Please set your exam date
Newborn Complications
Study Questions
Dosage Calculation RN Maternal Newborn Proctored Assessment 3.1
A nurse is preparing to administer docusate sodium PO to a postpartum client who has a prescription for 200 mg/day in two equally divided doses. The client states she has trouble swallowing tablets and capsules. Therefore, the nurse has obtained docusate sodium liquid 50 mg/5 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer per dose? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it
Explanation
The question is asking for the amount of docusate sodium liquid the nurse should administer per dose. The prescription is for 200 mg/day in two equally divided doses, and the liquid form of the medication is 50 mg/5 mL.
Step 1 is to determine the amount of medication needed per dose. Since the total daily dose is 200 mg and it’s divided into two doses, each dose will be 200 mg ÷ 2 = 100 mg.
Step 2 is to convert this dose from mg to mL using the concentration of the liquid medication. The concentration is 50 mg/5 mL, which means that 1 mL contains 50 mg ÷ 5 = 10 mg of the medication.
Step 3 is to calculate the volume of the medication needed for a 100 mg dose. Since 1 mL contains 10 mg, we need 100 mg ÷ 10 mg/mL = 10 mL.
So, the nurse should administer 10 mL of docusate sodium liquid per dose.
A nurse is preparing to administer enoxaparin 55 mg subcutaneous to a client who has a deep-vein thrombosis after undergoing a cesarean birth. Available is enoxaparin solution for injection 60 mg/0.6 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
60mg=0.6
55mg= 55*0.6/60
Volume (mL) = 0.55 mL
Rounding to the nearest tenth, the nurse should administer 0.6 mL of enoxaparin solution to the client.
A nurse prepares to administer 0.9% sodium chloride 200 mL over 30 min. The nurse should set the IV infusion pump to administer how many mL/hr? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Infusion rate (mL/hr) = 200 mL / 0.5 hr Infusion rate (mL/hr) = (200 mL/hr) *2
= 400mls/hr
1.A nurse is caring for a client who is postpartum and has a prescription for oxytocin 10 units IM one time only for the saturation of a perineal pad in 15 min or less. How should the nurse interpret this prescription?
Explanation
The correct answer is Choice B.
Choice A rationale: This is incorrect because the prescription is for one time only, not for repeated doses.Giving the medication each time the client saturates the perineal pad within 15 min could cause uterine hyperstimulation, water intoxication, or hypotension1.
Choice B rationale: This is correct because the prescription is for one time only and the indication is saturation of a perineal pad in 15 min or less.This is a sign of postpartum hemorrhage, which is a common and potentially life-threatening complication of childbirth2.Oxytocin is a uterotonic agent that helps the uterus contract and reduce bleeding3.
Choice C rationale: This is incorrect because waiting 15 min to administer the medication after the client saturates a perineal pad could result in excessive blood loss and hypovolemic shock. The medication should be given as soon as possible after the indication is met.
Choice D rationale: This is incorrect because offering the medication now to prevent saturation of perineal pad is not the intended use of the prescription. The medication is for treatment, not prevention, of postpartum hemorrhage. Prophylactic oxytocin is usually given intravenously or intramuscularly during or immediately after the delivery of the placenta.
A nurse is preparing to administer enoxaparin 55 mg subcutaneously to a client who has a deep-vein thrombosis after undergoing a cesarean birth. Available is enoxaparin solution for injection 60 mg/0.6 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
60mg=0.6ml 55mg= 55*0.6/60
Volume (mL) = 0.55 mL
Rounding to the nearest tenth, the nurse should administer 0.6 mL of enoxaparin solution to the client.
A nurse is reviewing a new prescription for propranolol 200 mg PO daily divided in equal doses every 12 hr for a client who has migraine headaches during the premenstrual period. Available is propranolol solution 4 mg/mL. How many mL should the client self-administer per dose? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
mL = mg / 4 mL = 100 / 4
mL = 25 / 1
This means that the client needs to take 25 mL of the propranolol solution every 12 hours to get the prescribed dose of 200 mg per day
A nurse is caring for a client who is postpartum and has a prescription for oxytocin 10 units IM one time only for the saturation of a perineal pad in 15 min or less. How should the nurse interpret this prescription?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B: The prescription states to administer the medication "one time only" if the client saturates the perineal pad within 15 minutes. The nurse should give the medication once when the pad becomes saturated within the specified time frame.
A. Give the medication each time the client saturates the perineal pad within 15 min.
This answer choice is incorrect. The prescription states that the medication is to be given "one time only" for the saturation of a perineal pad in 15 minutes or less. Therefore, it does not specify to administer the medication multiple times if the pad continues to saturate.
C. Wait 15 min to administer the medication after the client saturates a perineal pad.
This answer choice is incorrect. The prescription does not state to wait for 15 minutes before administering the medication. It specifies that the medication should be given if the pad becomes saturated within 15 minutes or less.
D. Offer the medication now to prevent saturation of perineal pad.
This answer choice is incorrect. The prescription does not indicate that the medication should be offered preemptively to prevent saturation of the perineal pad. It is only to be administered if the saturation occurs within 15 minutes
A nurse is caring for a newborn who weighs 3,500 g. The nurse should record the newborn's weight as how many kg. (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
1000g=1kg 3500g=3500*1/1000
=3.5kg
A nurse is caring for a client who is postpartum and has a prescription for oxytocin 10 units IM one time only for the saturation of a perineal pad in 15 min or less. How should the nurse interpret this prescription?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. The prescription indicates that the medication should be given "one time only" if the client saturates the perineal pad within 15 minutes.
The nurse should administer the medication once the pad becomes saturated within the specified time frame.
A. Give the medication each time the client saturates the perineal pad within 15 min.
This answer choice is incorrect. The prescription states that the medication should be administered "one time only" for the saturation of a perineal pad in 15 minutes or less. It does not specify giving the medication multiple times.
C. Wait a minute to administer the medication after the client saturates a perineal pad.
This answer choice is incorrect. The prescription does not mention waiting for any specific time before administering the medication. It states that the medication should be given if the pad becomes saturated within 15 minutes or less.
D. Offer the medication now to prevent saturation of the perineal pad.
This answer choice is incorrect. The prescription does not indicate that the medication should be offered preemptively to prevent saturation of the perineal pad. It is only to be administered if the saturation occurs within 15 minutes.
A nurse is caring for an infant. The mother states the infant took 2.5 oz of formula at the last feeding. How many mL should the nurse document as the intake on the 1&O record? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
One US fluid ounce is equal to 29.6 milliliters. Therefore Formula intake in mL = Formula intake in oz × 29.6 Plugging in the given value of 2.5 oz, we get:
Formula intake in mL = 2.5 × 29.6 Formula intake in mL = 74mls
A nurse assists with the admission of a client to the postpartum unit and reviews the client's prescribed medications. The nurse should clarify which of the following prescriptions with the provider.
Explanation
Bisacodyl is a stimulant laxative that works by increasing the activity of the intestines to cause a bowel movement. It is usually used on a short-term basis to treat constipation or to empty the bowels before surgery or certain medical procedures. However, bisacodyl should not be used in postpartum clients who have had a cesarean delivery or an episiotomy, as it may cause straining and increase the risk of bleeding or infection. Therefore, the nurse should clarify this prescription with the provider and suggest an alternative laxative that is safer for postpartum clients, such as docusate sodium or psyllium.
Calcium carbonate 750 mg PO.
There is no need to clarify this prescription. Calcium carbonate is a common supplement used to provide calcium to the body, and it is typically taken orally.
Oxycodone 5 mg PO every 4 hr PRN for severe pain.
There is no need to clarify this prescription. Oxycodone is a strong opioid analgesic commonly used for severe pain management, and the specified dose and frequency are within the usual range.
Ibuprofen 600 mg PO every 6 hr PRN for moderate pain.
There is no need to clarify this prescription. Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly used for pain relief, including moderate pain. The specified dose and frequency are within the usual range.
A nurse is preparing to administer ferrous sulfate 120 mg PO two times each day with meals to a client who is at 12 weeks of gestation and has anemia. Available is ferrous sulfate syrup 90 mg/5 mL. How many ml. should the nurse administer per dose? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
The question is asking for the volume of ferrous sulfate syrup that the nurse should administer per dose. The desired dose is 120 mg and the available syrup has a concentration of 90 mg/5 mL.
Let’s calculate this step by step:
Step 1: Identify the desired dose, which is 120 mg.
Step 2: Identify the concentration of the available medication, which is 90 mg/5 mL.
Step 3: Set up the equation to solve for the volume (V) in mL. The equation is (Desired dose ÷ Concentration) × Volume of the concentration = V.
Step 4: Substitute the known values into the equation: (120 mg ÷ 90 mg) × 5 mL = V.
Step 5: Solve the equation: V = (1.33) × 5 mL = 6.67 mL.
So, the nurse should administer approximately 6.7 mL of the ferrous sulfate syrup per dose.
A nurse is preparing to administer 0.45% sodium chloride 1,000 mL IV to infuse over 6 hr to a postpartum client. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
To find the infusion rate in mL/hr, divide the total volume of fluid by the total time of infusion.
Total volume of fluid = 1,000 mL Total time of infusion = 6 hr
Infusion rate = 1,000 mL / 6 hr = 166.67 mL/hr
Round the answer to the nearest whole number: 167 mL/hr
A nurse is caring for a newborn who weighs 6 lbs. The nurse should record the newborn's weight as how many g? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
The nurse should record the newborn's weight as 2722 g. 1 pound is equal to 453.59237 grams,
6 pounds times 453.59237 grams = 2721.55422 grams
Rounded off = 2722 grams.
A nurse is preparing to administer fentanyl 100 mcg IM one time for pain to a client who is in labor and requests pain medication. Available is fentanyl injection 0.05 mg/mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Volume (mL) = Dose (mcg) / Concentration (mcg/mL) Volume (mL) = 100 mcg / 50 mcg/mL
Volume (mL) = 2 mL
Therefore, the nurse should administer 2 mL of fentanyl injection 0.05 mg/mL to the client
A nurse is preparing to administer phytonadione 0.5 mg IM to a newborn. Available in phytonadione injection 1 mg/0.5 mL. How many mL should the nurse plan to administer? (Round the answer to the nearest hundredth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Amount of injection in mls = Dose ordered (mg) / Dose available Therefore:
Amount of injection in mls = 0.5 mg Therefore;
Amount of injection in mls = 0.5 mg x 0.5 mL / 1 mg Amount of injection in mls = 0.25 mL
A nurse is preparing to administer digoxin 0.25 mg PO to a client who has heart failure and is at 35 weeks of gestation. Available is digoxin 0.125 mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
To calculate the number of tablets to administer, you need to divide the prescribed dose by the available dose. In this case, the prescribed dose is 0.25 mg and the available dose is 0.125 mg. Therefore, the number of tablets is:
0.25 mg / 0.125 mg = 2 tablets
The nurse should administer 2 tablets of digoxin 0.125 mg to the client.
A nurse is preparing to administer nalbuphine 10 mg IV via intermittent bolus to a client who is in active labor. Available is nalbuphine 20 mg/ml. How many mL should the nurse plan to administer? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Dose / Concentration = Volume Plug in the values from the question:
10 mg / 20 mg/ml = 0.5 ml
Round the answer to the nearest tenth:
=0.5 ml
A nurse is preparing to administer lactated Ringer's 1,500 mL IV over 8 hr to a pregnant client who has gastroenteritis. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Infusion rate = Volume / Time Therefore;
Infusion rate= 1,500 mL / 8 hr
Infusion rate = 187.5 mL/hr
Rounded off to the nearest whole number; 188ml/hr
A nurse is preparing to administer oxycodone 10 mg PO every 6 hr PRN for severe pain to a client who is postpartum following a cesarean birth. Available in oxycodone 5 mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Number of tablets = (Dose ordered / Dose available) x Frequency Number of tablets = (10 mg / 5 mg) x 1
Number of tablets = 2 x 1 Number of tablets = 2
A nurse is preparing to administer phytonadione 0.5 mg IM to a newborn. Available is phytonadione injection 1 mg/0.5 mL. How many mL should the nurse plan to administer? (Round the answer to the nearest hundredth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
volume = 0.5 mg / (1 mg/0.5 mL) volume = 0.5 mg x 0.5 mL / 1 mg volume = 0.25 mL
A nurse is preparing to administer lactated Ringer's 1,500 mL IV over 8 hr to a pregnant client who has gastroenteritis. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Infusion rate= Volume / Time
Therefore;
Infusion rate = 1,500 mL / 8 hr Infusion rate = 187.5 mL/hr
Rounded off to the nearest whole number; 188ml/hr
A nurse is preparing to administer dobutamine 12 mcg/kg/min by continuous IV infusion to a preterm newborn who weighs 2 kg. Available is dobutamine 250 mg in 500 mL dextrose 5% in water. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Let’s calculate the IV pump rate for administering dobutamine to a preterm newborn.
Step 1 is to convert the dose from mcg/kg/min to mg/kg/min. We know that 1 mg = 1000 mcg, so we have:
12 mcg/kg/min ÷ 1000 = 0.012 mg/kg/min
Step 2 is to calculate the total amount of dobutamine the newborn needs per minute:
0.012 mg/kg/min × 2 kg = 0.024 mg/min
Step 3 is to convert this to an hourly rate:
0.024 mg/min × 60 min/hr = 1.44 mg/hr
Step 4 is to calculate the volume of the solution that contains this amount of dobutamine. We know that 250 mg of dobutamine is dissolved in 500 mL of solution, so:
(1.44 mg/hr ÷ 250 mg) × 500 mL = 2.88 mL/hr
So, the nurse should set the IV pump to deliver approximately 2.9 mL/hr (rounded to the nearest tenth).
A nurse is preparing to administer 2.5 L of lactated Ringer's to a client. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Step 1: Convert liters to milliliters.
1 liter is equal to 1000 milliliters. Therefore, we can convert 2.5 liters to milliliters as follows:
2.5 liters * 1000 milliliters/liter = 2500 milliliters
Step 2: Round the answer to the nearest whole number.
The answer is 2500 milliliters. Since we are instructed to round to the nearest whole number, we do not need to make any changes.
Therefore, the nurse should administer 2500 mL of lactated Ringer's to the client.
A nurse is preparing to administer medroxyprogesterone 150 mg IM to a client who has requested contraception. Available is medroxyprogesterone solution for injection 150 mg/mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Dosage (mL) = Ordered dose (mg) / Available dose (mg/mL) Therefore;
Dosage = 150 mg / 150 mg/mL Dosage = 1 mL
Therefore, the nurse should administer 1 mL of medroxyprogesterone solution for injection to the client.
A nurse is preparing to administer cephalexin 500 mg PO every 6 hr to an antepartum client who has a urinary tract infection. Available is cephalexin 250 mg tablets. How many tablets should the nursing staff administer in a 24-hour period? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Number of tablets = (Dose per administration x Number of administrations per day) / Tablet strength
Number of tablets = (500 mg x 4) / 250 mg
Number of tablets = 2000 mg / 250 mg Number of tablets = 8
Therefore, the nursing staff should administer 8 tablets in a 24hrs.
A nurse is preparing to administer acetaminophen 56 mg PO to a newborn. Available is acetaminophen oral solution 160 mg/5 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Dose = Desired dose / Available dose x Volume Therefore;
Dose = (56 mg / 160 mg) x 5 mL Therefore;
Dose = 0.35 x 5 mL Dose = 1.75 mL
Round to the nearest tenth: Dose = 1.8 mL
The nurse should administer 1.8 mL
A nurse is preparing to administer ketorolac 15 mg IM every 6 hr PRN for pain to a client who is postoperative following a cesarean birth and reports pain. Available is ketorolac injection 30 mg/mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Volume = Dose / Concentration Volume = 15 mg / 30 mg/mL
Volume = 0.5 mL
A nurse is preparing to administer nitroprusside 2 mcg/kg/min via continuous IV infusion to a client who weighs 75 kg. Available is nitroprusside 50 mg in dextrose 5% in water 250 mL. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Infusion rate in mL/h = Dose (mcg/kg/min) x Weight (kg) x 60 / Concentration (mcg/mL) In this case, the dose is 2 mcg/kg/min and the concentration is 50 mg/250 mL or 200 mcg/mL. Therefore, the infusion rate is:
Infusion rate (mL/h) = 2 x 75 x 60 / 200 Infusion rate (mL/h) = 45
The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver 45 mL/h.
A nurse is preparing to administer dopamine 5 mcg/kg/min via continuous IV infusion to a newborn who weighs 4.4 kg and has septic shock. Available in dopamine 200 mg in dextrose 5% in water 250 mL. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
The dose of dopamine in mg/hr: 5 mcg/kg/min x 4.4 kg x 60 min/hr = 1320 mcg/hr Converted to mg: 1320 mcg/hr / 1000 mcg/mg = 1.32 mg/hr
Infusion rate in mL/hr: 1.32 mg/hr / (200 mg/250 mL) = 1.65 mL/hr Rounded off to the nearest tenth: 1.7 mL/hr
A nurse is preparing to administer magnesium sulfate 4 g to a client by intermittent IV bolus over 20 min. Available is magnesium sulfate 4 g in 0.9% sodium chloride 50 mL. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Infusion rate = volume in mls/ infusion time in hrs
= 50mls divided by 20/60
= 150mls/hr
The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver 150 mL/hr.
A nurse is preparing to administer nitroprusside 2 mcg/kg/min via continuous IV infusion to a client who weighs 75 kg. Available is nitroprusside 50 mg in dextrose 5% in water 250 mL. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Pump rate in mL/hour = Dose (mcg/kg/min) x Weight (kg) x 60 / Concentration (mcg/mL)
The concentration of nitroprusside is given as 50 mg in 250 mL of dextrose 5% in water.
Convert this to mcg/mL; multiply by 1000
Concentration (mcg/mL) = 50 mg x 1000 / 250 mL = 200 mcg/mL Therefore;
Pump rate in mL/hour = 2 mcg/kg/min x 75 kg x 60 / 200 mcg/mL Pump rate in mL/hour = 45 mL/hour
Therefore, the nurse should set the IV pump to deliver 45 mL/hour
A nurse is preparing to administer lidocaine 1.7 mg/min via continuous IV infusion to a client who is pregnant and has a ventricular arrhythmia. Available is lidocainePrepared by Dr Brandel Andove1 g in dextrose 5% in water 250 mL. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
1.7mg/min = 1.7*60 = 102mg/hr 1g=1000mg
1000mg= 250mls of lidocaine dextrose 102mg = 102*250/1000 = 25.5ml/hr
Rounded off to the nearest whole number, the pump should be set deliver 26 mL/hr.
A nurse is reviewing a prescription to initiate an infusion of terbutaline at 2.5 mcg/min to a client PRN more than four uterine contractions in 1 hr and to increase the infusion by 5 mcg/min every 10 min until contractions stop, not to exceed a rate of 30 mcg/min. How should the nurse interpret this prescription?
Explanation
by 5 mL/hr when titrating the dosage. This is because terbutaline is a beta-2 agonist that relaxes the smooth muscles of the uterus and bronchi. It is
administered as a continuous infusion of a solution containing 3-5 mcg/mL of terbutaline. Therefore, increasing the infusion rate by 5 mcg/min every 10 min means increasing the drip rate by 5 mL/hr, assuming a drop factor of 60 drops/mL. The other options are incorrect because:
Choice A is wrong because The maximum rate of terbutaline infusion is 30 mcg/min, which corresponds to 18 mL/hr, not 18 mg/hr;
Choice B is wrong because The rate of terbutaline infusion is not based on the client's weight, but on the number and frequency of uterine contractions; Choice D is wrong since The nurse should initiate the infusion of terbutaline if the client has more than four contractions in 1 hr, not five or more.
A nurse is preparing to administer magnesium sulfate 4 g to a client by intermittent IV bolus over 20 min. Available is magnesium sulfate 4g in 0.9% sodium chloride 50 mL. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Infusion rate= volume of infusion/ time in hours 50 divided by 20/60 = 150mls/hr
A nurse is preparing to administer procaine penicillin G 800,000 units IM. Available is procaine penicillin G Injection 600,000 units/mL. How many mi should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Amount (mL) = Dose (units) / Concentration (units/mL) Substitute the given values into the formula:
Amount (mL) = 800,000 units / 600,000 units/mL Amount (mL) = 1.3 mL
Therefore, the nurse should administer 1.3 mL of procaine penicillin G injection
A nurse is preparing to administer heparin 1,000 units/hr via continuous IVinfusion to a client. Available is heparin 25,000 units in 0.9% sodium chloride 250 mL. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
IV pump rate (mL/hr) = (units/hr x volume) / total units
In this case, the units/hr is 1,000, the volume is 250 mL, and the total units is 25,000. IV pump rate (mL/hr) = (1,000 x 250) / 25,000
Therefore;
IV pump rate (mL/hr) = 250,000 / 25,000 IV pump rate (mL/hr) = 10
Therefore, the nurse should set the IV pump to deliver 10 mL/hr.
Introduction
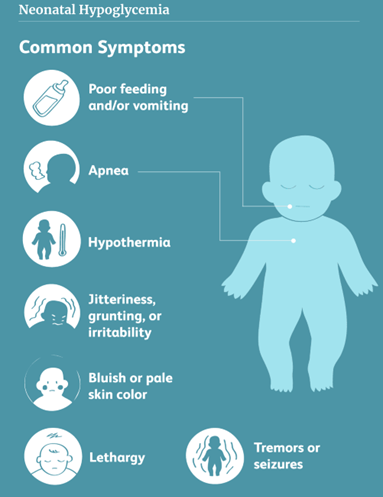
A nurse is caring for a newborn who exhibits signs of hypotonicity, weak reflexes, and a weak cry.
Explanation
Hypoglycemia is a condition where the blood glucose level is too low, which can affect the brain and nervous system function.Hypoglycemia can cause symptoms such as hypotonia (low muscle tone), weak reflexes, and a weak cry in newborns.
These symptoms are due to the lack of energy supply to the muscles and nerves.
Choice B. Hyperbilirubinemia is wrong because it is a condition where the blood level of bilirubin, a waste product from red blood cell breakdown, is too high.
Hyperbilirubinemia can cause jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), but not hypotonia, weak reflexes, or a weak cry.
Choice C. Preterm birth is wrong because it is a condition where the baby is born before 37 weeks of gestation.
Preterm birth can cause many complications, such as respiratory distress, bleeding in the brain, and infection, but not hypotonia, weak reflexes, or a weak cry.
Choice D. Macrosomia is wrong because it is a condition where the baby is larger than average at birth, usually weighing more than 4 kg (8 lb 13 oz).
Macrosomia can cause problems during delivery, such as shoulder dystocia, birth injury, and low blood sugar, but not hypotonia, weak reflexes, or a weak cry.
A nurse is assessing a newborn who appears wasted, with peely, cracked, and leathery skin.
This presentation is consistent with:.
Explanation
This presentation is consistent with a newborn who has been in the womb for longer than 42 weeks.Post-term newborns often have dry, peeling, loose skin and may appear abnormally thin.They may also have overgrown nails and large amount of hair on the head.
Choice A is wrong because preterm birth is associated with low birth weight, immature skin, and lanugo (fine hair) on the body.
Choice B is wrong because macrosomia is a condition where the newborn is significantly larger than average, usually due to maternal diabetes or obesity.
Choice C is wrong because hyperbilirubinemia is a condition where the newborn has high levels of bilirubin in the blood, causing jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
A nurse is caring for a newborn with elevated serum bilirubin levels and jaundice.
The nurse suspects that the newborn is experiencing:.
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. Pathologic jaundice.Pathologic jaundice is a type of jaundice that occurs due to an underlying health problem, such as blood group incompatibility, infection, liver disease, or enzyme deficiency.
Pathologic jaundice usually appears within the first 24 hours of life and can cause severe complications if not treated promptly.
Choice A is wrong because physiologic jaundice is a normal and common condition that occurs in most newborns due to the immaturity of their liver and the high turnover of red blood cells.Physiologic jaundice usually appears between the second and fourth day after birth and resolves within one to two weeks without treatment.
Choice C is wrong because hypoglycemia is a low blood sugar level that can cause symptoms such as jitteriness, poor feeding, lethargy, and seizures in newborns.Hypoglycemia is not directly related to bilirubin levels or jaundice, although some conditions that cause hypoglycemia, such as prematurity or infection, can also increase the risk of jaundice.
Choice D is wrong because preterm birth is a risk factor for jaundice, not a cause of it.Preterm babies have higher bilirubin levels because their liver is less developed and their red blood cells have a shorter lifespan than term babies.
Preterm birth can also be associated with other causes of pathologic jaundice, such as infection or hemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells)
A client is concerned about their newborn's risk for respiratory distress.
The nurse explains that the highest risk for respiratory distress is seen in:.
Explanation
Preterm infants are at the highest risk for respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), a common breathing disorder that affects newborns.RDS occurs because of a lack of surfactant, a foamy substance that keeps the lungs fully expanded.Surfactant is usually produced by the lungs during the third trimester of pregnancy, which starts after the 26th week.Therefore, babies born before their due date, especially before 28 weeks of pregnancy, are more likely to have RDS.
Choice B is wrong because macrosomic babies, or babies who are larger than average at birth, are not at increased risk for RDS.
However, they may have other complications such as birth injuries or low blood sugar levels.
Choice C is wrong because post-term infants, or babies who are born after 42 weeks of pregnancy, are not at increased risk for RDS.
However, they may have other complications such as meconium aspiration or low blood sugar levels.
Choice D is wrong because newborns with hyperbilirubinemia, or high levels of bilirubin in the blood, are not at increased risk for RDS.
However, they may have other complications such as jaundice or brain damage.
Other risk factors for RDS include being a white male, having multiple fetuses, having a mother with diabetes, and having premature rupture of membranes (PROM).
A client asks the nurse about the main complication associated with untreated hyperbilirubinemia.
The nurse explains that untreated hyperbilirubinemia can lead to:.
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Cerebral palsy.
Hyperbilirubinemia is a condition where there is too much bilirubin in the blood.
Bilirubin is a yellow pigment that is produced when red blood cells break down.
Normally, the liver processes bilirubin and excretes it in bile.
However, if the liver is immature or damaged, or if there is excessive hemolysis of red blood cells, bilirubin can accumulate in the blood and cause jaundice.
If the bilirubin level is very high, it can cross the blood-brain barrier and damage the brain cells, leading to a condition called kernicterus.
Kernicterus can cause cerebral palsy, which is a group of disorders that affect movement and posture.
Choice B. Hypoglycemia is wrong because it is a condition where the blood glucose level is too low.
It can be caused by many factors, such as inadequate intake, excessive insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents, infection, stress, or exercise.
Hypoglycemia can cause symptoms such as sweating, trembling, hunger, confusion, dizziness, or seizures.
It can be treated by giving glucose orally or intravenously.
Choice C. Necrotizing enterocolitis is wrong because it is a condition where the intestinal tissue becomes inflamed and dies.
It can affect premature infants or infants with low birth weight, congenital heart disease, or sepsis.
Necrotizing enterocolitis can cause symptoms such as abdominal distension, bloody stools, vomiting, lethargy, or shock.
It can be treated by stopping enteral feeding, giving antibiotics, and providing supportive care.
In severe cases, surgery may be needed to remove the necrotic tissue.
Choice D. Hypotonicity is wrong because it is a condition where the muscle tone is abnormally low.
It can be caused by many factors, such as nerve damage, spinal cord injury, brain injury, genetic disorders, or electrolyte imbalance.
Hypotonicity can cause symptoms such as weakness, flaccidity, poor posture, or difficulty swallowing.
It can be treated by physical therapy, braces, splints, or medication.
Hypoglycemia
A nurse is assessing a newborn who is displaying jitteriness, poor feeding, and seizures.
The nurse suspects the newborn is experiencing:.
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. Hypoglycemia.Hypoglycemia is a condition where the blood sugar level is too low, which can affect the brain function and cause symptoms such as jitteriness, poor feeding, and seizures.Hypoglycemia is common in newborns, especially in preterm, small for gestational age, and infants of diabetic mothers.
Choice A is wrong because hyperglycemia is a condition where the blood sugar level is too high, which can cause dehydration, increased urination, and ketoacidosis.Hyperglycemia does not usually cause seizures in newborns.
Choice C is wrong because hypertension is a condition where the blood pressure is too high, which can cause damage to the blood vessels and organs.Hypertension can cause seizures in older children and adults, but it is rare in newborns.
Choice D is wrong because hypocalcemia is a condition where the calcium level in the blood is too low, which can affect the nerve and muscle function and cause symptoms such as twitching, spasms, and tetany.Hypocalcemia can also cause seizures in newborns, but it is less common than hypoglycemia.
A client with diabetes gives birth to a premature newborn.
The nurse should anticipate that the newborn is at risk for:.
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. Hypoglycemia.
The newborn is at risk for hypoglycemia because of the maternal diabetes and the prematurity.Maternal diabetes causes fetal hyperinsulinism, which persists after birth and lowers the blood glucose level of the newborn.Prematurity causes inadequate glycogen stores and immature enzyme function, which also contribute to hypoglycemia.Hypoglycemia can cause symptoms such as tachycardia, cyanosis, seizures, and apnea.
Choice A is wrong because hyperglycemia is unlikely in a newborn with hyperinsulinism and deficient glycogen stores.
Choice C is wrong because hypertension is not a common complication of maternal diabetes or prematurity in newborns.
Choice D is wrong because hypothyroidism is not related to maternal diabetes or prematurity.Hypothyroidism can cause symptoms such as lethargy, poor feeding, jaundice, and hypotonia.
Normal ranges for blood glucose levels in newborns vary depending on the age, weight, and feeding status of the baby.
Generally, a level below 40 mg/dL (2.2 mmol/L) in symptomatic term newborns, below 45 mg/dL (2.5 mmol/L) in asymptomatic term newborns between 24 hours and 48 hours of life, or below 30 mg/dL (1.7 mmol/L) in preterm newborns in the first 48 hours is considered hypoglyc
A nurse is caring for a newborn who was born to a mother with diabetes mellitus.
The nurse should monitor the newborn for which of the following signs of hypoglycemia?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Jitteriness.Jitteriness or tremors are the most common signs of hypoglycemia in a newborn baby.
Hypoglycemia is when the level of sugar (glucose) in the blood is too low.
Glucose is the main source of fuel for the brain and the body.In a newborn baby, low blood sugar can happen for many reasons, such as poor nutrition for the mother during pregnancy, making too much insulin because the mother has diabetes, or not enough oxygen at birth.
Choice B. Tachycardia is wrong because it is not a typical sign of hypoglycemia in a newborn baby.
Tachycardia is a fast heart rate that can be caused by other conditions, such as fever, infection, or dehydration.
Choice C. Hyperthermia is wrong because it is not a sign of hypoglycemia in a newborn baby.
Hyperthermia is a high body temperature that can be caused by overheating, infection, or inflammation.Hypoglycemia can cause low body temperature (hypothermia), not high body temperature.
Choice D. Hypertonia is wrong because it is not a sign of hypoglycemia in a newborn baby.
Hypertonia is increased muscle tone or stiffness that can be caused by brain damage, nerve damage, or genetic disorders.Hypoglycemia can cause weak or floppy muscles (poor muscle tone), not increased muscle tone.
A nurse is assessing a newborn who has intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).
The nurse should recognize that this newborn is at risk for developing hypoglycemia because of which of the following factors?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. Increased insulin production.Infants with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) are at risk for hypoglycemia due to poor nutrient reserves and hyperinsulinism.
Hyperinsulinism is a condition where the pancreas produces too much insulin, which lowers the blood glucose level.Infants with IUGR may have hyperinsulinism because of placental insufficiency, maternal diabetes, or fetal stress.
Choice A is wrong because increased glycogen stores would protect against hypoglycemia, not cause it.
Glycogen is a form of stored glucose that can be broken down when blood glucose level is low.
Choice B is wrong because decreased gluconeogenesis would also protect against hypoglycemia, not cause it.
Gluconeogenesis is a process where the liver makes glucose from non-carbohydrate sources, such as amino acids or lactate.
Choice D is wrong because decreased glucose consumption would also protect against hypoglycemia, not cause it.
Glucose consumption is the rate at which cells use glucose for energy production.
If glucose consumption is low, blood glucose level would be high.
A nurse is performing a heel stick blood glucose test on a newborn who is preterm.
The nurse should apply a heel warmer to the newborn’s foot before obtaining the blood sample for which of the following reasons?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. To increase blood flow.A heel warmer is applied to the newborn’s foot before obtaining the blood sample to increase the blood flow to the area and make it easier to collect the sample.A heel warmer can also reduce pain and bruising by dilating the blood vessels and reducing the need for multiple punctures.
Choice A is wrong because a heel warmer does not prevent infection.Infection prevention requires proper cleaning of the puncture site and disposal of the lancet.
Choice C is wrong because a heel warmer does not reduce pain by itself.Pain reduction requires other measures such as cuddling, feeding, and distraction.
Choice D is wrong because a heel warmer does not prevent bruising.Bruising prevention requires applying pressure to the puncture site after collecting the sample.
Normal ranges for blood glucose levels in newborns vary depending on the method of measurement, but generally they are between 2.6 and 6.0 mmol/L.
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a pregnant client.
Which finding would be considered abnormal regarding hCG levels?
Explanation
Decreased hCG levels are abnormal regarding hCG levels in pregnancy.hCG is a hormone that plays an important role in pregnancy, and levels can vary widely at this time and between individuals.However, during early pregnancy, hCG levels typically double every two to three days.Low or declining hCG levels can signal a problem with the pregnancy, such as an impending miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
Choice B is wrong because unchanged hCG levels are also abnormal regarding hCG levels in pregnancy.
As mentioned above, hCG levels should increase rapidly during the first few weeks of pregnancy.
Choice C is wrong because increased hCG levels are normal regarding hCG levels in pregnancy.Levels of hCG can vary widely from one pregnant woman to another, but they generally peak at around 8 to 14 weeks after conception.
Choice D is wrong because increased prolactin levels are not related to hCG levels in pregnancy.
Prolactin is another hormone that stimulates milk production in the breasts.
Prolactin levels rise during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but they do not affect hCG levels.
A nurse is teaching a pregnant client about nutrition during pregnancy and lactation.
Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
I will need to increase my protein intake by 25 g per day while I am pregnant.” Protein is essential for the growth and development of the fetus and the placenta, as well as for the increased blood volume and maternal tissues.
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for protein during pregnancy is 71 g per day, which is 25 g more than the RDA for non-pregnant women.
Choice B is wrong because the calcium intake does not need to increase during lactation.
The RDA for calcium for lactating women is the same as for non-lactating women, which is 1000 mg per day for women aged 19 to 50 years.
Calcium absorption and retention are enhanced during lactation, and bone loss that may occur is usually reversible after weaning.
Choice C is wrong because the calorie intake does not need to increase by 500 kcal per day during the third trimester.
The estimated energy requirement (EER) for pregnant women increases by 340 kcal per day in the second trimester and by 452 kcal per day in the third trimester.
However, these values may vary depending on the pre-pregnancy weight, activity level, and rate of weight gain of the individual woman.
Choice D is wrong because the iron intake needs to increase by more than 10 mg per day while pregnant.
The RDA for iron during pregnancy is 27 mg per day, which is 9 mg more than the RDA for non-pregnant women.
However, this amount may not be enough to prevent iron deficiency anemia in some pregnant women, especially those who start pregnancy with low iron stores or have high iron losses due to bleeding or multiple pregnancies.
Therefore, iron supplements are often recommended for pregnant women, especially in the second and third trimesters.
A nurse is caring for a client at risk for falls. Which intervention is most important for fall prevention?
Explanation
nswer: b. Encouraging the client to use the call bell for assistance. Explanation: Encouraging the client to use the call bell for assistance is the most important intervention for fall prevention. It promotes the client's involvement in their own safety and ensures that help is readily available when needed.
Incorrect choices: a. Placing a sign on the client's room door indicating fall risk is a helpful visual reminder, but it does not actively prevent falls. c. Providing a nonskid mat on the floor beside the client's bed can reduce the risk of slipping but does not address other factors that contribute to falls. d. Ensuring the client has adequate lighting in the room is important for preventing falls, but it is not the most critical intervention. The client's ability to seek assistance when needed is more crucial.
A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetic ketoacidosis and is receiving intravenous fluids. Which of the following electrolytes should the nurse monitor closely for signs of imbalance? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Chloride is not a major electrolyte that is affected by diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) Chloride levels may be low, normal or high depending on the acid-base status and hydration of the client. Therefore, chloride is not a priority electrolyte to monitor for signs of imbalance.
Choice B reason:
Phosphate is also not a major electrolyte that is affected by DKA. Phosphate levels may be low due to insulin therapy or high due to renal impairment, but these are not directly related to DKA. Therefore, phosphate is not a priority electrolyte to monitor for signs of imbalance.
Choice C reason:
Bicarbonate is a major electrolyte that is affected by DKA. Bicarbonate levels are low in DKA due to metabolic acidosis caused by the accumulation of ketones in the blood. Low bicarbonate levels can lead to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion and coma. Therefore, bicarbonate is a priority electrolyte to monitor for signs of imbalance.
Choice D reason:
Sulfate is not a major electrolyte that is affected by DKA. Sulfate levels are not routinely measured in clinical practice and have no significant role in DKA. Therefore, sulfate is not a priority electrolyte to monitor for signs of imbalance.
Choice E reason:
Potassium is a major electrolyte that is affected by DKA. Potassium levels can be high or low in DKA depending on several factors such as insulin therapy, fluid replacement, renal function and acid-base status. High or low potassium levels can cause cardiac arrhythmias, muscle weakness, paralysis and respiratory failure. Therefore, potassium is a priority electrolyte to monitor for signs of imbalance.
The practical nurse (PN) is caring for a child who was admitted after experiencing a generalized tonic-clonic seizure. When witnessing the child begin to seize again, which actions should the PN implement immediately? (Select all that apply.).
No explanation
The diagnosis of pregnancy is based on which positive signs of pregnancy? (Select all that apply.)
No explanation
Medications used to manage postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) include (Select all that apply.):.Medications used to manage postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) include (Select all that apply.):
No explanation
Which data would be included in a health history? (Select all that apply.)
No explanation
Preterm birth
A nurse is assessing a preterm infant who has necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC).
Which of the following findings should alert the nurse to a possible bowel perforation?
Explanation
All of these findings can indicate a possible bowel perforation in a preterm infant with necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC).NEC is a serious condition that causes inflammation and necrosis of the intestinal tissue, and can lead to a hole (perforation) in the bowel wall.Bacteria can leak through this hole and cause infection and sepsis.NEC usually develops within two to six weeks after birth, and mostly affects premature babies.
Choice A is wrong because bloody stools are not specific for bowel perforation.They can also be seen in mild cases of NEC or other causes of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Choice B is wrong because abdominal distension is a common sign of NEC, but not necessarily of bowel perforation.It can be caused by gas accumulation, fluid retention, or inflammation of the bowel wall.
Choice C is wrong because bilious vomitus is also a non-specific sign of NEC or other causes of bowel obstruction.It can indicate a problem with the passage of food or bile through the intestines.
A nurse is measuring the head circumference of a preterm infant.
Which of the following methods should the nurse use to ensure accuracy?
Explanation
This is the recommended method for measuring the head circumference of a preterm infant.
It ensures accuracy by capturing the largest dimension of the head, which reflects the growth of the brain.
Choice B is wrong because it does not measure the widest part of the head, which may be above or below the occiput.
Choice C is wrong because it does not measure the widest part of the head, which may be above or below the ears.
Choice D is wrong because it does not measure the widest part of the head, which may be above or below the chin.
The normal range for head circumference at birth for preterm infants born between 32 and 42 weeks gestation is about 25 to 36 cm.Head circumference should be measured and plotted regularly until two years of age for preterm infants.
A nurse is educating the parents of a preterm infant who has retinopathy of prematurity (ROP).
Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
ROP is a condition that affects the blood vessels of the retina in premature infants.
It can cause vision loss or blindness if not treated.
The main treatment for ROP is laser therapy or cryotherapy to stop abnormal blood vessel growth.
However, these treatments do not restore normal vision and may have complications.
Therefore, regular eye exams are needed to monitor the condition and detect any changes or problems.
Choice B is wrong because surgery is not a common treatment for ROP.
Surgery may be done in some cases to reattach the retina if it detaches from the eye wall, but this is a rare and serious complication of ROP.
Choice C is wrong because oxygen therapy can actually worsen ROP.
High levels of oxygen can stimulate the abnormal blood vessel growth in the retina.
Oxygen therapy should be used with caution and only when necessary for premature infants.
Choice D is wrong because glasses do not improve vision in ROP.
Glasses can correct refractive errors such as nearsightedness or farsightedness, but they cannot fix the damage to the retina caused by ROP.
A nurse is providing developmental care for a preterm infant in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).
Which of the following interventions should the nurse implement?
Explanation
This is because preterm infants are born before or during critical periods of brain development and need to reduce stress and promote neurological development.Cluster care means grouping care activities together and timing them according to the infant’s cues, such as alertness, hunger, and sleepiness.This way, the infant can have longer periods of undisturbed sleep, which is essential for brain maturation.
Choice B is wrong because keeping the lights and noise level high can cause sensory overload and stress for the preterm infant.The NICU environment should be dimmed and quiet to mimic the womb and support the infant’s circadian rhythm.
Choice C is wrong because avoiding touching or holding the infant can deprive the infant of human contact and bonding, which are important for emotional and social development.Preterm infants can benefit from gentle touch, massage, and kangaroo care, which is holding the baby with direct skin-to-skin contact.These interventions can help with body temperature, breastfeeding, weight gain, and attachment.
Choice D is wrong because changing the infant’s position frequently can disrupt the infant’s sleep and cause stress.Preterm infants should be positioned in a way that supports their posture and alignment, such as flexion, midline orientation, and containment.Positioning aids such as blankets, rolls, or nests can be used to provide boundaries and comfort for the infant.
A nurse is evaluating a newborn who has hyperbilirubinemia and received phototherapy for 24 hours.
Which of the following outcomes indicates that phototherapy was effective?
Explanation
This indicates that phototherapy was effective because it lowers the level of bilirubin in the blood by converting it into a form that can be excreted in urine and stool.
Choice A is wrong because bronze discoloration of the skin is a side effect of phototherapy, not an outcome.
Choice C is wrong because increased urine output and specific gravity are signs of dehydration, which can occur with phototherapy due to insensible water loss.
Choice D is wrong because normal vital signs and neurological status do not reflect the effectiveness of phototherapy on bilirubin levels.
Normal ranges for serum bilirubin levels vary by age and risk factors, but generally they should be less than 15 mg/dL (257 μmol/L) for term newborns and less than 18 mg/dL (308 μmol/L) for preterm newborns.
Macrosomia
A nurse is caring for a newborn with macrosomia who was born vaginally with shoulder dystocia.
Which of the following assessments should the nurse perform to check for a possible brachial plexus injury?
Explanation
Observe the range of motion of the shoulders and arms.This is because a brachial plexus injury affects the nerve network that provides feeling and muscle control in the shoulder, arm, forearm, hand, and fingers.A baby with a brachial plexus injury may have full or partial lack of movement, a weakened grip, numbness, or an odd position of the affected arm.
Observing the range of motion of the shoulders and arms can help detect any signs of nerve damage or weakness.
Choice A is wrong because palpating the clavicles for crepitus or deformity is a way to check for a possible clavicular fracture, not a brachial plexus injury.
Choice C is wrong because measuring the head circumference and comparing it with the chest circumference is a way to check for a possible cephalopelvic disproportion (CPD), not a brachial plexus injury.
Choice D is wrong because auscultating the lungs for crackles or wheezes is a way to check for a possible respiratory distress, not a brachial plexus injury.
A nurse is teaching a pregnant client who has diabetes mellitus about the risk of having a baby with macrosomia.
Which of the following statements by the client indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
“I should expect to have a cesarean section because vaginal delivery is too risky.” This statement indicates a need for further teaching because it is not true that all women with diabetes mellitus and macrosomia need to have a cesarean section.
The mode of delivery depends on several factors, such as the estimated fetal weight, the maternal pelvic size, the fetal position, and the presence of any complications.
The nurse should explain to the client that vaginal delivery may be possible if the conditions are favorable and the risks are low.
Choice A is wrong because it is a correct statement.
Women with diabetes mellitus should monitor their blood glucose levels closely and follow their prescribed diet to prevent hyperglycemia and fetal macrosomia.
Choice B is wrong because it is also a correct statement.
Women with diabetes mellitus and macrosomia should have regular prenatal visits and ultrasounds to monitor their baby’s growth and well-being.
Choice D is wrong because it is another correct statement.
Women with diabetes mellitus and macrosomia should be aware of the signs of hypoglycemia in their baby after birth, such as jitteriness, lethargy, poor feeding, and low temperature.
The baby may need glucose supplementation or intravenous fluids to maintain normal blood glucose levels.
Normal ranges:
• Blood glucose levels: 70-110 mg/dL (3.9-6.1 mmol/L) for fasting; <140 mg/dL (<7.8 mmol/L) for postprandial
• Estimated fetal weight: 2500-4000 g (5.5-8.8 lb) for term
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a newborn with macrosomia who has polycythemia.
Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
A hematocrit of 75% indicates polycythemia, which is a condition of having too many red blood cells.Polycythemia is a common complication of macrosomia, which is a condition of having a birth weight of more than 8 pounds, 13 ounces.Polycythemia can cause problems such as jaundice, seizures, and organ dysfunction.
Choice B is wrong because a hemoglobin of 12 g/dL is within the normal range for a newborn, which is 14 to 24 g/dL.
Choice C is wrong because a platelet count of 150,000/mm3 is within the normal range for a newborn, which is 150,000 to 450,000/mm3.
Choice D is wrong because a white blood cell count of 9,000/mm3 is within the normal range for a newborn, which is 9,000 to 30,000/mm3.
A nurse is preparing to administer phototherapy to a newborn with macrosomia who has hyperbilirubinemia.
Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care?
Explanation
Cover the newborn’s eyes with eye shields or patches.This is because phototherapy exposes the newborn to high-intensity light that can damage the retina and cause eye irritation.Eye shields or patches should be removed every 4 hours to check for eye infection, injury, or displacement.
Choice B is wrong because sunscreen lotion can block the effect of phototherapy and increase the risk of skin irritation and infection.The newborn’s skin should be exposed as much as possible to the light source.
Choice C is wrong because feeding the newborn every 4 hours is not enough to prevent dehydration.Phototherapy can increase insensible water loss and fluid requirements.The newborn should be fed every 2 to 3 hours or on demand, and the urine output and weight should be monitored closely.
Choice D is wrong because turning off the phototherapy lights during blood draws can reduce the efficacy of the treatment and prolong the duration of exposure.The lights should be turned off only when absolutely necessary, such as during physical examination or parental bonding.
A nurse is feeding a newborn with macrosomia who has hypoglycemia.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Feed the newborn formula or breastmilk as prescribed.This is because newborns with macrosomia (large birth weight) are at risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) due to increased insulin production in response to high glucose levels in the womb.Formula or breastmilk provide adequate glucose and nutrients to prevent or treat hypoglycemia.
Choice B is wrong because glucose water does not provide enough calories or protein for growth and development.
Choice C is wrong because honey or corn syrup can cause infant botulism, a serious infection that affects the nervous system.
Choice D is wrong because rice cereal or oatmeal are not appropriate for newborns, as they can cause choking, allergies, or overfeeding.
Normal ranges for blood glucose levels in newborns are 40 to 150 mg/dL (2.2 to 8.3 mmol/L).Newborns with a suspected or confirmed genetic hypoglycemia disorder have a lower threshold of 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L).
Post-term birth
A nurse is caring for a post-term newborn who has meconium staining on the nails and umbilical cord.
What is the most likely cause of this finding?
Explanation
The newborn experienced fetal distress.Meconium staining is often caused by fetal hypoxia or other physiologic stress that triggers the fetus to pass meconium into the amniotic fluid before delivery.If the fetus aspirates the meconium, it can cause lung injury and respiratory distress, termed meconium aspiration syndrome.
Choice A is wrong because a bowel obstruction would not cause meconium staining of the nails and umbilical cord.
Choice B is wrong because a congenital anomaly would not necessarily cause meconium passage or staining.
Choice D is wrong because an infection may cause fetal distress, but it is not the direct cause of meconium staining.Meconium staining may be a sign of infection in the newborn.
A nurse is assessing a post-term newborn who has oligohydramnios.
What is the main complication associated with this condition?
Explanation
Oligohydramnios is a condition where there is too little amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus.
This can cause the umbilical cord to become compressed by the fetal body parts or the uterine wall, reducing blood flow and oxygen to the fetus.
This can lead to fetal distress, hypoxia, and acidosis.
Choice B is wrong because fetal malposition is not directly caused by oligohydramnios.
Fetal malposition is when the fetus is in an abnormal position for delivery, such as breech, transverse, or face presentation.
This can increase the risk of complications during labor and delivery, such as cord prolapse, dystocia, or birth trauma.
Choice C is wrong because placental abruption is not directly caused by oligohydramnios.
Placental abruption is when the placenta separates from the uterine wall before delivery, causing bleeding and reduced blood flow to the fetus.
This can be triggered by trauma, hypertension, or cocaine use.
Choice D is wrong because premature rupture of membranes (PROM) is not directly caused by oligohydramnios.
PROM is when the amniotic sac breaks before the onset of labor, causing leakage of fluid and increased risk of infection.
This can be caused by infection, cervical incompetence, or mechanical factors.
A nurse is preparing to perform a heel stick blood glucose test on a post-term newborn who has macrosomia.
What is the rationale for this test?
Explanation
A post-term newborn who has macrosomia is at risk of hypoglycemia because the fetus produces more insulin in response to the high glucose levels from the mother.
After birth, the glucose supply from the mother is cut off, but the newborn still has high insulin levels, which can cause low blood glucose.
A heel stick blood glucose test is done to monitor the newborn’s blood glucose level and prevent complications from hypoglycemia.
Choice B is wrong because hyperglycemia is not a common problem for post-term newborns with macrosomia.
Hyperglycemia occurs when there is too much glucose and not enough insulin in the blood.
This is more likely to happen in infants of diabetic mothers who have poor glycemic control during pregnancy.
Choice C is wrong because polycythemia is not related to insulin or glucose levels.
Polycythemia is a condition where there are too many red blood cells in the blood, which can cause increased blood viscosity and clotting.
This can happen in post-term newborns due to chronic hypoxia in utero, which stimulates erythropoietin secretion.
Choice D is wrong because anemia is not related to insulin or glucose levels.
Anemia is a condition where there are not enough red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood, which can cause decreased oxygen delivery to the tissues.
This can happen in newborns due to blood loss, hemolysis, or decreased production of red blood cells.
The normal range for blood glucose in newborns is 40 to 80 mg/dL (2.2 to 4.4 mmol/L).
A heel stick blood glucose test should be done within the first hour of life and repeated as needed based on the results and clinical signs of hypoglycemia.
A nurse is educating the parents of a post-term newborn who has hyperbilirubinemia and requires phototherapy.
What should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
This is because phototherapy exposes the newborn to intense light that can damage the eyes and skin, and also increases water loss through the skin.
Eye shields protect the eyes from the light and a diaper prevents overexposure of the genital area.The newborn should also be turned frequently to expose different parts of the body to light.
Choice A is wrong because exposing the newborn to sunlight is not an effective treatment for hyperbilirubinemia and can cause sunburn.Choice C is wrong because breast milk does not interfere with phototherapy and breastfeeding should be continued as normal.Choice D is wrong because blood tests are not needed every 12 hours, but only when indicated by the bilirubin level or risk factors.
Normal bilirubin levels vary by age, gestational age, and risk factors.The American Academy of Pediatrics provides hour-specific nomograms for initiating phototherapy based on these factors.
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a post-term newborn who has polycythemia and hypoxemia.
What is the most likely hematocrit value for this newborn?
Explanation
A hematocrit value of 65% indicates polycythemia, which is an abnormally high number of red blood cells.
Polycythemia can occur in post-term newborns who have hypoxemia, which is a low level of oxygen in the blood.Hypoxemia stimulates the production of erythropoietin, a hormone that increases red blood cell formation.
Choice A.35% is wrong because it is below the normal range for newborns, which is 45% to 61%.
A hematocrit value of 35% would indicate anemia, which is a low number of red blood cells.
Choice B.45% is wrong because it is at the lower end of the normal range for newborns.
A hematocrit value of 45% would not indicate polycythemia or hypoxemia.
Choice C.55% is wrong because it is within the normal range for newborns.
A hematocrit value of 55% would not indicate polycythemia or hypoxemia.
Hyperbilirubinemia
A nurse is caring for a newborn with hyperbilirubinemia who is receiving phototherapy.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
This is because phototherapy exposes the newborn to a special blue-to-green light that lowers the serum bilirubin level by transforming it into water-soluble isomers that can be eliminated without liver conjugation.However, this light can also damage the newborn’s eyes and cause retinal injury or blindness, so it is important to protect them with a mask.
Choice A is wrong because applying lotion to the newborn’s skin before phototherapy can interfere with the light penetration and reduce the effectiveness of the treatment.
It can also cause skin irritation or allergic reactions.
Choice B is wrong because removing the newborn from phototherapy every 4 hours can interrupt the continuous exposure to the light and delay the reduction of bilirubin levels.
The newborn should only be removed from phototherapy for feeding, diaper changes, and physical examination.
Choice D is wrong because placing the newborn on a radiant warmer during phototherapy can increase the risk of dehydration, hyperthermia, and skin burns.
The newborn should be monitored for temperature and fluid balance during phototherapy and kept in a crib or bassinet with a blanket.
A nurse is assessing a newborn for signs of jaundice.
Which of the following methods should the nurse use to detect jaundice in the newborn?
Explanation
This method allows the nurse to detect jaundice by observing the color of the skin after applying and releasing pressure.
This is a simple and noninvasive way to check for jaundice in a newborn.
Choice A is wrong because palpating the newborn’s abdomen for hepatomegaly is not a reliable way to detect jaundice.Hepatomegaly is an enlargement of the liver that may indicate liver disease, but it is not specific to jaundice.
Choice B is wrong because measuring the newborn’s serum bilirubin level is not a method to detect jaundice, but rather to confirm and quantify it.
Serum bilirubin level is the amount of bilirubin in the blood, which is responsible for the yellow color of jaundice.A blood test is required to measure this level.
Choice D is wrong because observing the newborn’s urine and stool color is not a reliable way to detect jaundice.
The color of urine and stool may vary depending on the hydration status, feeding type and other factors of the newborn.Moreover, urine and stool color may not change until the bilirubin level is very high.
A nurse is teaching a parent about how to prevent physiologic jaundice in a breastfed newborn.
Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
Explanation
This is because breastfeeding frequently can help the newborn pass more stools, which contain bilirubin, and reduce the risk of jaundice.
Choice A is wrong because supplementing breastfeeding with glucose water can reduce the amount of breast milk intake and increase the risk of jaundice.
Choice B is wrong because exposing the newborn to natural sunlight for short periods has not been proven to be effective in preventing or treating jaundice.
Moreover, sunlight can cause sunburn and dehydration in newborns.
Choice D is wrong because it includes choices A and B, which are incorrect.
Physiologic jaundice is a common and harmless condition that occurs in newborns due to the immature liver function and increased breakdown of red blood cells.It causes yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes due to the accumulation of bilirubin, a yellow pigment of red blood cells.Physiologic jaundice usually appears between the second and fourth day after birth and resolves within one to two weeks.Normal ranges of bilirubin levels vary depending on the age, gestational age, and health status of the newborn, but generally they are below 5 mg/dL (86 micromol/L) at term.
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a newborn who has pathologic jaundice due to blood incompatibility.
Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
Elevated direct bilirubin level: Pathologic jaundice is caused by an excessive breakdown of red blood cells due to blood incompatibility or liver disease.
This leads to an increased production of bilirubin, which is a yellow pigment that results from the breakdown of heme.
Bilirubin can be either unconjugated (indirect) or conjugated (direct), depending on whether it is bound to a protein called albumin or not.
Unconjugated bilirubin is not water-soluble and cannot be excreted in urine or bile.
It needs to be converted to conjugated bilirubin by the liver, which is water-soluble and can be eliminated from the body.However, if the liver is damaged or overwhelmed by the amount of bilirubin, some of the conjugated bilirubin can leak back into the bloodstream and cause an elevated direct bilirubin level.
• Decreased hematocrit level: Hematocrit is the percentage of red blood cells in the blood.When red blood cells are destroyed due to blood incompatibility or liver disease, the hematocrit level decreases.
This can lead to anemia, which is a condition where the blood does not carry enough oxygen to the tissues.
Positive direct Coombs test: A Coombs test is a blood test that detects antibodies that bind to red blood cells and cause them to clump together and be destroyed.
A direct Coombs test checks for antibodies that are attached to the red blood cells of the newborn.A positive direct Coombs test indicates that there is an immune reaction between the mother’s and the baby’s blood types, which can cause hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells) and jaundice.
Choice A is wrong because it only explains one aspect of pathologic jaundice, but not the other two.
Choice B is wrong because it only explains one aspect of pathologic jaundice, but not the other two.
Choice C is wrong because it only explains one aspect of pathologic jaundice, but not the other two.
Normal ranges for direct bilirubin are 0 to 0.3 mg/dL (0 to 5 mic
More questions on this topic
A nurse is preparing to gavage feed a preterm infant who is receiving IV antibiotics.
The infant expels a bloody stool.
What nursing action should the nurse implement?
Explanation
Institute contact precautions.This is because the infant may havenecrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), which is the most common cause of bloody stool in preterm infants.
NEC is a serious condition that involves inflammation and necrosis of the intestinal wall and can lead to perforation, sepsis, and death.NEC is also a potential source of infection for other infants in the NICU, so contact precautions are necessary to prevent cross-contamination.
Choice A is wrong because obtaining a rectal temperature is not indicated for an infant with bloody stool.Rectal temperature can cause irritation and bleeding of the rectal mucosa and can also increase the risk of perforation if there is intestinal necrosis.
Choice C is wrong because decreasing the amount of the feeding is not enough to manage an infant with bloody stool.
The infant may need to have the feeding stopped completely and receive parenteral nutrition until the bowel heals.Decreasing the feeding may also compromise the infant’s growth and development.
Choice D is wrong because assessing for abdominal distention is not a nursing action but a nursing assessment.
Abdominal distention is a common sign of feeding intolerance and NEC, but it is not specific or sensitive enough to diagnose the condition.Other signs and symptoms of NEC include bile-stained or bloody gastric residuals, emesis, diarrhea, temperature instability, apnea, bradycardia, hypotension, and lethargy.
A nurse is caring for a client who delivered a post-term infant vaginally with shoulder dystocia.
Which of the following findings should alert the nurse to possible injury in the infant?
Explanation
Absent Moro reflex on the affected side indicates a possible injury to the brachial plexus, which is the nerve network that controls the movements and sensations of the shoulder, arm, hand and fingers.Shoulder dystocia can cause brachial plexus injuries when the baby’s shoulder gets stuck behind the mother’s pubic bone during delivery.
Choice B is wrong because flaccid paralysis of both lower extremities is not a common complication of shoulder dystocia.
It could be a sign of spinal cord injury or other neurological disorders.
Choice C is wrong because facial asymmetry when crying or smiling is a sign of facial nerve palsy, which can occur due to compression of the facial nerve during delivery.
It is not specific to shoulder dystocia.
Choice D is wrong because inability to suck or swallow is not a typical sign of shoulder dystocia.
It could be caused by other factors such as prematurity, neurological problems, or congenital anomalies.
Normal ranges for Moro reflex are present at birth and disappear by 4 to 6 months of age.
Normal ranges for facial nerve function are symmetrical movements of both sides of the face.
Normal ranges for sucking and swallowing are coordinated and effective feeding within the first hour after birth.
A multigravida at 41-weeks gestation is receiving an oxytocin (Pitocin) infusion for induction of labor.
The nurse notes the fetal heart rate (FHR) drops sharply from the baseline for 30 seconds during the peak of a contraction and then returns to the baseline before the end of the contraction.
What action should the nurse implement at this time?
Explanation
Discontinue the oxytocin (Pitocin) infusion.This is because the fetal heart rate (FHR) drops sharply from the baseline for 30 seconds during the peak of a contraction and then returns to the baseline before the end of the contraction indicate alate deceleration, which is a sign offetal hypoxia.Oxytocin is a drug that stimulates uterine contractions and can causeuterine hyperstimulation, which reduces blood flow to the placenta and the fetus.By stopping the oxytocin infusion, the nurse can reduce the frequency and intensity of contractions and improve fetal oxygenation.
Choice A is wrong because administering oxygen via facemask may not be enough to reverse fetal hypoxia if oxytocin is still being infused.Choice B is wrong because placing the client on her left side may improve maternal blood flow to the placenta, but it will not reduce the effects of oxytocin on uterine activity.
Choice D is wrong because notifying the healthcare provider is not the most urgent action at this time.The nurse should first discontinue the oxytocin infusion and then notify the healthcare provider.
Normal ranges for FHR are 110 to 160 beats per minute, with a baseline variability of 6 to 25 beats per minute.
Normal ranges for uterine contractions are 2 to 5 contractions in 10 minutes, lasting
A nurse is caring for a client who had a post-term delivery and notes that the amniotic fluid was stained with meconium.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
This is because the infant born through meconium-stained amniotic fluid (MSAF) may have meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS), which is a condition that causes respiratory distress due to the inhalation of meconium into the lungs.The priority action for the nurse is to evaluate the infant’s breathing and circulation and initiate resuscitation if needed.
Choice A is wrong because suctioning the infant’s mouth and nose with a bulb syringe is not recommended unless the infant has obvious meconium in the airway and is not vigorous.Suctioning may cause bradycardia, hypoxia, or airway trauma.
Choice C is wrong because drying and stimulating the infant with a warm towel is part of the initial steps of resuscitation, but it should be done after assessing the infant’s heart rate and respiratory effort.Drying and stimulating may also increase the risk of meconium aspiration if the infant gasps.
Choice D is wrong because clamping and cutting the umbilical cord is not a priority action for an infant with possible MAS.The cord should be clamped and cut after ensuring that the infant is stable and has adequate oxygenation.
A nurse is assessing a post-term infant who was born with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).
Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
Loose, peeling skin without lanugo or vernix is a symptom of post-term infants who have intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).Post-term infants are born after 42 weeks of gestation and may have reduced placental function, resulting in less nutrition and oxygen for the fetus.This can cause them to have low birth weight, decreased subcutaneous fat and muscle mass, and dry skin.
Choice A is wrong because a large head in proportion to body size is not a sign of IUGR.It may indicate a congenital anomaly or a chromosomal disorder.
Choice C is wrong because increased subcutaneous fat and muscle mass are not signs of IUGR.They are signs of normal fetal growth and development.
Choice D is wrong because hypertonia and hyperreflexia are not signs of IUGR.They may indicate a neurological problem or a perinatal asphyxia (lack of oxygen during birth).
A nurse is planning care for a post-term infant who has hypoglycemia and is receiving IV dextrose solution.
Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan?
Explanation
This is because hypoglycemia in newborns can cause seizures, brain damage, and developmental delays, and frequent monitoring can help detect and correct low blood glucose levels promptly.
Some additional information about the other choices are:
Choice B. Administer glucagon subcutaneously as prescribed.This is wrong because glucagon is used to treat hypoglycemia caused by hyperinsulinism, which is a rare condition in newborns.Most cases of hypoglycemia in term infants are due to transient factors such as delayed feeding, maternal diabetes, or perinatal stress.
Choice C. Discontinue IV dextrose when blood glucose reaches 60 mg/dL.This is wrong because 60 mg/dL is still below the normal range of blood glucose for newborns, which is 70 to 100 mg/dL.Discontinuing IV dextrose too early can cause rebound hypoglycemia and increase the risk of neurologic complications.
Choice D. Feed breast milk or formula every four hours.This is wrong because feeding every four hours may not be enough to maintain adequate blood glucose levels in newborns with hypoglycemia.Infants with hypoglycemia should be fed more frequently, such as every two to three hours, or on demand.Breast milk or formula can also be supplemented with IV dextrose if needed.
A nurse is evaluating a preterm infant who has patent ductus arteriosus (PDA).
Which of the following findings should indicate to the nurse that the condition is improving?
Explanation
Increased oxygen saturation.This indicates that the condition is improving because it means that the blood is getting more oxygen in the lungs and less blood is shunting from the aorta to the pulmonary artery through the patent ductus arteriosus (PDA).
Choice A is wrong because decreased heart rate can be a sign of hypoxia, acidosis, or heart failure, which are complications of PDA.
Choice B is wrong because increased blood pressure can be a sign of increased systemic vascular resistance, which can result from decreased tissue perfusion due to PDA.
Choice C is wrong because decreased respiratory rate can be a sign of respiratory depression, which can be caused by some medications used to treat PDA, such as indomethacin or ibuprofen.
Normal ranges for oxygen saturation in preterm infants are between 88% and 95%.
Normal ranges for heart rate in preterm infants are between 120 and 160 beats per minute.
Normal ranges for blood pressure in preterm infants depend on gestational age and weight.
Normal ranges for respiratory rate in preterm infants are between 40 and 60 breaths per minute.
A nurse is evaluating the effectiveness of phototherapy for a post-term infant who has hyperbilirubinemia due to ABO incompatibility with the mother’s blood type O negative and infant’s blood type B positive.
Which of the following findings indicates that phototherapy is effective?
Explanation
Phototherapy is a treatment that uses light to break down bilirubin in the blood and make it easier for the liver to eliminate it.
Phototherapy is effective when:
• The bilirubin levels decrease within 24 hours of treatment.
This means that the bilirubin is being cleared faster than it is being produced.
• The urine output and stool frequency increase during treatment.
This means that the bilirubin is being excreted through the kidneys and intestines.
• The skin color and muscle tone improve after treatment.
This means that the bilirubin is no longer causing jaundice or affecting the nervous system.
Statement A is wrong because it only describes one aspect of phototherapy effectiveness.
Statement B is wrong because it only describes another aspect of phototherapy effectiveness.
Statement C is wrong because it only describes the outcome of phototherapy effectiveness.
Statement D is correct because it includes all three aspects of phototherapy effectiveness.
A nurse is reviewing laboratory results for a preterm infant who has anemia of prematurity.
Which of the following values should the nurse report to the provider?
Explanation
Reticulocyte count 2%.
A reticulocyte count measures the percentage of immature red blood cells (RBCs) in the blood.A low reticulocyte count indicates that the bone marrow is not producing enough RBCs, which is a characteristic feature of anemia of prematurity (AOP).A normal reticulocyte count for preterm infants is 3-6%.
Choice A is wrong because hemoglobin 10 g/dL is within the normal range for preterm infants.
Hemoglobin is the protein in RBCs that carries oxygen.
A low hemoglobin level indicates anemia.
Choice B is wrong because hematocrit 30% is within the normal range for preterm infants.
Hematocrit is the percentage of blood volume that is occupied by RBCs.
A low hematocrit level indicates anemia.
Choice D is wrong because platelet count 150,000/mm3 is within the normal range for preterm infants.
Platelets are cell fragments that help with blood clotting.
A low platelet count indicates thrombocytopenia, which is a different condition from anemia.
A nurse is preparing to administer an exchange transfusion to a newborn who has severe hyperbilirubinemia due to Rh incompatibility.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
Exchange transfusion (ET) is a procedure that involves removing the infant’s blood and replacing it with compatible donor blood to reduce the level of bilirubin and/or antibody-coated red blood cells.It is a high-risk intervention that can cause serious complications such as vascular accidents, cardiovascular compromise, and electrolyte and hematologic derangement.
Therefore, it is essential to obtain informed consent from the parent before performing ET.
Choice B is wrong because checking the newborn’s blood type and crossmatch is not the first action the nurse should take.
Although it is important to ensure compatibility between the donor and recipient blood, it is not as urgent as obtaining informed consent.
Choice C is wrong because inserting two umbilical catheters for blood withdrawal and infusion is not the first action the nurse should take.
Although it is necessary to establish vascular access for ET, it is not as crucial as obtaining informed consent.
Choice D is wrong because monitoring the newborn’s vital signs and oxygen saturation is not the first action the nurse should take.
Although it is vital to assess the newborn’s condition before, during, and after ET, it is not as imperative as obtaining informed consent.
Normal ranges for bilirubin levels vary depending on the gestational age and postnatal age of the newborn.The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) has published nomograms for initiating phototherapy and ET based on these factors.According to the AAP, ET should be considered when the bilirubin level exceeds 25 mg/dL (428 μmol/L) in term infants or 20 mg/dL (342 μmol/L) in preterm infants with risk factors for neurotoxicity.
A nurse is evaluating a newborn who has hyperbilirubinemia and is receiving phototherapy.
Which of the following outcomes indicates that the therapy is effective?
Explanation
The newborn’s skin color is pink.This indicates that the phototherapy is effective in lowering the serum bilirubin level by transforming it into water-soluble isomers that can be eliminated without liver conjugation.
A pink skin color also means that the newborn is not jaundiced, which is a sign of high bilirubin levels.
Choice B is wrong because clay-colored stools indicate a problem with the liver or bile ducts.Bile is needed to give stools their normal brown color, and if bile is absent or blocked, the stools may become pale or clay-colored.This could be a sign of a serious condition such as biliary atresia, which is a congenital defect that causes bile ducts to be absent or malformed.
Choice C is wrong because a bilirubin level of 12 mg/dL is still high for a newborn and may require further treatment.The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends phototherapy for newborns with bilirubin levels above 15 mg/dL at 25 to 48 hours of age, 18 mg/dL at 49 to 72 hours of age, and 20 mg/dL at more than 72 hours of age.However, these thresholds may vary depending on the gestational age, risk factors, and clinical condition of the newborn.
Choice D is wrong because dark yellow urine may indicate dehydration or concentrated urine, which can increase the risk of bilirubin toxicity.Newborns receiving phototherapy should be well hydrated and have frequent wet diapers to help eliminate bilirubin from the body.Normal urine color for a newborn is pale yellow or clear.
A nurse is caring for a preterm infant who has intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH).
Which of the following actions should the nurse take to prevent increased intracranial pressure (ICP)?
Explanation
All of the above.
The nurse should take all of the following actions to prevent increased intracranial pressure (ICP) in a preterm infant who has intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH):
• Elevate the head of the bed to 30 degrees.This helps to reduce venous congestion and improve cerebral blood flow.
• Avoid suctioning unless absolutely necessary.Suctioning can cause hypoxia, bradycardia, and increased ICP.
• Administer analgesics as prescribed.Pain can increase blood pressure and ICP.
Choice A is wrong because elevating the head of the bed alone is not enough to prevent increased ICP.
Choice B is wrong because avoiding suctioning alone is not enough to prevent increased ICP.
Choice C is wrong because administering analgesics alone is not enough to prevent increased ICP.
A nurse is educating a parent about how to care for a newborn who has hyperbilirubinemia at home.
Which of the following statements by the parent indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
This statement indicates that the parent understands the signs of acute bilirubin encephalopathy, a serious complication of hyperbilirubinemia that can cause brain damage.
The parent should seek immediate medical attention if these symptoms occur.
Choice B is wrong because “I will keep my baby fully clothed and wrapped in blankets.” This statement indicates that the parent does not understand the role of phototherapy in treating hyperbilirubinemia.Phototherapy is a treatment wherein a baby is placed under a special blue spectrum light to reduce the bilirubin levels.The baby should be exposed to as much light as possible, with only the eyes and genitals covered.
Choice C is wrong because “I will limit breastfeeding to no more than 10 minutes per session.” This statement indicates that the parent does not understand the importance of adequate hydration and nutrition in preventing and treating hyperbilirubinemia.Breastfeeding should not be interrupted or limited, as it provides fluids and calories that help the baby excrete bilirubin through urine and stool.The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends breastfeeding at least 8 to 12 times per day for newborns.
Choice D is wrong because “I will avoid exposing my baby to sunlight or artificial light.” This statement indicates that the parent does not understand the difference between natural and artificial light sources for phototherapy.Sunlight or artificial light from lamps or windows are not effective or safe for treating hyperbilirubinemia, as they do not emit the right wavelength or intensity of light, and they can cause overheating, dehydration, sunburn, or eye damage.
The baby should receive phot
A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving parenteral nutrition (PN) through a central venous catheter (CVC).
The current PN bag is empty, and a new PN bag is not available at this time.
Which of the following solutions should the nurse infuse until a new PN bag is available?
Explanation
Dextrose 10% in water.This is because parenteral nutrition (PN) is a mixture of nutrients that is given through a central venous catheter (CVC) that goes directly to the heart.PN contains high concentrations of nutrition and calories, and if the PN bag is empty, it needs to be replaced with a solution that has a similar osmolarity to prevent complications such as hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or phlebitis (inflammation of the vein).Dextrose 10% in water has an osmolarity of about 500 mOsm/L, which is close to the osmolarity of PN solutions.
Choice A is wrong because 0.9% sodium chloride has an osmolarity of about 300 mOsm/L, which is lower than PN solutions and can cause fluid overload and electrolyte imbalance.
Choice B is wrong because lactated Ringer’s has an osmolarity of about 275 mOsm/L, which is also lower than PN solutions and can cause similar problems as 0.9% sodium chloride.
Choice D is wrong because dextrose 5% in water has an osmolarity of about 250 mOsm/L, which is much lower than PN solutions and can cause rapid drop in blood sugar and vein irritation.
A nurse is caring for an infant who has a high Bilirubin level and is receiving phototherapy.
Which of the following is the priority finding in the newborn?
Explanation
This is a sign of dehydration, which can be caused by phototherapy.Phototherapy increases insensible water loss through the skin and can lead to fluid and electrolyte imbalance in the newborn.The nurse should monitor the newborn’s hydration status, weight, urine output, and serum electrolytes and provide adequate fluid intake.
Choice A is wrong because conjunctivitis is not a common complication of phototherapy.It can be prevented by using eye shields or patches to protect the newborn’s eyes from the light source.
Choice B is wrong because bronze skin discoloration is a rare complication of phototherapy that occurs when the bilirubin level is very high and the skin pigment changes.It is not a priority finding and usually resolves after phototherapy is discontinued.
Choice D is wrong because maculopapular skin rash is a benign side effect of phototherapy that does not require intervention.It usually disappears within a few days after phototherapy is stopped.
A nurse is assessing a newborn who was born at 35 weeks of gestation and has physiologic jaundice.
Which of the following factors increases the risk of hyperbilirubinemia in this newborn?
Explanation
All of the above factors increase the risk of hyperbilirubinemia in this newborn.Hyperbilirubinemia is a condition of high levels of bilirubin in the blood that can cause jaundice and brain damage.
Choice A is wrong because prematurity is a risk factor for hyperbilirubinemia, especially in babies born before 38 weeks of gestation.Premature babies have immature livers that are less able to process bilirubin and eliminate it from the body.
Choice B is wrong because breastfeeding is a risk factor for hyperbilirubinemia, particularly in some breast-fed babies who do not get enough milk or calories.Breastfeeding can also cause increased enterohepatic circulation of bilirubin, which means that bilirubin is reabsorbed from the intestines into the bloodstream instead of being excreted in the stool.
Choice C is wrong because Asian ethnicity is a risk factor for hyperbilirubinemia, as some Asian populations have higher rates of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, a genetic condition that causes red blood cells to break down more easily and release more bilirubin.Asian infants may also have lower levels of uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase, an enzyme that helps convert bilirubin into a form that can be excreted by the liver.
Normal ranges for bilirubin levels vary depending on the age, weight, and health status of the newborn.Generally, bilirubin levels peak between the third and seventh day after birth and then decline gradually.The AAP recommends using a nomogram based on the infant’s age in hours and serum bilirubin level to determine the risk of severe hyperbilirubinemia and the need for treatment.Treatment options include phototherapy and exchange transfusion.
A nurse is providing dietary teaching to a client who has celiac disease.
Which of the following food choices by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
Corn tortillas.
Celiac disease is a condition that causes damage to the small intestine when gluten is ingested.
Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, rye and oats.
Corn tortillas are made from corn flour, which does not contain gluten and is safe for people with celiac disease.
Choice A is wrong because whole wheat bread contains gluten, which can trigger an immune response and damage the small intestine in people with celiac disease.
Choice B is wrong because oatmeal cookies also contain gluten, either from the oats themselves or from cross-contamination with other grains.
Choice D is wrong because barley soup contains barley, which is another source of gluten that can harm people with celiac disease.
A nurse is reviewing the transcutaneous bilirubin measurement of a newborn who is 48 hours old and has physiologic jaundice.
The measurement is 16 mg/dL.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Transcutaneous bilirubin measurement is a useful screening tool for neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, but it has some limitations and sources of variability.Therefore, any bilirubin screening result obtained must be confirmed by a diagnostic method before treatment.
Choice A is wrong because initiating phototherapy without confirming the bilirubin level could expose the newborn to unnecessary treatment and potential adverse effects.
Choice C is wrong because increasing hydration by feeding more frequently may not be sufficient to lower the bilirubin level if it is too high or if there are other causes of jaundice.
Choice D is wrong because reassuring the parent that this is a normal finding could delay the diagnosis and treatment of severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, which can lead to serious complications such as kernicterus spectrum disorders.
Normal ranges for transcutaneous bilirubin measurement vary depending on the device used, the skin pigmentation, and the postnatal age of the newborn.However, a general guideline is that a measurement of 16 mg/dL at 48 hours of age is above the 95th percentile and warrants further investigation.
A nurse is assessing a client who has anaphylactic shock due to a bee sting.
Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
Bronchospasm.
Bronchospasm is a constriction of the airways that causes wheezing and trouble breathing.It is one of the symptoms of anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction that can occur within minutes of exposure to something you’re allergic to, such as a bee sting.
Choice A is wrong because bradycardia is a slow heart rate, not a fast one.Anaphylaxis causes a weak and rapid pulse due to low blood pressure.
Choice B is wrong because hypertension is high blood pressure, not low.Anaphylaxis causes blood pressure to drop suddenly and can lead to shock.
Choice D is wrong because warm, dry skin is not a sign of anaphylaxis.Anaphylaxis causes skin reactions such as hives, itching, flushed or pale skin.
A nurse is evaluating a client who received an immunization for tetanus one week ago.
The client reports pain and swelling at the injection site, low-grade fever, and body aches.
Which of the following responses should the nurse make?
Explanation
These are normal inflammatory responses to the vaccine.
The tetanus vaccine protects people from the bacteria that cause tetanus, a serious disease that causes muscle stiffness and spasms.
The vaccine stimulates the body’s immune system to produce antibodies against the bacteria.Sometimes, this immune response can cause mild symptoms such as pain, redness, swelling, fever, headache, or tiredness.
These are not signs of an infection or an allergic reaction, but rather the body’s way of building immunity.
Choice A is wrong because an allergic reaction to the vaccine would cause more severe symptoms such as hives, swelling of the face or throat, difficulty breathing, or shock.
These symptoms would usually occur within minutes or hours of getting the vaccine and require immediate medical attention.
Choice C is wrong because these are not signs of an active infection with tetanus.
Tetanus is a rare but potentially fatal disease that causes muscle spasms and paralysis.
It is caused by bacteria that enter the body through wounds or cuts.The symptoms of tetanus usually appear several days or weeks after exposure and include lockjaw, stiffness of the neck and abdomen, difficulty swallowing, fever, sweating, and seizures.
The tetanus vaccine prevents the disease by creating immunity before exposure.
Choice D is wrong because these are not adverse effects of preservatives in the vaccine.
Preservatives are substances that prevent contamination and spoilage of vaccines.The most common preservative used in tetanus vaccines is thimerosal, a mercury-based compound that has been proven to be safe and effective.
There is no evidence that thimerosal causes autism or any other health problems.
Some people may have a sensitivity to thimerosal or other ingredients in the vaccine, but this is very rare and would cause an allergic reaction as described in choice A.
A nurse is planning care for a newborn who has hyperbilirubinemia and is receiving phototherapy.
Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan?
Explanation
This is because phototherapy can cause dehydration and increase insensible water loss, so covering the genitalia can prevent excessive fluid loss and maintain thermoregulation.
Some possible explanations for the other choices are:
• Choice A is wrong because monitoring skin temperature every hour is not enough to prevent hyperthermia or hypothermia during phototherapy.The skin temperature should be monitored continuously or at least every 15 minutes.
• Choice C is wrong because repositioning newborn every 4 hours is not frequent enough to prevent pressure ulcers, skin breakdown, or eye damage from the light source.The newborn should be repositioned at least every 2 hours.
• Choice D is wrong because encouraging parent-infant interaction as tolerated is not a specific intervention for phototherapy.
While parent-infant interaction is important for bonding and development, it should not interfere with the effectiveness of phototherapy.The newborn should be exposed to the light as much as possible, except for feeding and diaper changes.
Normal ranges for serum bilirubin levels vary depending on the age, gestational age, and risk factors of the newborn.Generally, the levels should be below 5 mg/dL for term infants and below 7 mg/dL for preterm infants by the fifth day of life.
A nurse is caring for a client who has systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
The client asks why she has to have her blood drawn so often.
Which of the following responses should the nurse make?
Explanation
“We need to monitor your kidney function because SLE can cause glomerulonephritis.” Glomerulonephritis is kidney inflammation caused by SLE that can damage the filtering units of the kidneys called glomeruli.SLE is an autoimmune disease that can affect various organs and tissues, including the kidneys.About half of the people with lupus experience kidney involvement, which can lead to kidney failure if not treated.
Therefore, it is important to monitor the kidney function of people with SLE.
Choice B is wrong because SLE does not cause hepatic necrosis, which is the death of liver cells.SLE can cause inflammation of the liver, but this is less common and less severe than kidney involvement.
Choice C is wrong because SLE does not cause hypothyroidism, which is a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones.
SLE can affect the thyroid gland, but this is rare and usually does not affect the thyroid function.
Choice D is wrong because SLE does not cause diabetes mellitus, which is a condition where the body cannot regulate blood sugar levels.
SLE can cause inflammation of the pancreas, but this is uncommon and usually does not affect the insulin production.
A nurse is caring for a client who is at 42 weeks of gestation and is in labor.
The client asked the nurse what to expect because the baby is postmature.
Which of the following statements should the nurse make?
Explanation
This is because postmature babies lose the protective vernix that covers their skin in utero, and their skin becomes dry and cracked.Postmature babies also have less subcutaneous fat, which makes them look thin and wrinkled.
Choice A is wrong because postmature babies have less body fat than term babies, not more.They use up their fat stores to survive in the womb beyond 42 weeks of gestation.
Choice B is wrong because postmature babies have well-developed breast buds and areola, not flat ones.Breast development is a sign of fetal maturity that occurs around 36 weeks of gestation.
Choice C is wrong because postmature babies have less flexibility in their joints and muscles, not more.They have less amniotic fluid to cushion their movements, and their bones become more ossified as they grow older.
Normal ranges for gestational age are 37 to 42 weeks.Babies born before 37 weeks are considered preterm, and babies born after 42 weeks are considered postmature.
The nurse is educating a client about the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia in a newborn.
Which of the following should the nurse include?
Explanation
Jitteriness and poor feeding are common signs of hypoglycemia in a newborn.
Hypoglycemia is when the level of sugar (glucose) in the blood is too low.
Glucose is the main source of fuel for the brain and the body.In a newborn baby, low blood sugar can cause problems such as shakiness, blue tint to the skin, and breathing and feeding problems.
Choice A is wrong because hypertension and bradycardia are not typical symptoms of hypoglycemia in a newborn.
They may indicate other conditions such as heart problems or infection.
Choice B is wrong because diarrhea and vomiting are not specific symptoms of hypoglycemia in a newborn.
They may be caused by many other factors such as infection, food intolerance, or gastroesophageal reflux.
Choice D is wrong because hyperactivity and irritability are not usual symptoms of hypoglycemia in a newborn.
They may be signs of other conditions such as pain, hunger, or overstimulation.
Normal ranges for blood glucose levels in newborns vary depending on the age, gestational age, and feeding status of the baby.Most doctors consider blood glucose that is below 47 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl) to be the definition of hypoglycemia in newborns.
However, some babies may need higher levels to prevent brain injury.
A doctor will monitor the blood glucose levels of a newborn at risk for hypoglycemia and treat accordingly.
A baby with hemolytic jaundice is being treated with fluorescent phototherapy.
To provide safe newborn care, which of the following actions should the nurse perform?
Explanation
This is because phototherapy can damage the baby’s eyes and cause retinal injury.Eye pads should be used to protect the baby’s eyes from the light and should be removed every 4 hours to check for infection or injury.
Choice B is wrong because turning the lights off for ten minutes every hour would reduce the effectiveness of phototherapy and prolong the treatment time.Phototherapy aims to expose the baby’s skin to as much light as possible.
Choice C is wrong because clothing the baby in a shirt and diaper only would limit the amount of skin exposed to the light.The baby should be naked or wear only a diaper during phototherapy.
Choice D is wrong because tightly swaddling the baby in a baby blanket would also limit the amount of skin exposed to the light and increase the risk of overheating.The baby should be loosely wrapped or uncovered during phototherapy.
A newborn is diagnosed with hypoglycemia.
Which intervention should the nurse prioritize?
Explanation
Encouraging frequent breastfeeding.
This is because breastfeeding provides glucose to the newborn baby, which can help prevent or treat hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).Hypoglycemia can cause problems such as shakiness, blue tint to the skin, and breathing and feeding problems.
Choice A is wrong because administering IV insulin would lower the blood sugar level even more, which could be dangerous for the baby.
Choice C is wrong because monitoring blood pressure is not directly related to hypoglycemia.
Blood pressure may be affected by other factors such as stress, infection, or dehydration.
Choice D is wrong because administering a hypertonic saline solution would increase the sodium level in the blood, which could cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalance.
A hypertonic saline solution is not a source of glucose for the baby.
Normal ranges for blood glucose levels in newborns are between 47 to 85 mg/dL.Hypoglycemia is defined as blood glucose below 47 mg/dL.
A baby’s blood type is B negative.
The baby is at risk for hemolytic jaundice if the mother has which of the following blood types?
Explanation
The baby is at risk for hemolytic jaundice if the mother has a different blood type that is incompatible with the baby’s blood type.This can cause the mother’s immune system to produce antibodies that attack the baby’s red blood cells, leading to hemolysis or excessive destruction of red blood cells.Hemolysis can cause bilirubin, a yellowish pigment, to accumulate in the baby’s blood, tissues, and fluids, causing jaundice.It can also cause anemia, a condition where the blood does not have enough healthy red blood cells.
Choice A is wrong because O positive is compatible with B negative.
O positive is the universal donor, meaning it can donate blood to any other blood type without causing a reaction.
Choice B is wrong because AB negative is compatible with B negative.
AB negative is the universal recipient, meaning it can receive blood from any other blood type without causing a reaction.
Choice D is wrong because A negative is incompatible with B negative.
A negative and B negative are different blood types that can cause a reaction if mixed together.
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a newborn who has hypoglycemia.
The nurse should identify that a normal blood glucose level for a healthy term newborn is between which of the following ranges?
Explanation
A normal blood glucose level for a healthy term newborn is between 30 and 60 mg/dL.This range is lower than that of older children and adults, because newborns are adapting to life outside the womb and their glucose levels rise gradually after birth.
Choice A is wrong because 10 and 30 mg/dL is too low for a newborn and indicates hypoglycemia, which can cause symptoms such as jitteriness, poor feeding, lethargy, and cyanosis.
Choice C is wrong because 60 and 90 mg/dL is too high for a newborn and indicates hyperglycemia, which can cause symptoms such as dehydration, poor feeding, irritability, and seizures.
Choice D is wrong because 90 and 120 mg/dL is also too high for a newborn and indicates hyperglycemia, which can have the same consequences as choice C.
A nurse is educating the parents of a newborn who has hypoglycemia about how to feed their baby.
The nurse should instruct the parents to do which of the following actions?
Explanation
This is because newborns with hypoglycemia need to receive adequate nutrition to raise their blood glucose levels and prevent neurologic damage.Early feeding also helps establish breast milk supply for nursing mothers.
Choice B is wrong because feeding the baby only when he cries may delay the intake of glucose and worsen the hypoglycemia.Newborns with hypoglycemia should be fed on demand or at least every 2 to 3 hours.
Choice C is wrong because feeding the baby every 6 hours is too infrequent and may cause prolonged hypoglycemia.Newborns with hypoglycemia should be fed on demand or at least every 2 to 3 hours.
Choice D is wrong because feeding the baby with glucose water may not provide enough calories and nutrients for growth and development.Newborns with hypoglycemia should be fed with breast milk or formula.Glucose water may be used as a temporary measure until breast milk or formula is available.
Exams on Newborn Complications
Custom Exams
Login to Create a Quiz
Click here to loginLessons
 Nursingprepexams
Just Now
Nursingprepexams
Just Now
Notes Highlighting is available once you sign in. Login Here.
Objectives
- Identify common newborn complications and their causes
- Describe the signs and symptoms of newborn complications and how to assess them
- Explain the nursing interventions and rationales for newborn complications
- Evaluate the outcomes and potential complications of nursing interventions for newborn complications
- Apply evidence-based practice and ethical principles to the care of newborns with complications
- Educate parents and caregivers on how to prevent, recognize, and manage newborn complications
Introduction
Newborn complications are any conditions or problems that affect the health or well-being of a newborn baby. They can occur before, during, or after birth, and can be caused by various factors such as maternal health, genetic disorders, infections, birth trauma, prematurity, or congenital anomalies.
Newborn complications can range from mild to severe, and can affect different body systems such as respiratory, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, neurological, hematological, or metabolic. Some of the most common newborn complications are hypoglycemia, preterm birth, macrosomia, post-term birth, and hyperbilirubinemia.
These complications can have short-term or long-term effects on the newborn’s growth, development, and quality of life. Therefore, it is important for nurses to be able to identify, assess, intervene, and evaluate newborn complications using evidence-based practice and ethical principles. Nurses also have a key role in educating parents and caregivers on how to prevent, recognize, and manage newborn complications.
Hypoglycemia
- Definition: Blood glucose level less than 40 mg/dL in a newborn
- Causes: Maternal diabetes, intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), prematurity, birth asphyxia, cold stress, sepsis
- Signs and symptoms: Jitteriness, tremors, lethargy, poor feeding, hypotonia (low muscle tone), weak cry, apnea (cessation of breathing), cyanosis (bluish skin color), seizures
- Assessment: Perform heel stick blood glucose test using a glucometer; confirm with laboratory plasma glucose test if abnormal; monitor vital signs and neurological status; observe for signs of hypoglycemia
- Nursing interventions: Feed the baby as soon as possible after birth (breast milk or formula); if unable to feed orally or blood glucose level is very low (<25 mg/dL), administer intravenous (IV) dextrose solution as ordered; maintain thermoregulation by keeping the baby warm and dry; monitor blood glucose levels frequently until stable; educate parents on signs of hypoglycemia and how to feed the baby
-
Definition: When the baby's cheek is stroked, the baby turns their head towards the stroke and attempts to suck.
-
Timeline: Birth to 4 months.
-
Example: Stroking the baby's cheek with your finger should elicit the rooting reflex, indicating intact neurologic function.

A. Definition: Fall prevention involves identifying patients at risk for falls and implementing interventions to minimize the occurrence of falls and related injuries.
B. Risk Assessment:
1. Assessment Tools: Using validated tools, such as the Morse Fall Scale or Hendrich II Fall Risk Model, helps identify patients at risk for falls.
2. Factors Contributing to Falls: Assessing factors such as advanced age, impaired mobility, history of falls, cognitive impairment, medications, and environmental hazards aids in determining fall risk.
C. Interventions:
1. Environmental Modifications:
a. Removing obstacles and clutter: Ensuring clear pathways and removing tripping hazards reduces the risk of falls.
b. Adequate lighting: Maintaining well-lit areas helps patients see potential hazards and improves safety.
c. Grab bars and handrails: Installing grab bars in bathrooms and handrails along corridors and stairways provides support for patients.
2. Assistive Devices: a. Mobility aids: Providing appropriate assistive devices, such as canes, walkers, or wheelchairs, assists patients with impaired mobility.
b. Alarms and sensors: Using bed or chair alarms, pressure sensors, or motion detectors alerts healthcare providers when patients attempt to rise unassisted.
3. Patient Education:
a. Teaching about fall risks: Educating patients and their families about fall risks and the importance of following safety measures.
b. Call light usage: Encouraging patients to use call lights to request assistance before attempting to move independently.
c. Footwear: Emphasizing the need for patients to wear proper footwear with good traction and support.
D. Documentation:
1. Accurate and thorough documentation of fall risk assessments, interventions implemented, patient responses, and any incidents or near-misses related to falls.
2. Sharing information with the healthcare team to ensure continuity of care and appropriate interventions.
A. Safety and fall prevention are critical aspects of healthcare delivery that healthcare professionals must prioritize.
B. By implementing effective safety measures, healthcare providers can ensure optimal patient outcomes and create a safe environment for both patients and themselves.
Introduction
- Glomerulonephritis is a medical condition that affects the kidneys, specifically, the glomeruli, which are the tiny filters that remove waste, excess fluid, and electrolytes from the blood.
- Glomerulonephritis can be acute or chronic, depending on the onset and duration of the inflammation.
- Acute glomerulonephritis occurs suddenly and usually lasts for less than six months, while chronic glomerulonephritis develops gradually and lasts for more than six months. Glomerulonephritis can cause serious complications, such as chronic kidney disease, acute kidney failure, and nephrotic syndrome, if left untreated.
- Therefore, it is important for nurses to understand the pathophysiology, etiology, risk factors, clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluation, management, treatment, nursing care, and patient education of this condition.
Etiology and risk factors
- Glomerulonephritis can be caused by various factors, such as infections, immune disorders, vascular disorders, genetic disorders, or malignancies.
- Some of the common causes are:
- Infections: Glomerulonephritis can occur after recovering from a streptococcal throat infection or a skin infection. It can also happen when a patient has a viral infection such as HIV or hepatitis B or C, or a bacterial infection such as endocarditis or syphilis.
- Immune disorders: Lupus is an inflammatory disease that affects various organs, including the kidneys. It can cause lupus nephritis, which is a type of glomerulonephritis. Other immune disorders that can cause glomerulonephritis are Goodpasture syndrome, Wegener's granulomatosis, polyarteritis nodosa, and HenochSchönlein purpura.
- Vascular disorders: Vasculitis is a disorder of the blood vessels that can cause inflammation and damage to the glomeruli. Examples of vasculitis that can cause glomerulonephritis are microscopic polyangiitis and ChurgStrauss syndrome.
- Genetic disorders: Alport syndrome is an inherited disorder that affects the type IV collagen in the glomerular basement membrane. It can cause progressive glomerulonephritis and hearing loss. Other genetic disorders that can cause glomerulonephritis are Fabry disease and nail-patella syndrome.
- Malignancies: Lung cancer, leukemia, or myeloma can increase the risk of developing glomerulonephritis due to abnormal production of antibodies or immune complexes.
- Some of the risk factors that can worsen or complicate glomerulonephritis are:
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can damage the ability of the kidneys to filter blood and increase the risk of chronic kidney disease.
- Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes can lead to diabetic nephropathy, which is the damage of the kidneys due to high blood sugar levels and high blood pressure levels.
- Smoking: Smoking can impair blood flow to the kidneys and worsen kidney function.
- Medications: Some medications can have nephrotoxic effects or trigger allergic reactions that can cause glomerulonephritis. Examples are nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics such as penicillin or sulfonamides, contrast agents used for imaging tests, and immunosuppressants.

Introduction
- Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (NDI) is a rare but significant renal disorder characterized by the kidneys' inability to concentrate urine, leading to excessive urination (polyuria) and increased thirst (polydipsia).
- Unlike Diabetes Mellitus, which involves issues with insulin and blood glucose regulation, NDI is a disorder of water balance regulation, specifically affecting the response of the kidneys to Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH), also known as Vasopressin.
- NDI can be either acquired, often due to certain medications or underlying medical conditions or inherited as a genetic trait.
- This condition can present in various forms, including congenital NDI, which is present at birth and acquired NDI, which may develop later in life.
- The primary hallmark of NDI is the excretion of large volumes of dilute urine, which can lead to significant fluid loss and dehydration if not managed appropriately.
- Diagnosing NDI involves specialized tests, such as the water deprivation test, to differentiate it from other causes of excessive urination and thirst.
- Managing NDI necessitates a multidisciplinary approach, including fluid replacement, potential medication use, and addressing any underlying causes, with the goal of maintaining fluid balance and preventing complications.
Objectives:
-
Objectives:
- Understand the etiology of gastroenteritis in children.
- Explain the pathophysiology of gastroenteritis in children.
- Identify the clinical manifestations of gastroenteritis in children.
- Describe the diagnostic evaluation methods for gastroenteritis in children.
- Provide normal ranges for applicable parameters.
- Familiarize with commonly tested information in ATI/HESI nursing proctored MCQ exams related to gastroenteritis in children.
- Understand the nursing assessment process for children with gastroenteritis.
- Identify appropriate nursing interventions for managing gastroenteritis in children.
- Discuss the treatment options available for children with gastroenteritis.
- Recognize the importance of maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance in children with gastroenteritis.
Introduction: Gastroenteritis is a common gastrointestinal infection that affects children worldwide. It is characterized by inflammation of the stomach and intestines, leading to symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. This comprehensive nursing note will delve into the etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnostic evaluation of gastroenteritis in children.
Etiology of Gastroenteritis in Children:
- Gastroenteritis in children is commonly caused by viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections.
- Viral etiologies include rotavirus, norovirus, adenovirus, and astrovirus.
- Bacterial causes include Salmonella, Campylobacter, Escherichia coli, and Shigella.
- Parasitic infections can be caused by Giardia lamblia or Cryptosporidium.
Pathophysiology of Sickle Cell Disease:
- Hemoglobin S causes red blood cells to become rigid and sickle-shaped when deoxygenated.
- Sickle-shaped cells are less flexible and can block blood vessels, leading to impaired blood flow and tissue ischemia.
- Repeated sickling and unsickling of red blood cells cause damage to the cell membrane, leading to chronic hemolysis and anemia.
- The release of inflammatory mediators during sickling episodes further contributes to vascular injury and organ damage.
Some Manifestations Include:
- Painful vaso-occlusive crises: characterized by severe pain in various body parts due to the occlusion of blood vessels by sickled red blood cells.
- Anemia: resulting from the chronic destruction of red blood cells.
- Infections: individuals with sickle cell disease are more susceptible to infections due to functional asplenia and impaired immune function.
- Organ damage: chronic hypoxia and vascular occlusion can lead to damage in multiple organs, including the lungs, kidneys, liver, and spleen.
- Delayed growth and development: sickle cell disease may affect growth and development in children.
Preterm birth
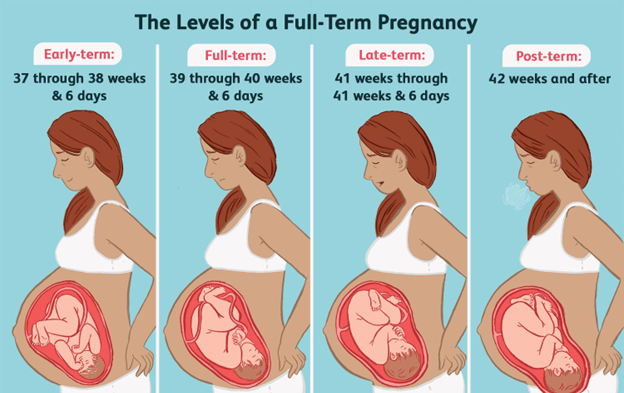
- Definition: Birth before 37 weeks of gestation
- Causes: Maternal infections, chronic diseases (e.g., hypertension, diabetes), multiple gestation (twins or more), placental problems (e.g., abruption, previa), cervical incompetence (weakness), preterm labor
- Signs and symptoms: Low birth weight (<2500 g), small size for gestational age (SGA), immature appearance (e.g., lanugo hair, vernix caseosa coating), large head relative to body size, thin skin with visible blood vessels, poor muscle tone, respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), anemia, infection, hypothermia, hypoglycemia, hyperbilirubinemia
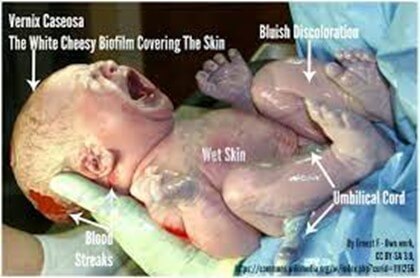
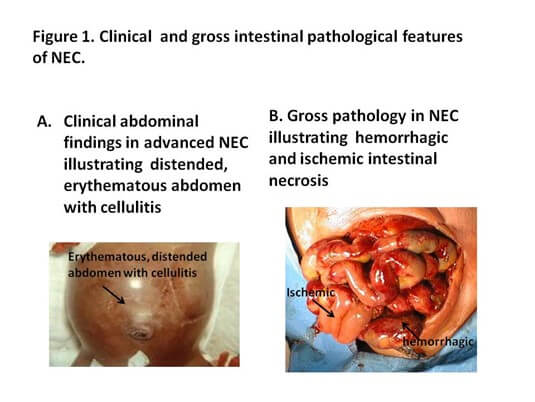
- Assessment: Determine gestational age using Ballard score; measure weight, length, head circumference; monitor vital signs and oxygen saturation; assess respiratory status using Silverman-Anderson index; observe for signs of distress or infection; perform laboratory tests as ordered (e.g., blood gas analysis, blood glucose level, bilirubin level); perform diagnostic tests as ordered (e.g., chest X-ray, cranial ultrasound, echocardiogram)
- Nursing interventions: Transfer the baby to neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) if needed; provide respiratory support as ordered (e.g., oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, surfactant administration); maintain thermoregulation by placing the baby in an incubator or under a radiant warmer; monitor fluid and electrolyte balance and administer IV fluids as ordered; provide nutrition support as ordered (e.g., parenteral nutrition, enteral feeding via nasogastric tube or gavage); prevent infection by using aseptic technique and hand hygiene; administer medications as ordered (e.g., antibiotics, steroids, indomethacin); provide developmental care by minimizing stimuli and promoting bonding; educate parents on preterm care and support them emotionally


Macrosomia
- Definition: Birth weight greater than 4000 g or above the 90th percentile for gestational age
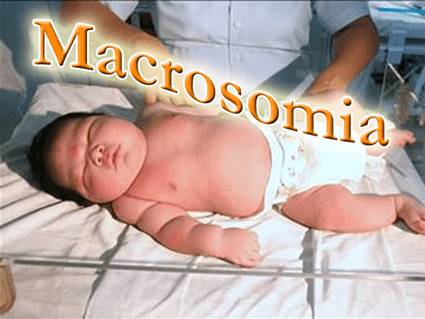
- Causes: Maternal diabetes or obesity, excessive weight gain during pregnancy, prolonged pregnancy (>40 weeks), male gender, genetic factors
- Signs and symptoms: Large size for gestational age (LGA), plump or full face, birth trauma (e.g., shoulder dystocia, brachial plexus injury), hypoxemia (low oxygen level in blood), hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia (low calcium level in blood), polycythemia (high red blood cell count), hyperbilirubinemia
- Assessment: Measure weight, length, head circumference; monitor vital signs and oxygen saturation; assess for signs of trauma or injury; perform heel stick blood glucose test using a glucometer; perform laboratory tests as ordered (e.g., blood gas analysis, calcium level, hematocrit); perform diagnostic tests as ordered (e.g., chest X-ray)
- Nursing interventions: Deliver the baby vaginally with assistance if needed (e.g., forceps, vacuum extraction) or by cesarean section if indicated; provide oxygen therapy if needed; maintain thermoregulation by keeping the baby warm and dry; feed the baby as soon as possible after birth; monitor blood glucose levels frequently until stable; administer IV dextrose solution if needed; monitor calcium levels and administer calcium gluconate if needed; monitor hematocrit levels and perform partial exchange transfusion if needed; monitor bilirubin levels and provide phototherapy if needed; educate parents on signs of hypoglycemia and how to feed the baby
Post-term birth
- Definition: Birth after 42 weeks of gestation
- Causes: Unknown; possible factors include inaccurate estimation of due date, genetic predisposition, placental insufficiency
- Signs and symptoms: Wasted appearance due to loss of subcutaneous fat; peeling, cracked, leathery skin; long hair and nails; meconium staining on nails or umbilical cord; macrosomia or intrauterine growth restriction; oligohydramnios (low amniotic fluid volume); fetal distress; hypoxemia; hypoglycemia; polycythemia; hyperbilirubinemia
- Assessment: Determine gestational age using ultrasound or last menstrual period date; measure weight, length, head circumference; monitor vital signs and oxygen saturation; assess for signs of distress or injury; perform heel stick blood glucose test using a glucometer; perform laboratory tests as ordered (e.g., blood gas analysis, hematocrit); perform diagnostic tests as ordered (e.g., chest X-ray)
- Nursing interventions: Deliver the baby vaginally with induction or augmentation of labor if needed or by cesarean section if indicated; provide oxygen therapy if needed; maintain thermoregulation by keeping the baby warm and dry; feed the baby as soon as possible after birth; monitor blood glucose levels frequently until stable; administer IV dextrose solution if needed; monitor hematocrit levels and perform partial exchange transfusion if needed; monitor bilirubin levels and provide phototherapy if needed; educate parents on signs of hypoglycemia and how to feed the baby
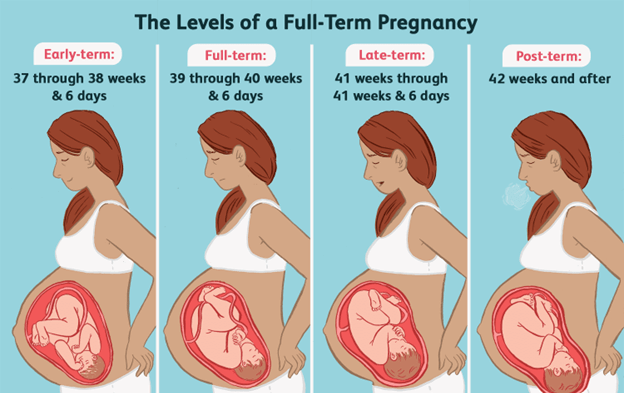
Hyperbilirubinemia
- Definition: Elevated serum bilirubin level that causes jaundice (yellowish skin color)
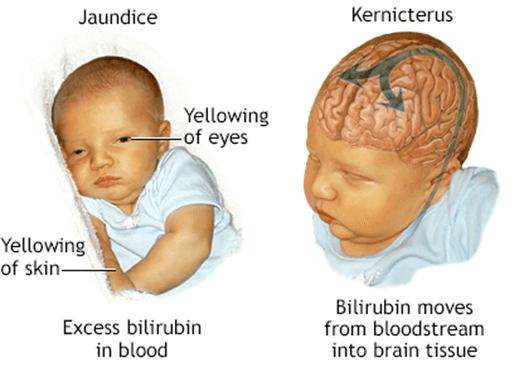
- Causes: Physiologic jaundice due to breakdown of fetal red blood cells and immaturity of liver enzymes that occurs after 24 hours of age; pathologic jaundice due to blood incompatibility between mother and baby or infection that occurs within 24 hours of age or lasts longer than 7 days; kernicterus due to untreated hyperbilirubinemia that causes brain damage
- Signs and symptoms: Yellowish skin color that progresses from head to toe; yellowish sclerae (whites of eyes); lethargy; poor feeding; dark urine; pale stools; high-pitched cry; seizures
- Assessment: Perform transcutaneous bilirubin measurement using a device that measures skin reflectance at multiple wavelengths; confirm with laboratory serum bilirubin test if abnormal; monitor vital signs and neurological status; observe for signs of jaundice; note the time that jaundice set in to determine whether physiologic or pathologic
- Nursing interventions
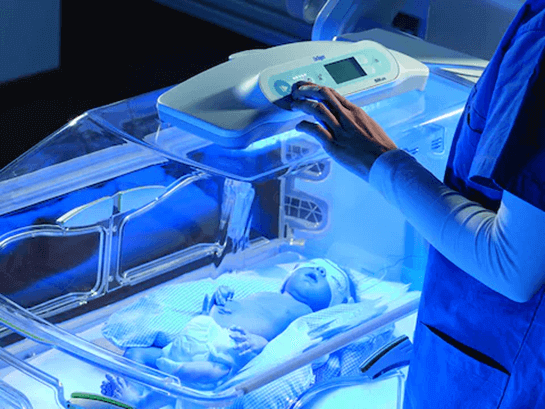
- Provide phototherapy as ordered if newborn’s bilirubin level is above 15 mg/dL before 48 hours of age or above 18 mg/dL before 72 hours of age or above 20 mg/dL at any point; place eye mask on baby, keep newborn undressed, cover genitalia; avoid applying lotions; remove newborn from phototherapy every 4 hours, remove eye mask; reposition newborn every 2 hours; bronze discoloration or rash is not a serious complication; monitor for dehydration by checking sunken fontanels and number of diapers produced per day; feed newborn frequently to promote bilirubin excretion through stool; administer IV fluids or blood transfusion if needed; educate parents on signs of hyperbilirubinemia and how to care for the baby
Summary
- Newborn complications are any conditions or problems that affect the health or well-being of a newborn baby
- Common newborn complications include hypoglycemia, preterm birth, macrosomia, post-term birth, and hyperbilirubinemia
- Newborn complications can be caused by various factors such as maternal health, genetic disorders, infections, birth trauma, prematurity, or congenital anomalies
- Newborn complications can affect different body systems such as respiratory, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, neurological, hematological, or metabolic
- Newborn complications can have short-term or long-term effects on the newborn’s growth, development, and quality of life
- Nurses need to identify, assess, intervene, and evaluate newborn complications using evidence-based practice and ethical principles
- Nurses need to educate parents and caregivers on how to prevent, recognize, and manage newborn complications
Conclusion
Newborn complications are any conditions or problems that affect the health or well-being of a newborn baby. They can have short-term or long-term effects on the newborn’s growth, development, and quality of life.
Therefore, it is important for nurses to be able to identify, assess, intervene, and evaluate newborn complications using evidence-based practice and ethical principles. Nurses also have a key role in educating parents and caregivers on how to prevent, recognize, and manage newborn complications.
Nursingprepexams
Videos
Login to View Video
Click here to loginTake Notes on Newborn Complications
This filled cannot be empty