ATI NURSING 137 Exam 3 Fall 2023
Total Questions : 48
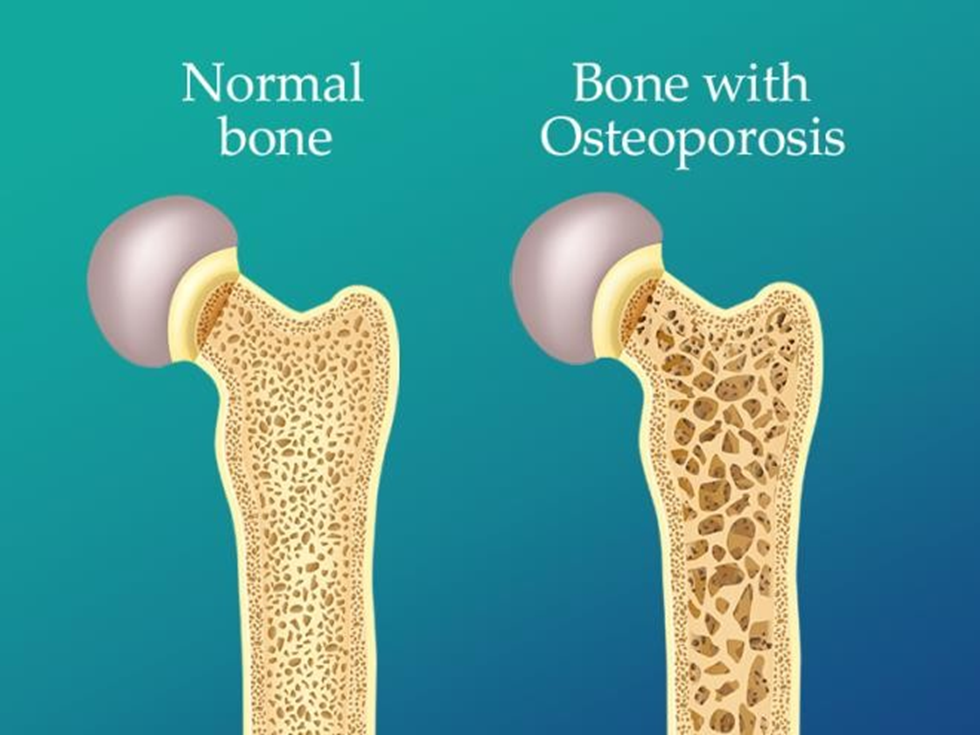
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreThe nurse is providing health promotion teaching to a group of clients. The nurse should include in her teaching which of the following populations has a greater risk factor for osteoporosis.
Explanation
A. African Americans typically have a higher bone density compared to Caucasians and tend to have a lower risk of osteoporosis.
B. Asian men also have a lower risk due to generally higher bone density than Caucasians.
C. Postmenopausal Caucasian women have a higher risk due to hormonal changes after menopause, leading to decreased bone density.
D. American Indians can have varying risks but are not typically considered a population with the highest risk for osteoporosis.
A male client with possible fertility problems asks the nurse where sperm is produced. Which answer should the nurse give the client?
Explanation
A. The vas deferens is a duct that transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct.
B. The epididymis is where sperm is stored and matures but not produced.
C. The prostate gland produces a fluid that contributes to semen but not sperm production.
D. The testes are responsible for producing sperm through the process of spermatogenesis.
The nurse is taking a health history from a client. The client tells the nurse that. "It feels like the room is spinning." How should the nurse document this finding?
Explanation
A. Vertigo is the sensation of spinning or movement when stationary and is often associated with inner ear problems.
B. Seizure activity involves abnormal electrical activity in the brain and might present with various symptoms but not necessarily the feeling of spinning.
C. Dizziness is a more general term that can include feelings of light-headedness or unsteadiness without a specific spinning sensation.
D. Syncope refers to fainting or loss of consciousness due to decreased blood flow to the brain, not the sensation of spinning.

A client reports pain in the left wrist after falling while playing basketball. After assessing the wrist, which of the following assessment finding would make the nurse suspect a fracture?
Explanation
A. Dull throbbing pain increasing with rest might suggest a strain or sprain but not necessarily a fracture.
B. A dull ache could indicate various issues but may not specifically point to a fracture.
C. Sharp pain that worsens with movement is a common indicator of a fracture due to the bones moving against each other.
D. Deep pain in the wrist could signify deep tissue injury but doesn't distinctly indicate a fracture without other signs.
The nurse is performing an assessment and finds that the client has a non-tarry and black stool. Which of the following subjective data should the nurse document as normal findings consistent with non-tarry black stool?
Explanation
A. Iron supplements typically lead to darker stools but may not necessarily present as a non-tarry black stool.
B. Dry heaves or vomiting could potentially indicate upper gastrointestinal bleeding but not specifically correlate with non-tarry black stool.
C. Consuming red meat can cause black stools due to its breakdown products, which is a normal finding.
D. Loss of appetite doesn't directly relate to stool color or consistency.
An adolescent male is brought to the emergency department with complaints of excruciating pain in his left testicle. Which of the following should be the priority action by the nurse?
Explanation
A. Reassurance is important, but it should be given after a thorough assessment and appropriate actions have been taken.
B. Completing an assessment and promptly informing the physician allows for timely intervention in case of testicular torsion or other serious conditions causing severe testicular pain.
C. Performing a focused assessment is crucial but shouldn't delay immediate notification of the physician in such a critical situation.
D. Documenting pain assessment is important but not the priority when a client presents with severe, acute pain in a sensitive area like the testicles.
The nurse is performing a neurological assessment on a client with a history of Diabetes.
When testing the ability to feel the vibrations of a tuning fork, the nurse notices that the client is unable to feel vibrations on the great toe or ankle bilaterally, but is able to feel vibrations on both patellae. What should the nurse suspect from these assessments?
Explanation
A. Hyperalgesia refers to increased sensitivity to pain stimuli, not specifically related to the inability to feel vibrations.
B. Peripheral neuropathy, a common complication of diabetes, often leads to sensory deficits, especially in distal extremities like the toes and feet.
C. Hyperparalysis is not a recognized term in neurology.
D. A lesion of the sensory cortex would likely present with broader sensory deficits rather than a specific loss of vibration sensation in the distal lower extremities.
A nurse is assessing a client's cranial nerves. Which of the following methods should the nurse use to assess cranial nerve V?
Explanation
A. Listening to speech primarily involves cranial nerves related to speech production (e.g., CN V, CN VII, CN XII) but not specifically for CN V.
B. Reading a Snellen chart assesses visual acuity, primarily involving cranial nerve II (optic nerve).
C. Identifying scented aromas involves olfactory nerve (cranial nerve I) assessment.
D. Asking the client to clench their teeth evaluates the function of the muscles of mastication, which is controlled by cranial nerve V (trigeminal nerve).
During an abdominal assessment, the nurse is unable to hear bowel sounds in a client's abdomen. How long should the nurse listen before reporting absent bowel sounds?
Explanation
A. One minute may not provide a sufficient duration to declare absent bowel sounds, especially if the client has a slower bowel motility.
B. Ten minutes in each quadrant is the recommended duration for assessing bowel sounds in all four abdominal quadrants to accurately determine the absence of sounds.
C. One minute in each quadrant might not provide an adequate assessment time.
D. Five minutes in each quadrant might be insufficient to confirm the absence of bowel sounds, especially in clients with slower gastrointestinal motility.
A client tells the nurse about being very unsteady and has difficulty in maintaining balance. The nurses recognize which area of the brain is involved and require further assessment.
Explanation
A. The brainstem is responsible for basic life functions like breathing and heart rate but isn't primarily associated with balance and coordination.
B. The cerebellum plays a crucial role in coordination, balance, and fine motor control. Issues here can result in problems with balance and coordination.
C. The extrapyramidal tract involves motor control but is not specifically responsible for balance and coordination.
D. The thalamus primarily serves as a relay center for sensory information but is not directly related to balance and coordination.
A nurse is educating a client about blood cell formation in the body. The nurse documents the education and refers to blood cell formation as?
Explanation
A. Hepatomegaly refers to an enlarged liver.
B. Hematopoiesis is the process of blood cell formation that occurs primarily in the bone marrow.
C. Osteogenesis is the process of bone formation.
D. Splenomegaly refers to an enlarged spleen.
The nurse has completed a peripheral vascular assessment on a client. Which of the following would the nurse document as expected findings?
Explanation
A. A capillary refill of less than 5 seconds is considered normal.
B. Radial pulses 2+ with regular rate and rhythm bilaterally indicate good peripheral circulation.
C. Feet that are pale and cool to the touch could indicate decreased perfusion or vascular compromise.
D. Right ankle 1+ edema may suggest some fluid retention but no perceptible swelling of the leg indicates relatively normal findings in that area.
During an assessment of the cranial nerves (CNS), the nurse finds the following asymmetry when the client smiles or frowns, uneven lifting of the eyebrows, and escape of air when the nurse presses against the right puffed cheek. The nurse recognized that these findings indicate dysfunction of which cranial nerve(s)?
Explanation
A. Dysfunction of the motor component of CN X (vagus nerve) and sensory component of CN VII (facial nerve) would present with different symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing and impaired taste sensation, not the observed facial asymmetry and puffing of cheeks.
B. CN XI (accessory nerve) dysfunction primarily affects the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles and wouldn't cause the observed facial asymmetry.
C. Dysfunction of CN IV (trochlear nerve) leads to issues with downward and inward eye movement, not the facial asymmetry described.
D. Dysfunction of the motor component of CN VII (facial nerve) leads to facial asymmetry during expressions and difficulty controlling facial muscles, which matches the observed findings.
The nurse teaches a client that there are shock absorbers in the back to cushion the spine and to help it move. The client understands that which of the following is another name for shock absorbers:
Explanation
A. The vertebral column refers to the series of vertebrae forming the backbone, not specifically the shock absorbers.
B. Intervertebral disks are the fibrocartilage pads between vertebrae that act as shock absorbers, allowing movement and cushioning the spine.
C. The vertebral foramen is the opening in the vertebrae through which the spinal cord passes.
D. The nucleus pulposus is the gel-like inner core of the intervertebral disk, contributing to its flexibility and shock-absorbing properties.
The nurse is assessing a female client who reports painful menstruation. Which of the following should the nurse document in the client's record about painful menstruation?
Explanation
A. Dysmenorrhea refers to painful menstruation, commonly associated with cramping in the lower abdomen.
B. Dysuria is painful or difficult urination, unrelated to menstrual pain.
C. Hematuria is the presence of blood in the urine, not associated with menstrual pain.
D. Dyschezia refers to painful bowel movements, not related to menstrual pain.
The nurse is performing a physical assessment of the client's mandible and temporal bone. The nurse recognizes that the articulation of the mandible and the temporal bone is called?
Explanation
A. The condyle of the mandible is the rounded protuberance at the end of the mandible bone but doesn't refer to the joint.
B. The zygomatic arch of the temporal bone is part of the skull structure and not directly associated with the mandibular joint.
C. The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is the joint where the mandible articulates with the temporal bone of the skull, allowing for jaw movement and chewing.
D. The intervertebral foramen is a space between vertebrae through which spinal nerves exit the spinal cord.
A 60-year-old man has been told that he has benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH). He expresses that his friend just died from prostate cancer and that he is concerned about dying from cancer. Which of the following is an appropriate response by the nurse?
Explanation
A. While prostate cancer risk increases with age, it's not rare for a 60-year-old man to have prostate cancer. This response might provide false reassurance.
B. Chemotherapy is not typically the primary treatment for benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) and doesn’t relate to the concerns raised by the client.
C. BPH is a chronic condition characterized by non-cancerous prostate enlargement, not temporary swelling that goes away.
D. BPH is commonly caused by hormonal changes and does not predispose a person to prostate cancer. It's important to differentiate between BPH and prostate cancer.
A client comes to the clinic and reports having weakness in the left arm and leg for the past week. The nurse should perform which type of neurological exam?
Explanation
A. The Glasgow Coma Scale assesses a patient's level of consciousness, not specifically limb weakness.
B. A complete neurological examination would involve assessing cranial nerves, motor and sensory functions, reflexes, coordination, and gait, which are essential when a client presents with unilateral weakness in the arm and leg.
C. A muscular examination might focus more on muscle strength and tone but might not cover the breadth of neurological assessment needed in this scenario.
D. Neurologic recheck examination suggests a reassessment after an initial neurological exam but doesn’t specify the need for a comprehensive evaluation.
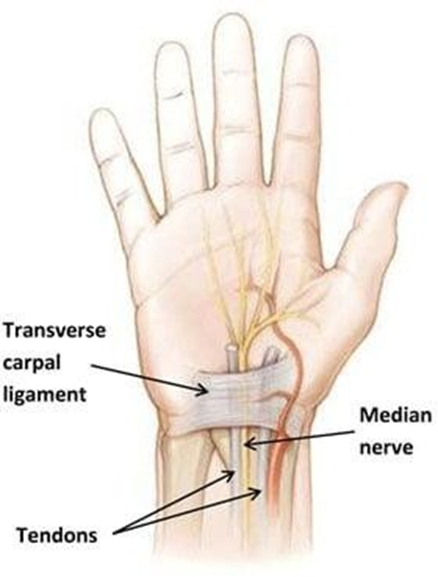
The nurse suspects that a client has carpal tunnel syndrome and prepares to conduct the Phalen test. What instructions should the nurse give the client to perform the Phalen test?
Explanation
A. Plantarflexion and dorsiflexion refer to movements of the foot and are unrelated to the Phalen test.
B. Hyperextension of the wrists with the palmar surfaces touching is not the correct maneuver for the Phalen test.
C. The Phalen test involves holding both hands back to back while flexing the wrists at a 90- degree angle for about 60 seconds, which may induce symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome in those affected.
D. Hyperextending the wrists with the palms together doesn’t simulate the stress on the median nerve in the same way as the Phalen test.
The nurse is performing a scrotal assessment on a male client. Which of the following findings of the scrotum should the nurse recognize as abnormal?
Explanation
A. Asymmetry of the scrotum is often normal; one side may hang lower than the other without indicating pathology.
B. Marked tenderness on palpation could suggest inflammation or infection but doesn’t necessarily indicate abnormality in all cases.
C. Easy sliding of scrotal contents is a normal finding; the testes should move easily within the scrotum.
D. The presence of small, firm, non-tender, yellowish nodules could indicate an abnormal finding such as sebaceous cysts or other nodules that may require further evaluation.
The nurse is assessing a client who reports cessation of menses. The nurse should document the cessation of menses in the client's record as:
Explanation
A. Salpingitis refers to inflammation of the fallopian tubes and doesn’t relate to cessation of menses.
B. Adnexa refers to the accessory structures of the uterus, such as the ovaries and fallopian tubes, but doesn’t describe the cessation of menses.
C. Menarche refers to the onset of menstruation, which is the opposite of cessation of menses.
D. Menopause is the natural cessation of menstruation that occurs typically around the age of 45-55 years in women.
The nurse tests the function of Cranial Nerve XI while performing a physical examination on a client. Which statement best describes the response the nurse should expect if Cranial Nerve XI is intact?
Explanation
A. Cranial Nerve XI (Accessory nerve) is not involved in tongue movement; it controls muscles involved in head and shoulder movement.
B. Eye movement and control relate more to Cranial Nerves III, IV, and VI, which control eye muscles.
C. Hearing is primarily assessed by Cranial Nerve VIII (Vestibulocochlear nerve).
D. Cranial Nerve XI innervates the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles, enabling movements like head turning and shoulder shrugging against resistance.
A nurse is caring for a client with severe bilateral lower extremity edema.
Nursing Assessment:
The client drove self to the Emergency Department. Stated, "My legs are swollen like balloons and I can hardly walk." The client has bilateral 4+ pitting edema from feet to knees. The nurse is preparing to assess the client's medical history. Which of the following should the nurse recognize to be the underlying cause of lower extremity edema?
Explanation
A. Heart failure can lead to fluid accumulation in the legs due to the heart's inability to effectively pump blood, causing increased pressure in the veins.
B. Excess fluid retention or consumption might cause edema, but heart failure specifically impacts the heart's pumping function.
C. Excess fluid consumption might contribute to temporary edema, but severe bilateral lower extremity edema is more likely due to a systemic issue like heart failure.
D. While a pulmonary embolism can lead to edema in the legs, it typically presents with sudden onset and might not present with bilateral edema from feet to knees.
A nurse is assessing a client's cranial nerves as part of a neurological examination. Which of the following actions should the nurse take to assess cranial nerve III?
Explanation
A. Observing for facial symmetry is more related to Cranial Nerve VII (Facial nerve) function.
B. Cranial Nerve III (Oculomotor nerve) controls the pupillary response to light, as well as eye movement.
C. Testing visual acuity is associated with Cranial Nerve II (Optic nerve).
D. Eliciting the gag reflex involves the Cranial Nerve IX (Glossopharyngeal nerve) and Cranial Nerve X (Vagus nerve).
During a community screening event for bone density, an elderly client asked the nurse why she is an inch shorter in height. Which of the following responses by the nurse is correct?
Explanation
A. Loss of subcutaneous fat might contribute to changes in appearance but is not primarily responsible for the decrease in height with aging.
B. Reduced spinal flexibility may contribute to posture changes but doesn’t sufficiently explain the decrease in height.
C. With aging, the intervertebral discs and cartilage between spinal bones wear down, leading to a decrease in height due to changes in the spine's structure.
D. Thickening of intervertebral discs is not a typical occurrence with aging and does not explain the decrease in height.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 48 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

