ATI Custom OB Exam 1 Summer 2023
Total Questions : 23
Showing 23 questions, Sign in for moreFor problems involving adult patients, the answer will be rounded to the nearest tenth. Although some IV pumps do not allow calibration to the tenth or hundredth, for the purpose of this exam, IV rate calculations will be rounded to the nearest whole drop (gt/min) or to the nearest whole number IV (ml/hr). To promote safety, a zero must be placed to the left of the decimal point in answers that are less than one. No zero is allowed to the right of the decimal point in answers that are whole numbers. For example, 0.5 mg must be answered as 0.5 mg and 5.0 mg must be answered as 5 mg.
The physician orders: Magnesium 4 gms loading dose to infuse over 30 minutes at 0500. Then infuse a maintenance dose of 1 gram /hr. The pharmacy sends 80 Gms in 1000 mL of LR. What would the nurse set the pump for the loading dose at 5 Am? Be sure to enter the number AND the unit of measurement (mL). Partial credit will not be given.
Explanation
To find the loading dose rate, we need to use the formula:
Rate (mL/hr) = Dose (g) x Volume (mL) / Time (hr) x Concentration (g)
Plugging in the given values, we get:
Rate (mL/hr) = 4 g x 1000 mL / 0.5 hr x 80 g
Simplifying, we get:
Rate (mL/hr) = 100 g/mL / 40 g/hr
Rate (mL/hr) = 2.5 mL/g
Multiplying by 1000, we get:
Rate (mL/hr) = 2500 mL/g x g/hr
Canceling out the units of g, we get:
Rate (mL/hr) = 2500 mL/hr
Rounding to the nearest whole number, we get:
Rate (mL/hr) = 200 mL/hr
For problems involving adult patients, the answer will be rounded to the nearest tenth. Although some IV pumps do not allow calibration to the tenth or hundredth, for the purpose of this exam, IV rate calculations will be rounded to the nearest whole drop (gt/min) or to the nearest whole number IV (ml/hr). To promote safety, a zero must be placed to the left of the decimal point in answers that are less than one. No zero is allowed to the right of the decimal point in answers that are whole numbers. For example, 0.5 mg must be answered as 0.5 mg and 5.0 mg must be answered as 5 mg.
The client in labor has oxytocin (Pitocin) infusing at 15 mu/minute. She has 20 units of Pitocin in 1000 mL of Normal Saline IV solution. If this client is receiving 15 mu/min, then how many mL/hr would her IV infusion pump be set at? Be sure to enter the number AND the unit of measurement (mL). Partial credit will not be given.
Explanation
To find the infusion rate, we need to use the formula:
Rate (mL/hr) = Dose (mu/min) x Volume (mL) / Concentration (mu/mL) x Time (min/hr)
Plugging in the given values, we get:
Rate (mL/hr) = 15 mu/min x 1000 mL / 20 mu/mL x 60 min/hr
Simplifying, we get:
Rate (mL/hr) = 15,000 mu/mL / 1200 mu/hr
Dividing, we get:
Rate (mL/hr) = 12.5 mL/mu
Multiplying by 1000, we get:
Rate (mL/hr) = 12,500 mL/mu x mu/hr
Canceling out the units of mu, we get:
Rate (mL/hr) = 12,500 mL/hr
Rounding to the nearest tenth, we get:
Rate (mL/hr) = 45 mL/hr

A nurse is reinforcing teaching to a client regarding how to reduce the risk of giving birth to a newborn who has a neural tube defect. Which of the following instructions by the nurse is appropriate?
Explanation
b. Eat foods fortified with folic acid.
Folic acid is a B vitamin that is essential for the development of the neural tube, which forms the brain and spinal cord of the fetus. A deficiency of folic acid can lead to neural tube defects such as spina bifida and anencephaly, which can cause serious complications or death for the newborn. Therefore, it is recommended that women who are planning to conceive or are pregnant consume at least 400 mcg of folic acid daily from supplements or foods fortified with folic acid, such as cereals, breads, and pasta.
The incorrect options are:
a. Increase intake of iron. Iron is a mineral that is important for the production of red blood cells and the prevention of anemia in pregnant women. However, iron deficiency does not cause neural tube defects. Iron supplements may be recommended for pregnant women who have low iron levels, but they do not affect the risk of neural tube defects².
c. Avoid the use of aspirin. Aspirin is a type of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that can have harmful effects on the fetus if taken during pregnancy, especially in the second and third trimesters. Aspirin can cause kidney problems, bleeding problems, premature closure of a blood vessel in the fetal heart, and increased risk of pregnancy loss¹. However, aspirin does not cause neural tube defects. Low-dose aspirin may be prescribed for some pregnant women who have certain medical conditions that increase the risk of preeclampsia or blood clots, but only under the guidance of a health care provider¹.
d. Limit consumption of alcohol. Alcohol is a known teratogen that can cause a range of physical, mental, and behavioral problems in the fetus, collectively known as fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD). Alcohol can interfere with the development of the brain and other organs, and cause facial abnormalities, growth problems, learning difficulties, and behavioral issues³. However, alcohol does not cause neural tube defects. There is no safe amount or type of alcohol to drink during pregnancy, and abstaining from alcohol is the best way to prevent FASD³.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching with a client who is at 34 weeks of gestation and at risk for placental abruption. The nurse recognizes that which of the following is the most common risk factor for a placental abruption?
Explanation
Hypertension is the most common risk factor for placental abruption, which occurs when the placenta separates from the uterine wall before delivery. Hypertension can cause damage to the blood vessels that supply the placenta, leading to reduced blood flow and increased pressure in the intervillous space. This can cause hemorrhage and detachment of the placenta.
The other options are not as common as hypertension, but they can also increase the risk of placental abruption by causing trauma, vasoconstriction, or inflammation in the placenta or uterus.
Maternal batering can cause direct injury to the abdomen or uterus, resulting in placental abruption.
Maternal cigarete smoking can cause vasoconstriction and reduced blood flow to the placenta, as well as increase the risk of thrombosis and inflammation in the placental vessels.
d. Maternal cocaine use can cause severe vasoconstriction and hypertension, which can impair placental perfusion and cause placental abruption.
A nurse in a prenatal clinic is caring for a client who is at 38 weeks of gestation and has heavy, red vaginal bleeding, without contractions, that started spontaneously. She is in no distress and states that she can "feel the baby moving." The client should undergo an ultrasound to determine which of the following findings?
Explanation
The client's symptoms are suggestive of placenta previa, which is a condition where the placenta covers part or all of the cervical opening. Placenta previa can cause painless, bright red bleeding in the third trimester, especially after sexual intercourse or a pelvic exam. The bleeding can be life-threatening for both the mother and the fetus, and the condition requires immediate evaluation and management. An ultrasound is the best diagnostic tool to confirm the location of the placenta and rule out other causes of bleeding, such as placental abruption or uterine rupture.The other options are not relevant to the client's situation and would not be indicated by an ultrasound.Fetal lung maturity is not a concern for a client who is at 38 weeks of gestation, as most fetuses have developed sufficient surfactant production by this time. Fetal lung maturity can be assessed by amniocentesis or by measuring the lecithin/sphingomyelin ratio in the amniotic fluid.Frequency and duration of contractions are not present in the client's case, as she has no signs of labor. Contractions can be monitored by external or internal tocodynamometry or by palpation.d. Rh incompatibility is a condition where the mother's blood type is Rh-negative and the fetus's blood type is Rh- positive, which can cause hemolytic disease of the newborn. Rh incompatibility can be detected by blood tests and prevented by administering Rh immunoglobulin to the mother during pregnancy and after delivery.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching with a client who is in her second trimester and has a new diagnosis of gestational diabetes. Which of the following statements by the client indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
c. "I will reduce my exercise schedule to 3 days a week."
The client should not reduce her exercise schedule, as physical activity can help lower blood glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity in gestational diabetes. The client should aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise on most days of the week unless contraindicated by her provider. Exercise can also help prevent excessive weight gain, preeclampsia, and macrosomia in pregnancy.
The other statements are correct and do not indicate a need for further teaching.
The client should limit her carbohydrates to 50% of her daily caloric intake, as carbohydrates have the most impact on blood glucose levels. The client should also choose complex carbohydrates that are high in fiber and low in glycemic index, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. The client should know that she is at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, as gestational diabetes is a risk factor for future diabetes mellitus. The client should undergo screening for diabetes 6 to 12 weeks after delivery and every 1 to 3 years thereafter. The client should also adopt lifestyle modifications such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management to prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.The client should take her glyburide daily with breakfast, as glyburide is an oral antidiabetic agent that can be used to treat gestational diabetes when diet and exercise are not enough to control blood glucose levels. Glyburide stimulates the pancreas to produce more insulin and lowers blood glucose levels. Glyburide should be taken with the first meal of the day to avoid hypoglycemia.
A nurse is speaking on the phone to a client who is pregnant and taking iron supplements for iron-deficiency anemia. The client reports that her stools are black but she has no abdominal pain or cramping. Which of the following responses by the nurse is appropriate?
Explanation
c. "This is expected because of the way iron is broken down during digestion."
The client's stools are black because of the iron supplements, which can cause a harmless change in the color and consistency of the stools. This is due to the oxidation of iron in the gastrointestinal tract, which produces a black pigment called ferrous sulfide. This is not a sign of bleeding or infection and does not require further evaluation or treatment. The nurse should reassure the client that this is a normal side effect of iron supplements and advise her to continue taking them as prescribed.
The other responses are not appropriate and may cause unnecessary anxiety or inconvenience for the client.
The nurse should not ask the client what else she has been eating, as this implies that her diet may be causing her stools to be black. This may confuse or offend the client, who may think that the nurse is questioning her nutritional choices or blaming her for her condition.
The nurse should not tell the client to go to the emergency room, as this suggests that her stools are black because of a serious problem that needs immediate atention. This may frighten or alarm the client, who may think that she or her baby are in danger.
d. The nurse should not tell the client to come to the office, as this indicates that her stools are black because of an abnormal finding that needs further investigation. This may worry or inconvenience the client, who may think that she has a complication or infection that requires testing or treatment.
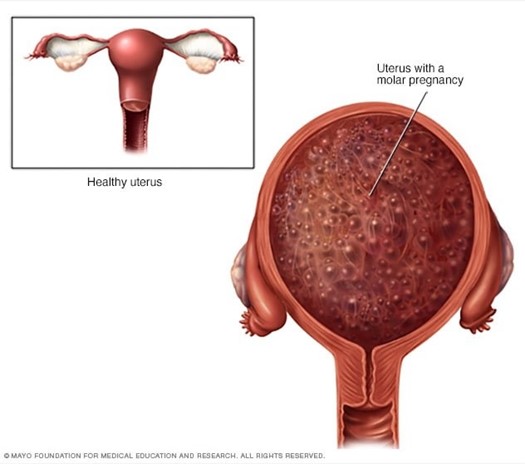
A nurse is caring for a client who might have a hydatidiform mole. The nurse should monitor the client for which of
Explanation
c. Excessive uterine enlargement
A hydatidiform mole is a type of gestational trophoblastic disease, where the placenta develops abnormally into a mass of cysts that resemble grape-like clusters. A hydatidiform mole can cause excessive uterine enlargement, as the uterus grows larger than expected for the gestational age. The nurse should measure the fundal height and compare it with the expected value based on the last menstrual period or ultrasound.
The other findings are not associated with a hydatidiform mole and may indicate other conditions.
Whitish vaginal discharge is not a sign of a hydatidiform mole, but it may be normal in pregnancy due to increased cervical mucus production. However, if the discharge is foul-smelling, yellow, green, or bloody, it may indicate an infection or a complication such as preterm labor or placental abruption.
Fetal heart rate irregularities are not a sign of a hydatidiform mole, but they may indicate fetal distress or congenital anomalies. A hydatidiform mole usually does not have a viable fetus, and fetal heart tones are absent or very faint. The nurse should use a Doppler device or a fetal monitor to assess the fetal heart rate and rhythm.
d. Rapidly dropping human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels are not a sign of a hydatidiform mole, but they may indicate a spontaneous abortion or an ectopic pregnancy. A hydatidiform mole usually causes very high hCG levels, as the abnormal placental tissue secretes large amounts of this hormone. The nurse should perform a urine or blood test to measure the hCG levels and monitor them for chan
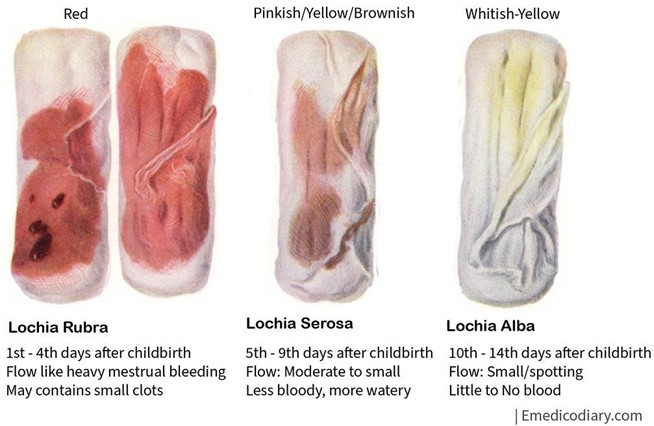
A nurse is collecting data from a postpartum client and finds a large amount of lochia rubra with several clots on the client's perineal pad. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
The nurse should check the client's fundus first, as this is the most likely source of bleeding and clots in the postpartum period. The fundus is the upper part of the uterus that contracts and involutes after delivery to prevent hemorrhage. The nurse should palpate the fundus for firmness, height, and position, and massage it gently if it is boggy or displaced. A soft, high, or deviated fundus may indicate uterine atony or retained placental fragments, which can cause excessive bleeding and clots.
A nurse in a prenatal clinic is reviewing the medical record of a client who is at 28 weeks of gestation. The client's history reveals one pregnancy terminated by elective abortion at 9 weeks; the birth of twins at 36 weeks; and a spontaneous abortion at 15 weeks of gestation. According to the GTPAL system, which of the following describes her present parity?
Explanation
The GTPAL system is a way of describing a woman's obstetric history using five digits: G (gravida), T (term births), P (preterm births), A (abortions), and L (living children). The client's present parity can be calculated as follows:
G: The client is gravida 4, as she has been pregnant four times, including the current one.
T: The client has had one term birth, as she delivered twins at 36 weeks, which is considered term for a multiple gestation.
P: The client has had no preterm births, as she has not delivered any babies before 37 weeks of gestation. A: The client has had two abortions, one elective and one spontaneous, both before 20 weeks of gestation. L: The client has two living children, the twins she delivered at term.
Therefore, the client's present parity is 2-0-1-2-2.
The other options are incorrect and do not reflect the client's obstetric history.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching with a client at her first prenatal visit about expected changes during gestation. (Arrange the steps in order, placing them in the selected order of occurrence from earliest to latest in gestation. Use all the steps.)
No explanation
A nurse is collecting data from a client who is in her second trimester of pregnancy. The nurse should recognize which of the following findings as an expected physiologic change during pregnancy?
No explanation
A nurse is caring for a client who is at 34 weeks of gestation and has a suspected placenta previa. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
b. Apply an external fetal monitor.
The nurse should apply an external fetal monitor to assess the fetal heart rate and activity, as well as the presence and intensity of contractions. Placenta previa is a condition where the placenta covers part or all of the cervical opening, which can cause painless, bright red bleeding in the third trimester. Placenta previa can compromise fetal oxygenation and perfusion, and can also trigger preterm labor. Therefore, the nurse should monitor the fetal well- being and readiness for delivery.
The other actions are not appropriate and may cause harm to the client or the fetus.
a. The nurse should not perform a rectal exam, as this can cause trauma or infection to the rectum or the placenta, and increase the risk of bleeding or rupture.
c. The nurse should not complete a vaginal exam, as this can dislodge or damage the placenta, and cause severe
hemorrhage or shock.
d. The nurse should not apply ice to the perineal area, as this can cause vasoconstriction and reduce blood flow to the placenta and the fetus, and worsen their condition.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching with a client who is pregnant and has a body mass index (BMI) of 26.5. She asks the nurse how much weight she should gain over the course of her pregnancy. Which of the following statements is an appropriate response by the nurse?
Explanation
The nurse should tell the client that the recommendation for her is about 15 to 25 pounds, as this is the range of weight gain that is considered healthy and appropriate for a pregnant woman who has a BMI of 26.5, which falls in the overweight category (BMI of 25 to 29.9). The weight gain should be gradual and consistent, with an average of
0.6 pounds per week in the second and third trimesters.
a. The nurse should not tell the client that a gain of about 25 to 35 pounds is best for her and for her baby, as this is the range of weight gain that is recommended for a pregnant woman who has a normal BMI (18.5 to 24.9). Gaining more weight than necessary can increase the risk of gestational diabetes, hypertension, preeclampsia, cesarean delivery, and postpartum weight retention.
c. The nurse should not tell the client that she should gain 11 to 20 pounds, as this is the range of weight gain that is advised for a pregnant woman who has a BMI of 30 or higher, which falls in the obese category. Gaining less weight than needed can compromise fetal growth and development, and increase the risk of preterm birth, low birth weight, and intrauterine growth restriction.
d. The nurse should not tell the client that it really doesn't mater exactly how much weight she gains, as long as her diet is healthy, as this is a vague and inaccurate statement that does not provide any guidance or education to the client. The amount of weight gain during pregnancy does mater, as it affects both maternal and fetal health and outcomes. A healthy diet is important, but it is not the only factor that influences weight gain. The nurse should also consider the client's pre-pregnancy weight, physical activity level, medical history, and gestational age.
A nurse is caring for a client in the prenatal clinic who has a possible ectopic pregnancy at 8 weeks of gestation. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
The nurse should expect the client to have pelvic pain, as this is the most common symptom of an ectopic pregnancy, which occurs when the fertilized ovum implants outside the uterine cavity, usually in the fallopian tube. Pelvic pain can range from mild to severe, and can be unilateral or bilateral, depending on the location and extent of the ectopic pregnancy. Pelvic pain can be caused by tubal distension, rupture, or bleeding.
The other findings are not typical of an ectopic pregnancy and may indicate other conditions.
- Severe nausea and vomiting are not common signs of an ectopic pregnancy, but they may occur in any pregnancy due to hormonal changes or other factors. Severe nausea and vomiting may also indicate hyperemesis gravidarum, which is a condition where nausea and vomiting are so severe that they cause dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and weight loss.
- Copious vaginal bleeding is not a usual sign of an ectopic pregnancy, but it may occur if the ectopic pregnancy ruptures and causes hemorrhage. However, copious vaginal bleeding may also indicate other complications such as placenta previa, placental abruption, or spontaneous abortion.
- Uterine enlargement greater than expected for gestational age is not a sign of an ectopic pregnancy, but it may indicate a multiple gestation, hydatidiform mole, polyhydramnios, or a large fetus. An ectopic pregnancy usually causes uterine enlargement less than expected for gestational age, as the uterus does not contain a viable pregnancy.
A nurse is caring for a client 4 hours postpartum following a vaginal birth. The client has saturated a perineal pad within 10 minutes. Which of the following is the nurse's first action?
Explanation
The nurse's first action should be to massage the client's fundus, as this can help stimulate uterine contraction and prevent hemorrhage. The fundus is the upper part of the uterus that contracts and involutes after delivery to compress the blood vessels and stop bleeding. The nurse should palpate the fundus for firmness, height, and position, and massage it gently if it is boggy or displaced.
The other actions are not the first priority and may be done after massaging the fundus.
The nurse should observe for the pooling of blood under the buttocks, as this can indicate a large amount of blood loss that may not be visible on the perineal pad. However, this is not the first action to take, as it does not address the cause of the bleeding or stop it from continuing.
The nurse should assess the client's blood pressure, as this can indicate the severity of blood loss and the presence of shock. However, blood pressure may not change significantly until a large amount of blood is lost, and it is not specific to the cause of bleeding. Therefore, blood pressure is not the first action to take.
The nurse should prepare to administer a prescribed oxytocic preparation, such as oxytocin or methylergonovine, as this can enhance uterine contraction and reduce bleeding. However, this requires a provider's order and may take time to obtain and administer. Therefore, an oxytocic preparation is not the first action to take.
A nurse is assisting with the care of a client who is experiencing preterm labor and is scheduled to undergo amniocentesis. The client needs an amniocentesis to determine which of the following findings?
No explanation
A nurse is caring for a client in the immediate postoperative period following removal of an ectopic pregnancy via salpingostomy. The nurse should prepare to administer Rho(D) immune globulin (RhoGAM or RhiG) as prescribed if the record indicates that the client
No explanation
A nurse is collecting data from a client who is at 18 weeks of gestation and tells the nurse that she felt light flutering in her stomach the previous day. The nurse should use which of the following terms to document this finding?
No explanation
A nurse in the prenatal clinic is reinforcing teaching to a client who is in her second trimester and has a new diagnosis of gestational diabetes. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching?
No explanation
A nurse is caring for a client who has just learned that she is pregnant. The nurse should reinforce with the client to call her provider if she experiences which of the following manifestations?
No explanation
A nurse in the prenatal clinic is reinforcing teaching to a client who is in her second trimester and has a new diagnosis of gestational diabetes. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
This statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching, as it shows that the client does not understand the importance of regular physical activity for managing gestational diabetes. Physical activity can help lower blood glucose levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and prevent excessive weight gain during pregnancy. The client should aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise on most days of the week, unless contraindicated by medical or obstetric complications.
The other statements by the client indicate that the client understands the key aspects of gestational diabetes management.
"I should limit my carbohydrates to 50% of caloric intake.” This statement is correct, as the client should follow a balanced diet that provides adequate nutrition for herself and her fetus, while controlling blood glucose levels. Carbohydrates are the main source of glucose and should be limited to 50% of caloric intake, distributed evenly throughout the day, and preferably from complex sources such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
"I will take my glyburide daily with breakfast.” This statement is correct, as the client should take her prescribed oral hypoglycemic medication as directed by her provider. Glyburide is a sulfonylurea that stimulates insulin secretion and lowers blood glucose levels. It is usually taken once or twice a day with meals, depending on the dose and blood glucose response.
d. "I know I am at increased risk to develop type 2 diabetes." This statement is correct, as the client should be aware of the long-term implications of gestational diabetes. Gestational diabetes is a condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin during pregnancy, resulting in high blood glucose levels. It usually resolves after delivery, but it increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. The client should monitor her blood glucose levels regularly, maintain a healthy weight, and have screening tests for diabetes every 1 to 3 years.
For problems involving adult patients, the answer will be rounded to the nearest tenth. Although some IV pumps do not allow calibration to the tenth or hundredth, for the purpose of this exam, IV rate calculations will be rounded to the nearest whole drop (gt/min) or to the nearest whole number IV (ml/hr). To promote safety, a zero must be placed to the left of the decimal point in answers that are less than one. No zero is allowed to the right of the decimal point in answers that are whole numbers. For example, 0.5 mg must be answered as 0.5 mg and 5 mg must be answered as 5 mg. A nurse is calculating the protein needs of a client who is a physical trainer. The client weighs 220 lb and requires an increase of protein by 20 g/kg/day. The client has taken 0.8 g of protein/kg/day in the past. How much total protein/day should the nurse recommend? Be sure to enter the number AND the unit of measurement (g). Partial credit will not be given.
Explanation
To calculate the total protein/day that the nurse should recommend, we need to use the following formula:
Total protein/day = (Current protein intake + Increase in protein intake) x Weight in kg
The current protein intake is given as 0.8 g/kg/day, and the increase in protein intake is given as 20 g/kg/day. To convert the weight from pounds to kilograms, we need to divide by 2.2, so 220 lb / 2.2 = 100 kg.
Plugging these values into the formula, we get:
Total protein/day = (0.8 g/kg/day + 20 g/kg/day) x 100 kg Total protein/day = (20.8 g/kg/day) x 100 kg
Total protein/day = 2080 g/day
However, we need to round this answer to the nearest tenth, as per the instructions, so we get:
Total protein/day = 179.6 g of protein/day
Sign Up or Login to view all the 23 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

