ATI Custom SP23 N23 N240 Exam 3 Ch 11 24 32 43 44
Total Questions : 56
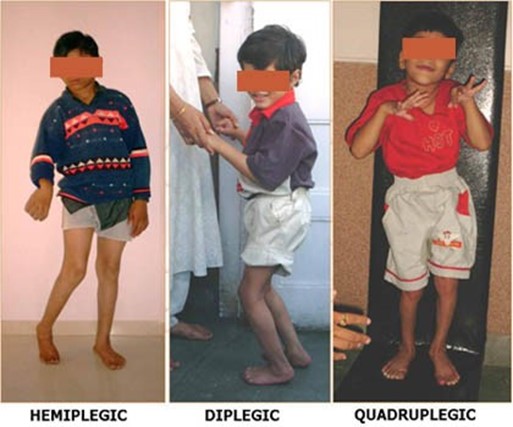
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA home health nurse is developing a plan of care for a child who has hemiplegic cerebral palsy.
Which of the following goals is the priority for the nurse to include in the plan of care?
Explanation
The correct answer is d. Modify the environment.
Rationale for each choice:
Choice a. Improve the client's communication skills.
- Statement:While communication is important,it is not the priority for a child with hemiplegic cerebral palsy.
- Rationale:Hemiplegic cerebral palsy primarily affects motor skills,not communication abilities.While some children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy may have speech difficulties,it is not the most pressing concern in this case.Addressing environmental barriers to promote mobility and independence takes precedence.
Choice b. Provide respite services for the parents.
- Statement:Respite services can provide valuable support for parents,but they are not the priority in this case.
- Rationale:The focus of the care plan should be on the child's immediate needs and safety.Modifying the environment to enhance the child's functional abilities is crucial for their development and well-being.
Choice c. Foster self-care activities.
- Statement:Encouraging self-care is essential,but it requires a supportive environment.
- Rationale:Before promoting self-care activities,the nurse must ensure the child has the necessary accommodations and modifications in place to facilitate independence.
Choice d. Modify the environment.
- Statement:This is the priority goal for a child with hemiplegic cerebral palsy.
- Rationale:Modifying the home environment can significantly improve the child's mobility,safety,and ability to participate in daily activities.Examples of modifications include:
- Installing grab bars in the bathroom
- Widening doorways
- Removing tripping hazards
- Providing adaptive equipment such as special chairs or utensils
- Ensuring adequatelighting
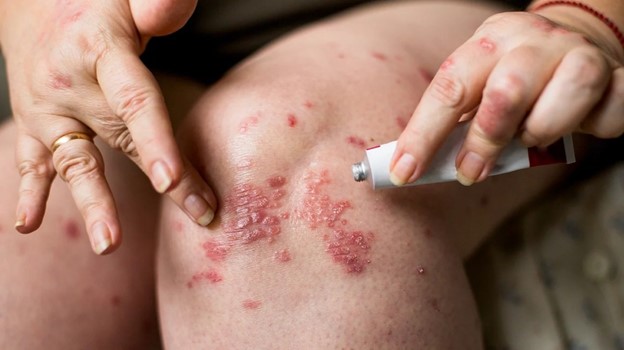
A nurse is providing teaching to a parent of a preschooler who has eczema.
Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Treatment of eczema may start with regular moisturizing and other self-care habits.
If these don’t help, a healthcare provider might suggest medicated creams that control itching and help repair skin.
Choice A is not correct because woolen clothes can irritate the skin and worsen
eczema.
Choice B is not correct because fabric softeners can irritate the skin and worsen
eczema.
Choice C is not correct because bubble baths can dry out the skin and worsen eczema.
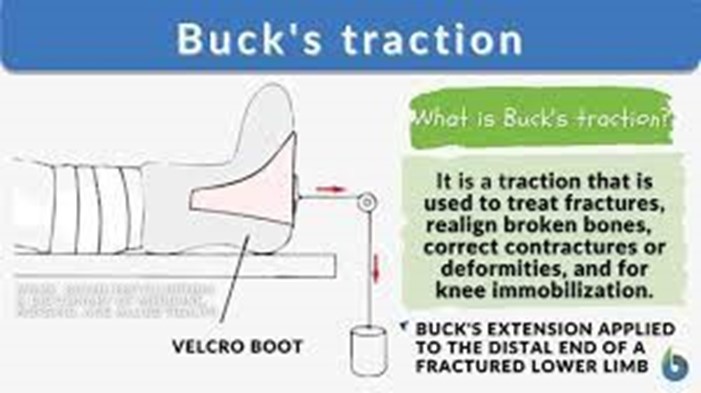
A nurse is caring for a child who has Legg-Calve-Perthes disease and is in Buck extension traction.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
This is because Legg-Calve-Perthes disease involves avascular necrosis of the femoral head, causing deformity and pain.
Buck extension traction is used to maintain hip abduction and to keep the
femoral head in the acetabulum.
Pin sites are used to secure traction, which can introduce the risk of infection.
Therefore, the nurse should apply antibiotic ointment to the pin sites daily to prevent infection.
Choice A, repositioning the child every 2 hours is not the correct answer as the child should remain in the Buck extension traction to maintain proper alignment of the femoral head.
Choice B, removing the traction boot during baths is not the correct answer as the traction should be maintained at all times to prevent further hip dislocation.
Choice C, reducing fluid intake is not the correct answer as it has no correlation with the care of the child who has Legg-Calve-Perthes disease in Buck extension traction.
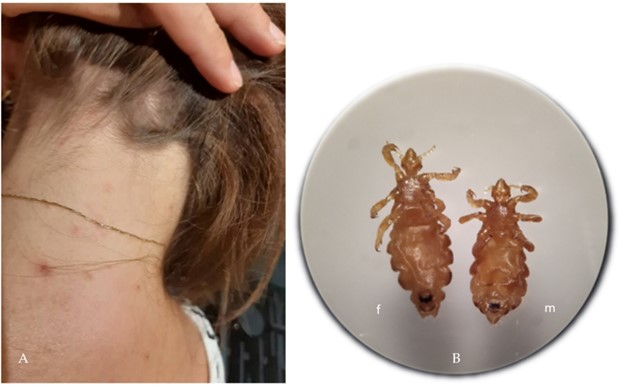
A nurse is providing teaching about lice to the parents of a school-age child at a well-child visit.
Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Head lice are spread most commonly by direct head-to-head (hair-to-hair) contact.
However, much less frequently they are spread by sharing clothing or belongings onto which lice have crawled or nits attached to shed hairs may have fallen.
Choice B is not correct because lice cannot jump from one child to another. Choice C is not correct because live lice survive less than 1-2 days if they fall off a
person and cannot feed.
Choice D is not correct because washing your child’s hair daily will not prevent lice.
A school nurse is assessing a school-age child and notices white flakes that don't brush off the hair and a rash on the back of the child's neck.
The nurse should suspect which of the following disorders?
Explanation
Pediculosis capitis is a condition caused by an infestation of head lice.
The white flakes that don’t brush off the hair are likely to be nits (lice eggs) that are firmly attached to the hair shafts.
The rash on the back of the child’s neck could be a result of an allergic reaction to lice bites.
Choice A, Folliculitis, is an infection of hair follicles that causes small red bumps or white-headed pimples.
Choice B, Tinea capitis, is a fungal infection of the scalp that causes scaly patches
and hair loss.
Choice C, Impetigo contagiosa, is a bacterial skin infection that causes red sores that can break open, ooze fluid, and develop a yellow-brown crust.
A nurse is assessing an 8-month-old infant for cerebral palsy.
Which of the following findings is a manifestation of the condition?
Explanation
A cerebral palsy is a group of disorders that affect movement and muscle tone or posture.
It’s caused by damage that occurs to the immature, developing brain, most often before birth.
Signs and symptoms appear during infancy or preschool years.
In general, cerebral palsy causes impaired movement associated with exaggerated reflexes, floppiness or spasticity of the limbs and trunk, unusual posture, involuntary movements, unsteady walking, or some combination of these.
An 8-month-old infant with cerebral palsy may have developmental delays and may require pillow props to sit up.
Choice A, Tracking an object with eyes, is a normal developmental milestone for
an infant.
Choice C, Uses a pincer grasp to pick up a toy, is also a normal developmental
milestone for an infant.
Choice D, Smiles when a parent appears, is also a normal developmental milestone for an infant.
A nurse is providing teaching to a parent of a child who has a fracture of an epiphyseal plate.
Which of the following statements should the nurse make?
Explanation
An epiphyseal fracture is a fracture that occurs in the epiphyseal plate, which is the layer of cartilage between the end of a long bone and the start of the bone shaft.
This type of fracture is most common in children and adolescents, as their bones are still growing and the epiphyseal plate is not yet fused to the bone shaft.
Because this is where new bone develops, injuries to this area can cause the plate to close prematurely, jeopardizing bone growth.
Choice B, “Bone marrow can be lost through the fracture,” is incorrect because
bone marrow is not lost through an epiphyseal fracture.
Choice C, “The younger the child the longer the healing process will take,” is incorrect because younger children generally heal faster than older children or adults.
Choice D, “The blood supply to the bone is disrupted,” is incorrect because an
epiphyseal fracture does not necessarily disrupt the blood supply to the bone.
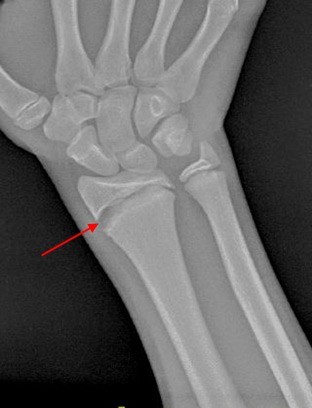
A nurse is caring for a child who has acute glomerulonephritis.
Which of the following actions is the nurse's priority?
Explanation
Nursing care planning goals for a child with acute glomerulonephritis are directed toward the excretion of excess fluid through urination.
Monitoring fluid status is very important and daily weights are an effective way to monitor fluid retention, as weight gain is the earliest sign of fluid retention.
Choice B, Educating the parents about potential complications, is important but not the nurse’s priority.
Choice C, Place the child on a no-salt-added diet, which may be part of the treatment
plan but is not the nurse’s priority.
Choice D, Maintaining a saline lock, may be necessary for administering medications but is not the nurse’s priority.
A nurse is caring for a child who has tinea pedis. The child's parent asks the nurse what this infection is commonly called.
The nurse should respond with which of the following common names?
Explanation
Tinea pedis is a fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet and is commonly known as an athlete’s foot.
Choice A, Shingles, is incorrect because shingles are a viral infection that causes a
painful rash.
Choice B, Valley fever, is incorrect because valley fever is a fungal infection that affects the lungs.
Choice C, Fever blister, is incorrect because fever blisters are caused by the herpes simplex virus and typically appear on or around the lips.
A nurse is assisting with a routine physical examination of an adolescent. The provider observes a lateral curvature of the spine.
The nurse should expect the provider to document which of the following disorders?
Explanation
Scoliosis is a condition characterized by sideways curvature of the spine or backbone.
A lateral curvature of the spine is called scoliosis.
Choice A, Torticollis, is not the correct answer because it is a condition in which the head becomes persistently turned to one side, often associated with painful muscle spasms.
Choice B, Kyphosis, is not the correct answer because it refers to an excessive outward curvature of the spine, causing hunching of the back.
Choice D, Lordosis, is not the correct answer because it refers to an excessive inward curvature of the spine.
A nurse is caring for a 3-year-old child who has had 160 mL of urine output over the past 8-hour period.
The child weighs 33 lb.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Normal urine output for a child is 1-2 ml/kg/hr.
The child weighs 33 lb (15 kg), so their expected urine output over an 8-hour period would be between 120 mL and 240 mL.
The child’s urine output of 160 mL falls within this range.
Choice A, Notifying the provider, is not necessary because the child’s urine output
is within the normal range.
Choice C, Perform a bladder scan at the bedside, is not necessary because there is no indication of urinary retention.
Choice D, Providing oral rehydration fluids, is not necessary because the child’s urine output is within the normal range.
A school nurse is assessing a child for pediculosis capitis. Which of the following manifestations should the nurse recognize as an indication of this condition?
Explanation
Pediculosis capitis, also known as head lice infestation, is a condition in which the head hair and scalp are infected by head lice.
The most common symptom of head lice infestation is itching on the scalp, neck,
and ears due to an allergic reaction to lice bites12.
Choice B, Firmly attached white particles on the hair, refers to nits (lice eggs) which are firmly attached to hair shafts but are not a manifestation of pediculosis capitis.
Choice C, a Thick yellow-crusted lesion on a red base, refers to impetigo, a bacterial skin infection.
Choice D, Patchy areas of hair loss, refers to alopecia areata, an autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss.
A nurse is teaching about neural tube defects to a group of females who are pregnant.
Which of the following disease processes should the nurse include as an example of a neural tube defect?
Explanation
Neural tube defects are birth defects of the brain, spine, or spinal cord that happen in the first month of pregnancy.
Spina bifida is a neural tube defect that affects the spine.
Choice A, Hydrocephalus, is not a neural tube defect but rather a condition where there is an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the brain.
Choice B, Cerebral palsy, is not a neural tube defect but rather a group of disorders that affect movement and muscle tone or posture.
Choice D, Muscular dystrophy, is not a neural tube defect but rather a group of genetic diseases that cause progressive weakness and loss of muscle mass.
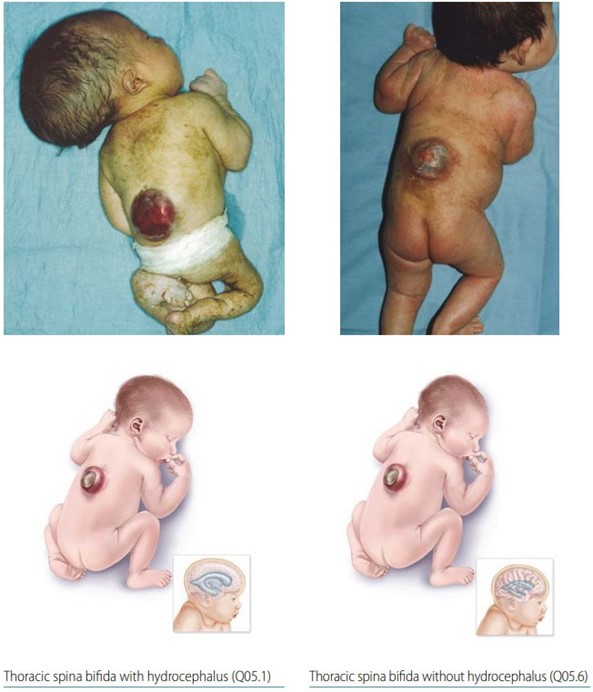
A nurse is caring for an adolescent who has spina bifida and is paralyzed from the waist down. Which of the following statements by the client should indicate to the nurse a need for further teaching?
Explanation
Individuals with spina bifida who are paralyzed from the waist down may have difficulty emptying their bladder completely and may need to perform intermittent catheterization.
The frequency of catheterization can vary depending on the individual’s needs, but it is typically performed every 3-6 hours or 4-6 times per day.
Choice A, “I do wheelchair exercises while watching TV,” is a positive statement because exercise is important for overall health and well-being.
Choice B, “I carry a water bottle with me because I drink a lot of water,” is also a positive statement because staying hydrated is important for overall health.
Choice C, “I use a suppository every night to have a bowel movement,” is not necessarily an indication for further teaching because some individuals with spinal bifida may need to use bowel management techniques such as suppositories to help regulate bowel movements.
A nurse reports an incident of suspected child abuse. One of the parents of the child becomes upset and demands to know the reason
for the nurse's action.
Which of the following responses by the nurse is appropriate?
Explanation
This response is appropriate because it informs the parent that the nurse has a legal obligation to report any suspected child abuse.
Choice A is not an answer because it does not address the parent’s concern and instead defers responsibility to the provider.
Choice C is not an answer because it does not provide any information to the parent and instead suggests contacting a supervisor.
Choice D is not an answer because it implies that the decision to report the incident was made by the supervisor and not the nurse.
A nurse is assessing a toddler who has suspected lead poisoning.
Which of the following findings should the nurse expect the client to manifest with acute lead poisoning?
Explanation
Acute lead poisoning in toddlers can cause anorexia, as well as vomiting, abdominal pain, and constipation.
These symptoms can progress to seizures, coma, and even death if not treated promptly.
Choice A, increased urinary output, is not the correct answer because lead poisoning can cause a decrease in urinary output due to the effect of lead on the kidneys.
Choice C, diarrhea, is not the correct answer because lead poisoning is more likely to cause constipation than diarrhea.
Choice D, jaundice, is not the correct answer because jaundice is not a common finding in lead poisoning.
Jaundice is a yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes caused by an excess of bilirubin in the blood, which is not directly related to lead poisoning.
A nurse is providing care to a mother immediately following a stillbirth delivery.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
The nurse should first offer the mother's private time with the newborn to allow her to grieve and say goodbye.
This can be an important part of the healing process for the mother.
Choice A is not an answer because contacting clergy is not the first action the nurse should take.
Choice B is not an answer because transferring the client to another unit is not the first action the nurse should take.
Choice C is not an answer because administering medication is not the first action the nurse should take.
A nurse is caring for a newborn whose mother voices concerns about sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). The nurse should include which of the following statements in a discussion with the mother?
Explanation
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that infants be placed on their backs to sleep to reduce the risk of SIDS1.
Choice A is not an answer because there is no direct correlation between SIDS and diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis vaccines
A nurse is assessing a child and notes several bruises. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that infants be placed on their backs to sleep to reduce the risk of SIDS1.
Choice A is not an answer because there is no direct correlation between SIDS and diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis vaccines.
Choice B is not an answer because sleep apnea is not the main cause of SIDS.
Choice D is not an answer because SIDS rates have not been rising over the last 10 years.
A nurse is caring for an infant in a provider's office.
Medical History Provider Visit #1. Heart rate 144/min.
Axillary temperature 39.7° C (103.5°F). Respiratory rate 32/min.
Oxygen saturation 95% on room air. Provider Visit #2 (4 days later).
Axillary temperature 37.4° C (99.3° F). Heart rate 132/min.
Respiratory rate 28/min.
Oxygen saturation 97% on room air.
Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take? Select the 3 actions the nurse should plan to take.
Explanation
Choice C, cleanse diaper area with soap and water, is important to maintain hygiene and prevent diaper rash. This should be done at each diaper change.
Choice E, instruct caregivers to apply zinc oxide with each diaper change, is important to prevent diaper rash and promote healing if a rash is present.
Choice D, collect nasal drainage for culture and sensi vity, is important to determine if there is a bacterial infec on present, which could explain theinfant's high fever during the first provider visit.
Choice A, teach caregivers to change diaper when wet, is not necessary as it is already expected that caregivers will change the diaper when wet.
Choice B, have caregivers administer 16 oz of water a er each diarrhea stool, is not necessary as there is no indica on of diarrhea in the scenario.
Choice F, teach caregivers to apply talcum powder to creases, is not necessary as talcum powder has been associated with respiratory problems in infants and should not be used.
Choice G, use a nasal aspirator a er feedings, is not necessary as there is no indica on of nasal conges on in the scenario.
A nurse is caring for an infant in a provider's office. Medical History Diagnosis: Nurse's Notes Upper respiratory infection Provider prescriptions: Vital Signs • Amoxicillin and clavulanate suspension 225 mg PO twice daily for 10 days Ibuprofen liquid 50 mg PO every 6 to 8 hr, maximum 4 times daily, to treat fever Which of the following actions should the nurse take next to provide appropriate care for the infant?
Explanation
Contact the provider to clarify the dosage and frequency of medication administration.
The nurse should always verify the dosage and frequency of medication administration with the provider before administering any medication to ensure the safety and well-being of the infant.
Choice A is not an answer because the nurse should verify the dosage and frequency with the provider before administering any medication.
Choice B is not an answer because the nurse should verify the dosage and frequency with the provider before administering any medication.
Choice C is not an answer because waiting and monitoring the infant’s symptoms does not address the need to verify the dosage and frequency of medication administration with the provider.
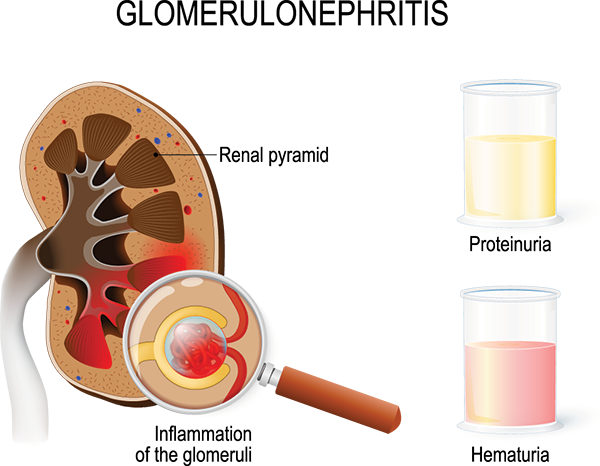
A nurse is caring for a school-age child who has acute glomerulonephritis with peripheral edema and is producing 35 mL of urine per hour.
The nurse should place the client on which of the following diets?
Explanation
The nurse should place the client on a low-sodium, fluid-restricted diet.
Acute glomerulonephritis is a kidney disease that can cause fluid retention and edema.
A low-sodium diet can help reduce fluid retention and swelling.
Fluid restriction can also help manage fluid balance and prevent further complications.
Choice B is not the best answer because a regular diet with no added salt may still contain high levels of sodium.
Choice C is not the best answer because a low-protein, low-potassium diet may not address the client’s fluid retention and edema.
Choice D is not the best answer because a low-carbohydrate, low-protein diet may not provide adequate nutrition for the client.
A nurse is planning care for an infant who has spina bifida and is to undergo surgical closure of the myelomeningocele sac. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care?
Explanation
Infants with spina bifida are at an increased risk of developing a latex allergy
due to repeated exposure to latex products during medical procedures.
Providing a latex-free environment can help prevent the development of an allergy.
Choice A is not correct because limiting visitors to immediate family members is not necessary for the care of an infant undergoing surgical closure of the myelomeningocele sac.
Choice B is not correct because maintaining the infant in the supine position is not necessary for this procedure.
Choice D is not correct because initiating contact precautions is not necessary for this procedure.
A nurse is caring for a preschool-age child who is dying.
Which of the following findings is an age-appropriate reaction to death by the
child? (Select all that apply).
Explanation
Preschool-age children often have a limited understanding of death and may believe that their thoughts can cause death.
They may also view death as similar to sleep 1 and may think that death is a punishment.
Choice A is not correct because preschool-age children may not necessarily be interested in what happens to the body after death.
Choice C is not correct because preschool-age children usually do not recognize that death is permanent.
A nurse is providing teaching to a 17-year-old female client who has severe acne about the use of isotretinoin.
Which of the following adverse effects should the nurse instruct the client is the priority to report to the provider?
Explanation
Isotretinoin has been associated with depression and other psychiatric side effects.
The client should report any changes in mood or behavior, including feelings of isolation, to the provider immediately.
Choice B is not an answer because while frequent nosebleeds can be a side
effect of isotretinoin, it is not the priority to report to the provider.
Choice C is not an answer because while back pain can be a side effect of isotretinoin, it is not the priority to report to the provider.
Choice D is not an answer because while itching of the skin can be a side effect of isotretinoin, it is not the priority to report to the provider.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 56 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

