Ati med surg adult care 2
Total Questions : 65
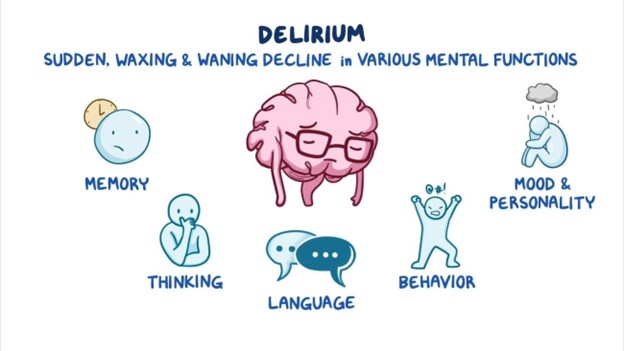
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreAccording to the ATI video case study, Cognition: Delirium and Dementia, which of the following is the best first action for the nurse to take when caring for a client with delirium?
Explanation
Identify the underlying cause. This is correct because delirium is a reversible condition that is often caused by an underlying medical problem, such as infection, medication, or dehydration.
Identifying and treating the cause can help resolve the delirium and prevent further complications.
Tell the client that hallucinations are not real. This is incorrect because it can increase the client's anxiety and confusion. The nurse should acknowledge the client's feelings and perceptions, but not reinforce or argue with them.
Speak slowly and clearly. This is incorrect because it is not the best first action. While speaking slowly and clearly can help communicate with the client, it does not address the root cause of the delirium.
Request the assistance of physical therapy. This is incorrect because it is not relevant to the question. Physical therapy may be helpful for some clients with delirium, but it is not a priority intervention.
A client is observed with unilateral twitching of facial muscles and repetitive tongue thrusting, with a decrease in level of consciousness. When the nurse reports her findings to the physician, what type of seizure will she indicate she observed?
Explanation
Febrile. This is incorrect because febrile seizures are associated with high fever and usually occur in children between 6 months and 5 years of age. They are typically generalized and brief, lasting less than 15 minutes.
Absence. This is incorrect because absence seizures are characterized by brief episodes of staring or loss of awareness, without any motor activity or change in level of consciousness.
Complex partial. This is correct because complex partial seizures involve impaired consciousness and automatisms, such as lip smacking, chewing, or fidgeting. They may also involve focal motor activity, such as twitching of one side of the face or body.
Clonictonic. This is incorrect because clonictonic seizures involve alternating muscle contraction and relaxation, resulting in jerking movements of the limbs and trunk. They are usually preceded by a loss of consciousness and followed by a period of confusion or sleepiness
A student nurse is caring for a client with acute hemorrhagic stroke who was admitted 1 day ago. Which is the priority assessment finding for the student to report to the primary nurse?
No explanation
A nurse is preparing to administer intravenous mannitol, an osmotic diuretic, to a client with increased intracranial pressure. Which of the following should the nurse identify as the purpose of the medication?
No explanation
An 84year old client is brought to the emergency department with reports that his mental status has slowly been declining. He fell 2 weeks ago but did not seek medical attention. Based on this information, what does the nurse suspect the client's diagnosis will be?
No explanation
Which of the following clients is most at risk for traumatic brain injury?
No explanation
A nurse is performing a neurological assessment for a client with head trauma. Which of the following assessments will give the nurse information about the function of cranial nerve II?
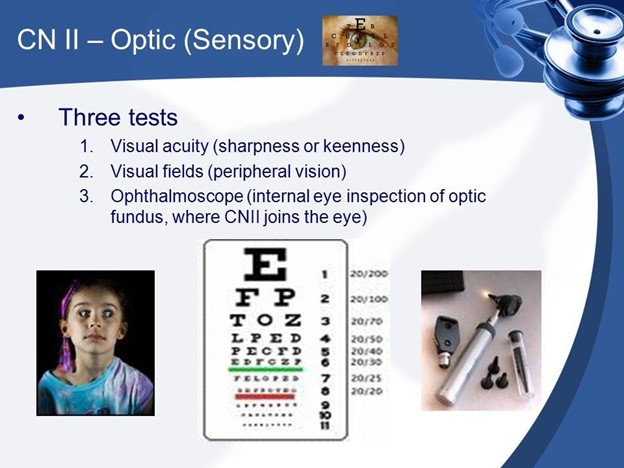
No explanation
The nurse caring for a client with a brain tumor will monitor for which of the following early signs of increased intracranial pressure?
No explanation
A nurse in the emergency department is caring for a client following an automobile crash in which the client was unrestrained and thrown from the vehicle. When assessing the client, the nurse observes clear fluid draining from the client's nose. Which of the following interventions should the nurse take?
No explanation
A client newly diagnosed with multiple sclerosis is receiving education about newly prescribed medications from the nurse. Which of the following will be included in the client teaching?
No explanation
After performing a neurological assessment, the student nurse shares the following findings with the primary nurse: Visual fields full to confrontation with Intact extraocular movements. No nystagmus, midline protrusion of tongue, and negative Romberg test. Which of the following will the primary nurse tell the student nurse to document?
No explanation
A nurse is assessing a client who has a score of 6 on the Glasgow Coma Scale. The nurse should expect which of the following outcomes based on this score?
No explanation
According to the ATI video case study, Cognition: Delirium and Dementia, when caring for
the client with Alzheimer's disease, which of the following are appropriate items to include in the client's room?
No explanation
A client arrives to the emergency department after a motor vehicle accident. The nurse records the following Glasgow Coma scores: E3, V2, M1. What is the best first action for the nurse to take.
No explanation
The nurse takes report on a client who was admitted with a severe heada
che, nausea, vomiting, photophobia, and a stiff neck. Which of the following is the priority intervention for the nurse to perform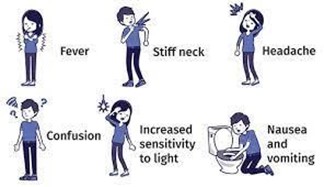 ?
?
No explanation
A nurse is assessing a client who has Parkinson's disease. Which of the following manifestations should the nurse expect?
No explanation
A nurse suspects that a client admitted for treatment of bacterial meningitis is experiencing increased Intracranial pressure (ICP). Which of the following assessment findings by the nurse supports this suspicion?
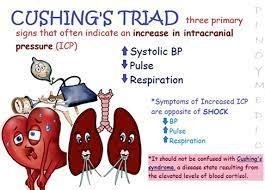
No explanation
A nurse is admitting a young adult client who has suspected bacterial meningitis. The nurse should closely monitor the client for increased intracranial pressure (ICP) as indicated by which of the following findings?
No explanation
A student nurse is asked by the preceptor to identify which of the assigned clients is at the highest risk for stroke. Which of the clients below, when selected by the student nurse, indicate an understanding of the highest risk factor for stroke?
No explanation
A client suspected of having a stroke is scheduled to have an angiogram. Which of the following is a priority action for the nurse?
No explanation
A nurse is assessing a client who has a traumatic head injury to determine motor function response. Which of the following client responses to painful stimulus is expected?
No explanation
A physician tells the family of a client involved in a motorvehicle accident that the client sustained a coupcontrecoup injury. Which of the following statements by the nurse indicates an understanding of this type of traumatic brain injury?
No explanation
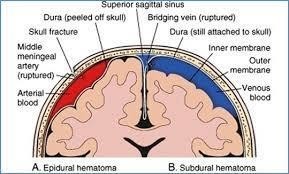
A nurse is caring for a client who has an epidural hematoma. Which of the following manifestations should the nurse expect?
No explanation
A nurse is caring for a client who has had a stroke involving the right hemisphere. Which of the following alterations in function should the nurse expect?
No explanation
A client has a history of atrial fibrillation. Which of the following is the nurse likely to see on the clients medication history to prevent stroke?
No explanation
Sign Up or Login to view all the 65 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

