ATI Fundamentals Exam Nursing 100 Exam 3
Total Questions : 49
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription for a stool test for occult. The nurse understands the purpose of the test is to check the stool for which of the following substances?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The stool test for occult blood is not primarily designed to detect bacteria.
Choice B rationale: Parasites are not typically detected through a stool test for occult blood.
Choice C rationale: Steatorrhea refers to the presence of excess fat in the stool and is not the primary focus of a stool test for occult blood.
Choice D rationale: The purpose of the stool test for occult blood is to check for the presence of blood in the stool, which may not be visible to the naked eye. This can be an indicator of gastrointestinal bleeding.
The nurse uses gait belts when assisting clients to ambulate. Which client would be a likely candidate for this assistive device?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: A client who is confined to bedrest may not need a gait belt as they are not ambulating.
Choice B rationale: A client with leg strength who can cooperate with movement is a likely candidate for a gait belt. This device provides support and stability during ambulation.
Choice C rationale: A client with a thoracic incision may not necessarily need a gait belt for ambulation unless there are specific mobility concerns.
Choice D rationale: A client with an abdominal incision may not necessarily need a gait belt for ambulation unless there are specific mobility concerns.

A nurse working in long-term care facility is assessing residents at risk for the development of a pressure injury. Which resident would be most at risk?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The client who is 92 years old, uses a walker, is incontinent, and has an extensive cardiac history is at higher risk for the development of pressure injuries due to age, immobility, and additional risk factors.
Choice B rationale: A client with paraplegia may be at risk for pressure injuries, but the combination of age, walker use, incontinence, and cardiac history increases the risk in Choice A.
Choice C rationale: A comatose client with a traumatic brain injury is at risk, but other factors in Choice A contribute to a higher overall risk.
Choice D rationale: A client who uses a cane and has dementia may be at risk, but the combination of age, walker use, incontinence, and cardiac history increases the risk in Choice A.
A nurse applies padded boots to maintain the foot in dorsiflexion to a client who is comatose. The nurse is protecting the client from:
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Decubitus ulcers (pressure ulcers) are not directly prevented by applying padded boots for dorsiflexion.
Choice B rationale: Applying padded boots for dorsiflexion helps prevent foot drop, a condition where the foot is permanently in a plantar-flexed position, which can lead to contractures.
Choice C rationale: Pooling of blood is not a primary concern addressed by applying padded boots for dorsiflexion.
Choice D rationale: Blood pressure changes are not directly addressed by applying padded boots for dorsiflexion.
A client at a healthcare facility has been diagnosed with polyuria. How would the nurse describe the client's condition in the medical record?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Polyuria refers to excessive production of urine, so "Inadequate elimination of urine" is not an accurate description.
Choice B rationale: Polyuria does not mean the absence of urine; rather, it implies an increased urinary volume.
Choice C rationale: Polyuria is not related to difficult or uncomfortable voiding.
Choice D rationale: Polyuria is characterized by greater than normal urinary volume, so this is the correct description.
Doctor's order: 750 mL NS to infuse over 8 hours.
How many mL/hr will you set the IV pump? Round to the nearest whole number.
Explanation
The total volume is divided by the total time
=750/8
=93.75 ml/hr
= 94 ml/hr (rounded off to the nearest whole number)
When moving a client up in bed with the assistance of another caregiver, the nurse should:
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Elevating the head of the bed is not the recommended action when moving a client up in bed.
Choice B rationale: Having the client fold the arms across the chest is not the primary action when moving a client up in bed.
Choice C rationale: Asking another nurse about the plan of care is not necessary in this situation and does not directly address the action needed when moving the client.
Choice D rationale: Maintaining a pillow under the client's head helps provide comfort and support during the movement.
A nurse is initiating a 24-hour urine collection for a client at home. What will be the first thing the nurse will ask the client to do at the beginning of the specimen collection?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Voiding and discarding the urine is the first step in a 24-hour urine collection to ensure that the collection starts with a fresh specimen.
Choice B rationale: Adding the first voiding to the specimen is not the correct initial step.
Choice C rationale: Keeping the urine warm during collection is important, but it is not the first step in the process.
Choice D rationale: Beginning the collection at a specific time is part of the process but not the initial step.
The nurse is leading an exercise class for a group of adults aged 65 years and older. The nurse incorporates isotonic. Isometric, and isokinetic exercises into the class. Which activity is an isometric exercise?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Carrying an air-filled ball while wading through the water across the width of a pool is an isotonic exercise.
Choice B rationale: Contracting the gluteal muscles while holding a simple yoga pose is an isometric exercise.
Choice C rationale: Walking at a rate of 3 miles (5 km)/hour around a racetrack is an isotonic exercise.
Choice D rationale: Sitting in a chair with a low weight on the side and lifting the knee to the seat level of the chair is an isotonic exercise.
The type of stool that will be expelled into the ostomy bag by a client who has undergone surgery for an ileostomy will be:
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Stool expelled into an ileostomy bag is often of liquid consistency. An ileostomy involves the diversion of the small intestine, where the stool is more liquid compared to a colostomy, which involves the large intestine and typically produces more formed stool.
Choice B rationale: Bloody stool is not a typical characteristic of stool from an ileostomy.
Choice C rationale: Mucus-filled stool is not the primary characteristic of stool from an ileostomy.
Choice D rationale: Soft semi-formed stool is not typical of an ileostomy; the stool is more liquid in consistency.
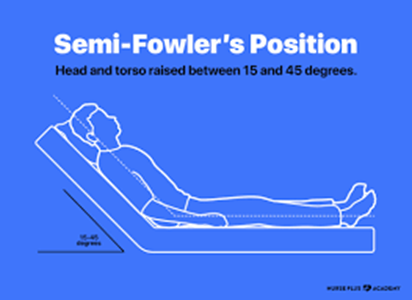
A client 80 years of age experienced dysphagia (impaired swallowing) in the weeks following a recent stroke, but the care team wishes to now begin introducing minced and pureed food. How should the nurse best position the client?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Protective supine positioning is not ideal for managing dysphagia or facilitating swallowing.
Choice B rationale: Semi-Fowlers positioning, with the head of the bed elevated at a 30 to 45-degree angle, is often recommended for clients with dysphagia. This position helps prevent aspiration during eating and promotes effective swallowing.
Choice C rationale: Low-Fowlers and Fowlers positions may not be as effective in preventing aspiration during eating as the Semi-Fowlers position.
Choice D rationale: Fowlers positioning alone may not be sufficient for managing dysphagia; Semi-Fowlers is a more specific recommendation.
A client with a urinary tract infection is to be discharged from the healthcare facility.
After teaching the client about measures to prevent urinary tract infections, the nurse determines that the education was successful when the client makes which statement?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The statement "I need to void after sexual intercourse to flush microorganisms away from my urethra" is correct. Voiding after sexual intercourse can help prevent the ascent of microorganisms into the urethra and reduce the risk of urinary tract infections.
Choice B rationale: Wearing snug-fitting pants can contribute to a warm and moist environment, potentially increasing the risk of urinary tract infections rather than preventing them.
Choice C rationale: Wiping from the anus to the vagina after going to the bathroom can introduce microorganisms into the urethral area, increasing the risk of urinary tract infections.
Choice D rationale: Frequent bubble baths can disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms in the genital area and increase the risk of urinary tract infections.
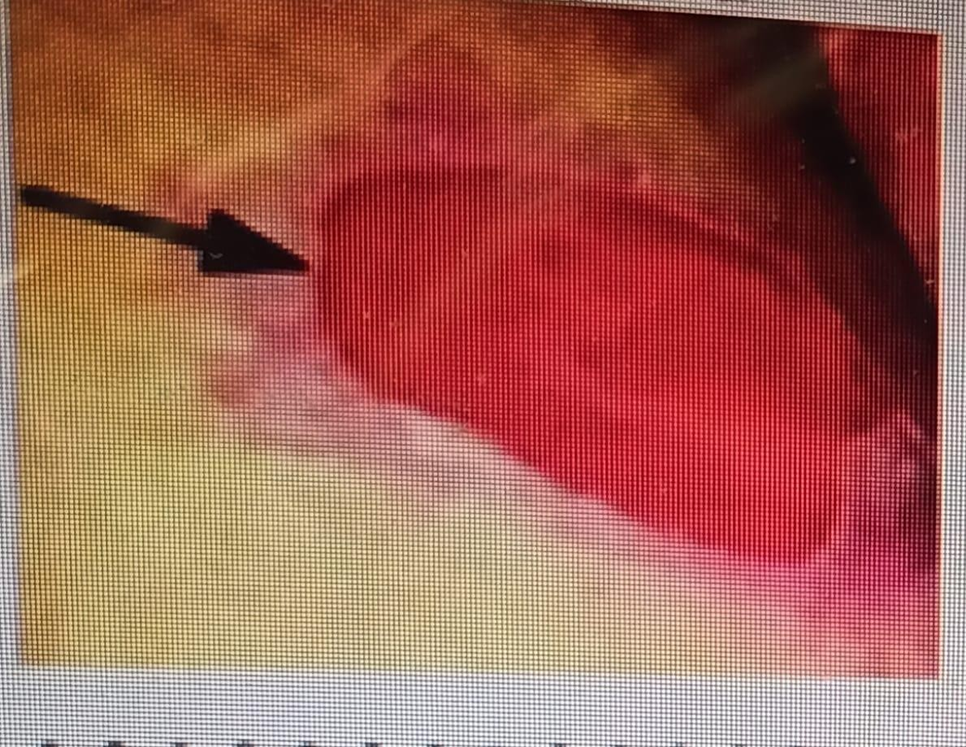
A nurse is completing her physical assessment on her newly admitted patient. She is assessing the patient's skin and documenting her findings. How should she document the following wound?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Stage I pressure ulcers consist of non-blanching erythema with an intact epidermis unlike in the above picture.
Choice B rationale: This is correct since Stage II pressure ulcers involve partial-thickness skin loss but do not extend into the deeper layers as shown in the image above.
Choice C rationale: Stage IV pressure ulcers involve full-thickness tissue loss with exposed muscle, bone, or other structures.
Choice D rationale: Stage III pressure ulcers involve full-thickness tissue loss with visible fat but do not extend to the underlying muscle.
Ordered: Morphine sulfate 12 mg IM Available: Morphine sulfate 15 mg/mL How many mL will you administer?
Round to the nearest tenth.
Explanation
Volume= dose/concentration
= 12/15
= 0.8 mL
The nurse is caring for a patient with a fractured left leg and is using crutches. Which statement indicates the patient has correct understanding of how to properly use her crutches?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Using the axilla to bear body weight can lead to nerve damage and is not a proper crutch technique.
Choice B rationale: Keeping the elbows extended can lead to discomfort and poor crutch control. The elbows should be slightly flexed.
Choice C rationale: When getting up from a chair, extending the uninjured leg first is not the correct technique. The patient should keep the injured leg extended for stability.
Choice D rationale: Placing weight on the unaffected leg first when climbing stairs is the correct technique, allowing for better balance and stability.
The nurse is caring for a client with a wound from a biking accident. She assesses the wound and notices that the surrounding skin is very red and warm. The wound looks swollen and is draining a green like drainage. The nurse would recognize these symptoms would be a sign of what?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Redness, warmth, swelling, and green drainage are not typically signs of anemia.
Choice B rationale: These symptoms are indicative of infection. Infections can cause localized redness, warmth, swelling, and the drainage of discolored material.
Choice C rationale: While wound healing may involve some inflammation, the described symptoms are more consistent with infection than normal wound healing.
Choice D rationale: Necrosis involves tissue death and is not typically associated with redness, warmth, and swelling.
Reflex incontinence is associated with neurologic dysfunction and occurs when no warning or stress precedes periodic involuntary urination.
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Stress incontinence is characterized by involuntary urine leakage during activities that increase intra-abdominal pressure, such as coughing or sneezing.
Choice B rationale: Transient incontinence is temporary and often related to factors like medications or medical conditions.
Choice C rationale: Total incontinence refers to continuous and unpredictable leakage of urine.
Choice D rationale: Reflex incontinence is associated with neurologic dysfunction, and the lack of warning or stress preceding involuntary urination aligns with this description.
A nurse is assessing a client who has a wound that is healing by first intention. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Wound healing by first intention involves the approximation of wound edges, often closed with sutures or staples, resulting in minimal scar formation.
Choice B rationale: Contamination at the time of injury is not characteristic of wounds healing by first intention.
Choice C rationale: Granulation tissue forming at the bottom of the wound bed is characteristic of wounds healing by second intention, not first intention.
Choice D rationale: Healing of the wound is typically quicker and involves less scarring in wounds healing by first intention compared to second intention.
A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving heat applications using a heating pad. Which of the following actions should the nurse take when applying the pad?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: If the client's skin becomes red, the heat application should be stopped to prevent burns or skin damage.
Choice B rationale: Heat applications are generally recommended for 20-30 minutes, not at least 40 minutes, to avoid skin damage.
Choice C rationale: Safety pins should not be used to keep the heating pad in place, as they can damage the pad or cause injury to the client.
Choice D rationale: The temperature of the heating pad should be set to a comfortable and safe level, typically below 42.2° C (108° F).
What are the functions of the skin? (Select All that Apply.)
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The skin helps regulate body temperature by sweating and dilation or constriction of blood vessels.
Choice B rationale: The skin acts as a barrier, protecting the body from external threats such as pathogens and physical injury.
Choice C rationale: The skin is rich in sensory receptors, allowing for the perception of touch, pressure, pain, and temperature.
Choice D rationale: The skin plays a role in the production of vitamin D when exposed to sunlight.
Choice E rationale: Vitamin C production is not a function of the skin; vitamin C is obtained through diet.
A nurse is providing education for an older adult client who reports constipation. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: While dietary fiber is important for bowel health, raw vegetables can be harder to digest. Cooking or steaming vegetables may be a more suitable option for some individuals with constipation.
Choice B rationale: Limiting activity can contribute to constipation, as physical activity helps stimulate bowel movements.
Choice C rationale: Drinking four to five glasses of water daily is important for maintaining hydration and supporting normal bowel function. Dehydration can contribute to constipation.
Choice D rationale: Bearing down hard when defecating may increase the risk of complications and is not a recommended strategy for relieving constipation.
A nurse is assessing bowel sounds on post-operative day 2 abdominal surgery patients. He does not hear bowel sounds. What should the nurse conclude about his findings?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The absence of bowel sounds on post-operative day 2 may indicate paralytic ileus, which is a temporary impairment of bowel motility. Paralytic ileus can last for 3-5 days postoperatively and is considered a normal response to surgery.
Choice B rationale: It is not normal for all post-op patients to have absent bowel sounds on day 2. Bowel sounds should typically return within the first 24 hours after surgery.
Choice C rationale: The absence of bowel sounds can be a normal finding in the immediate postoperative period, especially within the first 24 hours. However, it becomes abnormal if prolonged.
Choice D rationale: Documenting absent bowel sounds is appropriate, but notifying the physician should be based on the overall clinical picture and other symptoms.
5 fl oz = ____ mL
Explanation
1 fluid ounce (fl oz) is approximately equal to 29.57 mL. 5 fl oz x 29.57= 147.85
=148 mL (rounded off to the nearest whole number)
A nurse caring for a postoperative client observes the drainage in the client's closed wound drainage system. The drainage is thin with a pale pink-yellow color. The nurse documents the drainage as:
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Purulent drainage is thick and opaque, often indicating infection.
Choice B rationale: Serous drainage is thin and watery, typically clear or slightly yellow.
Choice C rationale: Sanguineous drainage is bright red and indicates fresh bleeding.
Choice D rationale: Serosanguineous drainage is thin and pale pink-yellow, representing a mixture of serous and sanguineous components.
Upon assessment of a client's wound, the nurse notes the formation of granulation tissue. The tissue bleeds easily when the nurse performs wound care. What is the phase of wound healing characterized by the nurse's assessment?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Hemostasis is the initial phase of wound healing that involves vasoconstriction and clot formation to control bleeding.
Choice B rationale: The inflammatory phase involves the removal of debris and the influx of inflammatory cells to the wound site.
Choice C rationale: The maturation phase is characterized by the remodeling of collagen and scar formation.
Choice D rationale: Granulation tissue formation and easy bleeding during wound care are characteristic of the proliferation phase, which involves tissue repair and regeneration.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 49 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

