ATI Medical Surgical Exam 9
Total Questions : 46
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreFour days following an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair, the client is exhibiting edema of both lower extremities, and pedal pulses are not palpable. Which action should the nurse implement first?
Explanation
A. Elevate extremities on pillows:
While elevation can be beneficial for reducing dependent edema, the priority is to assess the pulses first to determine the adequacy of peripheral perfusion.
B. Evaluate edema for pitting:
Assessing edema for pitting is important for gathering additional information, but it is not the initial action in this scenario. Assessing pulses is more critical to evaluate perfusion.
C. Wrap the feet with warmed blankets:
Warming the feet with blankets may be appropriate in some situations, but it is not the priority when the client is exhibiting edema and non-palpable pedal pulses. The primary concern is assessing perfusion.
D. Assess pulses with a vascular Doppler:
This is the correct action. The non-palpable pedal pulses are concerning and require immediate assessment to determine the status of peripheral perfusion. Using a vascular Doppler will help the nurse assess the presence or absence of blood flow in the lower extremities.
The nurse reports that a client is at risk for a brain attack (stroke) based on which assessment finding?
Explanation
A. Jugular vein distention:
Jugular vein distention is not typically associated with an increased risk of a stroke. It may be indicative of issues related to cardiac or fluid volume status.
B. Carotid bruit:
This is the correct answer. A carotid bruit, an abnormal sound caused by turbulent blood flow through the carotid artery, may indicate the presence of atherosclerosis and increased risk of stroke. It suggests a narrowing or blockage in the carotid artery, which can potentially lead to emboli and subsequent stroke.
C. Nuchal rigidity:
Nuchal rigidity, stiffness of the neck, is associated with conditions such as meningitis but is not a direct risk factor for a stroke.
D. Palpable cervical lymph node:
Palpable cervical lymph nodes may be indicative of infection or inflammation in the head and neck region but are not directly associated with an increased risk of a stroke.
Which information should the nurse include in the teaching plan of a client diagnosed with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)?
Explanation
A. Minimize symptoms by wearing loose, comfortable clothing:
This is the correct answer. Wearing loose, comfortable clothing can help alleviate pressure on the abdomen, reducing the likelihood of exacerbating GERD symptoms.
B. Sleep without pillows at night to maintain neck alignment:
This recommendation is not specifically related to GERD. In fact, elevating the head of the bed or using extra pillows can be helpful in preventing acid reflux during sleep.
C. Adjust food intake to three full meals per day and no snacks:
It is generally recommended for individuals with GERD to have smaller, more frequent meals rather than three large meals. Eating smaller portions can help reduce the likelihood of gastric distention and reflux.
D. Avoid participation in any aerobic exercise programs:
Exercise is generally beneficial for overall health, but intense aerobic exercise immediately after eating may contribute to GERD symptoms. However, this does not mean avoiding all aerobic exercise. It is more appropriate to advise against vigorous exercise immediately after meals.
The nurse is providing teaching to a client with Type 2 diabetes mellitus and peripheral neuropathy. Which information should the nurse provide?
Explanation
A. Family members can help with regular foot exams:
This is the correct answer. Regular foot exams are essential for individuals with diabetes, especially those with peripheral neuropathy. Family members can assist in identifying any changes, cuts, or wounds on the feet that the client might not be able to perceive due to neuropathy.
B. Heating pads are useful if on the lowest setting:
The use of heating pads is generally not recommended for individuals with peripheral neuropathy. They may have reduced sensation, making it difficult to detect if the pad is too hot, leading to the risk of burns.
C. Aching feet may be soaked in lukewarm water for one hour or more:
Prolonged soaking of feet is not advisable, as it can lead to maceration of the skin and increase the risk of infection. A short, lukewarm foot soak is generally acceptable, but the duration should be limited.
D. Shoes should be worn outside the house, but it is fine to be barefoot inside:
Individuals with diabetes and peripheral neuropathy should wear protective footwear both inside and outside the house to prevent injuries and reduce the risk of complications.
A client with a history of asthma reports having episodes of bronchoconstriction and increased mucous production while exercising. Which action should the nurse implement?
Explanation
A. Assess client for signs and symptoms of upper airway infection:
While upper airway infections can contribute to respiratory symptoms, the client's history of asthma and the exacerbation of symptoms during exercise suggest that asthma management should be a priority.
B. Determine if the client is using an inhaler before exercising:
This is a relevant consideration, and ensuring proper pre-exercise use of bronchodilators (such as an inhaler) is an important aspect of asthma management. However, the question is broader and involves a review of the client's overall asthma management.
C. Teach client to use pursed lip breathing when episodes occur:
Pursed lip breathing is a technique that can help manage symptoms, especially during episodes of bronchoconstriction. However, the focus here is on a more comprehensive assessment and review of the client's routine asthma management.
D. Review the client's routine asthma management prescriptions:
This is the correct answer. The client's reported symptoms during exercise suggest a potential need for adjustments to the routine asthma management plan. Reviewing the client's prescriptions, including the type and timing of medications, can help ensure optimal control of symptoms, especially during physical activity.
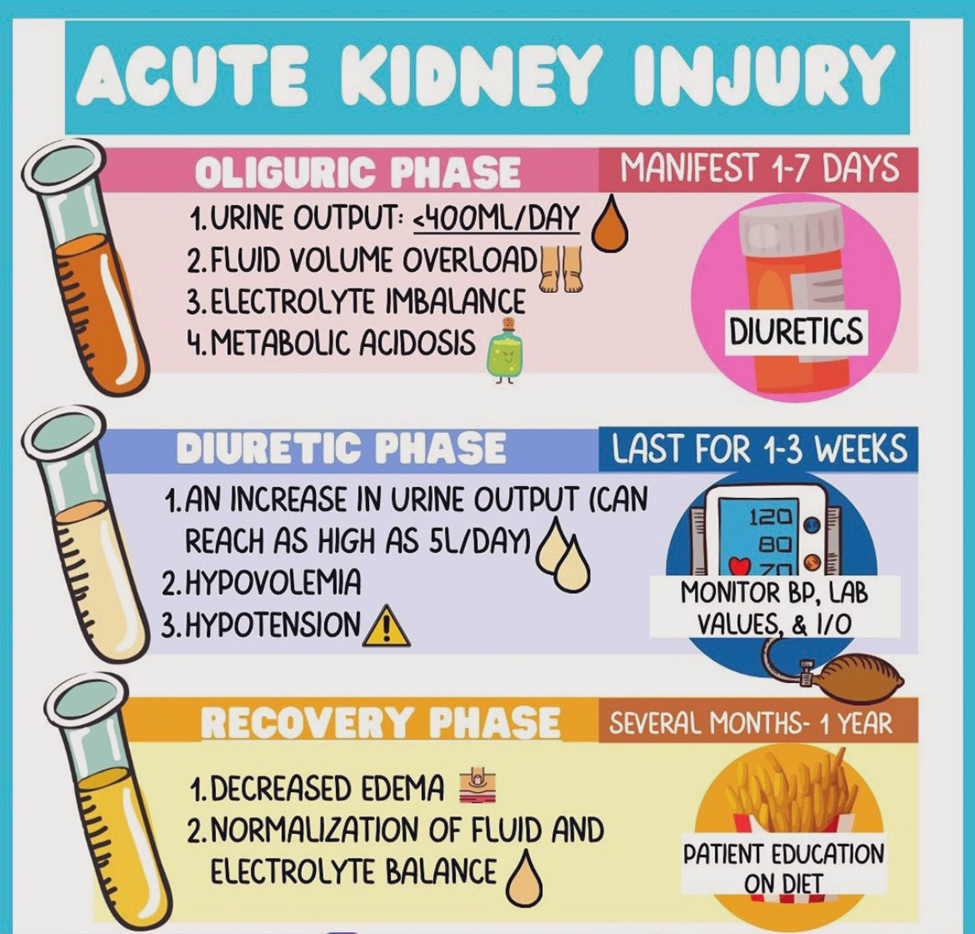
A client who has developed acute kidney injury (AKI) due to an aminoglycoside antibiotic has moved from the oliguric phase to the diuretic phase of AKI Which parameters are most important for the nurse to plan to carefully monitor?
Explanation
A. Hypovolemia and electrocardiographic (ECG) changes:
During the diuretic phase of AKI, there is an increased urine output, and the risk of dehydration and hypovolemia is elevated. The nurse should closely monitor fluid balance to prevent dehydration, and ECG changes may occur due to electrolyte imbalances (such as hypokalemia) associated with diuresis.
B. Uremic irritation of mucous membranes and skin surfaces:
Uremic symptoms are more prominent in the oliguric phase of AKI when waste products accumulate in the blood. In the diuretic phase, the focus shifts more toward managing fluid and electrolyte balance.
C. Side effects of total parental nutrition (TPN) and Intralipids:
TPN and Intralipids are not directly related to the diuretic phase of AKI. Monitoring for side effects of TPN and Intralipids may be relevant in other clinical contexts but is not the primary concern in the diuretic phase.
D. Elevated creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN):
Monitoring creatinine and BUN levels is important for assessing kidney function, but in the diuretic phase, the focus shifts to managing fluid and electrolyte balance. The risk of hypovolemia and electrolyte imbalances is more immediate during this phase.
The nurse has conducted a cancer prevention community education program. In evaluating the participants understanding of the carcinogens, which statement indicates an accurate understanding?
Explanation
A. Carcinogens are substances that contain cancerous cells:
This statement is incorrect. Carcinogens are substances that have the potential to cause cancer, but they do not necessarily contain cancerous cells themselves.
B. Substances that change a cell so that it becomes cancerous are potential sources of cancer:
This is the correct answer. Carcinogens are agents that can induce changes in the genetic material of cells, leading to the development of cancer. They can initiate or promote the process of carcinogenesis.
C. Environmental factors such as sunlight and chemicals can cause cancer to spread:
This statement is not accurate. Carcinogens can contribute to the initiation or promotion of cancer, but the spread of cancer (metastasis) involves complex biological processes and is not directly caused by environmental factors.
D. Carcinogens are in the environment and cannot be avoided:
This statement is not accurate. While carcinogens may be present in the environment, efforts can be made to minimize exposure and adopt preventive measures. Avoidance of known carcinogens and the promotion of a healthy lifestyle can contribute to cancer prevention.
The nurse is preparing a client for surgery who was admitted to the emergency center following a motor vehicle collision. The client has an open fracture of the femur and is bleeding moderately from the bone protrusion site. During the preoperative assessment, the nurse determines that the client currently receives heparin sodium 5,000 units subcutaneously daily. What is the priority nursing action?
Explanation
A. Have the client sign the surgical and transfusion permits:
While obtaining signed consent is important, the immediate concern is addressing the client's medication history, especially the use of heparin, which can contribute to bleeding.
B. Ensure that the potential for bleeding is explained to the client:
Education about the potential for bleeding is important, but the immediate action is to communicate the client's medication history to the healthcare provider for appropriate guidance.
C. Observe the heparin injection sites for signs of bruising:
Monitoring for bruising at injection sites is a consideration, but it is not the priority when the client is actively bleeding from an open fracture.
D. Notify the healthcare provider of the client's medication history:
This is the correct answer. Heparin is an anticoagulant, and its use can increase the risk of bleeding during surgery. The healthcare provider needs to be informed of the client's current medication history to make decisions regarding the timing and management of heparin therapy in the perioperative period.
A client who was recently diagnosed with Raynaud's disease is concerned about pain management. Which nursing instruction should the nurse provide?
Explanation
A. Return appointments will be needed for IV medication:
This statement does not address the specific concern related to pain management in Raynaud's disease, and routine IV medication may not be the primary approach for pain relief in this condition.
B. Wearing gloves when handling cold items guards against painful spasms:
This is the correct answer. Raynaud's disease is characterized by vasospasm of small arteries, often triggered by exposure to cold or stress. Wearing gloves helps to minimize exposure to cold and can prevent painful spasms associated with Raynaud's.
C. Enrolling in a pain clinic can provide pain relief alternatives:
While pain clinics can offer various pain management strategies, the specific recommendation for Raynaud's disease involves minimizing exposure to cold and stress rather than enrolling in a pain clinic.
D. Painful areas should be rubbed gently until the pain subsides:
Rubbing painful areas may not be recommended, as it can potentially aggravate vasospasm in individuals with Raynaud's disease. The emphasis is on preventing triggers like cold exposure.
A client with gouty arthritis reports tenderness and swelling of the right ankle and great toe. The nurse observes the area of inflammation extends above the ankle area. The client receives prescriptions for colchicine and indomethacin. Which instruction should the nurse include in the discharge teaching?
Explanation
A. Drink at least 8 cups (1920 mL) of water per day:
This is the correct answer. Adequate hydration is important in the management of gout because it helps to flush out uric acid and prevent the formation of urate crystals. Increasing fluid intake, especially water, is a key component of gout management.
B. Eat high protein foods to achieve ideal body weight:
While maintaining a healthy weight is important in managing gout, the emphasis should be on a balanced diet that includes adequate hydration and avoidance of foods high in purines, which can contribute to increased uric acid levels.
C. Encourage active range of motion to limit stiffness:
Active range of motion exercises can be beneficial for joint health, but the primary emphasis in gout management is on dietary and pharmacological interventions.
D. Use an electric heating pad when pain is at its worse:
Applying heat may provide some relief, but it is not the primary intervention for gout. Cold compresses or ice may be more appropriate for acute gout attacks.
The nurse is preparing to obtain a rapid coronavirus (COVID-19) test for a client who was exposed to the virus eight days ago. The client is experiencing fever, cough, and shortness of breath. Which action is most important for the nurse to take?
Explanation
A. Move the client to a private room, keep the door closed, and initiate droplet precautions:
This is the correct answer. Given the client's symptoms and potential exposure to COVID-19, it is important to take infection control measures. Placing the client in a private room, keeping the door closed, and initiating droplet precautions help prevent the potential spread of the virus.
B. Start an intravenous infusion for antiviral drug to be administered for positive COVID-19 test results:
Antiviral medications are typically prescribed based on confirmed COVID-19 test results and the severity of symptoms. Starting an intravenous infusion at this stage, before test results are available, is premature and not indicated.
C. Counsel family members to monitor for illness symptoms for 2 weeks after last contact with the patient:
While it is important for family members to monitor for symptoms, the immediate concern is the isolation and testing of the symptomatic client. Contact tracing may follow, but infection control measures for the client are the priority.
D. Assist the client to recall everyone possibly exposed since onset of symptoms:
While contact tracing is important, the immediate action is to isolate the client and initiate precautions. Contact tracing can be done as part of a broader public health response but is not the initial step.
The nurse is evaluating a client's understanding of diet teaching about the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) eating plan. Which behavior indicates that the client is adhering to the eating plan?
Explanation
A. Carefully cleans and peels all fresh fruit and vegetables:
While cleaning and peeling fresh fruits and vegetables may contribute to food safety, it is not a specific indication of adherence to the DASH eating plan.
B. Uses only lactose-free dairy products:
The DASH eating plan encourages the consumption of low-fat or fat-free dairy products. Using lactose-free dairy products may be necessary for individuals with lactose intolerance, but it is not a specific behavior related to the DASH plan.
C. No longer includes grains in the daily diet:
The DASH eating plan includes whole grains as part of a balanced diet. Eliminating grains altogether is not consistent with the DASH plan, which encourages the consumption of whole grains.
D. Enjoys fat-free yogurt as an occasional snack food:
This is the correct answer. The DASH eating plan recommends the inclusion of low-fat or fat-free dairy products as part of a heart-healthy diet. Choosing fat-free yogurt as an occasional snack aligns with the principles of the DASH plan, which emphasizes low-fat dairy options.
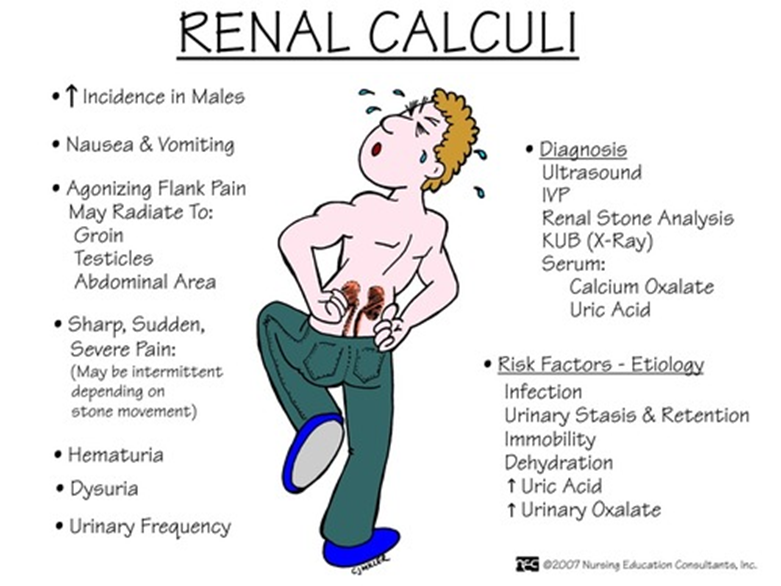
The nurse is obtaining a health history from a new client who has a history of kidney stones. Which statement by the client indicates an increased risk for renal calculi?
Explanation
A. Jogs more frequently than usual daily routine:
Exercise, including jogging, is generally not associated with an increased risk of renal calculi. In fact, regular physical activity can have health benefits.
B. Eats a vegetarian diet with cheese 2 to 3 times a day:
A vegetarian diet alone is not necessarily a risk factor for renal calculi. However, the inclusion of high-oxalate foods, such as certain types of cheese, may contribute to the formation of kidney stones.
C. Experiences additional stress since adopting a child:
Stress is not a direct risk factor for renal calculi. However, certain dietary and lifestyle factors play a more significant role in stone formation.
D. Drinks several bottles of carbonated water daily:
This is the correct answer. Consuming large amounts of carbonated water, especially if it is high in phosphoric acid, can contribute to the formation of kidney stones. Carbonated beverages may increase the excretion of calcium in the urine, potentially leading to stone formation.
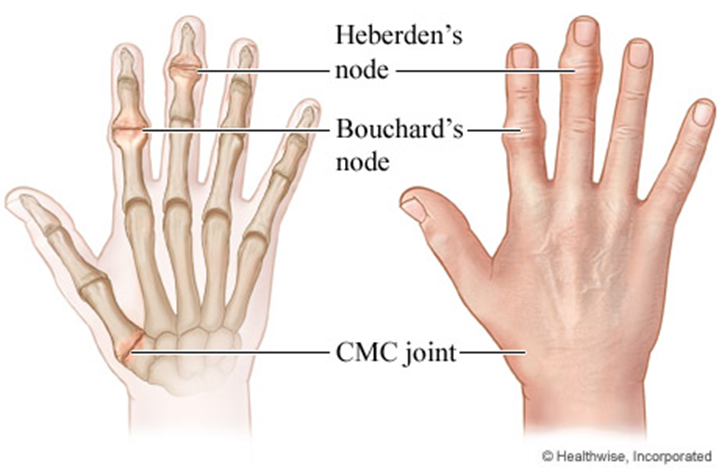
While assessing a client with degenerative joint disease, the nurse observes Heberden's nodes, large prominences on the client's fingers that are reddened. The client reports that the nodes are painful. Which action should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. Discuss approaches to chronic pain control with the client:
This is the correct answer. Heberden's nodes are bony enlargements that can occur in osteoarthritis, particularly in the joints of the fingers. These nodes can be associated with pain. Discussing approaches to chronic pain control with the client is an appropriate nursing intervention to address the client's pain and improve quality of life.
B. Review the client's dietary intake of high-protein foods:
Dietary intake of high-protein foods is not directly related to the management of Heberden's nodes in degenerative joint disease. Pain control and joint protection measures are more relevant.
C. Notify the healthcare provider of the finding immediately:
While it's important to communicate significant findings to the healthcare provider, the presence of Heberden's nodes in degenerative joint disease may not require immediate notification unless there are other concerning symptoms or complications.
D. Assess the client's radial pulses and capillary refill time:
Assessing radial pulses and capillary refill time is not directly related to managing Heberden's nodes in degenerative joint disease. These nodes are primarily a result of joint changes in osteoarthritis.
The nurse is performing the preoperative assessment for a client scheduled for a vertebroplasty of the cervical spine. Which finding should the nurse alert the healthcare provider of prior to the procedure?
Explanation
A. Platelet count 40,000 x10/μL (40.000 x109/L):
This is the correct answer. A platelet count of 40,000 x10/μL is significantly below the normal range (usually around 150,000 to 450,000/μL). Low platelet count (thrombocytopenia) can increase the risk of bleeding during and after a surgical procedure. The healthcare provider should be alerted to assess the risk and determine the appropriate management.
B. White blood cells 9,000/μL (9x109/L):
The white blood cell count is within the normal range, and it is not a significant concern for a vertebroplasty procedure.
C. Hematocrit 38% (0.38):
The hematocrit level is within the normal range and is not a significant concern for a vertebroplasty procedure.
D. Hemoglobin 12 g/dL (120 g/L):
The hemoglobin level is within the normal range and is not a significant concern for a vertebroplasty procedure.
An adult client who had a gastric bypass surgery 2 weeks ago, is admitted with possible anastomosis leakage. The client's abdomen is tender to touch, and the vital signs are: temperature 101° F (38.3° C), heart rate 130 beats/minute, respiratory rate 26 breaths/minute, and blood pressure 100/50 mmHg Which intervention is most important for the nurse to include in the client's plan of care?
Explanation
A. Encourage regular turning:
While turning is important for preventing complications like pressure ulcers, in this acute situation, addressing fluid imbalance and potential sepsis take precedence.
B. Monitor skin for breakdown:
Monitoring for skin breakdown is essential but is not the most critical intervention at this moment.
C. Assess wound drainage daily:
Daily assessment of wound drainage is important for evaluating the status of the surgical site. However, in this situation of potential anastomosis leakage with signs of systemic infection and hypotension, immediate interventions to stabilize the client's condition are of higher priority.
D. Strict IV fluid replacement:
This is the correct answer. The client is displaying signs of systemic infection (fever) and possible sepsis (tachycardia, hypotension), which might be due to an anastomosis leakage following gastric bypass surgery. Ensuring adequate IV fluid replacement is crucial to address hypotension, maintain perfusion, and support hemodynamic stability in this critical situation.

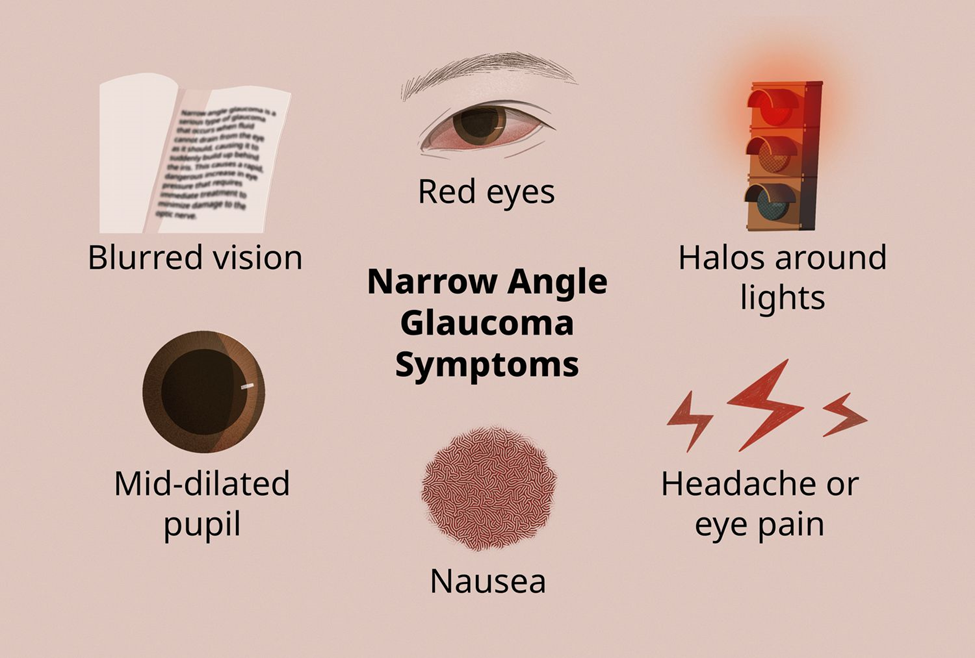
An adult who was recently diagnosed with glaucoma tells the nurse, "it feels like I am driving through a tunnel." The client expresses great concern about going blind. Which nursing instruction is most important for the nurse to provide this client?
Explanation
A. Eat a diet high in carotene:
While a healthy diet is important for overall well-being, there is no evidence to suggest that a diet high in carotene specifically prevents or treats glaucoma. The focus in glaucoma management is on intraocular pressure control.
B. Wear prescription glasses:
Prescription glasses may be beneficial for addressing refractive errors, but they do not specifically address the management of glaucoma. The client's concern about driving through a tunnel is more likely related to changes in peripheral vision associated with glaucoma.
C. Avoid frequent eye pressure measurements:
This is not the most important instruction. Monitoring intraocular pressure is a crucial aspect of glaucoma management, and the frequency of measurements is determined by the healthcare provider. Regular monitoring helps assess the effectiveness of treatment and disease progression.
D. Maintain the prescribed eye drop regimen:
This is the correct answer. The most important instruction for the client is to adhere to the prescribed eye drop regimen. Medications, often in the form of eye drops, are commonly used to lower intraocular pressure and manage glaucoma. Consistent use of prescribed medications is critical for controlling the condition and preventing further vision loss.
An older client who is agitated, dyspneic, orthopneic, and using accessory muscles to breathe is admitted for further treatment. Initial assessment includes a heart rate 128 beats/minute and irregular, respirations 38 breaths/minute, blood pressure 168/100 mmHg, wheezes and crackles in all lung fields. An hour after the administration of furosemide 60 mg IV, which assessments should the nurse obtain to determine the client's response to treatment? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
A. Skin elasticity:
Assessing skin elasticity is a measure of hydration status. Improved skin turgor may suggest that the client is responding positively to diuretic therapy by eliminating excess fluid. However, this may not be as immediate or specific as other indicators of response.
B. Urinary output:
Monitoring urinary output is crucial when administering diuretics like furosemide. Increased urine output indicates that the diuretic is promoting the elimination of excess fluid from the body, which is a desired effect in managing heart failure and fluid overload.
C. Oxygen saturation:
Assessing oxygen saturation is important in monitoring respiratory status. Improvement in oxygen saturation levels indicates that the client is responding to interventions aimed at relieving respiratory distress, such as the administration of furosemide.
D. Lung sounds:
Monitoring lung sounds is a key aspect of assessing respiratory function. Reduction in wheezes and crackles suggests that the diuretic is helping to alleviate pulmonary congestion and fluid accumulation in the lungs, contributing to improved respiratory function.
E. Pain scale:
Assessing pain is relevant if the client has reported chest pain or discomfort associated with heart failure. Reduction in pain may indicate improved cardiac function and response to treatment. However, it's important to note that pain assessment may not be as specific to the effects of furosemide as other respiratory and fluid status indicators.
The healthcare provider prescribes penicillin 200, 000 units intramuscularly for a client with pneumonia. The available vial is labeled, "Penicillin 500,000 units/mL". How many mL should the nurse administer to this client? (Enter numerical value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest tenth.)
Explanation
To answer this question, you need to use the formula:
mL = units prescribed / units per mL
Plug in the given values:
mL = 200,000 / 500,000
Simplify the fraction:
mL = 2 / 5
Convert the fraction to a decimal:
mL = 0.4
Therefore, the nurse should administer 0.4 mL of penicillin to this client.
A client with eczema is applying 10% urea cream onto the affected skin areas. Which finding reflects the expected therapeutic response?
Explanation
A. Reduced pain in eczematous areas:
While hydration of the skin may contribute to reduced pain in some cases, the primary goal of urea cream is to moisturize and hydrate the skin rather than directly address pain.
B. Healing with a return to normal skin appearance:
Urea cream can contribute to the healing process by hydrating the skin and promoting the removal of dry, scaly skin. However, complete healing and a return to normal skin appearance may also depend on the underlying cause of eczema and other factors.
C. Decreased weeping of ulcerations in affected areas:
Urea cream can help reduce excessive dryness and weeping in eczematous areas by promoting hydration and moisture balance. However, it may not directly address ulcerations, and other interventions may be needed for open wounds.
D. Hydration of affected dry skin areas:
This is the correct answer. Urea is a natural moisturizing factor that helps retain water in the skin. Applying urea cream to affected dry skin areas is expected to hydrate the skin, reduce dryness, and improve the overall moisture balance.
An overweight, young adult client who was recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus is admitted for a hernia repair. The client reports feeling very weak and jittery. Which actions should the nurse implement? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
A. Measure pulse and blood pressure:
This action is crucial to assess the client's cardiovascular status. Weakness and jitteriness can be related to changes in blood pressure or cardiac function. Measuring pulse and blood pressure helps determine the client's hemodynamic stability.
B. Document anxiety on the surgical checklist:
While anxiety is a valid consideration, addressing the physiological aspects of the client's symptoms takes precedence.
C. Assess skin temperature and moisture:
Assessing skin temperature and moisture provides information about the client's perfusion and hydration status. Changes in skin characteristics can be indicative of underlying issues, and in a diabetic patient, it's important to monitor for potential complications affecting skin integrity.
D. Check fingerstick glucose level:
Given the client's recent diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus and the reported symptoms of weakness and jitteriness, checking the fingerstick glucose level is crucial. Fluctuations in blood glucose levels, whether hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia, can contribute to these symptoms. This test provides immediate information about the client's glycemic status.
E. Administer a PRN dose of regular insulin:
If the fingerstick glucose level indicates hyperglycemia and the healthcare provider has prescribed a PRN (as needed) dose of regular insulin for high blood sugar, administering insulin may be necessary to address hyperglycemia promptly. This is in line with diabetes management protocols, and the nurse should follow specific orders and guidelines for insulin administration.
When providing care for an unconscious client who has seizures, which nursing intervention is most essential?
Explanation
A. Keep the room at a comfortable temperature:
While maintaining a comfortable room temperature is important for the overall well-being of the client, it is not the most essential intervention during a seizure. The priority during a seizure is to ensure the client's safety, particularly focusing on airway management.
B. Ensure oral suction is available:
This is the most essential intervention. During a seizure, the client may produce excessive saliva, and having oral suction readily available helps prevent airway obstruction and ensures a clear airway. It is crucial for the safety and well-being of the client.
C. Provide frequent mouth care:
Mouth care is important for the overall hygiene of the unconscious client, but it may not be the most immediate priority during a seizure. The focus during a seizure is on preventing complications such as aspiration or airway obstruction.
D. Maintain the client in a semi-Fowler's position:
Positioning is important for the comfort and safety of the unconscious client, but maintaining a semi-Fowler's position may not be the primary concern during an active seizure. The immediate focus is on airway management and preventing injury.
While caring for a client with a full thickness burn covering 40% of the body, the nurse observes purulent drainage at the wound. Before reporting this finding to the healthcare provider, the nurse should review which of the client's laboratory values?
Explanation
A. Blood pH level:
The blood pH level is important for assessing the acid-base balance in the body. However, in the context of purulent drainage from a wound, it is not the primary laboratory value to review for signs of infection.
B. Platelet count:
Platelet count is important for assessing blood clotting ability. While it is a valuable parameter in overall care, it may not be directly related to the observation of purulent drainage from a wound, which typically suggests infection rather than a clotting issue.
C. Hematocrit:
Hematocrit measures the proportion of blood that is cellular. Like platelet count, it is important for assessing overall blood composition and oxygen-carrying capacity. However, it may not be the first parameter to review when evaluating signs of infection.
D. White blood cell (WBC) count:
The WBC count is a crucial parameter when assessing for infection. An elevated WBC count is a common response to infection as the body mobilizes its immune defenses. Reviewing the WBC count is particularly relevant when purulent drainage is observed, as it may indicate an inflammatory response to infection.
The nurse is caring for a client with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) who has developed oral thrush and is experiencing burning and soreness in the mouth. Which intervention should the nurse implement first?
Explanation
A. Administer a topical analgesic:
Administering a topical analgesic can help alleviate pain and discomfort associated with oral thrush. However, it addresses the symptom rather than the cause of the issue.
B. Cleanse the mouth with swabs:
Cleansing the mouth with swabs can be part of the care plan for managing oral thrush. It helps remove debris and may reduce the fungal load in the mouth.
C. Obtain a soft diet for the client:
Providing a soft diet is important for clients with oral thrush as it minimizes irritation to the affected area. However, it may not be the first intervention; rather, it is part of the overall care plan.
D. Encourage frequent mouth care:
Encouraging the client to perform frequent mouth care is the most immediate and direct intervention. This includes gentle rinsing with a mild solution, which can help relieve symptoms and prevent the spread of the infection.
Which action should the nurse implement to reduce the risk of vesicant extravasation in the client who is receiving intravenous chemotherapy?
Explanation
A. Instruct the client to drink plenty of fluids during the treatment.
This option focuses on hydration, which is generally important during chemotherapy to flush out toxins and maintain overall health. However, it does not specifically address the risk of vesicant extravasation.
B. Keep the head of the bed elevated until the treatment is completed.
Keeping the head of the bed elevated is a measure that may be taken for certain conditions or treatments, but it is not directly related to preventing vesicant extravasation.
C. Monitor the client's intravenous site hourly during the treatment.
This is the correct choice. Monitoring the intravenous site for signs of extravasation, such as swelling, redness, or pain, is crucial when administering vesicant chemotherapy drugs. Early detection allows for prompt intervention to minimize potential tissue damage.
D. Administer an antiemetic before starting the chemotherapy.
Administering an antiemetic (a medication to prevent or alleviate nausea and vomiting) is important for managing side effects of chemotherapy, but it does not specifically address the prevention of vesicant extravasation.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 46 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

