ATI Pharmacology Endocrine and Hematology
Total Questions : 45
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is assisting with the care of a client who has a prescription for 3,000 mL of intravenous fluids over the next 24 hours.
The nurse should set the volumetric pump to deliver how many milliliters per hour?
Explanation
To calculate the rate at which the volumetric pump should be set to deliver the intravenous fluids, you need to divide the total volume of fluid (3,000 mL) by the total time in hours (24 hours).
This gives you 3,000 mL ÷ 24 hours = 125 mL/hr.
Therefore, the nurse should set the volumetric pump to deliver 125 mL of fluid per hour.

Choice B is incorrect because 130 mL/hr would result in a total of 3,120 mL over 24 hours.
Choice C is incorrect because 135 mL/hr would result in a total of 3,240 mL over 24 hours.
Choice D is incorrect because 140 mL/hr would result in a total of 3,360 mL over 24 hours.
A nurse is preparing to administer cefixime to a patient. The dose is 200 mg PO.
Available is cefixime oral suspension 100 mg/mL.
How many milliliters should the nurse administer?
Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.
Explanation
To calculate the volume of cefixime oral suspension that the nurse should administer, you need to divide the prescribed dose (200 mg) by the concentration of the suspension (100 mg/mL).
This gives you 200 mg ÷ 100 mg/mL = 2 mL.
Therefore, the nurse should administer 2 mL of cefixime oral suspension.
Choice A is incorrect because 1.9 mL would provide a dose of 190 mg.
Choice C is incorrect because 2.1 mL would provide a dose of 210 mg.
Choice D is incorrect because 2.2 mL would provide a dose of 220 mg.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching with a patient who has hypertension and a new prescription for verapamil.
The nurse should instruct the patient to avoid taking this medication with which of the following foods?
Explanation
The nurse should instruct the patient to avoid taking verapamil with grapefruit.
Studies have demonstrated an interaction between verapamil and grapefruit juice, which is likely due to an inhibition of intestinal metabolism resulting in increased oral bioavailability1.
This means that grapefruit can interfere with the enzymes that break down verapamil in your digestive system, potentially leading to dangerous health problems2.
Choices B, C, and D are incorrect because there is no known interaction between verapamil and spinach, broccoli, or carrots.
A nurse is caring for a client who is taking levothyroxine for hypothyroidism.
Which of the following indicates the client's dose is too high?
Explanation
Taking too much levothyroxine can cause side effects such as an elevated pulse1.
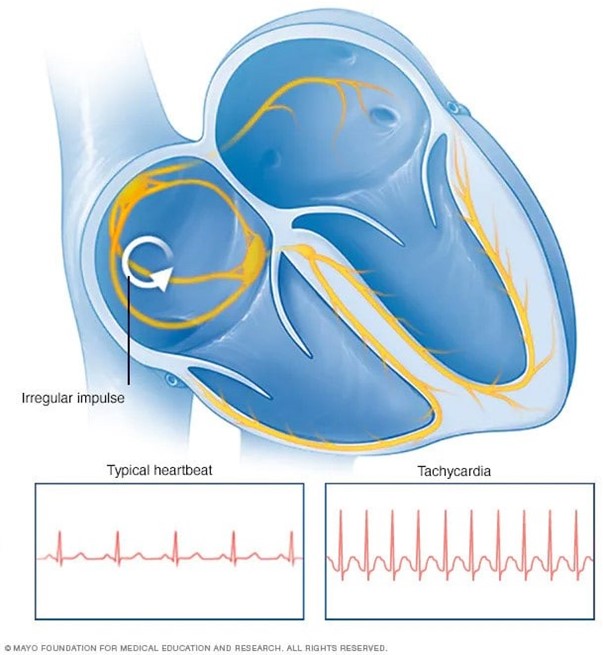
Choice A is not the answer because a decreased temperature is not a side effect of taking too much levothyroxine.
Choice B is not the answer because hypotension is not a side effect of taking too much levothyroxine.
Choice D is not the answer because constipation is not a side effect of taking too much levothyroxine.
A male client tells the nurse that he does not want the female assistive personnel (AP) involved in his care.
Which of the following statements should the nurse give?
Explanation
“I understand your request to have only male staff members attend to your care.” This response acknowledges the client’s request and shows that the nurse is willing to listen to his concerns.
Choice A is not the correct answer because it can be perceived as confrontational and may make the client feel uncomfortable.
Choice C is not the correct answer because it dismisses the client’s request and may make him feel unheard.
Choice D is not the correct answer because it implies that the nurse will immediately comply with the client’s request without further discussion or consideration of other options.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching with a client who is to self-administer regular insulin and NPH insulin from the same syringe.
Which of the following instructions should the nurse provide?
Explanation
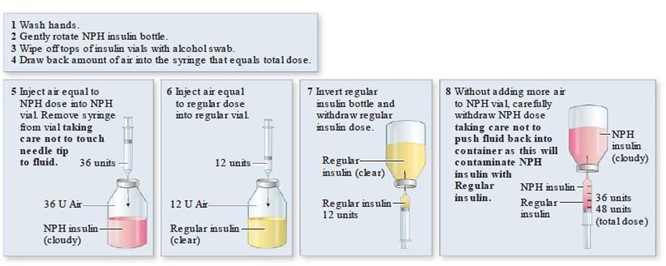
“Inject air into the regular insulin first.” When mixing regular insulin and NPH insulin in the same syringe, the nurse should instruct the client to inject air into the NPH insulin vial first, then inject air into the regular insulin vial.
After that, the client should draw up the regular insulin into the syringe first, followed by the NPH insulin.
Choice B is not correct because NPH insulin should not be shaken vigorously as it can damage the insulin molecules.
Choice C is not correct because the regular insulin should be drawn up into the syringe first.
Choice D is not correct because regular insulin is a clear solution and should not appear cloudy.
A nurse is reviewing laboratory data from a client who has a pulmonary embolism and is receiving IV heparin.
Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider?
Explanation
“Patient’s platelets 100,000.” A nurse should report a low platelet count to the provider because it may indicate heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), a serious complication of heparin therapy.
Choice B is not correct because a Prothrombin time (PT) of 12 seconds is within the normal range and does not need to be reported.
Choice C is not correct because Thrombin time (TT) is not typically used to monitor heparin therapy.
Choice D is not correct because a Hematocrit of 35% is within the normal range and does not need to be reported.
A nurse is reinforcing discharge instructions for a client who has asthma and is about to start taking theophylline.
The nurse should instruct the client to monitor which of the following findings is an adverse effect of the medication.
Explanation
“Tachycardia.” Theophylline can cause a number of side effects, including tachycardia (fast heart rate) 1.
The nurse should instruct the client to monitor for this adverse effect and report it to their healthcare provider if it occurs.
Choice A is not correct because drowsiness is not a common side effect of theophylline.
Choice B is not correct because constipation is not a common side effect of theophylline.
Choice D is not correct because tachycardia is a known adverse effect of theophylline.

A nurse is preparing to administer heparin subcutaneously to a client.
Which of the following is an appropriate action by the nurse?
Explanation
“Inject the medication into the abdomen above the level of the iliac crest.” When administering heparin subcutaneously, it is appropriate to inject the medication into the abdomen above the level of the iliac crest 1.
Choice A is not correct because a 1-inch needle may be too long for subcutaneous injection.
A shorter needle, such as a 3/8 to 5/8 inch needle, is typically used for subcutaneous injections.
Choice B is not correct because a 22-gauge needle may be too large for subcutaneous injection.
A smaller gauge needle, such as a 25- or 27-gauge needle, is typically used for subcutaneous injections.
Choice C is not correct because massaging the injection site after administering heparin can increase the risk of bruising and should be avoided.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching for a client who has angina pectoris and a new prescription to apply a nitroglycerin transdermal patch daily.
Which of the following instructions should the nurse give the client?
Explanation
The nurse should instruct the client to cleanse the skin before applying a nitroglycerin transdermal patch 1.
This is because it is important to apply the patch to a clean, dry skin area with little or no hair that is free of scars, cuts, or irritation 1.

Choice A is incorrect because it is not recommended to use an old patch with medication residue.
Instead, always remove a previous patch before applying a new one 1.
Choice B is incorrect because a nitroglycerin patch should not be kept in place for 72 hours before replacing.
Instead, it should be worn for 12 to 14 hours and then removed 2.
Choice C is incorrect because the patch should not be applied to a hairy area of the skin for better adherence.
Instead, it should be applied to an area with little or no hair 1.
A nurse is preparing to administer heparin subcutaneously to a client who has deep vein thrombosis.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
The nurse should insert the needle at a 90-degree angle when administering heparin subcutaneously 1.
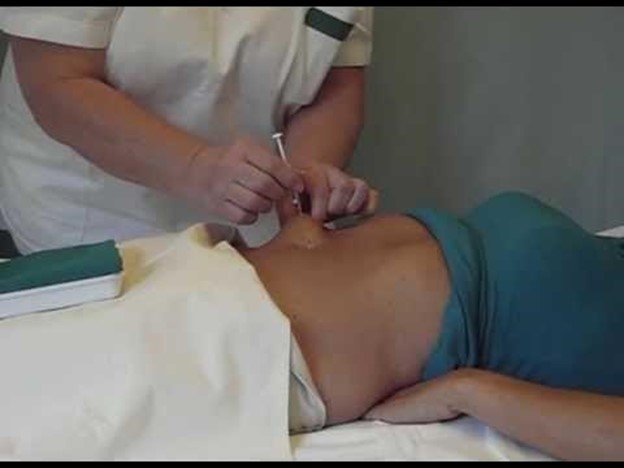
Choice B is incorrect because the nurse should not massage the injection site after administering the heparin.
Choice C is incorrect because it is not necessary to prepare for a blood test prior to injecting the heparin.
Choice D is incorrect because there is no specific requirement to select a 22-gauge needle for heparin administration.
A nurse is preparing to administer risperidone 5 mg PO.
Available is risperidone 2 mg tablets.
How many tablets should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth, Use a leading zero if it applies.
Do not use a trailing zero).
Explanation
The nurse should administer 2.5 tablets.
To determine the number of tablets needed to administer a dose of 5 mg using 2 mg tablets, you can divide the desired dose (5 mg) by the available tablet strength (2 mg/tablet): 5 mg ÷ 2 mg/tablet = 2.5 tablets.
Choice A is incorrect because administering 2 tablets would only provide a dose of 4 mg (2 tablets x 2 mg/tablet = 4 mg).
Choice C is incorrect because administering 2.6 tablets would provide a dose of 5.2 mg (2.6 tablets x 2 mg/tablet = 5.2 mg).
Choice D is incorrect because administering 3 tablets would provide a dose of 6 mg (3 tablets x 2 mg/tablet = 6 mg).
A nurse is reinforcing teaching with a client who has a new prescription for nebulizer treatments.
Which of the following client statements indicates to the nurse a need for further teaching?
Explanation
The statement “I won’t seal my lips around the mouthpiece and take slow, deep breaths” indicates a need for further teaching.
When using a nebulizer, the client should place the mouthpiece in their mouth between their teeth and close their lips around it 1.
They should also take slow, deep breaths to ensure that the medication is properly inhaled 1.
Choice A is incorrect because washing the mouthpiece with warm soapy water each day is a recommended action 2.
Choice B is incorrect because storing the nebulizer at room temperature is acceptable.
Choice D is incorrect because it is not necessary to keep medication in the nebulizer at all times.
A nurse is preparing to administer dextrose 5% in water IV to infuse at 100 mL/60 min.
The drop factor on the manual IV tubing is 60 gtt/mL.
The nurse should set the IV flow rate to deliver how many gtt/min. (Round to the nearest whole number.).
Explanation
The nurse should set the IV flow rate to deliver 100 gtt/min.
To calculate the flow rate in gtt/min, you can use the formula: (Volume to be infused (mL) x Drop factor (gtt/mL)) ÷ Time (min) = Flow rate (gtt/min).
Plugging in the values from the question: (100 mL x 60 gtt/mL) ÷ 60 min = 100 gtt/min.
Which medication should the nurse have available to reverse heparin's effects for a client who has thrombophlebitis and is receiving a continuous heparin infusion?
Explanation
Protamine sulfate is a medication that can be used to reverse the anticoagulant effects of heparin1.
It is a polycationic protein drug obtained from the sperm of fish and is used to reverse the anticoagulant effect of unfractionated heparin (UFH)2.
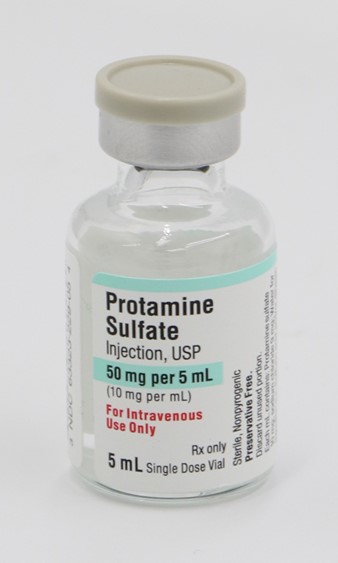
Choice B, Deferoxamine, is not the correct answer because it is a medication used to treat iron overload, not to reverse heparin’s effects.
Choice C, Sodium polystyrene sulfonate, is not the correct answer because it is a medication used to treat high levels of potassium in the blood, not to reverse heparin’s effects.
Choice D, Acetylcysteine, is not the correct answer because it is a medication used to treat acetaminophen overdose and to loosen thick mucus in individuals with cystic fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
A nurse is caring for a client who has hypertension and is to start taking Atenolol.
Explanation
Postural hypotension is a potential adverse effect of atenolol.
It can cause dizziness, faintness, or lightheadedness when getting up from a lying or sitting position suddenly12.
Choice A, Constipation, is not the correct answer because it is not a commonly reported adverse effect of atenolol.
Choice C, Dermatitis, is not the correct answer because it is not a commonly reported adverse effect of atenolol.
Choice D, Cardiac arrest, is not the correct answer because it is not a commonly reported adverse effect of atenolol.
A nurse is preparing to administer lorazepam 2 mg PO.
Available in lorazepam 1 mg tablets.
How many tablets should the nurse administer?
Explanation
The nurse should administer 2 tablets of lorazepam 1 mg to give a total dose of 2 mg.
This is calculated by dividing the desired dose (2 mg) by the available dose (1 mg/tablet) to get the number of tablets needed: 2 mg / (1 mg/tablet) = 2 tablets.
Choice A, 1 tablet, is not the correct answer because it would only provide a total dose of 1 mg.
Choice C, 3 tablets, is not the correct answer because it would provide a total dose of 3 mg.
Choice D, 4 tablets, is not the correct answer because it would provide a total dose of 4 mg.
A nurse in a provider's office is collecting data from a client who has hypothyroidism.
Which of the following should the nurse expect?
Explanation
Hypothyroidism can cause a slowed heart rate, also called bradycardia1.
Choice B, Moist skin, is not the correct answer because it is not a commonly reported symptom of hypothyroidism.
Choice C, Blurred vision, is not the correct answer because it is not a commonly reported symptom of hypothyroidism.
Choice D, Insomnia, is not the correct answer because it is not a commonly reported symptom of hypothyroidism.
A nurse is teaching a newly licensed nurse about insulin storage.
Which of the following statements by the newly licensed nurse indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
The current vial of insulin in use can be stored at room temperature for up to 28 days.
Unopened vials of insulin should be stored in the refrigerator to maintain their potency until their expiration date.
Choice C is not the correct answer because the current vial of insulin does not need to be discarded after six doses have been taken.
Choice D is not the correct answer because unused vials of insulin do not need to be returned to the healthcare provider’s office for disposal.
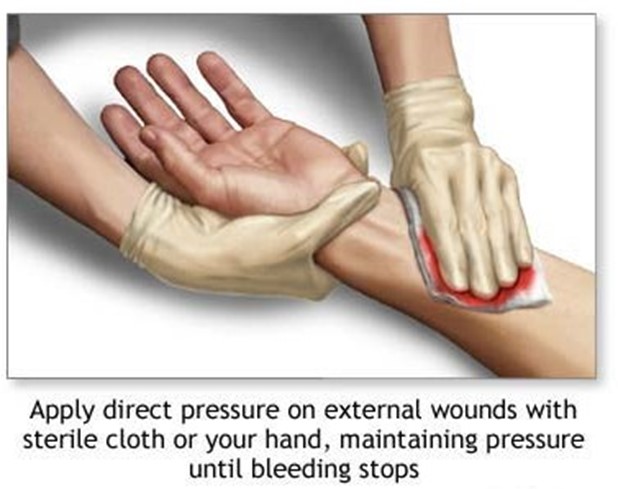
A nurse in the emergency department is assisting with the care of a client who has a deep laceration on her left lower forearm and is bleeding heavily from the wound.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
This is the first step in controlling bleeding and preventing hematoma formation 1.
Applying direct pressure to the wound with a sterile gauze or a clean cloth can help stop the bleeding 2.
Choice A is not the best answer because a tourniquet should only be used as a last resort to control life-threatening bleeding from a limb 2.
Choice B is not the best answer because placing the client in a modified Trendelenburg position is not necessary for this situation.
Choice D is not the best answer because settling the client in a reclining position is not necessary for this situation.
A nurse is preparing to administer levothyroxine 100mcg po to a client who has hypothyroidism.
Available levothyroxine is 50 mcg tablets.
How many tablets should the nurse administer? (Round off to the nearest whole number.
Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
The nurse should administer 2 tablets of levothyroxine 50 mcg to give the client a total dose of 100 mcg.
Choice A is not the best answer because administering 1 tablet of levothyroxine 50 mcg would only give the client a total dose of 50 mcg, which is not enough.
Choice C is not the best answer because administering 3 tablets of levothyroxine 50 mcg would give the client a total dose of 150 mcg, which is too much.
Choice D is not the best answer because administering 4 tablets of levothyroxine 50 mcg would give the client a total dose of 200 mcg, which is too much.
Which of the following statements indicates that the client understands the effects of warfarin (coumadin)?
Explanation
A nurse should never share her password for access to the facility’s computer system with anyone.
Sharing passwords can compromise the security and confidentiality of patient information.
For the second question you asked, the correct answer is choice A.
“I’ll use my electric razor for shaving.” This statement indicates that the client understands that warfarin (coumadin) can increase the risk of bleeding and that using an electric razor can help reduce the risk of cuts and bleeding while shaving.
Choice B is not the best answer because taking aspirin while on warfarin (coumadin) can increase the risk of bleeding.
Choice C is not the best answer because eating foods high in vitamin K can interfere with the effectiveness of warfarin (Coumadin).
Choice D is not the best answer because drinking alcohol while on warfarin (coumadin) can increase the risk of bleeding.
A nurse is preparing to administer amoxicillin 250 mg PO.
Available is amoxicillin oral suspension 125 mg/5 mL.
How many mL should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number.
Use a leading zero if it applies.
Do not use a trailing zero.).
Explanation
The nurse should administer 10 mL of amoxicillin oral suspension 125 mg/5 mL to give the client a total dose of 250 mg.
Choice A is not the best answer because administering 2 mL of amoxicillin oral suspension 125 mg/5 mL would only give the client a total dose of 50 mg, which is not enough.
Choice B is not the best answer because administering 5 mL of amoxicillin oral suspension 125 mg/5 mL would only give the client a total dose of 125 mg, which is not enough.
Choice C is not the best answer because administering 8 mL of amoxicillin oral suspension 125 mg/5 mL would give the client a total dose of 200 mg, which is not enough.
A nurse is preparing to administer Lactated Ringer's solution IV to infuse at 120 mL/hr for a client who has a respiratory disorder. The drop factor in the manual IV tubing is 60 gtt/mL. The nurse should set the flow rate to deliver how many gtts/min?
Explanation
The nurse should set the flow rate to deliver 40 gtts/min.
This can be calculated by multiplying the infusion rate (120 mL/hr) by the drop factor (60 gtt/mL) and then dividing by the number of minutes in an hour (60 min/hr): (120 mL/hr) * (60 gtt/mL) / (60 min/hr) = 120 gtt/hr / 60 min/hr = 2 gtt/min.
Choice A is not the best answer because setting the flow rate to deliver 20 gtts/min would not provide the desired infusion rate of 120 mL/hr.
Choice B is not the best answer because setting the flow rate to deliver 30 gtts/min would not provide the desired infusion rate of 120 mL/hr.
Choice D is not the best answer because setting the flow rate to deliver 50 gtts/min would provide a higher infusion rate than desired.
The physician orders vancomycin hydrochloride 2 g/day by mouth in 4 divided doses.
The pharmacy fills the client's prescription with 500 mg vancomycin hydrochloride capsules.
The nurse should instruct the client to take______capsule(s) per dose.
Explanation
The physician has ordered a total of 2 g/day of vancomycin hydrochloride to be taken in 4 divided doses.
This means that each dose should be 2 g/day ÷ 4 = 0.5 g/dose.
Since the pharmacy has filled the prescription with 500 mg capsules, and 500 mg is equivalent to 0.5 g, the client should take 1 capsule per dose.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 45 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

