Please set your exam date
Prenatal Diagnostic Tests And Procedures
Study Questions
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the procedure?
Explanation
This is because chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is a prenatal test that involves taking a sample of tissue from the placenta to test for chromosomal abnormalities and certain other genetic problems.There are two types of CVS procedures: transcervical and transabdominal.In the transcervical procedure, a catheter is inserted through the cervix into the placenta to obtain the tissue sample.In the transabdominal procedure, a needle is inserted through the abdomen and uterus into the placenta to obtain the tissue sample.
Choice A is wrong because it describes the transabdominal procedure, not the transcervical one.
Choice B is wrong because it describes the transabdominal procedure, but with a catheter instead of a needle.
Choice D is wrong because it describes the transcervical procedure, but with a needle instead of a catheter.
The normal ranges for CVS are between 10 and 12+6 weeks of gestation.CVS does not provide information on neural tube defects, so women who undergo CVS also need a follow-up blood test between 16 to 18 weeks of their pregnancy to screen for neural tube defects.
A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
This is because chorionic villus sampling (CVS) involves taking a small sample of tissue from the placenta, which may cause some discomfort and bleeding.
Choice B is wrong because you may not experience leaking of amniotic fluid after the procedure.CVS does not involve puncturing the amniotic sac, unlike amniocentesis.
Choice C is wrong because you may not experience Rh sensitization after the procedure.
Rh sensitization is a condition where the mother’s immune system attacks the baby’s blood cells if they have different Rh factors.CVS can prevent this by testing the baby’s blood type and giving an injection of anti-D immunoglobulin to the mother if needed.
Choice D is wrong because you may not experience neural tube defects after the procedure.
Neural tube defects are birth defects that affect the brain and spinal cord of the baby.CVS cannot detect these conditions, but amniocentesis can.Therefore, women who undergo CVS also need a follow-up blood test between 16 to 18 weeks of their pregnancy to screen for neural tube defects.
A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
The procedure can detect chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome.This is because CVS involves taking a sample of tissue from the placenta, which contains the same genetic material as the fetus.By analyzing the chromosomes in the tissue sample, CVS can identify conditions caused by missing or extra chromosomes, such as Down syndrome.
Choice B is wrong because CVS cannot detect neural tube defects such as spina bifida.Neural tube defects are problems with the development of the brain and spinal cord that occur early in pregnancy.CVS does not provide information on neural tube defects, so women who undergo CVS also need a follow-up blood test between 16 to 18 weeks of their pregnancy to screen for these conditions.
Choice C is wrong because CVS can only detect some genetic disorders such as cystic fibrosis, not all of them.Genetic disorders are caused by changes in the DNA sequence of a gene, which affect how the gene works.CVS can test for some genetic disorders that are inherited in a simple pattern, such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, thalassaemia and muscular dystrophy.However, CVS cannot test for all genetic disorders, especially those that are complex or rare.
Choice D is wrong because CVS cannot detect neural tube defects such as anencephaly.Anencephaly is a severe condition where the baby is born without parts of the brain and skull.As mentioned above, CVS does not provide information on neural tube defects, so women who undergo CVS also need a follow-up blood test between 16 to 18 weeks of their pregnancy to screen for these conditions.
A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
“The procedure is usually performed between 10 and 13 weeks of gestation.”This is because CVS can provide early diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities and genetic disorders in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Choice B is wrong because the procedure has a risk of miscarriage of about 0.5% to 1%.This is higher than the risk of amniocentesis, which is another prenatal diagnostic test.
Choice C is wrong because the procedure has a risk of infection of about 0.5%.This is due to the insertion of a needle or a catheter through the abdomen or the cervix to obtain a sample of chorionic villi.
Choice D is wrong because the procedure has a risk of bleeding of about 1% to 2%.This is caused by the disruption of blood vessels in the placenta during the sampling.
A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. Results are usually available within 24 hours.This is known as the rapid CVS result.A more detailed set of CVS results will be available within 10 to 14 days, but may take up to 3 weeks in some cases.
Choice A is wrong because results are not usually available within 10 to 14 days.
This is the time frame for the final result, not the preliminary one.
Choice C is wrong because results are not usually available within 7 days.
This is too long for the rapid result and too short for the final result.
Choice D is wrong because results are not usually available within 30 days.
This is much longer than the usual time frame for both the rapid and the final result.
Amniocentesis
A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for an amniocentesis.
Which of the following should the nurse include in the client’s teaching?
Explanation
“You will need to have someone drive you home after the procedure.” Amniocentesis is a procedure in which your doctor removes a small amount of amniotic fluid from your uterus for testing or treatment.The procedure can cause some cramping, bleeding, or leaking of fluid, so you should rest and avoid strenuous activities for the rest of the day.
Having someone drive you home is a safety precaution.
Choice A is wrong because you will need to have anemptybladder for the procedure.This reduces the risk of puncturing the bladder with the needle and makes it easier to see the uterus on ultrasound.
Choice B is wrong because you will need to lie on yoursidefor the procedure.This prevents putting pressure on a major blood vessel called the vena cava, which can reduce blood flow to your baby.
Choice D is wrong because you willnotneed to avoid eating or drinking before the procedure.There is no evidence that fasting reduces the risk of complications from amniocentesis.
A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for an amniocentesis.
Which of the following should the nurse report to the provider?
Explanation
The client has a history of bleeding disorders.
This is because amniocentesis is an invasive procedure that involves passing a needle through the abdomen and into the uterus to collect a sample of amniotic fluid.This can cause bleeding and increase the risk of miscarriage.
A client with a bleeding disorder may have difficulty clotting and may experience excessive bleeding after the procedure.
Choice A is wrong because asthma is not a contraindication for amniocentesis.
Asthma is a chronic lung condition that causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways.
It does not affect the ability to perform amniocentesis or the risk of complications.
Choice B is wrong because diabetes is not a contraindication for amniocentesis.
Diabetes is a condition that affects how the body uses glucose, a type of sugar that is the main source of energy for cells.
It does not affect the ability to perform amniocentesis or the risk of complications.
Choice D is wrong because hypertension is not a contraindication for amniocentesis.
Hypertension is a condition that causes high blood pressure, which can damage the heart and blood vessels.
It does not affect the ability to perform amniocentesis or the risk of complications.
Normal ranges for blood pressure are less than 120/80 mmHg, for blood glucose are 70-130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL after meals, and for clotting time are 8-15 minutes.
A nurse is caring for a patient who is at 15 weeks gestation, is rh-negative, and just had an Amniocentesis.
Which of the following interventions is the nurse’s priority following the procedure?
Explanation
Administer Rho-Immunoglobulin.This is because the patient is Rh-negative and has a risk of developing antibodies against the Rh antigen of the fetus, which can cause hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN) in subsequent pregnancies.Rho-Immunoglobulin prevents the maternal immune system from recognizing the fetal Rh antigen and producing antibodies.
Choice A is wrong because checking the patient’s temperature is not the priority intervention following an amniocentesis.
Temperature may be monitored to detect infection, but this is not as urgent as preventing Rh sensitization.
Choice B is wrong because observing for uterine contractions (UCs) is not the priority intervention following an amniocentesis.
UCs may indicate preterm labor, but this is not as common or as serious as HDFN.
Choice D is wrong because monitoring the fetal heart rate (FHR) is not the priority intervention following an amniocentesis.
FHR may be checked to assess fetal well-being, but this is not as important as preventing Rh sensitization.
Normal ranges:
• Temperature: 36.5°C to 37.2°C
• FHR: 110 to 160 beats per minute
• Anti-D antibody titer: < 1:8
A nurse is caring for a patient who had an amniocentesis performed at 16 weeks gestation and reports cramping and vaginal bleeding 24 hours later which action should be taken first?
Explanation
Monitor fetal heart rate.This is because cramping and vaginal bleeding after amniocentesis are signs of possible complications such as miscarriage, infection, or injury to the fetus.
Monitoring the fetal heart rate can help assess the well-being of the fetus and detect any signs of distress.
Choice A is wrong because administering Rho(D) immune globulin is only necessary if the mother has Rh-negative blood and the baby has Rh-positive blood, which can cause Rh sensitization.
This is not given routinely to all women who have amniocentesis.
Choice C is wrong because assessing maternal vital signs is not the first action to be taken.
While maternal vital signs can indicate infection or bleeding, they are less important than the fetal heart rate in this situation.
Choice D is wrong because obtaining an order for an ultrasound exam is not the first action to be taken.
While an ultrasound exam can help evaluate the amount of amniotic fluid and the position of the placenta and the fetus, it is not as urgent as monitoring the fetal heart rate.An ultrasound exam may be done later if there are concerns about the fetal condition or the amniotic fluid level.
Normal ranges for fetal heart rate are 110 to 160 beats per minute.Normal ranges for amniotic fluid index are 5 to 25 cm.Normal ranges for maternal vital signs vary depending on the stage of pregnancy, but generally they are: blood pressure 110/70 to 140/90 mmHg, pulse 60 to 100 beats per minute, respiratory rate 12 to 20 breaths per minute, and temperature 36.5 to 37.5°C.
A nurse is caring for a patient who had an amniocentesis performed at 16 weeks gestation and reports cramping and vaginal bleeding 24 hours later which action should be taken first?
Explanation
Monitor fetal heart rate.This is because cramping and vaginal bleeding after amniocentesis are signs of possible complications such as miscarriage, infection, or injury to the fetus.
Monitoring the fetal heart rate can help assess the well-being of the fetus and detect any signs of distress.
Choice A is wrong because administering Rho(D) immune globulin is only necessary if the mother has Rh-negative blood and the baby has Rh-positive blood, which can cause Rh sensitization.
This is not given routinely to all women who have amniocentesis.
Choice C is wrong because assessing maternal vital signs is not the first action to be taken.
While maternal vital signs can indicate infection or bleeding, they are less important than the fetal heart rate in this situation.
Choice D is wrong because obtaining an order for an ultrasound exam is not the first action to be taken.
While an ultrasound exam can help confirm the diagnosis of complications such as placental abruption or fetal injury, it is not as urgent as monitoring the fetal heart rate.
Normal ranges for fetal heart rate are 110 to 160 beats per minute.Normal ranges for maternal vital signs are: temperature 36.1°C to 37.2°C, pulse 60 to 100 beats per minute, blood pressure 120/80 mm Hg or lower, and respiratory rate 12 to 20 breaths per minute.
Non-Stress Test (NST)
A nurse is performing a non-stress test on a pregnant client.
What does a reactive NST indicate?
Explanation
A reactive NST indicates adequate fetal oxygenation and normal fetal neurological function.This means that the baby’s heart rate increases when it moves, which is a sign of health and well-being.
Choice B is wrong because inadequate fetal oxygenation means that the baby is not getting enough oxygen, which can cause complications and distress.
Choice C is wrong because abnormal fetal neurological function means that the baby’s brain is not functioning properly, which can affect its development and survival.
Choice D is wrong because both inadequate fetal oxygenation and abnormal fetal neurological function are serious problems that require immediate medical attention.
A non-stress test (NST) is a test in pregnancy that measures fetal heart rate in response to movement and contractions.It is usually done after 28 weeks of pregnancy, or earlier if there are risk factors or concerns.It is safe and painless for both the mother and the baby.
A nurse is performing a non-stress test on a pregnant client.
What does a nonreactive NST indicate?
Explanation
Inadequate fetal oxygenation and abnormal fetal neurological function.A nonreactive NST shows no increase in the fetal heart rate (no accelerations) in response to fetal movement or contractions.This may indicate that the fetus is not getting enough oxygen or has a problem with its nervous system.
Choice A is wrong because adequate fetal oxygenation and normal fetal neurological function would result in a reactive NST, which shows at least two accelerations of the fetal heart rate within 20 minutes.
Choice B is wrong because inadequate fetal oxygenation and normal fetal neurological function would still cause some accelerations of the fetal heart rate, but not enough to be considered reactive.
Choice C is wrong because adequate fetal oxygenation and abnormal fetal neurological function would not affect the fetal heart rate response to movement or contractions unless the abnormality is severe.
A nonreactive NST does not necessarily mean there is a problem with the fetus.Sometimes the fetus may be asleep, exposed to medications, or affected by maternal smoking.
In such cases, further testing may be needed to confirm the fetal well-being.
A nurse is performing a nonstress test on a pregnant client who is at 32 weeks’ gestation and has diabetes mellitus type I.
Which finding indicates that the test is reactive?
Explanation
Fetal heart rate (FHR) increases by at least 15 beats/min for at least 15 seconds twice or more in a 20-minute period.This indicates that the test is reactive, which means the baby is healthy and getting enough oxygen.
Choice B is wrong because FHR decreases by at least 15 beats/min for at least 15 seconds twice or more in a 20-minute period.
This indicates a deceleration, which may be a sign of fetal distress.
Choice C is wrong because FHR remains stable throughout the test.
This indicates that the test is nonreactive, which means the baby’s heartbeat didn’t change when moving, or the baby wasn’t moving much.A nonreactive result doesn’t always mean your baby has a health problem, but it can mean more tests may be necessary.
Choice D is wrong because FHR increases by less than 10 beats/min for less than 10 seconds twice or more in a 20-minute period.This indicates that the test is nonreactive, which means the baby’s heart rate did not increase enough to meet the criteria for a reactive test.
A pregnant client asks the nurse how long the Non-Stress Test (NST) is usually performed.
How should the nurse respond ?
Explanation
The NST is usually done for 20 to 40 minutes or until at least two fetal movements are recorded.This is because the NST monitors the fetal heart rate in response to fetal movement, in order to assess fetal well-being.A reactive test indicates that the fetal heart rate accelerates by 15 bpm above the baseline and lasts for 15 to 30 seconds in association with fetal movement.
Choice B is wrong because it does not answer the question of how long the NST is usually performed.It only states when the NST is usually performed, which is after 28 weeks of gestation or earlier if there are risk factors.
Choice C is wrong because it does not answer the question of how long the NST is usually performed.It only describes how the NST is performed, which is by placing two belts with sensors on the client’s abdomen.
Choice D is wrong because it does not answer the question of how long the NST is usually performed.It only explains how the NST is interpreted, which is as reactive or nonreactive.
During a Non-Stress Test (NST), the fetal heart rate (FHR) increases by at least 15 beats per minute for at least 15 seconds twice or more in a 20-minute period.
How should the nurse interpret this finding?
Explanation
A reactive NST indicates adequate fetal oxygenation and normal fetal neurological function.This means that the fetal heart rate increases by at least 15 beats per minute for at least 15 seconds twice or more in a 20-minute period.
This is a sign of a healthy and active fetus.
Choice B is wrong because a nonreactive NST does not necessarily mean that there is a problem with the fetus.
It could mean that the fetus is asleep, not moving enough, or has a medication effect.A nonreactive NST requires further evaluation such as a biophysical profile (BPP) or a contraction stress test (CST) to confirm fetal well-being.
Choice C is wrong because NST has some risks and complications for the pregnant person or the fetus.For example, NST may cause anxiety, false-positive results, or unnecessary interventions if the test is not interpreted correctly.
Choice D is wrong because NST is not a prenatal screening test that measures the FHR in response to fetal movements.NST is a prenatal diagnostic test that measures the FHR in response to uterine contractions.
Fetal movements are recorded by the pregnant person using a button during the test.
Biophysical Profile (BPP)
A nurse is explaining when a biophysical profile (BPP) is usually performed.
At what gestational age is a BPP typically performed?
Explanation
A biophysical profile (BPP) is typically performed after 28 weeks of gestation to evaluate the fetal well-being.A BPP measures five parameters: fetal heart rate, fetal breathing movements, fetal body movements, fetal tone and amniotic fluid volume.Each parameter is scored as 0 (abnormal) or 2 (normal), and the total score ranges from 0 to.
Choice A is wrong because a BPP is not usually performed at 12-14 weeks of gestation.This is too early to assess the fetal biophysical parameters reliably.
Choice B is wrong because a BPP is not usually performed at 20-22 weeks of gestation.This is also too early to assess the fetal biophysical parameters reliably.
Choice C is wrong because a BPP is not usually performed at 24-26 weeks of gestation.This is still too early to assess the fetal biophysical parameters reliably.
A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetes mellitus and is at 36 weeks of gestation.
The nurse should expect the provider to order which of the following tests to assess fetal well-being?
Explanation
A BPP is a test that combines an ultrasound and a nonstress test (NST) to assess fetal well-being.It measures fetal heart rate, breathing, movement, muscle tone, and amniotic fluid level.A BPP is typically performed after 28 weeks of pregnancy, especially if there are any risk factors or complications.
Choice B.Nonstress test (NST) is wrong because it only measures fetal heart rate in response to movement or contractions.
It does not assess other aspects of fetal well-being such as breathing, movement, muscle tone, and amniotic fluid level.
Choice C. Contraction stress test (CST) is wrong because it measures fetal heart rate in response to induced contractions of the uterus.
It does not assess other aspects of fetal well-being such as breathing, movement, muscle tone, and amniotic fluid level.
Choice D. Amniocentesis is wrong because it is a procedure that involves inserting a needle into the uterus to collect a sample of amniotic fluid for testing.
It does not assess fetal well-being directly, but rather tests for genetic or chromosomal abnormalities, infections, or lung maturity.
A nurse is reviewing the results of a biophysical profile (BPP) for a client who is at 38 weeks of gestation.
The nurse should recognize that a total BPP score of which of the following indicates acute fetal asphyxia?
Explanation
A biophysical profile (BPP) score of 4 or less indicates acute fetal asphyxia.A BPP score is calculated by adding the scores of five parameters: fetal breathing movements, fetal body movements, fetal tone, amniotic fluid volume and nonstress test.
Each parameter is scored as either 0 (abnormal) or 2 (normal), except for the nonstress test which is scored as either 0 (nonreactive) or 1 (reactive).A total score of 8 or more is considered normal, while a score of 6 or less is considered abnormal and requires further evaluation or delivery.
Choice B is wrong because a BPP score of 6 or less, not 6 or more, indicates acute fetal asphyxia.
Choice C is wrong because a BPP score of 8 or less is considered borderline and may require repeat testing or delivery depending on the clinical situation.
It does not necessarily indicate acute fetal asphyxia.
Choice D is wrong because a BPP score of 10 or less is considered normal and does not indicate acute fetal asphyxia.
Contraction Stress Test (CST)
A nurse is explaining the Contraction Stress Test (CST) to a pregnant client.
Which statement accurately describes a positive CST?
Explanation
Late decelerations of the FHR with at least 50% of contractions.This indicates a positive CST, which means that the baby may be under stress and unable to tolerate labor contractions.A positive CST may require a cesarean section or further observation.
Choice B is wrong because late decelerations of the FHR with less than 50% of contractions indicate an equivocal CST, which means that the results are unclear and the test may need to be repeated.
Choice C is wrong because no late decelerations of the FHR during contractions indicate a negative CST, which means that the baby is healthy and can handle the stress of labor.
Choice D is wrong because variable decelerations of the FHR with or without contractions indicate cord compression, not placental insufficiency, which is what the CST is testing for.
A client is scheduled for a Contraction Stress Test (CST).
When should the CST be performed?
Explanation
A contraction stress test (CST) is performed near the end of pregnancy (34 weeks’ gestation) to determine how well the fetus will cope with the contractions of childbirth.The test triggers contractions and monitors the fetal heart rate using a cardiotocograph.A normal heartbeat is a good sign that the fetus will be healthy during labor.
Choice A is wrong because a CST is usually done after 32 weeks of gestation, not before 28 weeks.Doing the test too early may not be safe for the fetus.
Choice C is wrong because a CST is not only done for clients with diabetes mellitus.It may be done for clients who have complications during their pregnancy or who have abnormal results from other tests, such as a nonstress test or a biophysical profile.
Choice D is wrong because a CST is not only done for clients with hypertension.It may be done for clients who have complications during their pregnancy or who have abnormal results from other tests, such as a nonstress test or a biophysical profile.
A nurse is preparing a pregnant client for a Contraction Stress Test (CST).
What is the purpose of inducing uterine contractions during the test?
Explanation
The purpose of inducing uterine contractions during the test is to simulate labor contractions and check how the baby’s heart rate reacts to the stress of reduced blood and oxygen supply.A normal heart rate indicates that the baby will be healthy during labor.
Choice B is wrong because monitoring the FHR is not the purpose of the test, but a means to assess fetal well-being.
Choice C is wrong because achieving at least three contractions lasting 40 to 60 seconds is not the purpose of the test, but a criterion for a satisfactory test.
Choice D is wrong because identifying fetal hypoxia or distress is not the purpose of the test, but a possible outcome of an abnormal test.
A client asks the nurse about the interpretation of a negative CST result.
What should the nurse explain to the client?
Explanation
This means that the fetus is well oxygenated and tolerating labor well.A negative CST result is reassuring and has a high negative predictive value.
Choice B is wrong because late decelerations of the FHR are a sign of fetal hypoxia and placental insufficiency.They occur after the peak of a contraction and are associated with fetal distress.
Choice C is wrong because variable decelerations of the FHR are caused by cord compression and can occur with or without contractions.They are abrupt decreases in FHR that vary in onset, depth, and duration.
They may indicate fetal compromise if they are severe or persistent.
Choice D is wrong because late decelerations of the FHR with at least 50% of contractions indicate a positive CST result, which means that the fetus is at risk of hypoxia and acidosis.
This requires further evaluation and possible intervention.
Normal ranges for FHR are 110 to 160 bpm during late pregnancy and labor.Normal ranges for uterine contractions are 2 to 5 per 10 minutes, lasting less than 90 seconds each.
During a CST, the nurse notices late decelerations of the FHR with at least 50% of contractions.
How should the nurse interpret this finding?
Explanation
Late decelerations of the FHR are a sign of uteroplacental insufficiency, meaning that the placenta is not delivering enough oxygen to the fetus.
This can lead to fetal distress and hypoxia.
A positive CST result means that there is evidence of fetal compromise during uterine contractions.
Choice B is wrong because a negative CST result would mean that there are no late decelerations or significant variable decelerations of the FHR with at least three contractions in 10 minutes.
This would indicate adequate fetal oxygenation and normal placental function.
Choice C is wrong because an equivocal CST result would mean that there are either variable decelerations of the FHR with more than 50% of contractions, or late decelerations with less than 50% of contractions.
This could indicate cord compression, fetal head compression, or mild fetal hypoxia.
Choice D is wrong because an unsatisfactory CST result would mean that there are either no contractions in 10 minutes, or less than three contractions in 10 minutes with an uninterpretable FHR tracing.
This would require repeating the test or performing a biophysical profile (BPP) to assess fetal well-being.
Alpha-fetoprotein Test (AFP)
A nurse is explaining the Alpha-fetoprotein Test (AFP) to a pregnant client.
What does a high level of AFP (>2.5 MoM) potentially indicate?
Explanation
A high level of AFP (>2.5 MoM) potentially indicates that the unborn baby has a neural tube defect, such as spina bifida.
This is a condition where the spinal cord does not develop properly and can cause serious complications.
Choice B.Chromosomal abnormality is wrong because a high level of AFP is not associated with chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome.In fact, a low level of AFP may indicate this type of defect.
Choice C.Maternal weight-related factors is wrong because maternal weight does not affect the level of AFP in the blood.However, other factors such as gestational age, multiple pregnancies, and maternal diabetes can influence the AFP level.
Choice D.Fetal demise is wrong because a high level of AFP does not indicate fetal demise or death.A very low or undetectable level of AFP may suggest this possibility.
Normal ranges for AFP vary depending on the stage of pregnancy and the laboratory that performs the test.Generally, the normal range for AFP in the second trimester is between 10 and 150 ng/mL.
A client is scheduled for an Alpha-fetoprotein Test (AFP).
When is this test usually performed ?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. Between 15 and 20 weeks of gestation.This is because an AFP test is usually done between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy to check the baby’s risk for having certain genetic problems and birth defects.AFP is a protein that a developing baby makes in the liver.Normally, some AFP passes from the baby into the pregnant person’s blood.
Choice A is wrong because before 15 weeks of gestation, the AFP levels are too low to be measured accurately.
Choice C is wrong because after 20 weeks of gestation, the AFP levels start to decline and may not reflect the fetal condition.
Choice D is wrong because an AFP test is not only for people who have diabetes mellitus.It is routinely offered to all pregnant people between the 15th and 20th week of pregnancy.Diabetes mellitus may affect the accuracy of the test, but it is not a requirement for having it.
During a prenatal visit, a pregnant client asks the nurse about the timing of the Alpha-fetoprotein Test (AFP).
What is the appropriate response?
Explanation
The AFP test is usually performed between 20 and 24 weeks of gestation.
This test is a screening tool that measures the level of AFP in the blood of a pregnant woman.It can help detect some genetic disorders or neural tube defects in the fetus.
Choice A is wrong because the AFP test is not typically performed during the first trimester.It is most accurate between the 16th and 18th weeks of pregnancy.
Choice C is wrong because the AFP test is not done at the same time as the glucose tolerance test.The glucose tolerance test is usually done between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy to check for gestational diabetes.
Choice D is wrong because the AFP test is not performed in the immediate postpartum period.It is a prenatal screening test that is done before the baby is born.
During a discussion about the Alpha-fetoprotein Test (AFP), a pregnant client asks about the risks associated with the test.
What is the appropriate response by the nurse?
Explanation
The AFP test can result in false-positive or false-negative findings.This means that the test may show a high or low level of AFP when there is no problem with the baby, or it may show a normal level of AFP when there is a problem with the baby.
False-positive results can cause unnecessary worry and further testing, while false-negative results can delay diagnosis and treatment of a serious condition.
Choice A is wrong because the AFP test carries some risks or complications for the mother or the fetus.The test involves drawing blood from a vein in the mother’s arm, which can cause bleeding, bruising, infection, or fainting at the puncture site.The test may also cause anxiety or stress for the mother if the results are abnormal.
Choice B is wrong because the AFP test may cause bleeding or infection at the blood draw site, but this is not the only risk or complication associated with the test.
As mentioned above, the test can also result in false-positive or false-negative findings, which can have serious consequences for the mother and the baby.
Choice D is wrong because the AFP test may induce preterm labor or premature rupture of membranes.This is a very rare complication that can occur if the test is done by amniocentesis, which involves inserting a needle into the uterus to collect amniotic fluid.However, most AFP tests are done by blood tests, which do not pose this risk.
Normal ranges for AFP levels vary depending on the gestational age of the baby and the laboratory that performs the test.Generally, AFP levels increase until about 15 weeks of pregnancy and then decrease until delivery.The normal range for AFP levels at 16–18 weeks of pregnancy is about 10–150 ng/mL.
However, different laboratories may use different units or methods to measure AFP levels, so it is important to compare your results with the reference values provided by your laboratory.
A nurse is discussing the limitations of the Alpha-fetoprotein Test (AFP) with a pregnant client.
What should the nurse include as a limitation of this test?
Explanation
An AFP test is a blood test that measures the amount of AFP present in blood.It’s usually part of a screening test for genetic problems and birth defects in the second trimester of pregnancy.
However, it has some limitations, such as:
• Choice A is wrong because the AFP test can detect neural tube defects, such as spina bifida or anencephaly.
• Choice B is wrong because the AFP test does not pose any risk of preterm labor.It is a simple blood test that does not affect the pregnancy.
• Choice D is wrong because the AFP test is not very expensive and is usually covered by insurance.
The main limitation of the AFP test is that it is not very accurate and can have false-positive or false-negative results.
A false-positive result means that the test suggests a problem when there is none.
A false-negative result means that the test misses a problem that exists.Therefore, if the AFP test shows an abnormal result, it needs to be confirmed by more invasive procedures, such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS).These procedures involve taking samples of fluid or tissue from the womb and can have some risks, such as infection, bleeding, or miscarriage.
Ultrasound
A nurse is educating a pregnant client about prenatal ultrasound.
Which of the following statements accurately describes the ultrasound procedure?
Explanation
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the fetus and its surroundings.Ultrasound is a safe and painless test that can be done in any trimester of pregnancy.
Choice A is wrong because ultrasound can assess more than just fetal growth and development.It can also check for pregnancy complications, such as ectopic pregnancy, molar pregnancy, miscarriage, placenta previa, placental abruption, congenital abnormalities, and amniotic fluid levels.
Choice B is wrong because ultrasound is not typically performed during the first trimester of pregnancy.It is usually done between 18 and 22 weeks of pregnancy to screen for fetal anomalies.However, some providers may do an ultrasound earlier to confirm pregnancy, check the fetal heartbeat, determine the gestational age and due date, or diagnose an ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage.
Choice C is wrong because transabdominal ultrasound does not involve inserting a transducer into the vagina.Transabdominal ultrasound involves placing a transducer on the abdomen with gel to improve the transmission of sound waves.
Transvaginal ultrasound involves inserting a transducer into the vagina to get a clearer image of the fetus and reproductive organs.It is usually done in early pregnancy or when there are concerns about the cervix.
A nurse is preparing a client for a transvaginal ultrasound.
Which of the following instructions should the nurse provide to the client?
Explanation
The transducer covered with a condom and gel will be inserted into your vagina.This is because a transvaginal ultrasound is an internal scan of the female reproductive organs that involves inserting a small ultrasound probe into the vagina to produce images of the cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries.
Choice A is wrong because a full bladder is not necessary for a transvaginal ultrasound, unlike an abdominal ultrasound.
Choice B is wrong because the client does not need to wear loose-fitting clothing or lie on their side during the procedure.They will lie on their back with their knees bent and their feet in stirrups.
Choice C is wrong because the gel will not be applied on the abdomen, but on the transducer that will be inserted into the vagina.
Normal ranges for transvaginal ultrasound vary depending on the reason for the scan and the stage of pregnancy or menstrual cycle.
However, some general parameters are:
• The uterus should measure about 7.5 x 4.5 x 3 cm and have a smooth contour and uniform echogenicity.
• The endometrium should measure less than 4 mm in postmenopausal women, 2-4 mm in early proliferative phase, 6-10 mm in late proliferative phase, and 10-16 mm in secretory phase.
• The ovaries should measure about 3 x 2 x 1.5 cm and contain multiple small follicles.
• The fallopian tubes should not be visible unless they are dilated or contain fluid.
A client is scheduled for a dating ultrasound.
When is this ultrasound typically performed?
Explanation
Between 8 and 12 weeks of gestation.A dating ultrasound is an ultrasound scan done between 8 and 14 weeks of pregnancy to help estimate your baby’s due date.It is the most accurate method to establish or confirm gestational age in the first trimester.It is based on the size of the embryo or fetus, which is measured from the top of the head (crown) to the bottom of the spine (rump) (CRL).
Choice A is wrong because it is not the typical time for a dating ultrasound, but for a nuchal translucency screening, which assesses the risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
Choice B is wrong because it is not the typical time for a dating ultrasound, but for a third trimester ultrasound, which checks the growth and position of the baby, the amount of amniotic fluid, and the placenta location.
Choice C is wrong because it is not the typical time for a dating ultrasound, but for an anatomy scan, which examines the development of your baby’s organs and structures.
A nurse is performing an ultrasound on a pregnant patient.
The patient asks the nurse what the purpose of the ultrasound is.
What is the best response by the nurse?
Explanation
The ultrasound can assess fetal growth, development, anatomy, position, movement, heart rate, and placental location.This is the best response by the nurse because it covers the most common and general purposes of an ultrasound in pregnancy.
Choice B is wrong because the ultrasound can detect fetal anomalies such as neural tube defects, cardiac defects, cleft lip/palate, skeletal dysplasia, but this is not the only or primary purpose of the ultrasound.It is also not a reassuring answer for the patient who may be anxious about possible abnormalities.
Choice C is wrong because the ultrasound can also detect multiple gestations, placenta previa, placental abruption, ectopic pregnancy, but these are not the main reasons for performing an ultrasound.They are also rare complications that may scare the patient unnecessarily.
Choice D is wrong because the ultrasound can estimate gestational age, due date, fetal weight, and amniotic fluid volume, but these are not the only or most important aspects of the ultrasound.They are also not very accurate measurements and may vary depending on the type and timing of the ultrasound.
A nurse is performing an ultrasound on a pregnant patient.
The patient asks the nurse what type of ultrasound will be performed.
What is the best response by the nurse?
Explanation
Transabdominal ultrasound and transvaginal ultrasound are two types of ultrasound that can be performed on a pregnant patient.
They have different advantages and disadvantages depending on the gestational age, the position of the fetus, and the anatomy of the pregnant person.
Choice A is not wrong, but it is incomplete.
Transabdominal ultrasound is the most common type of ultrasound in pregnancy.
It can provide a wide view of the fetus and its surroundings, but it may not be able to detect some abnormalities or complications in early pregnancy or in obese patients.
Choice B is not wrong, but it is also incomplete.
Transvaginal ultrasound is usually done in the first trimester of pregnancy or when there is a suspicion of ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, or placenta previa.
It can provide a clearer and more detailed image of the fetus and its surroundings, but it may be uncomfortable or invasive for some patients.
Choice D is wrong because it contradicts both A and B. Both types of ultrasound are valid and accurate methods of assessing fetal development and well-being.
They are not mutually exclusive and may be used together or separately depending on the clinical situation.
A client is scheduled for an ultrasound in two weeks.
The client asks the nurse if there are any risks associated with having an ultrasound.
What is the best response by the nurse?
Explanation
Ultrasound has no known risks or complications for the pregnant person or the fetus.This is based on a systematic review of the literature by the World Health Organization (WHO) that found no evidence of adverse maternal or perinatal outcomes, impaired physical or neurological development, increased risk for malignancy in childhood, subnormal intellectual performance or mental diseases associated with ultrasound in pregnancy.
Choice B is wrong because ultrasound does not cause harm to both the pregnant person and fetus.There is no scientific basis for this claim and it contradicts the findings of the WHO review.
Choice C is wrong because ultrasound does not cause harm to only the pregnant person.There is no scientific basis for this claim and it contradicts the findings of the WHO review.
Choice D is wrong because ultrasound does not cause harm to only the fetus.There is no scientific basis for this claim and it contradicts the findings of the WHO review.
Some sources suggest that ultrasound may have some bioeffects on the tissues it traverses, such as thermal or mechanical effects, but these have not been proven to be harmful or clinically significant.
Maternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (MSAFP) Test
A nurse is explaining the purpose of the Maternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (MSAFP) test to a pregnant client.
What does this test primarily detect?
Explanation
This is because the Maternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (MSAFP) test primarily detects the level of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the blood of a pregnant person.AFP is a protein that a developing baby makes and normally passes into the mother’s bloodstream.Too much AFP may indicate that the baby has a neural tube defect or an abdominal wall defect, which are conditions that cause abnormal development of the baby’s body.An abdominal wall defect is a hole in the muscles and skin that cover the abdomen, which allows some of the baby’s organs to protrude outside the body.
Choice A is wrong because renal anomalies are not detected by the MSAFP test.Renal anomalies are problems with the kidneys or urinary tract of the baby.
Choice B is wrong because fetal growth and development are not detected by the MSAFP test.Fetal growth and development are assessed by other prenatal tests, such as ultrasound scans.
Choice C is wrong because chromosomal abnormalities are not detected by the MSAFP test alone.Chromosomal abnormalities are genetic disorders that affect the number or structure of the chromosomes in the baby’s cells.The MSAFP test may be combined with other tests, such as hCG, estriol, and inhibin-A, to form a quadruple screening test (or quad screen) that can check the baby’s risk of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome.
However, the MSAFP test by itself cannot detect these conditions.
Normal ranges for MSAFP levels vary depending on the gestational age of the baby and the laboratory that performs the test.Generally, MSAFP levels increase until about 32 weeks of pregnancy and then decrease until delivery.
The normal range for MSAFP levels at 16 weeks of pregnancy
A client is scheduled to undergo the MSAFP test.
When is this test typically performed?
Explanation
This is because the maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP) test is a screening tool indicated for all high-risk pregnant clients between 15 and 20 weeks gestation.The test measures the level of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the mother’s blood, which is produced by the fetus and can indicate certain birth defects or chromosomal abnormalities.
Choice A is wrong because the MSAFP test is not done during the first trimester of pregnancy.The first trimester screening usually includes a nuchal translucency screening, which measures the fluid at the back of the fetus’s neck to assess the risk of Down syndrome.
Choice B is wrong because the MSAFP test is not done between 11 and 14 weeks of gestation.
This is too early to detect the level of AFP in the mother’s blood.The MSAFP test is most accurate between 16 and 18 weeks of pregnancy.
Choice D is wrong
A nurse is reviewing the MSAFP test results with a client.
A high level of MSAFP (>2.5 MoM) may indicate which of the following conditions?
Explanation
A high level of MSAFP (>2.5 MoM) may indicate that the fetus has a neural tube defect such as spina bifida, which results from incomplete development of the brain and spinal cord.A neural tube defect causes an opening in the head, spine, or stomach wall that allows high levels of AFP to enter the mother’s blood.
Choice A is wrong because chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome are associated with low levels of MSAFP, not high levels.Chromosomal abnormalities involve an extra or missing chromosome that affects the fetus’s development.
Choice B is wrong because fetal demise or death is not related to MSAFP levels.
Fetal demise can be caused by various factors such as infections, placental problems, or umbilical cord accidents.
Choice D is wrong because multiple gestation or having more than one fetus can also cause low levels of MSAFP, not high levels.
Multiple gestation increases the risk of complications such as preterm labor, preeclampsia, and fetal growth restriction.
Normal ranges for MSAFP vary depending on the gestational age of the fetus and the laboratory methods used.Generally, the normal range for MSAFP at 15 to 21 weeks’ gestation is 10 to 150 ng/mL.
A pregnant client asks the nurse about the risks associated with the MSAFP test.
What is the nurse's best response?
Explanation
The MSAFP test is a screening test that measures the amount of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the mother’s blood.
AFP is a protein produced by the baby during pregnancy.The test helps to assess the baby’s risk of certain birth defects, such as neural tube defects or chromosomal abnormalities.
A.“The MSAFP test carries a risk of miscarriage.” This statement is wrong because the MSAFP test is a blood test that does not involve any invasive procedures or harm to the baby.
C. “The MSAFP test may cause harm to the fetus.” This statement is wrong because the MSAFP test does not affect the fetus in any way.It only measures the amount of AFP in the mother’s blood.
D. “Pregnant individuals should avoid the MSAFP test due to potential radiation exposure.” This statement is wrong because the MSAFP test does not involve any radiation exposure.It is a simple blood test that uses a needle to draw blood from a vein.
The normal range of MSAFP levels varies depending on the gestational age of the baby and the laboratory methods used.Generally, the MSAFP levels increase until about 15 weeks of pregnancy and then decrease until delivery.The average MSAFP level at 16 weeks of pregnancy is about 44 ng/mL.However, different laboratories may have different reference ranges, so it is important to consult your healthcare provider for your specific results and interpretation.
A nurse is providing education to a client about the MSAFP test.
Which of the following statements accurately describes the MSAFP results?
Explanation
This is because MSAFP is a screening test that measures the level of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the maternal blood, which is produced by the fetus.The MoM value compares the AFP level of the mother to the average level for women of the same gestational age.A MoM value that is too high or too low may indicate a risk of certain fetal anomalies, such as neural tube defects or chromosomal abnormalities.
However, MSAFP results are not diagnostic and do not confirm the presence or absence of any condition.They only indicate the need for further testing, such as ultrasound, amniocentesis, or chorionic villus sampling.
Choice A is wrong because MSAFP results are not diagnostic and do not confirm the presence of fetal anomalies.They only indicate the risk of certain conditions and the need for further evaluation.
Choice B is wrong because MSAFP results require further evaluation or testing if they are abnormal.A normal MSAFP result does not rule out the possibility of fetal anomalies, nor does it guarantee a healthy outcome.
Choice D is wrong because MSAFP results do not indicate the gestational age of the fetus.They are compared to the average level for women of the same gestational age to calculate the MoM value.Gestational age can be estimated by other methods, such as ultrasound or last menstrual period.
More questions on this topic
A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Which of the following statements should indicate to the nurse that the client understands the procedure?
Explanation
Choice A is wrong because it describes a transabdominal CVS procedure, which involves a needle instead of a catheter.
Choice C is wrong because it describes a procedure that is not used for CVS.A needle inserted through the cervix could damage the fetal membranes or cause bleeding.
Choice D is wrong because it describes a procedure that is not possible.A catheter cannot be inserted through the abdomen and uterus into the placenta.
Normal ranges for CVS are not applicable as it is a diagnostic test, not a screening test.
It provides a definitive result of whether the fetus has a chromosomal abnormality or a genetic disorder.CVS is usually done between 10 and 13+6 weeks of pregnancy.
A nurse is caring for a client who had chorionic villus sampling (CVS) performed at 12 weeks’ gestation and asks when she can expect results from this test.
The nurse should inform her that results are typically available within which timeframe?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. The nurse should inform her that results are typically available within 7 days.
This is known as the rapid CVS result.
A more detailed set of CVS results will be available within 2 weeks.
Choice A is wrong because 24 hours is too short for the laboratory to test the sample of cells from the placenta.
Choice C is wrong because 10-14 days is the timeframe for the more detailed set of CVS results, not the rapid CVS result.
Choice D is wrong because 30 days is too long for the results to be available.
The woman would need to know the results sooner to make informed decisions about her pregnancy.
A nurse is providing education to a client who is scheduled to undergo chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of this test?
Explanation
This test can detect genetic disorders.
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is a prenatal test that involves taking a sample of tissue from the placenta to test for chromosomal abnormalities and certain other genetic problems.
The placenta is a structure in the uterus that provides blood and nutrients from the mother to the fetus.
Choice A is wrong because CVS does not provide information on neural tube defects, such as spina bifida.
For this reason, women who undergo CVS also need a follow-up blood test between 16 to 18 weeks of their pregnancy to screen for neural tube defects.
Choice C is wrong because CVS can detect chromosomal abnormalities, but not all chromosomal abnormalities are genetic disorders.
For example, Down syndrome is a chromosomal abnormality caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21, but it is not inherited from the parents.
Choice D is wrong because CVS cannot detect Rh sensitization, which is a condition where the mother’s immune system produces antibodies against the fetus’s blood type.
Rh sensitization can be detected by a blood test that measures the level of antibodies in the mother’s blood.
A nurse is providing education to a client who is scheduled to undergo chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of this test?
Explanation
This test can detect genetic disorders.
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is a prenatal test that involves taking a sample of tissue from the placenta to test for chromosomal abnormalities and certain other genetic problems.
The placenta is a structure in the uterus that provides blood and nutrients from the mother to the fetus.
Choice A is wrong because CVS does not provide information on neural tube defects, such as spina bifida.
For this reason, women who undergo CVS also need a follow-up blood test between 16 to 18 weeks of their pregnancy to screen for neural tube defects.
Choice C is wrong because CVS can detect chromosomal abnormalities, but not all chromosomal abnormalities are genetic disorders.
For example, Down syndrome is a chromosomal abnormality that occurs randomly and is not inherited from the parents.
Choice D is wrong because CVS cannot detect Rh sensitization, which is a condition where the mother’s immune system produces antibodies against the fetus’s blood cells.
Rh sensitization can be detected by a blood test that measures the level of antibodies in the mother’s blood.
A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for an amniocentesis.
Which of the following should the nurse report to the provider?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice D. The client has a history of placenta previa.
Placenta previa is a condition where the placenta covers all or part of the cervix, blocking the baby’s exit from the uterus.
This can cause severe bleeding during pregnancy and delivery and increase the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby.
Therefore, the nurse should report this condition to the provider before performing an amniocentesis.
Choice A is wrong because having Rh-negative blood type is not a contraindication for amniocentesis.
However, the client may need an injection of Rh immunoglobulin after the procedure to prevent Rh sensitization.
Choice B is wrong because having a history of preterm labor is not a contraindication for amniocentesis.
However, the client may need to be monitored closely for signs of preterm labor after the procedure.
Choice C is wrong because having a history of gestational diabetes is not a contraindication for amniocentesis.
However, the client may need to have their blood glucose levels checked before and after the procedure.
Amniocentesis is a diagnostic procedure that involves removing and testing a small sample of amniotic fluid from the uterus for genetic or chromosomal conditions, such as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome or Patau syndrome.
It can also be used to diagnose fetal infections, treat excess amniotic fluid, or test fetal lung maturity
A nurse is caring for a client scheduled for a CST.
Which statement indicates the client understands the test procedure?
Explanation
“I will have sensors placed on my abdomen to monitor the FHR and uterine contractions.” This statement indicates the client understands the test procedure of a CST, which is a test that triggers contractions and registers how the baby’s heart reacts.
The test is done by placing two sensor belts around the abdomen, one to measure the baby’s heartbeat and the other to measure contractions.
The client may receive oxytocin through an IV to induce contractions.
Choice B is wrong because the client does not need to fast for 24 hours before the test.
There is no evidence that fasting is required for a CST.
Choice C is wrong because the client will not be sedated during the test.
Sedation is not necessary for a CST and may interfere with the results.
Choice D is wrong because the client does not need to drink plenty of fluids before the test.
There is no evidence that drinking fluids is required for a CST.
During a Non-Stress Test (NST), the client needs to press a button whenever they feel the fetus move.
What is the purpose of this action?
Explanation
To measure the fetal heart rate (FHR) in response to fetal movements.
This is because the FHR should increase by at least 15 beats per minute for at least 15 seconds when the fetus moves, which indicates a healthy and reactive fetus.
This is called an acceleration.
Choice B is wrong because the uterine contractions are not related to the fetal movements or the button pressing.
The uterine contractions are measured by a tocodynamometer or an intrauterine pressure catheter.
Choice C is wrong because the fetal oxygenation and neurological function are not directly measured by the button pressing.
The fetal oxygenation can be assessed by the FHR variability and decelerations, while the neurological function can be evaluated by other tests such as biophysical profile or fetal acoustic stimulation.
Choice D is wrong because the fetal well-being and hypoxia or distress are not indicated by the button pressing alone.
The fetal well-being and hypoxia or distress are determined by the FHR patterns, such as baseline, variability, accelerations and decelerations.
A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for an amniocentesis at 16 weeks gestation.
Which of the following should the nurse report to the provider?
Explanation
. The client’s cervix is dilated.
This indicates that the client may be in preterm labor, which is a contraindication for amniocentesis.
Amniocentesis is a procedure that involves inserting a needle into the amniotic sac to obtain a sample of amniotic fluid for genetic testing or other purposes.
It is usually performed between 15 and 20 weeks of gestation.
Choice A is wrong because the client’s bladder should be full for amniocentesis.
This helps to push the uterus upward and away from the bladder, reducing the risk of injury and making it easier to visualize the fetus and the needle.
Choice B is wrong because the client’s uterus should be above the symphysis pubis at 16 weeks of gestation.
This is a normal finding and does not affect the procedure.
Choice D is wrong because the client’s fundal height should measure around 16 cm at 16 weeks of gestation.
A fundal height of 20 cm may indicate a large for gestational age fetus, multiple gestation, or polyhydramnios (excess amniotic fluid), but these are not absolute contraindications for amniocentesis.
However, they may require further evaluation and adjustment of the technique.
A nurse is preparing a client for a Contraction Stress Test (CST).
Which method can be used to induce uterine contractions during the test?
Explanation
This method can be used to induce uterine contractions during the test by stimulating the uterus with a hormone that causes contractions.
Oxytocin is also the hormone that naturally triggers labor contractions.
Choice A is wrong because nipple stimulation can also induce contractions, but it is not as reliable or controllable as oxytocin infusion.
Choice C is wrong because oral medications are not used to induce contractions during a CST.
Some medications may interfere with the test results or cause side effects.
Choice D is wrong because applying warm compresses to the abdomen does not induce contractions.
It may help with pain relief or relaxation, but it does not affect the uterus.
Normal ranges for uterine contractions during a CST are three contractions in 10 minutes, each lasting 40 to 60 seconds.
Normal ranges for fetal heart rate during a CST are 110 to 160 beats per minute, with no decelerations after contractions.
A nurse is caring for a client who had an amniocentesis at 16 weeks gestation and reports cramping and vaginal bleeding 24 hours later.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. Monitor fetal heart rate.
This is because cramping and vaginal bleeding after amniocentesis are signs of possible complications such as miscarriage, preterm labor, or injury to the fetus.
Monitoring fetal heart rate can help assess the well-being of the fetus and detect any signs of distress.
Choice A is wrong because administering Rho(D) immunoglobulin is only necessary if the mother has Rh-negative blood and the baby has Rh-positive blood, which can cause Rh sensitization.
This is not given routinely to all women who have amniocentesis.
Choice C is wrong because assessing maternal vital signs is not the first priority when there is a risk of fetal compromise.
Maternal vital signs can be affected by many factors and are not specific indicators of fetal health.
Choice D is wrong because obtaining an order for an ultrasound exam is not the first action to take.
An ultrasound exam can help confirm the diagnosis of complications such as placental abruption or fetal demise, but it requires time and equipment that might delay immediate intervention.
Monitoring fetal heart rate can be done quickly and easily at the bedside.
A nurse is preparing a client for a biophysical profile (BPP).
The nurse should instruct the client that the test involves which of the following procedures?
Explanation
The test involves an ultrasound and a nonstress test.
A biophysical profile (BPP) is a way to check on the overall fetal health by observing the fetus’s heart rate, breathing, movement, muscle tone, and the amount of amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus in the uterus.
It is typically performed after 28 weeks of pregnancy, especially for high-risk pregnancies or if there is a chance of complications.
Choice B is wrong because a contraction stress test is not part of a BPP.
A contraction stress test measures how the fetus’s heart rate changes during contractions induced by oxytocin or nipple stimulation.
It is a different test from a nonstress test, which measures the fetus’s heart rate while moving and at rest without any stimulation.
Choice C is wrong because a Doppler ultrasound is not part of a BPP.
A Doppler ultrasound uses sound waves to measure the blood flow in the umbilical cord and other blood vessels.
It is a different type of ultrasound from the one used in a BPP, which uses sound waves to create images of the fetus and the amniotic fluid.
Choice D is wrong because it combines two incorrect components from choices B and C. A BPP does not involve a Doppler ultrasound or a contraction stress test.
A nurse is explaining the purpose of a Contraction Stress Test (CST) to a pregnant client.
What does the CST aim to assess?
Explanation
A contraction stress test (CST) is performed near the end of pregnancy to determine how well the fetus will cope with the contractions of childbirth.
The aim is to induce contractions and monitor the fetus to check for heart rate abnormalities using a cardiotocograph.
A normal heartbeat is a good sign that the fetus will be healthy during labor.
Choice B is wrong because a CST does not measure maternal blood pressure.
Choice C is wrong because a CST does not assess placental function directly.
Choice D is wrong because a CST does not measure amniotic fluid volume.
Normal ranges for fetal heart rate are between 110 and 160 beats per minute.
Normal ranges for uterine contractions are between 2 and 5 contractions in 10 minutes, lasting less than 90 seconds each.
A nurse is caring for a patient who had an amniocentesis performed at 16 weeks gestation and reports cramping and vaginal bleeding 24 hours later which action should be taken first?
Explanation
This is because cramping and vaginal bleeding after an amniocentesis may indicate a possible miscarriage or placental abruption, which can compromise fetal oxygenation and perfusion.
Monitoring fetal heart rate can help detect signs of fetal distress and guide further interventions.
Choice A is wrong because administering Rho(D) immune globulin is indicated for Rh-negative mothers who undergo amniocentesis to prevent isoimmunization, but it is not a priority action in this scenario.
Choice C is wrong because assessing maternal vital signs is important to monitor for signs of infection, hemorrhage, or shock, but it is not as urgent as monitoring fetal well-being.
Choice D is wrong because obtaining an order for an ultrasound exam can help confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the placenta and amniotic fluid, but it is not the first action to take in this situation.
A nurse is caring for a patient who had an amniocentesis performed at 16 weeks gestation and reports cramping and vaginal bleeding 24 hours later.
Which action should be taken first?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Notify the health care provider immediately.
This is because cramping and vaginal bleeding 24 hours after amniocentesis are signs of possible complications, such as injury to the baby or mother, leaking of amniotic fluid, infection, Rh sensitization, preterm labor, or miscarriage.
These complications are rare, but they can be serious and require immediate medical attention.
Choice B is wrong because administering pain medication to the patient does not address the underlying cause of the cramping and bleeding, and may delay seeking help.
Choice C is wrong because encouraging the patient to rest and elevate her legs may not prevent further complications, and may also delay seeking help.
Choice D is wrong because offering emotional support and reassurance to the patient is not enough to ensure the safety of the baby and the mother, and may give a false sense of security.
Normal ranges for amniocentesis are:
No chromosomal defects detected in the fetus and no abnormal proteins present in amniotic fluid
No signs of infection or other illness in the baby
Fetal lungs mature enough for birth if delivery is planned sooner than 39 weeks
A nurse is interpreting the results of a biophysical profile (BPP) for a client who is at 34 weeks of gestation.
The nurse should understand that each of the five variables is assigned a score of how many points?
Explanation
Each of the five variables in a biophysical profile (BPP) is assigned a score of either 0 or 2 points, depending on whether it meets the criteria or not.
The five variables are:
Fetal breathing: 2 points if there is at least one episode of rhythmic breathing lasting at least 30 seconds within 30 minutes, 0 points otherwise.
Fetal movement: 2 points if there are at least three discrete body or limb movements within 30 minutes, 0 points otherwise.
Fetal tone: 2 points if there is at least one episode of extremity extension and subsequent return to flexion, 0 points otherwise.
Amniotic fluid volume: 2 points if there is a pocket of amniotic fluid measuring at least 2 cm in two perpendicular planes, 0 points otherwise.
Nonstress test: 2 points if there are at least two accelerations of fetal heart rate with or without fetal movement within 20 minutes, 0 points otherwise.
Choice A is wrong because each variable can have a score of either 0 or 2, not 0 or.
Choice C is wrong because there is no score of 1 for any variable.
Choice D is wrong because it is incomplete and does not provide the full range of possible scores.
A nurse is reviewing the contraindications for a Contraction Stress Test (CST) with a pregnant client.
Which condition would be a contraindication for the test?
Explanation
This is a contraindication for the Contraction Stress Test (CST) because it increases the risk of infection and umbilical cord prolapse.
A CST is a test that measures the baby’s heart rate during uterine contractions induced by oxytocin or nipple stimulation.
Choice A is wrong because gestational diabetes is not a contraindication for the CST.
It is a condition that affects how the body processes glucose during pregnancy and may cause complications such as macrosomia (large baby), hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or preeclampsia (high blood pressure and protein in urine).
Choice B is wrong because mild preeclampsia is not a contraindication for the CST.
It is a condition that causes high blood pressure and protein in urine after 20 weeks of pregnancy and may affect the placenta, kidneys, liver or brain.
Choice C is wrong because preterm labor is a relative contraindication for the CST, not an absolute one.
It means that the test may be performed if the benefits outweigh the risks, but it should be avoided if possible because it may trigger early labor or delivery.
Preterm labor is defined as regular uterine contractions with cervical changes before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
Normal ranges for blood pressure are below 120/80 mmHg, for glucose are 70-100 mg/dL (fasting) or below 140 mg/dL (2 hours after eating), and for protein in urine are less than 300 mg/24 hours.
A nurse is educating a pregnant client about the Non-Stress Test (NST).
Which statement by the client indicates understanding of the test?
Explanation
"NST is performed after 28 weeks of gestation or earlier if there are risk factors."12 This statement indicates that the client understands when and why an NST is done.
Choice B is wrong because it describes a reactive NST, not a nonreactive one.
A reactive NST means that the fetal heart rate increases by at least 15 beats per minute for at least 15 seconds twice or more in a 20-minute period.2
Choice C is wrong because it confuses NST with contraction stress test (CST), which requires monitoring uterine contractions.
NST does not involve contractions.2
Choice D is wrong because it describes possible causes of a nonreactive NST, not a reactive one.
A nonreactive NST may indicate fetal hypoxia, distress, sleep, medication effect, or neurological abnormality.2
A client's CST result is interpreted as equivocal.
What additional diagnostic test may be recommended to further evaluate fetal well-being?
Explanation
An NST is a test that measures the fetal heart rate in response to fetal movement.
It is a non-invasive and simple way to assess fetal well-being.
An NST may be recommended to further evaluate fetal well-being if the CST result is equivocal, meaning that occasional but not persistent late decelerations are present.
Choice B. Amniocentesis is wrong because it is an invasive procedure that involves inserting a needle into the uterus to collect amniotic fluid for genetic testing or fetal lung maturity.
It is not used to evaluate fetal well-being in response to contractions.
Choice C. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is wrong because it is an imaging technique that uses magnetic fields to create detailed pictures of the fetus and the placenta.
It is not used to evaluate fetal well-being in response to contractions.
Choice D. Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is wrong because it is an invasive procedure that involves inserting a catheter or a needle into the placenta to collect chorionic villi for genetic testing.
It is not used to evaluate fetal well-being in response to contractions.
Normal ranges for CST are negative (normal) or positive (abnormal).
Equivocal and unsatisfactory are special categories of test outcomes that require further testing.
Normal ranges for NST are reactive (reassuring) ornon-reactive (non-reassuring).
A nurse is performing an abdominal ultrasound for a client who is at 28 weeks of gestation.
The nurse should instruct the client to do which of the following before the procedure?
Explanation
The woman should drink several glasses of water before the abdominal ultrasound procedure.
This is because a full bladder helps to push the intestines away and improve the visibility of the uterus and the fetus.
Drinking water also helps to avoid gas buildup in the abdomen, which could interfere with the sound waves.
Choice B is wrong because emptying the bladder would make it harder to see the uterus and the fetus.
Choice C is wrong because lying on the right side would not affect the quality of the ultrasound image.
Choice D is wrong because fasting is not necessary for an abdominal ultrasound, unless instructed by the doctor for a specific reason.
A nurse is explaining the purpose of an Alpha-fetoprotein Test (AFP) to a pregnant client.
What is the test primarily used for ?
Explanation
An alpha-fetoprotein test (AFP) is a blood test that measures the amount of AFP present in blood.
It’s usually part of what’s called a triple screen or quad screen in the second trimester of pregnancy.
The yolk sac, GI tract, and liver of an unborn baby produce AFP.
It then circulates through the fetal and maternal blood.
High levels of AFP in pregnant people can indicate that the baby has a neural tube defect, such as spina bifida or anencephaly.
Choice B is wrong because assessing placental function is not the primary purpose of an AFP test.
However, low levels of AFP can indicate problems with the placenta or the baby’s growth.
Choice C is wrong because determining fetal gender is not the primary purpose of an AFP test.
However, some genetic tests that use a sample of the baby’s DNA from the pregnant person’s blood can reveal the baby’s sex as early as 10 weeks of pregnancy.
Choice D is wrong because diagnosing chromosomal abnormalities is not the primary purpose of an AFP test.
However, an AFP test is usually part of a quad screen that also tests for other markers that can indicate the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome.
A nurse is caring for a client who has oligohydramnios and is undergoing a biophysical profile (BPP).
The nurse should expect to see which of the following findings on the ultrasound?
Explanation
An amniotic fluid index (AFI) of 4 cm indicates oligohydramnios, which is a low amount of amniotic fluid.
Oligohydramnios can be caused by various factors, such as uteroplacental insufficiency, rupture of membranes, postterm pregnancy, fetal anomalies, or certain medications.
Oligohydramnios can lead to complications such as fetal death, intrauterine growth restriction, limb contractures, or delayed lung maturation.
Choice A is wrong because an AFI of 8 cm is within the normal range for amniotic fluid volume.
Choice C is wrong because a single vertical pocket of amniotic fluid measuring 3 cm is also within the normal range for amniotic fluid volume.
Choice D is wrong because a single vertical pocket of amniotic fluid measuring 5 cm is also within the normal range for amniotic fluid volume.
Normal ranges for AFI and single vertical pocket are > 5 to < 24 cm and ≥ 2 to < 8 cm, respectively.
During a CST, the nurse observes variable decelerations of the FHR with or without contractions.
What does this finding indicate?
Explanation
This finding indicates that the umbilical cord is being compressed, which can reduce the blood flow and oxygen supply to the fetus.
Variable decelerations are abrupt decreases in the fetal heart rate (FHR) that vary in shape, duration, and degree of fall below the baseline.
They are seen as W- or U-shaped waves on the monitor.
Choice B is wrong because fetal hypoxia is not indicated by variable decelerations, but by late decelerations, which are gradual decreases in the FHR that begin after the peak of the contraction and return to baseline after the contraction ends.
Late decelerations are associated with uteroplacental insufficiency, which means that the placenta is not delivering enough oxygen to the fetus.
Choice C is wrong because normal placental function is not indicated by variable decelerations, but by reassuring FHR patterns, such as moderate variability (6 to 25 beats per minute) and accelerations (increases in the FHR above the baseline).
Normal placental function ensures adequate fetal oxygenation and well-being.
Choice D is wrong because adequate fetal oxygenation is not indicated by variable decelerations, but by reassuring FHR patterns, such as moderate variability and accelerations.
Adequate fetal oxygenation means that the fetus is not experiencing hypoxia or distress.
Normal ranges for FHR are 110 to 160 beats per minute at term and 120 to 160 beats per minute before term.
Normal ranges for uterine contractions are 2 to 5 contractions in 10 minutes, lasting less than 90 seconds each.
A client's Alpha-fetoprotein Test (AFP) result is reported as 1.2 MoM.
How should the nurse interpret this result?
Explanation
Normal level of AFP for the given gestational age.
AFP is a protein that the liver makes when its cells are growing and dividing to make new cells.
It is normally high in unborn babies and drops very low after birth.
The AFP test measures the amount of AFP present in blood and can help diagnose certain types of cancer and check how well treatment is working.
It can also help detect some birth defects in pregnant women.
Choice B is wrong because high level of AFP indicating a neural tube defect.
Neural tube defects are abnormalities that affect the brain and spinal cord of the fetus.
They can cause spina bifida, which is a condition where the spine does not close properly.
High levels of AFP can be a sign of neural tube defects, but they can also be caused by other factors, such as multiple pregnancies, inaccurate dating of pregnancy, or fetal death.
Choice C is wrong because low level of AFP indicating a chromosomal abnormality.
Chromosomal abnormalities are genetic disorders that affect the number or structure of chromosomes in the fetus.
They can cause Down syndrome, which is a condition where the fetus has an extra copy of chromosome 212.
Low levels of AFP can be a sign of chromosomal abnormalities, but they can also be caused by other factors, such as inaccurate dating of pregnancy, fetal death, or maternal obesity.
Choice D is wrong because inconclusive result, requiring further evaluation.
An inconclusive result means that the AFP level is neither too high nor too low to indicate a problem with the fetus.
It does not necessarily mean that there is something wrong with the fetus, but it may require further testing to confirm or rule out any abnormalities.
Normal ranges for AFP levels vary depending on the gestational age and the laboratory that performs the test.
Generally, the normal range for AFP levels in pregnant
A nurse is observing fetal breathing movements on an ultrasound for a client who is undergoing a biophysical profile (BPP).
The nurse should document how many points for this variable if the fetus has at least one episode of breathing lasting for 20 seconds within a 30-minute period?
Explanation
According to the ACOG guidelines on antepartum fetal surveillance, one of the components of the biophysical profile is fetal breathing movements, which are scored as 2 points if there is one or more episodes of rhythmic fetal breathing movements of 30 seconds or more within 30 minutes.
Choice A is wrong because 0 points are given for absent or no breathing episode for ≥30 seconds within a 30 minute observation period.
Choice B is wrong because there is no 1 point score for this variable.
Choice D is wrong because there is no 3 point score for this variable.
The maximum score for each variable is 2 points.
A nurse is educating a pregnant client about the Alpha-fetoprotein Test (AFP).
What should the nurse include as a reason why AFP results are reported as multiples of the median (MoM)?
Explanation
This is because AFP levels vary according to the gestational age of the fetus, and reporting them as multiples of the median (MoM) allows for a standardized comparison.
Choice B is wrong because AFP results do not differentiate between neural tube defects and chromosomal abnormalities.
They only indicate an increased risk for these conditions, which need further testing to confirm.
Choice C is wrong because AFP results do not assess the risk of fetal demise or multiple gestation.
They only measure the amount of AFP in the maternal blood, which can be affected by various factors such as maternal weight, race, diabetes, and fetal anomalies.
Choice D is wrong because AFP results are reported as MoM regardless of factors such as maternal weight and race.
These factors are taken into account when calculating the MoM value, which adjusts for the expected variation in AFP levels among different populations.
Normal ranges for AFP MoM vary depending on the laboratory and the method used, but generally they are between 0.5 and 2.52.
Values above or below this range may indicate an increased risk for certain fetal conditions or complications.
A nurse is educating a pregnant client about the Contraction Stress Test (CST).
Which statement accurately describes a negative CST?
Explanation
This means that the baby’s heart rate did not slow down after the contractions induced by oxytocin, which is a sign of normal fetal well-being.
A negative CST is normal and desirable.
Choice A is wrong because no contractions were induced during the test.
This means that the test was inconclusive and could not assess the baby’s response to stress.
Choice B is wrong because late decelerations of the FHR were observed with at least 50% of contractions.
This means that the baby’s heart rate slowed down and stayed slow after the contractions, which is a sign of fetal distress and hypoxia.
A positive CST is abnormal and concerning.
Choice D is wrong because the client experienced mild uterine cramping during the test.
This is not a relevant factor for interpreting the CST results, which depend on the FHR patterns.
Uterine cramping can be a side effect of oxytocin administration or nipple stimulation.
A client's Alpha-fetoprotein Test (AFP) result is reported as 0.8 MoM.
What does this result suggest?
Explanation
This result suggests that the baby has a low risk of having a genetic disorder or a neural tube defect.
Choice B is wrong because a high level of AFP indicating a neural tube defect would be greater than 2 MoM.
Choice C is wrong because a low level of AFP indicating a potential chromosomal abnormality would be less than 0.5 MoM.
Choice D is wrong because an inconclusive result, requiring further evaluation, would depend on other factors such as ultrasound findings and maternal age.
MoM stands for multiples of the median, which is a way of comparing the AFP level of a pregnant person to the average level for their gestational age.
Values between 0.5 and 2.49 MoM are considered normal.
A nurse is reviewing the results of an Alpha-fetoprotein Test (AFP) with a pregnant client.
What does a low level of AFP (<0.5 MoM) potentially indicate?
Explanation
A low level of AFP (<0.5 MoM) in a pregnant woman can indicate that the fetus has a chromosomal abnormality, such as Down syndrome or Edwards syndrome.
This is because these conditions affect the development of the fetal liver, which produces AFP.
Choice A is wrong because neural tube defects, such as spina bifida, are associated with high levels of AFP (>2.5 MoM) in the maternal blood.
This is because AFP can leak from the open spinal canal of the fetus into the amniotic fluid and then into the maternal blood.
Choice C is wrong because maternal weight-related factors do not affect the level of AFP in the maternal blood.
However, they can affect the interpretation of the AFP test results, as the test needs to be adjusted for maternal weight, age, ethnicity, and gestational age.
Choice D is wrong because fetal demise (death) can also cause high levels of AFP in the maternal blood, as the AFP from the dead fetus can leak into the amniotic fluid and then into the maternal blood.
Normal ranges of AFP in pregnant women vary depending on the gestational age and the method of measurement.
Generally, normal levels of AFP are below 10 ng/ml in nonpregnant adults and below 2.5 MoM in pregnant women.
A client asks the nurse about the risks and complications associated with prenatal ultrasound.
Which of the following responses by the nurse is accurate?
Explanation
There are no known risks or complications for the pregnant person or the fetus.
Prenatal ultrasound is a safe and noninvasive procedure that uses sound waves to create images of the fetus and the placenta.
It does not use radiation or harm the fetal tissues.
Choice A is wrong because ultrasound does not cause harm to the fetus.
There is no evidence that ultrasound has any adverse effects on fetal development, growth, or health.
Choice C is wrong because pregnant individuals do not need to avoid ultrasound due to potential radiation exposure.
Ultrasound does not involve radiation, unlike x-rays or CT scans.
Choice D is wrong because ultrasound does not lead to miscarriage or preterm labor.
Ultrasound is not associated with any increased risk of pregnancy complications, such as miscarriage, preterm labor, or birth defects.
A nurse is explaining the purpose of a nuchal translucency (NT) ultrasound to a pregnant client.
What does this ultrasound measure?
Explanation
This is because a nuchal translucency ultrasound measures the amount of fluid behind the baby’s neck in the first trimester of pregnancy, which can indicate the risk of having a chromosomal condition like Down syndrome.
Some possible explanations for the other choices are:
Choice A is wrong because fetal growth and development are not directly related to the nuchal translucency measurement.
Fetal growth and development are assessed by other parameters such as crown-rump length, biparietal diameter, abdominal circumference, etc.
Choice B is wrong because blood flow in the umbilical cord is not measured by the nuchal translucency ultrasound.
Blood flow in the umbilical cord is assessed by Doppler ultrasound, which evaluates the resistance and velocity of blood flow in the umbilical artery and vein.
Choice D is wrong because structural abnormalities in the baby’s organs are not detected by the nuchal translucency ultrasound.
Structural abnormalities in the baby’s organs are diagnosed by a detailed anatomy scan, which is usually performed in the second trimester of pregnancy.
The normal range for nuchal translucency is between 1 mm and 3 mm.
A measurement above 3 mm is considered increased and may indicate a higher risk of chromosomal or genetic conditions.
However, a nuchal translucency ultrasound is a screening test and not a diagnostic test, so it does not confirm or rule out any condition.
It only provides a probability based on statistical calculations.
Therefore, further testing may be recommended if the nuchal translucency measurement is increased or if other risk factors are present.
A nurse is discussing the factors that can affect Alpha-fetoprotein Test (AFP) results with a pregnant client.
Which factor should the nurse mention?
Explanation
The level of AFP in a pregnant woman’s blood depends on how far along she is in her pregnancy.
AFP levels are normally high in the early weeks of pregnancy and then decline as the pregnancy progresses.
If the AFP level is too high or too low for the gestational age, it may indicate a problem with the baby’s development.
Choice A is wrong because maternal weight does not affect AFP levels.
Choice B is wrong because fetal heart rate does not affect AFP levels.
Choice D is wrong because the placental function does not affect AFP levels directly, but it may affect the levels of other hormones that are measured along with AFP in a quad screen.
A nurse is explaining the purpose of a Doppler ultrasound blood flow analysis to a client who has intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).
The nurse should inform the client that this test measures which of the following?
Explanation
A Doppler ultrasound blood flow analysis measures the velocity of blood flow in the uterine and fetal vessels.
This test can help assess the fetal well-being and oxygenation in cases of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).
Choice B is wrong because the amount of amniotic fluid in the uterine cavity is measured by ultrasound, not Doppler.
Choice C is wrong because the pressure of blood flow in the umbilical cord is not directly measured by Doppler, but rather inferred from the resistance index or pulsatility index.
Choice D is wrong because the oxygen saturation level of fetal blood is not measured by Doppler, but rather by fetal scalp sampling or pulse oximetry.
A client is scheduled for an abdominal ultrasound in two weeks.
The client asks the nurse what they should do to prepare for the test.
What is the best response by the nurse?
Explanation
The patient should wear loose-fitting clothing and lie supine on an examination table.
This is because loose-fitting clothing allows easy access to the abdomen and lying supine helps relax the abdominal muscles.
The patient should also avoid food and drinks for 8 to 12 hours before the test, as undigested food can interfere with the sound waves and affect the image quality.
Choice A is wrong because a full bladder is not necessary for an abdominal ultrasound, unless the patient is pregnant or has a pelvic condition.
A transvaginal ultrasound is a different type of ultrasound that uses a probe inserted into the vagina to examine the reproductive organs.
Choice B is wrong because tight-fitting clothing can restrict the movement of the ultrasound probe and make it harder to get a clear image.
Lying prone (on the stomach) can also tense up the abdominal muscles and obscure the organs.
Choice D is wrong because lying prone can have the same disadvantages as choice B. Additionally, wearing loose-fitting clothing does not mean that the patient can eat or drink anything before the test, as this can affect the results.
A client asks the nurse about the significance of Alpha-fetoprotein Test (AFP) results.
How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
AFP is a screening tool that can indicate the possibility of certain fetal anomalies, such as neural tube defects, abdominal wall defects, or chromosomal abnormalities.
However, AFP results are not diagnostic and cannot confirm the presence or absence of these conditions.
Therefore, further tests, such as ultrasound or amniocentesis, are needed to verify the results.
Choice A is wrong because AFP results are not diagnostic for fetal anomalies.
They only indicate a risk level that needs to be confirmed by other tests.
Choice C is wrong because AFP results can detect not only neural tube defects, but also other fetal anomalies, such as abdominal wall defects or chromosomal abnormalities.
Choice D is wrong because AFP results are not affected by maternal race and ethnicity.
They are affected by maternal age, weight, diabetes, multiple gestation, and gestational age.
A nurse is reviewing the results of a Contraction Stress Test (CST) with a pregnant client.
What does an equivocal CST indicate?
Explanation
An equivocal CST indicates late decelerations of the FHR with less than 50% of contractions.
This means that the fetus may have some degree of hypoxia or distress, but not enough to warrant immediate delivery.
An equivocal CST may also result from hyperstimulation of the uterus, which can cause excessive contractions and reduce blood flow to the placenta.
Choice B is wrong because late decelerations of the FHR with at least 50% of contractions is a positive CST, which indicates a high risk of fetal death due to hypoxia and is a contraindication to labor.
Choice C is wrong because no late decelerations of the FHR during contractions is a negative CST, which indicates a good fetal wellbeing and tolerance of labor.
Choice D is wrong because variable decelerations of the FHR with or without contractions are not related to uterine activity and may indicate cord compression or other fetal problems.
Variable decelerations are not used to interpret CST results.
A nurse is reviewing contraception options for four clients.
The nurse should identify that which of the following clients has a contraindication for receiving oral contraceptives?
Explanation
This is because migraine headaches with aura are a contraindication for receiving oral contraceptives, as they increase the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular complications.
Some possible explanations for the other choices are:
Choice B: A 32-year-old client who has endometriosis.
This is not a contraindication for receiving oral contraceptives, as they can actually help reduce the symptoms of endometriosis by suppressing ovulation and reducing menstrual bleeding.
Choice C: A 28-year-old client who has polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
This is not a contraindication for receiving oral contraceptives, as they can help regulate the menstrual cycle and lower the levels of androgens (male hormones) that cause acne, hirsutism (excess hair growth), and other problems in women with PCOS.
Choice D: A 22-year-old client who has irregular menstrual cycles.
This is not a contraindication for receiving oral contraceptives, as they can help normalize the menstrual cycle and prevent unintended pregnancy.
Normal ranges for oral contraceptive doses are:
Estrogen: 10 to 35 mcg of ethinyl estradiol or estradiol valerate
Progestin: varies depending on the type and brand of oral contraceptive
A client is scheduled for a transvaginal ultrasound in two weeks.
The client asks the nurse what they should do to prepare for the test.
What is the best response by the nurse?
Explanation
“The patient should have a full bladder for a transabdominal US and an empty bladder for a transvaginal US.”1 This is because a full bladder helps to lift the uterus and improve the visibility of the pelvic organs in a transabdominal US, while an empty bladder prevents distortion of the image in a transvaginal US.
Choice B is wrong because tight-fitting clothing is not necessary and lying prone on an examination table is uncomfortable and may interfere with the insertion of the vaginal probe.
Choice C is wrong because loose-fitting clothing is not necessary and lying supine on an examination table may cause supine hypotension syndrome in pregnant women.
Choice D is wrong because loose-fitting clothing is not necessary and lying prone on an examination table is uncomfortable and may interfere with the insertion of the vaginal probe.
A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for a maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein test at 15 weeks of gestation.
The nurse provides which of the following explanations about this test to the client?
Explanation
A maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein test is a type of prenatal blood test that measures the levels of MSAFP in the blood of a pregnant person.The test helps the healthcare provider assess the baby’s risk of certain medical conditions, such as neural tube defects and chromosomal abnormalities.The test is usually done between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy.
A screening test means that it does not diagnose any health conditions, but only indicates the probability of having them.
A positive test means that the baby has a higher risk of having a birth defect, but it does not confirm it.
A negative test means that the baby has a lower risk of having a birth defect, but it does not rule it out.Further tests are needed to confirm or exclude the diagnosis.
A diagnostic test means that it can provide a definite diagnosis of a health condition.A maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein test is not a diagnostic test for spinal defects or chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus.
Statement A is wrong because it says that the test is a diagnostic test for spinal defects in the fetus, which is not true.
Statement C is wrong because it says that the test is a diagnostic test for chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, which is not true.
Statement D is wrong because it says that the test is a screening test for chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, which is only partially true.The test can screen for some chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome, but not all of them.
The test also screens for neural tube defects, which are not chromosomal abnormalities.
Normal ranges for MSAFP vary depending on the gestational age and the laboratory methods used.Generally, MSAFP levels increase until about 32 weeks of pregnancy and then decrease until delivery.
High levels of MSAFP may indicate neural tube defects, multiple pregnancies, incorrect dating of pregnancy, or other conditions.Low levels of MSAFP may indicate Down syndrome, other chromosomal abnormalities, or other conditions.
A nurse is discussing the risks associated with a Contraction Stress Test (CST) with a pregnant client.
Which complication should the nurse mention?
Explanation
A contraction stress test (CST) is a test that simulates labor contractions to see how the baby’s heart rate responds to the stress of uterine contractions.
The biggest risk of the test is that it may cause the pregnant person to go into labor before their due date.
Some possible explanations for the other choices are:
Choice B. Premature rupture of membranes.
This is a condition where the amniotic sac breaks before labor begins.
It can increase the risk of infection and cord prolapse, but it is not a direct complication of CST.
Choice C. Infection.
This is a possible risk of any invasive procedure, but CST is usually done with external fetal monitoring and oxytocin infusion, which do not require breaking the skin or entering the uterus.
Choice D. Bleeding.
This is a potential risk of CST for people who have placenta previa, a condition where the placenta covers the cervix and can detach during contractions.
However, CST is not recommended for people who have placenta previa or other conditions that increase the risk of uterine rupture or bleeding.
A client is scheduled for an abdominal ultrasound in two weeks to assess fetal growth and development during pregnancy.
Which of these statements made by the client indicates that further teaching is needed?
Explanation
The client should not eat a light meal before an abdominal ultrasound because it can interfere with the quality of the images.
The client should fast for 8 to 12 hours before the procedure.
Some additional information about the other choices are:
Choice A is correct.
The client should drink plenty of fluids before an appointment for an abdominal ultrasound because it helps to fill the bladder and push the uterus up for better visualization.
Choice C is correct.
The client should wear comfortable clothing that can be easily removed or lifted up to expose the abdomen.
Choice D is correct.
The client should arrive at the appointment with a full bladder because it acts as an acoustic window and improves the quality of the ultrasound images.
Normal ranges for fetal growth and development during pregnancy vary depending on the gestational age, but some general parameters are:
Fetal heart rate: 110 to 160 beats per minute
Biparietal diameter: 2.4 to 9.5 cm
Crown-rump length: 0.8 to 8.4 cm
Femur length: 1.0 to 7.8 cm
Abdominal circumference: 9.4 to 35.6 cm
A nurse is teaching about fetal development to a group of clients in the antenatal clinic.
Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
The baby’s heart beat is audible by a Doppler stethoscope at 12 weeks of pregnancy.
This is a device that uses sound waves to create an image of the baby’s heart and measure its rate and rhythm.
Some possible explanations for the other choices are:
Choice B is wrong because the baby’s sex can not be determined by ultrasound at 8 weeks of pregnancy.
The external genitalia are not fully developed until around 14 to 16 weeks of pregnancy.
Even then, the accuracy of ultrasound depends on factors such as the position of the baby, the quality of the equipment, and the skill of the sonographer.
Choice C is wrong because the baby’s lungs are not fully mature by 24 weeks of pregnancy.
The lungs are one of the last organs to develop in the fetus and they continue to grow and mature until near term.
The production of surfactant, a substance that helps the lungs expand and prevent collapse, begins around 24 weeks but is not sufficient until around 34 to 36 weeks.
Choice D is wrong because the baby’s eyes do not open and close by 16 weeks of pregnancy.
The eyelids are fused together until around 26 to 28 weeks of pregnancy, when they start to open and close periodically.
The baby can also respond to light and dark stimuli around this time.
A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for a maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein test at 15 weeks of gestation.
The nurse provides which of the following explanations about this test to the client?
Explanation
"It is a screening test for spinal defects in the fetus."
The MSAFP test is a blood test that measures the amount of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the mother’s blood.
AFP is a protein produced by the baby during pregnancy.The test helps to assess the baby’s risk of certain birth defects, such as neural tube defects, which are abnormalities in the development of the brain and spine.
A. “It is a diagnostic test for spinal defects in the fetus.” This statement is wrong because the MSAFP test is not a diagnostic test.
It only indicates the probability of having a spinal defect, but it does not confirm or rule out the condition.A diagnostic test, such as an ultrasound or amniocentesis, is needed to make a definitive diagnosis.
C. “It is a diagnostic test for chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus.” This statement is wrong because the MSAFP test is not a diagnostic test for chromosomal abnormalities either.
It only indicates the probability of having a chromosomal abnormality, such as Down syndrome, but it does not confirm or rule out the condition.A diagnostic test, such as a chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis, is needed to make a definitive diagnosis.
D. “It is a screening test for chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus.” This statement is partially correct, but not the best answer.
The MSAFP test alone is not very accurate for screening chromosomal abnormalities.It is usually combined with other blood tests and an ultrasound to form a more reliable screening test called a quad screen or an integrated screen.
The normal range of MSAFP levels varies depending on the gestational age of the baby and the laboratory methods used.Generally, the MSAFP levels increase until about 15 weeks of pregnancy and then decrease until delivery.The average MSAFP level at 15 weeks of pregnancy is about 38 ng/mL.However, different laboratories may have different reference ranges, so it is important to consult your healthcare provider for your specific results and interpretation.
Exams on Prenatal Diagnostic Tests And Procedures
Custom Exams
Login to Create a Quiz
Click here to loginLessons
 Nursingprepexams
Just Now
Nursingprepexams
Just Now
- Objectives
- Introduction
- Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
- Amniocentesis
- Non-Stress Test (NST)
- Biophysical Profile (BPP)
- Contraction Stress Test (CST)
- Alpha-fetoprotein Test (AFP)
- Ultrasound
- Maternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (MSAFP) Test
- Cell-free Fetal DNA Testing
- Percutaneous Umbilical Blood Sampling (PUBS)
- Conclusion
- Summary
- More questions on this topic
Notes Highlighting is available once you sign in. Login Here.
Objectives
- To understand the purpose, indications, and limitations of prenatal screening and diagnostic tests
- To describe the types, methods, and risks of prenatal screening and diagnostic tests
- To identify the markers and normal ranges of prenatal screening and diagnostic tests
- To explain the implications and management of abnormal prenatal screening and diagnostic test results
- To compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of different prenatal screening and diagnostic tests
- To apply ethical principles and patient-centered care to prenatal screening and diagnostic testing
Introduction
- Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests are procedures that provide information about the health and development of a fetus before birth
- Prenatal screening tests estimate the risk or probability of a fetus having certain genetic or chromosomal conditions, such as Down syndrome, neural tube defects, or cystic fibrosis
- Prenatal diagnostic tests confirm or rule out the presence of a specific condition in a fetus
- Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests are optional and informed consent is required before performing them
- Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests have benefits and limitations, and the results may have physical, emotional, social, and financial implications for the pregnant person and their family
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
- CVS is a prenatal diagnostic test that involves obtaining a small sample of placental tissue (chorionic villi) for chromosomal analysis
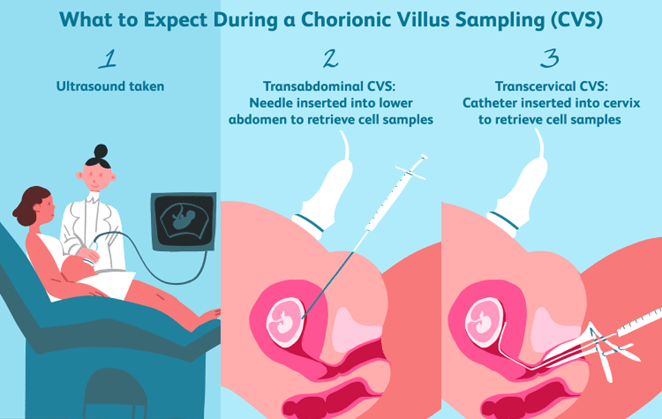
- CVS can detect chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome, trisomy 13, trisomy 18, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, .
- CVS can also detect some genetic disorders such as cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs disease, sickle cell disease, .
- CVS cannot detect neural tube defects such as spina bifida or anencephaly
- CVS is usually performed between 10 and 13 weeks of gestation
- CVS can be done by two methods: transcervical or transabdominal
- Transcervical CVS involves inserting a thin catheter through the cervix and suctioning a small amount of chorionic villi under ultrasound guidance
- Transabdominal CVS involves inserting a thin needle through the abdomen and uterus and aspirating a small amount of chorionic villi under ultrasound guidance
- CVS has a risk of miscarriage of about 0.5% to 1%
- CVS has a risk of infection, bleeding, cramping, leaking of amniotic fluid, Rh sensitization, limb defects.
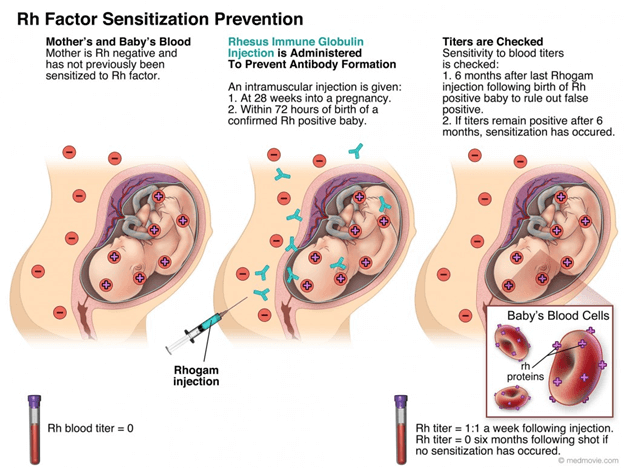
- CVS results are usually available within 10 to 14 days.
Amniocentesis
- Amniocentesis is a prenatal diagnostic test that involves obtaining a small sample of amniotic fluid for chromosomal analysis
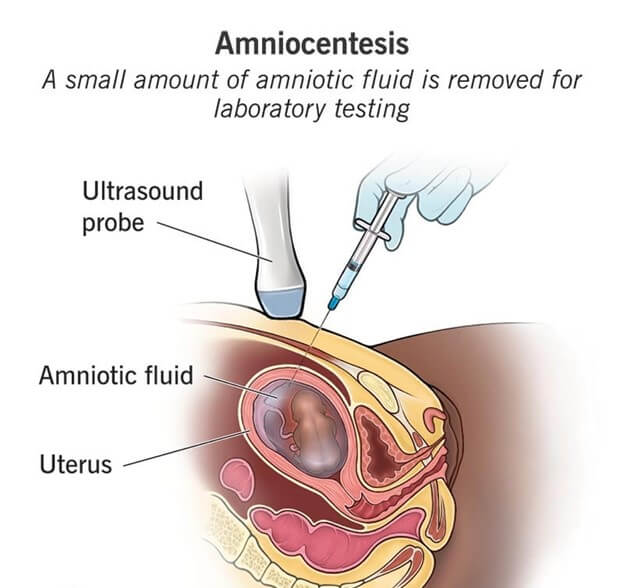
- Amniocentesis can detect chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome, trisomy 13, trisomy 18, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, .
- Amniocentesis can also detect some genetic disorders such as cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs disease, sickle cell disease, .
- Amniocentesis can also detect neural tube defects such as spina bifida or anencephaly by measuring the level of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the amniotic fluid
- Amniocentesis is usually performed between 15 and 20 weeks of gestation
- Amniocentesis involves inserting a thin needle through the abdomen and uterus and withdrawing a small amount of amniotic fluid under ultrasound guidance
- Amniocentesis has a risk of miscarriage of about 0.1% to 0.3%
- Amniocentesis has a risk of infection, bleeding, cramping, leaking of amniotic fluid, Rh sensitization, injury to the fetus or placenta.
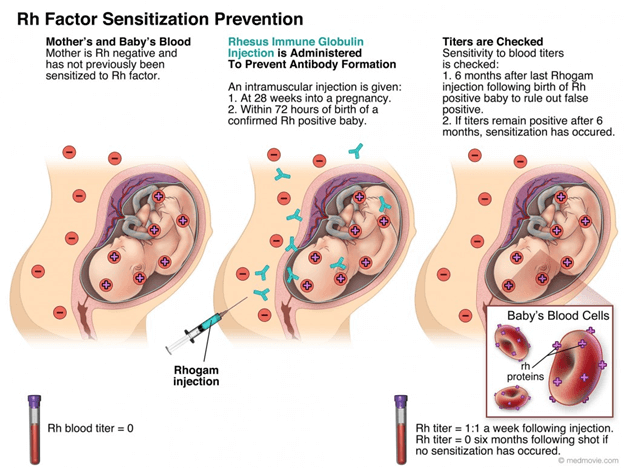
- Amniocentesis results are usually available within 10 to 14 days
Non-Stress Test (NST)
- NST is a prenatal screening test that measures the fetal heart rate (FHR) in response to fetal movements

- NST can assess fetal well-being and identify fetal hypoxia or distress
- NST is usually performed after 28 weeks of gestation or earlier if there are risk factors such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), .
- NST involves placing two belts with sensors on the pregnant person’s abdomen: one to monitor the FHR and one to monitor the uterine contractions
- NST requires the pregnant person to press a button whenever they feel the fetus move
- NST is usually done for 20 to 40 minutes or until at least two fetal movements are recorded
- NST is interpreted as reactive or nonreactive
- A reactive NST means that the FHR increases by at least 15 beats per minute for at least 15 seconds twice or more in a 20-minute period
- A reactive NST indicates adequate fetal oxygenation and normal fetal neurological function
- A nonreactive NST means that the FHR does not meet the criteria for a reactive NST
- A nonreactive NST may indicate fetal hypoxia, distress, sleep, medication effect, or neurological abnormality
- A nonreactive NST requires further evaluation such as a biophysical profile (BPP) or a contraction stress test (CST)
- NST has no risks or complications for the pregnant person or the fetus
Biophysical Profile (BPP)
- BPP is a prenatal screening test that combines an NST with an ultrasound to assess five fetal biophysical variables: FHR, fetal breathing movements, fetal body movements, fetal tone, and amniotic fluid volume
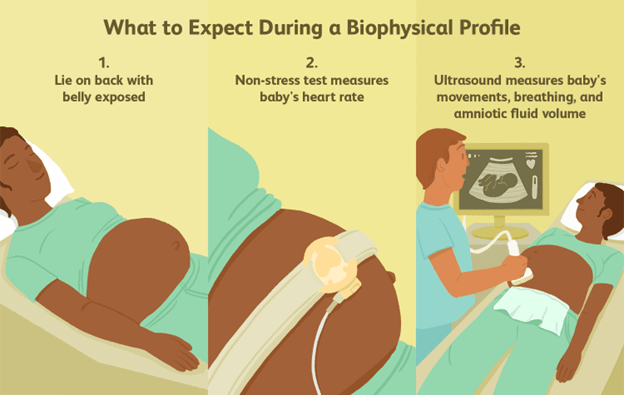
- BPP can evaluate fetal well-being and identify fetal hypoxia or distress
- BPP is usually performed after 28 weeks of gestation or earlier if there are risk factors such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, IUGR, .
- BPP involves performing an NST and an ultrasound for 30 minutes
- BPP assigns a score of 0 or 2 to each of the five variables based on predefined criteria
- A total BPP score of 8 to 10 is normal and indicates a low risk of fetal asphyxia
- A total BPP score of 6 is equivocal and may indicate chronic fetal asphyxia
- A total BPP score of 4 or less is abnormal and indicates acute fetal asphyxia
- A low BPP score requires further evaluation such as a CST or delivery depending on the gestational age and fetal condition
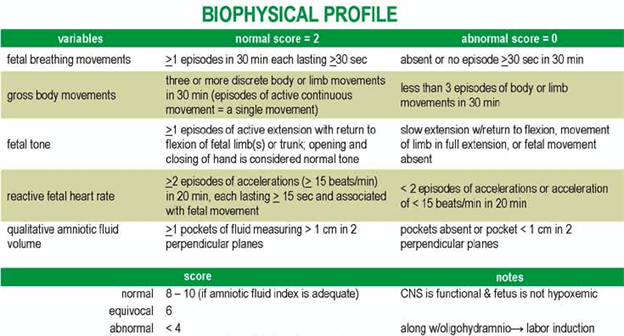
- BPP has no risks or complications for the pregnant person or the fetus
Contraction Stress Test (CST)
- CST is a prenatal screening test that measures the FHR in response to uterine contractions
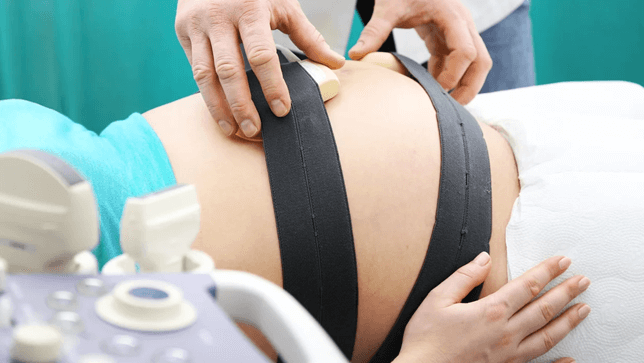
- CST can assess fetal well-being and identify fetal hypoxia or distress
- CST is usually performed after 28 weeks of gestation or earlier if there are risk factors such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, IUGR, .
- CST involves placing two belts with sensors on the pregnant person’s abdomen: one to monitor the FHR and one to monitor the uterine contractions
- CST requires inducing uterine contractions by either nipple stimulation or intravenous oxytocin infusion
- CST aims to achieve at least three contractions lasting 40 to 60 seconds in a 10-minute period
- CST is interpreted as negative, positive, equivocal, or unsatisfactory
- A negative CST means that there are no late decelerations of the FHR during contractions
- A negative CST indicates adequate fetal oxygenation and normal placental function
- A positive CST means that there are late decelerations of the FHR with at least 50% of contractions
- A positive CST indicates fetal hypoxia and compromised placental function
- An equivocal CST means that there are late decelerations of the FHR with less than 50% of contractions or variable decelerations of the FHR with or without contractions
- An equivocal CST may indicate cord compression, fetal head compression, or mild fetal hypoxia
- An unsatisfactory CST means that there are insufficient contractions or poor quality of FHR tracing
- An unsatisfactory CST requires repeating the test or performing a BPP
- CST has a risk of preterm labor, premature rupture of membranes, infection, bleeding, .
Alpha-fetoprotein Test (AFP)
- AFP is a prenatal screening test that measures the level of AFP in the pregnant person’s blood


- AFP is a protein produced by the fetal liver and yolk sac that crosses the placenta and enters the maternal circulation
- AFP can detect neural tube defects such as spina bifida or anencephaly by measuring the level of AFP in the maternal serum (MSAFP) or in the amniotic fluid (AFAFP)
- AFP can also detect other fetal anomalies such as abdominal wall defects, renal anomalies, chromosomal abnormalities, .
- AFP is usually performed between 15 and 20 weeks of gestation
- AFP involves drawing a blood sample from the pregnant person’s arm and sending it to a laboratory for analysis
- AFP results are reported as multiples of the median (MoM), which compare the measured level of AFP to the expected level for a given gestational age
- A high level of AFP (>2.5 MoM) may indicate a neural tube defect, an abdominal wall defect, a fetal demise, or a multiple gestation
- A low level of AFP (<0.5 MoM) may indicate a chromosomal abnormality such as Down syndrome, trisomy 18, or trisomy 13
- AFP results are affected by factors such as maternal weight, diabetes mellitus, race, ethnicity, .
- AFP results are not diagnostic and require further evaluation such as ultrasound, amniocentesis, or karyotyping
- AFP has no risks or complications for the pregnant person or the fetus
Ultrasound
- Ultrasound is a prenatal screening test that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the fetus and its surroundings.
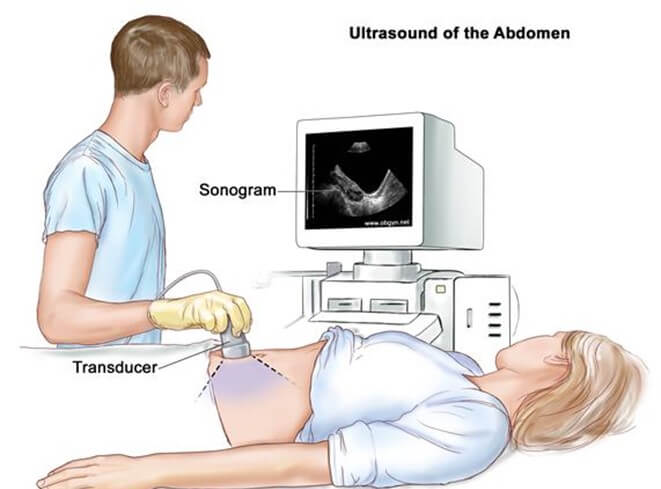
- Ultrasound can assess fetal growth, development, anatomy, position, movement, heart rate, and placental location
- Ultrasound can also estimate gestational age, due date, fetal weight, and amniotic fluid volume
- Ultrasound can detect fetal anomalies such as neural tube defects, cardiac defects, cleft lip/palate, skeletal dysplasia, .
- Ultrasound can also detect multiple gestations, placenta previa, placental abruption, ectopic pregnancy, .
- Ultrasound can be performed at any time during pregnancy but is usually done at specific intervals depending on the purpose and indication
- Ultrasound can be done by two methods: transabdominal or transvaginal
- Transabdominal ultrasound involves placing a transducer coated with gel on the pregnant person’s abdomen and moving it to obtain images of the fetus and its surroundings
- Transvaginal ultrasound involves inserting a transducer covered with a condom and gel into the pregnant person’s vagina and obtaining images of the fetus and its surroundings
- Ultrasound has no known risks or complications for the pregnant person or the fetus
Preparation and Procedure of Prenatal Ultrasound
-
- The patient should have a full bladder for a transabdominal US and an empty bladder for a transvaginal US.
- The patient should wear loose-fitting clothing and lie supine on an examination table.
- A gel is applied to the abdomen or the vaginal probe to facilitate sound transmission.
- The sonographer moves the transducer over the abdomen or inserts it into the vagina to obtain images of the fetus and the placenta.
- The images are displayed on a monitor and recorded for interpretation by a radiologist or an obstetrician.
- The procedure usually takes 15 to 30 minutes, depending on the type and purpose of the US.
Different types of Prenatal Ultrasounds
- Dating Ultrasound: Typically performed between 8 and 12 weeks of gestation. It is used to estimate the due date, confirm the number of fetuses, and assess early pregnancy development.
- Nuchal Translucency (NT) Ultrasound: Conducted between 11 and 14 weeks of gestation. It measures the thickness of the fluid-filled space at the back of the baby's neck to screen for chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome.
- Anatomy Ultrasound (Anomaly scan): Usually performed between 18 and 22 weeks of gestation. It provides a detailed examination of the baby's organs, limbs, and overall anatomy, helping to detect any structural abnormalities.
- Growth Ultrasound: This ultrasound may be performed at various intervals throughout the pregnancy, depending on individual circumstances. It assesses the baby's growth, including measurements of the head, abdomen, and femur length, and compares them to standardized growth charts.
- Doppler Ultrasound: It can be performed at different gestational ages as needed. Doppler ultrasound measures blood flow in the umbilical cord, placenta, and fetal vessels to evaluate the baby's circulation and oxygenation.
- Third-Trimester Biophysical Profile (BPP): Typically conducted during the third trimester, usually after 28 weeks of gestation. The BPP combines ultrasound with a non-stress test to evaluate the baby's well-being by assessing various parameters, such as fetal movement, breathing, muscle tone, amniotic fluid volume, and heart rate patterns.
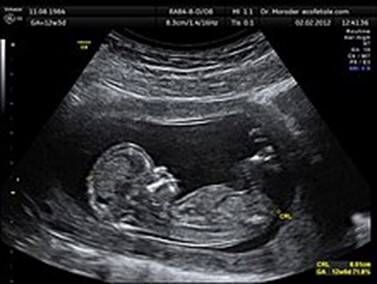
Maternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (MSAFP) Test
- MSAFP is a prenatal screening test that measures the level of AFP in the pregnant person’s blood as part of a multiple marker test
- MSAFP can detect neural tube defects such as spina bifida or anencephaly by measuring the level of AFP in the maternal serum
- MSAFP can also detect other fetal anomalies such as abdominal wall defects, renal anomalies, chromosomal abnormalities, .
- MSAFP is usually performed between 15 and 20 weeks of gestation along with other markers such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), unconjugated estriol (uE3), and inhibin A
- MSAFP involves drawing a blood sample from the pregnant person’s arm and sending it to a laboratory for analysis
- MSAFP results are reported as multiples of the median (MoM), which compare the measured level of AFP to the expected level for a given gestational age
- A high level of MSAFP (>2.5 MoM) may indicate a neural tube defect, an abdominal wall defect, a fetal demise, or a multiple gestation
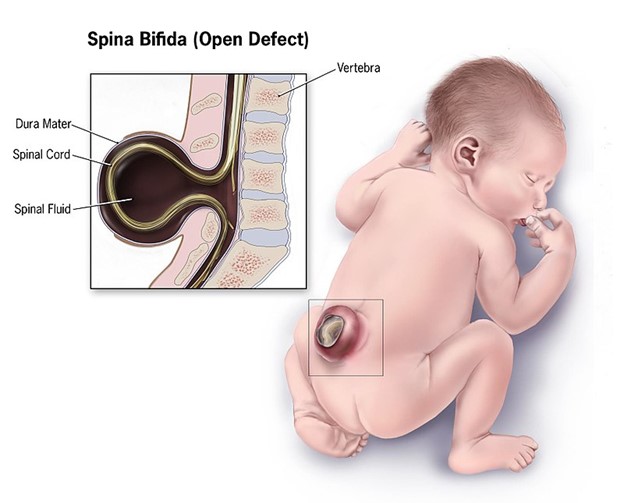
- A low level of MSAFP (<0.5 MoM) may indicate a chromosomal abnormality such as Down syndrome, trisomy 18, or trisomy 13
- MSAFP results are affected by factors such as maternal weight, diabetes mellitus, race, ethnicity, .
- MSAFP results are not diagnostic and require further evaluation such as ultrasound, amniocentesis, or karyotyping
- MSAFP has no risks or complications for the pregnant person or the fetus
Cell-free Fetal DNA Testing
- Cell-free fetal DNA testing is a prenatal screening test that analyzes the fragments of fetal DNA that circulate in the pregnant person’s blood
- Cell-free fetal DNA testing can detect chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome, trisomy 13, trisomy 18, .
- Cell-free fetal DNA testing can also determine the fetal sex and Rh blood type
- Cell-free fetal DNA testing is usually performed after 10 weeks of gestation
- Cell-free fetal DNA testing involves drawing a blood sample from the pregnant person’s arm and sending it to a laboratory for analysis
- Cell-free fetal DNA testing has a high accuracy (>99%) and a low false-positive rate (<0.5%)
- Cell-free fetal DNA testing is recommended for pregnant people who have a high risk of having a fetus with chromosomal abnormalities such as advanced maternal age, abnormal ultrasound findings, positive screening tests, .
- Cell-free fetal DNA testing is not recommended for pregnant people who have a low risk of having a fetus with chromosomal abnormalities or who have multiple gestations, donor eggs, or in vitro fertilization
- Cell-free fetal DNA testing results are not diagnostic and require further evaluation such as ultrasound, amniocentesis, or karyotyping
- Cell-free fetal DNA testing has no risks or complications for the pregnant person or the fetus
Percutaneous Umbilical Blood Sampling (PUBS)
- PUBS is a prenatal diagnostic test that involves obtaining a small sample of fetal blood from the umbilical cord for chromosomal analysis
- PUBS can detect chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome, trisomy 13, trisomy 18, .
- PUBS can also detect some genetic disorders such as cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs disease, sickle cell disease, .
- PUBS can also detect some blood disorders such as hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, .
- PUBS can also provide fetal blood transfusion or medication delivery if needed
- PUBS is usually performed after 18 weeks of gestation
- PUBS involves inserting a thin needle through the abdomen and uterus and into the umbilical cord under ultrasound guidance
- PUBS has a risk of miscarriage of about 1% to 2%
- PUBS has a risk of infection, bleeding, cramping, leaking of amniotic fluid, Rh sensitization, injury to the fetus or placenta, .
- PUBS results are usually available within 24 to 48 hours
Conclusion
- Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests are procedures that provide information about the health and development of a fetus before birth
- Prenatal screening tests estimate the risk or probability of a fetus having certain genetic or chromosomal conditions or other anomalies
- Prenatal diagnostic tests confirm or rule out the presence of a specific condition in a fetus
- Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests are optional and informed consent is required before performing them
- Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests have benefits and limitations, and the results may have physical, emotional, social, and financial implications for the pregnant person and their family
Summary
- Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests are procedures that provide information about the health and development of a fetus before birth
- The types of prenatal screening and diagnostic tests include:
- Chorionic villus sampling (CVS): a diagnostic test that obtains a sample of placental tissue for chromosomal analysis
- Amniocentesis: a diagnostic test that obtains a sample of amniotic fluid for chromosomal analysis
- Non-stress test (NST): a screening test that measures the fetal heart rate in response to fetal movements
- Biophysical profile (BPP): a screening test that combines an NST with an ultrasound to assess five fetal biophysical variables
- Contraction stress test (CST): a screening test that measures the fetal heart rate in response to uterine contractions
- Alpha-fetoprotein test (AFP): a screening test that measures the level of AFP in the maternal blood or amniotic fluid
- Ultrasound: a screening test that uses sound waves to create images of the fetus and its surroundings
- Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP) test: a screening test that measures the level of AFP in the maternal blood as part of a multiple marker test
- Cell-free fetal DNA testing: a screening test that analyzes the fragments of fetal DNA that circulate in the maternal blood
- Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (PUBS): a diagnostic test that obtains a sample of fetal blood from the umbilical cord for chromosomal analysis
- The purpose, indications, methods, risks, and results of each prenatal screening and diagnostic test vary depending on the type of test and the gestational age
- Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests are optional and informed consent is required before performing them
- Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests have benefits and limitations, and the results may have physical, emotional, social, and financial implications for the pregnant person and their family
Nursingprepexams
Videos
Login to View Video
Click here to loginTake Notes on Prenatal Diagnostic Tests And Procedures
This filled cannot be empty

