ATI Maternal Newborn 2019 with NGN Updated 2024
Total Questions : 71
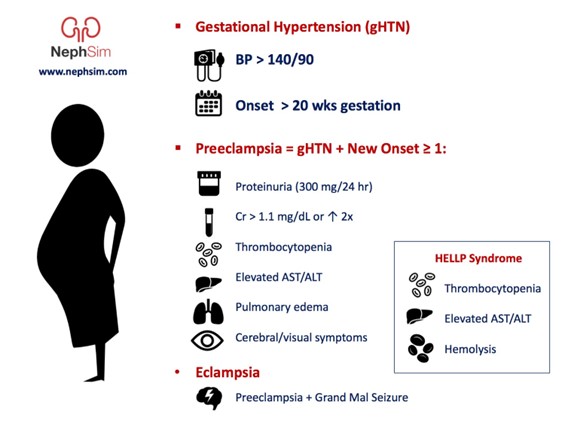
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is assessing a client who has preeclampsia during a prenatal visit. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider?
Explanation
Answer is: a. Urine protein of 3+
Explanation:
- Urine protein of 3+ indicates severe proteinuria, which is a sign of preeclampsia and can lead to kidney damage. The nurse should report this finding to the provider as it may require medication or delivery intervention.
- Deep tendon reflexes of 2+ are normal and do not indicate preeclampsia. The nurse should monitor the client for hyperreflexia, which is a sign of increased neuromuscular irritability and can precede seizures.
- Hemoglobin 13 g/dL is within the normal range for a pregnant client and does not indicate preeclampsia. The nurse should monitor the client for anemia, which can cause maternal and fetal complications.
- Blood glucose 110 mg/dL is slightly elevated but not diagnostic of gestational diabetes, which is a different condition from preeclampsia. The nurse should advise the client to follow a balanced diet and exercise regimen and to undergo a glucose tolerance test at 24 to 28 weeks of gestation.
. 
A nurse is planning care for a newborn who is scheduled to start phototherapy using a lamp. Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C, Ensure the newborn's eyes are closed beneath the shield. Phototherapy is a treatment used to reduce high bilirubin levels in newborns. It involves exposing the newborn's skin to special lights, which helps to break down the excess bilirubin in the blood. It is important to ensure that the newborn's eyes are closed beneath the shield to prevent damage to the eyes from the bright lights. Giving the newborn 1 oz of glucose water every 4 hr, applying lotion to the newborn's skin every 8 hr, and dressing the newborn in a thin layer of clothing during therapy are not indicated interventions during phototherapy.
A nurse is performing an assessment for a newborn and notes breast tissue that has a flat areola with no bud. The nurse should identify that this finding indicates which of the following conditions?
Explanation
Answer and explanation
The correct answer is choice A, Decreased maternal hormones during pregnancy. Breast tissue with a flat areola and no bud is a normal finding in newborns and indicates that the infant did not receive significant amounts of maternal hormones during pregnancy. Preterm gestational age, ambiguous secondary sex characteristics, and congenital anomalies would not typically present with this finding.
A nurse is caring for a newborn immediately following birth and notes a large amount of mucus in the newborn's mouth and nose. Identify the sequence the nurse should follow when performing suction with a bulb syringe.
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B, D, C, A. The sequence the nurse should follow when performing suction with a bulb syringe is to compress the bulb syringe, place the bulb syringe in the newborn's mouth, use the bulb syringe to suction the newborn's nose, and then assess the newborn for reflex bradycardia. That sequence is the most effective way to suction a newborn's mouth and nose, as it ensures that the newborn's airway is cleared of mucus before assessing for reflex bradycardia, which can be triggered by suctioning.

A nurse is assessing a client who is at 39 weeks of gestation and determines that the fetus is in a left occipitoanterior position. On which of the following sites should the nurse place the external fetal monitor to hear the point of maximum impulse of the fetal heart rate?

Explanation
The correct statement is C. left lower quadrant. The location where the monitor is placed depends on the position of the fetus. When the fetus is in a left occiput anterior position, the point of maximum impulse of the fetal heart rate is located in the left lower quadrant of the mother's abdomen. This is where the nurse should place the external fetal monitor to obtain an accurate reading of the fetal heart rate.
A nurse is caring for a 2-day-old newborn who was born at 35 weeks of gestation. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? (Click on the "Exhibit" button for additional information about the newborn. There are three tabs that contain separate categories of data.)
Exhibit 1
Diagnostic results
Escherichia coli infection resulting in necrotizing enterocolitis Hgb 10g/dL
Platelet count 50,000 mm
WBC count 4,000 mm3
Exhibit 2
Graphic record
Oxygen saturation level 90% Respirations shallow 70/min
Behavioral indicators of pain: Rigid extremities: grimacing:
Irritability
Exhibit 3
Nurses' notes
Decreased activity level over the last 12 hr
Abdominal distension
Three bloody stools over the last 8 hr
Superficial rash on the abdominal wall
Light palpation of the abdomen leads to fist clenching,
Explanation
The nurse should insert an orogastric decompression tube with low wall suction. The newborn has Escherichia coli infection resulting in necrotizing enterocolitis, which can cause abdominal distention, decreased activity level, and bloody stools. The newborn also has a superficial rash on the abdominal wall, which may indicate a bacterial infection. The presence of a fist clenching, thrashing, and crying during light palpation of the
abdomen may indicate pain caused by bowel distention. An orogastric decompression tube with low wall suction can help decompress the bowel and relieve abdominal distention.
A nurse is performing an assessment for a newborn and notes breast tissue that has a flat areola with no bud. The nurse should identify that this finding indicates which of the following conditions?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Breast tissue that has a flat areola with no bud indicates that the newborn received decreased maternal hormones during pregnancy. Maternal hormones stimulate breast tissue growth in the fetus during pregnancy. A flat areola with no bud is a finding that is commonly seen in newborns who received decreased maternal hormones.
A nurse is assessing a postpartum client during a follow-up visit.
Exhibit 1: Vital Signs 0930:
Temperature 37° C (98.6° F)
Pulse rate 78/min
Respiratory rate 12/min
Blood pressure 124/80 mm Hg
Pulse oximetry 100%
The nurse is teaching the client about postpartum depression. The nurse should encourage the client to______________and________________to help prevent postpartum depression.
- Maintain a set schedule and exercise 30 min per day
- Practice meditation while the newborn naps and take her medication as prescribed
- Eat a well-balanced diet and exercise 30 min per day
- Limit caffeine and alcohol intake and try to sleep when the newborn sleeps.
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. Eating a well-balanced diet and exercising for 30 minutes per day can help to reduce stress and improve mood, which can help to prevent postpartum depression. This provide the body with the essential nutrients it needs to function properly and maintain good health. Exercise can help to reduce stress and improve mood by releasing endorphins, which are hormones that can help to improve mood and reduce stress.
A nurse on the labor and delivery unit is planning care for a client who has human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Which of the following is an appropriate action for the nurse to take following the birth of the newborn?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. The nurse should initiate contact precautions for the newborn. The newborn of an HIV-positive mother is at risk of acquiring HIV infection during delivery. To reduce the risk of infection, the newborn should be placed under contact precautions until the results of the newborn's HIV test are available. The nurse should also ensure that the newborn receives appropriate antiretroviral prophylaxis to prevent HIV transmission.
A nurse is teaching a newly hired nurse about Apgar scoring. Which of the following statements by the newly hired nurse indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice D. "The nurse should measure the newborn's muscle tone when assigning an Apgar score." components of the Apgar score:
|
Component |
0 Points |
1 Point |
2 Points |
|
Heart Rate |
Absent |
<100 bpm |
>100 bpm |
|
Respiratory Effort |
Absent |
Slow, irregular |
Good, crying |
|
Muscle Tone |
Flaccid |
Some flexion |
Active motion |
|
Reflex Irritability |
No response |
Grimace |
Vigorous cry |
|
Color |
Blue, pale |
Body pink, extremities blue |
Completely pink |
The score for each component is summed up to a maximum score of 10, with 10 indicating the healthiest newborn. The NRP guidelines emphasize that resuscitation efforts should be initiated immediately after delivery, regardless of the Apgar score, thus choice C is wrong.
A nurse is caring for a client who is at 30 weeks of gestation and is receiving magnesium sulfate for preeclampsia. The nurse should recognize which of the following manifestations as an adverse reaction to the medication.
Explanation
The correct answer is choice D. Urine output of 20 mL/hr is a manifestation of an adverse reaction to magnesium sulfate. Magnesium sulfate is a medication used to treat preeclampsia, a potentially life-threatening condition that can occur during pregnancy. Adverse reactions to magnesium sulfate include hypotension, respiratory depression, and decreased urine output. The nurse should monitor the client's vital signs and urine output closely while the client is receiving magnesium sulfate. Normal urine output in a healthy individual should be between 0.5-1.5 mL/kg/hour, and patients should generally be urinating at least every 6 hours.
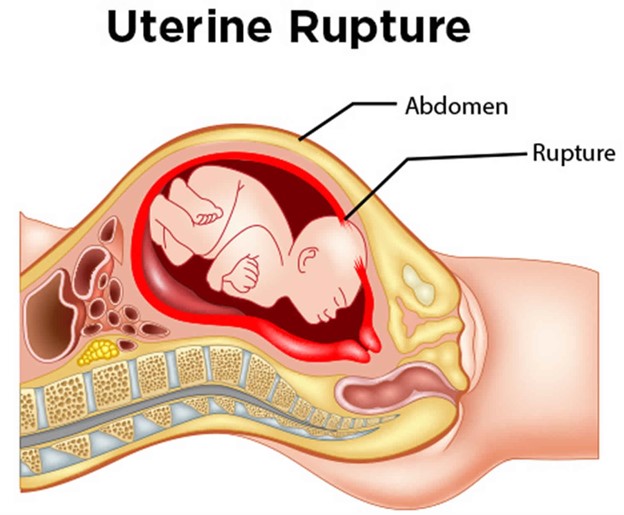
A nurse is caring for a client who is in active labor and reports sudden, severe lower abdominal pain. The nurse observes a drop in the client's blood pressure and notes cool skin and pallor. The fetal heart rate tracing shows prolonged bradycardia. Which of the following complications should the nurse suspect?
Explanation
Uterine rupture. The sudden, severe lower abdominal pain, drop in blood pressure, and signs of shock such as cool skin and pallor all point to a potential intra-abdominal hemorrhage most likely due to Uterine rupture. Additionally, the prolonged bradycardia on the fetal heart rate tracing indicates that the baby may be experiencing fetal distress due to a compromised blood supply. Amniotic fluid embolism triggers an allergic reaction, causing a sudden onset of respiratory distress, hypotension, and cardiac arrest. Option D, placenta previa, occurs when the placenta implants in the lower uterine segment, partially or completely covering the cervical os. This can lead to painless vaginal bleeding but typically does not present with sudden, severe abdominal pain or signs of shock.
A nurse is caring for a client who is 1 day postpartum and breastfeeding her newborn. The client reports sore nipples. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
This suggests that the nurse should assess the newborn's latch while breastfeeding. Sore nipples are a common concern among breastfeeding mothers, and the most common cause is an improper latch. The nurse should ensure that the baby is latching on correctly and not causing trauma to the mother's nipples. A proper latch involves the baby taking in a good portion of the areola and not just the nipple. Assessing the newborn's latch can help identify any issues with the baby's mouth or tongue that may be causing difficulty latching on. If the baby is not latching correctly, the nurse can provide education and support to help the mother correct the issue. Offering supplemental formula between feedings (choice A) is not recommended as it can decrease the frequency of breastfeeding and reduce the stimulation for milk production, leading to decreased milk supply. Instructing the client to wait 4 hours between daytime feedings (choice C) is not recommended as it can decrease milk production and lead to inadequate nutrition for the newborn.
suggests that the nurse should assess the newborn's latch while breastfeeding. Sore nipples are a common concern among breastfeeding mothers, and the most common cause is an improper latch. The nurse should ensure that the baby is latching on correctly and not causing trauma to the mother's nipples. A proper latch involves the baby taking in a good portion of the areola and not just the nipple. Assessing the newborn's latch can help identify any issues with the baby's mouth or tongue that may be causing difficulty latching on. If the baby is not latching correctly, the nurse can provide education and support to help the mother correct the issue. Offering supplemental formula between feedings (choice A) is not recommended as it can decrease the frequency of breastfeeding and reduce the stimulation for milk production, leading to decreased milk supply. Instructing the client to wait 4 hours between daytime feedings (choice C) is not recommended as it can decrease milk production and lead to inadequate nutrition for the newborn.
A nurse is calculating the estimated date of delivery for a client who reports that the first day of her last menstrual period was August 10. Using Nägele's Rule, which of the following is the client's estimated date of delivery?
Explanation
May 13. Nägele's Rule is used to calculate the estimated date of delivery (EDD) based on the first day of the last menstrual period (LMP). To use this rule, the nurse subtracts 3 months from the first day of the LMP and adds 7 days and 1 year.
For this client, the first day of her LMP was August 10. Subtracting 3 months gives us May 10. Adding 7 days gives us May 17. Adding 1 year gives us May 17, 2022. Therefore, the estimated date of delivery is May 17, 2022.
It is important to note that Nägele's Rule is an estimation, and not all pregnancies follow the typical 280-day gestational period. Other factors, such as irregular menstrual cycles, can affect the accuracy of the estimated date of delivery. The nurse should monitor the client's pregnancy and adjust the estimated date of delivery as needed based on ultrasound results and other clinical findings.
A nurse is monitoring a client who is undergoing a nonstress test at 35 weeks of gestation. Which of the following findings requires intervention by the nurse?
Explanation
Three uterine contractions within a 20-min period require intervention by the nurse during a nonstress test at 35 weeks of gestation. The nonstress test is used to assess fetal well-being by monitoring the fetal heart rate (FHR) response to fetal movement. The test is considered reactive if there are two or more accelerations of the FHR within a 20-min period, each lasting at least 15 seconds and peaking at least 15 beats above the baseline. In this scenario, the finding that requires intervention by the nurse is three uterine contractions within a 20-min period. This is because frequent or prolonged contractions can indicate preterm labor, which requires immediate intervention
to prevent premature delivery. The nurse should assess the client for signs and symptoms of preterm labor, such as pelvic pressure, low back pain, vaginal bleeding or discharge, and abdominal cramping. The nurse should also notify the provider and prepare the client for further evaluation and possible interventions, such as tocolytic therapy to stop the contractions.
A nurse is developing an educational program about hemolytic disease in newborns for a group of newly licensed nurses. Which of the following genetic information should the nurse include in the program as a cause of hemolytic disease?
Explanation
The mother is Rh negative and the father is Rh positive. Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) is caused by an incompatibility between the blood types of the mother and fetus. Specifically, it occurs when a Rh-negative mother carries a fetus who is Rh-positive, and the mother's immune system produces antibodies against the Rh antigen on the fetal red blood cells. These antibodies can cross the placenta and destroy the fetal red blood cells, leading to anemia and other complications in the newborn. If a mother has Rhnegative blood, it means that she lacks the Rh antigen on her red blood cells. If the father has Rh-positive blood, there is a chance that the fetus will inherit the Rh antigen from the father. If the fetal Rh-positive blood enters the mother's bloodstream during pregnancy or delivery, the mother's immune system can produce antibodies against the Rh antigen, causing HDN in subsequent pregnancies with Rh-positive fetuses.
A nurse is caring for a client who is in active labor. The nurse administers butorphanol IV bolus for pain. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider following this medication?
Explanation
The nurse should report a respiratory rate of 10/min to the provider following the administration of butorphanol IV bolus. Butorphanol is an opioid agonist-antagonist analgesic that can cause respiratory depression as a side effect. Therefore, it is important to monitor the client's respiratory rate and depth closely after administration of the medication. A respiratory rate of 10/min is significantly lower than the normal range of 1220/min, and may indicate respiratory depression. The nurse should also monitor the client's blood pressure, urinary output, and fetal heart rate for any changes, but these findings are not necessarily indicative of a complication following the administration of butorphanol.
A nurse on an antepartum unit is reviewing the medical records for four clients. Which of the following clients should the nurse assess first?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C, the client who has hyperemesis gravidarum and a sodium level of 110 mEq/L should be assessed first. This client's low sodium level indicates hyponatremia, which can lead to seizures and brain damage if not corrected promptly. The nurse should assess the client's neurologic status, including level of consciousness, reflexes, and motor function, and notify the provider immediately. The other clients also require close monitoring and intervention, but their conditions are not as urgent as the client with hyponatremia. Clients with preeclampsia require monitoring of blood pressure and kidney function, clients with placenta previa require monitoring of bleeding and hematocrit levels, and clients with diabetes mellitus require monitoring of blood glucose levels and HbA1c.
A nurse is providing teaching about increasing dietary fiber to an antepartum client who reports constipation. Which of the following food selections has the highest fiber content per cup?
Explanation
Lentils. Lentils have the highest fiber content per cup compared to the other options. One cup of cooked lentils provides approximately 15.6 grams of fiber. Oatmeal provides approximately 4 grams of fiber per cup, asparagus provides approximately 3.6 grams of fiber per cup, and cabbage provides approximately 2.6 grams of fiber per cup. Increasing dietary fiber is an effective way to manage constipation during pregnancy, as it can promote bowel regularity and prevent complications such as hemorrhoids. The nurse can provide additional education on other high-fiber food options, the importance of drinking adequate fluids, and the need to increase physical activity to help manage constipation. 
A nurse is teaching a newly licensed nurse about the uses of ultrasonography in the first trimester of pregnancy. Which of the following statements by the newly licensed nurse indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. Ultrasonography is a diagnostic tool used during pregnancy to visualize the fetus and the maternal reproductive organs. In the first trimester of pregnancy, it is primarily used to determine gestational age, confirm the presence of an intrauterine pregnancy, and assess for fetal viability. It can also be used to identify multiple gestations, evaluate for ectopic pregnancy, and detect certain fetal anomalies. Ultrasound is not typically used to observe for placental maturity or to perform a biophysical profile in the first trimester. Intrauterine growth restriction is typically assessed later in pregnancy using serial ultrasound measurements.
A nurse is admitting a client to the birthing unit who reports her contractions started 1 hr ago. The nurse determines the client is 80% effaced and 8 cm dilated. The nurse realizes that the client is at risk for which of the following conditions?
Explanation
The client's cervical dilation and effacement indicate that she is in active labor and progressing rapidly. Because the client is already 8 cm dilated and has been in labor for only 1 hour, the nurse should recognize that the client is at risk for a rapid delivery, which can increase the risk of postpartum hemorrhage. The other options listed are not associated with cervical dilation and effacement during active labor.
A nurse is assessing a full-term newborn. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider?
Explanation
Respiratory rate 55/min. This finding is abnormal and requires immediate reporting to the provider. The normal range for a newborn respiratory rate is 30-60 breaths per minute, and a rate above this range may indicate respiratory distress or another underlying issue that requires further assessment and intervention. The heart rate, temperature, and blood pressure are within the normal range for a full-term newborn and do not require reporting to the provider unless they deviate significantly from the expected range.
A nurse is caring for a client who is in labor. Which of the following findings should prompt the nurse to reassess the client?
Explanation
A sense of excitement and warm, flushed skin should prompt the nurse to reassess the client, as it may indicate hyperventilation, which can lead to respiratory alkalosis and decreased uterine blood flow. The nurse should encourage the client to breathe slowly and deeply during contractions to help prevent hyperventilation. Choices A, B, and C are normal findings during labor and do not require immediate reassessment. Progressive sacral discomfort during contractions can indicate the descent of the fetal head. Intense contractions lasting 45 to 60 seconds can indicate active labor. The urge to have a bowel movement during contractions can indicate fetal descent and pressure on the rectum.
A nurse in a provider's office is caring for a 20-year-old client who is at 12 weeks of gestation and requests an amniocentesis to determine the sex of the fetus. Which of the following responses should the nurse make?
Explanation
The nurse should explain to the client that amniocentesis is a diagnostic test that is performed between 15 and 20 weeks of gestation to determine if the fetus has genetic or congenital disorders. While the procedure can also determine the sex of the fetus, this is not typically the primary reason for the test. The nurse should clarify any misconceptions the client has about the procedure and provide education on its purpose, risks, and benefits. The nurse should also assess the client's understanding of the information provided and address any questions or concerns the client may have.
A nurse is caring for a client who is in active labor and is receiving oxytocin via IV infusion. The nurse has applied an internal fetal heart monitor and recognizes an early deceleration of the fetal heart rate tracing. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
An early deceleration is a type of fetal heart rate deceleration that is typically benign and caused by the pressure of the baby's head on the cervix during contractions. However, it can also be caused by uterine hyperstimulation, which is a potential complication of oxytocin administration. Discontinuing the oxytocin can help to alleviate uterine hyperstimulation and prevent further decelerations. Administering oxygen, assisting the client to lay on her right side, and continuing to monitor the client may also be appropriate interventions, but discontinuing the oxytocin is the priority action in this situation.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 71 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

