Ati Dosage Calculations RN Fundamentals
Total Questions : 29
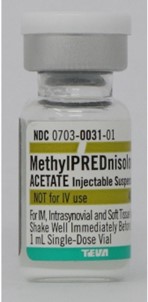
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is preparing to administer methylprednisolone acetate 60 mg IM weekly. Methylprednisolone acetate suspension for injection 80 mg/mL is available. How many mL should the nurse administer per dose? Round the answer to the nearest hundredth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.
Explanation
The correct answer and explanation is:
0.75 mL.
To calculate the mL needed, divide the dose (60 mg) by the concentration (80 mg/mL): 60 mg ÷ 80 mg/mL = 0.75 mL
Therefore, the correct answer is 0.75 mL.
A nurse is preparing to administer quinapril 20 mg PO. Quinapril 40 mg tablets are available. How many tablets should the nurse administer? Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.
Explanation
To calculate the number of tablets to be administered, the nurse should divide the prescribed dose (20 mg) by the strength of the available medication (40 mg/tablet): 20 mg / 40 mg/tablet = 0.5 tablets.

A nurse is preparing to administer lidocaine 200 mg IM stat and repeat in 60 min. Lidocaine injection 300 mg/3 mL is available. How many mL should the nurse administer per dose? Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.
Explanation
To calculate the volume to be administered, the nurse should divide the prescribed dose (200 mg) by the
concentration of the available medication (300 mg/3 mL): 200 mg / (300 mg/3 mL) = 2 mL.

A nurse is preparing to administer furosemide 20 mg PO to a client. How should the nurse expect the medication to appear? Refer to the medication label options below to answer the question.

Explanation
As a round, white tablet with "EP116" stamped on one side of the tablet.
This is because the medication label indicates that the tablets contain furosemide USP 20 mg and are white, square tablets.
A nurse is preparing to administer nifedipine 20 mg PO three times a day. Available is nifedipine 10 mg capsules. How many capsules should the nurse administer per dose? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
To calculate the number of capsules to be administered, the nurse should divide the prescribed dose (20 mg) by the strength of the available medication (10 mg/capsule): 20 mg / 10 mg/capsule = 2 capsules.

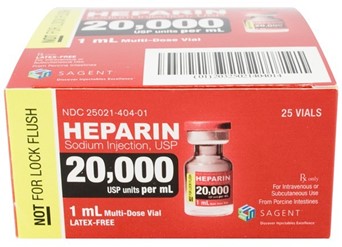
A nurse is preparing to administer heparin 10,000 units subcutaneously every 8 hours. The available heparin injection is 20,000 units/mL. How many milliliters should the nurse administer per dose? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
To calculate the required mL of heparin injection per dose, we need to use the following formula: mL = (units per dose) ÷ (units per mL)
Substituting the given values in the formula, we get:
mL = (10,000 units) ÷ (20,000 units/mL) mL = 0.5 mL
A nurse is reinforcing teaching with a parent of an infant who has a prescription for amoxicillin 100 mg PO every 8 hours. The available amoxicillin suspension is 200 mg/5 mL. The nurse should tell the parent to administer how many teaspoons per dose? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
To calculate the required teaspoons (tsp) of amoxicillin suspension per dose, we need to use the following
formula:
tsp = (dose in mg) ÷ (concentration in mg/mL) ÷ 5 mL per tsp Substituting the given values in the formula, we get:
tsp = (100 mg) ÷ (200 mg/5 mL) ÷ 5 mL per tsp
tsp = 0.5 tsp
A nurse is reviewing a new prescription for alendronate 70 mg PO once per week upon waking to be taken 30 min before food, fluids, or medication with a client who has osteoporosis. The client is to remain upright for 30 min after administration. How should the nurse interpret this prescription for the client?
Explanation
c) Choose the same day of each week to take this medication.
The nurse should interpret the prescription for alendronate 70 mg PO once per week upon waking to be taken 30 min before food, fluids, or medication with a client who has osteoporosis as instructing the client to choose the same day of each week to take the medication. This will help to ensure that the medication is taken consistently and at the appropriate time.
Taking the medication at 1800, 30 min after the evening meal (option A) is not consistent with the prescription, which specifies that the medication should be taken upon waking and before food, fluids, or other medications. Over-the-counter oral preparations can be taken with this medication (option B) is not accurate; the prescription specifies that alendronate should be taken 30 min before other medications. The client can return to bed after taking the medication, but before eating (option D) is not consistent with the prescription, which specifies that the client should remain upright for 30 min after administration.

|
The correct answer is c. Choose the same day of each week to take this medication. Rationale for each choice: Choice a. Take the medication at 1800, 30 min after the evening meal. is incorrect.
Choice b. Over-the-counter oral preparations can be taken with this medication. is incorrect.
Choice d. The client can return to bed after taking the medication, but before eating. is incorrect.
Choice c. Choose the same day of each week to take this medication. is the correct interpretation of the prescription.
|
|
A nurse is reinforcing teaching with a parent of an infant who has a prescription for amoxicillin 100 mg PO every 8 hours. The available amoxicillin suspension is 200 mg/5 mL. The nurse should tell the parent to administer how many teaspoons per dose? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
To calculate the volume to be administered, the nurse should first divide the prescribed dose (100 mg) by the concentration of the available medication (200 mg/5 mL): 100 mg / (200 mg/5 mL) = 2.5 mL. Since there are 5 mL in a teaspoon, the parent should administer 2.5 mL / 5 mL/teaspoon = 0.5 teaspoons per dose.
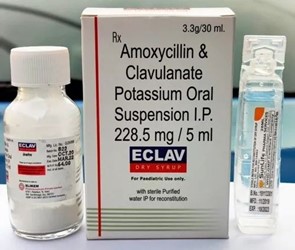
A nurse is preparing to reconstitute amoxicillin/clavulanate oral suspension for a client. According to the medication label, what will the total volume of medication in the container be following reconstitution? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
The correct answer and explanation is:
Explanation
According to the medication label, the total volume of medication in the container following reconstitution will be 75 mL.
The label states that when reconstituted, the total volume of the medication will be 75 mL.
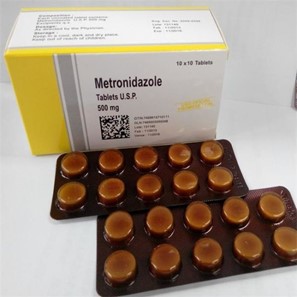
A nurse is preparing to administer metronidazole 7.5 mg/kg PO to a client who weighs 146.7 lb. Available is metronidazole 500 mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
The first step is to convert the client's weight from pounds (lb) to kilograms (kg).
146.7 lb ÷ 2.2 lb/kg = 66.68 kg
Next, the nurse should calculate the total dose of metronidazole the client needs.
7.5 mg/kg x 66.68 kg = 500.1 mg
Since the available tablets are 500 mg each, the nurse should administer:
500.1 mg ÷ 500 mg/tablet = 1 tablet (rounded to the nearest whole number)
A nurse is preparing to administer valproic acid 125 mg PO. Available is valproic acid syrup 250 mg/5 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
To determine how many mL of valproic acid syrup the nurse should administer, we need to use a ratio and proportion:
250 mg : 5 mL = 125 mg : x mL Cross-multiplying, we get:
250 mg x x mL = 5 mL x 125 mg Simplifying, we get:
x = (5 mL x 125 mg) / 250 mg x = 2.5 mL
A nurse is converting a medication dose from g to mcg. The amount available is 5g. The nurse should recognize that this amount is equal to how many mcg? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
To convert grams (g) to micrograms (mcg), we need to multiply the number of grams by 1,000,000 (because
there are 1,000,000 mcg in 1 g):
5 g x 1,000,000 mcg/g = 5,000,000 mcg
A nurse is preparing to administer filgrastim 480 mcg subcutaneously daily. Filgrastim injection 300 mcg/mL is available. How many mL should the nurse administer per dose? Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero."
Explanation
To calculate the number of mL the nurse should administer per dose, you need to divide the dose of filgrastim in mcg by the concentration of the filgrastim injection in mcg/mL.
480 mcg ÷ 300 mcg/mL = 1.6 mL
So, the nurse should administer 1.6 mL of filgrastim injection per dose.
A nurse is assisting an assistive personnel to document a client's weight in the medical record. Which of the following should the nurse identify as a metric unit?
Explanation
The nurse should identify **Kilogram** as a metric unit. The other units listed - Pound, Minim, and Ounce - are not metric units.
A nurse is preparing to administer diphenhydramine 1.25 mg/kg IM to a child who weighs 68 lb. Available is diphenhydramine injection 50 mg/mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
First, the child's weight needs to be converted from pounds to kilograms. There are approximately 2.2 pounds in 1 kilogram.
68 lb ÷ 2.2 = 30.9 kg
Next, the dose of diphenhydramine in mg can be calculated by multiplying the child's weight in kg by the dose in mg/kg.
1.25 mg/kg × 30.9 kg = 38.6 mg
Finally, to calculate the number of mL the nurse should administer, you need to divide the dose of diphenhydramine in mg by the concentration of the diphenhydramine injection in mg/mL.
38.6 mg ÷ 50 mg/mL = 0.8 mL
So, the nurse should administer 0.8 mL of diphenhydramine injection.
A nurse is preparing to administer bumetanide 1.5 mg PO daily. Available is bumetanide 0.5 mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
We need to calculate how many 0.5 mg tablets are needed to achieve a daily dose of 1.5 mg:
1.5 mg ÷ 0.5 mg/tablet = 3 tablets
Since we are asked to round to the nearest whole number, the final answer is 3 tablets.

A nurse is preparing to administer diclofenac sodium 200 mg PO daily in equally divided doses every 6 hours. How many mg should the nurse administer per dose? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
If the daily dose is 200 mg and it is to be given in equally divided doses every 6 hours, then we need to
calculate the amount per dose:
200 mg ÷ 4 doses = 50 mg per dose
A nurse is preparing to administer cyanocobalamin 100 mcg IM monthly. Available is cyanocobalamin injection 1,000 mcg/mL. How many mL should the nurse administer per dose? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
We need to calculate the volume of the cyanocobalamin injection that contains 100 mcg of the drug: 100 mcg ÷ 1,000 mcg/mL = 0.1 mL
Therefore, the nurse should administer 0.1 mL of cyanocobalamin injection per dose.
A nurse is preparing to administer duloxetine 120 mg PO once daily to a client. Available is duloxetine 40 mg capsules. How many capsules should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
If each capsule contains 40 mg of duloxetine, then we need to calculate how many capsules are required to
make up the daily dose of 120 mg:
120 mg ÷ 40 mg/capsule = 3 capsules
Therefore, the nurse should administer 3 capsules of duloxetine per dose.
A nurse is preparing to administer vancomycin 500 mg via intermitent IV bolus to a client. Available is vancomycin powder for injection 1 g vial. The nurse reconstitutes the powder for a final concentration of vancomycin 5 mg/mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
First, we need to determine how many milligrams of vancomycin are in each milliliter of the reconstituted solution:
1 g = 1,000 mg
If we reconstitute 1 g of vancomycin powder for injection in enough diluent to make a final volume of 200 mL, the concentration will be:
1,000 mg ÷ 200 mL = 5 mg/mL
Now, we can calculate how many milliliters of the reconstituted solution the nurse should administer to deliver 500 mg of vancomycin:
500 mg ÷ 5 mg/mL = 100 mL
Therefore, the nurse should administer 100 mL of the reconstituted vancomycin solution via intermitent IV
bolus.
A nurse is preparing to administer isoniazid 187 mg IM. Available is isoniazid injection 100 mg/mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
To calculate the number of mL the nurse should administer, you need to divide the dose of isoniazid (187 mg) by the concentration of the isoniazid injection (100 mg/mL). This gives you 187 mg / (100 mg/mL) =
1.87 mL. When rounded to the nearest tenth, this becomes 1.9 mL. So, the nurse should administer 1.9 mL of isoniazid injection.

A nurse is preparing to administer gentamicin 1 mg/kg IM to a client who weighs 154 lb. Available is gentamicin solution 40 mg/mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
First, we need to calculate the dose of gentamicin for the client based on their weight. The formula to calculate the dose is:
Dose (mg) = Weight (lb) × Dose (mg/kg)
Substituting the values given in the question, we get:
Dose (mg) = 154 lb × 1 mg/kg = 154 mg
Next, we need to determine the volume of gentamicin solution that contains 154 mg. We can use the
following formula:
Volume (mL) = Dose (mg) ÷ Concentration (mg/mL) Substituting the values given in the question, we get:
Volume (mL) = 154 mg ÷ 40 mg/mL = 3.85 mL
Rounding this value to the nearest tenth and using a leading zero as instructed, we get: The nurse should administer 3.9 mL of gentamicin solution.
A nurse is preparing to administer morphine 0.2 mg/kg IM to a client who weighs 99 lb. Available is morphine injection 10 mg/mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
First, you need to convert the client's weight from pounds to kilograms. There are approximately 2.2 pounds in 1 kilogram, so 99 lb / 2.2 = 45 kg. The dose of morphine is 0.2 mg/kg, so for a client who weighs 45 kg, the dose would be 0.2 mg/kg * 45 kg = 9 mg. To calculate the number of mL the nurse should administer, you need to divide the dose of morphine (9 mg) by the concentration of the morphine injection (10 mg/mL). This gives you 9 mg / (10 mg/mL) = 0.9 mL. When rounded to the nearest tenth, this remains
0.9 mL. So, the nurse should administer 0.9 mL of morphine injection.
A nurse is talking with the parent of a child who has asthma and a new prescription for albuterol inhalation aerosol 8.5 g, inhale 1 to 2 puffs orally every 4 to 6 hr as needed for asthma. The nurse interprets this medication as which of the following types of prescription?
Explanation
The prescription for albuterol inhalation aerosol 8.5 g, inhale 1 to 2 puffs orally every 4 to 6 hr as needed for asthma is a PRN prescription. PRN stands for "pro re nata," which means "as needed" in Latin. This type of prescription allows the patient to take the medication as needed for a specific condition or symptom, rather than on a regular schedule.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 29 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

