ATI Med Surg Exam – Neuro
Total Questions : 47
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nursing preceptor is reviewing life expectancy in the twentieth century with a new nurse. The nurse should recognize that which of the following was most responsible for the dramatic increase in life expectancy during the twentieth century.
Explanation
Choice A reason: Advances in surgical techniques and procedures have improved the outcomes of many patients, but they are not the main factor for the increase in life expectancy. Surgical interventions are often costly, risky, and inaccessible to many people, especially in developing countries.
Choice B reason: Sanitation and other public health activities have had a significant impact on reducing mortality from infectious diseases, such as cholera, typhoid, and tuberculosis. These activities include providing safe water, improving hygiene, promoting vaccination, and controlling vector-borne diseases. Sanitation and public health measures are relatively low-cost, effective, and preventive strategies that can benefit large populations.
Choice C reason: Technology increases in the field of medical laboratory research have contributed to the diagnosis and treatment of many diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, and genetic disorders. However, these technologies are often expensive, complex, and dependent on specialized equipment and personnel. Therefore, they are not the main reason for the increase in life expectancy.
Choice D reason: The use of antibiotics to fight infections has been a major breakthrough in medicine, saving millions of lives from bacterial infections. However, antibiotics have also led to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which pose a serious threat to public health. Moreover, antibiotics are not effective against viral infections, such as influenza, HIV, and COVID-19. Therefore, antibiotics are not the most responsible factor for the increase in life expectancy.
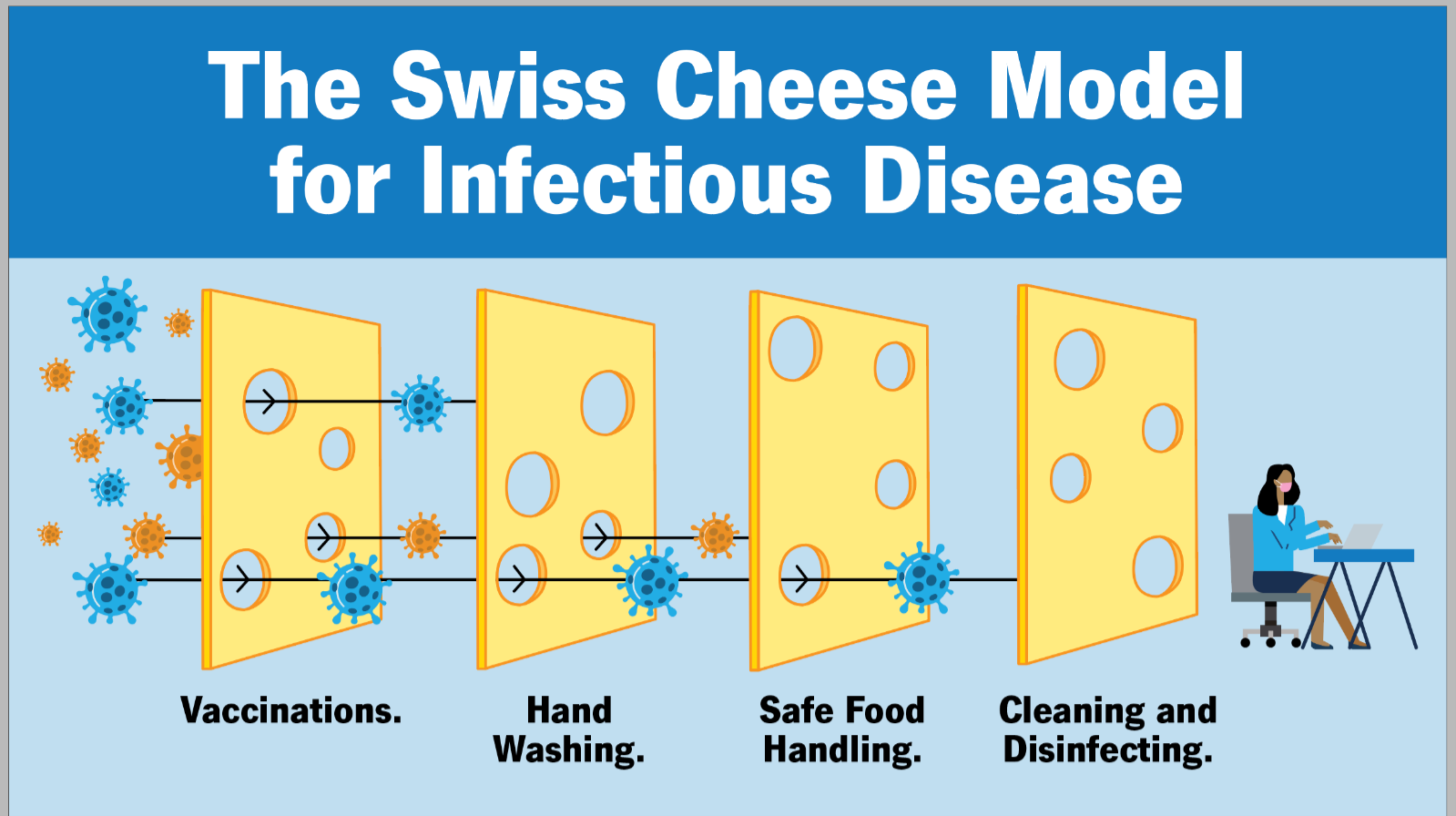
A nurse is using analytic epidemiology when conducting a research project on a comparison group. Which of the following research projects is the nurse most likely completing?
Explanation
Choice A: Reviewing communicable disease statistics. This is incorrect because this is an example of descriptive epidemiology, not analytic epidemiology. Descriptive epidemiology describes the distribution and patterns of health events in populations, such as the frequency, location, and time of occurrence.
Choice B: Tracking locations where family violence is increasing. This is incorrect because this is also an example of descriptive epidemiology, not analytic epidemiology. Descriptive epidemiology tracks the trends and variations of health problems in different groups or areas.
Choice C: Describing population characteristics for healthy older citizens. This is incorrect because this is another example of descriptive epidemiology, not analytic epidemiology. Descriptive epidemiology provides information about the demographic and social factors that influence health outcomes.
Choice D: Identifying factors contributing to childhood obesity. This is correct because this is an example of analytic epidemiology. Analytic epidemiology investigates the causes and associations of health events in populations, such as the risk factors, exposures, or interventions that affect health outcomes. Analytic epidemiology often uses comparison groups to test hypotheses and draw conclusions.
A nurse wishes to develop cultural competence when caring for clients. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Completing a survey of the various ethnicities represented in the nurse's community is a good way to learn about diversity, but it is not the first step in developing cultural competence. The nurse should first examine their own cultural background and biases, and how they affect their interactions with clients.
Choice B reason: Studying the beliefs and traditions of persons living in other cultures is a valuable way to gain knowledge and understanding, but it is not the first step in developing cultural competence. The nurse should first be aware of their own cultural values and assumptions, and how they influence their perceptions and judgments.
Choice C reason: Considering how the nurse's own personal beliefs and decisions are reflective of their culture is the first step in developing cultural competence. The nurse should recognize that culture is not only about ethnicity, but also about age, gender, religion, education, socioeconomic status, and other factors. The nurse should also acknowledge that culture is dynamic and complex and that each person has a unique cultural identity.
Choice D reason: Inviting a family from another culture to join the nurse for an event is a nice way to show respect and interest, but it is not the first step in developing cultural competence. The nurse should first develop self-awareness and sensitivity, and avoid making stereotypes or generalizations about other cultures.
The facility education nurse is providing a group of new nurses education regarding weaponized biological threats. When discussing anthrax, which of the following should be included as portals of entry? SELECT ALL THAT APPLY
Explanation
Choice A reason: The integumentary system is a portal of entry for anthrax because the bacteria can enter through cuts or abrasions on the skin. This is called cutaneous anthrax, and it is the most common and least deadly form of anthrax infection.
Choice B reason: The endocrine system is not a portal of entry for anthrax because the bacteria do not affect the glands or hormones of the body. The endocrine system is mainly involved in regulating metabolism, growth, development, and reproduction.
Choice C reason: The central nervous system is a portal of entry for anthrax because the bacteria can spread to the brain and spinal cord from other parts of the body. This is called meningeal anthrax, and it is a rare and fatal complication of anthrax infection.
Choice D reason: The renal system is not a portal of entry for anthrax because the bacteria do not infect the kidneys or urinary tract. The renal system is mainly involved in filtering waste products and excess fluids from the blood.
Choice E reason: The respiratory system is a portal of entry for anthrax because the bacteria can be inhaled into the lungs. This is called inhalation anthrax, and it is the most deadly form of anthrax infection.
A nurse is caring for a client with a myocardial infarction. The client questions the need for cardiac rehabilitation since "my heart is already damaged." Which of the following is the appropriate nursing response?
Explanation
Choice A reason: "Diet and exercise is good for you and good for your heart." This statement is true, but it is not the appropriate nursing response. It does not address the client's concerns or provide any specific information about cardiac rehabilitation. It may also sound dismissive or patronizing to the client.
Choice B reason: "It's not unusual to feel that way at first, but once you learn the routine, you'll enjoy it." This statement is empathetic, but it is not the appropriate nursing response. It does not explain the purpose or benefits of cardiac rehabilitation. It may also sound unrealistic or optimistic to the client.
Choice C reason: "Cardiac rehabilitation cannot undo the damage to your heart, but it can help you get back to your previous level of activity safely." This statement is the appropriate nursing response. It acknowledges the client's condition and provides factual information about cardiac rehabilitation. It also emphasizes the positive outcomes of cardiac rehabilitation, such as improving physical function, reducing symptoms, and preventing further complications.
Choice D reason: "Your doctor is the expert here, and I'm sure he would only recommend what is best for you." This statement is respectful, but it is not the appropriate nursing response. It does not answer the client's question or provide any education about cardiac rehabilitation. It may also sound evasive or deferential to the client.
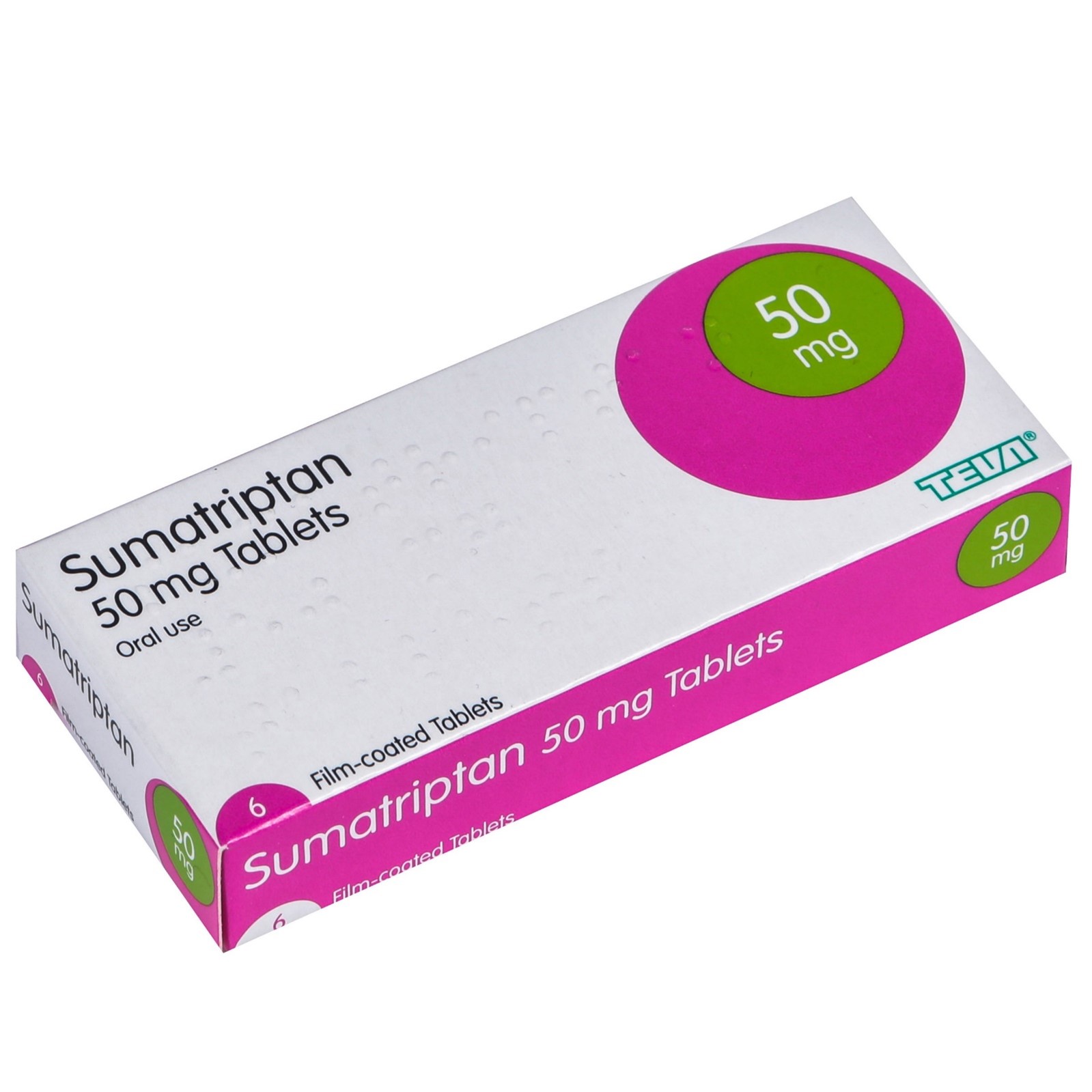
A nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for sumatriptan (Imitrex) tablets to treat migraine headaches. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Repeat dose in 1 hour for unrelieved headache. This instruction is incorrect because sumatriptan should not be taken more than twice in 24 hours. Taking too much sumatriptan can cause serious side effects, such as high blood pressure, stroke, or heart problems.
Choice B reason: Chew the tablet well before swallowing. This instruction is incorrect because sumatriptan tablets should be swallowed whole with water. Chewing the tablet may affect its absorption and effectiveness.
Choice C reason: If you experience chest pain, call your physician immediately. This instruction is correct because chest pain is a serious and potentially life-threatening side effect of sumatriptan. Chest pain may indicate a heart attack or coronary artery spasm, which require immediate medical attention.
Choice D reason: Take daily to prevent headaches. This instruction is incorrect because sumatriptan is not a preventive medication for migraines. It is only used to treat acute migraine attacks when they occur. Taking sumatriptan daily can cause rebound headaches, which are worse and more frequent than the original ones.

A nurse is delegating tasks to assistive personnel. Which of the following should the nurse consider when using one of the five rights of delegation?
Explanation
Choice A reason: The AP's ability to complete the task without assistance is not one of the five rights of delegation. The nurse is responsible for providing adequate supervision and guidance to the AP, and ensuring that the task is done correctly and safely.
Choice B reason: The AP's ability to prioritize is not one of the five rights of delegation. The nurse is responsible for assigning tasks based on their urgency and importance and communicating clear expectations and deadlines to the AP.
Choice C reason: The AP's rapport with clients is not one of the five rights of delegation. The nurse is responsible for maintaining a therapeutic relationship with clients and respecting their preferences and needs.
Choice D reason: The AP has the knowledge and skill to perform the task is one of the five rights of delegation. The nurse is responsible for assessing the AP's competence and readiness to perform the task, and providing appropriate training and feedback if needed.

The hospital's Emergency Operations Committee is working on their disaster plan. In which components should nurses be included? SELECT ALL THAT APPLY
Explanation
Choice A reason: Nurses performing duties outside of the nurses' typical job description is a component that should include nurses. In a disaster situation, nurses may have to assume roles and responsibilities that are beyond their usual scope of practice, such as triage, first aid, or mass casualty management. Nurses should be trained and prepared to perform these duties safely and effectively.
Choice B reason: A plan for comprehensive practice drills is a component that should include nurses. Practice drills are essential for testing and improving the disaster plan, as well as enhancing the skills and confidence of the staff. Nurses should participate in regular and realistic drills that simulate different types of disasters and scenarios.
Choice C reason: Identification of resources to meet anticipated needs for food, water, and supplies is a component that should include nurses. In a disaster situation, the demand for resources may exceed the supply, and the availability of resources may be disrupted or limited. Nurses should be involved in identifying and prioritizing the essential resources that are needed to provide care and support to the clients and staff.
Choice D reason: An internal and external communication plan is a component that should include nurses. In a disaster situation, communication is vital for coordinating actions, sharing information, and providing updates. Nurses should be aware of the communication channels and protocols that are used within and outside the hospital, such as radios, phones, or social media.
Choice E reason: Discharge all surgical clients who are one day or more post-op is not a component that should include nurses. This is not a realistic or appropriate strategy for reducing the hospital's occupancy or workload in a disaster situation. Discharging surgical clients who are still recovering may compromise their health outcomes and increase their risk of complications or readmission.
A nurse is caring for a client who has had a hemorrhagic stroke following a ruptured cerebral aneurysm. Which of the following manifestations should the nurse expect?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Gradual onset of several hours is not a manifestation of a hemorrhagic stroke. A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, causing bleeding into the surrounding tissue. This usually happens suddenly and without warning, and can cause rapid deterioration of the client's condition.
Choice B reason: Maintains consciousness is not a manifestation of a hemorrhagic stroke. A hemorrhagic stroke can cause increased intracranial pressure, which can compress the brain and impair its function. This can lead to loss of consciousness, coma, or death.
Choice C reason: Sudden severe headache is a manifestation of a hemorrhagic stroke. A hemorrhagic stroke can cause intense pain in the head, neck, or face, due to the pressure and irritation of the bleeding. The headache may be described as "the worst headache of my life" or "thunderclap headache".
Choice D reason: History of neurologic deficits lasting less than 1 hr. is not a manifestation of a hemorrhagic stroke. This is a characteristic of a transient ischemic attack (TIA), which is also known as a mini-stroke. A TIA occurs when a blood clot temporarily blocks an artery in the brain, causing temporary symptoms such as weakness, numbness, vision loss, or speech difficulty. A TIA does not cause permanent damage to the brain, but it is a warning sign of a possible future stroke.
A nurse who works in health promotion and safety for an automotive plant is functioning in what role?
Explanation
Choice A reason: A public health nurse is a nurse who works to improve the health and well-being of populations and communities, not specific workplaces. A public health nurse may focus on disease prevention, health promotion, environmental health, or emergency preparedness.
Choice B reason: A community nurse specialist is a nurse who has advanced education and training in a specific area of nursing practice, such as gerontology, oncology, or mental health. A community nurse specialist may work in various settings, such as hospitals, clinics, or schools, to provide specialized care and education to clients and families.
Choice C reason: A nurse clinician is a nurse who has expertise in clinical practice, research, and education. A nurse clinician may work in academic or clinical settings, such as universities, hospitals, or research centers, to develop and implement evidence-based practices and policies.
Choice D reason: An occupational health nurse is a nurse who works to protect and promote the health and safety of workers in various industries, such as manufacturing, mining, or construction. An occupational health nurse may provide services such as health assessment, injury prevention, emergency response, or wellness programs.
The nurse is providing education on epidemiology to a nursing student. Which of the following statements indicates the importance of epidemiology to the community health nurse? SELECT ALL THAT APPLY
Explanation
Choice A reason: Epidemiology interprets legislation in the community is not a statement that indicates the importance of epidemiology to the community health nurse. Epidemiology is not directly involved in interpreting legislation, but rather in providing evidence and recommendations that can inform policy-making and law-making.
Choice B reason: Epidemiology relates to the health status of a population is a statement that indicates the importance of epidemiology to the community health nurse. Epidemiology is the study of how diseases and other health-related factors are distributed and determined in populations. It helps the community health nurse to identify and monitor health problems, trends, and disparities in different groups and areas.
Choice C reason: Epidemiology analyzes and examines the root causes of health outcomes is a statement that indicates the importance of epidemiology to the community health nurse. Epidemiology uses various methods and tools to investigate and explain the causes and consequences of diseases and other health-related events. It helps the community health nurse to understand and address the complex and multifactorial factors that influence health, such as biological, environmental, social, behavioral, and economic factors.
Choice D reason: Epidemiology evaluates the effectiveness of nursing interventions is a statement that indicates the importance of epidemiology to the community health nurse. Epidemiology applies scientific principles and rigorous designs to assess and compare the outcomes and impacts of different interventions and programs on health. It helps the community health nurse to plan, implement, and evaluate evidence-based practices and policies that can improve health and quality of life.
Choice E reason: Epidemiology defines the burden of disease and determinants of health is a statement that indicates the importance of epidemiology to the community health nurse. Epidemiology measures and compares the frequency, severity, and impact of diseases and other health-related conditions on populations. It helps the community health nurse to prioritize and allocate resources, as well as to advocate for health equity and social justice.
The nurse is preparing for an initial home care visit for a client with diabetes. Which action by the nurse is appropriate? SELECT ALL THAT APPLY
Explanation
Choice A reason: Asking how they are managing at home is an appropriate action by the nurse. It shows respect and interest in the client's situation and helps to assess their needs, challenges, and goals.
Choice B reason: Going automatically into the client's bedroom is not an appropriate action by the nurse. It violates the client's privacy and autonomy and may make them feel uncomfortable or threatened. The nurse should ask for permission before entering any room in the client's home.
Choice C reason: Arranging mutual future visits is an appropriate action by the nurse. It demonstrates collaboration and commitment and helps to establish a trusting relationship with the client. It also allows the nurse to plan and coordinate the care and follow-up.
Choice D reason: Thanking the client for arranging a home visit is not an appropriate action by the nurse. It implies that the home visit is a favor or a burden, rather than a professional service that the client is entitled to. It may also undermine the nurse's authority and credibility.
Choice E reason: Sitting down and discussing with the client and family members is an appropriate action by the nurse. It indicates that the nurse values the client's perspective and input, and recognizes the family as an important source of support and information. It also facilitates communication and education and promotes shared decision-making.
The nurse provides education to a client who is newly diagnosed with multiple sclerosis (MS). Which client statements indicate the need for additional teaching? SELECT ALL THAT APPLY
Explanation
Choice A reason: "I may experience urinary incontinence." This statement does not indicate the need for additional teaching. It is a correct statement that reflects an understanding of one of the possible symptoms of MS. Urinary incontinence is caused by nerve damage that affects bladder control.
Choice B reason: "I should not exercise because this may trigger an exacerbation." This statement indicates the need for additional teaching. It is an incorrect statement that reflects a misconception about exercise and MS. Exercise does not cause or worsen MS relapses but rather has many benefits for people with MS, such as improving muscle strength, balance, mobility, mood, and quality of life.
Choice C reason: "I should alternate the eye patch every other day to help with the double vision." This statement indicates the need for additional teaching. It is an incorrect statement that reflects a misunderstanding of how to manage double vision, which is another possible symptom of MS. Alternating the eye patch every other day does not help with double vision, but rather may cause eye fatigue or confusion. The correct way to use an eye patch is to wear it on one eye only when needed, such as when reading or driving.
Choice D reason: "I may experience visual disturbances." This statement does not indicate the need for additional teaching. It is a correct statement that reflects an awareness of another possible symptom of MS. Visual disturbances may include blurred vision, loss of color vision, pain in one eye, or partial or complete blindness.
Choice E reason: "I need to check the water temperature before I take a bath." This statement does not indicate the need for additional teaching. It is a correct statement that reflects a precaution that people with MS should take. Checking the water temperature before taking a bath can prevent burns or scalds, as some people with MS may have reduced sensation or numbness in their skin.
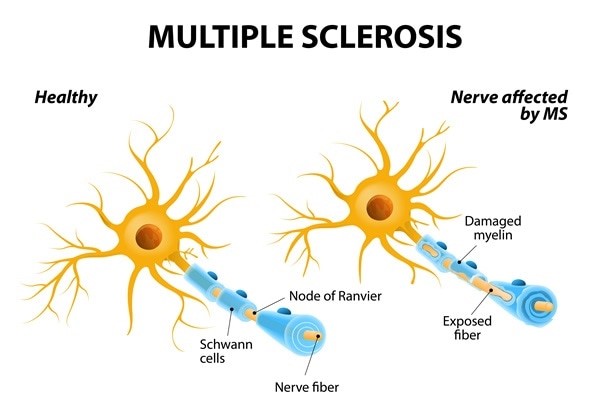
Discharge plans are being made for a 25-year-old hospitalized client diagnosed with multiple sclerosis. The client has significant muscle weakness in the lower extremities bilaterally. Which of the following facilities should the nurse expect this client to be discharged to?
Explanation
Choice A reason: A skilled nursing facility is a type of long-term care facility that provides 24-hour nursing care and supervision for residents who need assistance with activities of daily living, such as bathing, dressing, eating, and toileting. A skilled nursing facility may not be suitable for a young client with multiple sclerosis who has the potential for improvement and recovery.
Choice B reason: Home care services are a type of community-based care that provides medical and personal care to clients in their own homes. Home care services may include nursing, physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, social work, or home health aide services. Home care services may be appropriate for a client with multiple sclerosis who has mild to moderate symptoms and a supportive family or caregiver.
Choice C reason: A rehabilitation facility is a type of short-term care facility that provides intensive physical and occupational therapy to clients who have functional impairments due to injury, illness, or surgery. A rehabilitation facility may also provide medical, nursing, and psychological care to clients who need them. A rehabilitation facility may be suitable for a client with multiple sclerosis who has significant muscle weakness and needs to regain strength, mobility, and independence.
Choice D reason: A sub-acute care facility is a type of transitional care facility that provides medical and nursing care to clients who are stable but need complex monitoring or treatment that cannot be provided at home or in a skilled nursing facility. A sub-acute care facility may also provide rehabilitation services to clients who need them. A sub-acute care facility may not be appropriate for a young client with multiple sclerosis who has the potential for improvement and recovery.

An occupational health nurse in the clinic of an industrial plant is developing a guidebook for clinic workers. Which of the following actions should the nurse include as a secondary prevention strategy?
Explanation
Choice A: Collaborate with a physical therapist to develop programs for injured employees to return to work. This is incorrect because this is a tertiary prevention strategy, not a secondary prevention strategy. Tertiary prevention aims to restore function and prevent disability or complications after an injury or illness has occurred.
Choice B: Help plant workers identify signs of carpal tunnel syndrome. This is correct because this is a secondary prevention strategy. Secondary prevention aims to detect and treat health problems early before they become more serious or chronic. Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common occupational health problem that can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the hand and wrist. Early identification and treatment can prevent permanent nerve damage and disability.
Choice C: Organize an influenza immunization campaign. This is incorrect because this is a primary prevention strategy, not a secondary prevention strategy. Primary prevention aims to prevent disease or injury from occurring in the first place, by reducing exposure or risk factors. Influenza immunization can protect plant workers from getting infected by the flu virus and reduce the spread of the disease.
Choice D: Teach plant workers about proper lifting techniques. This is incorrect because this is also a primary prevention strategy, not a secondary prevention strategy. Proper lifting techniques can prevent musculoskeletal injuries such as sprains, strains, and herniated discs, by avoiding excessive stress on the spine and joints.
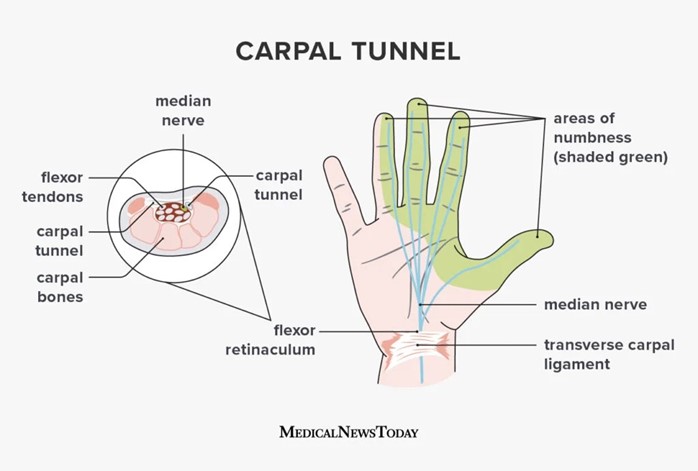
A charge nurse is making a room assignment for a client who has scabies. In which of the following rooms should the nurse place the client?
Explanation
Choice A reason: A negative-pressure isolation room is not a suitable room for a client who has scabies. A negative-pressure isolation room is used for clients who have airborne infections, such as tuberculosis or chickenpox. It prevents the contaminated air from escaping the room and infecting other people.
Choice B reason: A positive-pressure isolation room is not a suitable room for a client who has scabies. A positive-pressure isolation room is used for clients who have compromised immune systems, such as those undergoing bone marrow transplants or chemotherapy. It prevents the outside air from entering the room and exposing the client to germs.
Choice C reason: A private room is a suitable room for a client who has scabies. Scabies is a skin infection caused by tiny mites that burrow under the skin and cause intense itching and rash. Scabies can spread easily through direct skin-to-skin contact or sharing personal items, such as clothing or bedding. A private room can prevent the transmission of scabies to other clients or staff.
Choice D reason: A semi-private room with a client who has pediculosis capitis is not a suitable room for a client who has scabies. Pediculosis capitis is an infestation of head lice that feeds on human blood and causes itching and irritation on the scalp. Pediculosis capitis can also spread easily through direct contact or sharing personal items, such as combs or hats. Sharing a room with another client who has pediculosis capitis can increase the risk of cross-infection and complicate the treatment of both conditions.
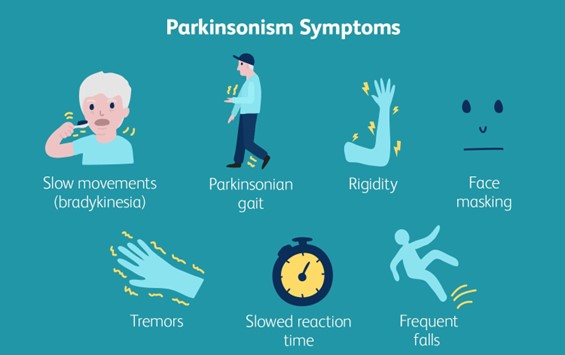
A nurse is caring for a client who has Parkinson's disease and is starting to display bradykinesia. Which of the following is an appropriate action by the nurse?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Giving the patient extra time to perform activities is an appropriate action by the nurse. Bradykinesia is a symptom of Parkinson's disease that causes slow and reduced movement, making it difficult for the patient to initiate and complete tasks. The nurse should respect the patient's autonomy and dignity, and allow them to do as much as they can by themselves, without rushing or interfering.
Choice B reason: Teaching the client to walk more quickly when ambulating is not an appropriate action by the nurse. Bradykinesia can affect the patient's gait and balance, making them prone to falls and injuries. The nurse should not encourage the patient to walk faster than their ability, but rather provide them with assistive devices, such as a cane or walker, and ensure a safe environment.
Choice C reason: Placing the client on a low-protein, low-calorie diet is not an appropriate action by the nurse. Bradykinesia does not require any specific dietary modifications, unless the patient has other comorbidities, such as diabetes or hypertension. The nurse should ensure that the patient has adequate nutrition and hydration, and avoid foods that may interfere with their medication absorption, such as high-fiber or high-fat foods.
Choice D reason: Completing passive range-of-motion exercises daily is not an appropriate action by the nurse. Bradykinesia can cause muscle stiffness and rigidity, which can limit the patient's range of motion and flexibility. The nurse should encourage the patient to do active range-of-motion exercises, which involve moving their own joints to their full extent, rather than passive ones, which involve someone else moving their joints for them. Active exercises can help maintain muscle strength and joint mobility and prevent contractures and deformities.
A nurse advises a client with osteoporosis to have three servings of milk or dairy products daily. Which of the following levels of prevention is being used by the nurse?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Proactive prevention is not a level of prevention, but rather a type of prevention that involves taking action before a problem occurs or worsens. It can be applied to any level of prevention, such as primary, secondary, or tertiary.
Choice B reason: Secondary prevention is a level of prevention that involves detecting and treating diseases or injuries early before they cause significant complications or disabilities. It includes activities such as screening tests, diagnostic tests, or medications.
Choice C reason: Tertiary prevention is a level of prevention that involves reducing the impact and consequences of diseases or injuries that have already occurred and caused damage or impairment. It includes activities such as rehabilitation, surgery, or palliative care.
Choice D reason: Primary prevention is a level of prevention that involves preventing diseases or injuries from occurring in the first place, by eliminating or reducing risk factors or enhancing protective factors. It includes activities such as immunization, education, or lifestyle modification. Advising a client with osteoporosis to have three servings of milk or dairy products daily is an example of primary prevention because it aims to prevent further bone loss and fractures by increasing calcium intake.
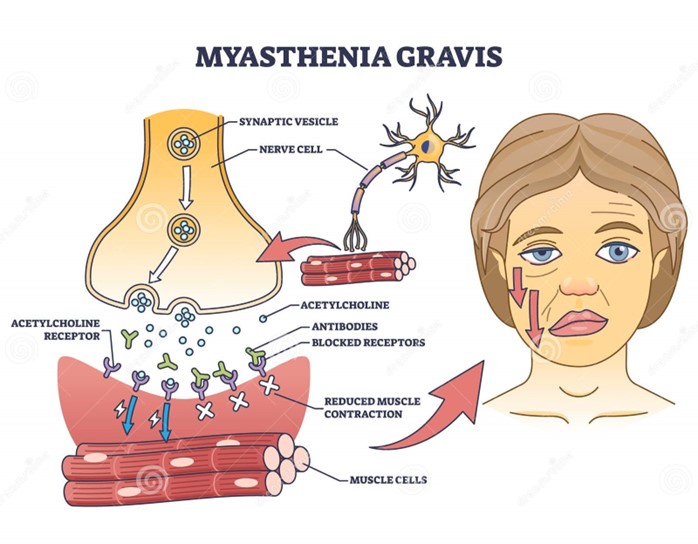
A client with myasthenia gravis has lost 6 kg of weight over the last 2 months. What should the nurse suggest to improve this client's nutritional status?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Planning medication doses to occur before meals is a good suggestion to improve the client's nutritional status. Myasthenia gravis is a neuromuscular disorder that causes weakness and fatigue of the voluntary muscles, especially those involved in chewing and swallowing. Taking anticholinesterase medications before meals can enhance muscle strength and coordination, and make it easier for the client to eat and avoid choking or aspiration.
Choice B reason: Restricting drinking fluids before and during meals is not a good suggestion to improve the client's nutritional status. Fluid intake is important for hydration and digestion, and should not be limited unless there is a medical reason, such as fluid overload or heart failure. Drinking fluids before and during meals can also help lubricate the food and prevent dryness or irritation of the mouth and throat.
Choice C reason: Increasing the amount of fat and carbohydrates in meals is not a good suggestion to improve the client's nutritional status. Fat and carbohydrates are sources of energy, but they can also increase the risk of obesity, diabetes, or cardiovascular disease if consumed excessively. A balanced diet that includes adequate protein, vitamins, minerals, and fiber is more beneficial for the client's health and well-being.
Choice D reason: Eating three large meals per day is not a good suggestion to improve the client's nutritional status. Eating large meals can be difficult and exhausting for the client with myasthenia gravis, as their muscle strength and endurance may decline over time. Eating smaller and more frequent meals can help maintain the energy level and prevent fatigue or hunger.
A nurse in the emergency room is assessing a client who was brought in following a seizure. The nurse suspects the client may have meningococcal meningitis when assessment findings include nuchal rigidity and a petechial rash. After implementing droplet precautions, which of the following actions should the nurse initiate next?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Administering an antipyretic is not the next action that the nurse should initiate. An antipyretic is a medication that lowers fever, which is a common symptom of meningococcal meningitis. However, fever is not a life-threatening condition, and it may have some beneficial effects on fighting infection. The nurse should first prioritize other actions that are more urgent or critical for the client's safety and outcome.
Choice B reason: Decreasing environmental stimuli is not the next action that the nurse should initiate. Decreasing environmental stimuli is a nursing intervention that can help reduce agitation, confusion, or seizures in clients with meningococcal meningitis. However, it is not an immediate or essential action, and it may not be effective if the client's condition worsens or progresses to coma.
Choice C reason: Assessing the cranial nerves is the next action that the nurse should initiate. Cranial nerve assessment is a neurological examination that evaluates the function of 12 pairs of nerves that originate from the brainstem and control various sensory and motor functions, such as vision, hearing, smell, taste, facial expression, eye movement, swallowing, speech, and balance. Meningococcal meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges, which are the membranes that cover and protect the brain and spinal cord. Meningeal inflammation can compress or damage the cranial nerves, causing various signs and symptoms, such as headache, photophobia, diplopia, facial palsy, dysphagia, dysarthria, or nystagmus. Assessing the cranial nerves can help detect any neurological deficits or complications early, and guide appropriate interventions or referrals.
Choice D reason: Completing a vascular assessment is not the next action that the nurse should initiate. A vascular assessment is a physical examination that evaluates the blood flow and circulation in different parts of the body, such as the arms, legs, abdomen, or neck. It may include checking pulses, blood pressure, capillary refill, skin color, temperature, or edema. A vascular assessment may be relevant for some clients with meningococcal meningitis who develop septic shock or disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), which are serious conditions that affect blood vessels and clotting factors. However, these are not common or early manifestations of meningococcal meningitis, and they require more advanced or specialized assessments and treatments.
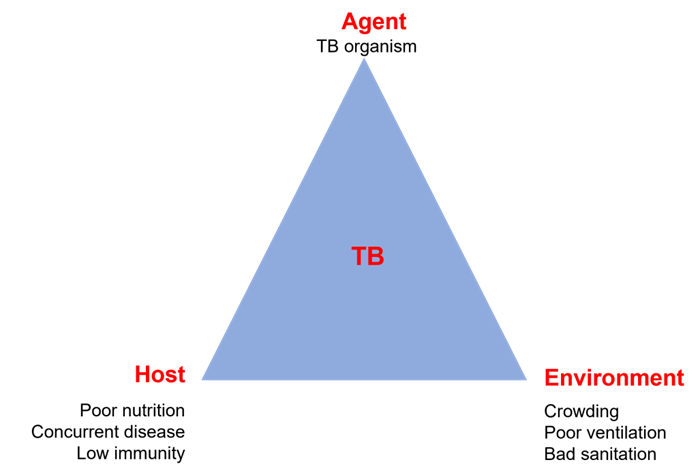
The community health nurse utilizes which of the following approaches to explain the factors that allow the reproduction and spread of infectious disease?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Natural history of disease is not an approach that explains the factors that allow the reproduction and spread of infectious disease. Natural history of disease is a concept that describes the progression and outcome of disease in the absence of any intervention. It includes stages such as susceptibility, exposure, incubation, prodrome, clinical, recovery, disability, or death.
Choice B reason: Health promotion is not an approach that explains the factors that allow the reproduction and spread of infectious diseases. Health promotion is a process that enables people to increase control over and improve their health. It involves strategies such as education, advocacy, policy, or community development.
Choice C reason: Levels of prevention is not an approach that explains the factors that allow the reproduction and spread of infectious disease. Levels of prevention is a framework that classifies different types of interventions based on their timing and purpose. It includes primary prevention (before disease occurs), secondary prevention (early detection and treatment), and tertiary prevention (reducing complications and disabilities).
Choice D reason: Epidemiologic triangle is an approach that explains the factors that allow the reproduction and spread of infectious disease. Epidemiologic triangle is a model that identifies three essential components of an infectious disease: agent (the microorganism that causes the disease), host (the person or animal that is infected), and environment (the physical, biological, or social factors that influence the transmission). The interaction and balance among these components determine the occurrence and spread of an infectious disease.
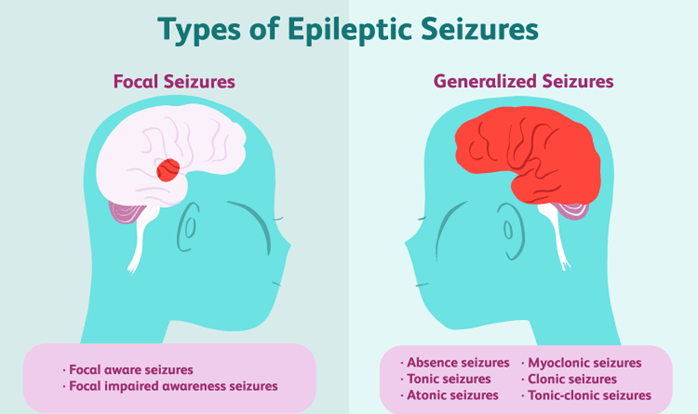
A nurse is teaching the family of a client who has a new diagnosis of epilepsy about actions to take if the client experiences a seizure. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A reason: "Move objects away from the client." This instruction should be included in the teaching. It is a safety measure that can prevent injury or harm to the client during a seizure. Moving objects away from the client can create more space and avoid contact with sharp, hard, or hot items.
Choice B reason: "Restrain the client." This instruction should not be included in the teaching. It is a harmful action that can worsen or prolong the seizure. Restraining the client can interfere with their natural movements, cause pain or discomfort, or damage their muscles or joints.
Choice C reason: "Place the client on his back." This instruction should not be included in the teaching. It is a dangerous position that can compromise the client's airway and breathing. Placing the client on his back can increase the risk of choking, aspiration, or suffocation.
Choice D reason: "Insert a padded tongue blade into the client's mouth." This instruction should not be included in the teaching. It is an outdated and ineffective practice that can cause more harm than good. Inserting a padded tongue blade into the client's mouth can damage their teeth, gums, tongue, or lips, or block their airway. Contrary to popular belief, it is impossible for a person to swallow their tongue during a seizure.
A nurse is determining if a homebound client is eligible for Meals-on-Wheels. Which of the following is the most important factor for the nurse to consider?
Explanation
Choice A reason: The client's financial resources is not the most important factor for the nurse to consider. Although Meals-on-Wheels is a low-cost or free service that provides nutritious meals to homebound seniors and people with disabilities, it does not require a specific income level or financial status to qualify. The nurse should focus on the client's nutritional and functional needs, rather than their economic situation.
Choice B reason: The client's level of family support is not the most important factor for the nurse to consider. Although having family members who can assist with meal preparation and delivery can be helpful and beneficial for the client, it is not a requirement or a guarantee for receiving Meals-on-Wheels. The nurse should assess the client's individual capabilities and preferences, rather than their family availability or involvement.
Choice C reason: The client's access to transportation is not the most important factor for the nurse to consider. Although having access to transportation can enable the client to obtain food and groceries from other sources, such as stores, markets, or restaurants, it is not a criterion or a barrier for receiving Meals-on-Wheels. The nurse should evaluate the client's dietary and health needs, rather than their mobility or transportation options.
Choice D reason: The client's ability to prepare meals is the most important factor for the nurse to consider. Meals-on-Wheels is designed to serve clients who are unable to cook or shop for themselves due to physical, mental, or social limitations. The nurse should determine if the client has any impairments or challenges that prevent them from preparing their own meals, such as vision loss, arthritis, dementia, or isolation. If the client has difficulty or inability to prepare meals, they may be eligible for Meals-on-Wheels.
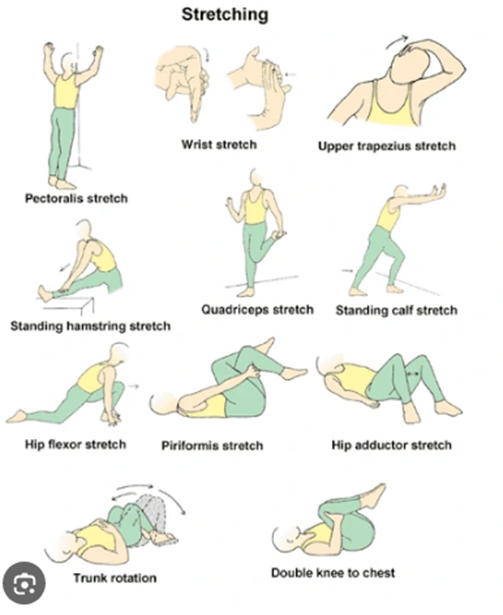
The nurse is creating an education plan for a client who has a recent diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the client's plan?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Providing total assistance with all ADLs is not an intervention that should be included in the client's plan. ADLs are activities of daily living, such as bathing, dressing, eating, and toileting. Providing total assistance with all ADLs can reduce the client's independence and self-esteem, and increase their dependence and learned helplessness. The nurse should encourage and assist the client to perform as much as they can by themselves and provide partial or intermittent assistance only when needed.
Choice B reason: Ordering a low-residue diet is not an intervention that should be included in the client's plan. A low-residue diet is a type of diet that limits foods that are high in fiber or indigestible material, such as whole grains, nuts, seeds, fruits, and vegetables. A low-residue diet may be recommended for clients who have inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), diverticulitis, or bowel obstruction, as it can reduce bowel frequency and irritation. However, it is not indicated for clients who have MS, unless they have other comorbidities that require it. A balanced diet that includes adequate fiber, fluids, and nutrients is more beneficial for clients who have MS.
Choice C reason: Encouraging the client to void every hour is not an intervention that should be included in the client's plan. Voiding every hour can be inconvenient and impractical for the client, and may not address their bladder problems effectively. MS can cause bladder dysfunction, such as urinary urgency, frequency, incontinence, or retention, due to nerve damage that affects bladder control. The nurse should assess the type and severity of the bladder dysfunction, and provide appropriate interventions, such as medication, catheterization, pelvic floor exercises, or bladder training.
Choice D reason: Instructing the client on daily muscle stretching is an intervention that should be included in the client's plan. Muscle stretching is a type of exercise that involves extending or elongating a muscle or group of muscles to their full length. Muscle stretching can help prevent or relieve muscle spasticity, stiffness, pain, or contractures that may occur in clients who have MS. The nurse should teach the client how to perform muscle stretching safely and correctly, and encourage them to do it daily or as prescribed.
A nurse is delegating tasks to the assistive personnel (AP). The nurse should direct the AP to complete which of the following tasks first?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Delivering a urine specimen to the laboratory is not a priority task, as it does not affect the client's immediate health or safety. This task can be done later or delegated to another staff member.
Choice B reason: Feeding a client who has bilateral casts is an important task, as it helps the client meet their nutritional needs and prevents complications such as pressure ulcers. However, this task is not as urgent as monitoring blood glucose levels, as it can be done within a reasonable time frame without causing harm to the client.
Choice C reason: Performing blood glucose monitoring of a client who has a prescription for short-acting insulin is a priority task, as it determines the dosage of insulin that the client needs to receive. Insulin is a high-alert medication that can cause serious adverse effects if given incorrectly. Therefore, this task should be done first by the AP who has been trained and certified to do so.
Choice D reason: Obtaining an extra box of tissues for a client who is concerned about running out of them is a low-priority task, as it does not affect the client's physical or psychological well-being. This task can be done at any time or delegated to another staff member.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 47 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

