ATI Med Surg Exam 4
Total Questions : 108
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA client diagnosed with a sty of the eye asks what can be done for treatment. Which of the following options will the nurse provide to the client?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: An antifungal cream is not indicated for a sty, which is an infection of the eyelash follicle or sebaceous gland caused by bacteria.
Choice B Reason: This is the correct answer because warm compresses can help relieve pain and inflammation, and promote drainage of the sty.
Choice C Reason: Ice and cold compresses are not recommended for a sty, as they can constrict blood vessels and delay healing.
Choice D Reason: There is no need to test the other eye for vision loss, as a sty does not affect vision unless it is very large or obstructs the pupil.

A nurse is caring for a client who has burns to his face, ears, and eyelids. The nurse should identify which of the following is the priority finding to report to the provider?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: A heart rate of 122/min is elevated, but not life-threatening. It could be due to pain, anxiety, dehydration, or infection.
Choice B Reason: A urinary output of 25 ml/hr is low, but not critical. It could indicate fluid loss, kidney damage, or inadequate fluid resuscitation.
Choice C Reason: A pain level of 6 on a scale of 0 to 10 is moderate, but not severe. It could be managed with analgesics and non-pharmacological interventions.
Choice D Reason: This is the correct answer because difficulty swallowing can indicate airway obstruction, inhalation injury, or edema of the throat. It can compromise breathing and require immediate intervention.
A client arrives to the clinic with reports of progressive weakness in his lower extremities. Which of the following findings in the client's history is consistent with the client developing Guillain-Barre syndrome?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: A facial tumor is not related to Guillain-Barre syndrome, which is an autoimmune disorder that affects the peripheral nerves.
Choice B Reason: Pregnancy is not a risk factor for Guillain-Barre syndrome, although it can occur during or after pregnancy in rare cases.
Choice C Reason: A puncture wound 3 weeks ago is unlikely to cause Guillain-Barre syndrome, which usually follows a respiratory or gastrointestinal infection.
Choice D Reason: This is the correct answer because cytomegalovirus is one of the common infections that can trigger Guillain-Barre syndrome. It can cause inflammation and damage to the myelin sheath that covers the nerves.

The nurse is providing care for a client with a recent transverse colostomy. Which observation requires immediate notification of the primary health care provider?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Soft pasty stool is normal for a transverse colostomy, as the stool has not reached the sigmoid colon where most of the water is absorbed.
Choice B Reason: This is the correct answer because purple discoloration of the stoma indicates ischemia or necrosis, which can lead to infection, perforation, or sepsis. It requires urgent intervention.
Choice C Reason: Stoma is beefy red is a normal finding for a healthy stoma, as it indicates adequate blood supply and healing.
Choice D Reason: There is skin excoriation around the stoma is a common complication of a colostomy, as the stool can irritate the skin. It can be managed with proper skin care and appliance fitting.

A nurse in the emergency department is caring for a client following an automobile crash in which the client was unrestrained and thrown from the vehicle. When assessing the client, the nurse observes clear fluid draining from the client's nose. Which of the following interventions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Inserting a nasal swab to observe the fluid is contraindicated, as it can introduce infection or increase intracranial pressure. The fluid can be tested for glucose or halo sign to confirm cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage.
Choice B Reason: Suctioning the nose gently with a bulb syringe is also contraindicated, as it can create negative pressure and increase CSF leakage or cause meningitis.
Choice C Reason: This is the correct answer because allowing the drainage to drip onto a sterile gauze pad can prevent contamination and facilitate observation of the amount and characteristics of the fluid.
Choice D Reason: Inserting sterile packing into the nares is not recommended, as it can obstruct the drainage and increase intracranial pressure or infection risk.
A nurse is caring for a client who is experiencing Cushing's Triad following a subdural hematoma. Which of the following manifestations will the nurse expect to find? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Slow even breathing is not a sign of Cushing's Triad, which is a late indicator of increased intracranial pressure (ICP). The breathing pattern may be altered due to brainstem compression, but not necessarily slow or even.
Choice B Reason: This is a correct answer because bradycardia and bounding pulse are part of Cushing's Triad, which reflects an increased vagal tone and decreased cardiac output due to increased ICP.
Choice C Reason: Systolic hypotension with a narrowing pulse pressure is not a sign of Cushing's Triad, which involves an increased systolic blood pressure and a widened pulse pressure due to increased ICP. Hypotension may occur due to shock or hemorrhage, but not as a result of increased ICP.
Choice D Reason: This is a correct answer because irregular respirations are part of Cushing's Triad, which reflects impaired respiratory control due to brainstem compression from increased ICP. The respirations may be Cheyne-Stokes, central neurogenic hyperventilation, apneustic, or ataxic.
Choice E Reason: Tachycardia and bounding pulse are not signs of Cushing's Triad, which involves bradycardia and bounding pulse due to increased ICP. Tachycardia may occur due to pain, anxiety, fever, or hypoxia, but not as a result of increased ICP.
Choice F Reason: This is a correct answer because systolic hypertension with a widening pulse pressure are part of Cushing's Triad, which reflects an increased cerebral perfusion pressure due to increased ICP. The diastolic blood pressure remains stable or decreases, resulting in a widened pulse pressure.

A client newly diagnosed with glaucoma has a history of asthma. Which of the following medications newly prescribed by the eye doctor will the nurse question?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Antibiotics are not contraindicated for a client with glaucoma and asthma, as they can treat or prevent infections that may affect the eye or the respiratory system.
Choice B Reason: This is the correct answer because non-selective beta blockers are contraindicated for a client with glaucoma and asthma, as they can reduce intraocular pressure but also cause bronchoconstriction and exacerbate asthma symptoms.
Choice C Reason: NSAIDs are not contraindicated for a client with glaucoma and asthma, as they can reduce inflammation and pain that may affect the eye or the respiratory system.
Choice D Reason: Anticoagulants are not contraindicated for a client with glaucoma and asthma, as they can prevent or treat thromboembolic events that may affect the eye or the respiratory system.

A nurse is caring for a client who has a complete spinal cord injury. Based on the nurse's understanding about the degree of this type of injury, what can the nurse expect will be the client's level of function?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: This is the correct choice because a complete spinal cord injury is a condition where there is no motor or sensory function below the level of injury. The client will have paralysis of all four limbs (quadriplegia) and loss of bladder, bowel, and sexual function. The client will also have impaired thermoregulation, breathing, and blood pressure. The client will need 24-hour a day care to assist with mobility, hygiene, elimination, nutrition, and prevention of complications.
Choice B) Reason: This is incorrect because a client who is able to assist with transfer and perform self-care has a partial spinal cord injury, not a complete one. A partial spinal cord injury is a condition where there is some motor or sensory function below the level of injury. The degree of impairment depends on the extent and location of the damage.
Choice C Reason: This is incorrect because a client who is able to roll over independently has a lower spinal cord injury, not a complete one. A lower spinal cord injury is a condition where there is damage to the lumbar or sacral segments of the spinal cord. The client will have paralysis of the lower limbs (paraplegia) and some loss of bladder, bowel, and sexual function. The client will still have some control over the upper limbs and trunk.
Choice D Reason: This is incorrect because a client who is able to drive an electric wheelchair has an upper spinal cord injury, not a complete one. An upper spinal cord injury is a condition where there is damage to the cervical or thoracic segments of the spinal cord. The client will have paralysis of all four limbs (quadriplegia) and loss of bladder, bowel, and sexual function. However, the client may still have some movement or sensation in the shoulders, arms, or hands.

A blind client reports that they are having difficulty with sleep that is affecting their daytime activities. Which of the following will the nurse include in her plan of care for the client?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: This is incorrect because a referral to a sleep study program is not the most appropriate plan of care for a blind client who has difficulty with sleep. A sleep study program is used to diagnose and treat sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, narcolepsy, or restless legs syndrome.
Choice B Reason: This is incorrect because assisting the client to see if a night shift job is available is not a helpful plan of care for a blind client who has difficulty with sleep. A night shift job can disrupt the circadian rhythm and worsen the sleep quality and quantity of the client.
Choice C Reason: This is incorrect because institution of opioids and sedatives is not a safe plan of care for a blind client who has difficulty with sleep. Opioids and sedatives can cause addiction, dependence, tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms. They can also impair the respiratory and cognitive functions of the client.
Choice D Reason: This is the correct choice because education about non-24 disorder is an essential plan of care for a blind client who has difficulty with sleep. Non-24 disorder is a condition where the internal clock of the body does not synchronize with the 24-hour day-night cycle. It can cause irregular sleep patterns, daytime fatigue, and mood disturbances. It is more common in blind people who lack light perception. The nurse should educate the client about the causes, symptoms, and treatments of non-24 disorder.
A nurse is planning to provide discharge teaching for a client who has hearing loss. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: This is incorrect because dimming the lights in the client's room is not a helpful action for providing discharge teaching for a client who has hearing loss. Dimming the lights can reduce the visibility and clarity of the nurse's facial expressions, gestures, and lip movements, which can aid in communication.
Choice B Reason: This is incorrect because increasing the rate of speech when talking with the client is not an effective action for providing discharge teaching for a client who has hearing loss. Increasing the rate of speech can make it harder for the client to follow and understand what the nurse is saying.
Choice C Reason: This is incorrect because answering client's questions using medical terminology is not an appropriate action for providing discharge teaching for a client who has hearing loss. Medical terminology can be confusing and unfamiliar to the client, which can impair comprehension and learning.
Choice D Reason: This is the correct choice because facing the client while talking is an important action for providing discharge teaching for a client who has hearing loss. Facing the client can enhance eye contact, attention, and rapport. It can also allow the client to see the nurse's facial expressions, gestures, and lip movements, which can facilitate communication.

A nurse caring for a client with acute peritonitis reviews the physician's orders. The orders include an NPO diet, insertion of a nasogastric tube set to low intermittent suction, and IV fluids at 50 mL per hour. When asked why he will need the NG tube, what is the nurse's best reply?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: This is incorrect because administering medications and electrolytes is not the primary purpose of inserting a nasogastric tube for a client with acute peritonitis. Medications and electrolytes can be given through other routes, such as IV or oral.
Choice B Reason: This is incorrect because dilating the stomach as a presurgical preparation is not a relevant Reason for inserting a nasogastric tube for a client with acute peritonitis. Dilating the stomach may be done before some types of gastric surgery, but it does not apply to peritonitis.
Choice C Reason: This is incorrect because stating that you will not be able to eat for several days is not an adequate explanation for inserting a nasogastric tube for a client with acute peritonitis. This statement does not address the rationale or the benefits of the procedure. It may also cause anxiety and resentment in the client.
Choice D Reason: This is the correct choice because removing secretions and decompressing the stomach is the main Reason for inserting a nasogastric tube for a client with acute peritonitis. Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, the membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. It can cause abdominal distension, pain, nausea, and vomiting. A nasogastric tube can suction out the gastric contents and reduce the pressure and irritation in the abdomen.
A nurse is admitting a client who has a partial hearing loss. Which of the following is the priority action by the nurse?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: This is incorrect because standing directly in front of the client is not the priority action by the nurse when admitting a client who has a partial hearing loss. Standing directly in front of the client can enhance communication, but it is not as important as assessing the client's hearing status and needs.
Choice B Reason: This is incorrect because rephrasing statements the client does not hear is not the priority action by the nurse when admitting a client who has a partial hearing loss. Rephrasing statements can improve understanding, but it is not as essential as evaluating the client's hearing level and preferences.
Choice C Reason: This is incorrect because speaking using his usual tone of voice is not the priority action by the nurse when admitting a client who has a partial hearing loss. Speaking using his usual tone of voice may or may not be appropriate, depending on the client's hearing ability and comfort. The nurse should adjust his tone of voice based on the client's feedback and response.
Choice D Reason: This is the correct choice because determining if the client uses hearing aids is the priority action by the nurse when admitting a client who has a partial hearing loss. Hearing aids are devices that amplify sound and improve hearing for people with hearing loss. The nurse should determine if the client uses hearing aids, and if so, check their function, fit, and battery life. The nurse should also ask about any other assistive devices or strategies that the client uses to communicate effectively.
Which of the following clients is most at risk for traumatic brain injury?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: This is the correct choice because driving a motorcycle is a high-risk activity that can expose the client to head trauma, especially if they do not wear a helmet. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a condition where the brain is damaged by an external force, such as a collision, fall, or assault.
Choice B Reason: This is incorrect because having high blood pressure is not a direct risk factor for traumatic brain injury. High blood pressure can increase the risk of stroke, which is a condition where the brain is damaged by an internal cause, such as a blood clot or hemorrhage.
Choice C Reason: This is incorrect because smoking and having a family history of brain cancer are not risk factors for traumatic brain injury. Smoking and genetic factors can increase the risk of developing brain tumors, which are abnormal growths of cells in the brain.
Choice D Reason: This is incorrect because golfing and driving a golf cart are low-risk activities that do not pose a significant threat to the client's head. Golfing and driving a golf cart may cause minor injuries, such as sprains, strains, or bruises, but not traumatic brain injury.

The nurse is reviewing the record of a client with a diagnosis of cirrhosis and notes that there is documentation of the presence of asterixis. How should the nurse assess for its presence?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Measuring the abdominal girth is not related to asterixis, which is a tremor of the hand when the wrist is extended. It may indicate ascites, which is a complication of cirrhosis, but not asterixis.
Choice B Reason: This is the correct choice. Asterixis is a flapping tremor of the hand when the wrist is extended, sometimes said to resemble a bird flapping its wings. It is caused by abnormal function of the diencephalic motor centers that regulate the muscles involved in maintaining posture. It is a sign of hepatic encephalopathy, which is a neuropsychiatric disorder that occurs in patients with liver disease.
Choice C Reason: Having the client flex and extend their foot is not related to asterixis, which affects the hand and wrist. It may test for ankle clonus, which is a rhythmic contraction of the calf muscles when the foot is dorsiflexed. It indicates an upper motor neuron lesion, but not hepatic encephalopathy.
Choice D Reason: Asking the client to walk heel to toe is not related to asterixis, which affects the hand and wrist. It may test for balance and coordination, which can be impaired in patients with hepatic encephalopathy, but it is not a specific sign of asterixis.
The nurse is monitoring a client admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of appendicitis. The client reports a sudden increase in abdominal pain and begins to vomit. On assessment, the nurse notes that the abdomen is distended and bowel sounds are diminished. Which is the best first action the nurse should take?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Requesting the charge nurse put the client on the surgery schedule is not the best first action, as it does not address the urgency of the situation. The client may have a perforated appendix, which is a life-threatening complication that requires immediate intervention.
Choice B Reason: Documenting the WBC count from the morning labs is not the best first action, as it does not address the client's current condition. The WBC count may be elevated due to inflammation or infection, but it does not indicate the severity of the problem.
Choice C Reason: This is the correct choice. Notifying the healthcare provider is the best first action, as it alerts them to the possibility of a perforated appendix and allows them to order appropriate tests and treatments.
Choice D Reason: Providing an antiemetic is not the best first action, as it does not address the underlying cause of the vomiting. The client may have peritonitis, which is inflammation of the abdominal cavity due to leakage of intestinal contents. An antiemetic may mask this symptom and delay diagnosis and treatment.
A client arrives to the emergency department after falling from a ladder. The client has a loss of sensation and flaccid paralysis. Which of the following complications of an acute spinal cord injury does the nurse suspect?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Hemorrhage is not a complication of an acute spinal cord injury, but rather a possible cause of it. Hemorrhage can occur due to trauma or rupture of blood vessels in or around the spinal cord, leading to compression and damage of the nerve tissue.
Choice B Reason: This is the correct choice. Spinal shock is a complication of an acute spinal cord injury that occurs within minutes to hours after the injury. It is characterized by loss of sensation, motor function, reflexes, and autonomic function below the level of injury. It is caused by transient disruption of nerve conduction and synaptic transmission in the spinal cord.
Choice C Reason: Apoptosis is not a complication of an acute spinal cord injury, but rather a cellular process that occurs after it. Apoptosis is programmed cell death that occurs in response to injury or stress. It can lead to further loss of neurons and glial cells in the spinal cord over time.
Choice D Reason: Neurogenic shock is a complication of an acute spinal cord injury that occurs within hours to days after the injury. It is characterized by hypotension, bradycardia, and peripheral vasodilation due to loss of sympathetic tone and unopposed parasympathetic activity. It is caused by disruption of autonomic pathways in the spinal cord.

A client receiving parenteral nutrition by central venous access reports feeling unwell. The nurse assesses the client and suspects that the central line has become infected. Which of the following findings indicate that the client has developed a systemic infection? Select all that apply.
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Edema is not a specific finding of a systemic infection, but rather a possible sign of fluid overload or impaired venous return. It can occur due to excessive infusion rate, heart failure, or obstruction of blood flow in or around the central line.
Choice B Reason: This is a correct choice. Purulent drainage at intravenous insertion site is a finding of a local infection that can spread systemically. It indicates bacterial invasion and inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue around the catheter.
Choice C Reason: Redness at insertion site is a finding of a local infection that can spread systemically. It indicates increased blood flow and inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue around the catheter.
Choice D Reason: Nausea is not a specific finding of a systemic infection, but rather a possible side effect of parenteral nutrition or a symptom of another condition. It can occur due to electrolyte imbalance, hyperglycemia, or gastrointestinal disorders.
Choice E Reason: This is a correct choice. Leukocytosis is a finding of a systemic infection that indicates increased production and release of white blood cells in response to infection. It can be detected by a blood test.
Choice F Reason: This is a correct choice. Fever is a finding of a systemic infection that indicates increased body temperature due to activation of the immune system and release of pyrogens. It can be measured by a thermometer.
A client has a patch test performed with the following results. Which of the following is the best response the nurse will offer the client regarding the observations from the test?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: The test does not assess for sun protection factor, but rather for contact dermatitis. Sun protection factor is a measure of how well a sunscreen protects the skin from ultraviolet radiation, which can cause sunburn and skin damage.
Choice B Reason: The test is not inconclusive, but rather positive for some allergens and negative for others. The test involves applying small patches of different substances to the skin and observing for any reactions after 48 hours.
Choice C Reason: This is the correct choice. The presence of erythema indicates you are allergic to the allergen, as it shows inflammation and irritation of the skin due to an immune response. Erythema is redness of the skin that can be accompanied by itching, swelling, or blisters.
Choice D Reason: The areas that did not turn red do not indicate low risk for skin cancer, but rather no reaction to the allergen. Skin cancer is a malignant growth of abnormal cells in the skin that can be caused by various factors, such as genetic mutations, exposure to carcinogens, or immunosuppression.
A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving total parenteral nutrition (TPN) therapy via an infusion pump. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Obtaining the client's blood glucose every 12 hr is not enough, as the nurse should monitor it more frequently, at least every 4 to 6 hr, to prevent hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. TPN is a high-glucose solution that can affect the blood sugar levels.
Choice B Reason: Changing the IV site dressing every 4 days is not enough, as the nurse should change it daily or as needed to prevent infection. TPN is a high-risk solution that can introduce microorganisms into the bloodstream.
Choice C Reason: This is the correct choice. Changing the IV tubing every 24 hr is recommended to prevent infection and maintain sterility. TPN is a complex solution that can support bacterial growth and contamination.
Choice D Reason: Weighing the client every other day is not enough, as the nurse should weigh the client daily to evaluate fluid balance and nutritional status. TPN can cause fluid retention or depletion, as well as weight gain or loss.

A client arrives to the emergency department after falling from a ladder. The client has a loss of sensation and flaccid paralysis. Which of the following complications of an acute spinal cord injury does the nurse suspect?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Hemorrhage is not a complication of an acute spinal cord injury, but rather a possible cause of it. Hemorrhage can occur due to trauma or rupture of blood vessels in or around the spinal cord, leading to compression and damage of the nerve tissue.
Choice B Reason: This is the correct choice. Spinal shock is a complication of an acute spinal cord injury that occurs within minutes to hours after the injury. It is characterized by loss of sensation, motor function, reflexes, and autonomic function below the level of injury. It is caused by transient disruption of nerve conduction and synaptic transmission in the spinal cord.
Choice C Reason: Apoptosis is not a complication of an acute spinal cord injury, but rather a cellular process that occurs after it. Apoptosis is programmed cell death that occurs in response to injury or stress. It can lead to further loss of neurons and glial cells in the spinal cord over time.
Choice D Reason: Neurogenic shock is a complication of an acute spinal cord injury that occurs within hours to days after the injury. It is characterized by hypotension, bradycardia, and peripheral vasodilation due to loss of sympathetic tone and unopposed parasympathetic activity. It is caused by disruption of autonomic pathways in the spinal cord.
A nurse provides education to a client diagnosed with inflammatory bowel syndrome (IBS) about measures to treat diarrhea caused by acute flare-ups. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is correct because eating frequent small meals can help the client with IBS to avoid overloading the digestive system and triggering diarrhea. The nurse should advise the client to eat slowly chew well, and avoid foods that are spicy, fatty, or gas-producing.
Choice B reason: This is incorrect because increasing the intake of leafy greens and other sources of dietary fiber can worsen diarrhea by increasing stool bulk and motility. The nurse should advise the client to limit or avoid high-fiber foods, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, during acute flare-ups of IBS. The client can gradually reintroduce fiber when the symptoms subside.
Choice C reason: This is correct because increasing fluids can help the client with IBS to prevent dehydration and electrolyte imbalance caused by diarrhea. The nurse should advise the client to drink at least 8 glasses of water per day and avoid caffeinated, alcoholic, or carbonated beverages that can irritate the bowel or cause gas.
Choice D reason: This is correct because taking prescribed medications on schedule can help the client with IBS to regulate bowel patterns and reduce diarrhea. The nurse should instruct the client on how to use medications, such as antidiarrheals, antispasmodics, or probiotics, as ordered by the provider. The nurse should also monitor the client for any adverse effects or interactions of the medications.
A client presents to the clinic with complaints of otalgia and muffled sounds. The client is diagnosed with external otitis. Which of the following will the nurse not include in client teaching?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Reporting itching if it becomes bothersome is part of client teaching, as it may indicate inflammation or infection of the ear canal. External otitis is also known as swimmer's ear, as it can be caused by water trapped in the ear after swimming or bathing.
Choice B Reason: Using earplugs when swimming is part of client teaching, as it can prevent water from entering and irritating the ear canal. External otitis can be prevented by keeping the ear dry and avoiding trauma or foreign objects.
Choice C Reason: This is the correct choice. Inserting a cotton-tip applicator to remove excess wax is not part of client teaching, as it can damage or scratch the ear canal and increase the risk of infection. Wax helps protect and lubricate the ear canal and should not be removed unless it causes hearing impairment or discomfort.
Choice D Reason: Using a hairdryer set to low, 6 inches away from ear is part of client teaching, as it can help dry the ear canal after swimming or bathing. External otitis can be treated by applying warm compresses, using topical antibiotics or antifungals, and taking pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs.
A client arrives with an upper respiratory infection and complains of otalgia, malaise, and nasal drainage. The client's temperature is 100.7 F. Which of the following will the nurse anticipate providing to the client?
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is incorrect because education about mastoidectomy is not relevant for a client with an upper respiratory infection. Mastoidectomy is a surgical procedure that removes part or all of the mastoid bone behind the ear, which can become infected or inflamed due to chronic or recurrent middle ear infections. The nurse should assess the client's ear for signs of mastoiditis, such as swelling, tenderness, or redness behind the ear, but mastoidectomy is not a common or first-line treatment for upper respiratory infection.
Choice B reason: This is incorrect because a referral for a hearing test is not necessary for a client with an upper respiratory infection. Hearing test is a diagnostic tool that measures how well a person can hear different sounds at different frequencies and intensities. The nurse should ask the client about any changes in hearing or tinnitus, which are possible complications of upper respiratory infection, but a hearing test is not a routine or urgent intervention for this condition.
Choice C reason: This is correct because education on the administration of oral antibiotics can help treat an upper respiratory infection. Antibiotics are drugs that kill or inhibit bacteria that cause infections. Upper respiratory infections can be caused by various pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, or fungi, but bacterial infections are more likely to cause fever, otalgia, or purulent nasal drainage. The nurse should instruct the client on how to take antibiotics as prescribed, such as dosage, frequency, duration, side effects, and interactions.
Choice D reason: This is incorrect because a prescription for an antifungal cream is not appropriate for a client
A nurse is creating an education plan for a client who has diverticulosis. The nurse should plan to include which of the following in the client education?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Increasing protein from red meat is not part of client education, as it can worsen the condition and increase the risk of complications. Red meat is high in fat and low in fiber, which can cause constipation and increase the pressure in the colon. Diverticulosis is a condition where small pouches or sacs form in the wall of the colon due to weak spots or increased pressure.
Choice B Reason: Decreasing fluid intake is not part of client education, as it can worsen the condition and increase the risk of complications. Fluid intake should be increased to prevent dehydration and promote bowel movements. Diverticulosis can cause abdominal pain, bloating, cramping, and changes in bowel habits.
Choice C Reason: Incorporating soft foods that are pureed in consistency is not part of client education, as it can worsen the condition and increase the risk of complications. Soft foods are low in fiber and can cause constipation and increase the pressure in the colon. Diverticulosis can lead to diverticulitis, which is inflammation or infection of the pouches or sacs.
Choice D Reason: This is the correct choice. Increasing dietary fiber is part of client education, as it can improve the condition and prevent complications. Fiber helps soften the stool and reduce the pressure in the colon. Diverticulosis can be managed by eating a high-fiber diet, drinking plenty of fluids, exercising regularly, and avoiding straining or holding stools.

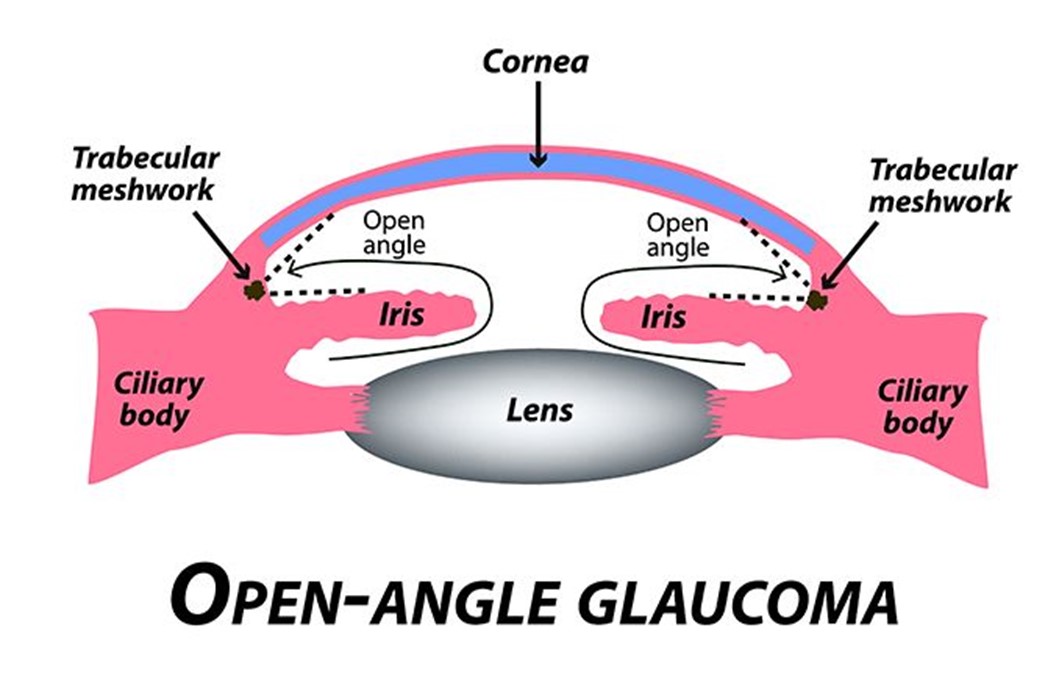
A nurse at an ophthalmology clinic is providing teaching to a client who has open-angle glaucoma and a new treatment regimen of timolol and pilocarpine eye drops. Which of the following instructions should the nurse provide?
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is incorrect because it is necessary to remove contact lenses before administering medications. Contact lenses can absorb or interfere with the absorption of eye drops and cause irritation or infection. The nurse should instruct the client to remove contact lenses before applying eye drops and wait at least 15 minutes before reinserting them.
Choice B reason: This is incorrect because administering the medications by touching the tip of the dropper to the sclera of the eye can cause contamination or injury. The sclera is the white part of the eye that covers most of the eyeball. The nurse should instruct the client to avoid touching the tip of the dropper to any part of the eye or eyelid and hold it about 1 cm above the lower eyelid.
Choice C reason: This is correct because administering the medications 5 min apart can prevent dilution or washout of one medication by another. Timolol and pilocarpine are two different types of eye drops that are used to treat open-angle glaucoma, which is a condition that causes increased pressure inside the eye and damage to the optic nerve. Timolol is a beta-blocker that reduces the production of fluid in the eye, and pilocarpine is a cholinergic agent that increases the drainage of fluid from the eye. The nurse should instruct the client to apply one drop of each medication in the affected eye(s) and wait at least 5 minutes between each medication.
Choice D reason: This is incorrect because holding pressure on the conjunctival sac for 2 min following the application of eye drops can reduce systemic absorption and side effects of eye drops. The conjunctival sac is the space between the lower eyelid and the eyeball. The nurse should instruct the client to gently close their eyes after applying eye drops and press their index finger against the inner corner of their eye for 2 minutes. This can block the tear duct that drains fluid from the eye to the nose and prevent it from entering the bloodstream.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 108 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

