ATI Custom Maternity Newborncare
Total Questions : 48
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreThe nurse admits a newborn to the admission nursery and prepares to bathe the baby for the first time after assessing which of the following?
Explanation
Temperature 36.2°C axillary on radiant warmer.
Choice A rationale:
Assessing whether it has been two hours since the baby's last feeding is important, but it is not directly related to preparing for the first bath. This information is more relevant for ensuring the baby is ready for feeding.
Choice B rationale:

The nurse should assess the baby's temperature before bathing to ensure it is within the normal range. A temperature of 36.2°C axillary on a radiant warmer is within the normal range for a newborn (normal axillary temperature ranges from 36.5°C to 37.5°C). Bathing a baby with a stable and appropriate temperature helps prevent hypothermia and maintains their well-being during the bathing process.
Choice C rationale:
Drying of the umbilical cord is not a crucial factor to consider before the first bath. While it is essential to keep the umbilical cord dry to prevent infection, it does not determine the baby's readiness for a bath.
Choice D rationale:
While maintaining a stable temperature for two hours is essential, it is not the most critical factor to consider before the first bath. The baby's axillary temperature assessment is a more direct and specific indicator of their readiness for a bath.
How do you prevent flat spots on the back of a baby's head?
Explanation
Back to sleep.
Choice A rationale:
Placing a baby on their back to sleep is the most effective way to prevent flat spots on the back of their head. This sleeping position, recommended by pediatric experts, helps reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) while also minimizing pressure on any one part of the baby's head, thus decreasing the likelihood of developing flat spots.
Choice B rationale:
Taking the baby for walks does not directly address the prevention of flat spots on the back of the head. Although it is beneficial for the baby's overall well-being, it does not specifically address the positional issue that leads to flat spots.
Choice C rationale:
Keeping the baby awake most of the day is not a suitable solution, as it may lead to sleep deprivation and hinder the baby's development. Adequate sleep is essential for a baby's growth and development.
Choice D rationale:
Tummy time is a valuable activity to promote the baby's neck and upper body strength. While it can indirectly contribute to preventing flat spots by encouraging different head positions, it is not as effective as placing the baby on their back to sleep.
A nurse is caring for a newborn who was delivered by vacuum extraction and has swelling on his head that crosses the suture line. The newborn's mother asks about the swelling on her newborn's head. Which of the following responses should the nurse make?
Explanation
"This is a caput succedaneum, which is a collection of fluid from the pressure of the vacuum extractor.”.
Choice A rationale:
A Mongolian spot is a benign, flat, bluish-gray pigmented area often found on the sacral or gluteal area of some newborns with darker skin tones. It is not related to the swelling on the newborn's head caused by vacuum extraction.
Choice B rationale:
A caput succedaneum is a localized swelling on the baby's scalp that occurs due to pressure from the vacuum extractor during delivery. It is typically soft and may cross the suture lines. This explanation accurately describes the swelling the baby has on his head.
Choice C rationale:
Erythema toxicum is a common rash that appears as small red bumps with white or yellow centers. It is a benign and self-resolving condition that does not cause swelling on the head or involve the suture lines.
Choice D rationale:
A cephalhematoma is a collection of blood between the skull and the periosteum that does not cross the suture lines. It is caused by trauma during birth and may take weeks to months to resolve. This does not match the description of the swelling caused by vacuum extraction.
The nurse enters the room and notices that the room feels cold. The mother says, "He has been crying and kicking and now he seems very tired.”. What is the nurse's priority concern?
Explanation
The nurse's priority concern is that the infant is overstimulated.
Choice A rationale:
Metabolic alkalosis and Choice B rationale:
Metabolic acidosis are not relevant concerns in this scenario, as there is no information provided to suggest any disturbances in the infant's acid-base balance. The symptoms described by the mother, such as crying, kicking, and tiredness, are more indicative of an emotional response rather than a metabolic disorder.
Choice C rationale:
While hunger could be a valid concern for the infant, it is not the nurse's priority concern in this situation. The infant's symptoms of crying, kicking, and tiredness indicate a need for soothing and comforting, which suggests overstimulation is the primary concern.
Choice D rationale:
The infant being overstimulated is the correct answer. The symptoms of crying, kicking, and tiredness, along with the cold room, suggest that the infant may be overwhelmed by sensory input, leading to overstimulation. The nurse's priority should be to provide a calm and soothing environment for the infant.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching about phenylketonuria (PKU) testing with the parent of a newborn. Which of the following statements by the parent indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
"My baby will be placed under special lights if the test is elevated.”.
Choice A rationale:

This statement indicates a need for further teaching. Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a metabolic disorder that leads to the accumulation of phenylalanine in the body. If the PKU test is elevated, it means that the baby has high levels of phenylalanine, and immediate dietary intervention is required. The parent's statement about special lights suggests a confusion with jaundice treatment, which is not related to PKU.
Choice B rationale:
This statement is accurate. Before the PKU test is done, the baby needs to consume formula or breast milk to ensure accurate test results.
Choice C rationale:
This statement is also accurate. PKU is a genetic disorder that can be managed with a special diet low in phenylalanine. By adhering to the prescribed diet, the harmful effects of PKU can be minimized.
Choice D rationale:
This statement is accurate. It is common for the PKU test to be repeated at the 2-week check- up to confirm the initial results and ensure early detection and management of PKU if present.
A nurse is collecting data from a newborn. Which of the following anatomical landmarks should the nurse use to measure chest circumference?
Explanation
The nurse should use the lower ribcage border to measure chest circumference.
Choice A rationale:
The sternal notch is not an appropriate landmark for measuring chest circumference. It is a notch at the top of the sternum and not indicative of chest circumference.
Choice B rationale:
The nipple line is not a suitable landmark for measuring chest circumference as it does not provide a consistent and standardized point of measurement.
Choice C rationale:
The lower ribcage border is the correct answer. Measuring chest circumference at this landmark ensures consistency and accuracy in the measurement, which is important for monitoring the growth and development of the newborn.
Choice D rationale:
The axillae (armpits) are not used as a landmark for measuring chest circumference. It is not a standardized anatomical point for this purpose.
A nurse is assisting a client with breastfeeding her newborn. The nurse should explain that which of the following reflexes will initiate sucking?
Explanation
Rooting. Choice A rationale:
The Moro reflex is a startle reflex characterized by the infant's sudden extension and abduction of the arms in response to a loud noise or sudden movement. It is not involved in the initiation of sucking and is unrelated to breastfeeding.
Choice B rationale:
The rooting reflex is a crucial reflex that helps initiate sucking in newborns. When the infant's cheek is stroked or touched, they will turn their head toward the stimulus and open their mouth, preparing for feeding. This reflex helps the infant find the mother's nipple and begin breastfeeding effectively.
Choice C rationale:
The stepping reflex is a primitive reflex observed in newborns when held upright with their feet touching a solid surface. The baby will make stepping movements, mimicking walking. However, this reflex is not related to the initiation of sucking and breastfeeding.
Choice D rationale:
The Babinski reflex is a reflex in which the big toe extends upward and the other toes fan out when the sole of the foot is stimulated. This reflex is present in newborns and disappears as the child grows older. It is not involved in the initiation of sucking.
Which statement about fetal circulation is true?
Explanation
Fetal circulation continues until after the stress of labor.
Choice A rationale:
Fetal circulation undergoes significant changes at birth. It becomes ineffective as the transition from intrauterine to extrauterine life occurs. The foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus, which allow blood to bypass certain fetal circulatory pathways, close as the baby breathes for the first time.
Choice B rationale:
Fetal circulation does not continue until red blood cells are broken down. Red blood cells in a fetus have a shorter lifespan than those in adults and are continually replaced throughout gestation. However, their breakdown is not the reason for the changes in fetal circulation.
Choice C rationale:
The correct answer. Fetal circulation continues until after the stress of labor. During labor, the baby experiences increased stress and pressure, which helps trigger various physiological changes, including the closure of specific fetal circulatory shunts.
Choice D rationale:
Fetal circulation does not continue until adulthood. As mentioned earlier, the transition from fetal to adult circulation occurs during and after birth, with the closure of specific fetal shunts and the establishment of a fully functional adult circulatory system.
A nurse is caring for several newborn clients. For which of the following findings should the nurse notify the charge nurse?
Explanation
A blood glucose fingerstick of 40 mg/dL for an infant who is 1- hour old.
Choice A rationale:
This finding should be notified to the charge nurse immediately because a blood glucose level of 40 mg/dL in a 1-hour-old infant is significantly lower than the normal range. Hypoglycemia in newborns can lead to serious complications, including neurological issues. Normal blood glucose levels in newborns are typically around 45-90 mg/dL.
Choice B rationale:
A hematocrit of 60% in an 8-hour-old infant may be considered relatively high, but this is a normal finding in newborns. Hematocrit levels can be higher in neonates due to their unique physiological adaptation to extrauterine life.
Choice C rationale:
Jaundice in a 4-hour-old infant is a common occurrence and is not typically a cause for immediate concern. Physiological jaundice often appears after 24 hours of birth and resolves on its own.
Choice D rationale:
Acrocyanosis, bluish discoloration of the hands and feet, is a normal finding in newborns and is not considered a cause for concern. It occurs due to the immature peripheral circulation and typically resolves within a few days.
Exhibit 1. The names of the newborn reflexes are? Select all that apply.
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
The newborn reflex called "rooting”. is characterized by turning the head and opening the mouth when the cheek or mouth area is touched. This reflex helps the newborn find the mother's breast for feeding.
Choice B rationale:
"Stepping”. is a newborn reflex where they make stepping movements when held upright with their feet touching a solid surface. This reflex is present at birth but tends to disappear after a few weeks.
Choice C rationale:
The "Moro”. reflex is also known as the startle reflex. It is elicited by a sudden loss of support or loud noise, causing the newborn to throw their arms and legs out and then bring them back in. This reflex usually disappears around 3 to 4 months of age.
Choice D rationale:
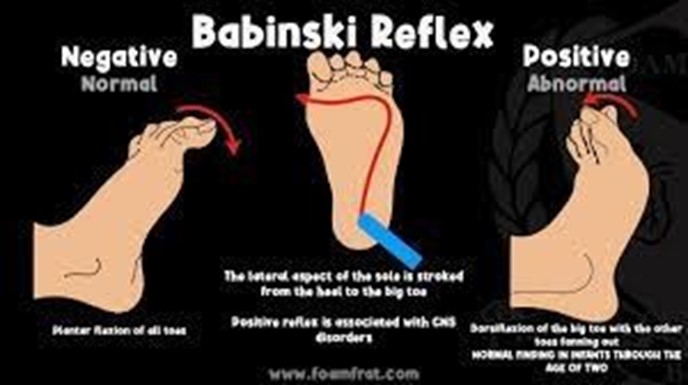
The "Babinski”. reflex is characterized by the extension of the big toe and fanning of the other toes when the sole of the foot is stroked. This reflex is present in newborns and should disappear by around 12 months of age.
Choice E rationale:
"Running”. is not a recognized newborn reflex. There is no reflex with this name related to newborns.
Choice F rationale:
The "gag”. reflex is present in newborns and helps protect the airway by causing a gagging response when the back of the throat is stimulated.
A newborn is most interested in eating in which wake and sleep state?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Newborns do not show interest in eating while crying. Crying is usually an indication of distress or hunger and not a state where they are interested in eating.
Choice B rationale:
Newborns are most interested in eating when they are in an "alert”. state. During this state, the baby is awake, calm, and attentive, making it an ideal time for feeding.
Choice C rationale:
In the "drowsy”. state, newborns may be sleepy and less interested in eating. They might feed less effectively in this state.
Choice D rationale:
"Active alert”. is a state where the newborn is awake, attentive, and active. While they may be interested in their surroundings, they may also be easily distracted during feeding.
A nurse is caring for a newborn who is at 34 weeks of gestation, weighs 1,550 g, and has nasal flaring, intercostal retractions, expiratory grunting, and mild cyanosis. The nurse should place the newborn in an incubator for which of the following reasons?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Placing the newborn in an incubator is essential because the newborn's temperature control mechanism is immature. Premature infants have an underdeveloped thermoregulatory system, making them susceptible to heat loss and cold stress. An incubator provides a controlled, warm environment to maintain the newborn's body temperature within the normal range (around 36.5°C to 37.5°C or 97.7°F to 99.5°F).
Choice B rationale:
Heat increasing the flow of oxygen to the newborn's extremities is not a valid reason for placing the newborn in an incubator. Oxygenation is primarily influenced by respiratory and circulatory mechanisms, not external heat.
Choice C rationale:
The newborn's small body surface area for his weight is not directly related to the need for an incubator. Premature infants have a higher surface area to weight ratio, making them more prone to heat loss, but this is not the primary reason for using an incubator.
Choice D rationale:
Heat facilitating the drainage of mucus is not a reason for placing the newborn in an incubator. Proper positioning and suctioning are used to manage mucus in premature infants, but incubators are primarily for temperature regulation.
The nurse notes that a newborn's white blood cell count (WBC) is 15,000. The nurse is aware that:.
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
A white blood cell count of 15,000 does not necessarily indicate a severe infection. In newborns, WBC counts are typically higher than in adults, and they gradually decrease over the first few days after birth. A value of 15,000 falls within the normal range for a newborn and is not indicative of a severe infection.
Choice B rationale:
A white blood cell count of 15,000 is considered a normal range for a newborn. Newborns have higher WBC counts as a natural response to the stress of birth and exposure to the outside environment. The immune system is still developing, and elevated WBC counts are normal during this period.
Choice C rationale:
Assuming there are no other indications of lab error, such as abnormal results in other tests, it would be premature to label the WBC count as a lab error. Additionally, healthcare professionals should always consider the overall clinical picture before assuming a lab error based on a single result.
Choice D rationale:
There is no immediate need to call the doctor based solely on the WBC count of 15,000. Medical decisions should be made in the context of the newborn's overall clinical condition, and a single lab result does not warrant an immediate call to the doctor.
A nurse is collecting data from a newborn who is 12 hours old. His respiration rate is 44/min, shallow, with periods of apnea lasting up to 5 seconds. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Activating respiratory arrest procedures is not necessary in this situation. The newborn's respiratory rate, although slightly elevated, does not indicate respiratory arrest. Instead, such procedures are reserved for situations where the newborn has stopped breathing or is in acute respiratory distress.
Choice B rationale:
Requesting an order for supplemental oxygen may be premature. The newborn's respiration rate of 44/min, although shallow with periods of apnea, is still within the normal range for a newborn. Providing supplemental oxygen should be considered when the newborn is showing signs of significant respiratory distress or if oxygen saturation levels are low.
Choice C rationale:
The most appropriate action in this scenario is to continue routine monitoring of the newborn's respiratory rate and overall condition. Newborns often exhibit irregular breathing patterns, including periods of apnea, especially in the first few hours after birth. As long as the newborn's color, heart rate, and overall appearance are stable, routine monitoring is appropriate.
Choice D rationale:
There is no need to report the observation to the charge nurse immediately, as the newborn's respiratory rate and pattern fall within the expected range for a 12-hour-old newborn.
Reporting should be considered when there are significant deviations from the norm or if the newborn's condition deteriorates.
Exhibit 1. A nurse understands which of the following assessment findings as a priority to indicate that a newborn may be experiencing cold stress and burning brown fat to produce heat? (Select all that apply.).
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Respiratory distress is a priority assessment finding that indicates a newborn may be experiencing cold stress. Cold stress can cause the baby's body to burn brown fat to generate heat, leading to increased oxygen demand and respiratory distress as a compensatory mechanism.
Choice B rationale:
Hyperglycemia is not associated with cold stress. Instead, hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) is a concern in newborns experiencing cold stress as they deplete their glucose stores to maintain body temperature.
Choice C rationale:
Metabolic alkalosis is not a priority assessment finding for cold stress. Metabolic acidosis (not listed in the options) can be associated with cold stress due to increased anaerobic metabolism, but it is not one of the provided choices.
Choice D rationale:
Hypoglycemia is a priority assessment finding associated with cold stress. As the baby's body uses glucose to produce heat from burning brown fat, it can lead to a drop in blood sugar levels, which is a significant concern in newborns.
Choice E rationale:
Metabolic acidosis is not listed among the provided choices, but it can be associated with cold stress due to the increased production of lactic acid from anaerobic metabolism when trying to generate heat.
The purpose of surfactant is to?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Providing a heat source for the newborn is not the purpose of surfactant. Surfactant is a substance produced in the lungs to reduce surface tension and prevent alveolar collapse during expiration. It helps with the exchange of gases, but it does not generate heat.
Choice B rationale:
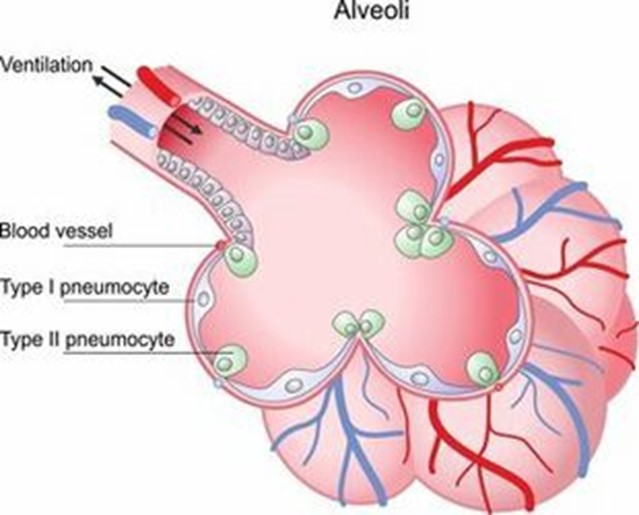
This is the correct answer. Surfactant plays a crucial role in assisting the alveoli to remain open by reducing surface tension. This, in turn, allows for proper gas exchange, especially of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Choice C rationale:
Assisting the ductus arteriosus to remain open is not the purpose of surfactant. The ductus arteriosus is a fetal blood vessel that connects the pulmonary artery to the aorta, bypassing the lungs. After birth, it should close on its own, and surfactant does not influence this process.
Choice D rationale:
Providing energy to the newborn is not the purpose of surfactant. Energy for the newborn comes from nutrition, particularly breast milk or formula, and not from surfactant
A nurse is reinforcing teaching with a client who is postpartum about bathing her newborn. Which of the following statements by the client indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
"Baby powder will help prevent a diaper rash.”.
Choice A rationale:
"I will use mild soap”. indicates an appropriate understanding of newborn bathing. Mild soap is suitable for newborn skin to avoid irritation.
Choice B rationale:
This is the correct answer. Baby powder is not recommended for newborns as it can cause respiratory issues when inhaled and may lead to skin irritation. Therefore, the client needs further teaching about the use of baby powder.
Choice C rationale:
"I will test the water on my wrist for temperature before bathing”. demonstrates proper safety measures, ensuring the water is not too hot for the baby.
Choice D rationale:
"I will use a basin during bathing”. is a reasonable approach to bathing the newborn and does not indicate a need for further teaching.
A nurse is caring for a newborn immediately after birth. Which of the following actions by the nurse reduces evaporative heat loss by the newborn?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Maintaining ambient room temperature at 24°C (75°F) is essential for the comfort of the newborn, but it does not specifically address evaporative heat loss. The focus here is on the prevention of heat loss through conduction.
Choice B rationale:
Drying the newborn's skin thoroughly is important for reducing conductive heat loss, not evaporative heat loss.
Choice C rationale:
This is the correct answer. Preventing air drafts is crucial in reducing evaporative heat loss in a newborn. Newborns are particularly sensitive to changes in temperature, and exposure to drafts can increase heat loss through evaporation from their skin.
Choice D rationale:
Placing the newborn on a warm surface helps prevent heat loss through conduction, but it does not specifically address evaporative heat loss. Warm surfaces are used to maintain the newborn's body temperature after birth.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching with a parent about using an iron-fortified formula to feed her newborn. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Iron facilitating bone growth is not the appropriate information to include in teaching about using an iron-fortified formula for a newborn. While iron is essential for various physiological processes, bone growth is not the primary focus when choosing an iron-fortified formula for newborns.
Choice B rationale:
This is the correct choice. Newborns do not metabolize iron adequately because they are born with a finite amount of iron stored in their bodies. They rely on external sources of iron, such as iron-fortified formula, to meet their iron needs as they grow. Without sufficient iron intake, newborns are at risk of iron deficiency anemia.
Choice C rationale:
The statement about the newborn's iron source depleting is not accurate. The newborn does not deplete their iron source but rather utilizes the stored iron over time. However, this choice is not the best answer because it does not provide useful information to the parent about using an iron-fortified formula.
Choice D rationale:
Iron facilitating eyesight development is not a relevant aspect to consider when discussing the use of iron-fortified formula for a newborn. While iron is essential for various physiological functions, it is not specifically linked to eyesight development.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching with a parent about using an iron-fortified formula to feed her newborn. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Iron will facilitate bone growth. This statement is not accurate in the context of feeding a newborn with iron-fortified formula. While iron is essential for overall growth and development, its primary role is not specifically related to bone growth. Instead, it plays a crucial role in the production of hemoglobin, which helps carry oxygen in the blood.
Choice B rationale:
Newborns do not metabolize iron adequately. This statement is the correct choice. Newborns have limited iron stores that are obtained from their mothers during pregnancy. As they grow, their iron requirements increase, but their ability to metabolize iron is not fully developed at
birth. Hence, iron-fortified formula is recommended to provide the necessary iron for the newborn's healthy development.
Choice C rationale:
The newborn's iron source will start to deplete. This statement is not accurate in the context of iron-fortified formula feeding. The newborn's initial iron source is the iron stores passed on by the mother during pregnancy. However, the iron-fortified formula is designed to supplement and fulfill the baby's iron needs, preventing depletion of iron stores.
Choice D rationale:
Iron will facilitate eyesight development. This statement is not entirely accurate. While iron is important for many bodily functions, including eye health, it is not specifically responsible for eyesight development in newborns. Visual development in newborns is influenced by various factors, but iron intake through formula feeding directly impacting eyesight is not a primary concern.
A nurse is reinforcing discharge teaching about circumcision care with the parent of a newborn who had a circumcision using the Plastibell device. Which of the following client statements indicates an understanding of the teaching? (Select all that apply.).
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Washing the penis with warm water and mild soap each day is not an appropriate statement regarding circumcision care with a Plastibell device. Keeping the area clean is essential, but soap may irritate the wound, and frequent washing can disrupt the healing process.
Choice B rationale:
Ensuring a loose diaper in the front is not directly related to circumcision care with a Plastibell device. It may be relevant for comfort, but it does not address specific care for the circumcision site.
Choice C rationale:
This is a correct statement indicating understanding of circumcision care with the Plastibell device. The plastic ring is expected to fall off on its own within a week, and this is a normal part of the healing process.
Choice D rationale:
Applying petroleum jelly to the penis during diaper changes is not recommended for circumcision care with a Plastibell device. The petroleum jelly can interfere with wound healing and should be avoided.
Choice E rationale:
This is also a correct statement indicating understanding of circumcision care. If bleeding occurs after the Plastibell has fallen off, it could be a sign of a complication, and the doctor should be notified promptly.
A nurse in the newborn nursery is receiving a report on four newborns. Which of the following newborns should the nurse see first?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
The nurse should prioritize the assessment of a newborn who is 18 hours old and has not voided (urinated). A healthy newborn typically passes urine within the first 24 hours after birth. Delayed or absent urine output in a newborn could indicate a potential urinary tract issue or dehydration. Prompt evaluation and intervention are essential to address any potential concerns regarding the newborn's renal function.
Choice B rationale:
This choice is the correct answer. As explained in Choice A, a newborn who is 18 hours old and has not voided should be seen first due to the urgency in assessing the urinary function.
Choice C rationale:
A newborn who is 24 hours old and has not passed meconium is not the most critical concern among the options provided. While meconium (the baby's first stool) should be passed within the first 24-48 hours, a slight delay may not be an immediate cause for concern. It is essential to monitor the newborn's bowel movements, but this situation does not warrant immediate action compared to the concern of urinary retention.
Choice D rationale:
A newborn who is 12 hours old and has an axillary temperature of 37.8°C (100°F) may have a mild fever, which could indicate an infection. While fever in a newborn is concerning, it is not as urgent as addressing potential urinary issues. The nurse should still assess and monitor the newborn's temperature and inform the healthcare provider, but it does not take priority over the newborn with no urine output.
In a newborn infant, which of the following is the liver's job related to bilirubin?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
The liver's job related to bilirubin is not changing conjugated bilirubin to unconjugated. Conjugated bilirubin is the water-soluble form of bilirubin that is excreted in bile and urine. Unconjugated bilirubin, on the other hand, is the fat-soluble form, which is transported to the liver and conjugated to become water-soluble. The conversion goes from unconjugated to conjugated, not the other way around.
Choice B rationale:
The liver's job related to bilirubin is not the synthesis of vitamin K. The liver is responsible for synthesizing clotting factors, including factors II (prothrombin), VII, IX, and X, but not vitamin K itself. Vitamin K is obtained from dietary sources or supplements and is essential for blood clotting.
Choice C rationale:
This choice is the correct answer. The liver's primary function related to bilirubin is changing unconjugated bilirubin to conjugated bilirubin. As mentioned earlier, unconjugated bilirubin is produced from the breakdown of heme in old red blood cells, and it needs to be processed in the liver to become water-soluble and eventually excreted in bile and urine.
Choice D rationale:
The liver's job related to bilirubin does not involve the removal of meconium. Meconium is the first stool passed by a newborn, and its elimination is unrelated to the liver's function in processing bilirubin.
How many ounces is 30 ml?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
30 ml is equal to approximately half an ounce. One ounce is equivalent to 29.57 ml. This conversion is essential in pediatric care, especially when administering medications to infants, as doses are often prescribed in milliliters.
Choice B rationale:
Three ounces is not the correct conversion for 30 ml. Three ounces would be equivalent to approximately 88.71 ml, which is significantly more than 30 ml.
Choice C rationale:
Two ounces is not the correct conversion for 30 ml. Two ounces would be approximately
59.15 ml, which is still more than 30 ml. Choice D rationale:
One ounce is not the correct conversion for 30 ml. As mentioned earlier, one ounce is approximately 29.57 ml, which is slightly less than 30 ml. The correct conversion is half an ounce (approximately 14.79 ml more than 29.57 ml), as stated in Choice A.
Rh: Positive. Action to Take 1: Obtain a transcutaneous bilirubin level. Action to Take 2: Administer methadone. Actions to Take: Monitor platelet count. Place the newborn under a radiant warmer. Check the newborn's capillary blood glucose level. Potential Conditions: Hyperbilirubinemia. Cytomegalovirus infection. Hypoglycemia. Neonatal abstinence syndrome. Parameters to Monitor 1: Temperature. Parameter to Monitor 2: Color and of bowel movements. Seizure activity. Frequent yawning. Petechiae. Respiratory rate: 68/min auscultation. Temperature: 36.1°C (96.9°F) axillary. Action to Take 1: Obtain a transcutaneous bilirubin level. Action to Take 2: Administer methadone. Actions to Take: Monitor platelet count. Place the newborn under a radiant warmer. Check the newborn's capillary blood glucose level. Potential Conditions: Hyperbilirubinemia. Cytomegalovirus infection.
Hypoglycemia. Neonatal abstinence syndrome. Parameters to Monitor 1: Temperature. Parameter to Monitor 2: Color and of bowel movements. Seizure activity. Frequent yawning.
Petechiae. Exhibit 1. What are the newborn vital sign ranges? Select all that apply. (Select All that Apply).
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
The normal temperature range for a newborn measured axillary (armpit) is 97.7-99.3°F (36.5- 37.4°C). This is a crucial vital sign to monitor, as any significant deviation from this range could indicate an underlying issue requiring further evaluation.
Choice B rationale:
The newborn's heart rate varies with their activity level. While asleep, it is around 100 bpm, and when awake, it is 120-160 bpm. During crying or agitation, it can go up to 180 bpm.
Monitoring the heart rate is essential, as any abnormal values might indicate cardiac or other health problems.
Choice D rationale:
The normal respiratory rate for a newborn is 30-60 breaths per minute. Respiratory rate is a critical parameter to monitor as rapid or slow breathing could be a sign of respiratory distress or other respiratory conditions.
Choice C rationale:
Blood pressure is not routinely assessed in newborns, as it is challenging to obtain accurate readings due to their small size and physiology. Instead, other vital signs are relied upon for assessment.
Choice E rationale:
The head circumference is not included in the normal vital sign ranges. However, monitoring head circumference is crucial during infancy to track brain growth and development.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 48 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

