ATI NUR 229 Pharmacology Test #1 OEK
Total Questions : 44
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is giving discharge instructions to a patient who has been ordered Guaifenesin (Mucinex) to take BID for 3 days after discharge. What response by the patient lets her know that he understands how to take his medication?
Explanation
This response demonstrates that the patient understands the dosing frequency (twice a day) and the importance of taking it with a full glass of water, which aligns with the instructions provided by the nurse.
The other choices are incorrect because:
A. "Taking this medication can cause me to develop a non-productive cough.": This response is about a potential side effect of the medication, rather than showing an understanding of the dosing instructions.
B. "I will take my medication Daily with a full glass of water.": This response indicates a misunderstanding of the dosing frequency, as the prescription specifically states "BID" (twice a day) rather than "daily."
D. "The medication will have to be given by my Home Health Nurse twice a day.": This response suggests a reliance on the home health nurse to administer the medication, which contradicts the instructions for the patient to take it themselves. It shows a misunderstanding of the patient's responsibility in self-administering the medication.
Which type of medication is the first-line treatment for nasal congestion?
Explanation
Nasal glucocorticoids, also known as intranasal corticosteroids, are considered the most effective and recommended first-line treatment for nasal congestion caused by allergic rhinitis or non-allergic rhinitis. They work by reducing inflammation in the nasal passages, relieving congestion, and improving other symptoms such as itching, sneezing, and runny nose.
Leukotriene modifiers, decongestants, and antihistamines can also be used to manage nasal congestion, but they are generally considered second-line options or adjunct therapies.
Decongestants provide temporary relief by constricting blood vessels in the nasal passages, while antihistamines help with symptoms related to allergies. Leukotriene modifiers are primarily used for managing asthma and are not typically the first choice for nasal congestion alone.
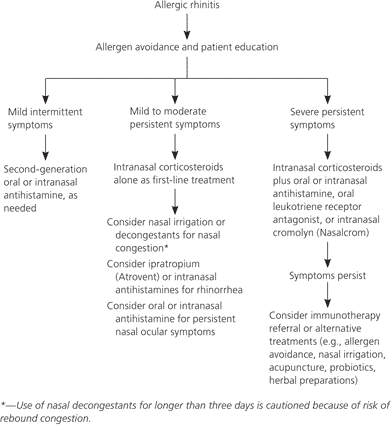
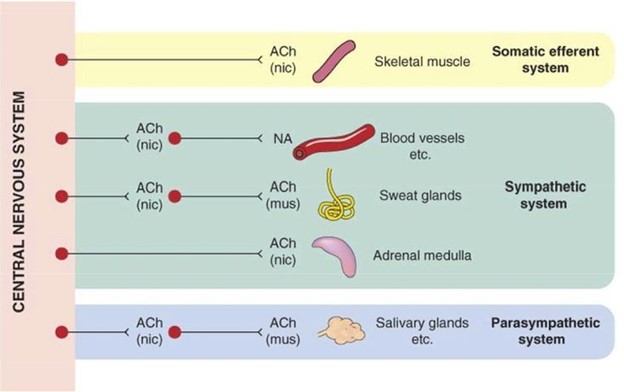
The sympathetic nervous system postganglionic neuron releases what neurotransmitter?
Explanation
The sympathetic nervous system postganglionic neurons primarily release norepinephrine as their neurotransmitter. These neurons are part of the autonomic nervous system and are responsible for coordinating the body's "fight or flight" response to stress or danger.
Norepinephrine acts as a neurotransmitter at the postganglionic synapses and binds to adrenergic receptors in the target tissues, mediating the physiological responses associated with sympathetic activation.
While acetylcholine is the primary neurotransmitter released by the preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system, it is not the neurotransmitter released by postganglionic neurons. Epinephrine (also known as adrenaline) is released into the bloodstream by the adrenal medulla and acts as a hormone, not a neurotransmitter. Arginine is an amino acid and is not directly involved in the neurotransmission of the sympathetic nervous system.
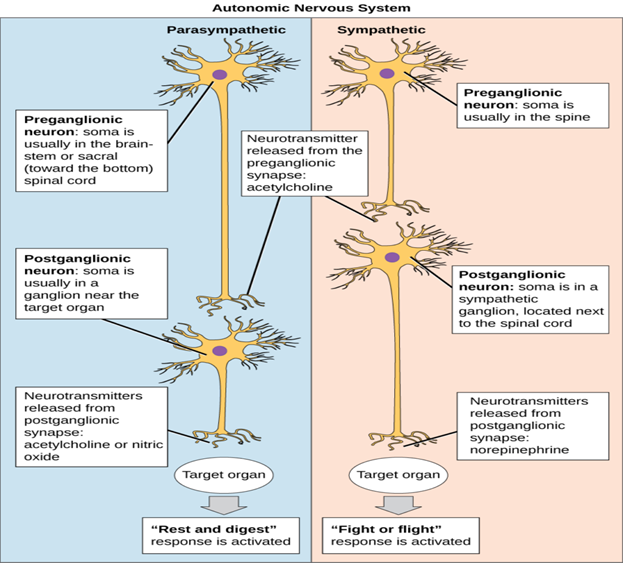
A nurse is caring for a client who is taking montelukast. Which of the following outcomes indicates a therapeutic effect of the medication?
Explanation
Montelukast is a leukotriene receptor antagonist commonly used to manage asthma and allergic rhinitis. Its primary therapeutic effect is to improve respiratory symptoms by reducing inflammation and constriction of the airways. Therefore, an increased ease of breathing would be an expected outcome indicating that the medication is working effectively.
The other options are incorrect because:
A. The client's seizure threshold is reduced: Montelukast does not have any effect on the seizure threshold. This outcome is unrelated to the medication and may be indicative of a different condition or treatment.
B. The client experiences less muscle pain: Montelukast is not indicated for reducing muscle pain. This outcome is unrelated to the medication and may be indicative of a different condition or treatment.
D. The client's platelet count is increased: Montelukast does not have an effect on platelet count. This outcome is unrelated to the medication and may be indicative of a different condition or treatment.
Patient teaching regarding expectorants should instruct the patient to perform which action?
Explanation
Expectorants are medications that help thin and loosen mucus in the respiratory tract, making it easier to cough up and clear from the airways. Increasing fluid intake, particularly water helps to keep the mucus thin and less sticky, facilitating its removal. Adequate hydration can help promote effective expectoration and relieve congestion.
The other options are incorrect because:
B. Taking the medication once a day only, usually at bedtime: The dosing frequency and timing of expectorants can vary depending on the specific medication prescribed. It is important to follow the healthcare provider's instructions regarding the dosing schedule.
C. Increase fiber and fluid intake to prevent constipation: This instruction is unrelated to expectorant use. Increasing fiber and fluid intake is commonly recommended to promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation, but it is not directly related to expectorant therapy.
D. Restrict fluids to decrease mucus production: Restricting fluids can lead to dehydration and thickening of mucus secretions. It is important to stay adequately hydrated to maintain thin and easily expectorated mucus. Restricting fluids is not recommended for managing mucus production.
A nurse is caring for a client who asks how albuterol helps his breathing. Which of the following responses should the nurse make? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
The nurse should make the following responses regarding how albuterol helps the client's breathing:
- The medication will open the airways.
- The medication will prevent wheezing.
Albuterol is a bronchodilator medication commonly used to treat respiratory conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It works by relaxing the smooth muscles in the airways, leading to the dilation of the bronchial tubes and increased airflow. This mechanism helps open up the airways and prevent or relieve symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
The other options are incorrect because:
The medication will decrease coughing episodes: While albuterol may indirectly reduce coughing episodes by opening up the airways and improving airflow, its primary effect is on bronchodilation rather than directly targeting coughing.
The medication will stimulate the flow of mucus: Albuterol is not known to stimulate mucus flow. Instead, it focuses on bronchodilation to improve airflow in the lungs.
The medication will reduce inflammation: Albuterol is primarily a bronchodilator and does not have a significant anti-inflammatory effect. Other medications, such as corticosteroids, are typically used to address inflammation in respiratory conditions.
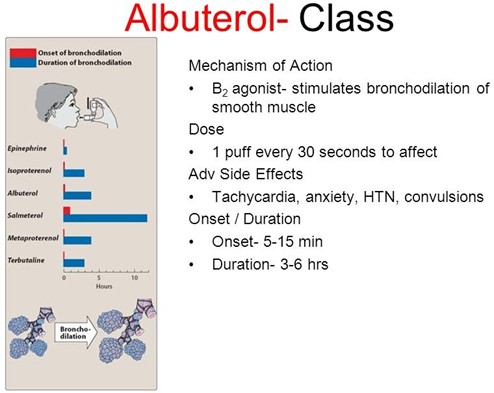
A patient is in an urgent care center with an acute asthma attack. The nurse expects which medication will be used for initial treatment.
Explanation
During an acute asthma attack, the airways become narrowed and inflamed, leading to symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. Short-acting beta2 agonists like Albuterol are the first-line medication for relieving acute asthma symptoms. They work by quickly relaxing the smooth muscles in the airways, resulting in bronchodilation and improved airflow. Albuterol provides rapid relief of symptoms and is often administered via inhalation.
A. Long-acting beta2 agonists (e.g., salmeterol) are typically used as maintenance therapy for long-term control of asthma symptoms, rather than for immediate relief during an acute attack.
C. Corticosteroids (e.g., fluticasone) are anti-inflammatory medications that are often prescribed for asthma, but they are more commonly used as part of a long-term management plan and may not provide immediate relief during an acute attack.
D. Anticholinergics (e.g., ipratropium) are sometimes used in combination with short-acting beta2 agonists for acute asthma exacerbations, but they are not typically the initial treatment choice for an acute asthma attack.
A nurse is preparing to administer a medication to a client who states. "That looks different from the pill I usually take." Which of the following responses should the nurse make?
Explanation
This response reassures the client that the medication they are about to receive is the one prescribed by their healthcare provider. It acknowledges their concern and provides the necessary reassurance regarding the medication's authenticity and appropriateness for their treatment.
The other options are not as appropriate because:
A. "This pill is probably from a different lot number than yours at home." While lot numbers may vary between different batches of medications, it does not address the client's concern about the difference in appearance. It does not provide a direct explanation or reassurance regarding the medication they are about to take.
B. "This hospital might use a different manufacturer, but the medication is the same." This response acknowledges the possibility of a different manufacturer but does not directly address the client's concern about the difference in appearance. It may not provide sufficient reassurance regarding the medication they are about to receive.
D. "Describe what the pill looks like." This response asks the client to describe the appearance of the pill, which does not directly address their concern or provide reassurance. It is important for the nurse to provide a clear explanation and reassurance in response to the client's statement.
A nurse is providing discharge instructions to a client who has asthma and is about to start taking theophylline (Theo-24). The nurse should tell the client that this medication might cause which of the following adverse effects?
Explanation
Theophylline is a bronchodilator medication used in the treatment of asthma and other respiratory conditions. It works by relaxing the smooth muscles in the airways, allowing for easier breathing. However, theophylline is associated with potential adverse effects, and one of the most significant concerns is its potential to cause dysrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms).
Dysrhythmias can include tachycardia (rapid heart rate), atrial fibrillation, or other disturbances in heart rhythm.
Constipation is not a commonly reported adverse effect of theophylline. Oliguria (decreased urine output) is not typically associated with theophylline use. Drowsiness can occur with theophylline, but dysrhythmias are considered a more significant and potentially serious adverse effect. It is crucial for the nurse to educate the client about the potential for dysrhythmias and advise them to report any irregular heartbeat or other cardiac symptoms promptly.

A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who has asthma and a new prescription for fluticasone/salmeterol. For which of the following adverse effects should the nurse instruct the client to report to the provider?
Explanation
White coating in the mouth: A white coating in the mouth could be a sign of a fungal infection such as oral thrush. Fluticasone, which is a corticosteroid, can increase the risk of developing fungal infections. Therefore, the nurse should instruct the client to report any signs of oral thrush or other unusual changes in the mouth, such as white patches or discomfort, to the provider.
Prompt identification and treatment of oral thrush are necessary to prevent its progression and ensure effective management of the client's condition.
Dry oral mucous membranes: Dry oral mucous membranes are not typically associated with fluticasone/salmeterol use. However, if the client experiences persistent or severe dryness in the mouth or any other unusual oral symptoms, it should be reported to the provider. Dry mouth can sometimes occur as a side effect of medications or indicate other underlying issues that need to be addressed.
Sedation: Sedation is not a common side effect of fluticasone/salmeterol. If the client experiences excessive drowsiness or sedation that interferes with their daily activities, it may be important to report this to the provider. While sedation is not a typical adverse effect of this medication, individual responses can vary, and it is essential to ensure appropriate monitoring and management.
Increased appetite is not typically associated with fluticasone/salmeterol use. It is not a commonly reported adverse effect of the medication. However, if the client experiences significant and unexplained changes in appetite that are concerning or persistent, it may be worth mentioning to the provider during a follow-up appointment or as part of ongoing monitoring.
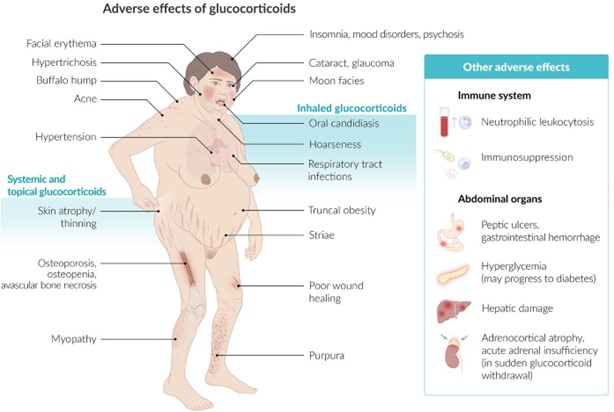
A 26-year-old female is brought to the emergency department while having an asthma attack. She is given a nebulizer treatment with the medication albuterol. The nurse's immediate assessment priority would be to
Explanation
During an asthma attack, the primary concern is the patient's ability to breathe and maintain adequate oxygenation. Monitoring the patient's respiratory rate and oxygen saturation (SpO2) with a pulse oximeter provides crucial information about the effectiveness of the albuterol treatment and the patient's respiratory status. It helps determine if the airway is opening up, if oxygen levels are improving, and if the patient is responding positively to the medication.
While determining the time of the patient's last meal can be relevant for certain interventions, it is not the immediate priority during an asthma attack. It is more important to focus on assessing and managing the patient's breathing and oxygenation first.
Monitoring the patient's temperature and blood pressure can be important for a comprehensive assessment, but they are not the immediate priority during an acute asthma attack. Addressing the patient's respiratory distress takes precedence.
Providing education on asthma management and treatment is an important aspect of care, but it should be done after the patient's acute symptoms are addressed and stabilized. In the immediate assessment phase, the focus is on assessing and managing the patient's respiratory status. Education can be provided once the patient's immediate needs are addressed.
The nurse teaches the client that the major disadvantage of antitussive therapy on Robitussin A-C is that:
Explanation
Robitussin A-C contains codeine, which is an opioid antitussive that can have sedating effects. One of the major disadvantages of using this medication is the potential for drowsiness as a side effect. This can impair the client's ability to perform tasks that require alertness and can interfere with daily activities.
The other options listed are not the major disadvantage of antitussive therapy with Robitussin A-C:
The medication is irritating to the bronchial tree: Robitussin A-C is primarily used as an antitussive (cough suppressant) rather than for its effects on the bronchial tree. While it may have some mild irritant properties due to certain ingredients, it is not considered a major disadvantage of this medication.
The client may use the medication for 14 days: The duration of use for Robitussin A-C is typically determined by the healthcare provider based on the client's condition. While prolonged use of antitussives is generally not recommended without medical supervision, the duration of use is not considered the major disadvantage of this medication.
The medication is very expensive: The cost of medication can vary, and while cost may be a consideration for some individuals, it is not considered the major disadvantage of Robitussin
A-C specifically. The major disadvantage relates more to the potential for drowsiness caused by the medication.
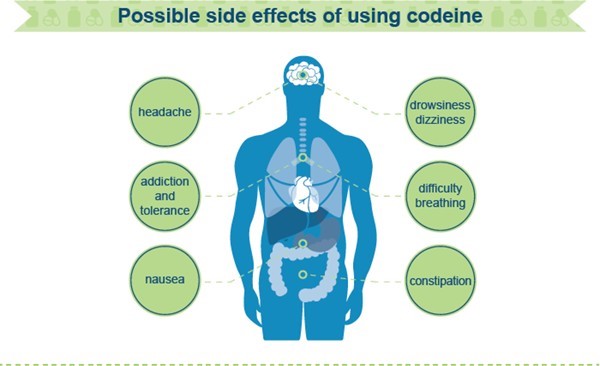
nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for codeine. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Codeine is an opioid medication that can cause drowsiness and dizziness. Changing positions quickly, especially from lying down to standing up, can increase the risk of falls or accidents.
Instructing the client to change positions slowly helps prevent orthostatic hypotension (a drop in blood pressure upon standing) and reduces the risk of falls.
The other options listed are not appropriate instructions for a client taking codeine:
A. "You should expect to experience diarrhea while taking this medication." While constipation is a common side effect of opioids, diarrhea is not typically associated with codeine use. Therefore, there is no need to expect or warn about diarrhea as an anticipated effect of taking codeine.
C. "You should limit alcohol intake to 12 ounces daily." Mixing alcohol with codeine can have harmful effects, such as increased sedation and respiratory depression. However, it is generally recommended to avoid alcohol completely while taking codeine, rather than setting a specific limit of 12 ounces daily.
D. "You should take the medication on an empty stomach to prevent nausea." Taking codeine with or without food can vary depending on individual factors and the specific instructions provided by the healthcare provider. However, taking codeine on an empty stomach does not necessarily prevent nausea. In fact, taking it with food may help reduce stomach upset for some individuals. It is best to follow the specific instructions provided by the healthcare provider regarding the timing of codeine administration with or without food.
A nurse is teaching a class about medication reconciliation. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
The nurse should include the following information in the teaching about medication reconciliation:
● Provide a list of the client's current medications during admission to a healthcare facility.
● Provide a list of the client's current medications during the change of shift report.
Medication reconciliation is a critical process that involves comparing the medications a patient is currently taking with the medications ordered or intended to be prescribed. It helps ensure accurate and safe medication management during transitions of care. The nurse should emphasize the importance of providing a list of the client's current medications during admission to a healthcare facility. This information helps establish a baseline for the patient's medication regimen and allows healthcare providers to verify and reconcile the medications accurately.
Additionally, the nurse should instruct the class to provide a list of the client's current medications during the change of shift report. This allows for effective communication between healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care and preventing medication errors or omissions.
While not specifically mentioned in the options, it is important to note that medication reconciliation should be performed at various points, including during the discharge process from a healthcare facility. Discharge medication reconciliation helps ensure a smooth transition to home or another healthcare setting, reduces the risk of medication-related issues, and promotes patient safety and adherence to the prescribed medication regimen.
Regarding over-the-counter medications, it is crucial to include them in the medication reconciliation process. Over-the-counter medications can interact with prescription medications and have potential side effects. Including them in the reconciliation report helps identify any potential interactions or duplications and ensures comprehensive medication management.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System utilizes which neurotransmitter?
Explanation
The Parasympathetic Nervous System utilizes the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is released by the postganglionic neurons of the parasympathetic nervous system and acts on target organs and tissues to elicit parasympathetic responses. It plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including digestion, heart rate, respiratory rate, and other rest and digestion activities.
A nurse is providing discharge instructions to a client who has asthma and a new prescription for montelukast. The nurse should instruct the client to report which of the following adverse effects to the provider?
Explanation
Montelukast is a medicine used to treat and prevent asthma and allergic rhinitis. It can cause some side effects, such as stomach pain, headache, cough, or fever. However, some side effects are more serious and need to be reported to the provider.
According to the sources I found, the most serious side effect of montelukast that should be reported to the provider is depression. Depression is a mental health condition that can affect your mood, thoughts, and behavior. It can cause symptoms such as feeling sad, hopeless, or worthless; losing interest in activities you used to enjoy; having trouble sleeping or concentrating; or having thoughts of harming yourself or others.
Montelukast has been linked to neuropsychiatric events, such as agitation, aggression, sleep disturbances, suicidal thoughts and behavior (including suicide). The mechanisms underlying these events are not well understood, but they can occur at any time during treatment. Therefore, patients and caregivers should be alert for changes in behavior or new neuropsychiatric symptoms when taking montelukast. If these occur, they should discontinue montelukast and contact a healthcare provider immediately.
The other options are not listed as serious side effects of montelukast that need to be reported to the provider. Constipation, blurred vision, and palpitations are possible side effects of other medicines used to treat asthma or allergic rhinitis, such as corticosteroids, antihistamines, or beta-agonists. However, they are not specific to montelukast and may not be related to its use.

A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has asthma and a new prescription for inhaled beclomethasone. Which of the following instructions should the nurse provide?
Explanation
Beclomethasone is an inhaled corticosteroid commonly used for the treatment of asthma. One of the potential side effects of inhaled corticosteroids is oral candidiasis, also known as thrush. Rinsing the mouth with water after each administration helps to reduce the risk of developing thrush by removing any residual medication from the mouth and throat.
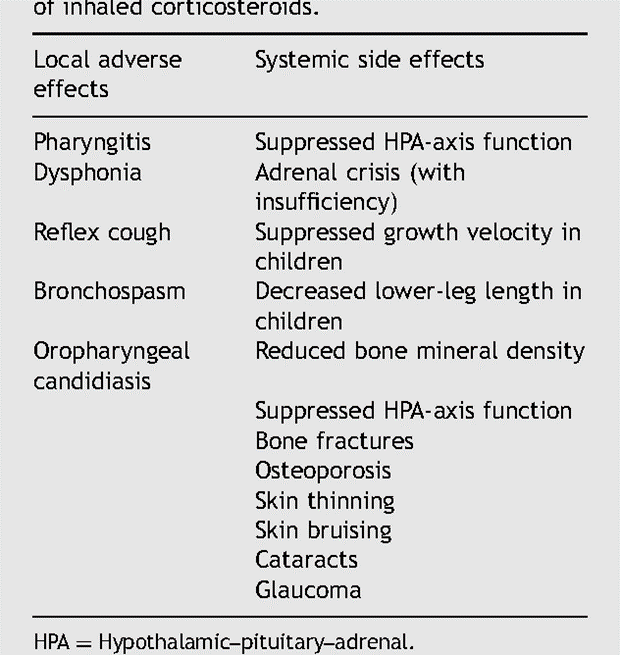
The other options listed are not specific instructions for inhaled beclomethasone:
A. Check the pulse after medication administration: While it is important to monitor vital signs, such as pulse, in certain situations, checking the pulse after inhaled beclomethasone administration is not a specific instruction for this medication.
B. Limit caffeine intake: There is no specific need to limit caffeine intake when taking inhaled beclomethasone. However, it is generally advisable to discuss dietary considerations, including caffeine, with a healthcare provider, as individual factors and medication interactions can vary.
C. Take the medication with meals: Inhaled beclomethasone is usually taken as prescribed by the healthcare provider, and the timing of administration with meals is not typically specified.
However, it is important for the client to follow the specific instructions provided by their healthcare provider regarding the timing and frequency of inhaled medication administration.
A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who reports taking pseudoephedrine for sinus congestion as needed. The nurse should identify that pseudoephedrine is contraindicated for which of the following client conditions?
Explanation
Pseudoephedrine is a sympathomimetic medication that acts as a decongestant by constricting blood vessels in the nasal passages, which helps to relieve sinus congestion. However, it can also cause vasoconstriction in other parts of the body, leading to an increase in blood pressure. Therefore, it is contraindicated for individuals with hypertension (high blood pressure).
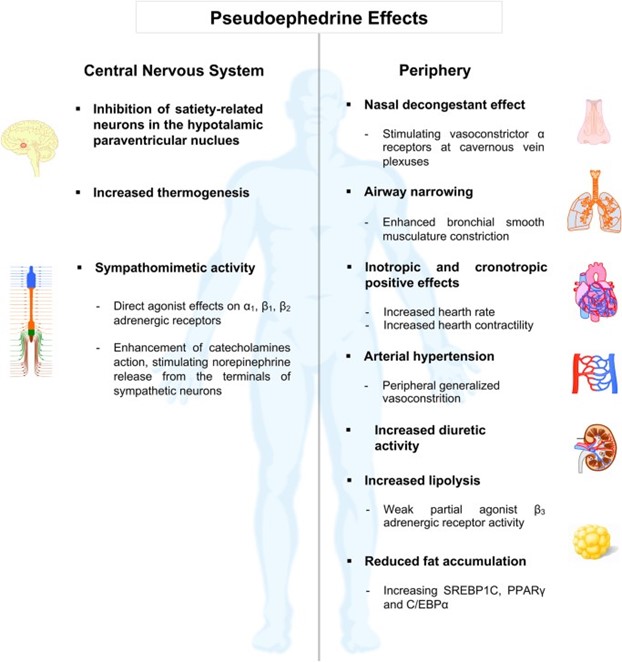
The other conditions mentioned, migraines, eczema, and diverticulitis, are not contraindications for the use of pseudoephedrine. However, it is important for individuals with these conditions to consult their healthcare provider before taking pseudoephedrine, as it may interact with other medications or exacerbate certain symptoms.
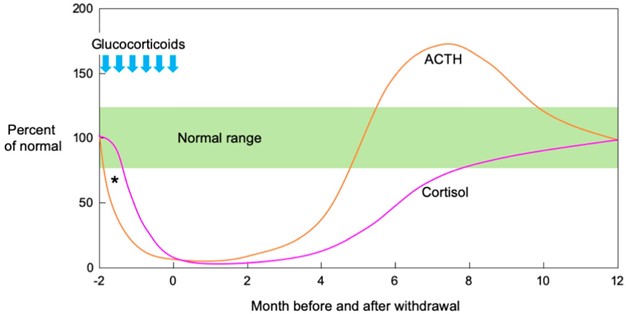
A nurse is teaching a client who has been taking prednisone to treat asthma and has a new prescription to discontinue the medication. The nurse should explain to the client to reduce the dose gradually to prevent which of the following adverse effects?
Explanation
Prednisone is a corticosteroid medication commonly used to treat asthma and other inflammatory conditions. When taken for a prolonged period at higher doses, it can suppress the body's natural production of cortisol, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands. Abruptly stopping prednisone after long-term use can lead to adrenocortical insufficiency, also known as adrenal insufficiency or adrenal crisis.
Adrenocortical insufficiency occurs because the body's adrenal glands need time to resume normal cortisol production after being suppressed by prednisone. Gradually reducing the dose of prednisone allows the adrenal glands to gradually increase their cortisol production, minimizing the risk of adrenal insufficiency.
Rebound pulmonary congestion, hyperglycemia, and severe dehydration are not specific adverse effects associated with discontinuing prednisone. However, it is important for clients who have been taking prednisone to follow their healthcare provider's instructions regarding the tapering schedule and any potential risks or side effects.
A nurse is caring for a child who has asthma and a prescription for montelukast granules. Which of the following instructions should the nurse provide the client's parent on administering the medication?
Explanation
Montelukast is a leukotriene receptor antagonist commonly used for the maintenance treatment of asthma in children and adults. The usual recommended dose is once daily in the evening for adults and once daily in the evening or in the morning for children, depending on the specific instructions from the healthcare provider.
A. Administering the granules mixed with 20 oz of water is not necessary. Montelukast granules can be administered directly into the mouth or mixed with a small amount of soft food (e.g., applesauce) if necessary. The specific instructions for administration should be provided by the healthcare provider or included in the product labeling.
B. Administering the medication 2 hours before exercise is not a general instruction for montelukast use. However, in some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe a short-acting bronchodilator such as albuterol to be taken before exercise to prevent exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. This should be discussed with the healthcare provider if applicable.
D. Administering the medication at the onset of wheezing is not the recommended approach. Montelukast is a daily maintenance medication for asthma and should be taken regularly as prescribed, regardless of wheezing symptoms. It is not intended to be used for immediate relief of wheezing or acute asthma symptoms. Short-acting bronchodilators are typically used for quick relief of wheezing or acute asthma symptoms.
A nurse is providing discharge teaching to the parent of a child who is prescribed diphenhydramine 25 mg elixir every 4 hr as needed. The amount available is diphenhydramine elixir 12.5 mg/5 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer per dose? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
To determine the mL of diphenhydramine elixir to administer per dose, we need to calculate the dose based on the prescribed amount and the concentration of the elixir.
Given:
Prescribed dose: 25 mg Concentration of elixir: 12.5 mg/5 mL
We can set up a proportion to find the equivalent mL for the prescribed dose: 25 mg / x mL = 12.5 mg / 5 mL
Cross-multiplying and solving for x, we get:
25 mg * 5 mL = 12.5 mg * x mL 125 mg = 12.5 mg * x mL
125 mg / 12.5 mg = x mL 10 mL = x mL
Therefore, the nurse should administer 10 mL of diphenhydramine elixir per dose.
A nurse is caring for a client who has poison ivy and is prescribed diphenhydramine. Which of the following instructions should the nurse give regarding the adverse effect of dry mouth associated with diphenhydramine?
Explanation
Dry mouth is a common side effect of diphenhydramine, which is an antihistamine medication commonly used to relieve symptoms of allergies, including itching and rash. Chewing on sugarless gum or sucking on hard, sour candies can help stimulate saliva production and alleviate the discomfort of dry mouth.
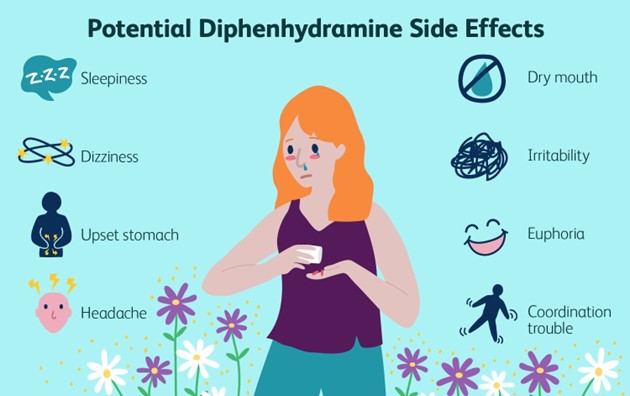
A. "Administer the medication with food": While taking diphenhydramine with food may help reduce the risk of stomach upset, it does not directly address the dry mouth side effect.
B. "Discontinue the medication and notify your provider": Discontinuing the medication without consulting the healthcare provider is not recommended unless specifically instructed to do so. Dry mouth is a common side effect of diphenhydramine and can be managed with supportive measures.
C. "Place a humidifier at your bedside every evening": While using a humidifier can help add moisture to the air and potentially alleviate dryness in the environment, it is not a specific instruction for managing dry mouth caused by diphenhydramine.
A nurse is teaching a client who has asthma about how to use an albuterol inhaler. Which of the following actions by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
When using an albuterol inhaler, it is important for the client to take a slow and deep inhalation while releasing the medication from the inhaler. After inhaling the medication, holding the breath for about 10 seconds allows the medication to reach deep into the airways and maximize its effectiveness.
The other actions mentioned are not correct:
A. Waiting 10 minutes between inhalations: Albuterol inhalers are typically used as a quick-relief medication for acute symptoms, and waiting 10 minutes between inhalations may not provide immediate relief when needed. The specific instructions on the frequency of inhalations should be provided by the healthcare provider.
B. Taking a quick inhalation while releasing the medication from the inhaler: It is important to take a slow and deep inhalation while releasing the medication to ensure that the medication reaches the lungs effectively. Taking a quick inhalation may result in less effective delivery of the medication.
D. Exhaling as the medication is released from the inhaler: It is important to exhale fully before using the inhaler to ensure that the medication is inhaled deeply into the lungs. Exhaling while releasing the medication can interfere with the proper inhalation technique.
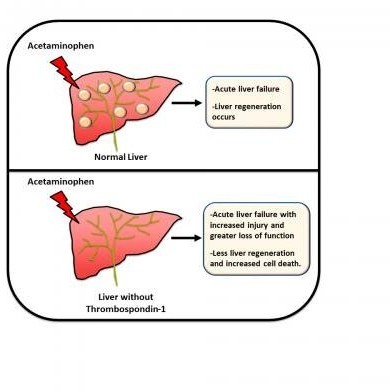
A contraindication for the use of Acetaminophen (Tylenol) in a patient is:
Explanation
Acetaminophen is generally considered safe and well-tolerated when used appropriately. However, it is primarily metabolized by the liver, and in cases of severe hepatic impairment or liver failure, the metabolism of acetaminophen can be significantly impaired. This can lead to the accumulation of toxic metabolites, which can cause further liver damage and potentially result in hepatotoxicity.
Hypertension, gallbladder disease, and tachyarrhythmias are not typically considered contraindications for the use of acetaminophen. However, it is important to consider any potential interactions or precautions when using acetaminophen in patients with these conditions, and consulting with a healthcare provider is recommended to ensure the safe and appropriate use of the medication.
A nurse is caring for a client who is prescribed diphenhydramine to relieve pruritus. The client asks the nurse how he can minimize the daytime sedation he is experiencing. Which of the following responses should the nurse give?
Explanation
Diphenhydramine is an antihistamine medication that can cause sedation as a side effect. Taking most of the daily dose at bedtime can help minimize daytime sedation. By taking the medication closer to bedtime, the sedative effects are more likely to occur during sleep, reducing the impact of sedation during waking hours.
The other options mentioned are not effective strategies to minimize daytime sedation caused by diphenhydramine:
A. "Distribute the doses evenly throughout the day": This approach may lead to a consistent level of sedation throughout the day and may not effectively minimize daytime sedation.
B. "Gradually decrease the dose once tolerance to the effect is reached": Gradually decreasing the dose of diphenhydramine is not a recommended strategy for minimizing daytime sedation. It is important to follow the prescribed dose and consult with a healthcare provider before making any changes to the medication regimen.
C. "Take the medication with meals": Taking diphenhydramine with meals may help reduce the risk of stomach upset but does not directly address the issue of daytime sedation.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 44 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

