Please set your exam date
Fetal Non-Stress Test (NST)
Study Questions
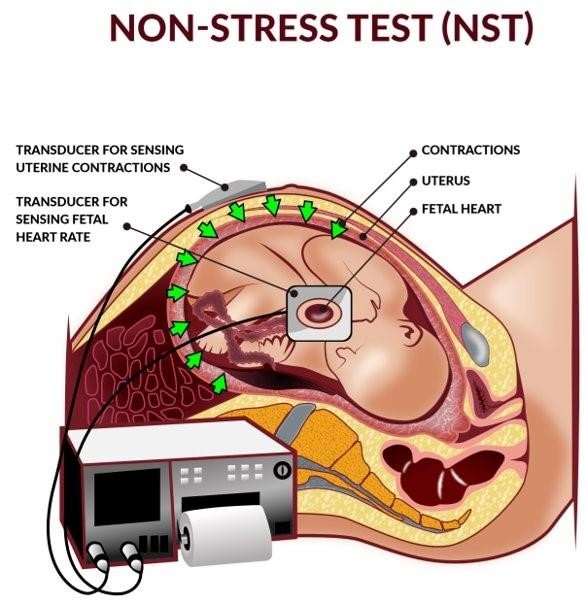
Procedure and equipment
A nurse is preparing to perform a nonstress test (NST) for a pregnant client at 38 weeks of gestation.
What equipment should the nurse gather for this procedure? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
A nonstress test (NST) is a non-invasive test used to evaluate a baby’s well-being by monitoring fetal heartbeat and movements.The equipment needed for this procedure includes a belt with two transducers and a paper strip or a computer screen.The belt with two transducers is used to measure the fetal heart rate and uterine contractions, while the paper strip or computer screen displays the results.
Choice A is wrong because a reclining chair or bed is not necessary for an NST.The test can be done while the pregnant person is seated comfortably in a chair or resting in a reclined position on a table.
Choice D is wrong because a button for the client to press is not required for an NST.The test does not depend on the client’s perception of fetal movement, but rather on the objective measurement of fetal heart rate and uterine activity.
Choice E is wrong because an acoustic stimulator is not part of the standard equipment for an NST.
An acoustic stimulator is a device that produces a loud noise to stimulate the fetus and elicit a heart rate response.It may be used in some cases when the NST results are nonreactive, but it is not routinely used.
A nurse is reviewing the results of a nonstress test (NST) for a pregnant client at 32 weeks of gestation.
The nurse notes that the fetal heart rate (FHR) baseline is 140 bpm with moderate variability and two accelerations of 15 bpm lasting 15 seconds each in a 20-minute period.
How should the nurse interpret these findings?
Explanation
The NST is reactive, indicating fetal well-being.A reactive NST means that the fetal heart rate increases by at least15 bpmfor at least15 secondstwice or more in a20-minuteperiod.This shows that the fetus is healthy and getting enough oxygen.
Choice B is wrong because a nonreactive NST means that the fetal heart rate does not show the expected accelerations in a 40-minute period, which may indicate fetal compromise.
Choice C is wrong because an inconclusive NST means that the test results are unclear or not enough data was collected, which may require further testing.
Choice D is wrong because an invalid NST means that the test was not performed correctly or there was interference with the fetal heart rate monitoring, which may require a repeat test.
Normal ranges for fetal heart rate are110 to 160 bpmwith moderate variability (5 to 25 bpm) and no decelerations.

A nurse is performing a nonstress test (NST) for a pregnant client at 36 weeks of gestation who reports decreased fetal movement.
The nurse observes that the fetal heart rate (FHR) baseline is 120 bpm with minimal variability and no accelerations in a 20-minute period.
What should the nurse do next?
Explanation
Offer the client a snack or juice to stimulate fetal activity.
A nonstress test (NST) is a pregnancy screening that measures fetal heart rate and reaction to movement.It is performed to make sure the fetus is healthy and getting enough oxygen.A reactive NST means that the fetal heart rate increases by at least 15 beats per minute for at least 15 seconds twice in a 20-minute period.A nonreactive NST means that this criteria is not met.
Choice B is wrong because applying an acoustic stimulator to elicit fetal movement is not recommended as a routine practice and may cause fetal distress.
Choice C is wrong because stopping the test and notifying the provider immediately is not necessary unless there are signs of fetal compromise, such as severe variable or late decelerations, or a nonreassuring fetal heart rate pattern.
Choice D is wrong because extending the test for another 20 minutes may not change the result and may prolong the discomfort of the client.A nonreactive NST does not mean there is a problem, but it may require further testing, such as a biophysical profile or a contraction stress test.
A nurse is teaching a pregnant client about the purpose and procedure of a nonstress test (NST).
Which of the following statements by the client indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
The test will require me to lie on my back for the duration of the test.This statement indicates a need for further teaching because lying on the back can compress the inferior vena cava and reduce blood flow to the baby.The test can be done in a reclining chair or on an exam table with a wedge under one hip to avoid this problem.
Choice A is correct because the test will measure how the baby’s heart rate changes when he moves.In most healthy babies, the heart rate increases during movement.
Choice B is correct because the test will take at least 20 minutes, but it may take longer if the baby is not active or moving during that time period.
Choice C is correct because the test will involve placing two belts around the abdomen.One will measure the baby’s heartbeat and the other will record contractions.
A nurse is evaluating the results of a nonstress test (NST) for a pregnant client at 34 weeks of gestation who has gestational diabetes mellitus.
The nurse notes that the fetal heart rate (FHR) baseline is 150 bpm with moderate variability and three accelerations of 20 bpm lasting 20 seconds each in a 10-minute period.
How should the nurse document these findings?
Explanation
Reactive NST.This means that the fetal heart rate increased by at least 15 beats per minute (bpm) for at least 15 seconds twice or more in a 20-minute period.This indicates that the baby is getting enough oxygen and is doing well.
Nonreactive NST is wrong because it means that the fetal heart rate did not meet the criteria for a reactive NST.This could mean that the baby is not getting enough oxygen, is asleep, or has a problem with the nervous system.
Positive NST is wrong because it is not a term used to describe the results of a nonstress test.It is a term used to describe the results of a contraction stress test (CST), which is a different test that measures how the fetal heart rate responds to uterine contractions.
Negative NST is wrong because it is also not a term used to describe the results of a nonstress test.It is another term used to describe the results of a contraction stress test (CST), which means that the fetal heart rate did not show any signs of distress during contractions.
The normal range for fetal heart rate is 110 to 160 bpm, with moderate variability.
Variability refers to how much the heart rate changes from beat to beat.Moderate variability means that the heart rate changes by 6 to 25 bpm.Accelerations are brief increases in the heart rate that are usually caused by fetal movement.
Interpretation of results
A nurse is performing a nonstress test (NST) on a pregnant client at 38 weeks of gestation.
The nurse observes that the fetal heart rate (FHR) increases by 20 beats per minute (bpm) for 20 seconds, twice in a 10-minute period.
How should the nurse interpret this result?
Explanation
This means that the fetal heart rate (FHR) increases by at least 15 beats per minute (bpm) for at least 15 seconds, twice in a 10-minute period.This indicates that the baby is healthy and getting enough oxygen.
Nonreactive.
This means that the FHR does not show the expected accelerations in response to movement.This may indicate that the baby is not well or needs further testing.
Indeterminate.
This means that the FHR shows some accelerations, but not enough to be considered reactive.This may indicate that the baby is asleep or needs more time to show reactivity.
Abnormal.
This means that the FHR shows decelerations, which are drops in the heart rate below the baseline.This may indicate that the baby is in distress or has a problem with the umbilical cord or placenta.
A nurse is reviewing the electronic fetal monitoring (EFM) tracing of a client in active labor.
The nurse notes that the baseline FHR is 150 bpm, with moderate variability and no decelerations.
The nurse also observes that the FHR increases by 25 bpm for 15 seconds, four times in a 20-minute period.
What term is used to describe these FHR changes?
Explanation
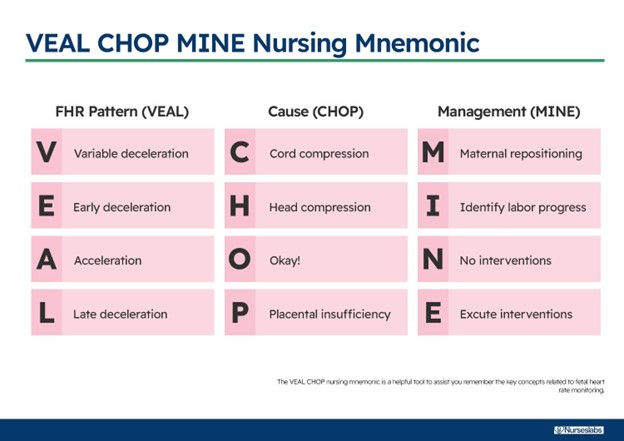
Accelerations.According to the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) terminology, accelerations are defined as transient increases in the FHR of at least 15 bpm above the baseline for at least 15 seconds.Accelerations are a reassuring sign of fetal well-being and oxygenation.
Early decelerations are decreases in the FHR that coincide with the onset and end of a uterine contraction.They are caused by fetal head compression and are usually benign.
Late decelerations are decreases in the FHR that begin after the peak of a uterine contraction and do not return to baseline until after the contraction ends.They are caused by uteroplacental insufficiency and are a sign of fetal hypoxia.
Variable decelerations are abrupt decreases in the FHR that vary in timing.
A nurse is caring for a client who is undergoing an oxytocin (pitocin) infusion for induction of labor.
The nurse notices that the FHR shows a pattern of late decelerations, which are decelerations that begin after the peak of the contraction and return to baseline after the contraction ends.
What is the most likely cause of these decelerations?
Explanation
Uteroplacental insufficiency.Late decelerations are decelerations that begin after the peak of the contraction and return to baseline after the contraction ends.They are caused by inadequate blood flow and oxygen delivery to the fetus through the placenta.This can be due to maternal hypotension, uterine hyperstimulation, placental abruption, or other factors.
Choice A is wrong because fetal head compression causes early decelerations, which are decelerations that begin and end with the contraction.
Choice B is wrong because umbilical cord compression causes variable decelerations, which are abrupt drops in the fetal heart rate that vary in shape and timing.
Choice D is wrong because maternal hypotension can cause uteroplacental insufficiency, but it is not the only cause.Also, maternal hypotension would affect the fetal heart rate baseline, not just the decelerations.
Normal ranges for fetal heart rate are 110 to 160 beats per minute for baseline and 15 beats per minute above or below baseline for variability.
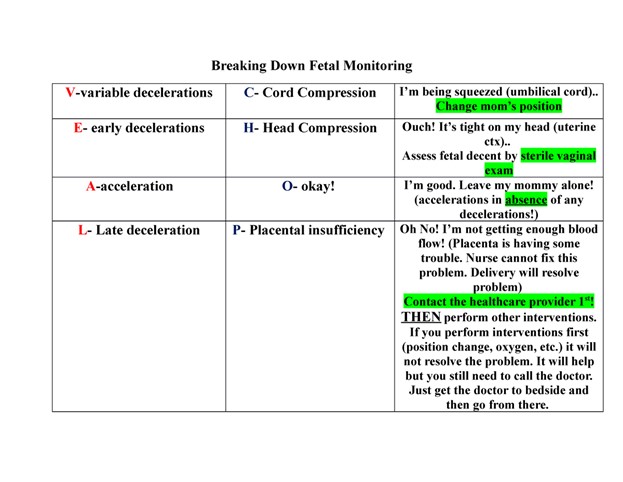
A nurse is assessing a client who is in labor and has meconium-stained amniotic fluid.
The nurse observes variable decelerations on the EFM tracing, which are decelerations that have an abrupt onset and vary in shape, duration, and degree of fall below the baseline FHR.
What is the most appropriate nursing intervention for this situation?
Explanation
Prepare for an amnioinfusion to dilute the meconium and relieve cord compression.
An amnioinfusion is a procedure in which sterile fluid is infused into the uterus through a catheter to increase the volume of amniotic fluid and reduce the risk of fetal distress caused by meconium aspiration or cord compression.
Variable decelerations are a sign of cord compression and can be alleviated by an amnioinfusion.
Choice A is wrong because repositioning the client may not be enough to improve placental blood flow and prevent fetal hypoxia.
Choice B is wrong because administering oxygen to the client may not be sufficient to increase fetal oxygenation if the cord is compressed.
Choice D is wrong because an emergency cesarean delivery may not be necessary if an amnioinfusion can resolve the variable decelerations and improve fetal well-being.
Nursing interventions and follow-up
A nurse is preparing to perform a nonstress test (NST) for a client who is at 36 weeks of gestation and reports decreased fetal movement.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
Explain the purpose, procedure, and possible outcomes of the test to the client.This is because the nurse should always obtain informed consent from the client before performing any procedure, and provide education and reassurance about the test.
Choice A is wrong because applying conduction gel to the client’s abdomen is not the first action the nurse should take.The nurse should first explain the test and obtain consent from the client before applying any equipment.
Choice B is wrong because instructing the client to press a button when she feels fetal movement is part of the nonstress test procedure, but not the first action.The nurse should first educate the client about the test and its purpose.
Choice D is wrong because activating a vibroacoustic stimulation device to wake up the fetus is not necessary for a nonstress test.This device may be used if the fetal heart rate is nonreactive, but only after explaining the test and obtaining consent from the client.
A nurse is reviewing the results of a nonstress test (NST) for a client who is at 32 weeks of gestation and has diabetes mellitus.
The nurse notes that the fetal heart rate (FHR) accelerates at least 10 beats/min for at least 10 seconds two or more times in a 30-minute period.
How should the nurse interpret this result?
Explanation
Reactive.This means that the fetal heart rate (FHR) accelerates at least 10 beats/min for at least 10 seconds two or more times in a 30-minute period.This result shows that the baby is getting enough oxygen and is doing well.
Nonreactive.
This means that the FHR does not accelerate as expected during the test.This result does not necessarily mean that there is a problem, but it may indicate that the baby is not getting enough oxygen or is asleep.
If this happens, more tests may be needed.
Unsatisfactory.This means that the test results are unclear or incomplete due to technical problems or poor quality of the recording.
If this happens, the test may need to be repeated.
Equivocal.This means that the test results are uncertain or inconclusive due to factors such as preterm gestation, fetal sleep, maternal medications, or fetal anomalies.
If this happens, more tests may be needed.
Normal ranges for FHR are between 110 and 160 beats/min at rest and between 120 and 180 beats/min during movement.
A nurse is performing a nonstress test (NST) for a client who is at 28 weeks of gestation and has intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).
The nurse observes that the fetal heart rate (FHR) does not accelerate with fetal movement after 20 minutes of monitoring.
Which of the following tests should the nurse anticipate to be ordered next for this client? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Abiophysical profile (BPP)is a test that combines a nonstress test with an ultrasound to assess fetal well-being.Aumbilical artery Doppler velocimetryis a test that measures the blood flow in the umbilical cord to detect fetal growth restriction.Both of these tests are indicated for a client who has a nonreactive nonstress test (NST), which means that the fetal heart rate does not accelerate with fetal movement after 20 minutes of monitoring.
Choice B is wrong because acontraction stress test (CST)is a test that stimulates uterine contractions to evaluate how the fetal heart rate responds to stress.It is not recommended for clients who have intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) because it can compromise fetal oxygenation.
Choice D is wrong because anamniocentesisis a test that obtains amniotic fluid for genetic testing, fetal lung maturity, or infection.It is not used to assess fetal well-being or growth.
Choice E is wrong because afetal kick countis a method of monitoring fetal movement at home by counting how many times the fetus kicks in a certain period of time.It is not a test that can be ordered by a health care provider.
A nurse is caring for a client who is at 34 weeks of gestation and has systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
The provider orders a nonstress test (NST) twice a week for this client.
Which of the following statements by the nurse is appropriate when educating the client about this test?
Explanation
“This test will evaluate your baby’s well-being by monitoring his or her movements.”
A nonstress test (NST) is a simple, noninvasive way of checking on your baby’s health.The test records your baby’s movement, heartbeat, and reaction to movement.It is done after 26 to 28 weeks of pregnancyto check the health and oxygen supply of the fetus.It is safe, painless, and non-invasive, and can be performed in a doctor’s office or a hospital.It usually takes 40 to 60 minutes.
Choice A is wrong because this test will not measure the amount of amniotic fluid around your baby.That is done by another test called an amniotic fluid index (AFI).
Choice B is wrong because this test will not check if your baby has any chromosomal abnormalities.That is done by other tests such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Choice C is wrong because this test will not assess how your baby’s heart rate responds to contractions.That is done by another test called a contraction stress test (CST).

A nurse is conducting a nipple-stimulated contraction stress test (CST) for a client who had a nonreactive nonstress test (NST).
Which of the following instructions should the nurse give to the client for this test?
Explanation
The nurse should instruct the client to brush her nipple with her palm for 2 minutes.
This will stimulate the release of oxytocin and cause uterine contractions.The fetal heart rate (FHR) will be monitored for any signs of fetal distress, such as decelerations.
Choice A is wrong because fasting is not required for a CST.Fasting may be necessary for other tests that involve anesthesia or sedation.
Choice B is wrong because drinking orange juice will not induce contractions.Orange juice may be given to increase fetal activity before a nonstress test (NST), which measures the FHR response to fetal movement.
Choice D is wrong because lying on the back can compress the inferior vena cava and reduce blood flow to the uterus and the fetus.The client should lie on her side during the test to prevent supine hypotension syndrome.
Normal ranges for FHR are 110 to 160 beats per minute, with moderate variability and no decelerations.Normal ranges for uterine contractions are less than five in a 10-minute period, lasting less than 90 seconds each.
Comparison with contraction stress test (CST)
A nurse is caring for a client who is undergoing a contraction stress test (CST).
The nurse observes late decelerations in the fetal heart rate (FHR) during three consecutive contractions.
How should the nurse interpret this result?
Explanation
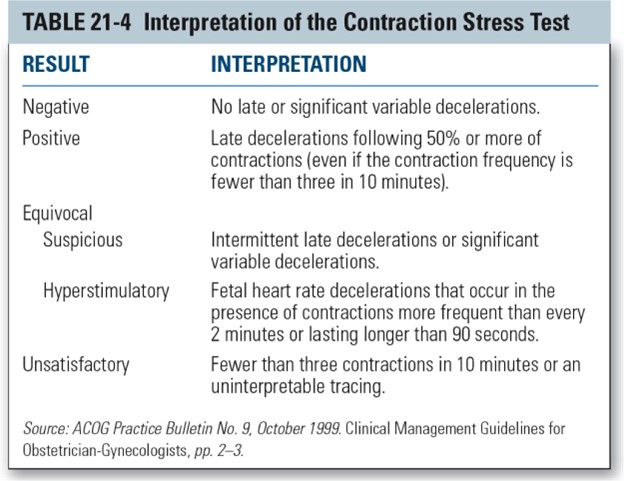
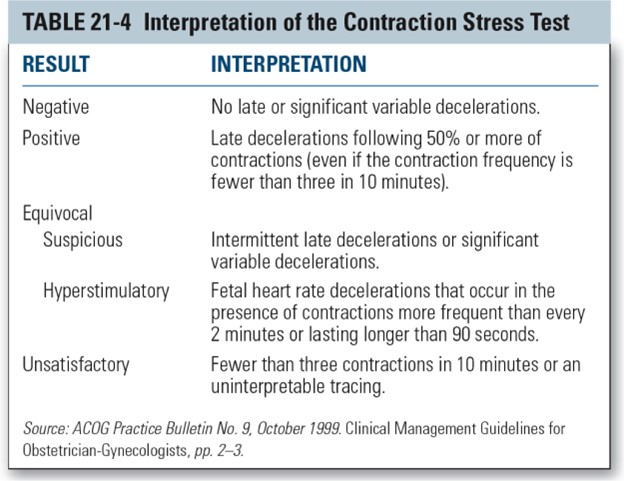
Positive.A positive CST means that there are late decelerations in the FHR during three or more contractions in a 10-minute period.Late decelerations are defined as decelerations that reach their lowest point after the peak of the contraction and that usually persist beyond the end of the contraction.They indicate fetal hypoxia and placental insufficiency.
Negative.A negative CST means that there are no late decelerations in the FHR during at least three contractions in a 10-minute period.A negative CST is reassuring and suggests that the fetus can tolerate labor contractions.
Equivocal.An equivocal CST means that there are late decelerations in the FHR during fewer than half of the contractions or there are variable decelerations with or without other nonreassuring features.An equivocal CST requires further evaluation with a biophysical profile or a repeat CST.
Unsatisfactory.An unsatisfactory CST means that there are fewer than three contractions in a 10-minute period or the tracing is technically inadequate for interpretation.An unsatisfactory CST should be repeated when possible.

A nurse is preparing a client for a nonstress test (NST).
The nurse explains that this test will measure the FHR response to:
Explanation
Fetal movement.This is because a nonstress test (NST) measures the fetal heart rate (FHR) accelerations in response to fetal movement in a defined period of time.A reactive NST is when there are two or more FHR accelerations of at least 15 beats per minute for at least 15 seconds duration in a 20-minute period.
Choice A is wrong because uterine contractions are not the stimulus for FHR accelerations in a NST.Uterine contractions are used in a contraction stress test (CST), which measures the FHR response to uterine contractions induced by oxytocin or nipple stimulation.
Choice C is wrong because oxytocin infusion is not used in a NST.Oxytocin infusion is another way of inducing uterine contractions for a CST.
Choice D is wrong because nipple stimulation is not used in a NST.Nipple stimulation is a natural way of inducing uterine contractions for a CST by releasing endogenous oxytocin.

A nurse is reviewing the results of a nonstress test (NST) for a client at 38 weeks of gestation.
The nurse notes that the baseline FHR is 140 bpm with moderate variability and no decelerations.
There are two episodes of FHR accelerations of at least 15 bpm above the baseline and lasting at least 15 seconds within a 20-minute period.
How should the nurse classify this result?
Explanation
Reactive.This result means that the baby’s heart rate went up to the expected level at least twice during the test, indicating that the baby is getting enough oxygen and is doing well.A nonstress test is a safe, noninvasive test for pregnant women that measures the fetal heart rate as the baby moves in the uterus.
Nonreactive.
This result means that the baby’s heart rate did not go up to the expected level during the test, which may indicate that the baby is not getting enough oxygen or is sleeping.This result does not necessarily mean there is a problem, but it may require further testing or treatment.
Suspicious.
This result is not a standard term for nonstress test interpretation, but it may be used to describe a test that shows some signs of fetal distress, such as decelerations or reduced variability of the fetal heart rate.This result may also require further testing or treatment.
Inconclusive.
This result means that the test did not provide enough information to determine the fetal well-being, either because the baby did not move enough or because of technical problems with the equipment.This result may require repeating the test or using another method of fetal assessment.
A nurse is comparing the advantages and disadvantages of external and internal fetal heart rate (FHR) monitoring.
Which of the following statements is true about external FHR monitoring?
Explanation
It can be used for both antepartum and intrapartum fetal assessment.External fetal heart rate monitoring uses a device to listen to or record the baby’s heartbeat through the mother’s abdomen.It does not require ruptured membranes or cervical dilation for application, unlike internal monitoring.It also does not provide a more accurate and continuous FHR tracing than internal monitoring, nor can it measure the intensity of uterine contractions.
Choice A is wrong because external monitoring is less accurate and consistent than internal monitoring, especially when there is movement or interference.
Choice B is wrong because external monitoring can be done without ruptured membranes or cervical dilation, while internal monitoring requires both.
Choice D is wrong because external monitoring can only measure the frequency and duration of uterine contractions, not the intensity.Internal monitoring can measure the intensity of uterine contractions with a fluid-filled catheter.
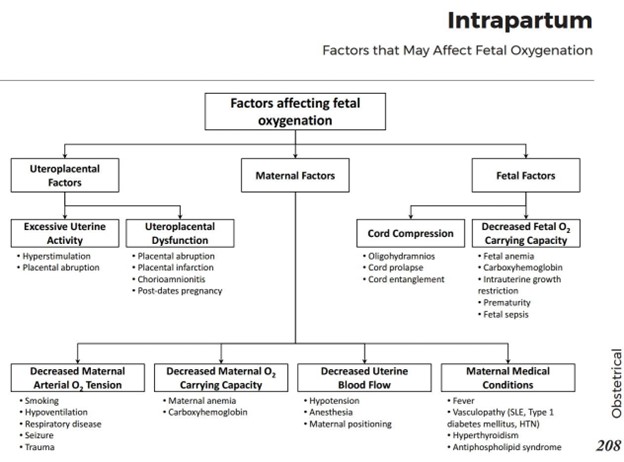
(Select all that apply) A nurse is educating a client about the factors that can affect fetal oxygenation during labor.
The nurse should include which of the following factors in the teaching?
Explanation
These are the factors that can affect fetal oxygenation during labor by decreasing the placental blood flow or the fetal oxygen carrying capacity.
• Choice A is correct because maternal hypotension can reduce the uterine blood flow and cause fetal hypoxia.
• Choice B is correct because maternal fever can increase the maternal and fetal metabolic rate and oxygen demand, as well as cause uteroplacental dysfunction due to chorioamnionitis.
• Choice C is correct because umbilical cord compression can impair the fetal blood flow and oxygen delivery.
• Choice D is wrong because fetal sleep cycles do not affect fetal oxygenation during labor.Fetal sleep cycles are normal variations in the fetal heart rate and variability.
• Choice E is wrong because fetal position does not affect fetal oxygenation during labor.Fetal position may affect the mode of delivery, but not the oxygen supply to the fetus.
Advantages and limitations of NST
A nurse is preparing to perform a nonstress test (NST) for a pregnant client at 36 weeks of gestation.
What is the primary purpose of this test?
Explanation
To assess fetal oxygenation.The primary purpose of a nonstress test (NST) is to check the baby’s heart rate before birth and see how it responds to movement and contractions.The test can help determine if the baby is healthy and has enough oxygen.The test is usually done in the third trimester of pregnancy, especially if there are any risk factors or concerns.The test is simple and noninvasive.
Choice B is wrong because measuring fetal growth is not the main goal of an NST.
Fetal growth can be assessed by other methods, such as ultrasound or fundal height measurement.
Choice C is wrong because evaluating fetal anomalies is not the main goal of an NST.
Fetal anomalies can be detected by other tests, such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling.
Choice D is wrong because monitoring fetal activity is not the main goal of an NST.
Fetal activity can be monitored by other ways, such as counting kicks or using a handheld Doppler device.
A nurse is reviewing the results of a nonstress test (NST) for a pregnant client at 34 weeks of gestation.
The nurse notes that the fetal heart rate (FHR) increased by at least 15 beats per minute (BPM) above the baseline for 15 seconds on two occasions within a 20-minute period.
How should the nurse interpret this finding?
Explanation
Reactive or reassuring.
This means that the fetal heart rate (FHR) increased by at least 15 beats per minute (BPM) above the baseline for 15 seconds on two occasions within a 20-minute period.This is a normal response that indicates that the baby is well oxygenated and not in distress.
Nonreactive or nonreassuring is wrong because this means that the FHR did not increase by at least 15 BPM above the baseline for 15 seconds on two occasions within a 40-minute period.This could indicate that the baby is not getting enough oxygen or has a problem with the nervous system.
Indeterminate or equivocal is wrong because this means that the FHR showed some variability but did not meet the criteria for a reactive or nonreactive test.This could be due to factors such as fetal sleep, medications, or maternal smoking.
Unsatisfactory or invalid is wrong because this means that the FHR was not recorded properly or there were too many contractions to interpret the test.This could be due to technical problems, maternal obesity, or fetal position.
Normal ranges for FHR are between 110 and 160 BPM at rest and between 120 and 180 BPM during movement.
A nurse is performing a nonstress test (NST) for a pregnant client at 32 weeks of gestation.
The nurse observes that the fetal heart rate (FHR) does not increase with fetal movement.
What factors could contribute to this result? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Maternal medications and technical errors can contribute to a nonreactive nonstress test (NST), which means that the fetal heart rate (FHR) does not increase with fetal movement.Some medications, such as narcotics, antihypertensives, and magnesium sulfate, can affect the FHR and its variability.Technical errors, such as poor transducer placement or loose belts, can also interfere with the accuracy of the NST.
Choice B is wrong because a fetal sleep cycle usually lasts 20 to 40 minutes, and the NST can be extended or repeated if the FHR is not reactive within 20 minutes.
Choice C is wrong because maternal obesity does not affect the FHR or its reactivity, but it may make it harder to obtain a clear signal from the transducer.
Choice D is wrong because fetal breathing movements are a sign of fetal well-being and do not cause a nonreactive NST.
A normal NST will show a baseline FHR between 110 and 160 beats per minute with moderate variability (5 to 25 interbeat variability) and two qualifying accelerations in 20 minutes with no decelerations.An acceleration is defined as an increase in the FHR of at least 15 beats per minute for at least 15 seconds.
A nurse is caring for a pregnant client who has a nonreactive or nonreassuring result on a nonstress test (NST).
The healthcare provider orders a biophysical profile (BPP) to further assess fetal well-being.
What components are included in a BPP? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
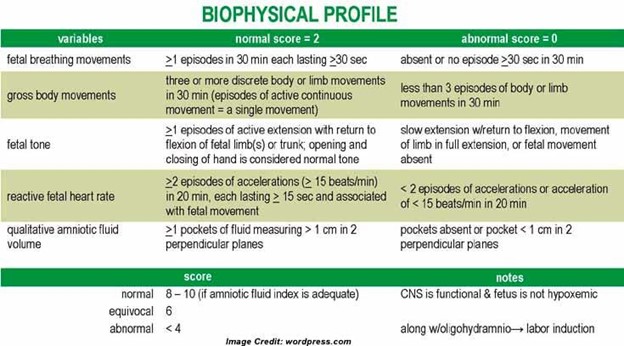
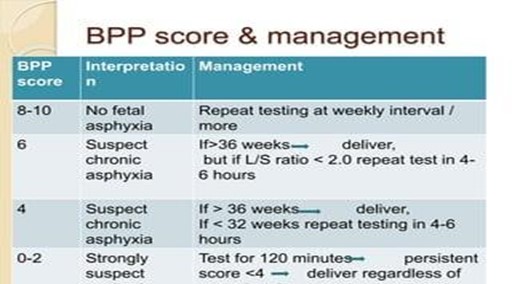
A biophysical profile (BPP) is a prenatal test that evaluates the well-being of the fetus by combining an ultrasound examination with a nonstress test.The test assesses five components: fetal heart rate, breathing, movement, tone, and amniotic fluid volume.Each component is scored as 2 (normal) or 0 (abnormal), and a total score of 8 or 10 is normal, 6 is equivocal, and 4 or less is abnormal.
Choice C is wrong because fetal heart rate is not part of the ultrasound assessment, but rather the nonstress test.The nonstress test evaluates fetal heart rate and response to fetal movement.
Normal ranges for each component are as follows:
• Fetal heart rate: At least two accelerations in 20 minutes
• Fetal breathing: At least one episode of > 30s or >20sin 30 minutes
• Fetal movement: At least three discrete body/limb movement in 30 minutes
• Fetal tone: At least one episode of active extension with return to flexion of fetal limb(s) or trunk, opening and closing of hand considered to be normal tone
• Amniotic fluid volume: At least one vertical pocket > 2 cm in the vertical axis or AFI of 5 cm
A nurse is teaching a pregnant client about the advantages and limitations of nonstress test (NST).
Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
The test can tell me if my baby has any birth defects.
This statement indicates a need for further teaching because a nonstress test (NST) does not detect birth defects.An NST is a prenatal test that measures the fetal heart rate and movement to assess the health and oxygen supply of the fetus.It is usually done for high-risk pregnancies or when there are concerns about fetal well-being.
Choice A is correct because an NST is safe and simple for both the pregnant person and the fetus.It is a noninvasive test that does not pose any physical risks or stress.
Choice B is correct because an NST is inexpensive and widely available.It is a common test that can be done in most healthcare settings with minimal equipment.
Choice D is correct because an NST can be repeated as often as needed without any harm.It can be done at certain intervals or during delivery depending on the situation.
More questions
A nurse is caring for a client who is pregnant and undergoing a contraction stress test (CST).
The nurse observes three uterine contractions in 10 minutes, with no late or significant variable decelerations of the fetal heart rate (FHR).
How should the nurse interpret this finding?
Explanation
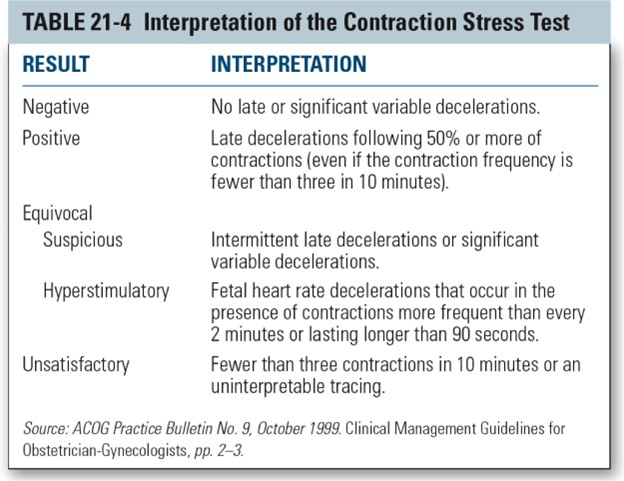
Negative CST.A negative CST means that there are no late or significant variable decelerations of the fetal heart rate (FHR) during three uterine contractions in 10 minutes.
This indicates that the fetus is well oxygenated and can tolerate the stress of labor contractions.
Choice A is wrong because a positive CST means that there are late decelerations of the FHR with 50% or more of the contractions.
This suggests that the fetus is at risk of hypoxia and may need early delivery.
Choice C is wrong because an unsatisfactory CST means that there are fewer than three contractions in 10 minutes or the tracing is not interpretable.
This does not provide enough information to assess the fetal well-being.
Choice D is wrong because an equivocal CST means that there are either intermittent late decelerations or significant variable decelerations.
This indicates that the fetus may have some degree of compromise and may need further testing.
Normal ranges for FHR are 110 to 160 beats per minute, and for uterine contractions are 2 to 5 per 10 minutes.
A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for an amniocentesis at 35 weeks of gestation to assess fetal lung maturity.
Which of the following laboratory tests will provide this information?
Explanation
Lecithin/sphingomyelin (L/S) ratio.
This is a test that measures the amount of two phospholipids in the amniotic fluid that are important for the production of surfactant, a substance that helps the lungs expand and prevents them from collapsing.A higher L/S ratio indicates more surfactant and greater fetal lung maturity.The normal range for L/S ratio is 2:1 or higher at term.
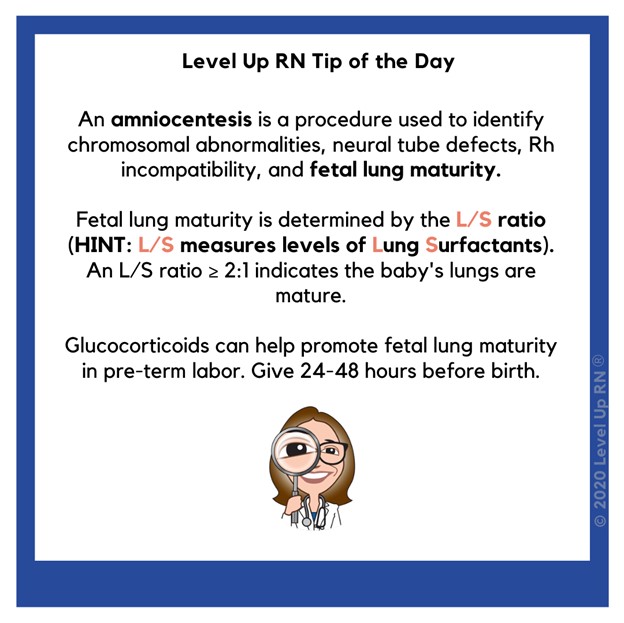
Choice A is wrong because alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a protein produced by the fetus that can be measured in the amniotic fluid or maternal blood.It is used to screen for neural tube defects and other abnormalities, not for fetal lung maturity.
Choice C is wrong because Kleihauer-Betke test is a blood test that detects fetal red blood cells in the maternal circulation.It is used to diagnose fetomaternal hemorrhage, a condition where fetal blood leaks into the mother’s blood, not for fetal lung maturity.
Choice D is wrong because indirect Coombs’ test is a blood test that detects antibodies in the mother’s blood that may attack the fetal red blood cells.It is used to screen for Rh incompatibility or other blood group sensitization, not for fetal lung maturity.
A nurse is reviewing the findings of a biophysical profile (BPP) for a client who is at 40 weeks of gestation.
The BPP score is 6 out of 10 points.
Which of the following components are included in this score? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A, B, C and D.These are the four components of a biophysical profile (BPP) that are scored as 2 (normal) or 0 (abnormal) based on ultrasound examination.The fifth component is the nonstress test (NST) that measures the fetal heart rate reactivity.A total score of 8 or 10 is normal, 6 is equivocal, and 4 or less is abnormal.
Choice E is wrong because fetal position is not a part of the BPP score.Fetal position is determined by ultrasound but it does not affect the score.
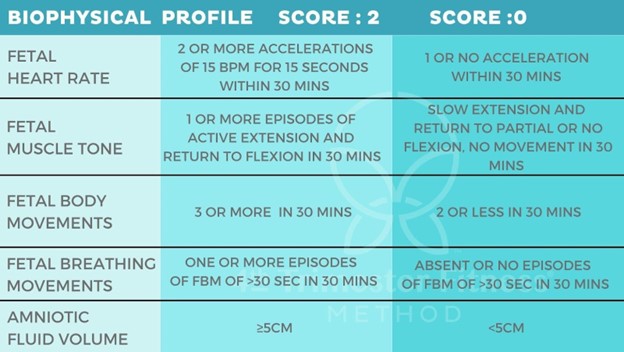
Normal ranges for each component are:
• Fetal breathing movement: One or more episodes of fetal breathing lasting at least 30 seconds within 30 minutes.
• Fetal tone: One or more episodes of active extension and flexion of a fetal extremity or opening and closing of the hand within 30 minutes.
• Reactive fetal heart rate: Two or more fetal heart rate accelerations that peak at least 15 beats per minute above the baseline and last at least 15 seconds from baseline to baseline during 20 minutes of observation.
• Amniotic fluid volume: A single deepest vertical pocket of amniotic fluid that measures at least 2 centimeters.
• Gross body movement: Three or more discrete body or limb movements within 30 minutes.
A nurse is caring for a client who is undergoing an external nonstress test at 40 weeks of gestation and notes variable decelerations on the fetal monitor tracing that are unresponsive to interventions such as repositioning and oxygen administration.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take next?
Explanation
Prepare the client for an amnioinfusion.An amnioinfusion is a procedure that adds fluid to the uterus during labor to relieve cord compression and improve fetal condition.Variable decelerations on the fetal monitor tracing are a sign of cord compression and fetal distress.If repositioning and oxygen administration do not resolve the decelerations, an amnioinfusion may be indicated.
Choice B is wrong because applying an internal fetal scalp electrode does not address the cause of variable decelerations, which is cord compression.
An internal fetal scalp electrode is used to monitor the fetal heart rate more accurately, but it does not improve fetal oxygenation or prevent cord compression.
Choice C is wrong because administering IV fluid bolus to the client may help increase maternal blood volume and placental perfusion, but it does not directly increase amniotic fluid volume or relieve cord compression.
Choice D is wrong because discontinuing oxytocin infusion if present may reduce uterine contractions and decrease cord compression, but it may also prolong labor and increase the risk of infection or fetal compromise.Oxytocin infusion should only be discontinued if there are signs of uterine hyperstimulation or fetal intolerance.
A nurse is performing an external nonstress test for a client who is at 41 weeks of gestation and has oligohydramnios.
The nurse notes that there are no accelerations in the fetal heart rate tracing after applying an acoustic stimulator to the maternal abdomen for several seconds.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Notify the provider and prepare for delivery.Oligohydramnios is a condition where the amniotic fluid volume is less than expected for gestational age and it is associated with maternal and fetal complications.
The nonstress test (NST) is a method of fetal surveillance that measures the fetal heart rate response to fetal movement.A reactive NST is defined as at least two accelerations of 15 beats per minute or more above the baseline, lasting 15 seconds or more, within a 20-minute period.
A nonreactive NST indicates fetal hypoxia or acidosis and requires further evaluation.An acoustic stimulator can be used to elicit fetal movement and accelerations, but it should not be repeated more than once in a 10-minute period.
Therefore, choice A is wrong because repeating the acoustic stimulation after 1 minute is too soon and may cause fetal distress.
Choice B is wrong because documenting the finding as a nonreactive NST is not enough to address the situation.Choice C is wrong because performing a contraction stress test (CST) is contraindicated in oligohydramnios because it may cause umbilical cord compression and fetal compromise.
The CST involves inducing uterine contractions with oxytocin or nipple stimulation and monitoring the fetal heart rate for signs of intolerance.
A negative CST means that there
A nurse is interpreting the results of a contraction stress test (CST) for a client who is at 38 weeks of gestation.
The nurse notes that there are no late or significant variable decelerations of the fetal heart rate (FHR).
How should the nurse document this finding?
Explanation
Negative CST.A negative CST means that the fetal heart rate does not slow down (decelerate) after a contraction, which indicates that the baby can tolerate the stress of labor.
This is a normal and reassuring result.
Choice A is wrong because a positive CST means that the fetal heart rate slows down and stays slow after more than half of the contractions, which indicates that the baby may be at risk for problems during labor.
This is an abnormal and concerning result.
Choice C is wrong because an unsatisfactory CST means that there are not enough contractions to produce a reliable result.
This may happen if the medication or nipple stimulation does not induce enough contractions, or if there are other factors that interfere with the test, such as maternal movement or fetal sleep.
Choice D is wrong because a suspicious CST means that the results are unclear or inconsistent.This may happen if the fetal heart rate slows down after some but not all of the contractions, or if there are other types of decelerations that are not clearly related to the contractions.
A suspicious CST may need to be repeated in a couple of days.
A nurse is caring for a client who is undergoing an oxytocin-stimulated contraction stress test (CST).
The nurse observes three contractions in 10 minutes with no late decelerations of the fetal heart rate (FHR).
Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Maintain oxytocin infusion and monitor the client until a negative CST result is confirmed.
A negative CST result means that there are no late decelerations of the FHR after three contractions in 10 minutes.This indicates that the fetus can tolerate the stress of labor and has adequate oxygenation.
Choice A is wrong because discontinuing oxytocin infusion and monitoring the client for another 10 minutes will not provide enough information about the fetal response to contractions.The test requires at least three contractions in 10 minutes to be valid.
Choice B is wrong because increasing oxytocin infusion and monitoring the client until four contractions occur in 10 minutes may cause uterine hyperstimulation, which can compromise fetal oxygenation and lead to fetal distress.
Choice C is wrong because stopping oxytocin infusion and notifying the provider of a positive CST result is not appropriate.A positive CST result means that there are late decelerations of the FHR after more than half of the contractions, indicating fetal hypoxia and placental insufficiency.
In this case, there are no late decelerations, so the test result is not positive.
A nurse is providing discharge instructions to a client who had a nonreactive nonstress test (NST) followed by a biophysical profile (BPP) with a score of 8/10.
Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
The client should count the baby’s kicks every day to monitor fetal well-being.A nonreactive nonstress test (NST) indicates that the fetal heart rate did not increase adequately with fetal movement, which may suggest fetal hypoxia or distress.A biophysical profile (BPP) is a combination of NST and ultrasound that assesses five parameters: fetal breathing, movement, tone, amniotic fluid volume, and NST.
Each parameter is scored 0 or 2, and the total score ranges from 0 to 10.A score of 8/10 or 10/10 is considered normal, while a score of 6/10 is equivocal and ≤ 4/10 is abnormal.A BPP score of 8/10 with a nonreactive NST means that the fetus has normal biophysical activities but may have chronic hypoxia.
Choice A is wrong because the client does not need to have another BPP in a week unless there are other indications of fetal compromise.The BPP may be repeated once or twice a week depending on the clinical situation.
Choice C is wrong because the client does not need to have an amniocentesis as soon as possible.
Amniocentesis is an invasive procedure that involves inserting a needle into the uterus to obtain amniotic fluid for analysis.It is usually done for prenatal diagnosis of genetic disorders or fetal lung maturity, not for fetal well-being.
Choice D is wrong because the client does not need to deliver the baby by cesarean section.Cesarean section is a surgical delivery that may be indicated for various maternal or fetal conditions, such as placenta previa, breech presentation, fetal distress, or failure to progress in labor.A BPP score of 8/10 with a nonreactive NST does not warrant a cesarean section unless there are other risk factors or complications.
A nurse is caring for a client in labor who has an internal fetal scalp electrode applied for continuous fetal heart rate (FHR) monitoring.
The nurse notes a pattern of late decelerations on the FHR tracing.
What is the priority nursing intervention?
Explanation
Notify the health care provider.Late decelerations are a sign of uteroplacental insufficiency, which means that the blood flow and oxygen supply to the placenta and the fetus are compromised.This is a serious condition that can lead to fetal hypoxia and acidosis.The priority nursing intervention is to inform the health care provider who can assess the situation and decide on the appropriate course of action, such as delivery by cesarean section.
Choice A is wrong because changing the client’s position may not improve the blood flow to the placenta if there is a problem with the placenta itself, such as placental abruption.
Choice B is wrong because administering oxygen via face mask may not be enough to correct the fetal hypoxia caused by uteroplacental insufficiency.
Choice C is wrong because increasing intravenous fluid rate may not improve the blood flow to the placenta if there is a problem with the maternal blood pressure, such as hypotension from epidural analgesia.
A nurse is assessing a fetal heart rate (FHR) tracing for a client who is in active labor.
The nurse notes that the baseline FHR is 150 bpm with absent variability and recurrent variable decelerations with slow return to baseline.
What category of FHR tracing does this represent?
Explanation
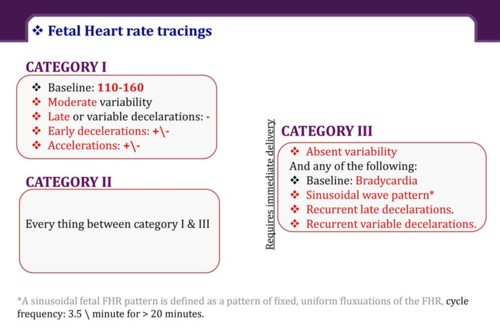
Category III.This category of FHR tracing represents an abnormal pattern that is predictive of fetal acidemia and requires prompt evaluation and intervention.A category III pattern is defined by any of the following criteria:
• Absent baseline FHR variability and any of the following:
➤ Recurrent late decelerations
➤ Recurrent variable decelerations
➤ Bradycardia
• Sinusoidal pattern
Choice A is wrong because category I is a normal pattern that is predictive of normal fetal acid-base balance at the time of observation.A category I pattern is defined by all of the following criteria:
• Baseline rate of 110 to 160 bpm
• Moderate baseline FHR variability
• No late or variable decelerations
• Early decelerations may be present or absent
• Accelerations may be present or absent
Choice B is wrong because category II is an indeterminate pattern that is not predictive of abnormal fetal acid-base balance but requires continued surveillance and reevaluation.A category II pattern includes all FHR tracings that are not category I or III.
Choice D is wrong because there is no category IV in the NICHD classification system for FHR tracings.
(Select all that apply) A nurse is performing a nonstress test (NST) for a client who is at 32 weeks of gestation and has gestational diabetes mellitus.
The nurse uses vibroacoustic stimulation to elicit fetal movement and acceleration of FHR.
What are the indications for using this method?
Explanation
The test result is nonreactive after 40 minutes.Vibroacoustic stimulation (VAS) is the application of a vibratory sound stimulus to the abdomen of a pregnant woman to induce fetal heart rate (FHR) accelerations.VAS is typically used during a nonstress test (NST) to elicit fetal movement and reactivity when the baseline FHR variability is minimal or the test result is nonreactive after 40 minutes.VAS can shorten the testing time and reduce the incidence of non-reactive cardiotocography.
Choice A is wrong because the fetus’s presentation does not affect the use of VAS.
Choice B is wrong because VAS is not indicated for a fetus that has not moved for 40 minutes, unless the NST result is also nonreactive.
Choice C is wrong because minimal baseline FHR variability is not a sufficient indication for VAS, unless the NST result is also nonreactive.
Choice D is wrong because a history of stillbirth does not affect the use of VAS.
A nurse is using vibroacoustic stimulation (VAS) to stimulate fetal movement during a nonstress test (NST).
What action should the nurse take when applying VAS?
Explanation
Place the device over the fetal back for 3 seconds.This is because vibroacoustic stimulation (VAS) is the application of a vibratory sound stimulus to the abdomen of a pregnant woman to induce fetal heart rate (FHR) accelerations.The presence of FHR accelerations reliably predicts the absence of fetal metabolic acidemia.VAS is typically used during a nonstress test (NST) to assess fetal well-being.The device should be placed over the fetal back for 3 seconds, as this is the optimal duration and location to elicit a fetal response.
Choice B is wrong because holding the device firmly against the maternal abdomen for 10 seconds may be too long and too strong for the fetus, and may cause discomfort or distress.
Choice C is wrong because moving the device around the maternal abdomen until fetal movement is detected may not be effective or efficient, as the device may not reach the optimal location or duration to stimulate the fetus.
Choice D is wrong because applying the device intermittently over the fundus for 15 seconds may not target the fetal auditory system, which is located near the fetal back, and may also be too long and too strong for the fetus.
Normal ranges for FHR are between 110 and 160 beats per minute, and FHR accelerations are defined as an increase of at least 15 beats per minute above baseline for at least 15 seconds.
A nurse is evaluating the results of a contraction stress test (CST) for a pregnant client who had a nonreactive or nonreassuring result on a nonstress test (NST).
The nurse notes that there are no late decelerations of the fetal heart rate (FHR) after three contractions in a 10-minute period.
How should the nurse interpret this finding?
Explanation
Negative or normal.This means that there are no late decelerations of the fetal heart rate (FHR) after three contractions in a 10-minute period, which indicates that the baby can tolerate the stress of labor contractions.
Choice A is wrong because positive or abnormal results mean that there are late decelerations of the FHR after three contractions in a 10-minute period, which suggests that the baby may be at risk of hypoxia or injury during labor.
Choice C is wrong because equivocal or suspicious results mean that there are either variable decelerations or late decelerations after fewer than half of the contractions, which require further testing or monitoring.
Choice D is wrong because unsatisfactory or incomplete results mean that there are either fewer than three contractions in a 10-minute period or poor quality of the FHR tracing, which prevent an accurate interpretation of the test.

A nurse is comparing nonstress test (NST) and contraction stress test (CST) for assessing fetal well-being.
What is an advantage of NST over CST?
Explanation
NST is less time-consuming and more comfortable than CST.This is because NST does not require any external stimulation of the uterus, while CST involves giving oxytocin to induce contractions.NST also does not pose any risk of preterm labor or fetal distress, which are possible complications of CST.
Choice A is wrong because NST does not provide more information about fetal status than CST.In fact, CST can detect fetal hypoxia more accurately than NST.
Choice C is wrong because NST does not have fewer contraindications than CST.Both tests have similar contraindications, such as placenta previa, multiple gestation, and previous cesarean section.
Choice D is wrong because NST does not have higher sensitivity and specificity than CST.
Sensitivity refers to the ability of a test to correctly identify positive cases, while specificity refers to the ability of a test to correctly identify negative cases.
NST has a high sensitivity but a low specificity, meaning it can detect most fetuses with hypoxia but also has many false positives.CST has a low sensitivity but a high specificity, meaning it can miss some fetuses with hypoxia but also has few false negatives.
Introduction
A nurse is caring for a client who is undergoing a fetal non-stress test (NST).
The nurse observes that the fetal heart rate (FHR) accelerates at least 10 bpm for at least 10 seconds with each fetal movement.
The client is 30 weeks pregnant.
How should the nurse interpret this finding?
Explanation
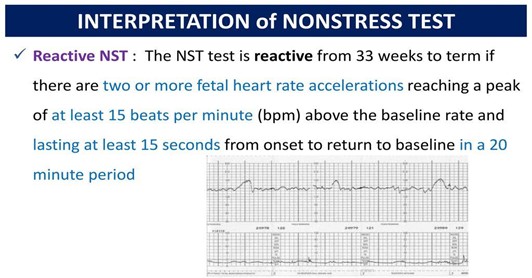
The NST is reactive and normal for gestational age.This means that the fetal heart rate (FHR) accelerates at least 10 bpm for at least 10 seconds with each fetal movement, indicating that the fetus is healthy and getting enough oxygen.A reactive NST is expected for fetuses at 26 to 30 weeks of gestation.
Choice B is wrong because a nonreactive NST means that the FHR does not accelerate with fetal movement, which could indicate fetal distress or hypoxia.A nonreactive NST is abnormal for any gestational age and requires further evaluation.
Choice C is wrong because a reactive NST is not abnormal for gestational age.It is a normal finding that shows the fetus is well-oxygenated and responsive.
Choice D is wrong because a nonreactive NST is not normal for gestational age.It is an abnormal finding that suggests the fetus may be compromised or in need of intervention.
A nurse is preparing a client for a fetal non-stress test (NST).
Which of the following instructions should the nurse give to the client?
Explanation
“You will need to press a button when you feel the baby move.” This is because a non-stress test (NST) is a pregnancy screening that measures fetal heart rate and reaction to movement.The test is performed to make sure the fetus is healthy and getting enough oxygen.By pressing a button when the baby moves, the patient can help the provider record the changes in the fetal heart rate.
Choice A is wrong because the patient does not need to fast for 8 hours before the test.There is no dietary restriction for an NST.
Choice B is wrong because the patient does not need to drink plenty of fluids before the test.However, drinking some fluids may help stimulate fetal movement.
Choice C is wrong because the patient does not need to lie on their back during the test.In fact, lying on the back can compress the blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the fetus.The patient can lie on their side or recline on a chair or exam table.
A nurse is reviewing the results of a fetal non-stress test (NST) for a client who is at 32 weeks of gestation.
The nurse notes that there are no accelerations of the fetal heart rate (FHR) during the 20-minute test.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take next? (Select all that apply.).
Explanation
Perform a biophysical profile (BPP).A BPP is a test that combines a non-stress test (NST) with an ultrasound to evaluate the fetal well-being.A BPP is indicated when an NST is non-reactive, meaning that there are no accelerations of the fetal heart rate (FHR) with fetal movements.A BPP measures five parameters: fetal movement, fetal tone, fetal breathing, amniotic fluid volume and FHR reactivity.
A BPP can help detect fetal hypoxemia or distress and guide further management.
Choice A is wrong because repeating the NST after 24 hours may delay the diagnosis and treatment of fetal compromise.A non-reactive NST requires further evaluation with a BPP or a contraction stress test (CST).
Choice B is wrong because performing a CST may not be safe for a fetus with a non-reactive NST.
A CST involves inducing uterine contractions with oxytocin or nipple stimulation and monitoring the FHR response.A CST can cause fetal distress or placental abruption if the fetus is already hypoxic.
Choice D is wrong because applying an acoustic vibration device to the abdomen may not elicit FHR accelerations if the fetus is hypoxic or asleep.An acoustic stimulation test (AST) is sometimes used to augment an NST, but it is not a substitute for a BPP.
Choice E is wrong because administering oxygen via face mask to the client may not improve the FHR reactivity if the cause of fetal compromise is not maternal hypoxia.Oxygen administration may also have adverse effects on maternal and fetal hemodynamics.
A nurse is teaching a client about the advantages and disadvantages of a fetal non-stress test (NST).
Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
“The NST can be affected by my smoking or medication use.” This statement indicates an understanding of the teaching because smoking and medication use can alter the fetal heart rate response and cause false-negative or false-positive results.
Some possible explanations for the other choices are:
• Choice A is wrong because the NST cannot detect chromosomal abnormalities in the baby.
The NST only measures the fetal heart rate and movement, not the genetic makeup of the baby.To detect chromosomal abnormalities, other tests such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling are needed.
• Choice B is wrong because the NST does not cause contractions or discomfort for the mother or the baby.The NST is a non-invasive and painless procedure that does not put any stress on the fetus.The only discomfort that may occur is from having a belt around the abdomen and a button to press when feeling fetal movement.
• Choice D is wrong because the NST cannot measure the amount of amniotic fluid around the baby.
The NST only monitors the fetal heart rate and movement, not the volume of fluid in the uterus.To measure the amount of amniotic fluid, other tests such as ultrasound or amniotic fluid index are needed.
A nurse is evaluating the results of a fetal non-stress test (NST) for a client who has diabetes mellitus and is at 36 weeks of gestation.
The nurse notes that the fetal heart rate (FHR) baseline is 150 bpm, with occasional increases of 20 bpm that last for 20 seconds.
There are no decelerations of the FHR.
How should the nurse document this finding?
Explanation
Reactive NST.This means that the fetal heart rate (FHR) increases by at least 15 bpm for at least 15 seconds twice in a 20-minute period.This indicates that the fetus is well-oxygenated and not in distress.
Choice B is wrong because a nonreactive NST means that the FHR does not show the expected accelerations, which could indicate fetal hypoxia or other problems.
Choice C is wrong because a positive NST is another term for a contraction stress test (CST), which measures the FHR response to uterine contractions.A positive CST means that the FHR shows late decelerations, which indicate uteroplacental insufficiency.
Choice D is wrong because a negative NST is also another term for a CST, but it means that the FHR does not show late decelerations, which indicate normal fetal oxygenation.
Exams on Fetal Non-Stress Test (NST)
Custom Exams
Login to Create a Quiz
Click here to loginFetal Non-Stress Test (NST)
Lessons
 Nursingprepexams
Just Now
Nursingprepexams
Just Now
Login to View Fetal Non-Stress Test (NST) Study Video
Notes Highlighting is available once you sign in. Login Here.
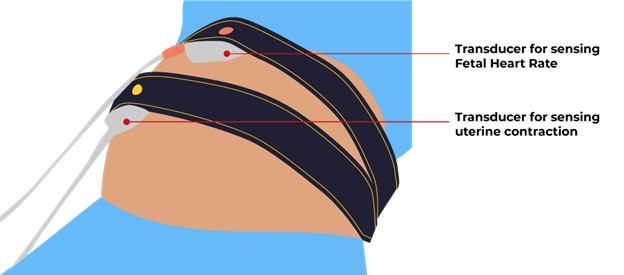
Procedure and equipment
- The mother lies on a reclining chair or bed with a belt around her abdomen that holds two transducers: one for FHR monitoring and one for uterine activity monitoring.
- The FHR and uterine activity are recorded on a paper strip or a computer screen for at least 20 minutes.
- The mother may be asked to press a button whenever she feels fetal movement, which is also marked on the recording.
- The mother may also be given a snack or juice to stimulate fetal activity, or an acoustic stimulator may be used to elicit fetal movement.
Interpretation of results
- A reactive NST result means that the FHR increases by at least 15 beats per minute (bpm) for at least 15 seconds, at least twice in a 20-minute period. This indicates that the fetus is well-oxygenated and healthy.
- A nonreactive NST result means that the FHR does not show the above criteria in a 40-minute period. This does not necessarily mean that the fetus is compromised, but it may indicate that the fetus is asleep, sedated, or hypoxic.
- Other FHR characteristics that are assessed include baseline rate, variability, accelerations, and decelerations. Normal FHR baseline rate is 110 to 160 bpm, normal variability is moderate (6 to 25 bpm), accelerations are normal and reassuring, early decelerations are benign and related to fetal head compression, late decelerations are abnormal and related to uteroplacental insufficiency, and variable decelerations are abnormal and related to umbilical cord compression.


Comparison with contraction stress test (CST)
- Contraction stress test (CST) is another screening test that measures FHR response to uterine contractions induced by oxytocin or nipple stimulation. It is used to evaluate fetal tolerance of labor and placental function.

- The main difference between NST and CST is that CST causes stress to the fetus by inducing contractions, while NST does not. Therefore, CST has more risks and contraindications than NST, such as preterm labor, placental abruption, or uterine rupture.
- The main similarity between NST and CST is that they both assess FHR patterns and their relation to fetal oxygenation. A negative CST result means that there are no late or significant variable decelerations in FHR during contractions, indicating a healthy fetus. A positive CST result means that there are late or significant variable decelerations in FHR during contractions, indicating fetal compromise.
Advantages and limitations of NST
-
Some advantages of NST are that it is safe, simple, noninvasive, inexpensive, widely available, and well-tolerated by mothers and fetuses. It has a high negative predictive value, meaning that a reactive result reliably excludes fetal hypoxia or acidosis. It can also be repeated as often as needed without adverse effects.
-
Some limitations of NST are that it has a low positive predictive value, meaning that a nonreactive result does not necessarily indicate fetal compromise. It may also have false-positive or false-negative results due to factors such as maternal medications, fetal sleep cycle, maternal obesity, or technical errors. It also does not provide information about other aspects of fetal well-being such as amniotic fluid volume or fetal breathing movements.
Summary
-
Fetal non-stress test (NST) is a screening test that measures FHR response to fetal movement.
-
It is used to assess fetal well-being and oxygenation in high-risk pregnancies or when there is decreased fetal movement or growth restriction.
-
It is performed after 28 weeks of gestation by placing two transducers on the mother’s abdomen and recording FHR and uterine activity for at least 20 minutes.
-
A reactive result means that FHR increases by at least 15 bpm for at least 15 seconds twice in 20 minutes. A nonreactive result means that FHR does not show this pattern in 40 minutes.
-
Other FHR characteristics include baseline rate, variability, accelerations, and decelerations. Normal baseline rate is 110 to 160 bpm; normal variability is moderate; accelerations are reassuring; early decelerations are benign; late decelerations are abnormal; variable decelerations are abnormal.
-
Nursing interventions include explaining the test; monitoring FHR and uterine activity; documenting fetal movements and interventions; providing emotional support and education; interpreting results; reporting results; providing referrals; providing follow-up care.
-
NST can be compared with CST which measures FHR response to induced contractions. CST causes stress to the fetus while NST does not. Both tests assess FHR patterns related to fetal oxygenation. Negative CST means no late or significant variable decelerations; positive CST means late or significant variable decelerations.
-
Advantages of NST include safety; simplicity; noninvasiveness; low cost; wide availability; high tolerance; high negative predictive value; repeatability. Limitations of NST include low positive predictive value; false-positive or false-negative results; lack of information on other aspects of fetal well-being.
Objectives
- Define fetal non-stress test (NST) and its purpose.
- Describe the procedure and equipment used for NST.
- Identify the criteria for a reactive and nonreactive NST result.
- Explain the nursing interventions and follow-up for NST results.
- Compare and contrast NST with contraction stress test (CST).
- Discuss the advantages and limitations of NST.
Introduction
- Fetal non-stress test (NST) is a screening test that measures fetal heart rate (FHR) and its response to fetal movement.
- It is used to assess fetal well-being and oxygenation, especially in high-risk pregnancies or when there is decreased fetal movement or growth restriction.
- It is called non-stress because it does not cause any stress or harm to the fetus or the mother.
- It is usually performed after 28 weeks of gestation, when FHR patterns are more mature and reactive.

Nursingprepexams
Videos
Login to View Video
Click here to loginTake Notes on Fetal Non-Stress Test (NST)
This filled cannot be empty

