ATI_Fundamental_of_nursing_exam_2Custom_NS_117_T_Winter_2023_Monroe
Total Questions : 43
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is providing care for an elderly patient who is experiencing constipation.
What action should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Requesting a prescription for a stool softener from the provider could be a potential solution, but it’s not the first step. Medications should be considered when lifestyle modifications and dietary changes are not effective.
Choice B rationale:
Incorporating more fluids and fiber into the patient’s diet is the most appropriate action. Constipation in older adults can be caused by dehydration and not eating enough. Dietary fiber adds bulk to the diet and is capable of absorbing water, which helps to soften the stool and promote regular bowel movements. Therefore, increasing fluid and fiber intake is often the first step in managing constipation.
Choice C rationale:
Encouraging the patient to engage in active range-of-motion exercises might not directly alleviate constipation. While physical activity is generally beneficial for overall health, increased exercise does not improve symptoms of constipation in nursing home residents or older adults.
Choice D rationale:
Advising the patient to avoid foods that cause gas might help if the patient has bloating or gas, but it won’t necessarily address the issue of constipation. The focus should be on increasing fiber and fluid intake.
A nurse is gathering data on a patient who is suffering from circulatory overload.
What symptoms should the nurse anticipate?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Circulatory overload, also known as hypervolemia or fluid overload, is a condition where the body has too much fluid. This excess fluid, especially in the circulatory system, can lead to a rapid heartbeat. This is because the heart needs to work harder to pump the increased volume of blood, leading to an increased heart rate.
Choice B rationale:
Weight loss is not typically associated with circulatory overload. In fact, quick weight gain might be observed due to the excess fluid in the body.
Choice C rationale:
Low blood pressure is not a common symptom of circulatory overload. On the contrary, high blood pressure can occur because the excess fluid in the circulatory system puts more pressure on the blood vessel walls.
Choice D rationale:
Excessive sweating is not a direct symptom of circulatory overload. However, symptoms such as shortness of breath and swelling in certain areas of the body are more common.
A nurse is collecting data on a patient who is experiencing oxygen toxicity.
What symptoms should the nurse anticipate?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Muscle twitching is a symptom of oxygen toxicity. Oxygen toxicity is a condition resulting from the harmful effects of breathing molecular oxygen (O2) at increased partial pressures. Severe cases can result in cell damage and death, with effects most often seen in the central nervous system, lungs, and eyes. Central nervous system symptoms can include muscle twitching.
Choice B rationale:
Redness of the face is not typically associated with oxygen toxicity. Oxygen toxicity primarily affects the central nervous system, lungs, and eyes. It does not typically cause redness of the face.
Choice C rationale:
Swelling around the eyes is not a common symptom of oxygen toxicity. The primary effects of oxygen toxicity are seen in the central nervous system, lungs, and eyes. However, this does not typically manifest as swelling around the eyes.
Choice D rationale:
A metallic taste in the mouth is not a known symptom of oxygen toxicity. Oxygen toxicity is a condition that results from the harmful effects of breathing molecular oxygen (O2) at increased partial pressures. It primarily affects the central nervous system, lungs, and eyes, but a metallic taste in the mouth is not a recognized symptom.
A nurse is implementing a bladder-training program for a patient.
Which of the following actions by the assistive personnel (AP) assisting with the patient’s care should the nurse intervene?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Assisting the patient to the bathroom every 2 hours is a common practice in bladder training programs. This regular schedule helps the patient gradually regain control over their bladder function.
Choice B rationale:
Offering the patient the opportunity to urinate 15 minutes before bathing is also a standard practice. This action is not only convenient but also helps prevent any potential accidents during bathing.
Choice C rationale:
Instructing the patient to urinate whenever they feel the urge is counterproductive to a bladder training program. The goal of bladder training is to help the patient regain control over their bladder and urinate on a set schedule, not whenever the urge occurs. Therefore, this action by the AP indicates a need for further instruction.
Please note that while these rationales provide a general understanding, the specifics may vary depending on the patient’s individual health condition and needs. Always consult with a healthcare professional for accurate information.
A nurse is caring for a patient who is experiencing nausea and vomiting.
The nurse should identify that the patient is at risk for which of the following acid-base imbalances?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Metabolic alkalosis can occur in clients who have excessive vomiting because of the loss of hydrochloric acid. When a person vomits, they lose hydrochloric acid, and the loss of this acid can cause the blood to become more basic. This shift in pH can lead to metabolic alkalosis, a condition characterized by high levels of bicarbonate in the blood, which makes it more alkaline (or less acidic). Symptoms of metabolic alkalosis can include muscle twitching, hand tremor, nausea or vomiting, and tingling in the face, hands or feet. In severe cases, it can cause prolonged muscle contractions or seizures.
Choice B rationale:
Respiratory acidosis is a condition that occurs when the lungs can’t remove enough carbon dioxide (CO2) from the body, which causes the body’s fluids, especially the blood, to become too acidic. This can occur due to conditions that affect the lungs such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, or sleep apnea. However, in the case of a patient experiencing nausea and vomiting, respiratory acidosis is less likely to be the primary concern.
Choice C rationale:
Metabolic acidosis occurs when the body produces too much acid, or when the kidneys aren’t removing enough acid from the body. This can be caused by conditions such as kidney disease, lactic acidosis, or ketoacidosis. In the case of a patient experiencing nausea and vomiting, the primary concern would not typically be metabolic acidosis, as vomiting leads to a loss of stomach acid, which would more likely result in a state of alkalosis, not acidosis.
Choice D rationale:
Respiratory alkalosis is a condition that occurs when you breathe too fast or too deep and carbon dioxide levels drop too low. This causes the pH of the blood to rise and become too alkaline. When the blood is too alkaline, it means that it is not carrying enough carbon dioxide. This condition can be caused by fever, hyperventilation, or lack of oxygen. In the case of a patient experiencing nausea and vomiting, respiratory alkalosis is not typically the primary concern.
A nurse is educating a patient who has an ileal conduit due to bladder cancer.
Which statement from the patient suggests that further instruction is needed?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
The patient does not need to catheterize the stoma multiple times a day. An ileal conduit is a type of urostomy where a small piece of the intestine, called the ileum, is used to create a new passage for urine to leave the body. One end of the ileum is attached to the ureters, and the other end is attached to a small opening in the abdomen, known as a stoma. After the surgery, urine flows from the kidneys, through the ureters and ileal conduit, and out of the stoma. The patient will wear a urostomy pouching system over the stoma to catch and hold the urine. Therefore, the statement “I need to catheterize the stoma multiple times a day” suggests that further instruction is needed because it is not accurate.
Choice B rationale:
The statement “I will need to measure my stoma each week” does not necessarily suggest that further instruction is needed. It is important for patients with an ileal conduit to monitor their stoma regularly for any changes in size, shape, or color, which could indicate complications. However, the frequency of these checks can vary depending on the individual’s condition and the healthcare provider’s instructions.
Choice C rationale:
The statement “I will always have to wear a pouch” is accurate. After the surgery, the patient’s urine will flow from the kidneys, through the ureters and ileal conduit, and out of the stoma. The patient will need to wear a urostomy pouching system over the stoma to catch and hold the urine. Therefore, this statement does not suggest that further instruction is needed.
Choice D rationale:
The statement “I need to clean around the stoma with soap and water” is accurate. It is important for patients with an ileal conduit to keep the skin around the stoma clean to prevent infection and skin irritation. Therefore, this statement does not suggest that further instruction is needed.
A nurse is assessing a patient with respiratory acidosis.
What symptoms should the nurse anticipate?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Numbness in the fingers is not typically a symptom of respiratory acidosis. This condition is characterized by an excess of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the body, which leads to a decrease in the pH of your blood, making it too acidic. Numbness in the fingers could be a symptom of other conditions, such as peripheral neuropathy or Raynaud’s disease.
Choice B rationale:
Abdominal pain is also not a common symptom of respiratory acidosis. While abdominal discomfort can occur in a variety of conditions, it is not directly associated with the acid-base balance disturbance that characterizes respiratory acidosis.
Conditions that commonly cause abdominal pain include gastrointestinal issues like gastritis, appendicitis, or gallstones.
Choice C rationale:
Dry skin is not a symptom of respiratory acidosis. The skin’s condition can be influenced by many factors, including hydration, environmental conditions, and certain skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis. Respiratory acidosis, on the other hand, is a condition that affects the acid-base balance in the body due to alveolar hypoventilation.
Choice D rationale:
Lethargy is indeed a symptom of respiratory acidosis. This condition occurs when the lungs can’t remove enough CO2, leading to an increase in the acidity of the blood. Symptoms of respiratory acidosis vary according to how long you’ve had the condition and its severity. Initial symptoms can include anxiety, blurred vision, and shortness of breath. If left untreated or in severe cases, symptoms may include fatigue, lethargy, delirium, or confusion. Therefore, a nurse assessing a patient with respiratory acidosis should anticipate lethargy among other symptoms.
A nurse is providing dietary advice to a patient at risk for hypokalemia.
Which food should the nurse recommend as a good source of potassium?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Spinach is one of the most nutrient-dense vegetables. Just 1 cup (190 grams) of frozen spinach packs 12% of the DV for potassium. It’s also loaded with other nutrients. The same serving of frozen spinach contains 127% of the DV for vitamin A, 857% for vitamin K, 58% for folate, and 37% for magnesium.
Choice B rationale:
Potatoes are a staple food and are high in potassium. They are a versatile and filling food that can be included in a variety of dishes. Potatoes are also a good source of vitamin C and dietary fiber.
Choice C rationale:
Bananas are known as potassium-rich foods. A medium banana contains around 9% of the DV for this mineral. Most people consider it the go-to food to increase their potassium intake. However, bananas are not the only good source of potassium.
Choice D rationale:
Apples are a healthy choice and provide some potassium, but they are not as high in potassium as the other choices. Therefore, while apples are a good part of a balanced diet, they would not be the first recommendation for someone needing to increase their potassium intake.
A nurse is preparing to insert an indwelling urinary catheter for a patient.
What actions should the nurse plan to take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Donning sterile gloves before inserting the indwelling urinary catheter is a standard practice in healthcare to prevent infection. The urinary tract is normally sterile, and the use of sterile gloves helps maintain this sterility during the catheter insertion process. Choice B rationale:
Oil-based lubricants should not be used with indwelling urinary catheters. These lubricants can damage the catheter material and increase the risk of infection. Instead, water-soluble lubricants are recommended as they do not damage the catheter and can reduce patient discomfort during the insertion process.
Choice C rationale:
Testing the balloon on the indwelling urinary catheter before insertion is a critical step. This is done to ensure that the balloon inflates and deflates properly. If the balloon does not function correctly, it could cause discomfort or injury to the patient during insertion and could fail to keep the catheter in place once inserted.
Choice D rationale:
Cleaning the patient’s urinary meatus with one cotton swab is a part of the standard procedure before inserting an indwelling urinary catheter. This step is taken to remove any bacteria present at the site of insertion, thereby reducing the risk of introducing bacteria into the bladder during the catheter insertion.
A nurse is preparing to insert an indwelling urinary catheter for a patient.
What actions should the nurse plan to take?
Explanation
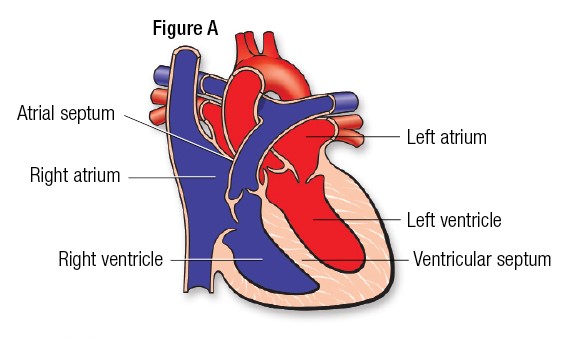
Choice A rationale:
The right ventricle is the correct answer because it is the chamber of the heart that pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs. The blood first enters the right atrium from the superior and inferior vena cava. It then flows through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. The blood then moves through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery.
Choice B rationale:
The pulmonary artery is not the correct answer because it is the vessel that carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs, not a location in the heart.
Choice C rationale:
The pulmonary veins are not the correct answer because they carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart. They do not carry blood from the heart to the lungs.
Choice D rationale:
The left ventricle is not the correct answer because it pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body through the aorta, not to the lungs.
A nurse is in the process of collecting a urine specimen for culture and sensitivity through straight catheterization.
Which step should the nurse take in this procedure?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Collecting urine from the catheter’s port is not the correct procedure when collecting a urine specimen for culture and sensitivity through straight catheterization. The port is not a sterile environment and could contaminate the specimen, leading to inaccurate results.
Choice B rationale:
Using a sterile specimen container is the correct procedure. This ensures that the specimen is not contaminated by any external bacteria or substances, which could affect the results of the culture and sensitivity test. The container must be sterile to prevent the growth of microbes that are not present in the urine sample. This helps to ensure that the results of the culture are accurate and reflect the microbes present in the urine, not those introduced during collection.
Choice C rationale:
Inflating the balloon with sterile water is not a step in this procedure. The balloon is part of an indwelling catheter, not a straight catheter. An indwelling catheter remains in the bladder for a longer period, and the balloon is inflated to keep it in place. A straight catheter is used for a single voiding or to obtain a sterile urine specimen.
Choice D rationale:
Instructing the patient to clean from front to back with an antiseptic solution is not a step in this procedure. While maintaining cleanliness is important, this specific instruction is more relevant to a clean-catch midstream urine specimen, not a specimen collected through straight catheterization.
A nurse is helping to implement a bowel training program for a patient.
To ensure the effectiveness of the program, when should the nurse take the patient to the bathroom?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Taking the patient to the bathroom every 2 hours while the patient is awake is not the most effective strategy for a bowel training program. This approach does not take into account the natural rhythms of the body and the patient’s personal comfort. It may lead to unnecessary trips to the bathroom, which can be physically and emotionally draining for the patient.
Choice B rationale:
This is the correct answer. A bowel training program aims to help the patient regain control over their bowel movements. Taking the patient to the bathroom when they have the urge to defecate aligns with this goal. It allows the patient to respond to their body’s signals, which can help improve their confidence and independence over time.
Choice C rationale:
Taking the patient to the bathroom immediately before meals is not the most effective strategy for a bowel training program. While it’s true that eating can stimulate bowel movements due to the gastrocolic reflex, this approach does not consider the patient’s comfort or individual needs. It may also disrupt the patient’s enjoyment of their meals.
Choice D rationale:
Waiting until the patient feels abdominal cramping is not the most effective strategy for a bowel training program. Abdominal cramping can be a sign of constipation or other digestive issues. It’s important to address these issues separately and not rely on them as indicators for when to take the patient to the bathroom.
A nurse is gathering data on a patient who has diarrhea.
Which of the following findings is a sign of hypokalemia?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Hypertension is not typically a sign of hypokalemia. Hypokalemia, or low potassium levels, can cause symptoms like fatigue, muscle weakness, digestive problems, and frequent urination. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is not commonly associated with hypokalemia.
Choice B rationale:
Cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain, is not a common symptom of hypokalemia. Hypokalemia is more likely to cause symptoms related to muscle function and digestion, as potassium is an essential mineral that helps regulate muscle contractions, maintain healthy nerve function, and regulate fluid balance.
Choice C rationale:
Muscle weakness is a common symptom of hypokalemia. Potassium helps regulate muscle contractions. When blood potassium levels are low, your muscles produce weaker contractions. This can result in symptoms like muscle weakness and fatigue.
Choice D rationale:
Hyperactive bowel sounds are not typically associated with hypokalemia. Hypokalemia can cause digestive problems, but these are more likely to be issues like constipation rather than increased bowel sounds.
A nurse is assisting with the care of a patient who is receiving supplemental oxygen for hypoxia.
Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication that the intervention was effective?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
A respiratory rate of 28/min is not an indication that the intervention was effective. A normal respiratory rate for an adult at rest is between 12 and 20 breaths per minute. A respiratory rate of 28/min is considered tachypnea, which could be a sign of respiratory distress, not an improvement.
Choice B rationale:
Pink mucous membranes are a good sign. They indicate effective oxygenation and perfusion. When the body is receiving an adequate amount of oxygen, the skin, lips, and mucous membranes can appear pink. This is a positive outcome of oxygen therapy for hypoxia.
Choice C rationale:
A heart rate of 110/min is not an indication that the intervention was effective. A normal resting heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute. A heart rate of 110/min is considered tachycardia, which could be a sign of distress or compensation for hypoxia, not an improvement.
Choice D rationale:
Restlessness is not an indication that the intervention was effective. On the contrary, restlessness can be a sign of inadequate oxygenation. When the brain does not receive enough oxygen, a patient can become restless or anxious. Therefore, restlessness is not a positive outcome of oxygen therapy for hypoxia.
A nurse is educating a newly licensed nurse about the side effects of medications.
Which medication can lead to constipation?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Iron supplements Iron supplements are commonly used to treat or prevent iron deficiency anemia. While beneficial in relieving iron deficiency, iron pills can cause side effects like constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dark stools, stomach cramps, and a metallic taste. However, constipation is not the primary side effect of iron supplements.
Choice B rationale:
Magnesium-containing antacids Magnesium-containing antacids are used to relieve the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), heartburn, or indigestion. By neutralizing stomach acid, antacids relieve symptoms such as burning behind the breast bone or throat area caused by acid reflux, a bitter taste in the mouth, a persistent dry cough, pain when lying down, or regurgitation. While these antacids can cause diarrhea, they do not typically lead to constipation.
Choice C rationale:
Anticholinergics/Antispasmodics Anticholinergics and antispasmodics are used to relieve cramps or spasms of the stomach, intestines, and bladder. Some are used together with antacids or other medicines in the treatment of peptic ulcers. Others are used to prevent nausea, vomiting, and motion sickness. While these medications can cause a variety of side effects, constipation is not a primary side effect.
Choice D rationale:
Opioid narcotics Opioids, also known as narcotics, are a class of drugs healthcare providers prescribe to manage moderate to severe pain, as well as chronic coughing and diarrhea. Common side effects of narcotics include constipation, decreased sweating, dizziness, dry mouth, nose, throat, or skin. Therefore, opioid narcotics are the medication most likely to lead to constipation among the options provided.
A nurse is caring for a school-age child suffering from respiratory failure due to pneumonia.
Which position should the nurse recommend for maximum lung expansion?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Prone The prone position, in which a patient lies facedown, is beneficial for patients with pneumonia as it helps shift the fluid away from the back of the lungs, allowing more air to enter. It also improves ventilation in the lungs and reduces the risk of lung collapse. However, this position is not the most effective for maximum lung expansion in pneumonia patients.
Choice B rationale:
Side-lying Lateral positioning, in which the patient lies on one side, is recommended for patients suffering from pneumonia in just one lung. In this position, the pneumatic lung is exposed to a higher blood flow, resulting in greater oxygenation levels and improved lung expansion. This position can also help prevent lung injury by helping regulate pressure and improve aeration.
But again, this is not the most effective position for maximum lung expansion in pneumonia patients.
Choice C rationale:
Supine The supine position, where the patient lies flat on their back, is not the best position for a pneumonia patient. This position can cause the secretions to pool in the lungs, making it harder for the patient to breathe and potentially worsening their condition. Choice D rationale:
Upright Elevating the head of the bed is an effective way to improve lung expansion and oxygenation levels in pneumonia patients. This position also helps eliminate airway obstruction, reduces pressure on the lungs, and promotes drainage of fluids from the lungs. Therefore, the upright position is the most recommended for maximum lung expansion in pneumonia patients.
A nurse is caring for a patient who has rheumatoid arthritis. Which of the following laboratory tests are used to diagnose the disease? (Select all that apply)
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Antinuclear antibody (ANA) titer is a blood test that detects the presence of antinuclear antibodies, which are autoantibodies that target the body's own tissues. These antibodies are often present in people with autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis.
While a positive ANA test does not definitively diagnose rheumatoid arthritis, it can support a diagnosis when considered alongside other clinical findings and laboratory tests.

Choice B rationale:
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) is a blood test that measures the amount of urea nitrogen in the blood. Urea nitrogen is a waste product that is produced when the body breaks down proteins.
BUN levels can be elevated in people with kidney disease, dehydration, or certain other medical conditions. However, BUN is not specifically used to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis.
Choice C rationale:
Urinalysis is a test that examines the urine for various substances, including cells, bacteria, and chemicals.
It can be used to diagnose a variety of conditions, including urinary tract infections, kidney disease, and diabetes. However, urinalysis is not typically used to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis.
Choice D rationale:
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a blood test that measures how quickly red blood cells settle at the bottom of a test tube.
A high ESR can indicate inflammation in the body.
ESR is often elevated in people with rheumatoid arthritis, as it is a marker of inflammation.
Choice E rationale:
White blood cell count (WBC) is a blood test that measures the number of white blood cells in the blood. White blood cells are part of the immune system and help fight infection.
A high WBC count can indicate an infection or inflammation.
WBC count can be elevated in people with rheumatoid arthritis, as it is a marker of inflammation.
A nurse is preparing to remove a patient’s urinary catheter.
After performing hand hygiene, what should the nurse do next?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Positioning the client supine is not the immediate next step after performing hand hygiene when preparing to remove a patient’s urinary catheter. While it is important to ensure the patient is in a comfortable and appropriate position for the procedure, the immediate next step should be focused on ensuring the area is clean to prevent infection.
Choice B rationale:
After performing hand hygiene, the nurse should cleanse the perineal area with an antiseptic. This is to ensure that the area is clean before proceeding with the removal of the urinary catheter. It helps to prevent the introduction of bacteria into the urinary tract, which could lead to a urinary tract infection. The use of an antiseptic is recommended to kill any potential pathogens that may be present.
Choice C rationale:
Deflating the balloon halfway and then pulling out the catheter is not the immediate next step after performing hand hygiene. This step is usually done later in the process. Before deflating the balloon, it is important to ensure that the area is clean to prevent infection. Moreover, deflating the balloon halfway could potentially cause discomfort or injury to the patient. The balloon should be fully deflated before the catheter is removed.
Choice D rationale:
Having the client bear down during removal is not the immediate next step after performing hand hygiene. This action might be suggested during the actual removal of the catheter to aid in the process, but it is not the immediate next step. The focus right after hand hygiene should be on cleaning the area to prevent infection.
A nurse is instructing a newly licensed nurse on how to obtain a fecal occult blood test from a patient.
What information should the nurse include?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Applying four drops of developing solution to each stool specimen is a correct procedure in a fecal occult blood test (FOBT). The developing solution is used to detect the presence of hidden (occult) blood in the stool, which may indicate conditions such as colon cancer or polyps.
Choice B rationale:
Using toilet paper to transfer the stool specimen is not recommended. The FOBT requires a clean sample of stool, and toilet paper may contaminate the sample or interfere with the test results.
Choice C rationale:
Waiting 30 seconds after applying the developing solution to obtain the results is incorrect. The exact waiting time can vary, but it is typically longer than 30 seconds. It’s important to follow the specific instructions provided with the test kit.
Choice D rationale:
Collecting two stool specimens from the same area of the stool is a correct procedure. For an FOBT, samples of stool are typically collected over several days. This increases the chance of finding blood, as bleeding may not occur every day.
Please note that these rationales are based on general information about FOBTs and may not apply to all situations. Always follow the specific instructions provided by healthcare professionals or test manufacturers.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching about elimination with an adolescent who is paralyzed from the waist down following a spinal cord injury.
Which statement by the adolescent indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
The statement “I do my wheelchair exercises sitting in my chair” is correct. Wheelchair exercises are designed to be performed while seated in a wheelchair. They help to maintain muscle strength and flexibility, which is crucial for individuals with paralysis.
Choice B rationale:
The statement “I use a suppository every night to have a bowel movement” is also correct. Individuals with paralysis often have difficulty with bowel movements due to lack of muscle control. Using a suppository can stimulate the rectum and induce a bowel movement. Choice C rationale:
The statement “I need to catheterize myself twice a day” indicates a need for further teaching. Individuals with paralysis from the waist down following a spinal cord injury typically need to perform intermittent self-catheterization every 4-6 hours, not just twice a day. This helps to prevent urinary tract infections and bladder overdistension.
Choice D rationale:
The statement “I carry a water bottle with me because I drink a lot of water” is correct. Drinking plenty of water is important for overall health and can help to prevent urinary tract infections, which are common in individuals who self-catheterize.
A nurse is assisting with the care of a client who has respiratory alkalosis and is hyperventilating.
What action should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Administering insulin to a client who is hyperventilating due to respiratory alkalosis would not be the appropriate action. Insulin is used to lower blood glucose levels in clients with hyperglycemia, such as those with diabetes mellitus. It does not directly address the issues of hyperventilation or respiratory alkalosis.
Choice B rationale:
Having the client breathe into a paper bag is the correct action in this case. When a person hyperventilates, they exhale more carbon dioxide (CO2) than they produce. This can lead to a state of respiratory alkalosis, where the blood becomes too alkaline due to the low levels of CO2. By breathing into a paper bag, the client re-inhales some of the exhaled CO2, helping to restore the balance of gases in the blood and alleviate the symptoms of respiratory alkalosis.

Choice C rationale:
Administering sodium bicarbonate to a client who is hyperventilating and has respiratory alkalosis would not be the appropriate action. Sodium bicarbonate is an alkalinizing agent used to treat conditions where there is too much acid in the body, such as metabolic acidosis. In this case, the client’s body is too alkaline due to the respiratory alkalosis, so administering an alkalinizing agent would exacerbate the condition.
Choice D rationale:
Having the client place their head between their knees would not be the appropriate action for a client who is hyperventilating due to respiratory alkalosis. This position is often used to help alleviate symptoms of dizziness or fainting, but it does not address the underlying issue of the imbalance of gases in the blood due to hyperventilation.
A nurse is gathering information on a patient who has pleural effusion.
What symptoms should the nurse anticipate?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Crackles are a common symptom of pleural effusion. They are abnormal lung sounds that are heard when a patient with pleural effusion breathes in. The sound is caused by the opening of small airways and alveoli collapsed by fluid, exudate, or lack of aeration during expiration.
Choice B rationale:
Crepitus is not typically associated with pleural effusion. Crepitus is a crackling or grating sound or feeling produced by air in subcutaneous tissue or by the rubbing together of fragments of broken bone. In the context of respiratory health, crepitus might be felt if there is subcutaneous emphysema, where air gets into tissues under the skin covering the chest wall or neck.
Choice C rationale:
Substernal retractions are not a typical symptom of pleural effusion. Retractions are a sign of respiratory distress, but they are more commonly associated with conditions that cause upper airway obstruction or severe lung disease, such as asthma or pneumonia. Choice D rationale:
Dullness upon percussion is a classic sign of pleural effusion. When there is fluid in the pleural space, it prevents the normal resonant sound produced by the air-filled lungs from being heard. Instead, a dull sound is heard when the chest is percussed.
A nurse is reinforcing discharge instructions with the parents of an infant who has been prescribed home oxygen and pulse oximetry monitoring.
Which statement by the parents suggests that further instruction is needed?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
The statement “The pulse oximeter may not be accurate during periods of excessive movement” is correct. Pulse oximeters measure the amount of oxygen in the blood by shining light through the skin, and movement can cause the light to scatter, leading to inaccurate readings.
Choice B rationale:
The statement “We will inform the doctor if the pulse oximeter consistently reads 100%” indicates further instruction is needed. A pulse oximeter reading of 100% is not necessarily a cause for concern. It simply means that the hemoglobin is fully saturated with oxygen. However, if the oxygen level is consistently at 100%, it could indicate that the oxygen flow is too high and needs to be adjusted. It’s important to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions regarding the desired oxygen saturation level for the infant.
Choice C rationale:
The statement “The probe of the pulse oximeter can be attached to a finger or a toe” is correct. The probe of a pulse oximeter can indeed be attached to a finger, toe, or even an earlobe. The important thing is that it’s attached to a part of the body with good blood flow. Choice D rationale:
The statement “We will move the probe of the pulse oximeter every 24 hours” is correct. It’s important to move the probe periodically to prevent skin damage, such as pressure sores or burns, especially in infants who have delicate skin.
A nurse is caring for a patient with diabetic ketoacidosis and hypoxia.
What is the first action the nurse should take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Administering insulin is a crucial step in managing diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), as insulin deficiency is a primary cause of DKA12. However, it is not the first action to take when a patient presents with both DKA and hypoxia. While insulin helps to reduce blood glucose levels and suppress the production of ketones, it does not address the immediate life-threatening condition of hypoxia.
Choice B rationale:
Hypoxia, or low levels of oxygen in the body, is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. Supplemental oxygen can help increase the oxygen levels in the patient’s blood, thereby alleviating hypoxia. In the context of a patient with DKA and hypoxia, providing supplemental oxygen would be the first action to take to stabilize the patient’s condition before addressing the DKA12.
Choice C rationale:
Checking the patient’s glucose level is an important part of managing DKA, as hyperglycemia is a key feature of this condition. However, it is not the first action to take in this scenario. While monitoring glucose levels can guide the administration of insulin and other treatments for DKA, it does not address the immediate threat posed by hypoxia.
Choice D rationale:
Administering intravenous fluids is another important step in managing DKA12. Dehydration is a common complication of DKA due to excessive urination caused by high blood sugar levels. However, similar to Choices A and C, while it is an important part of treatment, it is not the first action to take when a patient presents with both DKA and hypoxia.
A charge nurse in a long-term care facility is observing another nurse who is inserting an indwelling urinary catheter into a female patient.
Which action by the nurse should prompt the charge nurse to intervene?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
The nurse should not apply the sterile drape before cleaning the perineal area. This is because the sterile drape is meant to maintain a sterile field during the procedure. If the nurse applies the sterile drape before cleaning the perineal area, it could lead to contamination of the sterile field, increasing the risk of infection.
Choice B rationale:
Lubricating the indwelling urinary catheter is a standard practice in catheter insertion. This is done to minimize discomfort to the patient during the procedure. The lubricant used is usually water-soluble and does not interfere with the sterility of the catheter.
Choice C rationale:
The nurse separating the patient’s labia with her dominant hand is a correct procedure. This is done to expose the urethral meatus for catheter insertion. The hand used to separate the labia is considered ‘clean’ rather than ‘sterile’, while the other hand, which is ‘sterile’, is used to handle the catheter.
Choice D rationale:
Providing perineal care prior to inserting the urinary catheter is a correct procedure. This is done to reduce the risk of introducing bacteria into the urinary tract during catheter insertion. The perineal area should be cleaned from front to back to avoid contamination of the urethra.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 43 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

