite stones, also known as infection stones, can cause severe pain that radiates to the back and lower abdomen. They are often associated with urinary tract infections, and the presence of an infection can lead to costovertebral angle tenderness.
D) Cystine stones are rare and are more likely to cause chronic, dull pain rather than sudden and severe pain with tenderness.
Explanation
A) Smoking cessation is important for overall health, but it is not a primary lifestyle factor related to kidney stone formation.
B) Increased alcohol consumption is not recommended as a preventive measure for kidney stones. In fact, excessive alcohol intake can lead to dehydration, which is a risk factor for stone formation.
C) Regular exercise can be beneficial for overall health, but it is not a primary lifestyle factor related to kidney stone formation.
D) This is the correct answer. A high sodium diet can increase the excretion of calcium in the urine, leading to a higher risk of calcium-based kidney stones. Reducing sodium intake can help prevent stone formation.
Explanation
A) Limiting fluid intake is not recommended to prevent kidney stones. Adequate hydration is essential to prevent stone formation. Dehydration can lead to a higher concentration of minerals in the urine, increasing the risk of stones.
B) Including more foods high in oxalate is not recommended to prevent kidney stones, especially if the client has a history of calcium oxalate stones. Limiting the intake of oxalate-rich foods is a preventive measure.
C) Avoiding all dairy products is not recommended to prevent kidney stones. In fact, adequate dietary calcium intake from food sources may help reduce the risk of certain types of stones, such as calcium oxalate stones.
D) This is the correct answer. Staying hydrated and drinking plenty of water throughout the day is one of the most effective ways to prevent kidney stones. Adequate hydration helps dilute urine and reduce the concentration of minerals that can lead to stone formation.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While uric acid stones are one type of kidney stone, they do not represent the primary component of all kidney stones.
B) Correct. The most common types of kidney stones are composed of calcium, oxalate, and phosphate crystals.
C) Incorrect. Cholesterol and fatty deposits are not the primary components of kidney stones.
D) Incorrect. Bacteria do not represent the primary component of kidney stones. Kidney stones are typically mineral or crystal formations.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Dehydration actually leads to a decrease in urinary volume, which can contribute to the concentration of minerals in the urine and increase the likelihood of stone formation.
B) Correct. Dehydration reduces the amount of water in the urine, leading to a higher concentration of minerals like calcium, oxalate, and phosphate, which are key components of kidney stones.
C) Incorrect. Dehydration does not increase the production of protective substances that prevent stone formation; in fact, it has the opposite effect.
D) Incorrect. Dehydration does not slow down the filtration process in the kidneys. Instead, it can lead to the concentration of minerals in the urine.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While genetics can influence the likelihood of developing kidney stones, it does not guarantee that a person will develop them.
B) Correct. Genetics can influence factors like calcium metabolism, which in turn can affect the likelihood of stone formation.
C) Incorrect. Genetics do play a role in kidney stone formation, particularly in relation to factors like calcium metabolism.
D) Incorrect. Genetics have a broader impact on kidney stone formation beyond just color and shape.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Urinary stasis does not increase the volume of urine; in fact, it can lead to the pooling of urine, potentially contributing to stone formation.
B) Correct. Urinary stasis refers to the slowing or cessation of urine flow, which can allow minerals to aggregate and form kidney stones.
C) Incorrect. Urinary stasis does not promote the breakdown of minerals in the urine. Instead, it can lead to the concentration of minerals, potentially contributing to stone formation.
D) Incorrect. Urinary stasis does have a significant impact on the development of kidney stones, as it can lead to the pooling of minerals and the formation of stones.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. An acidic urine pH actually increases the risk of stone formation by promoting the aggregation and crystallization of minerals.
B) Incorrect. A more alkaline urine pH can actually increase the risk of certain types of kidney stones, particularly those composed of calcium phosphate.
C) Incorrect. The pH of urine does have an influence on the development of kidney stones. An acidic pH can contribute to certain types of stone formation.
D) Correct. An acidic urine pH can lead to the aggregation and crystallization of minerals, increasing the risk of stone formation.
Explanation
A) Sharp, stabbing pain in the lower abdomen is not typically associated with kidney stones. Kidney stone pain is usually felt in the back and flank regions of the body.
B) This is the correct answer. The pain caused by kidney stones is often described as a dull ache in the upper back and flank region, usually on the affected side where the kidney is located.
C) Burning sensation during urination is more commonly associated with urinary tract infections or inflammation of the urethra, not kidney stones.
D) Constant, generalized abdominal discomfort is not a specific symptom of kidney stones. Kidney stone pain is usually more localized to the back and flank regions.
Explanation
A) Fever and chills are more commonly associated with a urinary tract infection, which can sometimes be a complication of kidney stones. However, the severe pain described is more likely related to the presence of the stone itself.
B) This is the correct answer. Blood in the urine, also known as hematuria, is a common symptom of kidney stones. As the stone moves through the urinary tract, it may cause irritation and small blood vessels may be damaged, resulting in blood in the urine.
C) Difficulty starting the urine stream is not a specific symptom of kidney stones. It may be seen in other urinary conditions but is not typically associated with stones.
D) The frequent urge to urinate may be experienced if the stone causes irritation in the bladder, but it is not the most common symptom associated with kidney stones.
Explanation
A) This is the correct answer. Kidney stone pain is often described as colicky, which means it comes and goes in waves of severe pain. The pain can be intense and cramp-like, causing the client to writhe or be restless.
B) Gnawing pain is not typically associated with kidney stones. Gnawing pain is often described as a persistent, dull ache that can be more chronic in nature.
C) Stabbing pain is sharp and localized and is not typically used to describe kidney stone pain.
D) Numbing pain refers to a loss of sensation, which is not characteristic of kidney stone pain.
Explanation
A) Diarrhea and abdominal cramping are not typically associated with kidney stone pain. These symptoms are more commonly seen in gastrointestinal disorders.
B) Painful and frequent urination may occur if the stone causes irritation in the bladder or urethra, but it is not a direct symptom of kidney stone pain.
C) Fatigue and generalized weakness are not specific symptoms of kidney stone pain. They may be associated with other medical conditions but are not directly related to renal calculus.
D) This is the correct answer. Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms that may accompany kidney stone pain, especially if the stone causes obstruction in the urinary tract. The pain and irritation can trigger a reflex that leads to nausea and vomiting.
Explanation
A) Limiting fluid intake to 1 liter per day is not recommended to prevent kidney stone formation. Adequate hydration is essential to
help prevent stone formation, as it helps dilute the urine and reduce the concentration of minerals that can lead to stone formation.
B) Decreasing dietary fiber intake is not a preventive measure for kidney stones. In fact, increasing dietary fiber intake can be beneficial for overall health.
C) Reducing calcium intake from all sources is not recommended to prevent kidney stones. In some cases, reducing dietary calcium intake can actually increase the risk of certain types of kidney stones.
D) This is the correct answer. Increasing citric acid intake can help prevent certain types of kidney stones, such as calcium oxalate stones. Citric acid helps to bind calcium in the urine, reducing the risk of stone formation. Citric acid can be found in citrus fruits and juices, and the nurse may advise the client to include more of these foods in their diet.
Explanation
A) Pain relief is important in managing kidney stone pain, but potassium citrate is not primarily prescribed for this purpose.
B) Acid-base balance regulation may be one of the functions of potassium citrate, but it is not the primary purpose when prescribed to a client with renal calculus.
C) Urinary tract infection treatment is not the primary purpose of potassium citrate. While it may have some benefits in preventing certain types of urinary tract infections associated with stones, its primary purpose is not to treat infections.
D) This is the correct answer. Potassium citrate is prescribed to help dissolve certain types of kidney stones, particularly calcium oxalate stones and uric acid stones. It works by increasing the pH of the urine, making it more alkaline and less conducive to stone formation.
Explanation
A) Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) does not typically require general anesthesia. It is usually done under sedation or with the use of local anesthesia.
B) The procedure does not involve the insertion of a scope into the urinary tract. ESWL is a non-invasive procedure that uses shock waves to break up the stone from outside the body.
C) This is the correct answer. ESWL involves the use of high-energy shock waves that are focused on the stone to break it up into smaller fragments. The fragments are then passed out of the body through the urine.
D) A urinary catheter is not typically required after ESWL. The client may be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids to help flush out the stone fragments, but a catheter is not usually needed.
Explanation
A) Sharp, stabbing pain in the lower abdomen is not typically associated with kidney stones. Kidney stone pain is usually felt in the back and flank regions of the body.
B) This is the correct answer. The pain caused by kidney stones is often described as a dull ache in the upper back and flank region, usually on the affected side where the kidney is located.
C) Burning sensation during urination is more commonly associated with urinary tract infections or inflammation of the urethra, not kidney stones.
D) Constant, generalized abdominal discomfort is not a specific symptom of kidney stones. Kidney stone pain is usually more localized to the back and flank regions.
Explanation
A) Fever and chills are more commonly associated with a urinary tract infection, which can sometimes be a complication of kidney stones. However, the severe pain described is more likely related to the presence of the stone itself.
B) This is the correct answer. Blood in the urine, also known as hematuria, is a common symptom of kidney stones. As the stone moves through the urinary tract, it may cause irritation and small blood vessels may be damaged, resulting in blood in the urine.
C) Difficulty starting the urine stream is not a specific symptom of kidney stones. It may be seen in other urinary conditions but is not typically associated with stones.
D) The frequent urge to urinate may be experienced if the stone causes irritation in the bladder, but it is not the most common symptom associated with kidney stones.
Explanation
A) This is the correct answer. Kidney stone pain is often described as colicky, which means it comes and goes in waves of severe pain. The pain can be intense and cramp-like, causing the client to writhe or be restless.
B) Gnawing pain is not typically associated with kidney stones. Gnawing pain is often described as a persistent, dull ache that can be more chronic in nature.
C) Stabbing pain is sharp and localized and is not typically used to describe kidney stone pain.
D) Numbing pain refers to a loss of sensation, which is not characteristic of kidney stone pain.
Explanation
A) Diarrhea and abdominal cramping are not typically associated with kidney stone pain. These symptoms are more commonly seen in gastrointestinal disorders.
B) Painful and frequent urination may occur if the stone causes irritation in the bladder or urethra, but it is not a direct symptom of kidney stone pain.
C) Fatigue and generalized weakness are not specific symptoms of kidney stone pain. They may be associated with other medical conditions but are not directly related to renal calculus.
D) This is the correct answer. Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms that may accompany kidney stone pain, especially if the stone causes obstruction in the urinary tract. The pain and irritation can trigger a reflex that leads to nausea and vomiting.
Explanation
A) Limiting fluid intake to 1 liter per day is not recommended to prevent kidney stone formation. Adequate hydration is essential to
help prevent stone formation, as it helps dilute the urine and reduce the concentration of minerals that can lead to stone formation.
B) Decreasing dietary fiber intake is not a preventive measure for kidney stones. In fact, increasing dietary fiber intake can be beneficial for overall health.
C) Reducing calcium intake from all sources is not recommended to prevent kidney stones. In some cases, reducing dietary calcium intake can actually increase the risk of certain types of kidney stones.
D) This is the correct answer. Increasing citric acid intake can help prevent certain types of kidney stones, such as calcium oxalate stones. Citric acid helps to bind calcium in the urine, reducing the risk of stone formation. Citric acid can be found in citrus fruits and juices, and the nurse may advise the client to include more of these foods in their diet.
Explanation
A) Pain relief is important in managing kidney stone pain, but potassium citrate is not primarily prescribed for this purpose.
B) Acid-base balance regulation may be one of the functions of potassium citrate, but it is not the primary purpose when prescribed to a client with renal calculus.
C) Urinary tract infection treatment is not the primary purpose of potassium citrate. While it may have some benefits in preventing certain types of urinary tract infections associated with stones, its primary purpose is not to treat infections.
D) This is the correct answer. Potassium citrate is prescribed to help dissolve certain types of kidney stones, particularly calcium oxalate stones and uric acid stones. It works by increasing the pH of the urine, making it more alkaline and less conducive to stone formation.
Explanation
A) Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) does not typically require general anesthesia. It is usually done under sedation or with the use of local anesthesia.
B) The procedure does not involve the insertion of a scope into the urinary tract. ESWL is a non-invasive procedure that uses shock waves to break up the stone from outside the body.
C) This is the correct answer. ESWL involves the use of high-energy shock waves that are focused on the stone to break it up into smaller fragments. The fragments are then passed out of the body through the urine.
D) A urinary catheter is not typically required after ESWL. The client may be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids to help flush out the stone fragments, but a catheter is not usually needed.
Explanation
A) While increasing fluid intake can help with the passage of small stones, it is not likely to dissolve larger stones. The primary benefit of increased fluid intake is to help prevent the formation of new stones.
B) Drinking more fluids may help alleviate some discomfort, but the primary goal is not pain reduction.
C) This is the correct answer. Adequate fluid intake can help prevent the formation of new kidney stones by diluting the urine and reducing the concentration of minerals that can contribute to stone formation.
D) While adequate fluid intake can help reduce the risk of urinary tract infections, it is not the primary reason for recommending increased fluid intake in clients with kidney stones.
Explanation
A) This is a correct statement. Drinking plenty of water is important to help flush out any stone fragments that may have resulted from the procedure.
B) This is a correct statement. Strenuous activities should be avoided for a few days after the procedure to allow for proper healing.
C) This is a correct statement. It is common to have some blood in the urine for a short time after ureteroscopy due to irritation and manipulation of the urinary tract during the procedure.
D) This statement is not correct. After the procedure, the client may be advised to follow a specific diet that is low in certain minerals (such as oxalate and calcium) that can contribute to stone formation. The nurse should provide specific dietary guidelines and restrictions to the client.
Explanation
A) Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) is typically used for smaller stones that can be broken up into smaller fragments and passed more easily. It is not usually recommended for large stones.
B) This is the correct answer. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a procedure used to remove larger kidney stones. It involves making a small incision in the back and inserting a nephroscope to directly visualize and remove the stone.
C) Ureteroscopy with laser lithotripsy is used for stones in the ureter, not in the kidney itself.
D) Cystoscopy with stent placement is used for conditions involving the lower urinary tract, such as the urethra and bladder, and is not typically used to remove kidney stones.
Explanation
A) Alpha-blockers do not directly reduce inflammation in the urinary tract. They primarily work by relaxing the smooth muscle of the ureters, which can help ease the passage of kidney stones through the urinary tract.
B) Alpha-blockers do not dissolve kidney stones. They assist with stone passage by relaxing the ureters.
C) This is the correct answer. Alpha-blockers are prescribed to relax the smooth muscle of the ureters, allowing the stone to pass more easily through the urinary tract.
D) Alpha-blockers do not have a direct effect on preventing bacterial growth in the urinary tract. They are not antibiotics.
Explanation
A) Reducing calcium intake is not typically recommended for uric acid stones. In fact, low calcium intake can increase the risk of other types of kidney stones.
B) Increasing consumption of red meat and shellfish is not recommended for uric acid stones. These foods are high in purines, which can increase uric acid levels in the body.
C) This is the correct answer. Uric acid stones are formed from high levels of uric acid in the urine. Purine-rich foods can contribute to elevated uric acid levels, so limiting these foods is important in managing uric acid stones.
D) Increasing intake of oxalate-rich foods is not specifically relevant to uric acid stones. Oxalate-rich foods are associated with calcium oxalate stones, not uric acid stones.
Explanation
A) Thiazide diuretics do not directly increase the excretion of uric acid. They are primarily used to reduce calcium excretion and prevent the formation of calcium-based stones.
B) This is the correct answer. Thiazide diuretics help reduce the excretion of calcium in the urine, which can be beneficial in preventing the formation of certain types of kidney stones, particularly calcium oxalate stones.
C) Thiazide diuretics do not directly increase the pH of the urine. They primarily reduce calcium excretion.
D) Thiazide diuretics do not dissolve existing kidney stones. They are used to prevent stone formation, not to treat existing stones.
Explanation
A) This is the correct answer. After percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL), the client may experience urinary retention due to swelling and irritation around the bladder or urethra from the procedure. The nurse should monitor the client for signs of urinary retention, such as difficulty urinating or a distended bladder, and take appropriate measures to relieve the obstruction.
B) Hyperkalemia is not directly related to PCNL. It may occur in certain medical conditions but is not a common complication of this procedure.
C) Hypoglycemia is not related to PCNL. It is a condition related to low blood sugar levels and is not a typical complication of kidney stone removal.
D) Hypertension is not directly related to PCNL. While some clients with hypertension may be at increased risk for kidney stones, hypertension is not a common complication of PCNL itself.
Explanation
A) This statement is not correct. Adequate fluid intake is essential to help prevent kidney stones. Restricting fluid intake can increase the concentration of minerals in the urine and promote stone formation.
B) This statement is not correct. While calcium oxalate stones are common, reducing calcium intake is not recommended for most people. In fact, a low-calcium diet may increase the risk of other types of kidney stones.
C) This statement is not correct. Fruits and vegetables contain valuable nutrients and should not be avoided. However, some fruits and vegetables are high in oxalate, which may contribute to the formation of calcium oxalate stones. The key is to consume a balanced diet and drink plenty of fluids.
D) This is the correct answer. Adequate fluid intake is crucial in preventing kidney stones. It helps dilute the urine and reduce the concentration of minerals that can lead to stone formation.
Explanation
A) This statement is not correct. If a client has calcium oxalate stones, they should limit foods high in oxalate, such as spinach and nuts, to reduce the risk of stone formation.
B) This is the correct answer. Calcium oxalate stones are the most common type of kidney stone. Reducing dietary calcium intake can help prevent the formation of calcium oxalate stones. However, it is important to note that not all clients with kidney stones should reduce their calcium intake, as calcium is essential for bone health and other bodily functions.
C) Avoiding foods high in purines is more relevant to the prevention of uric acid stones, not calcium oxalate stones.
D) While reducing sodium and processed foods can be beneficial for overall health, it is not a specific dietary modification for preventing calcium oxalate stones.
Explanation
A) This statement is not correct. Limiting intake of calcium is not necessary for the prevention of uric acid stones. In fact, low calcium intake can increase the risk of other types of stones.
B) This is the correct answer. Uric acid stones are formed from high levels of uric acid in the urine. Purine-rich foods can contribute to elevated uric acid levels, so avoiding these foods is important in managing uric acid stones.
C) Increasing consumption of oxalate-rich foods like spinach is not relevant to preventing uric acid stones.
D) Reducing fluid intake is not recommended for preventing any type of kidney stone. Adequate fluid intake is essential for kidney health and preventing stone formation.
Explanation
A) This statement is not correct. Vitamin C supplements may increase the risk of calcium oxalate stones in some individuals.
B) This is the correct answer. High doses of vitamin C can be metabolized into oxalate in the body
, which can contribute to the formation of calcium oxalate stones. For individuals with a history of calcium oxalate stones, it is best to limit vitamin C supplements.
C) Taking vitamin C supplements in large doses is not recommended, especially for individuals prone to kidney stones.
D) Vitamin C supplements do have an effect on kidney stone formation, particularly for those at risk of calcium oxalate stones.
Explanation
A) Avoiding foods high in oxalate is more relevant to the prevention of calcium oxalate stones, not struvite stones.
B) Limiting intake of purine-rich foods is more relevant to the prevention of uric acid stones, not struvite stones.
C) This statement is not correct. Reducing calcium intake is not recommended for struvite stones. In fact, calcium is an essential nutrient for overall health.
D) This is the correct answer. Struvite stones are composed of magnesium, ammonium, and phosphate. Limiting the intake of high-phosphorus foods can help prevent the formation of these stones.
Explanation
A) Thiazide diuretics do not directly increase the excretion of uric acid. They are primarily used to reduce calcium excretion and prevent the formation of calcium-based stones.
B) This is the correct answer. Thiazide diuretics help reduce the excretion of calcium in the urine, which can be beneficial in preventing the formation of certain types of kidney stones, particularly calcium oxalate stones.
C) Thiazide diuretics do not directly increase the pH of the urine. They primarily reduce calcium excretion.
D) Thiazide diuretics do not dissolve existing kidney stones. They are used to prevent stone formation, not to treat existing stones.
Explanation
A) This is the correct answer. After percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL), the client may experience urinary retention due to swelling and irritation around the bladder or urethra from the procedure. The nurse should monitor the client for signs of urinary retention, such as difficulty urinating or a distended bladder, and take appropriate measures to relieve the obstruction.
B) Hyperkalemia is not directly related to PCNL. It may occur in certain medical conditions but is not a common complication of this procedure.
C) Hypoglycemia is not related to PCNL. It is a condition related to low blood sugar levels and is not a typical complication of kidney stone removal.
D) Hypertension is not directly related to PCNL. While some clients with hypertension may be at increased risk for kidney stones, hypertension is not a common complication of PCNL itself.
Explanation
A) This statement is not correct. Adequate fluid intake is essential in preventing kidney stones. Reducing fluid intake can increase the concentration of minerals in the urine and promote stone formation.
B) This statement is not correct. A high-protein diet can contribute to the formation of certain types of kidney stones, such as uric acid stones. It is not recommended as a preventive measure.
C) This statement is not correct. Dairy products are an important source of calcium, which is needed for overall health. However, individuals with calcium oxalate stones may need to limit high-oxalate foods in their diet.
D) This is the correct answer. Adequate fluid intake helps dilute urine and reduces the concentration of minerals that can lead to stone formation.
Explanation
A) This statement is not correct. Limiting calcium intake is not recommended for preventing calcium oxalate stones. In fact, adequate dietary calcium can help reduce the risk of stone formation.
B) This statement is not correct. Foods high in oxalate, such as spinach and nuts, should be limited to prevent calcium oxalate stones.
C) This statement is not correct. Fruits and vegetables are essential for overall health and should not be avoided. However, some fruits and vegetables are high in oxalate, which may contribute to calcium oxalate stone formation.
D) This is the correct answer. Reducing sodium intake can be beneficial for kidney health, as high sodium intake can increase calcium excretion in the urine and promote stone formation. Additionally, processed foods may contain high levels of sodium and should be limited.
Explanation
A) This statement is not correct. Potassium citrate does not dissolve existing kidney stones. It is used to prevent the formation of certain types of stones, particularly calcium oxalate stones.
B) This is the correct answer. Potassium citrate is an alkalizing agent that helps reduce the acidity of urine. By making the urine less acidic, it can help prevent the formation of certain types of stones, such as uric acid stones.
C) Potassium citrate does not increase calcium levels in the body. It may help prevent the formation of calcium oxalate stones, but it does not affect overall calcium levels.
D) Potassium citrate does not decrease urine output. It primarily works to reduce urine acidity and prevent stone formation.
Explanation
A) This statement is not correct. Increasing dairy product intake may provide calcium, which is important for overall health, but it is not a specific dietary modification to prevent struvite stones.
B) This is the correct answer. Struvite stones are composed of magnesium, ammonium, and phosphate. Limiting the intake of high-phosphorus foods can help prevent the formation of these stones.
C) Avoiding foods high in purines is more relevant to the prevention of uric acid stones, not struvite stones.
D) Limiting fluid intake is
not recommended for the prevention of struvite stones. Adequate fluid intake is essential in preventing stone formation.
Explanation
A) Allopurinol does not directly increase urine output. It is not a diuretic and is not used for that purpose.
B) Allopurinol does not dissolve existing kidney stones. It is primarily used to prevent the formation of uric acid stones, not to treat existing stones.
C) This is the correct answer. Allopurinol is a medication used to reduce the production of uric acid in the body. By lowering uric acid levels, it can help prevent the formation of uric acid stones.
D) Allopurinol does not increase the excretion of calcium. It is used specifically to address uric acid levels and prevent uric acid stone formation.
Explanation
A) This is the correct answer. After a ureteroscopy, the client may experience postoperative urinary retention due to swelling or irritation in the urethra or bladder. The nurse should monitor for signs of urinary retention and take appropriate measures to address it.
B) Hyperkalemia is not directly related to ureteroscopy. It may occur in certain medical conditions but is not a common complication of this procedure.
C) Hypertension is not directly related to ureteroscopy. While some clients with hypertension may be at increased risk for kidney stones, hypertension is not a common complication of the procedure itself.
D) Hypoglycemia is not related to ureteroscopy. It is a condition related to low blood sugar levels and is not a typical complication of kidney stone removal.
Explanation
A) Thiazide diuretics can lead to decreased calcium excretion in the urine, which may be beneficial for some clients with kidney stones. They are used to reduce the excretion of calcium and prevent the formation of calcium-based stones.
B) Hypernatremia is not directly related to thiazide diuretic use. Thiazide diuretics primarily affect sodium excretion in the urine, but they do not typically cause hypernatremia.
C) This is the correct answer. Thiazide diuretics can cause hypokalemia (low potassium levels) as they increase potassium excretion in the urine.
D) Thiazide diuretics do not cause hypermagnesemia. They do not have a significant effect on magnesium excretion in the urine.
Glomerulonephritis
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Glomerulonephritis primarily affects the glomeruli, not the renal tubules.
B) Incorrect. The renal pelvis is not the primary site of glomerulonephritis; it is a part of the renal collecting system.
C) Correct. Glomerulonephritis is an inflammatory condition that primarily affects the glomeruli, which are tiny structures in the kidneys responsible for filtering blood.
D) Incorrect. The renal medulla is not the primary site of glomerulonephritis; it is deeper within the kidney and not directly involved in this condition.
Explanation
A) Correct. Dark, cola-colored urine is often described as hematuria, which is the presence of blood in the urine, a common symptom of glomerulonephritis.
B) Incorrect. Proteinuria refers to the presence of excessive protein in the urine and may also occur in glomerulonephritis but is not specifically related to dark urine.
C) Incorrect. Oliguria is a condition characterized by decreased urine output and is not directly related to the color of urine in glomerulonephritis.
D) Incorrect. Dysuria refers to painful urination and is not typically associated with dark, cola-colored urine.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hypertension can be a complication of glomerulonephritis, but it is not a cause of poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN).
B) Correct. PSGN is often linked to recent respiratory infections, particularly those caused by streptococcal bacteria.
C) Incorrect. Diabetes mellitus is not a common cause of PSGN.
D) Incorrect. Familial history may be a risk factor for some kidney diseases, but it is not a direct cause of PSGN.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Reabsorption of water and electrolytes primarily occurs in the renal tubules, not the glomeruli.
B) Correct. The primary function of the glomeruli is to filter blood to form urine by removing waste products and excess substances.
C) Incorrect. Hormone secretion, including renin, is not a primary function of the glomeruli but may occur elsewhere in the kidney.
D) Incorrect. While the kidneys play a role in blood pressure regulation, this function involves other structures in addition to the glomeruli.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Renal calculi (kidney stones) are a separate condition and not a common complication of glomerulonephritis.
B) Incorrect. Glomerular hyperfiltration may occur in some kidney diseases but is not a primary complication of glomerulonephritis.
C) Incorrect. Nephrotic syndrome is a different kidney disorder with its own set of symptoms and complications.
D) Correct. Renal artery stenosis, a narrowing of the renal artery supplying the kidney, is a common complication of glomerulonephritis and can lead to hypertension and heart failure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Glomerulonephritis is not primarily characterized by reduced blood flow to the kidneys.
B) Incorrect. Increased GFR is not the primary mechanism involved in the pathophysiology of glomerulonephritis.
C) Correct. Inflammation and damage to the glomerular basement membrane, often triggered by immune responses, are central to the pathophysiology of glomerulonephritis.
D) Incorrect. Excessive reabsorption of sodium is not a primary factor in the development of glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Cell-mediated immunity is not the primary immune response associated with immune complex-mediated glomerulonephritis.
B) Correct. Immune complex-mediated glomerulonephritis typically involves the formation of immune complexes (antigen-antibody complexes) that deposit in the glomeruli and trigger an inflammatory response.
C) Incorrect. Innate immunity is a nonspecific defense mechanism and is not the primary immune response involved in glomerulonephritis.
D) Incorrect. Tolerance induction is a process by which the immune system recognizes self-antigens and does not directly relate to the development of glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Viral respiratory infections are not the most common type of infection associated with PSGN.
B) Incorrect. Bacterial skin infections are not typically linked to the development of PSGN.
C) Incorrect. Staphylococcal infections can lead to various illnesses, but they are not the primary cause of PSGN.
D) Correct. PSGN is most commonly associated with streptococcal infections, particularly group A streptococci.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Nephrotic syndrome is a different kidney disorder characterized by heavy proteinuria and edema but is not characterized by crescent-shaped structures in the glomeruli.
B) Correct. Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN) is characterized by the formation of crescent-shaped structures within the glomeruli and is a complication of glomerulonephritis.
C) Incorrect. Polycystic kidney disease involves the development of cysts within the kidneys and is unrelated to crescent formation in glomerulonephritis.
D) Incorrect. Acute pyelonephritis is a different kidney condition caused by a bacterial infection of the renal pelvis and is not characterized by crescent-shaped structures in the glomeruli.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Carbohydrates are not typically restricted in the diet of clients with glomerulonephritis.
B) Correct. Limiting sodium (salt) intake is important for managing blood pressure and reducing proteinuria in clients with glomerulonephritis.
C) Incorrect. Healthy fats are not the primary dietary component to restrict in the management of glomerulonephritis.
D) Incorrect. Fiber is an important dietary component for overall health but is not specifically related to reducing proteinuria or managing blood pressure in glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hypertension is not a common risk factor for PSGN.
B) Incorrect. Diabetes mellitus is not typically associated with an increased risk of PSGN.
C) Correct. Recent upper respiratory infections, especially those caused by streptococcal bacteria, are a common risk factor for PSGN.
D) Incorrect. While a familial history of kidney disease may be a risk factor for some kidney conditions, it is not a primary risk factor for PSGN.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Heavy alcohol consumption is not a common predisposing factor for APSGN.
B) Incorrect. Exposure to lead is unrelated to the development of APSGN.
C) Correct. APSGN is most commonly associated with streptococcal infections, particularly strep throat.
D) Incorrect. High dietary intake of calcium is not a common predisposing factor for APSGN.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Allergic rhinitis is not commonly linked to the development of RPGN.
B) Correct. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune condition that can lead to RPGN.
C) Incorrect. Type 2 diabetes is not commonly associated with RPGN.
D) Incorrect. Osteoarthritis is unrelated to RPGN.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Regular exercise is typically beneficial for overall health and does not increase the risk of chronic glomerulonephritis.
B) Correct. Smoking tobacco is a lifestyle factor associated with an increased risk of chronic glomerulonephritis.
C) Incorrect. A vegetarian diet is not commonly linked to an increased risk of chronic glomerulonephritis.
D) Incorrect. Adequate fluid intake is generally recommended for kidney health and does not increase the risk of chronic glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Recent gastrointestinal infection is not commonly associated with membranous glomerulonephritis.
B) Correct. Membranous glomerulonephritis is often linked to autoimmune disorders, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the glomerular basement membrane.
C) Incorrect. Exposure to heavy metals is unrelated to the development of membranous glomerulonephritis.
D) Incorrect. Elevated blood cholesterol levels may have cardiovascular implications but are not typically a predisposing factor for membranous glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hematuria (blood in the urine) is a common symptom but is not typically an early indicator of glomerulonephritis.
B) Incorrect. Proteinuria (excess protein in the urine) is a common symptom but is not typically an early indicator of glomerulonephritis.
C) Incorrect. Oliguria (decreased urine output) may occur in more advanced stages of glomerulonephritis but is not typically an early symptom.
D) Correct. Periorbital edema (swelling around the eyes) and edema in the lower extremities are often early indicators of glomerulonephritis due to fluid retention.
Explanation
A) Correct. In glomerulonephritis, renal damage can lead to increased renin production, which in turn raises blood pressure.
B) Incorrect. Glomerulonephritis may affect GFR, but decreased GFR alone is not the primary cause of hypertension in this condition.
C) Incorrect. Elevated blood glucose levels are associated with diabetes mellitus but are not the primary cause of hypertension in glomerulonephritis.
D) Incorrect. Hypercalcemia (high blood calcium levels) is not a common cause of hypertension in glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Correct. "Cola-colored" urine is often indicative of hematuria, which is the presence of blood in the urine, a common symptom of glomerulonephritis.
B) Incorrect. Dysuria refers to painful urination and is not specifically related to the color of urine in glomerulonephritis.
C) Incorrect. Oliguria refers to decreased urine output and is not related to the color of urine.
D) Incorrect. Proteinuria refers to the presence of excess protein in the urine and is not specifically related to the color of urine in glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While electrolyte imbalances can occur in glomerulonephritis, they are not typically associated with symptoms of fatigue, weakness, and pallor.
B) Correct. Anemia, often caused by a decrease in erythropoietin production due to kidney dysfunction, is a common cause of fatigue, weakness, and pallor in clients with glomerulonephritis.
C) Incorrect. Hyperglycemia (high blood glucose levels) is not typically associated with these symptoms in glomerulonephritis.
D) Incorrect. Excessive fluid intake is not a likely cause of fatigue, weakness, and pallor in glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine, not decreased urine output.
B) Incorrect. Proteinuria refers to the presence of excess protein in the urine, not decreased urine output.
C) Correct. Oliguria is a medical term that describes a decreased urine output, which can occur in glomerulonephritis.
D) Incorrect. Edema refers to swelling due to fluid retention and is not related to decreased urine output.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Elevated serum creatinine is indicative of impaired kidney function but does not directly reflect the presence of red blood cells in the urine.
B) Incorrect. Hyperkalemia is an electrolyte imbalance that can occur in kidney disease but does not directly indicate hematuria.
C) Correct. Hematuria, the presence of red blood cells in the urine, is a common diagnostic finding in glomerulonephritis.
D) Incorrect. Hyponatremia is an electrolyte imbalance and is not a direct indicator of hematuria in glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. MRI is not typically used as the first-line imaging study for evaluating kidney size and structure in glomerulonephritis.
B) Incorrect. CT scans involve radiation exposure and are usually reserved for specific indications in kidney evaluation.
C) Correct. Ultrasonography (ultrasound) is a non-invasive imaging technique commonly used to assess kidney size and detect structural abnormalities in glomerulonephritis.
D) Incorrect. PET scans are not typically used for kidney imaging in the context of glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Kidney biopsies are not primarily performed to assess electrolyte imbalances.
B) Incorrect. Identifying urinary tract infections can be done through other diagnostic methods, such as urinalysis and urine culture, and is not the primary purpose of a kidney biopsy.
C) Incorrect. While a kidney biopsy provides information about kidney function, its primary purpose in glomerulonephritis is to determine the underlying cause and assess the severity of kidney damage.
D) Correct. Kidney biopsies are essential for diagnosing glomerulonephritis because they help identify the specific type of glomerulonephritis, its cause, and the extent of renal damage.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine, not excessive protein.
B) Incorrect. Pyuria indicates the presence of white blood cells in the urine, which is not typically associated with glomerulonephritis.
C) Incorrect. Oliguria refers to decreased urine output, not excessive protein in the urine.
D) Correct. Proteinuria, the presence of excessive protein in the urine, is a common abnormality associated with glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. A complete blood count (CBC) provides information about red and white blood cell counts and is not primarily used to assess kidney function or GFR.
B) Incorrect. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) is a blood test that can be influenced by factors other than kidney function and is not a direct measure of GFR.
C) Correct. Serum creatinine is a commonly used blood test to assess kidney function and estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
D) Incorrect. C-reactive protein (CRP) is a marker of inflammation and is not typically used to assess kidney function or GFR in glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. A high-sodium diet can exacerbate hypertension and fluid retention, which are common issues in glomerulonephritis.
B) Incorrect. Protein restriction is not typically necessary unless there is severe kidney dysfunction. Some protein intake is needed for overall health.
C) Incorrect. Increased fluid intake may be restricted in cases of oliguria or fluid overload. It should be individualized based on the client's condition.
D) Correct. A low-sodium diet helps manage hypertension and reduces edema, which are common complications of glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Anticoagulants are not typically prescribed to control blood pressure in glomerulonephritis; they are used to prevent blood clot formation.
B) Correct. Diuretics, specifically thiazide diuretics, are often prescribed to manage hypertension and reduce fluid retention in glomerulonephritis.
C) Incorrect. Antibiotics are prescribed to treat underlying infections but may not directly control blood pressure.
D) Incorrect. Antacids are used to relieve symptoms of gastrointestinal conditions and do not play a primary role in managing blood pressure in glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Limiting fluid intake may be necessary in certain cases but is not typically a non-pharmacological intervention to reduce edema in glomerulonephritis.
B) Correct. Elevating the legs can help reduce edema by promoting venous return and decreasing fluid accumulation in the lower extremities.
C) Incorrect. Increasing sodium intake is not advisable as it can exacerbate edema and hypertension.
D) Incorrect. Avoiding protein-rich foods is not a non-pharmacological intervention for reducing edema in glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. ACE inhibitors do not enhance sodium reabsorption; they actually decrease sodium reabsorption in the kidneys.
B) Correct. ACE inhibitors are commonly prescribed to reduce proteinuria (excessive protein in the urine), which is a common symptom of glomerulonephritis.
C) Incorrect. ACE inhibitors do not promote potassium excretion; they can lead to hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) in some cases.
D) Incorrect. While ACE inhibitors can affect aldosterone levels, their primary role in glomerulonephritis is to reduce proteinuria and manage blood pressure.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Frequent monitoring of blood glucose levels is important for individuals with diabetes but is not a primary focus of follow-up care for glomerulonephritis.
B) Incorrect. Regular assessment of lung function is not a primary aspect of follow-up care for glomerulonephritis.
C) Correct. Routine kidney function tests and blood pressure checks are essential for monitoring the long-term health of the kidneys and managing hypertension, which are common concerns in glomerulonephritis.
D) Incorrect. Monthly dental check-ups are important for oral health but are not specifically related to glomerulonephritis follow-up care.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Increasing sodium intake can exacerbate hypertension and fluid retention, which are common in glomerulonephritis.
B) Incorrect. Limiting fluid intake may be necessary in specific cases but is not the primary dietary recommendation for managing glomerulonephritis.
C) Incorrect. Protein restriction is typically not necessary unless there is severe kidney dysfunction. Some protein intake is needed for overall health.
D) Correct. A low-sodium diet helps manage hypertension and reduces edema, common complications of glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. ACE inhibitors do not promote potassium excretion; they can lead to hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) in some cases.
B) Incorrect. ACE inhibitors are typically taken with food to minimize the risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
C) Incorrect. ACE inhibitors do not cause hypoglycemia; they are not directly related to blood sugar regulation.
D) Correct. ACE inhibitors are commonly prescribed in glomerulonephritis to reduce proteinuria and manage hypertension, helping to protect kidney function.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Avoiding all physical activity is not necessary to prevent recurrent episodes of glomerulonephritis.
B) Incorrect. While adequate protein intake is important, a high-protein diet is not specifically recommended to prevent recurrent episodes of glomerulonephritis.
C) Correct. Completing a course of prescribed antibiotics is crucial to treat underlying infections that may contribute to glomerulonephritis and prevent recurrence.
D) Incorrect. Limiting fluid intake should be individualized and is not a universal measure to prevent recurrent episodes of glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Correct. Elevating the legs can help reduce edema by promoting venous return and decreasing fluid accumulation in the lower extremities.
B) Incorrect. Increasing sodium intake is not advisable as it can exacerbate edema and hypertension.
C) Incorrect. Severely limiting daily fluid intake is not recommended without medical guidance and can lead to dehydration.
D) Incorrect. Avoiding all movement is not necessary and may not effectively reduce fluid accumulation in edematous areas.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Monitoring blood glucose levels and diabetes management may be relevant for clients with diabetes but is not the primary goal of follow-up visits for glomerulonephritis.
B) Incorrect. Assessing lung function and providing pulmonary care are not the primary focus of follow-up visits for glomerulonephritis.
C) Incorrect. Routine dental check-ups are important for oral health but are not the primary purpose of follow-up visits for glomerulonephritis.
D) Correct. The primary goal of follow-up visits for glomerulonephritis is to monitor kidney function, blood pressure, and overall health to ensure the client's well-being and the effectiveness of treatment.
Hematuria
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hematuria specifically involves the presence of blood in the urine.
B) Correct. Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine and can indicate various medical conditions.
C) Incorrect. Hematuria is not solely a type of kidney infection, and it is not primarily characterized by frequent urination.
D) Incorrect. While certain medications or supplements can affect urine color, hematuria is defined by the presence of blood in the urine and is not related to vitamins or dietary supplements.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Microscopic hematuria is not visible to the naked eye; it requires a microscope for detection.
B) Correct. Microscopic hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine that is not visible to the naked eye but can be detected under a microscope.
C) Incorrect. Microscopic hematuria is defined by the presence of blood in the urine and is not primarily characterized by severe pain during urination.
D) Incorrect. Microscopic hematuria is not a type of urinary tract infection; it is a finding indicating the presence of blood in the urine.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While hematuria can be a sign of underlying medical conditions, it is not always indicative of a serious condition.
B) Correct. Hematuria can have various causes, including infections, kidney stones, bladder cancer, and other factors.
C) Incorrect. Psychological stress and anxiety are not primary causes of hematuria.
D) Incorrect. Hematuria can result from multiple factors, not solely trauma to the urinary tract.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hematuria may not necessarily resolve on its own, and its consequences can vary depending on the underlying cause.
B) Correct. Untreated hematuria, especially when caused by conditions like kidney disease or bladder cancer, can lead to kidney damage and permanent loss of kidney function.
C) Incorrect. Hematuria should not be dismissed as causing only temporary discomfort, as it can be a sign of serious underlying conditions.
D) Incorrect. Hematuria can have various causes and consequences beyond urinary tract infections.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hematuria does not always involve pain or discomfort during urination.
B) Correct. Hematuria can be painless, but it can also present with symptoms such as urinary urgency,
abdominal pain, or back pain.
C) Incorrect. Excessive thirst and frequent urination are not the primary symptoms of hematuria.
D) Incorrect. Fever and chills are not typically associated with hematuria itself but may be related to an underlying infection if present.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Excessive blood clotting is not a common underlying mechanism of hematuria.
B) Correct. Inflammation and damage to blood vessels in the urinary tract or kidneys can lead to the leakage of blood into the urine, causing hematuria.
C) Incorrect. While bacterial infections can cause hematuria, they are not the primary underlying mechanism.
D) Incorrect. Kidney stones can cause hematuria, but they are not the primary cause of hematuria itself.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Kidney stones can cause hematuria, but this statement does not address UTIs.
B) Correct. UTIs can lead to irritation and inflammation of the urinary tract, which can result in hematuria.
C) Incorrect. UTIs typically do not involve bacteria directly entering the bloodstream and causing bleeding in the kidneys.
D) Incorrect. UTIs do not trigger excessive production of blood cells as a primary mechanism for hematuria.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Glomerulonephritis is not primarily caused by blockage of the urinary tract.
B) Correct. Glomerulonephritis involves inflammation of the glomeruli in the kidneys, leading to the leakage of blood and protein into the urine.
C) Incorrect. Excessive alcohol consumption is not a primary cause of glomerulonephritis.
D) Incorrect. Kidney stones are not the primary mechanism of glomerulonephritis.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Excessive blood clotting is not a primary mechanism of trauma-related hematuria.
B) Correct. Physical trauma can damage blood vessels in the urinary tract, leading to bleeding and hematuria.
C) Incorrect. Infection is not the primary cause of hematuria related to trauma.
D) Incorrect. Trauma-related hematuria is not primarily the result of an autoimmune response.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Kidney stones primarily affect the urinary tract upstream of the bladder and do not directly damage the bladder lining.
B) Incorrect. Kidney stones themselves do not create a favorable environment for bacterial infections.
C) Incorrect. While kidney stones can cause blockages in the urinary tract, this statement does not explain the primary mechanism of hematuria.
D) Correct. Passing kidney stones through the urinary tract can cause mechanical trauma to the urinary structures, leading to hematuria.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While infections can cause hematuria, it is not typically related to bacterial infections in the bladder.
B) Correct. Kidney stones are a common cause of hematuria.
C) Incorrect. Viral infections are not a primary cause of hematuria.
D) Incorrect. Excessive caffeine consumption is not a leading cause of hematuria.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Age can be a risk factor for hematuria, especially in older individuals.
B) Correct. Men are at a higher risk of developing hematuria compared to women.
C) Incorrect. A family history of kidney disease can be a risk factor for hematuria.
D) Incorrect. Smoking is associated with an increased risk of hematuria and kidney problems.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Excessive alcohol consumption is not a primary cause of hematuria.
B) Correct. UTIs are a common cause of hematuria.
C) Incorrect. While physical trauma can cause hematuria, it is not the main cause.
D) Incorrect. Spicy food consumption is not typically linked to hematuria.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. A diet high in fruits and vegetables is generally considered healthy and is not a common risk factor for hematuria.
B) Incorrect. Regular physical exercise is not a common risk factor for hematuria.
C) Correct. A history of kidney stones is a common risk factor for hematuria.
D) Incorrect. While maintaining a healthy body weight is important for overall health, it is not a primary risk factor for hematuria.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Emotional stress can exacerbate some health conditions, but it is not a primary cause of hematuria.
B) Correct. Excessive caffeine consumption can contribute to hematuria.
C) Incorrect. A lack of exercise is not a common cause of hematuria.
D) Incorrect. Genetic factors can play a role in the development of some kidney conditions that may lead to hematuria.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While blood tests may be conducted as part of the evaluation, they are not typically the initial step.
B) Incorrect. A physical examination may be performed, but it is not the initial diagnostic step for hematuria.
C) Correct. A urinalysis is the initial step in assessing hematuria, as it helps determine the source and characteristics of the blood in the urine.
D) Incorrect. A renal biopsy is an invasive procedure and is not typically the initial diagnostic step for hematuria.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While CT scans can detect kidney stones, the primary purpose of contrast is not to visualize stones.
B) Correct. Contrast is used to highlight blood vessels and enhance the visualization of the urinary tract.
C) Incorrect. Contrast is not primarily administered to minimize radiation exposure but rather to improve imaging quality.
D) Incorrect. Contrast enhances the visualization of blood vessels and structures in the urinary tract, not specifically the bladder lining.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. After cystoscopy, clients may need a short period of rest and recovery before resuming normal activities.
B) Incorrect. It is important to maintain hydration after cystoscopy; avoiding fluids is not recommended.
C) Correct. Temporary discomfort and mild bleeding are common after cystoscopy and should be expected.
D) Incorrect. The use of harsh soaps for perineal care can irritate the urinary tract and is not recommended.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Fasting is typically not required before a renal ultrasound.
B) Incorrect. Unlike some imaging modalities, renal ultrasound does not use radiation.
C) Incorrect. While drinking water may be necessary for other types of imaging studies, it is not a standard requirement for a renal ultrasound.
D) Correct. Renal ultrasound is a non-invasive procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the kidneys and surrounding structures.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Cystography primarily assesses the bladder and urinary tract, not kidney function.
B) Incorrect. Cystography is not used to evaluate blood clotting disorders.
C) Correct. Cystography is a diagnostic procedure that visualizes the bladder and urinary tract to assess for abnormalities.
D) Incorrect. Cystography typically does not involve the administration of radioactive substances for imaging.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Increasing dietary salt intake is not a recommended intervention for managing kidney stones; it can worsen the condition.
B) Incorrect. Drinking cranberry juice is not a specific treatment for kidney stones or hematuria associated with them.
C) Correct. Maintaining hydration and allowing the stone to pass naturally is a common approach to managing kidney stones and associated hematuria.
D) Incorrect. Pain medications may be needed for pain relief, but antibiotics are not typically indicated for kidney stones.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Cystoscopy is not a surgical procedure that requires hospitalization; it is typically done on an outpatient basis.
B) Correct. Having an empty bladder before the procedure allows for better visualization during cystoscopy.
C) Incorrect. Cystoscopy is a diagnostic procedure used to visualize the bladder and urinary tract but does not involve the removal of kidney stones.
D) Incorrect. Cystoscopy is usually performed with local anesthesia or sedation but not general anesthesia.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Antifungal antibiotics are used to treat fungal infections and are not typically prescribed for UTIs.
B) Correct. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed for UTIs when the specific bacteria causing the infection are not known, and they can help resolve hematuria associated with the infection.
C) Incorrect. Antiviral antibiotics are used to treat viral infections, not bacterial UTIs.
D) Incorrect. Narrow-spectrum antibiotics target specific types of bacteria and may not be as effective in treating a wide range of UTI-causing bacteria.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Administering diuretics may not be appropriate and can exacerbate dehydration in a client with hematuria.
B) Incorrect. Strenuous physical activity can increase the risk of bleeding and should be avoided in clients with hematuria and bleeding disorders.
C) Correct. Monitoring vital signs and assessing for signs of bleeding or hemorrhage is essential to ensure prompt intervention if excessive bleeding occurs.
D) Incorrect. Restricting fluid intake is not typically recommended unless there are specific medical indications. In many cases, adequate hydration is important.
Explanation
A) Correct. Maintaining good hydration and practicing good perineal hygiene are effective strategies to prevent future UTIs and hematuria.
B) Incorrect. Increasing alcohol consumption is not a recommended strategy for preventing UTIs and can have negative health effects.
C) Incorrect. Avoiding all sexual activity is not necessary to prevent UTIs, but practicing safe sex and good hygiene are important.
D) Incorrect. Using harsh, scented soaps and bath products can irritate the urinary tract and should be avoided for perineal care.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hematuria can have various causes, and it is not always related to kidney stones.
B) Correct. Hematuria can be caused by UTIs, kidney injury, bladder infections, and other medical conditions.
C) Incorrect. While caffeine consumption may irritate the urinary tract, it is not a primary cause of hematuria.
D) Incorrect. Dehydration may contribute to certain urinary issues, but it is not the primary cause of hematuria.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Administering pain medications may be necessary for pain relief but does not address the underlying cause of hematuria.
B) Incorrect. A high-protein diet is not a primary intervention for managing hematuria.
C) Correct. Monitoring vital signs and assessing for signs of shock is essential, especially if the hematuria is severe, to ensure the client's stability.
D) Incorrect. Restricting fluid intake is not typically recommended unless there are specific medical indications. In many cases, adequate hydration is important.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hematuria can be related to kidney disorders and is not solely caused by bladder infections.
B) Correct. Hematuria can signal various kidney conditions, and additional evaluation is necessary to determine the underlying cause.
C) Incorrect. Hematuria does not necessarily indicate kidney failure, but it should be investigated further to determine the cause.
D) Incorrect. Hematuria is not typically considered a normal occurrence and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Maintaining a low-protein diet is not typically recommended to prevent UTIs.
B) Correct. Completing the prescribed antibiotics and attending follow-up appointments are crucial to ensure the UTI is fully treated and to monitor for any complications, including recurrent hematuria.
C) Incorrect. Increasing caffeine intake is not a primary recommendation for improving urinary health.
D) Incorrect. Restricting fluid intake is not typically advised as it may lead to dehydration and does not prevent UTIs.
Explanation
A) Correct. Excessive caffeine consumption can irritate the bladder and lead to hematuria, even without kidney or urinary tract disorders.
B) Incorrect. Kidney stones are related to kidney and urinary tract disorders and can cause hematuria.
C) Incorrect. UTIs are infections of the urinary tract and can lead to hematuria.
D) Incorrect. Bladder cancer is a condition of the urinary tract and can cause hematuria.
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
A nurse is providing education about Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus to a client. Which statement by the nurse accurately describes this condition?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is not related to insulin deficiency; it is a disorder of the kidneys' ability to concentrate urine.
B) Correct. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is characterized by the kidneys' inability to properly concentrate urine, leading to excessive thirst and the production of large volumes of dilute urine.
C) Incorrect. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is not managed with insulin injections. It is managed through other approaches, such as fluid restriction and medication.
D) Incorrect. Dietary adjustments are not the main treatment for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. The focus is on managing fluid intake and using medications to help the kidneys concentrate urine.
A client diagnosed with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus asks the nurse about the cause of this condition. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Correct. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is primarily caused by a deficiency or insensitivity to antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also known as vasopressin.
B) Incorrect. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is not related to insulin overproduction; it is a disorder of the kidneys' response to ADH.
C) Incorrect. Excessive consumption of high-sugar foods and drinks does not directly cause Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
D) Incorrect. While Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus can be hereditary in some cases, it is not the primary cause of the condition.
A nurse is assessing a client with suspected Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. Which clinical manifestation is commonly associated with this condition?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hypertension is not typically associated with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. It may occur due to other underlying conditions.
B) Incorrect. Hyponatremia (low sodium levels) is not a primary characteristic of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. In fact, it can lead to hypernatremia (high sodium levels) due to excessive loss of water.
C) Correct. The hallmark clinical manifestations of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus are polyuria (excessive urination) and polydipsia (excessive thirst) due to the kidneys' inability to concentrate urine.
D) Incorrect. Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) is not directly associated with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. This condition primarily affects water balance.
A client with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus asks the nurse about dietary recommendations. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Limiting sodium intake is not the primary dietary concern for clients with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. The main focus is on managing fluid intake.
B) Incorrect. While potassium is important for overall health, increasing potassium intake is not the primary dietary recommendation for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
C) Correct. Maintaining a balanced diet is important, but clients with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus should be cautious about excessive fluid intake to prevent dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
D) Incorrect. A high-protein diet is not specifically indicated for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. The primary focus is on fluid management.
A nurse is explaining the treatment options for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus to a client. What intervention is commonly used in managing this condition?
Explanation
A) Correct. The primary treatment for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is the administration of synthetic ADH (desmopressin) to help the kidneys concentrate urine.
B) Incorrect. IV administration of insulin is not a standard treatment for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
C) Incorrect. High-dose diuretic therapy would exacerbate the symptoms of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, as it would increase urine production.
D) Incorrect. Strict restriction of dietary carbohydrates is not a primary intervention for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. The focus is on fluid management through the use of medications like desmopressin.
A nurse is educating a client about the risk factors associated with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. Which factor should the nurse include in the discussion?
Explanation
A) Correct. Genetic predisposition is a significant risk factor for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. It can be inherited or acquired due to genetic mutations.
B) Incorrect. Diet, specifically high-carbohydrate intake, is not a recognized risk factor for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
C) Incorrect. Sedentary lifestyle is not a known risk factor for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. This condition is primarily related to kidney function.
D) Incorrect. Excessive caffeine intake is not identified as a risk factor for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
A client recently diagnosed with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus asks the nurse about other conditions that may increase the risk. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hypertension is not a direct risk factor for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. However, it can be associated with various kidney disorders.
B) Incorrect. While heart disease can have implications for kidney function, it is not a specific risk factor for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
C) Correct. Chronic kidney disease is a condition that can be associated with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, as it involves impaired kidney function.
D) Incorrect. A high-fiber diet is not considered a risk factor for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
A nurse is reviewing the medical history of a client with suspected Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. Which condition should the nurse recognize as a potential risk factor?
Explanation
A) Correct. Polycystic kidney disease is a known risk factor for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, as it can lead to impaired kidney function.
B) Incorrect. Asthma is not a recognized risk factor for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
C) Incorrect. Osteoarthritis is not associated with an increased risk of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
D) Incorrect. Migraine headaches are not identified as a risk factor for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
A client diagnosed with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is curious about lifestyle factors that may have contributed. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While exercise and a balanced diet are important for overall health, they are not specific preventive measures for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
B) Correct. Limiting exposure to environmental toxins, which can potentially harm kidney function, can help decrease the risk of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
C) Incorrect. Avoiding stress and maintaining a positive outlook are important for well-being but are not direct factors in preventing Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
D) Incorrect. Engaging in social activities and hobbies is beneficial for mental health, but it is not a specific preventive measure for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
.
A nurse is providing education to a group of individuals about Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. What congenital condition should the nurse highlight as a risk factor?
Explanation
A) Correct. Down syndrome is a congenital condition that can be associated with an increased risk of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
B) Incorrect. Hypertension is not a congenital condition and is not directly associated with an increased risk of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
C) Incorrect. Type 2 diabetes is not a congenital condition and is not directly associated with an increased risk of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
D) Incorrect. Rheumatoid arthritis is not a congenital condition and is not directly associated with an increased risk of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
These cover various risk factors associated with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. If you have any further , feel free to let me know!
A nurse is explaining the pathophysiology of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus to a group of nursing students. What is the primary defect in this condition?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is not primarily caused by inadequate production of ADH; rather, it is related to the kidneys' inability to respond effectively to ADH.
B) Correct. The primary defect in Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is the impaired response of the renal tubules to ADH. This means that even if ADH is present, the kidneys are unable to reabsorb water as they should.
C) Incorrect. Excessive release of ADH is not characteristic of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. Instead, it is a condition where the kidneys do not respond appropriately to normal levels of ADH.
D) Incorrect. Dysfunction of the adrenal glands is not related to the pathophysiology of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
A client newly diagnosed with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus asks the nurse why they experience excessive thirst and urination. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is characterized by the kidneys' reduced response to ADH, not an excess of ADH production.
B) Correct. In Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, the kidneys do not respond effectively to ADH, which impairs their ability to reabsorb water. This leads to excessive urination and thirst.
C) Incorrect. Elevated blood glucose levels are not associated with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
D) Incorrect. Experiencing excessive thirst and urination in Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is not a normal response to changes in fluid balance; it is a result of the kidneys' reduced ability to reabsorb water.
A nurse is teaching a client with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus about their condition. What part of the nephron is primarily affected in this condition?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. The glomerulus is primarily responsible for the initial filtration of blood in the nephron, but it is not the part primarily affected in Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
B) Incorrect. The renal tubules play a crucial role in reabsorbing water and electrolytes, but in Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, it is primarily the collecting ducts that are affected.
C) Correct. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus primarily affects the collecting ducts, where the final adjustments to urine composition occur.
D) Incorrect. Bowman's capsule is involved in the initial filtration of blood, but it is not the primary site of dysfunction in Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
A client asks the nurse why they have to drink so much water when they have Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. What is the best explanation by the nurse?
Explanation
A) Correct. In Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, the kidneys produce excessive amounts of dilute urine, leading to fluid loss. Drinking more water helps
replenish the lost fluids.
B) Incorrect. Drinking more water does not directly stimulate the production of antidiuretic hormone in Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, as the primary issue lies in the kidneys' response to ADH.
C) Incorrect. While excessive thirst is a symptom of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, the main reason for increased water intake is to compensate for the excessive urine production.
D) Incorrect. Diluting urine to prevent kidney stones is not the primary reason for increased water intake in Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
A nurse is discussing the genetic forms of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. Which of the following is an X-linked recessive form of the condition?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Autosomal dominant Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, not as an X-linked recessive trait.
B) Incorrect. Autosomal recessive Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, not as an X-linked recessive trait.
C) Incorrect. X-linked dominant inheritance is not associated with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. This condition can be caused by mutations in the AVPR2 gene (X-linked recessive) or the AQP2 gene (autosomal recessive).
D) Correct. X-linked recessive Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is caused by mutations in the AVPR2 gene located on the X chromosome. It primarily affects males who inherit the mutated gene from their carrier mothers.
A client with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus asks the nurse about a common symptom they are experiencing. What should the nurse identify as a hallmark symptom of this condition?
Explanation
A) Correct. Increased thirst (polydipsia) and urination (polyuria) are hallmark symptoms of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. The kidneys are unable to concentrate urine, leading to excessive fluid loss.
B) Incorrect. Excessive hunger and weight loss are not typical symptoms of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. This condition primarily affects fluid balance, not metabolism.
C) Incorrect. While fatigue and weakness can occur in various conditions, they are not specific to Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
D) Incorrect. Blurred vision and headaches are not typically associated with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. These symptoms may be indicative of other conditions.
A nurse is assessing a client suspected of having Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. Which of the following findings would be consistent with this condition?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Elevated blood glucose levels are not a characteristic finding in Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. This condition primarily affects water balance, not glucose metabolism.
B) Correct. In Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, the kidneys are unable to concentrate urine, leading to the production of large volumes of dilute urine with a low specific gravity.
C) Incorrect. Hypertension and bradycardia are not typically associated with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. These findings may be indicative of other underlying conditions.
D) Incorrect. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is characterized by a reduced response of the renal tubules to antidiuretic hormone (ADH), leading to the inability to reabsorb water effectively.
A client diagnosed with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus complains of constant thirst and excessive urination. They ask the nurse why they always feel dehydrated. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is characterized by a reduced response of the renal tubules to antidiuretic hormone (ADH), leading to excessive urination and increased thirst.
B) Correct. In Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, the kidneys are unable to reabsorb water effectively, leading to excessive urination and dehydration.
C) Incorrect. While managing fluid balance is important in Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, the primary cause of dehydration in this condition is the excessive loss of water through urination.
D) Incorrect. Elevated blood sugar levels are not associated with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. This statement may be more applicable to diabetes mellitus.
A nurse is educating a client with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus about dietary considerations. What should the nurse recommend to help manage this condition?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While managing salt intake is important for overall health, it is not a primary consideration for managing Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. The focus is on fluid balance.
B) Incorrect. Increasing protein intake is not a specific dietary recommendation for managing Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
C) Correct. Monitoring fluid intake and avoiding excessive sodium can help manage fluid balance in individuals with Nephrogenic Diabetes Ins
ipidus.
D) Incorrect. While potassium is an important electrolyte, a high-potassium diet is not a specific recommendation for managing Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
A client with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus asks the nurse about potential complications. What is an important complication to monitor for in this client?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While hypertension can be a complication of certain kidney conditions, it is not a direct complication of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
B) Incorrect. Hyperkalemia (elevated blood potassium levels) is not a typical complication of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
C) Correct. Dehydration is a significant complication of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus due to the excessive loss of water through urination.
D) Incorrect. Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar levels) is not a characteristic complication of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. This condition primarily affects water balance, not glucose metabolism.
A client with suspected Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus asks the nurse about the diagnostic tests they may undergo. What test measures the concentration of urine to assess the kidney's ability to reabsorb water?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. A blood glucose test measures the concentration of glucose in the blood and is not specific to diagnosing Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
B) Correct. The urine osmolality test assesses the concentration of solutes in the urine, providing information about the kidney's ability to reabsorb water. In Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, urine osmolality remains low even when a person is dehydrated.
C) Incorrect. An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test used to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart and is not specific to diagnosing Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
D) Incorrect. A complete blood count (CBC) measures various components of the blood, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It is not specific to diagnosing Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
A nurse is explaining the water deprivation test to a client suspected of having Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. What is the primary purpose of this test?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. The water deprivation test is not primarily used to evaluate blood glucose levels. Its focus is on assessing kidney function and fluid balance.
B) Correct. The water deprivation test involves withholding fluids from the client while monitoring various parameters, including urine osmolality, weight changes, and blood chemistry. This test helps determine if the kidneys are able to concentrate urine appropriately.
C) Incorrect. While electrolyte levels may be monitored during the water deprivation test, the primary purpose is to assess kidney function and fluid balance.
D) Incorrect. Monitoring cardiac output and blood pressure is not the primary goal of the water deprivation test. It is specifically designed to evaluate kidney function.
A client asks the nurse about the potential risks or discomfort associated with the water deprivation test. What should the nurse inform the client?
Explanation
A) Correct. One of the potential risks associated with the water deprivation test is the development of low blood sodium levels (hyponatremia) due to dehydration.
B) Incorrect. Elevated blood pressure is not a typical response to the water deprivation test. In fact, blood pressure is usually closely monitored during the test.
C) Incorrect. The water deprivation test does not involve the use of contrast dye, so the risk of an allergic reaction is not applicable.
D) Incorrect. While the client may feel lightheaded or dizzy due to dehydration, close monitoring is an essential part of the test to ensure the client's safety.
A nurse is reviewing the results of a water deprivation test for a client suspected of having Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. Which finding would be consistent with this condition?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. In Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, the kidneys are unable to concentrate urine even when a person is dehydrated. Therefore, urine osmolality does not increase significantly.
B) Incorrect. Decreased urine output is not a characteristic finding in Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. Instead, individuals with this condition may have increased urine output even when dehydrated.
C) Correct. In Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, urine osmolality remains low even after a period of dehydration, indicating the kidneys' inability to reabsorb water effectively.
D) Incorrect. Elevated blood sodium levels (hypernatremia) may occur as a result of dehydration during the
water deprivation test, but this finding is not specific to Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
A client with suspected Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus asks the nurse about potential complications. What is an important complication to monitor for in this client?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While hypertension can be a complication of certain kidney conditions, it is not a direct complication of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
B) Incorrect. Hyperkalemia (elevated blood potassium levels) is not a typical complication of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
C) Correct. Dehydration is a significant complication of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus due to the excessive loss of water through urination.
D) Incorrect. Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar levels) is not a characteristic complication of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. This condition primarily affects water balance, not glucose metabolism.
A nurse is providing education to a client with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. What dietary recommendation should the nurse include to help manage this condition?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Increasing sodium intake is not a primary dietary recommendation for managing Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. It may exacerbate the condition by increasing thirst and fluid intake.
B) Correct. Limiting fluid intake is a crucial aspect of managing Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. By restricting fluid intake, the client can help reduce excessive urination and maintain better fluid balance.
C) Incorrect. While potassium is an important electrolyte, it is not specifically emphasized in the management of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
D) Incorrect. Avoiding foods high in calcium is not a specific dietary recommendation for managing Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. Calcium intake is important for bone health and other physiological functions.
A client with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus asks the nurse about medications to manage the condition. What class of medications is commonly used to treat Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus?
Explanation
A) Correct. Thiazide diuretics are commonly used to treat Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. They help the kidneys reabsorb more water, reducing excessive urination.
B) Incorrect. Beta-blockers are not used as a primary treatment for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. They are primarily indicated for conditions such as hypertension.
C) Incorrect. Anticoagulants are used to prevent blood clotting and are not directly related to the management of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
D) Incorrect. NSAIDs may have some effects on kidney function, but they are not the primary class of medications used to manage Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
A nurse is discussing lifestyle modifications with a client diagnosed with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. What recommendation should the nurse provide regarding outdoor activities?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While it's important to be mindful of hydration, avoiding outdoor activities entirely is not necessary. Proper fluid management and timing of activities can help.
B) Correct. Engaging in outdoor activities during cooler times of the day can help reduce the risk of excessive fluid loss through sweating. This allows the client to enjoy outdoor activities while minimizing the impact on fluid balance.
C) Incorrect. Engaging in vigorous outdoor activities does not directly stimulate kidney function in the context of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
D) Incorrect. While it's important to be mindful of hydration, limiting outdoor activities to short durations is not the only option. Timing activities and managing fluid intake can be effective strategies.
A client with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is prescribed thiazide diuretics. What important instruction should the client receive regarding medication administration?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Thiazide diuretics should be taken with food to reduce the risk of stomach upset. Taking them on an empty stomach is not recommended.
B) Incorrect. Taking the medication with a high-sodium meal is not necessary for its effectiveness. In fact, it's important to monitor sodium levels while taking thiazide diuretics.
C) Correct. Thiazide diuretics can lead to low potassium levels (hypokalemia) as they increase potassium excretion in the urine. Clients should be instructed to monitor for signs of hypokalemia, such as muscle weakness or irregular heart rhythm.
D) Incorrect. Discontinuing the medication if urine output decreases significantly is not the appropriate action. The client should follow the prescribed treatment plan and report any concerns to their healthcare provider.
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Monitoring blood glucose levels is not a primary concern for clients with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, as this condition primarily affects water balance, not glucose metabolism.
B) Incorrect. While regular weighing may be part of the overall healthcare routine, it is not as specific or crucial for managing Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus as keeping track of fluid intake and output.
C) Correct. Keeping a record of daily fluid intake and output is important for monitoring and managing Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. This information helps in assessing the effectiveness of interventions and maintaining fluid balance.
D) Incorrect. Engaging in high-intensity exercise daily is not a specific self-care strategy recommended for managing Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. The focus is on fluid management and medication adherence.
A nurse is providing education to a client with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus about managing fluid intake. What advice should the nurse give to the client?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Increasing fluid intake is not recommended for clients with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus as it can exacerbate the condition and lead to excessive urination.
B) Correct. Restricting fluid intake is a key nursing intervention for managing Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. This helps to reduce the volume of urine output and maintain better fluid balance.
C) Incorrect. Waiting until feeling extremely thirsty may lead to dehydration. Clients with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus should follow a prescribed fluid restriction plan rather than relying on thirst cues.
D) Incorrect. While having a fixed schedule for fluid intake can be helpful, it's important for the client to follow the prescribed fluid restriction plan, which may involve limiting total daily intake.
A client with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus asks the nurse about dietary recommendations. What guidance should the nurse provide regarding dietary sodium intake?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While monitoring sodium levels is important, increasing sodium intake is not a primary recommendation for managing Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
B) Incorrect. Avoiding high-sodium foods is not specifically emphasized in the management of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. The focus is on fluid restriction.
C) Incorrect. Consuming a low-sodium diet does not directly relate to reducing thirst sensation in the context of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
D) Correct. The client should monitor sodium levels as part of overall health, but there is no specific need for a special diet unless otherwise indicated by a healthcare provider.
A nurse is assessing a client with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. What clinical manifestation is commonly associated with this condition?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Polyphagia is not a common clinical manifestation of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. It refers to increased appetite.
B) Incorrect. While polydipsia (excessive thirst) is a characteristic feature of diabetes, it is not specific to Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
C) Correct. Polyuria, or excessive urination, is a hallmark sign of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. The kidneys are unable to reabsorb water properly, leading to increased urine output.
D) Incorrect. Polyarthralgia, or joint pain, is not a characteristic manifestation of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
A client with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is prescribed thiazide diuretics. What important instruction should the client receive regarding medication administration?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Thiazide diuretics should be taken with food to reduce the risk of stomach upset. Taking them on an empty stomach is not recommended.
B) Incorrect. Taking the medication with a high-sodium meal is not necessary for its effectiveness. In fact, it's important to monitor sodium levels while taking thiazide diuretics.
C) Correct. Thiazide diuretics can lead to low potassium levels (hypokalemia) as they increase potassium excretion in the urine. Clients should be instructed to monitor for signs of hypokalemia, such as muscle weakness or irregular heart rhythm.
D) Incorrect. Discontinuing the medication without consulting a healthcare provider is not advisable. If there are concerns about medication effectiveness or side effects, the client should discuss them with their healthcare provider.
A nurse is caring for a client with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. The client reports feeling lightheaded and dizzy. What action should the nurse take first?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Administering diuretics without first assessing vital signs could potentially worsen the client's condition. It's important to determine the client's current hemodynamic status.
B) Correct. The client's report of feeling lightheaded and dizzy warrants an immediate assessment of blood pressure and pulse. This will provide crucial information about the client's cardiovascular status.
C) Incorrect. Increasing fluid intake may not be appropriate if the client is already experiencing symptoms of volume overload or fluid imbalance. Assessing vital signs takes precedence.
D) Incorrect. While notifying the healthcare provider is important, it is not the first action to take in this situation. Assessing the client's vital signs is more immediate and directly addresses the reported symptoms.
Renal Cancers
A client recently diagnosed with renal cancer asks the nurse about the function of the kidneys. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While the kidneys play a role in maintaining blood glucose levels, their primary function is to filter waste products and excess substances from the blood.
B) Correct. One of the primary functions of the kidneys is to filter waste products, excess substances, and toxins from the blood, helping to maintain overall homeostasis.
C) Incorrect. The production of digestive enzymes is not a primary function of the kidneys.
D) Incorrect. While the kidneys do play a role in regulating blood pressure, their primary function is related to filtration and waste removal.
A nurse is explaining risk factors for renal cancer to a client. Which of the following should the nurse include?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Smoking is indeed associated with an increased risk of renal cancer, so it is an important risk factor to consider.
B) Correct. Hypertension (high blood pressure) and obesity are recognized risk factors for the development of renal cancer.
C) Incorrect. Physical activity and a balanced diet can influence the risk of renal cancer. Regular exercise and a healthy diet may help reduce the risk.
D) Incorrect. Genetics and family history can contribute to the development of renal cancer. It's important to consider these factors in assessing risk.
A client with a family history of renal cancer asks the nurse about screening recommendations. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Individuals with a family history of renal cancer may require special screening to detect any potential early signs of the disease.
B) Incorrect. While monitoring blood pressure is important for overall health, it is not the primary screening method for renal cancer in those with a family history.
C) Correct. For individuals with a family history of renal cancer, annual imaging studies such as ultrasounds or CT scans are recommended to monitor for any potential signs of the disease.
D) Incorrect. Genetic testing may be considered in some cases, but it is not the primary screening method for renal cancer in individuals with a family history.
A nurse is educating a client about the potential signs and symptoms of renal cancer. What should the nurse include?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Pain in the chest and shortness of breath are not typical symptoms of renal cancer. They may be indicative of other conditions.
B) Correct. Hematuria, or blood in the urine, is a common symptom of renal cancer. It occurs due to bleeding from the tumor.
C) Incorrect. Excessive thirst and frequent urination are not characteristic signs of renal cancer. They may be related to other conditions.
D) Incorrect. Significant weight gain and bloating are not typical symptoms of renal cancer. They may be associated with other health issues.
A client diagnosed with renal cancer asks the nurse about the potential spread of the disease. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Correct. Renal cancer can metastasize (spread) to other parts of the body, commonly to the lungs and bones.
B) Incorrect. Renal cancer has the potential to spread beyond the kidneys, particularly to other organs and tissues.
C) Incorrect. Renal cancer can spread to both nearby and distant organs and tissues, not just nearby ones.
D) Incorrect. Renal cancer does have the potential to metastasize, meaning it can spread to other parts of the body. It is not strictly localized to the kidneys.
A client asks the nurse about potential risk factors for renal cancer. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Consuming a diet high in fruits and vegetables is generally associated with a reduced risk of various cancers, including renal cancer.
B) Correct. Tobacco use and exposure to certain chemicals, such as asbestos, organic solvents, and heavy metals, are known risk factors for the development of renal cancer.
C) Incorrect. Engaging in regular physical activity can actually help reduce the risk of renal cancer, along with providing other health benefits.
D) Incorrect. Family history and genetics can indeed contribute to the development of renal cancer. It's important to consider these factors in assessing risk.
A nurse is discussing risk factors for renal cancer with a client. Which of the following should the nurse include?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Renal cancer is associated with specific risk factors, and it's important to educate clients about them.
B) Correct. Chronic kidney disease is considered a potential risk factor for the development of renal cancer.
C) Incorrect. Consuming a diet high in fiber is generally associated with a reduced risk of various cancers, including renal cancer.
D) Incorrect. Regular exercise and physical activity can help reduce the risk of renal cancer, along with providing other health benefits.
A client with a family history of renal cancer asks the nurse about potential risk factors. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Having a family history of renal cancer can increase the risk of developing the disease.
B) Correct. Genetics and family history are recognized risk factors for the development of renal cancer.
C) Incorrect. While sunlight and UV radiation are associated with skin cancers, they are not primary risk factors for renal cancer.
D) Incorrect. Dietary factors can influence the risk of various cancers, including renal cancer. It's important to consider them in assessing risk.
A nurse is educating a group of individuals about occupational risk factors for renal cancer. What should the nurse include?
Explanation
A) Correct. Occupational exposure to certain chemicals and substances, such as asbestos, organic solvents, and heavy metals, can increase the risk of developing renal cancer.
B) Incorrect. Occupational risk factors, particularly exposure to specific chemicals and substances, can indeed impact the risk of renal cancer.
C) Incorrect. Working in an office environment is not a recognized occupational risk factor for renal cancer.
D) Incorrect. Occupational factors can influence the risk of various cancers, including renal cancer, not just lung cancer.
A client asks the nurse about the primary type of cells from which renal cancers typically originate. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Renal cancers do not typically originate from nerve cells.
B) Correct. Renal cell carcinoma, the most common type of renal cancer, arises from the epithelial cells lining the renal tubules.
C) Incorrect. Renal cancers do not develop from muscle cells within the kidney.
D) Incorrect. Renal cancers do not primarily arise from blood cells in the kidney.
A nurse is explaining the pathophysiology of renal cancers to a client. What is a key factor in the development of renal cell carcinoma?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Excessive production of insulin within the kidney is not a key factor in the development of renal cell carcinoma.
B) Correct. Renal cell carcinoma typically arises due to mutations in the DNA of renal cells, leading to uncontrolled growth and the formation of tumors.
C) Incorrect. Abnormalities in the bone marrow do not directly affect kidney function or contribute to the development of renal cell carcinoma.
D) Incorrect. Decreased blood flow to the kidneys can lead to kidney damage, but it is not a primary factor in the development of renal cell carcinoma.
A nurse is explaining the pathophysiology of renal cancers to a client. What is a key factor in the development of renal cell carcinoma?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Excessive production of insulin within the kidney is not a key factor in the development of renal cell carcinoma.
B) Correct. Renal cell carcinoma typically arises due to mutations in the DNA of renal cells, leading to uncontrolled growth and the formation of tumors.
C) Incorrect. Abnormalities in the bone marrow do not directly affect kidney function or contribute to the development of renal cell carcinoma.
D) Incorrect. Decreased blood flow to the kidneys can lead to kidney damage, but it is not a primary factor in the development of renal cell carcinoma.
A client asks the nurse how renal cancers spread to other parts of the body. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Correct. Renal cancers, particularly renal cell carcinoma, often spread through the bloodstream to distant organs, a process known as metastasis.
B) Incorrect. While direct invasion of neighboring tissues and organs can occur, metastasis through the bloodstream is a common route of spread for renal cancers.
C) Incorrect. Renal cancers do have the capacity to spread to other parts of the body, primarily through the bloodstream.
D) Incorrect. While lymphatic spread can occur, renal cancers often spread primarily through the bloodstream.
A nurse is discussing the role of the immune system in combating renal cancers with a client. What is a characteristic of renal cell carcinoma in relation to the immune response?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Renal cell carcinoma does not typically lead to rapid tumor regression due to its ability to evade the immune system.
B) Correct. Renal cell carcinoma has mechanisms that allow it to evade the immune system, which can make it challenging for the body to mount an effective response against the cancer.
C) Incorrect. Renal cell carcinoma does interact with the immune system, but it can evade immune surveillance to some extent.
D) Incorrect. The immune system's response to renal cell carcinoma is not limited to the kidney, as it can involve various components of the immune system throughout the body.
A client asks the nurse about the role of genetics in the development of renal cancers. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Genetics do play a role in the development of renal cancers, particularly certain genetic mutations.
B) Correct. Certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of developing renal cell carcinoma, highlighting the importance of genetic factors in assessing risk.
C) Incorrect. Genetic factors can influence various aspects of renal cancers, including their development and progression, not just their size.
D) Incorrect. Genetics influence various aspects of renal cancers, but they do not solely determine the location of the cancer within the kidney.
A client experiencing weight loss, fatigue, and abdominal pain asks the nurse about the possible signs of renal cancer. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Weight loss, fatigue, and abdominal pain can be associated with renal cancer, and it's important for the client to seek medical evaluation.
B) Correct. Weight loss, fatigue, and abdominal pain can be signs of renal cancer. It's crucial for the client to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and testing.
C) Incorrect. While these symptoms can occur in aging adults, they can also be indicative of various health conditions, including cancer.
D) Incorrect. Weight loss, fatigue, and abdominal pain can be associated with renal cancer, and it's important for the client to seek medical evaluation.
A nurse is assessing a client suspected of having renal cancer. What urinary symptom is commonly associated with renal cell carcinoma?
Explanation
A) Correct. Hematuria, or the presence of blood in the urine, is a common urinary symptom associated with renal cell carcinoma.
B) Incorrect. Urinary retention is not a typical urinary symptom of renal cell carcinoma.
C) Incorrect. While changes in urinary frequency can occur in various conditions, it is not a specific symptom associated with renal cell carcinoma.
D) Incorrect. Urinary incontinence is not a typical symptom of renal cell carcinoma.
A client reports experiencing back pain that doesn't seem related to any specific injury or strain. The client asks the nurse if this could be a sign of renal cancer. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Back pain can be associated with renal cancer, especially if there are other concerning symptoms present.
B) Correct. Back pain can have various causes, but it's important to consider the possibility of renal cancer, especially if there are other concerning symptoms like weight loss and hematuria.
C) Incorrect. While musculoskeletal issues can cause back pain, it's important to consider other potential causes, including conditions like renal cancer.
D) Incorrect. The severity of pain alone does not necessarily rule out the possibility of a serious underlying condition like renal cancer.
A nurse is educating a client about potential signs of advanced renal cancer. Which systemic symptom is often associated with advanced stages of renal cell carcinoma?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hyperactivity and restlessness are not typical systemic symptoms associated with advanced stages of renal cell carcinoma.
B) Incorrect. Profuse sweating and fever are not typically associated with advanced stages of renal cell carcinoma.
C) Correct. Unexplained weight loss and fatigue are common systemic symptoms associated with advanced stages of renal cell carcinoma.
D) Incorrect. Increased appetite and weight gain are not typical systemic symptoms associated with advanced stages of renal cell carcinoma.
A client asks the nurse about the possibility of having renal cancer due to experiencing swelling in the lower extremities. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Swelling in the lower extremities can be associated with advanced stages of renal cancer, and it's important for the client to seek medical evaluation.
B) Correct. Swelling in the lower extremities can be a sign of advanced renal cancer, and it's crucial for the client to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and testing.
C) Incorrect. While swelling in the lower extremities can be related to heart conditions, it can also be associated with other health conditions, including cancer.
D) Incorrect. The presence or absence of pain does not definitively rule out the possibility of a serious underlying condition like advanced renal cancer.
A client asks the nurse about the diagnostic tests for renal cancer. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While a CT scan is an important imaging test for diagnosing renal cancer, it is not the only test needed. Other imaging modalities and a biopsy may also be required.
B) Correct. The diagnosis of renal cancer typically involves a combination of imaging tests like CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds, along with a biopsy for confirmation.
C) Incorrect. Blood tests alone cannot definitively diagnose renal cancer. They can provide supportive information, but imaging tests and biopsy are usually required for a conclusive diagnosis.
D) Incorrect. While a physical examination and medical history are important components of the diagnostic process, they alone are not sufficient for diagnosing renal cancer. Imaging tests and biopsy are typically needed.
A nurse is preparing a client for a renal cancer diagnostic procedure. The client asks about the purpose of a renal ultrasound. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Correct. A renal ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test that helps visualize the structures of the kidney. It can detect tumors, cysts, and other abnormalities.
B) Incorrect. While a renal ultrasound is important for assessing the kidney, it is not typically used to confirm metastases in other organs. Imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs are more suitable for that purpose.
C) Incorrect. While a renal ultrasound can detect tumors within the kidney, it is not used for direct biopsy. Biopsy procedures are separate and may be performed if a tumor is detected.
D) Incorrect. While a renal ultrasound provides information about kidney structure, it is not primarily used to assess blood flow or kidney function. Other tests like Doppler ultrasound or renal scintigraphy may be used for that purpose.
A client diagnosed with renal cancer is scheduled for a CT scan. The client asks the nurse about the purpose of this test. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While CT scans may be used to monitor treatment progress, their primary purpose in renal cancer diagnosis is to provide detailed images of the kidneys and surrounding structures.
B) Correct. A CT scan is a valuable imaging tool for assessing the size, location, and extent of a renal tumor. It provides detailed images that aid in diagnosis and treatment planning.
C) Incorrect. A CT scan is not used for direct sampling and analysis of cancerous tissue within the kidney. Biopsy procedures are performed separately for that purpose.
D) Incorrect. While a CT scan provides anatomical information, it is not primarily used to assess blood flow or kidney function. Other tests may be employed for those purposes.
A nurse is explaining the purpose of a biopsy to a client suspected of having renal cancer. What is the primary goal of a renal biopsy?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. The primary goal of a renal biopsy is to obtain a tissue sample for microscopic examination, not to remove the entire tumor.
B) Correct. A renal biopsy is performed to obtain a tissue sample from the kidney, which is then examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer and provide further information about the type and grade of the tumor.
C) Incorrect. Assessing blood flow within the kidney is not the primary purpose of a renal biopsy. Other tests may be used for that purpose.
D) Incorrect. Evaluating kidney function is not the primary goal of a renal biopsy. There are other tests and assessments specifically designed for evaluating kidney function.
A client diagnosed with renal cancer asks the nurse about the purpose of a bone scan. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. A bone scan is not used for direct visualization and biopsy of tumors in the bones. It is an imaging test for identifying abnormalities in bone metabolism.
B) Incorrect. While a bone scan provides information about bone metabolism, it is not primarily performed to assess blood flow within the bones.
C) Correct. A bone scan is used to detect whether cancer has spread (metastasized) to the bones. This information is crucial for staging the cancer and planning appropriate treatment.
D) Incorrect
. While a bone scan provides information about bone health, its primary purpose is to identify abnormalities related to bone metabolism, such as metastases from cancer.
A client recently diagnosed with renal cancer asks the nurse about treatment options. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Correct. Surgery is the primary treatment for renal cancer, and the extent of the procedure may involve removing part (partial nephrectomy) or all (radical nephrectomy) of the affected kidney.
B) Incorrect. While chemotherapy may be used in some cases, it is not the main treatment for renal cancer. Other treatments, such as surgery or targeted therapy, are often more effective.
C) Incorrect. Radiation therapy is not typically the first-line treatment for renal cancer. It may be used in certain situations, but surgery is usually the initial approach.
D) Incorrect. Hormone therapy is not a standard treatment for renal cancer. It is more commonly used for cancers influenced by hormonal factors, such as some types of breast or prostate cancer.
A nurse is providing preoperative education to a client scheduled for a nephrectomy as part of renal cancer treatment. What information should the nurse include?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. It is important for the client to understand that they will have restrictions on activities after a nephrectomy. Resuming normal activities immediately without any restrictions would not be accurate.
B) Correct. After a nephrectomy, clients should avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities for several weeks to promote healing and prevent complications.
C) Incorrect. Postoperative follow-up care is essential after a nephrectomy. The client will likely have scheduled appointments for monitoring recovery and addressing any concerns.
D) Incorrect. While pain relief will be provided, it may not be immediate, and the client should be prepared for some discomfort after surgery.
A client with renal cancer is scheduled for targeted therapy. The client asks the nurse about the purpose of this treatment. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While targeted therapy may provide some relief from cancer-related symptoms, its primary purpose is to target cancer cells at the molecular level.
B) Correct. Targeted therapy is designed to target specific molecular features of cancer cells, inhibiting their growth and spread while minimizing damage to normal cells.
C) Incorrect. Targeted therapy is not primarily focused on strengthening the immune system. It is a distinct form of treatment that acts directly on cancer cells.
D) Incorrect. Targeted therapy is not a form of radiation treatment. It involves the use of drugs that target specific molecules involved in cancer cell growth.
A nurse is providing postoperative care to a client who underwent a radical nephrectomy for renal cancer. What is a priority nursing intervention for this client?
Explanation
A) Correct. Monitoring vital signs, including blood pressure and heart rate, is a priority after a radical nephrectomy. Changes in blood pressure or heart rate can indicate potential complications.
B) Incorrect. Administering chemotherapy medications is not typically part of the immediate postoperative care for a radical nephrectomy.
C) Incorrect. Encouraging vigorous physical activity is not recommended immediately after a radical nephrectomy. The client will need time to recover and gradually resume normal activities.
D) Incorrect. Providing a high-sodium diet is not typically indicated after a radical nephrectomy. The client's diet will be based on their specific needs and any potential dietary restrictions.
A client with renal cancer is prescribed immunotherapy. The client asks the nurse about the purpose of this treatment. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Correct. Immunotherapy works by enhancing the body's immune system, enabling it to recognize and target cancer cells more effectively.
B) Incorrect. Immunotherapy does not directly target and destroy cancer cells; instead, it boosts the body's natural defenses against cancer.
C) Incorrect. Immunotherapy is not a form of radiation treatment. It is a distinct type of treatment that harnesses the immune system's power.
D) Incorrect. Immunotherapy is not primarily used to treat cancer-related pain and discomfort. Its main purpose is to enhance the body's ability to fight cancer.
A nurse is caring for a client with renal cancer who has just returned from surgery. What is the priority nursing intervention for this client at this time?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While pain management is important, assessing the surgical incision for signs of infection takes priority to ensure early detection and intervention.
B) Correct. Assessing the surgical incision is a priority to monitor for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, warmth, or drainage. Early detection allows for prompt treatment and prevention of complications.
C) Incorrect. While ambulation is important for postoperative recovery, assessing the incision for signs of infection takes precedence.
D) Incorrect. Offering a full meal may not be appropriate immediately after surgery. The client's dietary intake should be assessed, and they may start with lighter foods as tolerated.
A client with renal cancer asks the nurse about strategies to manage fatigue during treatment. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. While regular exercise is beneficial, it should be balanced with rest, especially if the client is experiencing fatigue.
B) Incorrect. Long naps during the day may disrupt the client's sleep pattern at night. Short, well-timed naps may be more effective.
C) Correct. Conserving energy by prioritizing activities and taking rest breaks can help manage fatigue. This allows the client to allocate energy for essential tasks and rest when needed.
D) Incorrect. Increasing caffeine intake is not a sustainable or recommended strategy for managing fatigue. It may lead to disrupted sleep patterns and other negative effects.
A nurse is providing education to a client with renal cancer who will undergo radiation therapy. What should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
A) Correct. Skin changes, such as redness or irritation, are common side effects of radiation therapy. Applying moisturizer can help soothe discomfort and minimize skin-related issues.
B) Incorrect. While a balanced diet is important, there is no specific evidence to suggest that a high-protein diet specifically boosts the effects of radiation therapy.
C) Incorrect. Maintaining physical activity within recommended guidelines can be beneficial during radiation therapy. However, the client should avoid excessive or strenuous activities.
D) Incorrect. Pain relief from radiation therapy may not be immediate, and the client should be prepared for some discomfort during and after the sessions.
A client with renal cancer asks the nurse about the importance of hydration during treatment. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. Hydration is important during cancer treatment to help support the body's response to treatment and manage side effects. It is not advisable to dismiss its importance.
B) Correct. Staying well-hydrated is crucial during cancer treatment to support the body's response to therapy and minimize potential side effects, such as nausea and fatigue.
C) Incorrect. While there may be specific cases where fluid intake needs to be monitored, limiting hydration in general is not advisable, especially during cancer treatment.
D) Incorrect. It is important for the client to stay hydrated throughout the day, not just immediately before and after treatment sessions.
A client diagnosed with renal cancer asks the nurse about the purpose of a bone scan. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
A) Incorrect. A bone scan is not used for direct visualization and biopsy of tumors in the bones. It is an imaging test for identifying abnormalities in bone metabolism.
B) Incorrect. While a bone scan provides information about bone metabolism, it is not primarily performed to assess blood flow within the bones.
C) Correct. A bone scan is used to detect whether cancer has spread (metastasized) to the bones. This information is crucial for staging the cancer and planning appropriate treatment.
D) Incorrect. While a bone scan provides information about bone health, its primary purpose is to identify abnormalities related to bone metabolism, such as metastases from cancer.
Exams on Pathophysiology of the renal system
Custom Exams
Login to Create a Quiz
Click here to loginLessons
 Nursingprepexams
Just Now
Nursingprepexams
Just Now
Notes Highlighting is available once you sign in. Login Here.
Objectives
- Investigate early detection methods and diagnostic tools for Acute Kidney Injury (AKI).
- Identify interventions to prevent AKI in high-risk patient populations, such as those undergoing surgery or with certain medical conditions.
- Identify education programs on lifestyle modifications and medical management to slow the progression of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD).
- Identify resources for improved access to affordable and comprehensive care for individuals with Nephrotic Syndrome.
- Investigate genetic and environmental factors contributing to the development of Nephrotic Syndrome.
- Develop effective strategies for the prevention and management of Renal Calculi (Kidney Stones).
- Identify the screening and monitoring programs to detect Glomerulonephritis in its early stages.
- Develop interventions to manage and improve the quality of life for individuals with Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
- Implement comprehensive screening programs for early detection of renal cancers, especially in high-risk populations.
Acute Kidney Failure
Introduction to acute renal failure
- Acute renal failure (ARF), also known as acute kidney injury (AKI), is a sudden loss of kidney function due to damage or dysfunction of the kidneys.
- It can affect anyone, but it is more common in hospitalized patients, especially those in critical care units.
- Acute renal failure is defined as a rapid decline in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which is the rate at which the kidneys filter blood and remove waste products.
- GFR is measured by serum creatinine, which is a waste product of muscle metabolism. A normal GFR is about 90 to 120 mL/min/1.73 m2.
- ARF is diagnosed when there is an increase in serum creatinine of 0.3 mg/dL or more within 48 hours or a decrease in urine output of less than 0.5 mL/kg/hour for 6 hours or more.
- ARF can be classified into three categories, depending on the site of the problem:
- Prerenal ARF: This occurs when there is reduced blood flow to the kidneys, resulting in decreased GFR. This can be caused by conditions such as dehydration, hypovolemia, heart failure, shock, sepsis, or renal artery stenosis.
- Intrinsic ARF: This occurs when there is damage to the kidney tissue itself, resulting in impaired filtration and tubular function. This can be caused by conditions such as acute tubular necrosis (ATN), acute interstitial nephritis (AIN), glomerulonephritis, vasculitis, or contrast-induced nephropathy.
- Postrenal ARF: This occurs when there is an obstruction to the urine flow from the kidneys, resulting in increased pressure and backflow of urine into the kidney. This can be caused by conditions such as kidney stones, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), tumors, blood clots, or neurogenic bladder.
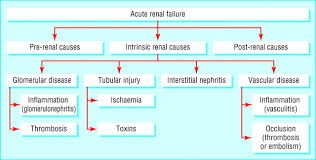
Pathophysiology
- The pathophysiology of acute renal failure is complex and can be classified into three main categories:
- pre-renal
- intrinsic renal
- post-renal causes.
- Each category has distinct mechanisms that lead to kidney dysfunction.
- Pre-renal causes of acute renal failure are those that disrupt the blood flow to the kidneys, reducing their ability to receive an adequate supply of blood, for instance, due to hypovolemia, hypotension, renal artery stenosis, and impaired cardiac output such as myocardial infarction. Pre-renal causes result in reduced glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and decreased urine output. The kidneys attempt to compensate for the decreased blood flow by activating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, which constricts blood vessels and retains sodium and water to maintain blood pressure.
- Intrinsic renal causes of acute renal failure involve damage or injury to the renal parenchyma (the functional tissue of the kidney), for example, glomerulonephritis, and nephrotoxic agents such as aminoglycosides. Intrinsic renal causes result in impaired filtration and reabsorption functions of the nephrons, leading to decreased GFR and urine output. In response to injury, inflammatory and repair processes may be activated within the kidneys.
- Post-renal causes of acute renal failure occur when there is an obstruction in the urinary tract that prevents the normal flow of urine from the kidneys to the bladder, for instance, due to urinary calculi, tumors, prostatic hyperplasia, and strictures. Post-renal causes lead to increased pressure in the renal pelvis and renal tubules, impairing renal function and causing damage over time. If the obstruction is relieved promptly, kidney function may recover.
- The examples of the causes for each category are discussed below under the etiology.
Etiology
- The most common causes of ARF vary depending on the category and the setting.
- In general, prerenal ARF accounts for about 60% to 70% of cases, intrinsic ARF accounts for about 25% to 40% of cases, and postrenal ARF accounts for about 5% to 10% of cases.
Some of the specific causes of each category are:
- Prerenal ARF: Hypovolemia (due to hemorrhage, vomiting, diarrhea, burns), hypotension (due to septic shock, cardiogenic shock, anaphylactic shock), heart failure (due to myocardial infarction, arrhythmias, valvular disease), renal artery stenosis (due to atherosclerosis, fibromuscular dysplasia), hepatorenal syndrome (due to liver cirrhosis), drugs that affect renal perfusion (such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs], angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors [ACEIs], angiotensin receptor blockers [ARBs])
- Intrinsic ARF: Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) (due to ischemia from prerenal causes or nephrotoxins such as antibiotics [aminoglycosides], antivirals [acyclovir], antifungals [amphotericin B], chemotherapeutic agents [cisplatin], contrast media [iodinated]), acute interstitial nephritis (AIN) (due to allergic reactions to drugs such as antibiotics [penicillins], anticonvulsants [phenytoin], diuretics [furosemide], NSAIDs [ibuprofen] or infections such as streptococcal pharyngitis, cytomegalovirus [CMV], etc.), glomerulonephritis (due to immune-mediated diseases such as lupus nephritis, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, IgA nephropathy), vasculitis (due to systemic diseases such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis, microscopic polyangiitis, polyarteritis nodosa), thrombotic microangiopathy (due to disorders such as hemolytic uremic syndrome [HUS], thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura [TTP])
- Postrenal ARF: Kidney stones (due to hypercalcemia, hyperuricemia, hyperoxaluria), benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) (due to hormonal changes in aging men), tumors (such as bladder cancer, prostate cancer, cervical cancer), blood clots (due to trauma, surgery, anticoagulation), neurogenic bladder (due to spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, diabetes mellitus)
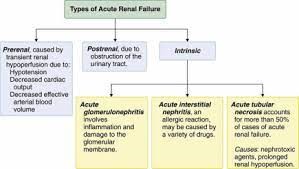
Pathophysiology and clinical presentation
- The clinical presentation of ARF depends on the category and the severity of the condition.
- In general, ARF leads to the accumulation of waste products and fluid in the body, resulting in metabolic acidosis, hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, uremia, edema, and hypertension.
- ARF also affects other organ systems, such as the cardiovascular system (causing arrhythmias, pericarditis), the respiratory system (causing pulmonary edema, pleural effusion), the hematologic system (causing anemia, bleeding tendency), the gastrointestinal system (causing nausea, vomiting, anorexia), the nervous system (causing confusion, lethargy, seizures), and the skin (causing pruritus, uremic frost).
- Some of the specific pathophysiological mechanisms and clinical manifestations of each category are:
I. Prerenal ARF: The reduced blood flow to the kidneys triggers a series of compensatory mechanisms to maintain GFR and renal perfusion.
- These include activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which causes vasoconstriction of the efferent arterioles and increased sodium and water reabsorption; stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS), which causes vasoconstriction of the afferent arterioles and increased cardiac output; and release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which causes increased water reabsorption.
- These mechanisms result in oliguria (<400 mL/day), low urine sodium (<20 mEq/L), high urine osmolality (>500 mOsm/kg), high urine specific gravity (>1.020), and low fractional excretion of sodium (<1%).
- The clinical presentation of prerenal ARF is usually related to the underlying cause of hypoperfusion. For example:
- patients with hypovolemia may present with tachycardia, hypotension, dry mucous membranes, poor skin turgor
- patients with heart failure may present with dyspnea, orthopnea, jugular venous distension, crackles
- patients with septic shock may present with fever, chills, tachycardia, hypotension, and altered mental status.
II. Intrinsic ARF: The damage to the kidney tissue causes inflammation, necrosis, and apoptosis of the renal cells. This leads to impairment of the glomerular filtration barrier and tubular function.
- Depending on the site and extent of injury:
- there may be leakage of protein and blood into the urine (proteinuria and hematuria),
- loss of sodium and water into the urine (hyponatremia and hypovolemia),
- decreased reabsorption of bicarbonate and increased production of hydrogen ions (metabolic acidosis),
- decreased reabsorption of potassium and increased secretion of potassium into the urine (hypokalemia or hyperkalemia),
- decreased reabsorption of phosphate and increased secretion of phosphate into the urine (hyperphosphatemia),
- decreased production of erythropoietin (anemia),
- and decreased activation of vitamin D (hypocalcemia).
- The clinical presentation of intrinsic ARF is usually related to the type and severity of kidney injury. For example,
- patients with ATN may present with oliguria or anuria (<100 mL/day), high urine sodium (>40 mEq/L), low urine osmolality (<350 mOsm/kg), low urine specific gravity (<1.010), and high fractional excretion of sodium (>2%)
- patients with AIN may present with fever, rash, eosinophilia, and pyuria patients with glomerulonephritis may present with hematuria, proteinuria, edema, and hypertension
- patients with vasculitis may present with hematuria, proteinuria, purpura, and arthralgia
- patients with thrombotic microangiopathy may present with hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, fever, and neurologic symptoms.
III. Postrenal ARF: The obstruction to the urine flow causes increased pressure and backflow of urine into the kidney. This leads to compression and dilation of the renal tubules and vessels. This impairs GFR and renal perfusion. Depending on the level and duration of obstruction, there may be various degrees of impairment in kidney function, which is known as postrenal acute renal failure (ARF).
- Postrenal ARF, also referred to as obstructive nephropathy, occurs when there is a blockage or obstruction in the urinary tract that prevents the normal flow of urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- The obstruction can occur at any level of the urinary tract, including the ureters, bladder, or urethra.
- Some common causes of postrenal ARF include kidney stones, tumors, enlarged prostate gland in men, urinary tract infections, and certain congenital abnormalities.
- Common clinical presentations of post-renal AKI include:
- Decreased urine output (oliguria): One of the hallmark signs of post-renal AKI is a reduction in the amount of urine produced. The urine output may be significantly lower than normal or even absent in severe cases. This occurs because the obstruction prevents urine from flowing freely out of the kidneys.
- Flank pain: Patients with post-renal AKI may experience pain in the sides of their abdomen, known as flank pain. The pain can be dull, aching, or sharp and may be localized to one or both sides depending on the location of the obstruction.
- Urinary retention: In cases where the obstruction occurs in the lower urinary tract, such as in the bladder or urethra, patients may have difficulty passing urine. This can result in urinary retention, leading to a feeling of fullness or discomfort in the lower abdomen.
- Signs of uremia: As the kidney function is impaired, waste products and toxins that are normally eliminated in the urine can build up in the bloodstream. This can lead to uremia, a condition characterized by elevated levels of waste products in the blood. Signs of uremia may include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fatigue, confusion, and altered mental status.
- Fluid and electrolyte imbalances: Post-renal AKI can disrupt the normal balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body. This can lead to symptoms such as edema (swelling), especially in the legs and ankles, as well as imbalances in sodium, potassium, and other essential electrolytes.
- Systemic symptoms: In severe cases, post-renal AKI can cause systemic symptoms such as fever, chills, and signs of infection if the obstruction is related to a urinary tract infection or kidney stones.
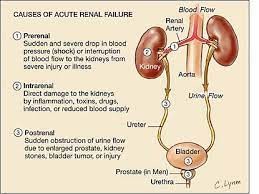
Diagnostic Tests and Imaging
- The diagnosis of acute renal failure is based on the history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
- The following tests and imaging may be used to diagnose acute renal failure:
- Serum creatinine and BUN: These are blood tests that measure the levels of creatinine and urea in the blood. Creatinine is a waste product of muscle metabolism that is normally filtered by the kidneys. Urea is a waste product of protein metabolism that is normally excreted by the kidneys. A rise in serum creatinine and BUN indicates a decrease in kidney function. The ratio of BUN to creatinine can help differentiate prerenal from intrinsic causes of acute renal failure. A ratio greater than 20:1 suggests prerenal causes, whereas a ratio less than 10:1 suggests intrinsic causes.
- Urine output: This is a measure of how much urine is produced in 24 hours. A normal urine output is about 1.5 liters per day for adults. A urine output of less than 0.5 ml/kg/hour for more than 6 hours indicates oliguria, which is a sign of acute renal failure.
- Urine tests: These include urinalysis, urine electrolytes, urine osmolality, urine specific gravity, and urine sediment examination. Urinalysis can reveal abnormalities such as proteinuria, hematuria, pyuria, or casts that suggest kidney damage or infection. Urine electrolytes can help assess tubular function and differentiate prerenal from intrinsic causes of acute renal failure. Urine osmolality and specific gravity can help assess the concentration ability of the kidneys and differentiate prerenal from intrinsic causes of acute renal failure. Urine sediment examination can help identify cellular or crystalline components that indicate glomerular or tubular injury.
- Blood tests: These include serum electrolytes, blood gas analysis, complete blood count (CBC), and other tests depending on the suspected cause of acute renal failure. Serum electrolytes can reveal imbalances such as hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, or hypermagnesemia that result from impaired kidney function. Blood gas analysis can reveal metabolic acidosis due to the accumulation of acids or loss of bicarbonate by the kidneys. CBC can reveal anemia due to decreased erythropoietin production by the kidneys or blood loss.
- Other tests may include liver function tests, coagulation studies, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), haptoglobin, antinuclear antibody (ANA), antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA), complement levels, serum protein electrophoresis, blood cultures, or drug levels.
- Imaging tests: These include renal ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or renal scintigraphy.
- Renal ultrasound is the preferred imaging modality for renal assessment, as it can provide valuable information such as kidney size, shape, echogenicity, blood flow, and the presence of obstruction, cysts, masses, or stones.
- CT or MRI can provide more detailed information on the renal parenchyma, vessels, and collecting system, and can help identify causes such as renal artery stenosis or thrombosis, renal vein thrombosis, pyelonephritis, abscess, infarction, or tumor.
- Renal scintigraphy can help evaluate renal perfusion and function using radioactive tracers that are filtered by the kidneys.
- Biopsy: This is a procedure that involves removing a small sample of kidney tissue for microscopic examination. A biopsy can help confirm the diagnosis and determine the cause and extent of kidney damage in cases of acute renal failure that are unexplained or refractory to treatment. A biopsy can also help differentiate acute from chronic kidney injury by assessing the degree of fibrosis and scarring in the kidney tissue.
Management and Treatment
- The management and treatment of acute renal failure depend on the cause and severity of the condition, as well as the presence of complications and comorbidities.
- The general goals of management and treatment are to:
- Restore renal perfusion and function
- Correct or eliminate any reversible causes of kidney injury
- Provide supportive care to prevent or treat complications
- Preserve residual kidney function and prevent progression to chronic kidney disease
- The specific interventions may include:
- Fluid resuscitation: This involves administering intravenous (IV) fluids to restore fluid volume and blood pressure in patients with acute renal failure due to hypovolemia or hypotension. Isotonic crystalloids such as normal saline or lactated Ringer's solution are preferred over colloids as they have no clear renal or mortality benefit and may increase the risk of bleeding or infection. The amount and rate of fluid administration should be guided by the patient's hemodynamic status, urine output, serum creatinine, and BUN levels. Fluid overload should be avoided as it can worsen edema, pulmonary congestion, and heart failure.
- Diuretics: These are medications that increase urine output by inhibiting sodium and water reabsorption in the kidneys. Diuretics may be used to treat fluid overload in patients with acute renal failure who are oliguric or anuric. Loop diuretics such as furosemide (Lasix) or bumetanide (Bumex) are preferred over thiazide diuretics as they are more effective in patients with low GFR. Diuretics should be used with caution as they can cause dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, ototoxicity, or nephrotoxicity. The dose and frequency of diuretics should be adjusted according to the patient's response and laboratory values.
- Discontinuation of Nephrotoxic medications: These are medications that can cause or worsen kidney injury by affecting the blood flow to the kidneys or by directly damaging the kidney cells. Nephrotoxic medications should be discontinued or avoided in patients with acute renal failure whenever possible. Some examples of nephrotoxic medications include:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), aminoglycosides,
- amphotericin B,
- vancomycin,
- contrast media,
- cyclosporine,
- tacrolimus,
- cisplatin,
- and methotrexate.
- Drug dose adjustment: This involves modifying the dose or frequency of medications that are eliminated by the kidneys according to the patient's renal function. Drugs that are renally excreted may accumulate in patients with acute renal failure and cause toxicity or adverse effects. The degree of dose adjustment depends on the drug's pharmacokinetics, therapeutic index, and toxicity profile. Some examples of drugs that require dose adjustment in patients with acute renal failure include:
- digoxin,
- lithium,
- gabapentin,
- metformin,
- warfarin.
- Dialysis: This is a process that removes waste products and excess fluid from the blood using a machine (hemodialysis) or the abdomen (peritoneal dialysis). Dialysis may also be indicated in patients with acute renal failure who have chronic kidney disease, volume overload, or drug overdose. The timing and modality of dialysis should be individualized based on the patient's clinical condition, preferences, and availability of resources.
Dialysis may be indicated in patients with acute renal failure who have life-threatening complications such as:
- severe hyperkalemia,
- metabolic acidosis,
- uremic encephalopathy,
- pericarditis,
- pulmonary edema that is unresponsive to medical therapy.
- Renal replacement therapy: This is a term that encompasses dialysis and kidney transplantation as methods of replacing kidney function in patients with end-stage renal disease. Renal replacement therapy may be initiated in individuals with nephrotic syndrome who progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD). ESRD refers to the advanced stage of kidney disease where the kidneys can no longer function adequately to sustain life, necessitating the need for renal replacement therapy.
Nursing Interventions and supportive care
- Nursing interventions for ARF depend on the cause, stage, and severity of the condition, as well as the patient's individual needs and preferences.
- Some of the general nursing interventions for ARF include:
- Monitoring and managing fluid and electrolyte balance: The nurse should assess the patient's fluid status by measuring intake and output, daily weight, vital signs, central venous pressure (CVP), and urine-specific gravity. The nurse should also monitor the patient's serum electrolyte levels, especially potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, and report any abnormalities to the physician. The nurse should administer intravenous fluids or blood products as ordered, and adjust the rate and type of fluid according to the patient's response. The nurse should also restrict fluid intake if indicated, and educate the patient on signs of fluid overload or dehydration.
- Optimizing nutrition: The nurse should consult with a dietitian to provide a suitable diet for the patient with ARF. The diet should be low in protein, sodium, potassium, phosphorus, and fluids, but high in calories, vitamins, and minerals. The nurse should also monitor the patient's nutritional status by checking serum albumin, prealbumin, transferrin, and nitrogen balance. The nurse should encourage oral intake if possible, or administer enteral or parenteral nutrition as ordered. The nurse should also supplement the patient with vitamins and minerals as needed.
- Ensuring medication safety: The nurse should be aware of the potential nephrotoxic effects of some medications, such as aminoglycosides, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), contrast agents, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs). The nurse should avoid or minimize the use of these medications in patients with ARF, or adjust the dosage and frequency according to the patient's renal function. The nurse should also monitor the patient's serum drug levels and report any signs of toxicity to the physician. The nurse should also administer medications that can help improve renal function or prevent complications, such as diuretics, vasodilators, antihypertensives, bicarbonates, calcium gluconate, insulin, albuterol, kayexalate, or dialysis solutions.

Summary
- ARF is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment.
- The main goals of treatment are to correct or eliminate the underlying cause of kidney damage, restore renal function, prevent or treat complications, and support the patient's recovery.
- Preventive measures, such as avoiding nephrotoxic medications, managing underlying medical conditions, and maintaining good hydration, can play a vital role in reducing the risk of acute renal failure.
- Advances in medical knowledge and technology continue to improve our understanding and management of acute renal failure.
- However, the prevention of this condition remains a key goal, emphasizing the importance of public health awareness, early detection of kidney dysfunction, and multidisciplinary collaboration in patient care.
- Nursing interventions for ARF are based on the patient's individual needs and preferences but generally include monitoring and managing fluid and electrolyte balance, optimizing nutrition, and ensuring medication safety.
Conclusion
- Acute renal failure, also known as acute kidney injury (AKI), is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition characterized by a rapid and abrupt decline in kidney function.
- It can arise from various underlying causes, including reduced blood flow to the kidneys (prerenal), damage to the kidney tissue (intrinsic renal), or obstruction of the urinary tract (postrenal).
- The clinical presentation of acute renal failure varies, but common features include decreased urine output, alterations in fluid and electrolyte balance, signs of uremia, and potential systemic symptoms.
- Timely recognition and diagnosis are crucial to initiate appropriate interventions and prevent further damage to the kidneys.
- Management of acute renal failure involves addressing the underlying cause, optimizing hemodynamic status, and providing supportive care to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance.
- In some cases, temporary renal replacement therapy, such as dialysis, may be necessary to support kidney function until recovery occurs.
- While many cases of acute renal failure are reversible with prompt and appropriate treatment, some patients may progress to more severe forms of kidney injury or chronic kidney disease.
- Acute renal failure is a critical condition that demands timely and comprehensive evaluation to determine the cause and implement appropriate interventions.
- Its successful management requires a multidimensional approach, including identifying and treating the underlying cause, providing supportive care, and closely monitoring kidney function. By addressing acute renal failure with diligence and diligence, healthcare professionals can improve patient outcomes and contribute to the prevention and management of kidney diseases more effectively.
- Nurses play a vital role in the care and management of patients with ARF. They provide supportive interventions that can help improve renal function or prevent complications.
- They also educate the patient on self-care and prevention strategies that can reduce the risk of future kidney damage.
- By applying evidence-based nursing practice and collaborating with other health care professionals, nurses can help improve the outcomes and quality of life of patients with ARF.
Chronic Renal Failure
Introduction to chronic renal failure
- Chronic renal failure (CRF) is the end result of a gradual, progressive loss of kidney function due to various causes such as:
- chronic infections
- high blood pressure
- vascular diseases
- obstructive processes
- collagen diseases
- nephrotoxic agents
- endocrine diseases such as diabetes mellitus
- CRF can lead to serious complications, such as high blood pressure, anemia, weak bones, nerve damage, and heart disease.
- It is a systemic disease that affects all body systems and leads to uremia, a condition where the end products of protein metabolism accumulate in the blood.
- CRF is also referred to as chronic kidney disease (CKD) and has five stages based on the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), with stage 5 being the most severe and requiring renal replacement therapy.
- Early detection and treatment of CRF can help prevent or delay the progression of kidney disease and reduce the risk of kidney failure, which requires dialysis or a kidney transplant to sustain life.
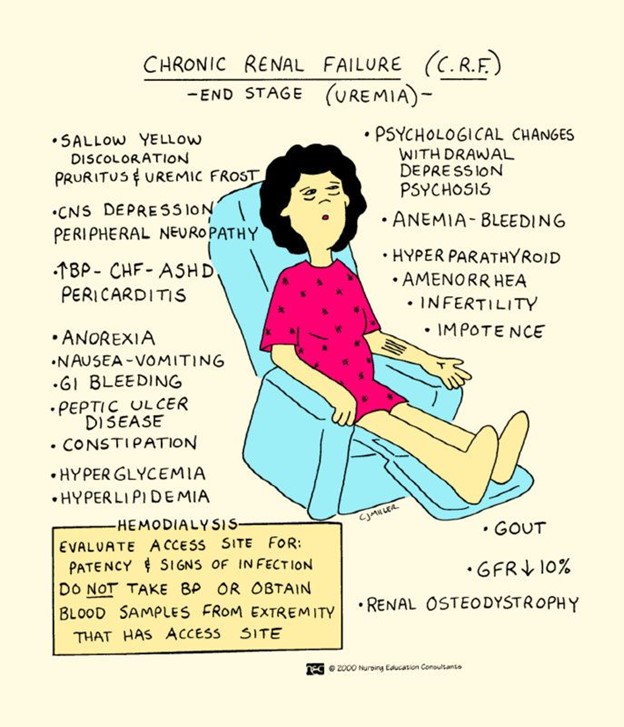
Pathophysiology
- The pathophysiology of CKD involves several cellular and molecular mechanisms that contribute to the progressive deterioration of kidney structure and function.
- One of the main features of CKD is the development of glomerulosclerosis and interstitial fibrosis, which are forms of scarring in the kidney tissue.
- Glomerulosclerosis refers to the hardening and thickening of the glomeruli, which are the filtering units of the kidneys.
- Interstitial fibrosis refers to the deposition of excess extracellular matrix (ECM) in the space between the tubules, which are the structures that reabsorb water and solutes from the filtered fluid.
- Both processes result in the loss of functional nephrons, which are the basic units of kidney function.
- The pathogenesis of glomerulosclerosis and interstitial fibrosis is complex and involves multiple factors, such as:
- Inflammation
- oxidative stress
- hypoxia
- apoptosis
- epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)
- endothelial dysfunction
- activation of various signaling pathways.
- Some of these factors are briefly described below:
- Inflammation: In response to kidney injury, inflammatory cells such as macrophages, lymphocytes, and mast cells infiltrate the kidney tissue and secrete cytokines and chemokines that promote further inflammation and fibrosis. Inflammatory mediators can also activate fibroblasts, which are the main source of ECM production.
- Oxidative stress: Oxidative stress refers to the imbalance between the production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are highly reactive molecules that can damage cellular components. Oxidative stress can induce inflammation, apoptosis, EMT, and ECM synthesis in kidney cells.
- Hypoxia: Hypoxia refers to the reduced oxygen supply to the kidney tissue due to reduced blood flow or capillary loss. Hypoxia can induce inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, EMT, and ECM synthesis in kidney cells. Hypoxia can also activate hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF), which is a transcription factor that regulates genes involved in angiogenesis, erythropoiesis, metabolism, and survival.
- Apoptosis: Apoptosis refers to the programmed cell death that occurs in response to various stimuli. Apoptosis can lead to the loss of functional nephrons and the release of pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic factors from dying cells.
- Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT): EMT refers to the process by which epithelial cells lose their polarity and differentiation and acquire mesenchymal characteristics such as motility and ECM production. EMT can be induced by various factors such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), ROS, hypoxia, or mechanical stress. EMT can contribute to tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis by reducing tubular function and increasing ECM synthesis.
- Endothelial dysfunction: Endothelial dysfunction refers to the impairment of endothelial cells that line the blood vessels. Endothelial dysfunction can be caused by various factors such as inflammation, oxidative stress, or angiotensin II. Endothelial dysfunction can lead to reduced nitric oxide (NO) production, increased endothelin-1 (ET-1) production, increased vascular permeability, increased leukocyte adhesion, increased thrombosis, and reduced angiogenesis. Endothelial dysfunction can contribute to glomerulosclerosis and interstitial fibrosis by affecting glomerular filtration barrier integrity and renal blood flow.
- The above factors can interact with each other and activate various signaling pathways that modulate gene expression and cellular behavior in kidney cells. Some of these pathways include:
- TGF-β/Smad pathway: TGF-β is a cytokine that plays a key role in fibrosis by inducing ECM synthesis and inhibiting ECM degradation. TGF-β binds to its receptors on the cell surface and activates Smad proteins, which translocate to the nucleus and regulate gene expression.
- Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) pathway: RAAS is a hormonal system that regulates blood pressure and fluid balance. RAAS consists of renin
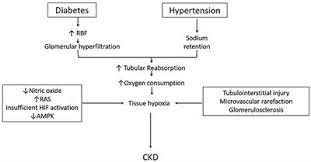
Etiology and risk factors
- The most common causes of CRF are diabetes mellitus and hypertension, which account for about two-thirds of the cases.
- Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetes is the leading cause of chronic kidney disease worldwide. Prolonged high blood sugar levels in diabetes can damage the small blood vessels and filters in the kidneys, leading to impaired kidney function over time.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Uncontrolled high blood pressure puts strain on the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to their gradual deterioration and eventual failure.
- Other causes include:
- Glomerulonephritis: This term refers to inflammation of the glomeruli, which are the tiny filters in the kidneys responsible for filtering waste and fluids from the blood. Chronic inflammation can lead to scarring and impaired kidney function.
- Pyelonephritis: This is a type of kidney infection that, if left untreated or recurrent, can cause damage to the kidney tissues and impair their function.
- Nephrosclerosis: This condition involves the hardening and narrowing of the blood vessels in the kidneys, often caused by high blood pressure or aging. The reduced blood flow can damage the kidney tissues and lead to CRF.
- Renal Calculi (Kidney Stones): When kidney stones block the flow of urine and cause repeated obstructions, they can damage the kidneys and lead to chronic kidney disease.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): SLE is an autoimmune disease that can affect various organs, including the kidneys. Immune system abnormalities may cause inflammation and damage to kidney tissues.
- Aminoglycosides: These are a class of antibiotics that, when used inappropriately or at high doses, can be toxic to the kidneys and lead to CRF.
- Hyperparathyroidism: Overactive parathyroid glands can disrupt calcium and phosphorus balance in the body, leading to kidney damage over time.
- Risk Factors for Developing CRF:
- Older Age: As people age, the risk of developing chronic kidney disease increases. The kidneys naturally undergo some decline in function with age.
- Family History: A family history of kidney disease may increase an individual's risk of developing CRF, indicating a possible genetic predisposition.
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to the progression of kidney disease, as it can worsen blood vessel damage and decrease blood flow to the kidneys.
- Obesity: Obesity is associated with an increased risk of diabetes and hypertension, both of which are major causes of CRF.
- Dyslipidemia: Abnormal levels of lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides) in the blood can contribute to kidney damage and the progression of CRF.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Conditions like heart disease and atherosclerosis can affect kidney health due to decreased blood flow and increased strain on the kidneys.
- Exposure to Nephrotoxins: Certain medications, environmental toxins, and substances like heavy metals can be harmful to the kidneys and contribute to CRF development.
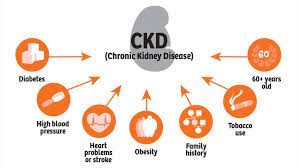
Clinical manifestations and symptoms
- The clinical manifestations and symptoms of CRF depend on the stage of the disease and the degree of uremia.
- They may be nonspecific and vary from person to person. Some of the common signs and symptoms are:
- Fatigue, weakness, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, weight loss
- Pruritus, dry skin, uremic frost
- Edema, hypertension, dyspnea, chest pain
- Anemia, bleeding tendency, bruising
- Confusion, lethargy, seizures, coma
- Polyuria, oliguria, anuria
- Hematuria, proteinuria
- Nocturia, dysuria
- Flank pain
- Bone pain, fractures
- Muscle cramps, restless leg syndrome
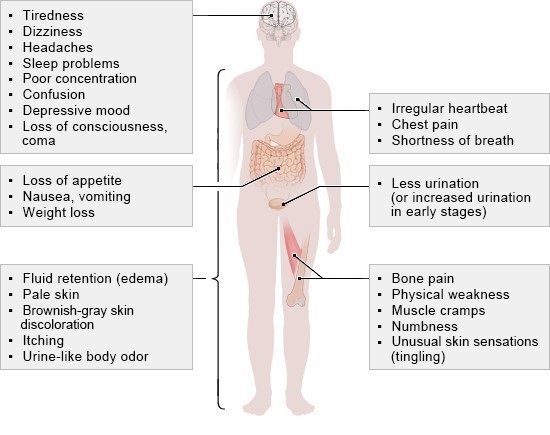
Diagnostic Evaluation and GFR Calculation
- The diagnosis of CRF is based on the presence of kidney damage or decreased GFR for three or more months.
- The GFR can be estimated by using serum creatinine level and other factors such as age, sex, race, and body size.
- The most commonly used formula is the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation:
- GFR = 141 x min (Scr/κ, 1)^α x max(Scr/κ , 1)^-1.209 x 0.993^Age x 1.018 [if female] x 1.159 [if black]
where Scr is serum creatinine in mg/dL,
κ is 0.7 for females and 0.9 for males,
α is -0.329 for females and -0.411 for males,
min indicates the minimum of Scr/κ or 1,
and max indicates the maximum of Scr/κ or 1.
- The stages of CKD are defined by the GFR as follows:
Stage 1: GFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m2 with evidence of kidney damage
Stage 2: GFR 60-89 mL/min/1.73 m2 with evidence of kidney damage
Stage 3a: GFR 45-59 mL/min/1.73 m2
Stage 3b: GFR 30-44 mL/min/1.73 m2
Stage 4: GFR 15-29 mL/min/1.73 m2
Stage 5: GFR <15 mL/min/1.73 m2 or on dialysis
- Other diagnostic tests that may be performed include:
- Blood tests: to measure electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), calcium, phosphorus, parathyroid hormone (PTH), albumin, hemoglobin, hematocrit, platelets, coagulation factors
- Urine tests: to measure urine volume, specific gravity, osmolality, pH, sodium, potassium
- Urine culture: to rule out infection
- Urine protein electrophoresis: to identify the type of proteinuria
- Renal ultrasound: to assess the size and shape of the kidneys and detect any obstruction or cysts
- CT scan or MRI: to provide more detailed images of the kidneys and detect any masses or lesions. They can reveal structural changes, such as cysts, tumors, or kidney stones, that may be contributing to kidney damage.
- Kidney biopsy: to obtain a tissue sample for histological examination and diagnosis of the underlying cause
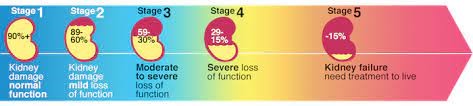
Management and Treatment
- The management and treatment of CRF aim to slow down the progression of the disease, prevent or treat the complications, and improve the quality of life of the patients.
- The main strategies include:
- Control of blood pressure: The target blood pressure for most patients with CKD is <140/90 mmHg, or <130/80 mmHg if there is significant proteinuria.
- Antihypertensive drugs that block the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), are preferred as they have renal-protective effects.
- However, they should be used with caution in patients with hyperkalemia, bilateral renal artery stenosis, or pregnancy.
- Other antihypertensive drugs that may be used include calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers, diuretics, and alpha-blockers.
- Control of blood glucose: The target glycemic control for patients with diabetes and CKD is a hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level of <7%.
- However, this may vary depending on the individual risk-benefit ratio. Oral hypoglycemic agents that are safe and effective in CKD include metformin, sulfonylureas, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors. Insulin therapy may be required in some cases.
- The dose and frequency of these agents may need to be adjusted according to the renal function.
- Control of dyslipidemia: The target lipid levels for patients with CKD are a low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level of <100 mg/dL, or <70 mg/dL if there is a high cardiovascular risk.
- Statins are the first-line drugs for lowering LDL-C and reducing cardiovascular events in CKD.
- However, they should be avoided in patients with advanced CKD (stage 4 or 5) or on dialysis, as they have no proven benefit and may increase the risk of adverse effects.
- Other lipid-lowering drugs that may be used include ezetimibe, fibrates, niacin, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Correction of anemia: The target hemoglobin level for patients with CKD is 10-12 g/dL.
- Anemia in CKD is mainly due to the reduced production of erythropoietin (EPO) by the kidneys.
- The treatment of anemia includes iron supplementation (oral or intravenous), EPO-stimulating agents (ESAs), and blood transfusions.
- Iron supplementation is indicated if the serum ferritin level is <100 ng/mL or the transferrin saturation is <20%.
- ESAs are indicated if the hemoglobin level is <10 g/dL and the iron status is adequate.
- Blood transfusions are indicated if the hemoglobin level is <7 g/dL or there are signs of tissue hypoxia.
- Management of mineral and bone disorders: The target levels for patients with CKD are a serum calcium level of 8.4-9.5 mg/dL, a serum phosphorus level of 2.7-4.6 mg/dL, and a serum PTH level of 2-9 times the upper limit of normal.
- Mineral and bone disorders in CKD are due to the impaired excretion of phosphorus, reduced synthesis of vitamin D, and increased secretion of PTH by the parathyroid glands.
- The treatment of mineral and bone disorders includes phosphate binders (such as calcium carbonate, calcium acetate, sevelamer, lanthanum carbonate, or iron-based binders), vitamin D analogs (such as calcitriol, paricalcitol, or doxercalciferol), and calcimimetics (such as cinacalcet).
- Dietary restriction of phosphorus intake and regular exercise are also recommended.
- Management of acid-base disorders: The target serum bicarbonate level for patients with CKD is 22-26 mEq/L.
- Acid-base disorders in CKD are due to the reduced ability of the kidneys to excrete hydrogen ions and reabsorb bicarbonate ions.
- The treatment of acid-base disorders includes sodium bicarbonate supplementation (oral or intravenous) and correction of any underlying causes such as dehydration, infection, or respiratory failure.
- Management of fluid and electrolyte disorders: The target fluid balance for patients with CKD is a weight gain of <5% between dialysis sessions or a urine output of >500 mL/day. Fluid and electrolyte disorders in CKD.
- Diet: A dietitian can help plan a diet that meets the nutritional needs of the patient while limiting the intake of sodium, potassium, phosphorus, protein, and fluid. This can help reduce the workload on the kidneys and prevent further damage.
- Lifestyle: Smoking cessation, regular exercise, weight management, stress reduction, and avoiding nephrotoxic substances (such as NSAIDs, contrast agents, and herbal remedies) can help improve the overall health of the patient and slow down the progression of CRF.
- Dialysis: This is a procedure that uses a machine or a membrane to filter the blood and remove waste products and excess fluid.
- It is usually indicated when the kidney function falls below 10% to 15% of normal or when the patient develops life-threatening complications such as uremia, hyperkalemia, or pulmonary edema.
- There are two types of dialysis: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. The choice depends on the patient's preference, medical condition, availability, and suitability.
- Kidney transplantation: This is a surgery that involves replacing a diseased kidney with a healthy one from a donor. It can restore normal kidney function and improve the quality of life of the patient. However, it also carries risks such as rejection, infection, and side effects of immunosuppressive drugs.

Nursing care and patient education
- The nursing care and patient education for CRF aim to provide holistic support to the patient and family, monitor the patient's condition and response to treatment, prevent complications, and promote self-care and adherence.
- Some of the nursing interventions include:
- Assessing the patient's history, physical examination, laboratory tests, vital signs, fluid balance, nutritional status, mental status, pain level, skin integrity, and potential complications.
- Administering medications as prescribed and monitoring for adverse effects.
- Providing dialysis care as ordered and ensuring proper access to site care, infection control, anticoagulation therapy, and complication management.
- Educating the patient and family about the disease process, treatment options, dietary restrictions, fluid intake, medication regimen, signs and symptoms of complications, when to seek medical attention and available resources and support groups.
- Encouraging the patient to participate in self-care activities such as daily hygiene, oral care, skin care, exercise, relaxation techniques, hobbies, and social interactions.
- Providing emotional support and counseling to the patient and family to cope with the stressors and challenges of living with CRF.

Summary
- CRF is a serious condition that affects multiple body systems and functions. It can be caused by various diseases that damage the kidneys over time.
- The management and treatment of CRF depend on the stage of the disease, the underlying cause, and the presence of complications.
- The main goals are to prevent the progression of the disease, manage symptoms, and prevent complications.
- The nursing care and patient education for CRF aim to provide holistic support to the patient and family, monitor the patient's condition and response to treatment, prevent complications, and promote self-care and adherence.
- It's essential to recognize and manage these risk factors early on to reduce the likelihood of chronic kidney disease development and its progression.
- Regular health checkups, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and controlling conditions like diabetes and hypertension can help in preventing CRF or delaying its onset.
- Moreover, if an individual is at higher risk due to family history or other factors, proactive monitoring of kidney function is advisable to catch any issues at an early stage and intervene appropriately.
Conclusion
- CRF is a challenging condition that requires multidisciplinary collaboration and individualized care.
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a significant and increasingly prevalent health condition worldwide, characterized by the progressive and irreversible decline in kidney function over an extended period.
- CKD poses a significant burden on individuals, families, and healthcare systems due to its potential to lead to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) requiring dialysis or kidney transplantation.
- The prevalence of CKD has been steadily rising, largely due to the increasing incidence of risk factors such as diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and aging populations.
- Early detection and intervention are vital in managing CKD effectively, as the condition often develops silently with few noticeable symptoms in its early stages.
- CKD is classified into five stages based on the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and the presence of kidney damage.
- Each stage represents varying degrees of kidney function impairment, ranging from mild (Stage 1) to severe (Stage 5), known as ESRD.
- Patients with CKD are at increased risk of developing cardiovascular complications, bone disorders, anemia, and other related comorbidities.
- Preventive measures play a pivotal role in tackling CKD, with lifestyle modifications, regular health check-ups, and the management of underlying conditions being essential in reducing the risk of disease progression.
- Additionally, early identification of CKD allows for interventions to slow down its progression and preserve kidney function.
- The management of CKD includes comprehensive care, focusing on blood pressure control, glycemic control (in diabetic patients), proteinuria reduction, and the use of medications to address complications and coexisting conditions.
- Diet and lifestyle modifications, including a low-sodium diet, regular physical activity, and smoking cessation, can also contribute to better outcomes.
- In advanced stages of CKD, renal replacement therapies such as dialysis or kidney transplantation become necessary.
- Kidney transplantation offers the best long-term outcomes and quality of life for eligible candidates with ESRD, but access to transplantation remains a challenge due to organ shortage and logistical barriers.
- By addressing CKD comprehensively through early detection, proper management, and education, healthcare professionals and policymakers can make significant strides in enhancing the lives of individuals living with this challenging condition.
- Nurses play a vital role in providing quality care and education to patients with CRF and their families.
- By applying evidence-based practice, nurses can help improve the outcomes and quality of life of patients with CRF.
Nephrotic Syndrome
Introduction to nephrotic syndrome
- Nephrotic syndrome is a condition that results from damage to the glomeruli, the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys that filter waste and excess water from the blood.
- Normally, the glomeruli keep blood protein (mainly albumin) from leaking into the urine, as it is needed to maintain the right amount of fluid in the body.
- When the glomeruli are damaged, they allow too much protein to escape into the urine, leading to nephrotic syndrome.
- Nephrotic syndrome can be caused by many diseases and conditions that affect the kidneys, such as:
- Diabetes
- lupus
- amyloidosis
- minimal change disease
- focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
- membranous nephropathy.
- Nephrotic syndrome is a kidney disorder that causes your body to lose too much protein in your urine. It can lead to swelling, high cholesterol, blood clots, infections, and kidney failure.
- The underlying cause of nephrotic syndrome determines the prognosis and treatment of the condition.
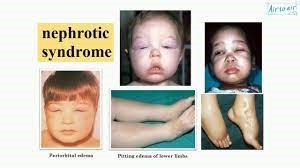
Pathophysiology
- The pathophysiology of nephrotic syndrome is complex and involves various mechanisms that disrupt the normal function of the glomerular filtration barrier.
- The primary components of this barrier include the glomerular endothelium, basement membrane, and podocytes (specialized cells in the kidney).
- The pathophysiology of nephrotic syndrome can be summarized as follows:
- Glomerular Injury: Nephrotic syndrome often begins with injury to the glomeruli. Various factors can trigger this injury, including infections (e.g., streptococcal infection), autoimmune diseases (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus), medications, and underlying kidney diseases (e.g., minimal change disease, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis).
- Increased Permeability of the Glomerular Capillaries: In response to injury, the glomerular capillaries become more permeable. This increased permeability allows larger molecules, including proteins like albumin, to leak from the blood into the urinary space (glomerular ultrafiltrate).
- Proteinuria: The increased permeability of the glomerular capillaries leads to significant proteinuria, which is the hallmark of nephrotic syndrome. Large amounts of protein, especially albumin, are lost in the urine. This loss of proteins from the blood results in decreased oncotic pressure in the bloodstream.
- Hypoalbuminemia: As a consequence of proteinuria, the levels of albumin in the blood decrease, leading to hypoalbuminemia. This reduction in circulating albumin affects the colloid osmotic pressure in the blood vessels, causing a decrease in plasma oncotic pressure.
- Edema Formation: The decrease in plasma oncotic pressure results in reduced colloid osmotic pressure within the blood vessels. As a result, fluid from the blood vessels tends to leak into the interstitial spaces, leading to generalized edema, especially in the face, abdomen, and lower extremities.
- Hyperlipidemia: The liver responds to the decreased oncotic pressure by increasing the synthesis of lipoproteins and cholesterol. This leads to hyperlipidemia, characterized by elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood.
- Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Activation: The decrease in blood volume due to fluid leakage and hypoalbuminemia activates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). This system leads to increased sodium and water retention by the kidneys, exacerbating edema.
- Hypercoagulability: Nephrotic syndrome is associated with a hypercoagulable state, increasing the risk of thromboembolic complications, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). The loss of antithrombin III in the urine contributes to this hypercoagulability.
- Immunosuppression: Nephrotic syndrome can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, particularly bacterial infections.
- Complications: Chronic nephrotic syndrome can lead to progressive kidney damage and, in some cases, chronic kidney disease (CKD). Additionally, the loss of immunoglobulins in the urine may lead to an increased risk of infections.
- It's important to note that nephrotic syndrome can have various underlying causes, and the exact pathophysiology may differ depending on the specific etiology.
- However, the common feature in all cases is the disruption of the glomerular filtration barrier, leading to proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, edema, and other associated complications.
Clinical manifestations and symptoms
- The main signs and symptoms of nephrotic syndrome are:
- Proteinuria: The presence of large amounts of protein in the urine (>3.5 g per day or >40 mg per hour in children), which can make the urine foamy or frothy.
- Hypoalbuminemia: The low level of albumin in the blood (<3.5 g/dL), which can cause fluid to leak out of the blood vessels into the tissues.
- Edema: The swelling of body parts due to fluid accumulation, especially in the ankles, feet, legs, face, and around the eyes. Edema can also affect the abdomen (ascites) and the lungs (pleural effusion).
- Hyperlipidemia: The high level of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood, can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Weight gain: The increase in body weight due to fluid retention and increased fat deposits.
- Fatigue: The feeling of tiredness and weakness due to low protein levels and anemia.
- Loss of appetite: The reduced desire to eat due to nausea, abdominal discomfort, or altered taste sensation.
- Blood clots: The formation of clots in the blood vessels due to the loss of proteins that prevent clotting, such as antithrombin III. Blood clots can cause serious complications such as pulmonary embolism (clot in the lung) or deep vein thrombosis (clot in the leg).
- Infections: The increased susceptibility to infections due to the loss of immunoglobulins (antibodies) and complement proteins that fight against bacteria and viruses.
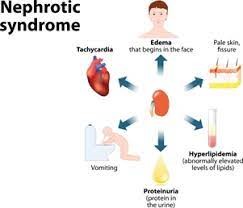
Diagnostic Evaluation
- The diagnosis of nephrotic syndrome is based on:
- Urine test: To check for proteinuria, which is usually confirmed by a 24-hour urine collection or a spot urine sample with a protein-to-creatinine ratio.
- Blood test: To measure albumin, cholesterol, triglycerides, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, electrolytes, glucose, and complete blood count (CBC). These tests can help assess the severity of nephrotic syndrome and its complications.
- Kidney biopsy: To obtain a small sample of kidney tissue for microscopic examination. This can help identify the cause and type of glomerular damage and guide treatment decisions.
Management and Treatment
- The treatment of nephrotic syndrome depends on:
- The underlying cause: Some causes of nephrotic syndrome are treatable with specific medications or interventions, such as diabetes (with insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents), lupus (with corticosteroids or immunosuppressants), or blood clot (with anticoagulants).
- The severity of symptoms: Some symptoms of nephrotic syndrome are manageable with supportive measures, such as edema (with diuretics or fluid restriction), hyperlipidemia (with statins or dietary modification), or infections (with antibiotics or prophylaxis).
- The response to treatment: Some patients with nephrotic syndrome may respond well to corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, which can reduce inflammation and proteinuria. Others may require more aggressive treatments such as plasmapheresis (removal of plasma from the blood) or dialysis (removal of waste products from the blood).
- The management of nephrotic syndrome involves both non-pharmacological and pharmacological approaches. Here are the key aspects of treatment:
- Non-pharmacological Management:
- a. Dietary Modifications: Reducing salt intake can help manage edema by minimizing fluid retention. A low-sodium diet is often recommended. Additionally, dietary changes to control cholesterol and triglyceride levels may be advised.
- b. Fluid Management: In some cases, fluid intake may need to be restricted to prevent fluid overload and further edema.
- c. Rest and Physical Activity: Adequate rest and appropriate levels of physical activity can help manage symptoms and promote overall well-being.
- d. Infection Prevention: Since nephrotic syndrome can increase the risk of infections, especially in children, steps to prevent infections such as vaccinations and hygiene measures are essential.
- Pharmacological Treatment:
- a. Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are the mainstay of treatment for many cases of nephrotic syndrome. They help reduce inflammation in the kidneys, which can lead to decreased proteinuria and improved kidney function.
- b. Immunosuppressants: In cases where corticosteroids alone are not effective, or if the underlying cause of nephrotic syndrome is an immune-related condition, immunosuppressive medications like cyclophosphamide or mycophenolate mofetil may be prescribed to suppress the immune system and reduce kidney inflammation.
- c. Diuretics: Diuretics, commonly known as water pills, may be used to help control edema by promoting urine output and reducing fluid retention.
- d. ACE Inhibitors or ARBs: Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are blood pressure medications that also have protective effects on the kidneys. They can help reduce proteinuria and slow the progression of kidney damage.
- e. Statins: Statins may be prescribed to manage elevated cholesterol levels in nephrotic syndrome.
- Treatment of Complications:
- a. Blood Clot Prevention: Individuals with nephrotic syndrome are at an increased risk of blood clot formation. Medications to prevent blood clots, such as anticoagulants, may be prescribed when necessary.
- b. Treatment of Infections: Prompt treatment of infections is essential to prevent complications and exacerbation of kidney damage.
- Monitoring and Follow-up:
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial to monitor kidney function, blood pressure, and response to treatment. Adjustments to the treatment plan may be made based on the individual's condition and response to therapy.
Nursing Care and Patient Education
- The nursing care and patient education for nephrotic syndrome include:
- Monitoring vital signs, especially blood pressure and weight, to detect changes in fluid status and cardiovascular risk.
- Assessing urine output and appearance, to evaluate proteinuria and renal function.
- Measuring edema, using a tape measure or a pitting scale, to monitor fluid retention and response to diuretics.
- Checking laboratory results, such as albumin, cholesterol, BUN, creatinine, and electrolytes, to identify abnormalities and complications.
- Administering medications, such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, diuretics, statins, anticoagulants, or antibiotics, as prescribed by the physician. Monitoring for side effects and adverse reactions, such as infection, bleeding, or hyperglycemia.
- Providing dietary education, such as limiting sodium intake (to <2 g per day), reducing saturated fat and cholesterol intake (to <7% and <200 mg per day, respectively), increasing protein intake (to 0.8-1 g per kg per day), and avoiding alcohol and caffeine. Encouraging adequate fluid intake (to 1.5 L per day or as prescribed).
- Promoting skin care, such as applying moisturizers, avoiding scratching, and preventing pressure ulcers. Educating the patient on how to prevent skin infections and report signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, swelling, or pus.
- Encouraging physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, to improve circulation, muscle strength, and mood. Advise the patient to avoid strenuous exercise or activities that increase the risk of injury or bleeding.
- Providing emotional support, such as listening to the patient's concerns, fears, and frustrations. Offering reassurance, information, and resources. Refer the patient to a counselor or a support group if needed.

Summary
- Nephrotic syndrome is a kidney disorder that causes excessive protein loss in the urine.
- It can lead to swelling, high cholesterol, blood clots, infections, and kidney failure.
- It can be caused by many diseases and conditions that damage the glomeruli. The diagnosis is based on the urine test, blood test, and kidney biopsy.
- The treatment depends on the underlying cause, the severity of symptoms, and the response to treatment.
- Nursing care and patient education focus on monitoring vital signs, urine output, edema, and laboratory results; administering medications; providing dietary education; promoting skin care; encouraging physical activity; and providing emotional support.
- Nephrotic syndrome is a multifaceted kidney disorder with diverse underlying causes and complex clinical manifestations.
- Early detection, accurate diagnosis, and timely and appropriate intervention are crucial in mitigating its impact and preventing long-term complications.
- Ongoing research and advances in treatment modalities offer hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for individuals living with nephrotic syndrome.
Conclusion
- Nephrotic syndrome is a complex and potentially serious kidney disorder characterized by the abnormal excretion of protein in the urine, low levels of proteins in the blood, edema (swelling), and elevated cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
- It can affect individuals of all ages, but it is more prevalent in children, particularly between the ages of 2 and 6.
- The condition results from damage to the glomeruli, which are the tiny filtering units within the kidneys responsible for removing waste products and excess fluids from the blood.
- Various underlying causes can lead to nephrotic syndrome, including primary glomerular diseases such as minimal change disease, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and membranous nephropathy, as well as secondary causes like diabetes, lupus, and certain infections.
- Clinically, nephrotic syndrome presents with hallmark symptoms such as significant edema, particularly around the eyes, ankles, and feet, along with foamy urine due to excessive protein loss.
- Patients may also experience fatigue, weight gain, and a heightened risk of infections and blood clots.
- Diagnosis is based on a combination of clinical presentation, urine analysis revealing proteinuria, and blood tests indicating hypoalbuminemia and hyperlipidemia. A kidney biopsy is often necessary to identify the specific underlying cause and guide appropriate treatment.
- Treatment for nephrotic syndrome primarily focuses on managing the symptoms, reducing proteinuria, and preventing complications. Corticosteroids are the mainstay of therapy for many primary glomerular diseases, with additional immunosuppressive agents used for more severe or refractory cases. Diuretics are commonly prescribed to alleviate edema, while ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers are used to control blood pressure and reduce proteinuria.
- Despite advances in treatment, some cases of nephrotic syndrome may progress to chronic kidney disease, leading to end-stage renal failure and requiring dialysis or kidney transplantation. Long-term monitoring and management are essential to preserve kidney function and improve the overall quality of life for affected individuals.
- Nurses can help patients with nephrotic syndrome achieve optimal outcomes and quality of life by collaborating with the healthcare team and empowering the patients to manage their condition.
Renal Calculus
Introduction to Renal Calculus
- Renal calculus, commonly known as kidney stones, is a prevalent urological condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide.
- These stones are solid masses formed within the kidneys due to the crystallization of minerals and salts in the urine.
- Renal calculus presents a significant health challenge, causing pain, urinary obstruction, and potential complications if left untreated.
- This introduction aims to provide an overview of renal calculus, including its causes, symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and the crucial role of nursing care in its management.
- By understanding the complexities of renal calculus, healthcare professionals can enhance their ability to provide comprehensive care and support for patients affected by this condition.
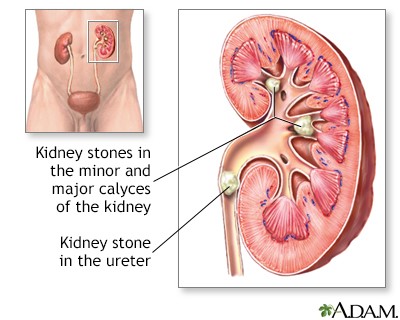
Etiology and Risk Factors
- The etiology of renal calculus is multifactorial and involves genetic, metabolic, environmental, dietary, and lifestyle factors
- Some of the risk factors for renal calculus are:
- Family or personal history of renal calculus
- Dehydration or low fluid intake
- High intake of animal protein, sodium, oxalate, or calcium
- Low intake of citrate or magnesium
- Obesity or diabetes mellitus
- Hyperparathyroidism or gout
- Urinary tract infection or stasis
- Medications such as diuretics, antacids, or vitamin C supplements
Pathophysiology
- Supersaturation of urine Urine contains various substances like calcium, oxalate, uric acid, and phosphate. When the concentration of these substances becomes too high, the urine becomes supersaturated, meaning it contains more dissolved solutes than it can normally hold.
- Nucleation Supersaturation provides an environment where the substances can crystallize and form solid particles. This initial process is called nucleation.
- Crystal growth Once nucleation occurs, these tiny crystals can grow larger over time. This growth is influenced by factors like the concentration of substances, pH levels, and the presence of inhibitors or promoters of crystal formation.
- Aggregation Crystals may stick together, forming aggregates. This is facilitated by various factors, including the physical shape of the crystals and the presence of substances that promote aggregation.
- Retention in the kidney Depending on their size, crystals or small stones may pass out of the kidney and into the urinary tract. However, larger stones may become trapped in the kidney's collecting system.
- Obstruction and stasis When a stone becomes lodged in the urinary tract, it can cause partial or complete obstruction. This leads to stasis or a slowdown of urine flow. Stasis allows for further crystallization and stone growth.
- Inflammatory response The presence of a kidney stone can lead to irritation and inflammation of the surrounding tissues. This can result in symptoms like pain, hematuria (blood in urine), and occasionally, infection.
- Secondary factors Various factors can contribute to stone formation, including genetics, dietary habits, dehydration, certain medical conditions (e.g., hyperparathyroidism), medications, and urinary tract abnormalities.
- Types of stones The composition of kidney stones can vary. The most common types include calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, uric acid, and struvite (associated with infections).
- Location of stone formation Stones can form anywhere in the urinary tract, including the kidney (nephrolithiasis), ureter (ureterolithiasis), bladder (cystolithiasis), or urethra (urethrolithiasis).
Clinical Manifestations and Symptoms
- The clinical manifestations and symptoms of renal calculus depend on the size, location, and movement of the stone
- The most common symptom of renal calculus is renal colic, which is a sudden and severe pain in the flank, back, or abdomen that radiates to the groin or genitalia
- Other symptoms of renal calculus are:
- Hematuria or blood in the urine
- Dysuria or painful urination
- Frequency or urgency of urination
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fever or chills
Diagnostic Evaluation
- The diagnostic evaluation of renal calculus involves a combination of history taking, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies
- Some of the diagnostic tests for renal calculus are:
- Urinalysis to detect hematuria, infection, pH, specific gravity, and crystals
- Urine culture and sensitivity to identify the causative organism and antibiotic susceptibility in case of infection
- Serum chemistry to measure electrolytes, calcium, phosphorus, uric acid, creatinine, and blood urea nitrogen levels
- Complete blood count to detect leukocytosis or anemia in case of infection or bleeding
- Imaging studies such as ultrasound, plain abdominal x-ray (KUB), intravenous pyelogram (IVP), computed tomography (CT) scan, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to visualize the size, shape, location, and number of stones
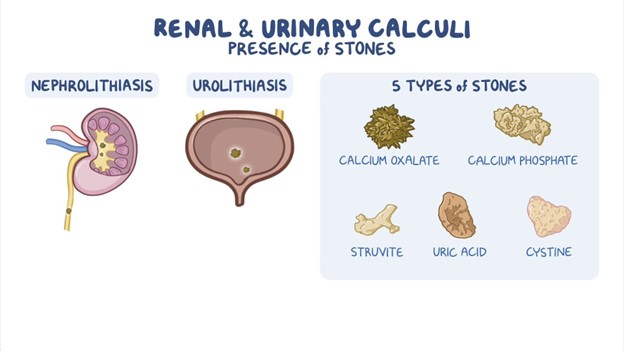
Management and Treatment
- The management and treatment of renal calculus aim to relieve pain, facilitate stone passage, prevent infection, and prevent recurrence
- Some of the management and treatment options for renal calculus are:
- Analgesics such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioids to reduce pain and inflammation
- Antispasmodics such as hyoscyamine or oxybutynin to relax the smooth muscle of the ureter and facilitate stone passage
- Antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin or nitrofurantoin to treat or prevent infection
- Fluid therapy to increase urine output and dilute urine concentration
- Dietary modifications such as increasing fluid intake; reducing intake of animal protein, sodium, oxalate, or calcium; increasing intake of citrate or magnesium; and adjusting pH according to stone type
- Lithotripsy such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) or percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) breaks up large stones into smaller fragments that can be passed in the urine
- Surgery such as ureteroscopy (URS), cystoscopy (CS), or open surgery to remove stones that are too large, impacted, infected, or causing obstruction
Prevention Strategies and Lifestyle Modifications
- The prevention strategies and lifestyle modifications for renal calculus aim to reduce the risk factors and recurrence of stone formation
- Some of the prevention strategies and lifestyle modifications for renal calculus are:
- Drinking at least 2.5 liters of fluid per day to maintain urine output above 2 liters per day
- Avoiding dehydration and excessive sweating
- Limiting intake of animal protein, sodium, oxalate, or calcium according to stone type
- Increasing intake of citrate or magnesium according to stone type
- Adjusting pH according to stone type
- Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding obesity
- Controlling blood glucose and blood pressure levels
- Treating underlying conditions such as hyperparathyroidism or gout
- Taking medications such as thiazide diuretics, potassium citrate, allopurinol, or antibiotics as prescribed to prevent stone formation
Nursing Care and Patient Education
- The nursing care and patient education for renal calculus involve providing physical and emotional support, monitoring vital signs and urine output, administering medications and fluids, teaching self-care measures, and providing discharge instructions
- Some of the nursing care and patient education for renal calculus are:
- Assessing pain level and location and administering analgesics as prescribed
- Encouraging fluid intake and offering oral or intravenous fluids as ordered
- Straining urine and inspecting for stone passage
- Collecting urine specimens for urinalysis, culture, and sensitivity as ordered
- Monitoring vital signs, especially temperature, pulse, and blood pressure
- Observing for signs of infection such as fever, chills, leukocytosis, or positive urine culture
- Educating the patient about the etiology, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of renal calculus
- Instructing the patient to drink adequate fluids; follow dietary modifications; take medications as prescribed; report any changes in pain, urine color, or urine output; and seek medical attention if symptoms worsen or persist
- Referring the patient to a urologist or nephrologist for follow-up care and stone analysis
Summary
- Renal calculus is a common urologic disorder that can cause significant morbidity and complications if not treated promptly and effectively
- Renal calculus is caused by the crystallization of minerals and organic substances in the urine due to various genetic, metabolic, environmental, dietary, and lifestyle factors
- Renal calculus can present with renal colic, hematuria, dysuria, frequency, urgency, nausea, vomiting, fever, or chills depending on the size, location, and movement of the stone
- Renal calculus can be diagnosed by history taking, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies that can reveal the size, shape, location, and number of stones
- Renal calculus can be managed by analgesics, antispasmodics, antibiotics, fluid therapy, dietary modifications, lithotripsy, or surgery depending on the severity and type of the stone
- Renal calculus can be prevented by drinking adequate fluids; limiting intake of animal protein, sodium, oxalate, or calcium; increasing intake of citrate or magnesium; adjusting pH according to stone type; maintaining a healthy weight; controlling blood glucose and blood pressure levels; treating underlying conditions; and taking medications as prescribed
Conclusion
- Renal calculus is a challenging condition that requires comprehensive knowledge and skills from nurses to provide optimal care and education for patients.
- Nurses play a vital role in relieving pain, facilitating stone passage, preventing infection, preventing recurrence, and promoting health and well-being for patients with renal calculus.
- Their expertise in managing the condition and offering holistic care significantly impacts patient outcomes and quality of life.
- Through diligent monitoring, timely interventions, and patient education, nurses contribute to the successful management and long-term prevention of renal calculus.
- The compassionate and attentive care provided by nurses plays a crucial role in supporting patients throughout their journey with renal calculus, fostering a positive and comforting healthcare experience.
Glomerulonephritis
Pathophysiology
- Glomerulonephritis is caused by an immunologic mechanism that triggers inflammation and proliferation of glomerular tissue.
- This can result in damage to the glomerular basement membrane, mesangium, or capillary endothelium.
- The damage can impair the filtration function of the glomeruli, leading to hematuria (blood in urine), proteinuria (protein in urine), azotemia (increased waste products in blood), hypertension (high blood pressure), and edema (swelling).
- The inflammation can also activate the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which further increases blood pressure and fluid retention.
- The type and location of the immune complex deposition determine the different types of glomerulonephritis, such as:
- post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
- IgA nephropathy
- membranous nephropathy
- rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis
- lupus nephritis

Clinical manifestations and symptoms
- The signs and symptoms of glomerulonephritis vary depending on the type, severity, and duration of the condition.
- Some of the common signs and symptoms are:
- Hematuria: Blood in urine can make it appear pink or brown-colored. It indicates the presence of red blood cells in urine due to damage to the glomeruli.
- Proteinuria: Protein in urine can make it appear foamy. It indicates the loss of protein from the blood due to increased permeability of the glomeruli.
- Azotemia: Increased waste products such as creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in the blood indicate the reduced filtration function of the kidneys.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can result from fluid retention, activation of the RAAS, or damage to the renal arteries.
- Edema: Swelling can result from fluid retention due to decreased urine output or loss of protein from the blood. It is usually seen in the face, hands, feet, and abdomen.
- Weight gain: Weight gain can result from fluid retention due to decreased urine output or loss of protein from the blood.
- Oliguria or anuria: Decreased or absent urine output can result from severe damage to the glomeruli or acute kidney failure.
- Fatigue: Fatigue can result from anemia, electrolyte imbalance, or uremia (buildup of waste products in the blood).
- Headache: Headache can result from hypertension, electrolyte imbalance, or uremia.
- Nausea and vomiting: Nausea and vomiting can result from electrolyte imbalance or uremia.
- Dyspnea: Difficulty breathing can result from pulmonary edema due to fluid overload or uremic pleuritis (inflammation of the lining of the lungs).
- Flank pain: Pain in the back or side can result from inflammation or enlargement of the kidneys.
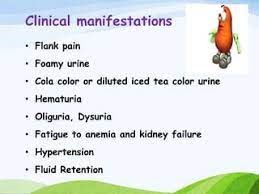
Diagnostic Evaluation
- The diagnosis of glomerulonephritis is based on the history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
- Some of the diagnostic tests are:
- Urinalysis: Urinalysis can detect hematuria, proteinuria, and red blood cell casts in the urine. It can also measure the specific gravity, pH, and presence of nitrites, leukocytes, glucose, or ketones in the urine.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can measure the levels of creatinine, BUN, electrolytes, albumin, cholesterol, and complement components in the blood. They can also detect antibodies such as antistreptolysin O (ASO), antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA), anti-glomerular basement membrane (antiGBM) antibodies, or antinuclear antibodies (ANA) in the blood.
- Kidney biopsy: Kidney biopsy is the definitive test for glomerulonephritis. It involves taking a small sample of kidney tissue and examining it under a microscope. It can reveal the type, location, and extent of damage to the glomeruli and help determine the cause and prognosis of glomerulonephritis.
- Imaging studies: Imaging studies such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or renal angiography can assess the size, shape, and function of the kidneys and detect any abnormalities or complications.
Management and Treatment
- The management and treatment of glomerulonephritis depend on the underlying cause, the severity of symptoms, and the extent of kidney damage.
- The main goals are to reduce inflammation, prevent complications, and preserve kidney function. Some of the common interventions include:
- Antibiotics. If the glomerulonephritis is caused by a bacterial infection, such as strep throat, antibiotics are prescribed to eliminate the infection and prevent further damage to the kidneys.
- Corticosteroids and immunosuppressants. These drugs are used to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation in the glomeruli. They are usually given for autoimmune disorders, such as lupus, or for severe cases of glomerulonephritis that do not respond to other treatments.
- Diuretics. These drugs help increase urine output and reduce fluid retention and swelling. They also help lower blood pressure, which can reduce the strain on the kidneys.
- Antihypertensives. These drugs help control high blood pressure, which is a common complication of glomerulonephritis. High blood pressure can worsen kidney damage and increase the risk of cardiovascular problems.
- Anticoagulants. These drugs help prevent blood clots from forming in the kidneys or other parts of the body. They are usually given to patients with nephrotic syndrome, which is a condition that causes high levels of protein in the urine and low levels of protein in the blood.
- Dialysis. This is a procedure that uses a machine to filter the blood and remove waste products and excess fluid when the kidneys are unable to do so. Dialysis may be needed temporarily or permanently for patients with acute or chronic kidney failure.
- Kidney transplant. This is a surgery that involves replacing a damaged kidney with a healthy one from a donor. Kidney transplant may be an option for patients with end-stage renal disease who do not respond to dialysis or other treatments.
Nursing care and patient education
- The nursing care for patients with glomerulonephritis involves monitoring their vital signs, urine output, fluid balance, electrolyte levels, and kidney function tests.
- The nurse also administers medications as prescribed and provides supportive care to relieve symptoms and prevent complications.
- Some of the nursing interventions include:
- Assessing for signs and symptoms of fluid overload, such as edema, weight gain, crackles in the lungs, jugular vein distension, and shortness of breath. The nurse measures the patient's intake and output, daily weight, and abdominal girth, and reports any abnormal findings to the physician.
- Administering diuretics as ordered and monitoring their effects on urine output, fluid balance, electrolyte levels, and blood pressure. The nurse also educates the patient on the importance of taking diuretics as prescribed and reporting any side effects, such as dehydration, muscle cramps, or dizziness.
- Restricting fluid intake as ordered and providing oral care to prevent dryness of the mouth. The nurse also educates the patient on how to measure and record their fluid intake and how to recognize signs of dehydration, such as thirst, dry skin, or dark urine.
- Restricting sodium intake as ordered and providing low-sodium diet options to prevent fluid retention and hypertension. The nurse also educates the patient on how to read food labels and avoid high-sodium foods, such as processed meats, canned soups, or salty snacks.
- Restricting protein intake as ordered and providing high-quality protein sources to prevent proteinuria and malnutrition. The nurse also educates the patient on how to choose foods that are rich in protein but low in phosphorus and potassium, such as eggs, lean meats, or dairy products.
- Administering corticosteroids and immunosuppressants as ordered and monitoring their effects on inflammation, infection, blood sugar levels, and bone density. The nurse also educates the patient on how to take these drugs as prescribed and reports any side effects, such as weight gain, mood changes, increased susceptibility to infections, or osteoporosis.
- Administering antihypertensives as ordered and monitoring their effects on blood pressure and kidney function. The nurse also educates the patient on how to take these drugs as prescribed and reports any side effects, such as hypotension, headache, or fatigue.
- Administering anticoagulants as ordered and monitoring their effects on bleeding time and clotting factors. The nurse also educates the patient on how to take these drugs as prescribed and reports any side effects, such as bruising, bleeding gums, or hematuria.
- Preparing the patient for dialysis or kidney transplant if indicated and providing preoperative and postoperative care. The nurse also educates the patient on what to expect during and after the procedure, how to care for the dialysis access site or the transplanted kidney, and how to prevent infection and rejection.
- The patient education for glomerulonephritis involves teaching the patient about the disease process, the treatment options, and the lifestyle modifications that can help prevent or delay kidney damage.
- Some of the topics that the nurse should cover include:
- The causes and risk factors of glomerulonephritis and how to prevent or treat them. For example, the nurse should advise the patient to seek medical attention for any signs of infection, such as fever, sore throat, or skin rash, and to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed.
- The signs and symptoms of glomerulonephritis and how to monitor them. For example, the nurse should instruct the patient to check their urine for color, clarity, and odor, and to report any changes, such as blood, protein, or foul smell, to the physician.
- The complications of glomerulonephritis and how to recognize and prevent them. For example, the nurse should warn the patient about the signs and symptoms of acute or chronic kidney failure, such as nausea, vomiting, confusion, or seizures, and to seek emergency care if they occur.
- The importance of adhering to the prescribed medication regimen and following up with regular blood tests and urine tests to evaluate the kidney function and the response to treatment. The nurse should also remind the patient to keep a list of their medications and their dosages and to inform their health care providers about any allergies or drug interactions.
- The importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle that can support kidney health and overall wellbeing. The nurse should encourage the patient to quit smoking, limit alcohol intake, exercise regularly, manage stress, and follow a balanced diet that is low in sodium, protein, phosphorus, and potassium. The nurse should also provide resources and referrals for smoking cessation programs, nutrition counseling, physical therapy, or mental health services as needed.

Summary
- Glomerulonephritis is a condition that causes inflammation and damage to the glomeruli, which are the tiny filters in the kidneys that remove waste products and excess fluid from the blood.
- Glomerulonephritis can be caused by various factors, such as infections, immune disorders, vascular disorders, or genetic disorders.
- Glomerulonephritis can lead to impaired kidney function and potential complications, such as chronic kidney disease, acute kidney failure, nephrotic syndrome, or cardiovascular problems.
- Glomerulonephritis is diagnosed by physical examination, medical history, urine tests, blood tests, kidney biopsy, or imaging tests.
- Glomerulonephritis is treated by addressing the underlying cause, reducing inflammation, preventing complications, and preserving kidney function.
- The treatment options may include antibiotics, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, diuretics, antihypertensives, anticoagulants, dialysis, or kidney transplants.
- The nursing care for patients with glomerulonephritis involves monitoring their vital signs, urine output, fluid balance, electrolyte levels, and kidney function tests; administering medications as prescribed; and providing supportive care to relieve symptoms and prevent complications.
- The patient education for glomerulonephritis involves teaching the patient about the disease process, the treatment options, and the lifestyle modifications that can help prevent or delay kidney damage.
Conclusion
- Glomerulonephritis is a serious renal disorder that requires vigilant nursing care and prompt intervention.
- By understanding the pathophysiology, the clinical manifestations, the diagnostics, the medical management, and the nursing interventions of glomerulonephritis, the nurse can provide effective care and education to patients with this condition and help them achieve optimal outcomes.
- The consequences of glomerulonephritis extend far beyond the kidneys, impacting the overall health and well-being of affected individuals.
- It can lead to a range of symptoms, such as hematuria, proteinuria, hypertension, and edema, which, if left untreated, can progress to chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal failure.
- As a result, early detection, accurate diagnosis, and prompt intervention are paramount in managing this condition effectively.
- Treatment strategies for glomerulonephritis are diverse and depend on the underlying cause and severity of the disease.
- Immunosuppressive medications, antihypertensive drugs, and dietary modifications are often components of the therapeutic approach.
- In some cases, particularly those associated with autoimmune conditions, targeted therapies aimed at modulating the immune response may be employed.
- The long-term prognosis for individuals with glomerulonephritis varies significantly, with some experiencing complete remission and others facing a chronic and progressive course.
- Regular monitoring, adherence to treatment plans, and lifestyle modifications can play crucial roles in managing the condition and preserving kidney function.
Hematuria
Introduction
- Hematuria is the presence of blood or blood cells in the urine.
- It can be classified as gross hematuria, which is visible to the naked eye, or microscopic hematuria, which is detected only by laboratory tests.
- Hematuria can be a sign of various urinary tract disorders, such as infections, stones, tumors, trauma, or systemic diseases.
- Hematuria is not a disease in itself but rather a symptom that may signal an array of diverse and often complex medical conditions affecting the urinary system or other bodily systems.
- The discovery of blood in the urine, whether visible to the naked eye (gross hematuria) or only detectable through microscopic examination (microscopic hematuria), can evoke a range of emotions and concerns.
- While it may sometimes result from benign and self-limiting causes, hematuria can also serve as a red flag for potentially serious and life-altering conditions, including urinary tract infections, kidney disease, bladder cancer, or systemic disorders affecting the body's coagulation system.

Pathophysiology
- Hematuria can result from injury or damage to any part of the urinary tract, from the kidneys to the urethra.
- The kidneys filter blood and produce urine, which passes through the ureters to the bladder.
- The bladder stores urine until it is expelled through the urethra during urination.
- Blood can enter the urine at any point along this pathway, either from the glomeruli (the filtering units of the kidneys), the renal tubules (the structures that reabsorb water and electrolytes from the urine), the interstitium (the tissue between the tubules), the renal pelvis (the funnel-shaped structure that collects urine from the kidneys), the ureters, the bladder, or the urethra.
- The amount and color of blood in the urine depend on the site and severity of bleeding, as well as the presence of other substances that may alter its appearance.
Etiology and risk factors
- Hematuria can have many possible causes, which can be divided into glomerular and non-glomerular categories.
- Glomerular causes are related to inflammation or damage to the glomeruli which can impair their filtering function and allow blood cells to leak into the urine.
- Some examples of glomerular causes are:
- glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the glomeruli due to various immune-mediated or infectious processes)
- IgA nephropathy (a common form of glomerulonephritis caused by deposits of IgA antibodies in the glomeruli)
- Alport syndrome (a genetic disorder that affects the structure of collagen in the glomeruli)
- thin basement membrane disease (a benign condition characterized by a thinning of the glomerular basement membrane)
- Non-glomerular causes are related to injury or disease of any other part of the urinary tract such as:
- infections (e.g. cystitis pyelonephritis prostatitis urethritis)
- stones (e.g. kidney stones bladder stones)
- tumors (e.g. renal cell carcinoma bladder cancer prostate cancer)
- trauma (e.g. blunt or penetrating injury to the kidneys or lower urinary tract)
- systemic diseases (e.g. sickle cell anemia hemophilia anticoagulant therapy)
- medications (e.g. aspirin warfarin rifampin)
- Some risk factors for hematuria are:
- age (older adults are more likely to have urinary tract disorders that cause hematuria)
- sex (men are more likely to have prostate problems that cause hematuria)
- family history (genetic disorders such as Alport syndrome or polycystic kidney disease can cause hematuria)
- race (African Americans are more likely to have sickle cell anemia that causes hematuria) occupation (exposure to certain chemicals or substances such as benzene or aristolochic acid can cause hematuria)
- smoking (increases the risk of bladder cancer that causes hematuria)
- strenuous exercise (can cause transient hematuria due to mechanical stress on the urinary tract or dehydration)
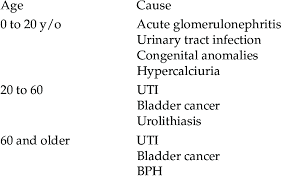
Diagnostic Evaluation
- The diagnosis of hematuria involves a thorough history and physical examination, as well as laboratory and imaging tests.
- The history should include questions about the onset, duration, frequency, and severity of hematuria, as well as any associated symptoms, risk factors, medications, family history, or recent procedures.
- The physical examination should focus on the abdomen, flank, genitals, and rectum.
- The laboratory tests should include a urinalysis to confirm the presence of blood and to look for other abnormalities such as proteinuria, leukocyturia, or nitrites. A urine culture may be done to identify the causative organism if an infection is suspected. A complete blood count (CBC), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, and coagulation studies may also be ordered to assess the renal function and bleeding tendency.
- The imaging tests may include an ultrasound, a computed tomography (CT) scan, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, or a cystoscopy to visualize the urinary tract and to detect any structural abnormalities such as stones, tumors, or polyps.
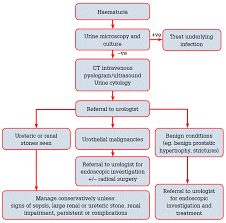
Management and Treatment
- The management and treatment of hematuria depend on the underlying cause and the severity of bleeding.
- Some general principles are:
- Fluid intake: Increasing fluid intake can help flush out bacteria and small stones from the urinary tract and prevent dehydration.
- Pain relief: Analgesics such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help relieve pain associated with hematuria. However, NSAIDs should be avoided in patients with renal impairment or bleeding disorders.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are indicated for patients with hematuria caused by urinary tract infections. The choice of antibiotic depends on the type and sensitivity of the organism.
- Surgery: Surgery may be required for patients with hematuria caused by large stones, tumors, or polyps that obstruct or damage the urinary tract. The type of surgery depends on the location and size of the lesion.
- Transfusion: Transfusion may be needed for patients with severe hematuria that causes anemia or hypovolemia. The type and amount of blood product depend on the patient's hemoglobin level and vital signs.
- Consultation: Consultation with a urologist or a nephrologist may be necessary for patients with hematuria that is recurrent, persistent, or unexplained by initial evaluation.
Nursing care and patient education
- The nursing care and patient education for patients with hematuria include:
- Monitoring: Monitoring the patient's vital signs, urine output, color, and clarity; assessing for signs of infection, obstruction, or bleeding complications; reporting any changes or abnormalities to the physician; documenting the interventions and outcomes.
- Comfort: Providing comfort measures such as applying heat pads to the lower back or abdomen; encouraging relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation; offering emotional support and reassurance.
- Education: Educating the patient about the possible causes and complications of hematuria; explaining the diagnostic tests and treatments; instructing the patient to report any worsening or new symptoms; advising the patient to avoid irritants such as caffeine, alcohol, or spicy foods; encouraging the patient to drink plenty of fluids; teaching the patient about preventive measures such as hygiene, hydration, and regular check-ups.

Summary
- Hematuria is a condition that requires prompt evaluation and management to identify and treat the underlying cause.
- Hematuria can be caused by various conditions affecting the urinary tract such as infections, stones, enlarged prostate, kidney disease, cancer, trauma, medications, or inherited disorders. Hematuria can be classified into gross hematuria or microscopic hematuria depending on the visibility of blood in the urine.
- The diagnosis of hematuria involves a thorough history and physical examination as well as laboratory and imaging tests.
- The management and treatment of hematuria depend on the underlying cause and severity of bleeding.
- The nursing care and patient education for patients with hematuria include monitoring and comfort measures education.
Conclusion
- Hematuria is a common but potentially serious condition that requires prompt evaluation and management.
- Hematuria can be classified into two main categories: gross hematuria, where blood is visibly noticeable in the urine, and microscopic hematuria, where blood is detected only under a microscope.
- The underlying causes of hematuria are diverse, encompassing both benign and potentially serious conditions.
- Common causes include urinary tract infections, kidney stones, trauma, and vigorous exercise. However, more concerning etiologies such as bladder cancer, kidney disease, and coagulation disorders must be considered and thoroughly evaluated, especially in cases of persistent or recurrent hematuria.
- Nurses play a vital role in providing care and education for patients with hematuria.
- Nurses should be familiar with the causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of hematuria and be able to provide holistic and evidence-based care for patients with hematuria.
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
Risk factors
1. Genetic Predisposition: NDI can be inherited as an X-linked recessive trait, which means that males are more commonly affected. It can also occur sporadically due to mutations in specific genes.
2. Acquired NDI: Certain medications, particularly lithium, are known to be a significant risk factor for developing acquired NDI. Other medications, such as demeclocycline and foscarnet, can also contribute to this condition.
3. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Individuals with CKD, especially if it has progressed to advanced stages, are at an increased risk of developing NDI. This is due to the impaired functioning of the renal tubules.
4. Electrolyte Imbalances: Conditions that lead to imbalances in electrolytes, particularly imbalances in sodium and potassium levels, can increase the risk of developing NDI.
5. Hypercalcemia: Elevated levels of calcium in the blood (hypercalcemia) can disrupt the normal functioning of the renal tubules, potentially leading to NDI.
6. Urinary Tract Obstruction: Conditions that obstruct the urinary tract, such as kidney stones or structural abnormalities, can lead to impaired urine concentration and an increased risk of NDI.
7. Certain Systemic Disorders: Some systemic conditions, such as Sjögren's syndrome or sickle cell disease, can be associated with a higher risk of NDI.
8. Dehydration: Chronic dehydration or recurrent episodes of severe dehydration can lead to kidney damage and increase the risk of developing NDI.
9. Certain Infections: In rare cases, infections affecting the kidneys, such as pyelonephritis, may contribute to the development of NDI.
- It's important to note that while these factors can increase the risk of NDI, the condition can still occur without any known predisposing factors, particularly in cases of genetic inheritance or sporadic mutations. Additionally, not everyone with these risk factors will develop NDI.
Pathophysiology
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (NDI) is a condition characterized by the kidney's inability to respond effectively to Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH), also known as Vasopressin. This leads to an impaired ability to concentrate urine, resulting in excessive urine production (polyuria) and increased thirst (polydipsia). The pathophysiology of NDI can be explained as follows:
1. Normal ADH Action:
- In normal physiology, ADH is produced by the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary gland in response to high blood osmolality or low blood volume.
- ADH acts on specific receptors (V2 receptors) located on the renal collecting ducts' epithelial cells.
2. ADH-Mediated Water Reabsorption:
- When ADH binds to its receptors, it triggers a cascade of intracellular events that result in the insertion of water channels, known as aquaporins, into the luminal membrane of the collecting duct cells.
- These aquaporins allow water to move passively from the urine back into the bloodstream, concentrating the urine.
3. Impaired ADH Response in NDI:
- In NDI, there is a defect or dysfunction in the V2 receptors or the intracellular signaling pathways involved in ADH action.
- As a result, despite normal or elevated levels of circulating ADH, the kidneys do not respond appropriately to its presence.
4. Reduced Water Reabsorption:
- Without the normal response to ADH, the water channels (aquaporins) are not inserted into the luminal membrane of the collecting duct cells.
- This leads to a reduced ability of the kidneys to reabsorb water, resulting in the production of large volumes of dilute urine.
5. Increased Urine Output:
- Due to the reduced water reabsorption, a substantial amount of water remains in the urine, leading to polyuria (excessive urination).
- The urine produced is clear and lacks the usual concentration seen in healthy individuals.
6. Compensatory Thirst Mechanism:
- In response to the excessive urine output, individuals with NDI experience intense thirst (polydipsia) as the body attempts to maintain fluid balance.
7. Risk of Dehydration and Electrolyte Imbalance:
- Without proper intervention or management, the continual loss of fluids through excessive urination can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, particularly hypernatremia (elevated blood sodium levels).
8. Underlying Genetic or Acquired Causes:
- NDI can be caused by genetic mutations affecting the V2 receptors or other proteins involved in ADH signaling pathways (congenital NDI).
- Acquired NDI can result from factors such as certain medications (e.g., lithium, demeclocycline), chronic kidney disease, or electrolyte imbalances.
Clinical Presentation
- Polyuria Excretion of large volumes of dilute urine (often exceeding 3-15 liters per day).
- Polydipsia Excessive thirst to compensate for fluid loss.
- Nocturia Frequent urination during the night, disrupting sleep.
- Dehydration and Electrolyte Imbalance Without adequate fluid intake, patients are at risk of dehydration, hypernatremia, and other electrolyte disturbances.
- Growth Failure (in children) Chronic excessive fluid loss can lead to growth impairment.
- Enuresis (in children) Involuntary nighttime bedwetting due to excessive urine production.
- High Risk of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) Dilute urine may not effectively flush out bacteria.
Diagnostic Tests
- The water Deprivation Test Helps differentiate between central diabetes insipidus (inadequate ADH secretion) and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (kidney's insensitivity to ADH).
- Serum and Urine Electrolyte Levels Assess for electrolyte imbalances like hypernatremia, which can occur due to excessive fluid loss.
- Urine Osmolality Measures the concentration of solutes in the urine. In NDI, it remains low even when the patient is dehydrated.
Management
- Fluid Replacement Patients with NDI require constant access to water to prevent dehydration. They should be encouraged to drink water regularly.
- Diuretics (in some cases) Thiazide diuretics can be prescribed as they enhance renal tubular reabsorption of sodium and water, thereby reducing urine output.
- Low-Sodium Diet A low-sodium diet can help reduce the amount of solute in the urine, which in turn reduces the need for excessive water intake.
- Monitoring Electrolytes Regular monitoring of serum electrolyte levels, especially sodium, is crucial to detect and address any imbalances promptly.
- Treating Underlying Causes If NDI is secondary to a specific condition or medication, addressing the underlying cause is essential.
Nursing Care and Interventions
- Fluid Monitoring Documenting intake and output is crucial to track fluid balance and identify any deficits or excesses.
- Educating on Fluid Intake Providing education on the importance of consistent fluid intake and recognizing signs of dehydration.
- Monitoring Electrolytes Regularly monitoring serum sodium levels and other electrolytes to ensure they remain within normal ranges.
- Assisting with Medication Administration If prescribed, assisting with the administration of thiazide diuretics and educating on their purpose and potential side effects.
- Collaborating with Dietitian Coordinating with a dietitian to develop a low-sodium diet plan that meets the patient's nutritional needs while helping manage NDI.
- Addressing Emotional Impact Providing emotional support and counseling for patients dealing with the chronic nature of NDI, which can impact their quality of life.
- Promoting Skin Care Educating on proper skin care to prevent irritation or breakdown from frequent urination.
Conclusion
- Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus is a rare disorder characterized by impaired kidney response to ADH, leading to excessive urination and thirst.
- Effective management involves fluid replacement, medication (if prescribed), dietary adjustments, and addressing any underlying causes.
- Regular monitoring of fluid balance, and electrolytes, and providing ongoing education and support are crucial components of care.
Summary
- Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus results from the kidneys' inability to respond to ADH, causing excessive urination and thirst.
- It can be inherited or acquired due to various factors, including certain medications and kidney disease.
- Diagnosis involves specialized tests like the water deprivation test and monitoring electrolyte levels.
- Management focuses on fluid replacement, potential use of diuretics, low-sodium diet, and addressing underlying causes.
- Nursing care includes fluid monitoring, education on fluid intake, electrolyte monitoring, medication assistance, collaboration with a dietitian, emotional support, and skin care promotion.
Renal Cancers
Introduction
- Renal cancers, also known as kidney cancers, are a group of malignancies that originate within the kidneys, vital organs responsible for filtering waste and regulating fluid balance in the body.
- Among renal cancers, Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) is the most prevalent form, accounting for the majority of cases. Other types include transitional cell carcinoma and Wilms tumor, primarily affecting children.
- Renal cancers can arise from various cell types within the kidney, including those in the renal tubules, renal pelvis, and collecting ducts, each presenting unique clinical characteristics and treatment approaches.
- These cancers are often asymptomatic in their early stages, and symptoms may not manifest until the disease has progressed. Common signs include hematuria, flank pain, and an abdominal mass.
- While certain risk factors like smoking, hypertension, and family history may increase susceptibility, renal cancers can affect individuals of varying ages and backgrounds.
- Early detection and accurate diagnosis are crucial for successful management and improved outcomes. Diagnostic tools include imaging studies, biopsies, and blood tests to confirm the presence of cancerous cells.
- Timely intervention through a combination of surgical resection, targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and radiation forms the cornerstone of effective treatment for renal cancers.
Risk factors
- Smoking Cigarette smoking is a major risk factor for renal cell carcinoma, increasing the likelihood of developing the disease.
- Hypertension Long-term, uncontrolled high blood pressure is associated with an elevated risk of renal cancer.
- Obesity Individuals with higher body mass index (BMI) have an increased risk of developing renal cancers.
- Family History A family history of renal cancer or certain genetic conditions (e.g., Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome) can predispose individuals to the disease.
- Certain Occupational Exposures Occupational exposure to certain chemicals or substances like asbestos or cadmium may increase the risk.
- Chronic Kidney Disease Individuals with chronic kidney disease are at a higher risk of developing renal cancers.
- Gender and Age Men are more likely than women to develop renal cancers, and the risk increases with age.
Pathophysiology
- Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) This is the most common type of kidney cancer. It typically arises from the cells lining the small tubes within the kidney.
- Tumor Growth and Invasion RCC tumors grow in the kidney and can invade surrounding tissues and organs, including blood vessels.
- Metastasis RCC is known for its potential to metastasize, often spreading to the lungs, bones, liver, and other distant sites.
- Angiogenesis RCC tumors stimulate the formation of new blood vessels to supply nutrients, facilitating their rapid growth.
- Genetic and Molecular Alterations Various genetic mutations and molecular changes contribute to the development and progression of RCC.
- Paraneoplastic Syndromes Some renal cancers may produce hormones or other substances that lead to paraneoplastic syndromes, affecting other organ systems.
Clinical Presentation
- Hematuria Blood in the urine is a common early sign, often presenting as pink, red, or cola-colored urine.
- Flank Pain Dull, persistent pain in the back or side near the affected kidney may occur as the tumor grows or presses against surrounding tissues.
- Palpable Abdominal Mass In advanced cases, a mass or lump may be felt during a physical examination.
- Fatigue and Weakness As the cancer progresses, individuals may experience generalized fatigue and weakness.
- Weight Loss and Loss of Appetite Unexplained weight loss and decreased appetite are common symptoms, particularly in advanced stages.
- Fever and Night Sweats These constitutional symptoms may be indicative of more advanced disease or paraneoplastic syndromes.
- Hypertension Elevated blood pressure may occur, especially in cases where the tumor affects the adrenal glands.
Diagnostic Tests
- Imaging Studies CT scans, MRI, and ultrasound are used to visualize the kidneys and detect any abnormalities or tumors.
- Biopsy A tissue sample may be obtained for pathological examination, confirming the presence of cancerous cells.
- Blood Tests These may include tests to evaluate kidney function, as well as tumor markers like erythropoietin or parathyroid hormone-related protein.
Management
- Surgery The primary treatment for localized renal cancers involves surgical removal of the tumor, either through partial nephrectomy (removing part of the kidney) or radical nephrectomy (removing the entire kidney).
- Targeted Therapies Medications that target specific pathways involved in cancer growth and angiogenesis may be used to inhibit tumor progression.
- Immunotherapy Drugs that boost the immune system's ability to recognize and attack cancer cells can be effective in some cases.
- Radiation Therapy While not typically a first-line treatment, it may be used in certain cases to target specific areas of metastasis or for palliative care.
- Chemotherapy Traditional chemotherapy is generally less effective against renal cancers, but some specific types of chemotherapy drugs may be used in certain cases.
- Active Surveillance In select cases, particularly for smaller, low-risk tumors, a watchful waiting approach may be taken, with regular monitoring to detect any progression.
Nursing Care and Interventions
- Preoperative Care Providing education and emotional support, ensuring informed consent, and preparing the patient for surgery.
- Postoperative Care Monitoring for complications, managing pain, assessing for signs of infection, and supporting wound healing.
- Pain Management Implementing pain relief strategies and monitoring for any adverse effects of pain medications.
- Psychosocial Support Offering emotional support, providing resources, and addressing any anxiety or distress related to the diagnosis and treatment.
- Nutritional Support Collaborating with dietitians to develop individualized dietary plans, especially in cases where surgery or treatment impacts nutritional intake.
- Fluid Balance Management Monitoring fluid intake and output, especially in cases of nephrectomy where there may be changes in fluid balance.
- Monitoring for Complications Keeping a vigilant eye out for postoperative complications, such as bleeding, infection, or impaired wound healing.
Conclusion
- Renal cancers encompass a range of malignancies that originate in the kidneys, with renal cell carcinoma being the most common type.
- Early detection, appropriate treatment, and supportive care are essential for optimizing outcomes and quality of life for individuals with renal cancers.
- Nursing care focuses on pre-and postoperative care, pain management, psychosocial support, nutrition, fluid balance, and monitoring for complications.
Summary
- Renal cancers can have a range of risk factors, including smoking, hypertension, obesity, and certain genetic predispositions.
- RCC, the most common type, arises from cells lining the kidney tubules, with the potential for tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis.
- Clinical presentation includes hematuria, flank pain, palpable mass, fatigue, weight loss, and hypertension.
- Diagnostic tests involve imaging studies, biopsy, and blood tests to confirm the presence of cancer.
- Management options include surgery, targeted therapies, immunotherapy, radiation, and, in select cases, active surveillance.
Nursingprepexams
Videos
Login to View Video
Click here to loginTake Notes on Pathophysiology of the renal system
This filled cannot be empty

