ATI PN Nursing Care of Children with NGN 2020
Total Questions : 66
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is caring for a child who is brought to the urgent care clinic following exposure to poison ivy 1 hr ago. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
The correct answer is Choice D.
Choice A rationale: Administering an oral corticosteroid is not the first action the nurse should take. Corticosteroids are used to reduce inflammation and itching caused by poison ivy. However, they are usually prescribed if the symptoms are severe or if the rash covers a large area of the body. It’s important to note that corticosteroids can have side effects, especially when used for a long time, so they should be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider.
Choice B rationale: Applying calamine lotion to the affected area can help soothe the skin and relieve itching caused by poison ivy. However, this is not the first action the nurse should take. The first step is to remove the oil from the skin that causes the allergic reaction. Calamine lotion can be applied after the area has been thoroughly washed.
Choice C rationale: Instructing the parent to give the child an oatmeal bath twice daily can help soothe the skin and relieve itching. However, this is not the first action the nurse should take. Similar to calamine lotion, an oatmeal bath can be beneficial after the area has been thoroughly washed to remove the oil from the skin.
Choice D rationale: The first action the nurse should take when caring for a child exposed to poison ivy is to flush the area with cold, running water. This helps to remove the oil (urushiol) from the skin that causes the allergic reaction. It’s important to do this as soon as possible after exposure to help prevent the spread of the oil to other areas of the body or to other people. After flushing the area, the nurse can then apply calamine lotion or recommend an oatmeal bath to help soothe the skin and relieve itching.
A nurse is preparing to perform suctioning for an infant who has a partial mucus occlusion of her tracheostomy tube. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take?
Explanation
Answer: d. Apply suction in 3 to 4-second increments.
Rationale:
- a. Instill 2 mL of 0.9% sodium chloride prior to suctioning:While saline instillations may be used in some cases,it is not universally recommended for infants with tracheostomies and depends on the specific situation and healthcare provider's protocol.The priority in this case is to quickly clear the partial mucus occlusion to prevent respiratory distress.
- b. Select a catheter that fits snugly into the tracheostomy tube:This isincorrect.Selecting a catheter that fits tightly can damage the delicate tracheal mucosa and increase the risk of bleeding.A smaller-diameter catheter that allows for gentle passage is preferred.
Opens in a new window
www.researchgate.net
Tracheostomy tube and different catheter sizes
- c. Use a clean technique when performing suctioning:This is absolutely essential for all suctioning procedures to minimize the risk of infection.However,it is not the specific action that addresses the immediate concern of clearing the partial mucus occlusion.
- d. Apply suction in 3 to 4-second increments:This is thecorrectapproach for suctioning an infant with a tracheostomy.Applying short,intermittent suction bursts minimizes the risk of hypoxia and tissue trauma while effectively removing secretions.
Therefore, the most important action for the nurse to take is to apply suction in short, 3-4 second bursts to effectively clear the mucus occlusion while minimizing risks to the infant.
Additional Points:
- The nurse should use sterile suction equipment and sterile technique throughout the procedure.
- The suction pressure should be set at the lowest effective level,typically 80-120 mmHg.
- The nurse should monitor the infant for signs of respiratory distress,such as increased work of breathing,retractions,and oxygen desaturation,before,during,and after suctioning.
- If the mucus occlusion is not cleared after several attempts,the nurse should seek assistance from ahealthcareprovider.
A nurse is caring for a school-age child who has a new prescription for continuous pulse oximetry monitoring. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Answer: B. Reposition the probe every 2 hours.
Rationale:
- A. Warm the skin prior to probe placement:While cold fingers can lead to inaccurate readings,warming the skin is not an essential step and is not routinely recommended in clinical practice.
- B. Reposition the probe every 2 hours:This iscorrect.Continuous pressure from the probe in one spot can cause skin breakdown and pressure injuries.Repositioning the probe every 2 hours helps to prevent this and ensure accurate readings.
- C. Tape the wire to the palm of the hand:This is incorrect.The pulse oximeter probe should be placed on a vascular site,such as a fingertip or earlobe.Taping the wire to the palm would not provide accurate readings.
- D. Apply the sensor to the index fingernail:This is incorrect.The fingernail does not have sufficient blood flow for accurate pulse oximetry readings.The probe should be placed on the fleshy pad of the fingertip.
Therefore, the most important action for the nurse to take is to reposition the probe every 2 hours to prevent skin breakdown and ensure accurate readings.
Additional Points:
- The nurse should also choose a clean and dry site for probe placement.
- The probe should be snug but not too tight.
- The nurse should monitor the child for signs of skin breakdown,such as redness,swelling,or pain.
- If the child is restless or active,the nurse may need to secure the probe with additional tape or a special wrap.
A nurse is assisting with the care of a preschooler who is postoperative following tetralogy of Fallot correction. Which of the following manifestations indicates the child is possibly experiencing decreased cardiac output?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Extremities warm to the touch. This manifestation is not indicative of decreased cardiac output. Warm extremities suggest adequate peripheral perfusion and circulation. In a child with decreased cardiac output, the body might attempt to shunt blood away from the extremities to prioritize vital organs, leading to cooler extremities.
Choice B rationale:
Capillary refill 2 seconds. A capillary refill time of 2 seconds is within the normal range for a preschool-aged child. This quick capillary refill suggests adequate circulation and is not a sign of decreased cardiac output. Prolonged capillary refill time might be indicative of poor peripheral perfusion.
Choice C rationale:
Blood pressure 112/66 mm Hg. While a blood pressure of 112/66 mm Hg might be within the normal range for a preschooler, it is not the most reliable indicator of decreased cardiac output. Blood pressure can be influenced by various factors, and a seemingly normal blood pressure does not rule out decreased cardiac output if other manifestations are present.
Choice D rationale:
Diminished pulses. This is the correct choice. Diminished or weak pulses are indicative of decreased cardiac output. Inadequate blood volume being pumped by the heart can lead to reduced peripheral perfusion, resulting in diminished pulses. This sign is important in assessing the child's cardiovascular status postoperatively, especially after a corrective procedure for tetralogy of Fallot.
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory report of a newly admitted school-age child who has a fever. The nurse should identify which of the following laboratory results is an indication of an infection and should be reported to the charge nurse immediately.
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Urine osmolality 500 mOsm/kg. Urine osmolality is a measure of urine concentration and is not a reliable indicator of infection. It reflects the kidney's ability to concentrate urine and can vary based on hydration status and other factors. An elevated urine osmolality could suggest dehydration, not necessarily infection.
Choice B rationale:
WBC 17,500/mm3. This is the correct choice. An elevated white blood cell count (WBC) is a hallmark sign of infection. The body's immune response to an infection often includes an increase in WBC count, particularly the neutrophil count. This elevation is known as leukocytosis and is a red flag for infection.
Choice C rationale:
BUN 12 mg/dL. Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) measures kidney function and hydration status. While an elevated BUN can indicate dehydration, it is not a specific marker for infection. BUN levels can be influenced by various factors, including diet and renal function.
Choice D rationale:
Urine specific gravity 1.014. Urine-specific gravity reflects the concentration of solutes in urine and the kidney's ability to concentrate or dilute urine. While changes in urine specific gravity can indicate dehydration or overhydration, it is not a direct indicator of infection. An infection is better detected through changes in WBC count and other clinical signs.
A nurse is planning to collect a stool specimen from an infant to check for the presence of ova and parasites. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Obtain the specimen by swabbing the infant's rectum using a sterile culture swab. This is the correct choice. When collecting a stool specimen from an infant, the rectal swab method is commonly used. A sterile culture swab helps prevent contamination and ensures accurate results for detecting the presence of ova and parasites in the stool.

Choice B rationale:
Place a urine collection device on the infant until the specimen is obtained. This choice is not appropriate for collecting a stool specimen. A urine collection device is used for collecting urine, not stool. The specimen for ova and parasites needs to be taken directly from the rectum or diaper to accurately identify any infestations.
Choice C rationale:
Transfer the specimen to the collection container using povidone-iodine-soaked gauze. While povidone-iodine is an antiseptic, it is not typically used to transfer stool specimens. Using a sterile swab or a clean, dry container is more suitable for collecting and transporting stool samples to the lab.
Choice D rationale:
Maintain the specimen at room temperature after collection until it is transferred to the lab. Stool specimens for ova and parasites usually require refrigeration to prevent the degradation and growth of potential pathogens. Room temperature might lead to the overgrowth of bacteria and parasites, affecting the accuracy of test results.
A nurse is contributing to the plan of care for an adolescent client who has sickle cell anemia and is experiencing a vaso-occlusive crisis. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Decrease daily oral fluid intake. Rationale: This choice is not appropriate for a client experiencing a vaso-occlusive crisis in sickle cell anemia. In this crisis, there is a risk of dehydration due to increased fluid loss, and decreasing oral fluid intake would exacerbate this issue. Adequate hydration is important to prevent further sickling of red blood cells and maintain organ perfusion.
Choice B rationale:
Maintain bed rest to prevent hypoxemia. Rationale: This is the correct choice. During a vaso-occlusive crisis in sickle cell anemia, blood flow to certain tissues is restricted, leading to tissue hypoxia and pain. Bed rest is recommended to reduce metabolic demands and oxygen consumption, helping to prevent further tissue damage and improve oxygenation. It also reduces the risk of complications such as thrombosis and respiratory compromise.
Choice C rationale:
Apply cold compresses to painful joints. Rationale: Applying cold compresses is not a recommended intervention for vaso-occlusive crisis in sickle cell anemia. Cold can exacerbate vasoconstriction and further compromise blood flow to the affected tissues. Warm compresses or warm baths might be more appropriate to promote vasodilation and alleviate pain.
Choice D rationale:
Administer meperidine to eliminate a fever. Rationale: Administering meperidine solely to eliminate a fever is not the primary focus of care for a vaso-occlusive crisis. The priority is to manage pain and improve tissue perfusion. Meperidine is an opioid analgesic that can be used to manage severe pain associated with sickle cell crises, but it should be given with caution due to the risk of respiratory depression and the potential for addiction.
A nurse is assisting with the care of an adolescent client who is in skeletal traction for the treatment of a fractured femur. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Gently lift the traction weights off the floor when repositioning the client. Rationale: This choice is not recommended in the care of a client in skeletal traction. Traction weights should never be lifted off the floor as they provide the necessary counter traction to align and immobilize the fractured bone. Lifting the weights could disrupt the traction and jeopardize the healing process.
Choice B rationale:
Reduce intake of foods containing fiber while nonambulatory. Rationale: While constipation can be a concern for clients in skeletal traction due to decreased mobility, reducing fiber intake is not the appropriate intervention. Adequate fiber intake is important to promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation. Hydration and mobility exercises are more suitable approaches to manage constipation.
Choice C rationale:
Perform passive range-of-motion exercises to the affected extremity every 2 hours. Rationale: Passive range-of-motion exercises are important to maintain joint mobility and prevent muscle atrophy in a nonambulatory client. However, performing these exercises every 2 hours might be excessive and could cause unnecessary discomfort for the client. Range-of-motion exercises are usually done every 4 to 8 hours to strike a balance between maintaining joint health and providing rest.
Choice D rationale:
Apply protective padding to the end of the pin sites. Rationale: This is the correct choice. Applying protective padding to the end of the pin sites is crucial to prevent pressure ulcers and infection. The pin sites are potential entry points for bacteria, and protecting them helps reduce the risk of infection. Padding also prevents pressure on the skin and underlying tissues, reducing the potential for pressure injuries.
A nurse in a well-child clinic is collecting data from four clients. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider as a potential indication of child maltreatment?
Explanation
A history of frequent urinary tract infections (UTIs) is a sign of child maltreatment. It may indicate sexual abuse, which can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.Sexual abuse may also cause genital or anal trauma, sexually transmitted infections, or pregnancy1. UTIs are uncommon in children, especially in boys.The normal frequency of UTIs in children is around 1 in 10 girls and 1 in 30 boys by the age of 16 years
A nurse is reinforcing teaching with a parent of a child who has a sprained wrist. Which of the following interventions should the nurse instruct the parent to implement during the first 12 to 24 hours to minimize swelling?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Encouraging active range of motion of the extremity is not recommended during the first 12 to 24 hours after a sprained wrist. Early movement can potentially worsen the swelling and delay the healing process.
Choice B rationale:
Applying warm compresses to the extremity is not the best choice to minimize swelling in the initial 12 to 24 hours after a sprained wrist. Heat can actually increase blood flow and promote more swelling in the injured area.
Choice C rationale:
Elevating the extremity above the level of the heart is the correct choice for minimizing swelling in the first 12 to 24 hours after a sprained wrist. Elevating the injured area helps to reduce blood flow to the area, which in turn decreases swelling and promotes healing.
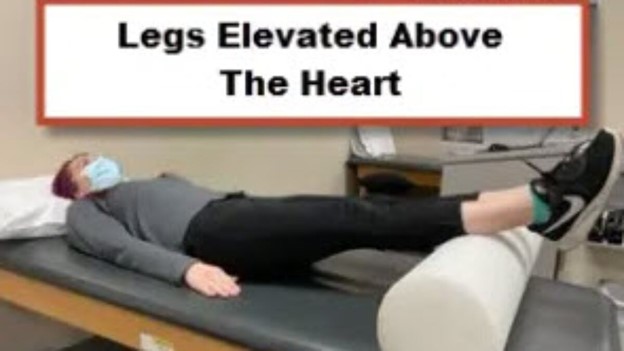
Choice D rationale:
Wrapping the extremity loosely with an elastic bandage might be beneficial for providing support, but it's not the primary intervention for minimizing swelling in the first 12 to 24 hours after a sprained wrist. Elevation is more effective for reducing swelling during this initial period.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching about food choices with a parent of a child who has celiac disease. Which of the following responses by the parent indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
This response indicates an understanding of the teaching about celiac disease. Rice is a gluten-free grain, which makes rice pudding a suitable dessert option for a child with celiac disease. Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, and individuals with celiac disease need to avoid gluten-containing foods.
Choice B rationale:
Barley is a gluten-containing grain, and feeding a child a barley-based breakfast cereal is not appropriate for someone with celiac disease. Gluten-containing grains can trigger adverse reactions in individuals with celiac disease due to their inability to properly digest gluten.
Choice C rationale:
Rye bread contains gluten, and making sandwiches using rye bread is not a suitable choice for a child with celiac disease. Gluten-free bread options, typically made from rice, corn, or other gluten-free flour, should be chosen instead.
Choice D rationale:
Chocolate malt may contain ingredients that could potentially contain gluten, and it's not a safe snack option for a child with celiac disease. Individuals with celiac disease need to be cautious about hidden sources of gluten in processed foods.
A nurse is preparing a child who has suspected bacterial meningitis for a lumbar puncture. Which of the following cerebrospinal fluid findings supports the diagnosis?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Decreased white blood cells (WBCs) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) would not support the diagnosis of bacterial meningitis. In bacterial meningitis, the presence of bacteria triggers an inflammatory response, leading to an increase in WBCs in the CSF (pleocytosis).
Choice B rationale:
Elevated glucose levels in CSF would actually be more consistent with viral rather than bacterial meningitis. In bacterial meningitis, glucose levels are typically decreased due to the high metabolic demands of bacteria on the glucose present in the CSF.
Choice C rationale:
Elevated total protein in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is indicative of inflammation and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Bacterial meningitis causes an intense inflammatory response, leading to an increase in total protein in the CSF.
Choice D rationale:
Decreased pressure in the CSF would not be a characteristic finding in bacterial meningitis. In fact, bacterial meningitis often leads to an increase in CSF pressure due to the inflammation and accumulation of inflammatory cells and proteins.
A nurse is assisting with the plan of care for an infant who has heart failure. Which of the following actions should the nurse recommend to include in the plan of care?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Ensuring the infant bottle feeds for 45 minutes is not recommended for an infant with heart failure. Prolonged feeding sessions can lead to increased fatigue and stress on the infant's cardiovascular system, exacerbating the heart failure symptoms.
Choice B rationale:
Administering digoxin for a pulse of 70/min is not appropriate. Digoxin is commonly used in heart failure cases to improve cardiac contractility and reduce heart rate. However, giving digoxin solely based on the heart rate without considering other factors can lead to potential overdose and adverse effects.
Choice C rationale:
(Correct Choice) Allowing for frequent rest periods is crucial in the plan of care for an infant with heart failure. Infants with heart failure often experience fatigue and difficulty feeding due to compromised cardiac function. Allowing them to rest between activities helps conserve energy and supports their overall well-being.
Choice D rationale:
Maintaining the infant in a supine position is not the best choice for an infant with heart failure. While the supine position is recommended for safe sleep to reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), it may not be optimal for an infant with heart failure. An inclined position may be more suitable to alleviate potential respiratory distress.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching with a group of adolescents about safety. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Sun protection is necessary even when using self-tanning creams. Self-tanning creams do not provide protection against the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Adolescents should be educated about the importance of using sunscreen to prevent skin damage and reduce the risk of skin cancer.
Choice B rationale:
The risk of injury from firearms does not necessarily decrease as children enter adolescence. Adolescents may still lack proper judgment and decision-making skills, making them susceptible to accidents and injuries related to firearms. Educating adolescents about firearm safety and promoting responsible firearm storage is essential.
Choice C rationale:
(Correct Choice) Driving skills can indeed be impaired when friends are present. Teenagers often face distractions while driving, especially when friends are in the car. Peer pressure and social interactions can divert their attention from the road, leading to an increased risk of accidents. Educating adolescents about the importance of focused and responsible driving can help reduce this risk.
Choice D rationale:
Medroxyprogesterone, a form of hormonal contraception, does not provide protection against gonorrhea. It offers contraception by preventing ovulation and altering the cervical mucus to impede sperm penetration. However, it does not offer any protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Adolescents should be educated about safe sex practices to prevent STIs.
A nurse is contributing to the plan of care for a school-age child who is being admitted for diabetic ketoacidosis. Which of the following interventions should the nurse recommend?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Implementing fluid restrictions is not recommended for a child with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA is characterized by dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, and fluid replacement is a crucial aspect of its management. Restricting fluids could worsen dehydration and hinder the correction of metabolic imbalances.
Choice B rationale:
(Correct Choice) Monitoring vital signs every 8 hours is an important intervention for a school-age child with DKA. Vital signs, including heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and temperature, provide valuable information about the child's overall condition, fluid status, and response to treatment. More frequent monitoring might be necessary during the acute phase of DKA.
Choice C rationale:
Initiating continuous cardiac monitoring is not typically indicated for a school-age child with DKA. While DKA can have effects on the cardiovascular system, continuous cardiac monitoring is reserved for more critical situations where immediate changes in heart rhythm need to be detected.
Choice D rationale:
Administering subcutaneous insulin 30 minutes before meals is not appropriate for a child with DKA. In DKA management, insulin is typically administered intravenously to achieve more precise control over blood glucose levels. Subcutaneous insulin might not provide the rapid and consistent action needed to address the acute hyperglycemia and metabolic acidosis in DKA.
A nurse is preparing to administer nasogastric tube feedings to a 2-month-old infant. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Stabilizing the nasogastric tube by taping it to the infant's cheek is a crucial step in preventing accidental removal or displacement of the tube during feedings. Infants are known for their active movements, which could lead to unintentional removal of the tube. Taping the tube securely helps maintain its proper placement and ensures the delivery of nutrients.
Choice B rationale:
Positioning the infant in a supine (lying on the back) position during feedings is not recommended. This position could lead to an increased risk of aspiration, where the feedings could enter the airway and lungs, causing respiratory issues. The recommended position for nasogastric tube feedings is semi-upright or upright to minimize this risk.
Choice C rationale:
Aspirating residual fluid from the infant's stomach and discarding it is not standard practice for nasogastric tube feedings. Aspirating can introduce the risk of infection or cause irritation to the stomach lining. Additionally, residual fluid can provide valuable information about the infant's digestion and absorption, and its presence should be taken into consideration when adjusting feedings.
Choice D rationale:
Microwaving the infant's formula to a temperature of 41°C (105.8°F) is not safe. Formula should be warmed gently using warm water or a bottle warmer to avoid overheating, which could burn the infant's mouth and esophagus. Microwaving can cause uneven heating and lead to hot spots within the formula, posing a risk of burns.
A nurse in a clinic is speaking with a parent of a 1-year-old toddler who received her scheduled immunizations 1 hour ago. Which of the following findings reported by the parent is the nurse's priority?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Swelling around the eyelids and mouth could indicate an allergic reaction, which can be severe in some cases. Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening reaction that can occur after immunizations. The nurse's priority is to assess and address any signs of an allergic reaction promptly. Swelling of the face, particularly around the eyes and mouth, is a red flag for potential anaphylaxis, and immediate intervention is necessary to prevent further complications.
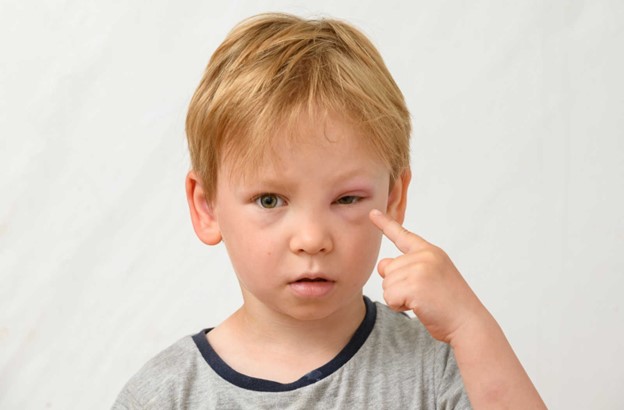
Choice B rationale:
A temperature of 100.7 degrees Fahrenheit is considered a mild fever. While it's important to monitor for fever after immunizations, a mild fever alone may not be the nurse's top priority, especially if the child is otherwise stable. Fever can be a common post-immunization response and is often self-limiting.
Choice C rationale:
While monitoring the child's intake is important, only eating 2 ounces during the last feeding is not a priority concern compared to potential allergic reactions or fever. A temporary decrease in appetite following immunizations can be expected and might resolve on its own.
Choice D rationale:
Crying when the injection site is touched is a common response to discomfort from the shot. While it's essential to provide comfort and support to the child, this finding is not indicative of a severe reaction. It's not the nurse's priority compared to potential signs of an allergic reaction or a more significant fever.
A nurse is collecting data from a school-age child who has hypothyroidism. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Lethargy, or extreme fatigue and sluggishness, is a characteristic symptom of hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism occurs due to an underactive thyroid gland, which leads to a decrease in metabolic activity and energy levels. Children with hypothyroidism often exhibit lethargy, weakness, and a lack of interest in activities. This is due to the reduced metabolic rate and overall slowing down of bodily functions.
Choice B rationale:
Diarrhea is not a common finding associated with hypothyroidism. In fact, hypothyroidism tends to slow down gastrointestinal motility, leading to constipation rather than diarrhea. Therefore, diarrhea is not expected as a symptom in a child with hypothyroidism.
Choice C rationale:
Tachycardia, an elevated heart rate, is not typically associated with hypothyroidism. Instead, hypothyroidism often leads to bradycardia (a slower-than-normal heart rate) due to the overall slowing of the body's metabolic processes.
Choice D rationale:
Hirsutism, which refers to excessive hair growth in areas where hair growth is typically seen in males, is not a common finding in hypothyroidism. Hirsutism is more commonly associated with hormonal imbalances such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) rather than hypothyroidism.
A nurse is reviewing the medical records of a group of clients. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to local authorities?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
The nurse should report the finding of a 6-month-old infant with a spiral fracture to a lower extremity to local authorities. Spiral fractures in infants, especially those who are not yet independently mobile, raise concerns about possible child abuse or non-accidental trauma. The unique pattern of spiral fractures is often associated with twisting forces, which are unlikely to occur accidentally in infants who cannot perform such movements. Reporting such cases is essential to ensure the safety and well-being of the child.
Choice B rationale:
A 9-month-old infant exposed to bedbugs and cellulitis is not an emergency that requires reporting to local authorities. While cellulitis can be serious, it is not an immediate threat to the child's safety, and the focus should be on providing appropriate medical care.
Choice C rationale:
A 4-year-old preschooler with rivalry among siblings does not indicate a need for reporting to local authorities. Sibling rivalry is a common occurrence in families and does not pose a threat to the child's safety. It is a social and developmental issue that can be addressed within the family.
Choice D rationale:
A 24-month-old toddler experiencing occasional incontinence does not require reporting to local authorities. Occasional incontinence can be a normal part of toddler development as they learn to control their bladder. It does not indicate abuse or immediate danger to the child.
A nurse is caring for a preschooler who is terminally ill. Which of the following reactions to death should the nurse expect?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
In the context of terminal illness and considering the developmental stage of a preschooler (3 to 6 years old), the understanding that death is permanent is a typical reaction. At this age, children begin to comprehend the finality of death, although they might not fully grasp the nuances of its irreversibility. They might use concrete terms to describe death and might associate it with sleep or as something that can be reversed. However, the understanding that death is not a temporary state but rather a permanent cessation of life emerges during this period.
Choice B rationale:
Perceiving death as a punishment is not a common developmental reaction for a preschooler. Such perception is more aligned with the magical thinking characteristic of younger children (around 2 to 4 years old). Preschoolers typically have a growing awareness of death's permanence and might feel sadness or confusion about it, rather than interpreting it as a form of punishment.
Choice C rationale:
Worries about physical body changes are more likely to be relevant to adolescents who are undergoing puberty and experiencing significant physical changes. Preschoolers might not be as concerned about these changes in the context of terminal illness.
Choice D rationale:
Feelings of isolation can occur in response to terminal illness, but this emotional reaction is not specific to the preschool developmental stage. Isolation might be experienced by individuals of various ages in response to the awareness of their impending mortality. However, preschoolers might not express this feeling in the same way as older children or adults.
A nurse is collecting data from a child who has type 1 diabetes mellitus and has slurred speech, is diaphoretic, and has a blood glucose reading of 45 mg/dL. Which of the following should the nurse administer?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Insulin administration is not appropriate in this situation. The child's symptoms (slurred speech, diaphoresis, low blood glucose reading) indicate hypoglycemia, which is a state of low blood sugar. Administering insulin, which lowers blood glucose further, would exacerbate the hypoglycemia and could lead to more severe symptoms or even unconsciousness.
Choice B rationale:
Metformin is not indicated in this scenario. Metformin is an oral medication used to treat type 2 diabetes, not type 1 diabetes mellitus. The child in the scenario has type 1 diabetes, which is characterized by an absolute deficiency of insulin production.
Choice C rationale:
Offering a 6 oz diet soft drink is not the appropriate intervention for hypoglycemia. Diet soft drinks do not contain significant amounts of sugar, which is needed to rapidly raise the child's blood glucose levels. In cases of hypoglycemia, a source of quickly absorbable sugar, such as a regular soft drink or fruit juice, is recommended.
Choice D rationale:
Administering a 6 oz regular soft drink is the appropriate intervention in this situation. The child is experiencing hypoglycemia, which means their blood glucose levels are dangerously low. Regular soft drinks contain rapidly absorbable sugar that can quickly raise the child's blood glucose levels, alleviating the symptoms of hypoglycemia. The child's symptoms, including slurred speech and diaphoresis, are indicative of a need for immediate intervention to raise blood sugar levels.
A nurse is collecting data from a 6-month-old infant during a well-child visit. The infant weighed 3.26 kg (7 lb 2 oz) at birth. Which of the following is the anticipated weight at 6 months of age?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
The anticipated weight gain for a healthy infant during the first year of life is a crucial indicator of growth and development. Infants usually double their birth weight by around 5-6 months of age and triple it by one year. Considering the infant's birth weight of 3.26 kg (7 lb 2 oz), the expected weight at 6 months would be approximately 8.6 to 9.5 kg (19 to 21 lb). This growth trajectory falls within the normal range and indicates healthy development, appropriate nutrition, and general well-being.
Choice B rationale:
The weight range of 4.1 to 5 kg (9 to 11 lb) is not a typical weight for a 6-month-old infant. This range is considerably lower than the expected weight gain for a healthy baby. It might suggest inadequate nutrition or potential growth-related concerns.
Choice C rationale:
The weight range of 6.8 to 7.7 kg (15 to 17 lb) falls below the expected weight gain for a 6-month-old infant. While there might be some variability in weight gain among infants, this range is still lower than the average weight gain. It could raise concerns about the infant's growth and nutritional intake.
Choice D rationale:
The weight range of 10.4 to 11.3 kg (23 to 25 lb) is beyond the expected weight gain for a 6-month-old infant. While growth can vary, this weight range is considerably higher than what is typical for infants at this age. It could suggest overfeeding or other underlying health issues.
A nurse is assisting with the collection of a bone marrow specimen from a preschooler. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Positioning the child sitting with their buttocks at the edge of the table is not appropriate for collecting a bone marrow specimen from a preschooler. This position does not provide adequate access to the bone marrow aspiration site and may lead to discomfort for the child.
Choice B rationale:
Placing the child in a prone position (lying face down) is suitable for collecting a bone marrow specimen from a preschooler. This position exposes the posterior iliac crest, which is a common site for bone marrow aspiration. It allows for easier access to the bone marrow and reduces the risk of injury.
Choice C rationale:
Positioning the child side-lying to expose the vertebrae is not the recommended position for bone marrow aspiration. The iliac crest, not the vertebrae, is the usual site for this procedure in children. Placing the child in a side-lying position would make it difficult to access the appropriate site.
Choice D rationale:
Placing the child supine with legs flexed outward into a frog-like position is suitable for collecting a bone marrow specimen. This position provides access to the iliac crest while allowing for better immobilization of the child. It also ensures the child's safety and comfort during the procedure.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching about sibling adaptation with a parent of a child who has cystic fibrosis. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Avoiding discussions about the child's diagnosis with the sibling might create confusion and anxiety for the sibling. Open communication is essential for helping siblings understand their brother or sister's condition and cope with the changes in the family dynamic.
Choice B rationale:
Encouraging phone calls between the siblings is a positive step in promoting sibling adaptation when one of them has a chronic illness like cystic fibrosis. Maintaining connections through communication helps siblings feel involved, valued, and informed about each other's lives and challenges.
Choice C rationale:
Designating one parent to stay at home with the sibling might lead to feelings of isolation and neglect for the child with cystic fibrosis. Siblings also need support and attention during this time, and isolating one parent could hinder healthy sibling relationships.
Choice D rationale:
Avoiding having the sibling visit the child in the facility may prevent the sibling from understanding the condition and create a sense of fear or confusion. Controlled, supervised visits can actually be beneficial, as they allow the siblings to interact and support each other in a safe environment.
A nurse is caring for an adolescent client who is scheduled for surgery. Which of the following actions should the nurse take to prepare the child based on their developmental stage?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Adolescents are at a stage of development where body image and appearance are of significant importance. Discussing how the procedure might affect the client's appearance allows the nurse to address the adolescent's concerns and fears related to changes in their body. This can help alleviate anxiety and promote a sense of control over the situation, fostering a more positive psychological response to the surgery.
Choice B rationale:
Avoiding involving the client in decisions regarding treatment (Choice B) would not be appropriate for an adolescent. Adolescents are at a stage where they are developing autonomy and decision-making skills. Excluding them from decisions about their treatment could lead to feelings of powerlessness and hinder their sense of control.
Choice C rationale:
Emphasizing that the procedure is not a punishment (Choice C) might be suitable for younger children who might associate medical procedures with punishment. However, adolescents typically do not perceive medical procedures as punishments, so this explanation may not address their specific concerns.
Choice D rationale:
Keeping equipment out of the client's sight (Choice D) might be more relevant for younger children who might be frightened by medical equipment. Adolescents are generally better able to comprehend and cope with the presence of medical equipment. Open communication about the procedure and addressing their concerns directly would be more beneficial.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 66 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

