ATI NURSING 135 Exam Spring 2023
Total Questions : 40
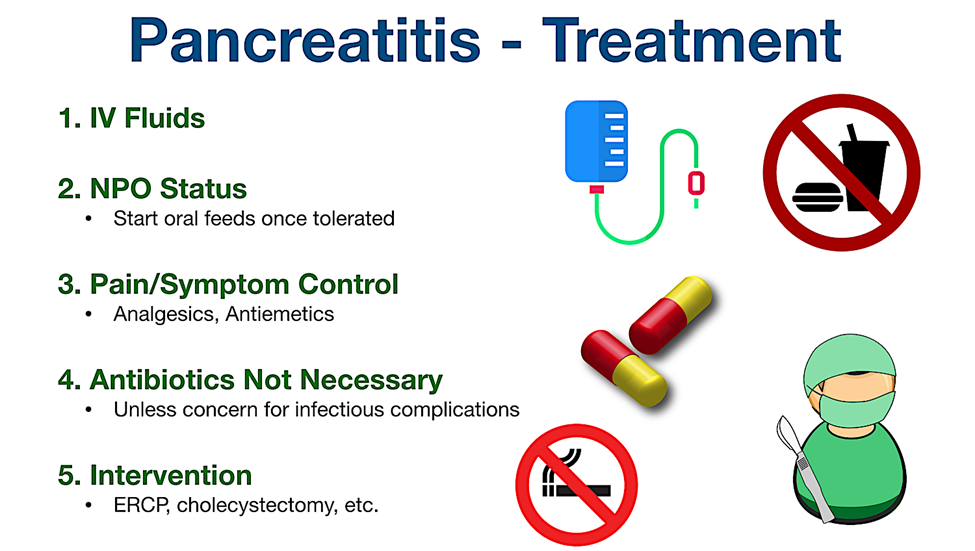
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with acute pancreatitis. After treating the client's pain, which of the following should the nurse address as the priority intervention?
Explanation
A. Provide oral hygiene.
Providing oral hygiene is important for the client's comfort and overall well-being. However, in the context of acute pancreatitis, the immediate priority is to address the gastrointestinal symptoms and prevent further pancreatic stimulation.
B. Assist the client to a side-lying position.
Assisting the client to a side-lying position can be beneficial for comfort and may help prevent complications such as aspiration. However, it is not the immediate priority after treating the pain. Withholding oral fluids and food takes precedence in the initial management of acute pancreatitis.
C. Auscultate the client's lungs.
Auscultating the client's lungs is a routine nursing assessment and is important for respiratory monitoring. However, in the context of acute pancreatitis, the primary focus is on addressing gastrointestinal symptoms, and respiratory assessment becomes more critical if respiratory distress is suspected.
D. Withhold oral fluids and food.
Withholding oral fluids and food is the priority intervention after treating the pain in acute pancreatitis. This is done to reduce pancreatic stimulation, allowing the pancreas to rest and recover. NPO (nothing by mouth) status is often initiated in the early management of acute pancreatitis.
A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving total parenteral nutrition via a peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC). When assessing the client, the nurse notes edema of the client's arm above the PICC insertion site. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
A. Applying a cold pack to the client's upper arm is not the first action. The priority is to assess and address the cause of the edema. Cold packs may be used for comfort, but they do not address the underlying issue.
B. Removing the PICC line is not the first action. Before considering removal, it is essential to assess the extent and cause of the edema. Removing the line without proper evaluation could lead to premature discontinuation of necessary treatment.
C. Notifying the provider who inserted the PICC line is important, but it is not the first action. The nurse needs to assess and intervene promptly. The provider should be informed after initial actions are taken.
D. Stopping the infusion and measuring the circumference of both upper arms is the first action. This helps determine the extent of the edema and whether it is related to the infusion. It is crucial to assess for complications such as infiltration or extravasation of the TPN solution.
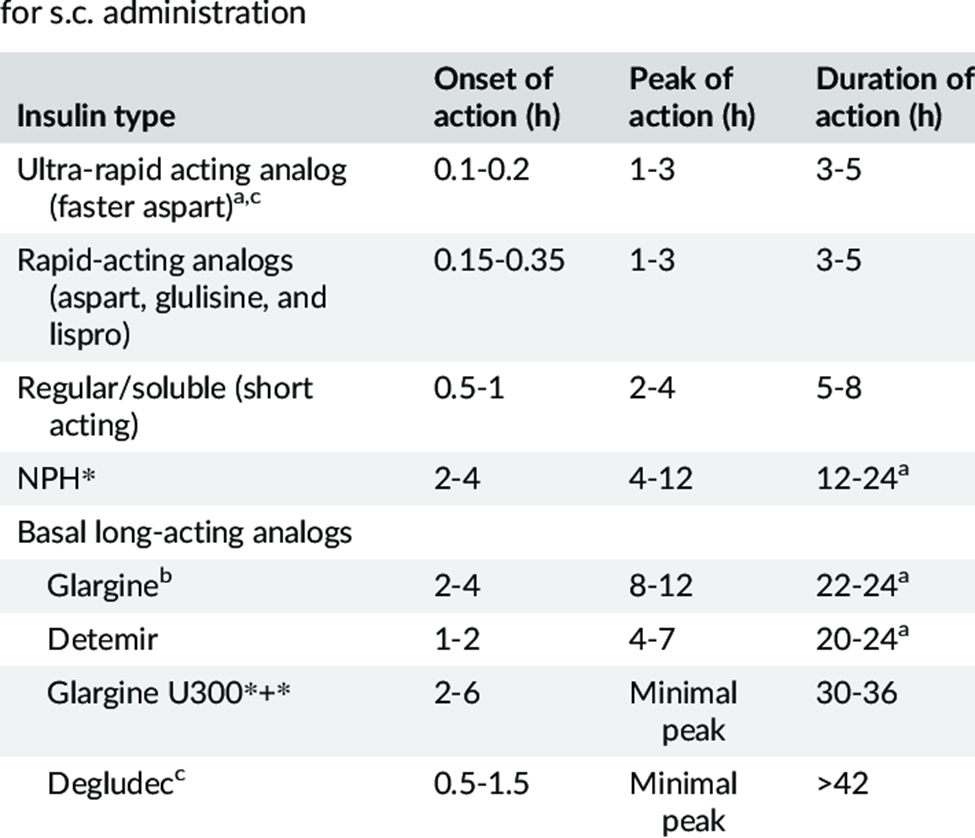
A nurse is providing teaching for a client who has diabetes and a new prescription for Insulin glargine. Which of the following instructions should the nurse provide regarding this type of insulin?
Explanation
A. Insulin glargine does not have a duration of 3 to 6 hours. This duration of action is much shorter than the actual duration of insulin glargine.
B. Insulin glargine does not have a duration of 14 to 22 hours. This duration is shorter than the typical duration of action for insulin glargine.
C. Insulin glargine, a long-acting insulin, has a duration of action that lasts approximately 24 to 36 hours. It provides a slow and steady release of insulin, offering a relatively consistent blood sugar-lowering effect over an extended period.
D. Insulin glargine does not have a duration of 6 to 10 hours. This duration is shorter than the actual duration of action for insulin glargine.
A nurse is providing teaching to a school-age child who has a new diagnosis of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Which of the following statements by the child indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
A. Storing unopened bottles of insulin in the freezer is incorrect. Insulin should be stored in the refrigerator, and freezing can damage the insulin.
B. Having a morning blood glucose level between 200 and 230 is too high. The target range for fasting blood glucose is generally lower, and elevated levels may indicate the need for adjustment in insulin or other medications.
C. Eating a snack half an hour before playing soccer is a correct understanding. This helps prevent hypoglycemia during physical activity. Physical activity can lower blood glucose levels, and a pre-activity snack can provide additional carbohydrates to prevent low blood sugar.
D. Not taking regular insulin when sick is incorrect. In fact, insulin needs may increase during illness, and it is usually recommended to continue taking insulin even when sick. Adjustments to the insulin regimen may be needed under the guidance of healthcare providers.
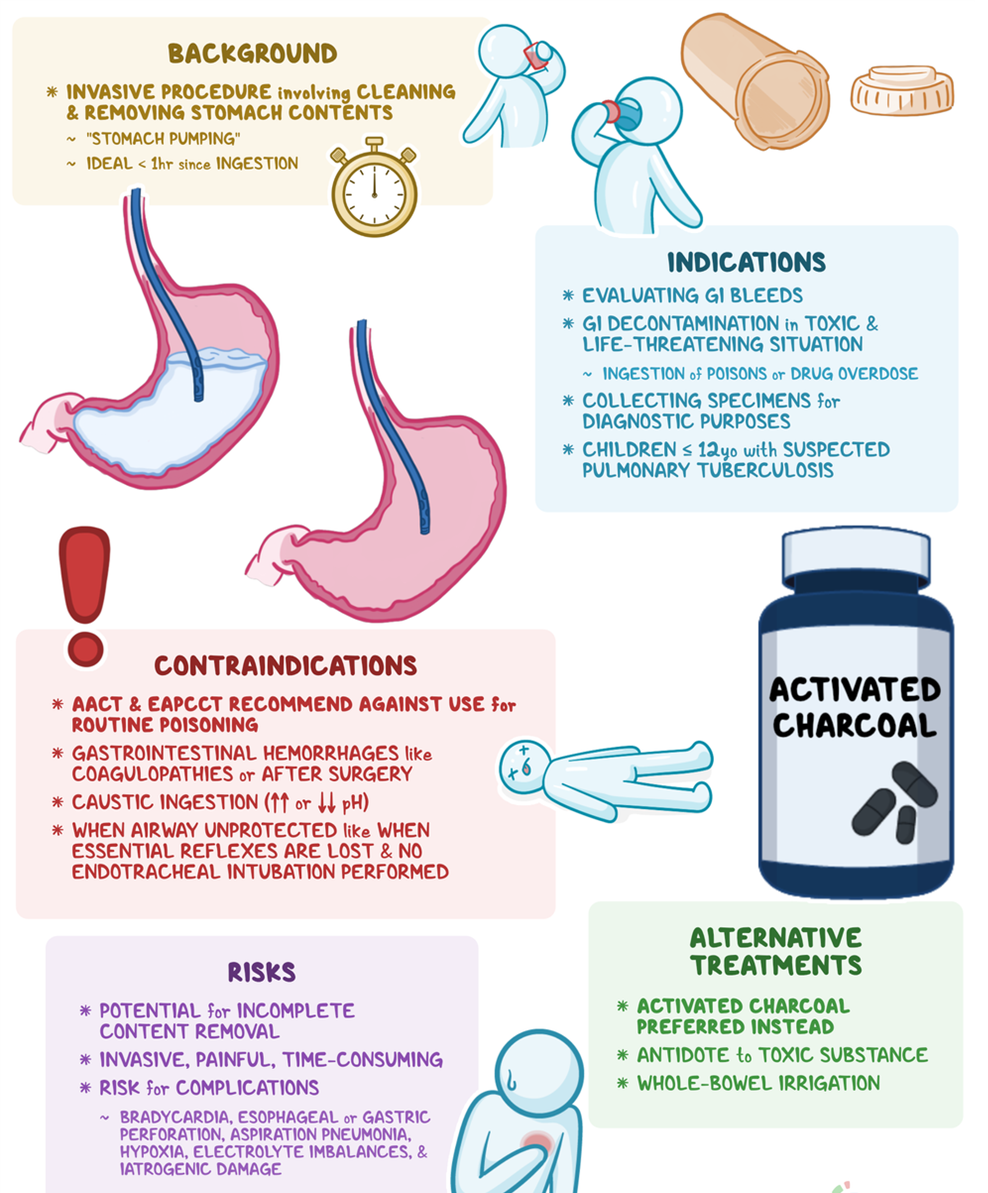
A nurse is performing gastric lavage on a client using a large-bore NG tube. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. Positioning the client on the right side is not a standard recommendation for gastric lavage. The standard position is typically on the left side to facilitate the drainage of gastric contents.
B. Instilling 1000 mL of sterile saline is not a recommended action for gastric lavage. Gastric lavage involves the removal of stomach contents rather than instilling fluids.
C. Withdrawing fluid until it is clear is the correct action. Gastric lavage is a medical procedure used to empty the stomach contents. The process involves introducing small amounts of fluid (such as saline) into the stomach and then aspirating it back, along with gastric contents, until the aspirate is clear.
D. Connecting the NG tube to high continuous suction is not a standard approach for gastric lavage. Gastric lavage involves intermittent instillation and withdrawal of small amounts of fluid to clear the stomach.
A nurse is reviewing the medication list for a client who has a new diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. The nurse should recognize which of the following medications can cause glucose intolerance?
Explanation
A. Atorvastatin: Atorvastatin is a statin medication used to lower cholesterol levels. It is not known to cause glucose intolerance.
B. Prednisone: Prednisone is a corticosteroid and can cause glucose intolerance by increasing blood glucose levels. Corticosteroids can lead to insulin resistance, impaired glucose utilization, and increased gluconeogenesis.
C. Ranitidine: Ranitidine is an H2 receptor antagonist used to reduce stomach acid production. It is not known to cause glucose intolerance.
D. Guaifenesin: Guaifenesin is an expectorant used to help loosen mucus in the airways. It is not known to cause glucose intolerance.
A nurse is caring for a client who has gastrointestinal bleeding. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
A. Testing the client's emesis for blood is an important assessment, but assessing orthostatic blood pressure is a priority. Orthostatic blood pressure measurement helps identify if the client is experiencing significant blood loss, as changes in blood pressure upon standing may indicate hypovolemia.
B. Assessing orthostatic blood pressure is the priority action. Orthostatic hypotension can be a sign of decreased circulating blood volume, which is a concern in clients with gastrointestinal bleeding.
C. Explaining the procedure for an upper gastrointestinal series is not the first priority. While diagnostic tests may be needed, addressing the immediate concern of potential hypovolemia takes precedence.
D. Administering pain medication is not the first action. The priority is to assess and address the potential complications of gastrointestinal bleeding, such as hypovolemia.
A nurse is teaching a client diagnosed with hepatitis A about preventing transmission of the virus. Which of the following strategies should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
A. Avoiding eating at fast food restaurants is not a specific preventive measure for hepatitis A transmission. The primary mode of transmission for hepatitis A is through the fecal-oral route, often due to contaminated food or water.
B. Avoiding serving raw foods is a reasonable precaution as raw or undercooked shellfish and contaminated fruits and vegetables can be a source of hepatitis A transmission. However, practicing effective hand hygiene is a more general and fundamental preventive measure.
C. Wearing barrier protection during vaginal intercourse is not directly related to the prevention of hepatitis A. Hepatitis A is primarily transmitted through the fecal-oral route, and sexual transmission is not a common mode for this virus.
D. Practicing effective hand hygiene is a key strategy for preventing the transmission of hepatitis A. Proper handwashing with soap and water, especially after using the bathroom and before handling food, can help reduce the risk of contamination and transmission of the virus.
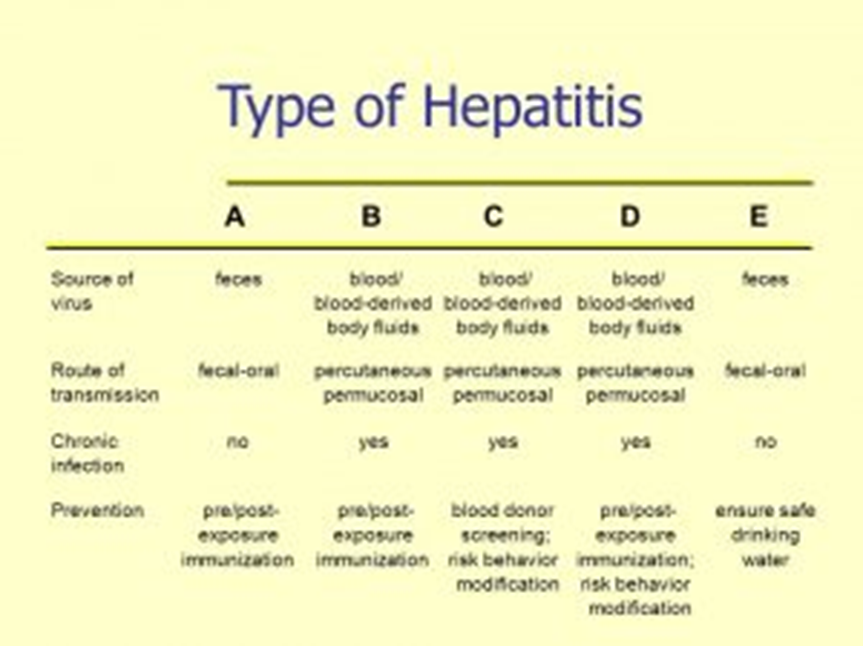
A nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with diabetic ketoacidosis. Which of the following manifestations should the nurse expect?
Explanation
A. Blood glucose level below 40 mg/dL is not typical in diabetic ketoacidosis. DKA is characterized by hyperglycemia, and blood glucose levels are usually significantly elevated.
B. Acetone odor to breath is a classic sign of diabetic ketoacidosis. The presence of ketones, including acetone, can result in a fruity or sweet odor to the breath. This is often referred to as "ketone breath."
C. Malignant hypertension is not a typical manifestation of diabetic ketoacidosis. DKA is more commonly associated with dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and metabolic acidosis.
D. Cheyne-Stokes breathing is not a characteristic respiratory pattern seen in diabetic ketoacidosis. Respiratory changes in DKA are more likely to involve rapid and deep breathing (Kussmaul respirations) as the body attempts to compensate for metabolic acidosis.
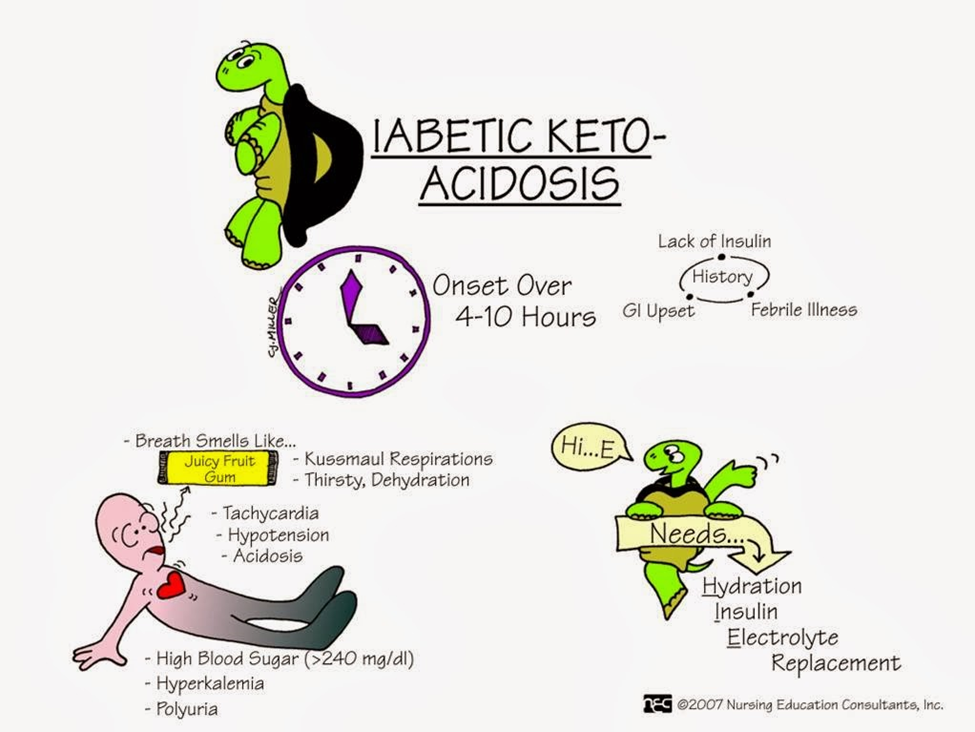
A nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription for a stool test for guaiac. The nurse should recognize the purpose of the test is to check the stool for which of the following substances?
Explanation
A. Steatorrhea:
Steatorrhea refers to the presence of excessive fat in the stool. If a healthcare provider suspects malabsorption or fat digestion issues, they might order a fecal fat test to assess the amount of fat in the stool. This test is different from a guaiac fecal occult blood test (gFOBT), which is designed to detect blood.
B. Parasites:
The detection of parasites in the stool involves specific testing methods, such as microscopic examination of stool samples or specialized tests aimed at identifying the presence of parasitic organisms. A guaiac fecal occult blood test is not designed to detect parasites; its primary purpose is to identify occult (hidden) blood.
C. Blood:
A stool test for guaiac is specifically designed to detect the presence of occult (hidden) blood in the stool. The guaiac test involves placing a small sample of stool onto a test card containing guaiac, and a color change indicates the presence of blood. This test is commonly used to screen for gastrointestinal bleeding.
D. Bacteria:
Detecting bacteria in the stool typically involves stool cultures or specific tests designed to identify bacterial infections or imbalances in the gut microbiota. The guaiac test is not intended for detecting bacteria; its primary focus is on identifying the presence of blood in the stool.
A nurse is Interviewing a client who has acute pancreatitis. Which of the following factors should the nurse anticipate finding in the client's history?
Explanation
A. COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) is not directly associated with acute pancreatitis. The common risk factors for acute pancreatitis include gallstones, alcohol use, and certain medications.
B. Hypolipidemia (low blood lipid levels) is not a typical factor associated with acute pancreatitis. Elevated levels of lipids in the blood (hyperlipidemia) can be a risk factor, but hypolipidemia is not commonly linked to pancreatitis.
C. Diabetes mellitus, while not a direct cause of acute pancreatitis, can be associated with an increased risk. Uncontrolled diabetes may contribute to the development of pancreatitis, but it is not a primary risk factor.
D. Gallstones are a significant risk factor for acute pancreatitis. Gallstones can obstruct the pancreatic duct, leading to inflammation and damage to the pancreas. This obstruction is one of the common causes of acute pancreatitis.
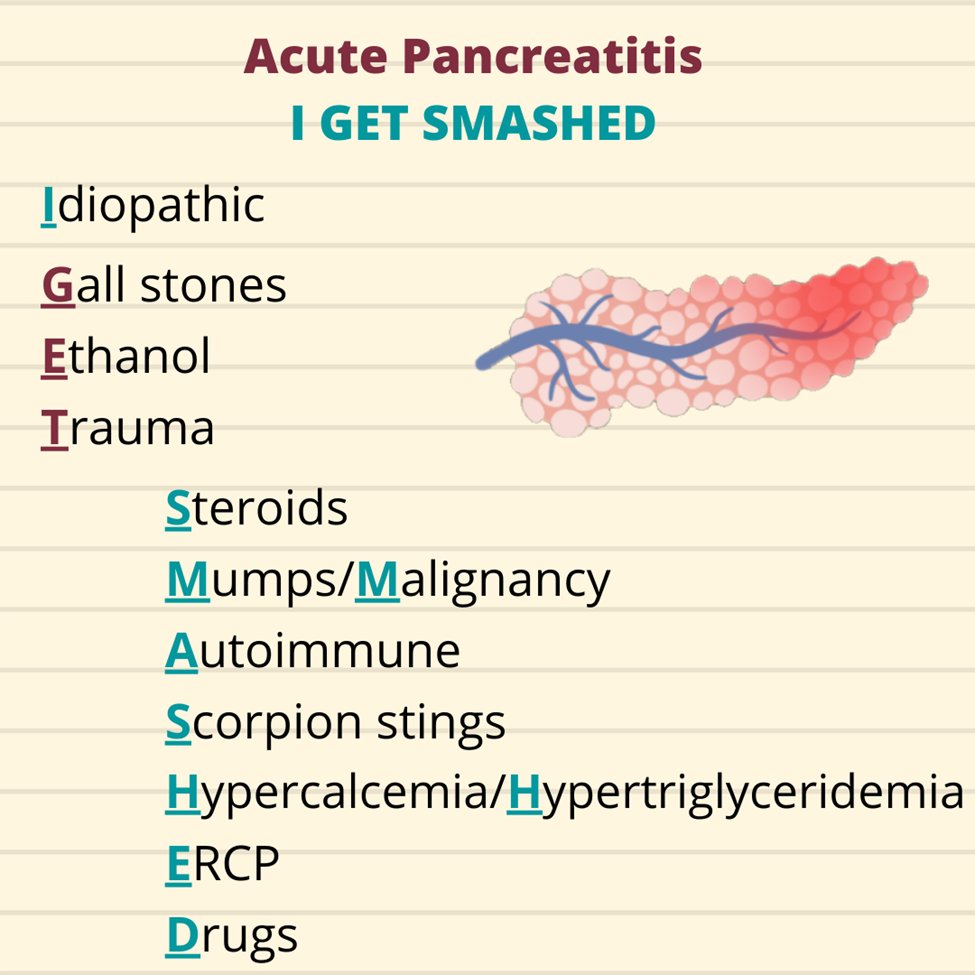
A nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with peptic ulcer disease. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following findings as an indication of gastrointestinal perforation?
Explanation
A. Bradycardia is not typically associated with gastrointestinal perforation. Instead, tachycardia may be observed due to the body's response to a potential emergency or shock.
B. Hyperactive bowel sounds are not typically associated with gastrointestinal perforation. In fact, bowel sounds may decrease or become absent in severe cases of peritonitis or abdominal emergencies.
C. Increased blood pressure is not typically associated with gastrointestinal perforation. Hypotension may be observed due to hypovolemia resulting from fluid leakage into the peritoneal cavity.
D. Sudden abdominal pain is a key clinical manifestation of gastrointestinal perforation. The perforation of the stomach or intestines allows the contents to leak into the abdominal cavity, leading to peritonitis. Sudden and severe abdominal pain is a hallmark symptom, often described as sharp, stabbing, and constant.
A nurse is teaching students about the use of isotonic solutions. The nurse recognizes which statements made by a student about isotonic solutions are correct. (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY)
Explanation
A. Is used to replace fluid loss.
Isotonic solutions, such as normal saline (0.9% NaCl) and lactated Ringer's solution, are used to replace fluid loss in situations such as dehydration, surgery, trauma, or other conditions where there is a need for fluid resuscitation.
B. Usually do not provide calories.
Isotonic solutions typically do not contain calories. They are designed primarily for fluid replacement and do not contribute to the nutritional needs of the patient.
C. Does not expand intravascular volume.
This statement is incorrect. Isotonic solutions are used to expand intravascular volume. When infused into the bloodstream, isotonic solutions help restore and maintain adequate blood volume. They do not cause significant shifts of fluids between compartments.
D. Mostly do not provide free water.
Isotonic solutions generally do not provide free water. They have the same osmolality as body fluids, meaning that they do not cause a net movement of water into or out of cells, and they maintain the osmotic balance.
E. Has the same osmolality as body fluids.
Isotonic solutions have the same osmolality as body fluids, which means they do not cause a net movement of water into or out of cells. This characteristic makes them suitable for situations where there is a need to expand intravascular volume without causing significant shifts in fluid compartments.
A nurse is preparing a teaching session about reducing the risk of complications of diabetes mellitus. Which of the following information should the nurse plan to include in the teaching? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
A. Increase physical activity and daily exercise.
Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, manage blood glucose levels, and lower the risk of cardiovascular complications associated with diabetes.
B. Reduce cholesterol and saturated fat intake.
Managing cholesterol levels and reducing saturated fat intake can help lower the risk of cardiovascular disease, which is a common complication of diabetes.
C. Maintain optimal blood pressure to prevent kidney damage.
Controlling and maintaining blood pressure within optimal ranges is crucial in preventing kidney damage, a common complication of diabetes.
D. Enroll in a smoking-cessation program.
Smoking increases the risk of cardiovascular complications and can exacerbate other diabetes-related health issues. Quitting smoking is important in reducing the risk of complications.
E. Sustain hyperglycemia to reduce deterioration of nerve cells.
Sustaining hyperglycemia (high blood sugar levels) is detrimental and contributes to the progression of diabetic complications, including nerve damage (neuropathy). Lowering and controlling blood glucose levels are essential in preventing complications rather than sustaining hyperglycemia.
A nurse is teaching a client diagnosed with hepatitis A. Which of the following information should the nurse include?
Explanation
A. Hepatitis A does not infect the kidneys. Hepatitis A is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver, causing inflammation.
B. Manifestations of hepatitis A are indeed similar to flu-like symptoms. Common symptoms include fever, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
C. The incubation period for hepatitis A is typically 15 to 50 days, not 5 days. The incubation period is the time between exposure to the virus and the onset of symptoms.
D. A family history is not a significant risk factor for acquiring hepatitis A. Hepatitis A is primarily transmitted through the fecal-oral route, often due to contaminated food or water. It is more commonly associated with exposure to the virus through contaminated environments or ingestion of contaminated food or water.
A nurse is preparing to administer a dose of lactulose to a client diagnosed with cirrhosis. The client states, "I don't need this medication. I am not constipated." The nurse should explain that in clients who have cirrhosis, lactulose is used to decrease levels of which of the following components in the bloodstream?
Explanation
A. Lactulose is not used to decrease potassium levels. It is a laxative that works by drawing water into the colon, softening stools and promoting bowel movements.
B. Lactulose is used to decrease ammonia levels in clients with cirrhosis. Ammonia is a byproduct of protein metabolism, and when the liver is compromised, it may not effectively convert ammonia into urea, leading to elevated ammonia levels in the bloodstream. Lactulose helps reduce ammonia absorption in the colon.
C. Lactulose does not decrease glucose levels significantly. It is not primarily used as an antidiabetic medication.
D. Lactulose does not affect bicarbonate levels significantly. It primarily targets ammonia reduction in clients with cirrhosis.
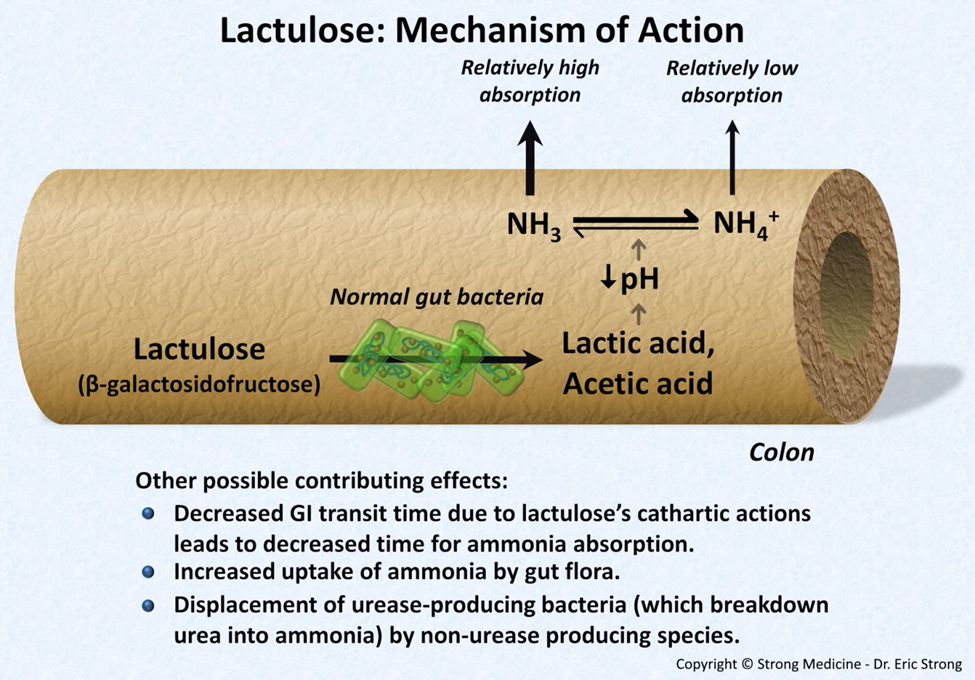
A nurse is teaching a client who has a prescription of a nasogastric tube (NG) to treat a pyloric obstruction. Which of the following rationales for the use of the nasogastric tube should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
A. Administer medications:
While nasogastric tubes can be used to administer medications, this is not the primary rationale for their use in pyloric obstruction. The primary goal is often decompression.
B. Supply nutrients via tube feedings:
Providing nutrients via tube feedings is not the primary purpose in the context of a pyloric obstruction. Decompression is more relevant in this scenario.
C. Decompress the stomach:
Decompressing the stomach is a common use of nasogastric tubes in the context of pyloric obstruction. The tube helps to remove excess air and gastric contents, relieving pressure in the stomach.
D. Determine the pH of the gastric secretions:
While determining the pH of gastric secretions is a possible use, it is not the primary rationale for nasogastric tube placement in pyloric obstruction. The primary goal is often to relieve obstruction and decompress the stomach.
The charge nurse on a hospital unit is leading a committee that must choose new paint colors for the nurse's station. She elicits the opinions of all group members and then organizes a vote. The charge nurse's leadership style can be said to be
Explanation
A. Autocratic:
Autocratic leadership involves making decisions without seeking input from others. In this scenario, the charge nurse is eliciting opinions from all group members and organizing a vote, which suggests a more collaborative approach rather than a purely autocratic one.
B. Scientific:
Scientific leadership, often associated with Frederick Taylor's principles of scientific management, involves using data and analysis to make decisions. The scenario does not provide information suggesting a strong emphasis on scientific principles in the decision-making process.
C. Democratic:
Democratic leadership involves including team members in decision-making, seeking their opinions, and often using a voting or consensus-building approach. The charge nurse's approach of eliciting opinions and organizing a vote aligns with democratic leadership.
D. Laizzez-faire:
Laissez-faire leadership involves a hands-off approach, where the leader allows group members considerable freedom to make decisions. In the scenario, the charge nurse is actively seeking input and organizing a vote, which is more indicative of a democratic style rather than laissez-faire.
A nurse working for a home health agency is teaching a client diagnosed with diabetes mellitus about disease management. Which of the following glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) values should the nurse include in the teaching as an indicator that the client is appropriately controlling their glucose levels?
Explanation
A. 7.8%
An HbA1c value of 7.8% indicates an average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months that is higher than the optimal range. This suggests that the client may not be achieving optimal glucose control.
B. 8.5%
An HbA1c value of 8.5% also indicates elevated average blood sugar levels over the past few months. This value suggests poorer control of diabetes, and adjustments to the management plan may be needed.
C. 10%
An HbA1c value of 10% indicates higher average blood sugar levels, signifying inadequate control of diabetes. This value suggests a need for intervention and modification of the treatment plan to achieve better glucose management.
D. 6.3%
An HbA1c value of 6.3% is considered a relatively good indicator of glucose control. This value suggests that the client has been successful in maintaining lower average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months, reflecting effective diabetes management.
A nurse is caring for a client who has a history of diabetes mellitus and is being admitted to the unit confused, flushed, and with an acetone odor on the breath. Diabetic ketoacidosis is suspected. The nurse should anticipate using which of the following types of insulin to treat this client?
Explanation
A. Regular insulin:
Regular insulin, also known as short-acting insulin, is commonly used in the initial management of diabetic ketoacidosis. It has a relatively rapid onset of action, making it suitable for addressing the acute and severe nature of DKA.
B. Insulin detemir:
Insulin detemir is a long-acting insulin analog. It is not the preferred choice for addressing the acute insulin needs in DKA; instead, it is used for basal insulin requirements in the maintenance phase of diabetes management.
C. Insulin glargine:
Insulin glargine is a long-acting insulin analog used for basal insulin coverage. Like insulin detemir, it is not the first choice for addressing the acute insulin needs in the initial treatment of DKA.
D. NPH insulin:
NPH (Neutral Protamine Hagedorn) insulin is an intermediate-acting insulin. While it has a role in diabetes management, it is not the preferred choice for the initial treatment of DKA. NPH insulin has a slower onset and longer duration compared to regular insulin.
A nurse is preparing dietary instructions for a client who has episodes of billary colic from chronic cholecystitis. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching plan?
Explanation
A. Avoid foods high in fat:
Dietary fat can trigger the gallbladder to release bile, and for individuals with chronic cholecystitis, high-fat meals can exacerbate symptoms such as biliary colic. Therefore, advising the client to avoid foods high in fat can help manage symptoms.
B. Include foods high in starch and proteins:
While protein-rich foods can be included in the diet, a high-fat content should be avoided. Starches can be a part of a balanced diet, but it's essential to focus on low-fat options.
C. Include foods high in fiber:
Including foods high in fiber is generally a good recommendation for digestive health. However, the emphasis here is on avoiding high-fat foods, and the recommendation for fiber should not overshadow the importance of minimizing dietary fat.
D. Avoid foods high in sodium:
Sodium restriction may be relevant for certain health conditions, but it is not the primary dietary consideration for managing chronic cholecystitis. The emphasis in this context is on reducing dietary fat.

A nurse is planning care for a client who has cirrhosis of the liver. Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
A. Encourage weight lifting during physical therapy:
Encouraging weight lifting or strenuous physical activities might not be advisable for individuals with advanced cirrhosis. Engaging in intense physical activity could potentially strain the liver or increase the risk of injury or bleeding, which is already heightened in individuals with cirrhosis.
B. Measure the client's abdominal girth:
Monitoring the client's abdominal girth is essential because cirrhosis can lead to the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, known as ascites. Changes in abdominal girth can indicate the progression or resolution of ascites, guiding treatment and interventions.
C. Administer warfarin:
Administering warfarin, an anticoagulant, might not be ideal in cirrhosis due to the increased risk of bleeding. Liver dysfunction in cirrhosis can impair the production of clotting factors, increasing the risk of bleeding complications.
D. Administer furosemide:
Furosemide, a diuretic, can be utilized in managing ascites by promoting the elimination of excess fluid. However, its use requires careful monitoring, considering the electrolyte balance and potential adverse effects, especially in individuals with liver impairment.
E. Implement a low-sodium diet:
A low-sodium diet is crucial in managing cirrhosis-related complications, particularly ascites and edema. Sodium restriction helps reduce fluid retention, lessening the burden on the liver and alleviating symptoms associated with fluid accumulation.
A nurse is teaching a client diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus about foot care. Which of the following statements by the client about foot care is correct?
Explanation
A. "I'll wear sandals in warm weather":
While wearing sandals in warm weather can be comfortable, it may not provide adequate protection for the feet, especially for individuals with diabetes. Closed, protective shoes are generally recommended to prevent injuries.
B. "I'll put lotion between my toes after drying my feet":
Applying lotion between the toes can create a moist environment, which may increase the risk of fungal infections. It is generally advisable to keep the skin between the toes dry to prevent infections.
C. "I'll check my feet every day for sores and bruises":
This statement is correct. Regular foot checks are crucial for individuals with diabetes to identify any signs of sores, bruises, or other abnormalities early. Early detection and prompt treatment can help prevent complications.
D. "I’ll soak my feet in cool water every night before I go to bed":
Soaking the feet in cool water is generally not recommended, as it can lead to maceration of the skin and increase the risk of fungal infections. Daily inspection and proper hygiene are more important aspects of foot care.
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory data of a client diagnosed with acute pancreatitis. The nurse should expect to find an elevation of which of following values?
Explanation
A. Calcium:
While calcium levels can be affected in pancreatitis, it is more commonly associated with a decrease in calcium levels due to fat necrosis and the formation of calcium soaps. However, the primary electrolyte disturbance is more likely to involve magnesium.
B. Magnesium:
Magnesium levels may be decreased in acute pancreatitis due to factors such as vomiting, malabsorption, and poor oral intake. Hypomagnesemia is a possible consequence, but it's not as specific to pancreatitis as the elevation of amylase.
C. Amylase:
Elevated amylase levels are a hallmark of acute pancreatitis. Amylase is an enzyme released by the pancreas, and its elevation in the blood is a key diagnostic marker for pancreatitis.
D. RBC count:
Acute pancreatitis does not typically result in a significant impact on the red blood cell (RBC) count. The elevation of amylase and lipase levels, along with imaging studies, is more indicative of pancreatitis.
A nurse is caring for a client who has cirrhosis and a prothrombin time of 30 seconds. Which of the following medications should the nurse plan to administer?
Explanation
A. Warfarin:
Warfarin is an anticoagulant that works by inhibiting the synthesis of certain clotting factors, including factors II, VII, IX, and X. While it is used to prevent thromboembolic events, in a client with cirrhosis and an elevated PT, the priority is addressing the coagulation factor deficiency rather than adding an anticoagulant.
B. Vitamin K:
Vitamin K is the antidote for warfarin, and it helps in the synthesis of clotting factors. In cirrhosis, there can be impaired synthesis of clotting factors due to liver dysfunction. Administering vitamin K can aid in correcting coagulation abnormalities.
C. Heparin:
Heparin is another anticoagulant, but it does not reverse the effects of warfarin. It works by a different mechanism and is typically used in acute settings, such as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. It is not the primary intervention for an elevated PT in cirrhosis.
D. Ferrous sulfate:
Ferrous sulfate is an iron supplement and is not indicated for the correction of an elevated PT. Iron supplements are typically used to address iron deficiency anemia.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 40 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

