ATI RN Pharmacology 2019 Exam 6
Total Questions : 66
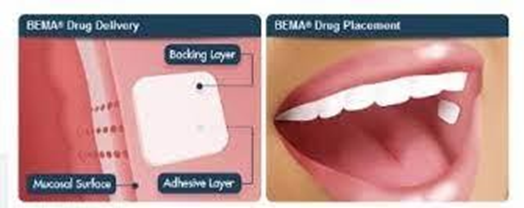
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is caring for a client who is receiving hospice care and has a prescription for fentanyl buccal film. Which of the following methods should the nurse use to administer this medication?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Dissolving the fentanyl buccal film in water isn't the appropriate method of administration. It's specifically formulated for buccal (cheek) administration to facilitate absorption, and dissolving it in water may alter its efficacy.
Choice B rationale: Swallowing the fentanyl buccal film isn't the intended method of administration. It's designed for absorption through the mucous membrane, not for ingestion.
Choice C rationale: Fentanyl buccal film is designed for absorption through the mucous membrane of the cheek. This route allows for rapid absorption of the medication
directly into the bloodstream, offering quicker relief for the patient.
Choice D rationale: Placing the fentanyl buccal film on the tongue for dissolution is not the correct method. The medication is formulated for buccal administration, not oral dissolution.
A nurse is completing medication reconciliation for a client prior to their transfer to a rehabilitation facility. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: While medications received during surgery are essential to the client's history, they might not be pertinent to the current medication regimen and reconciliation process for transfer.
Choice B rationale: Sending a list of prescribed medications to the pharmacy isn't a direct action for medication reconciliation, which involves cross-checking current and new medications for discrepancies.
Choice C rationale: Discussing adverse effects with the client is important for their understanding but doesn't directly address the reconciliation process.
Choice D rationale: During medication reconciliation, comparing the current medications with newly prescribed ones is crucial. Noting any differences or discrepancies helps
ensure the accuracy of the client's medication regimen during their transfer to another facility.
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a client who has rheumatoid arthritis and a prescription for cyclosporine. The nurse should report which of the following laboratory values to the provider?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: While monitoring sodium levels is important, a level of 139 mEq/L is within the normal range and might not directly correlate with cyclosporine
administration.
Choice B rationale: Though BUN levels can indicate kidney function, a level of 18 mg/dL falls within the normal range and might not immediately indicate adverse effects related to cyclosporine.
Choice C rationale: Cyclosporine, often prescribed for rheumatoid arthritis, can impact kidney function. An elevated creatinine level (2.5 mg/dL) might signify potential kidney impairment, necessitating immediate attention from the provider to assess and manage any adverse effects of the medication on renal function.
Choice D rationale: A potassium level of 4.2 mEq/L is within normal limits and might not directly relate to potential complications due to cyclosporine therapy.
A nurse is initiating IV therapy for client who had a right-sided mastectomy. In which of the following locations should the nurse place a catheter?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The wrist might not be the optimal site for IV catheter placement following a mastectomy due to potential limitations in venous access and increased risk of complications.
Choice B rationale: The most proximal site is not a specific location and may vary depending on the client's condition and anatomy.
Choice C rationale: The nurse should also avoid placing a catheter in a cordlike vein because they are more prone to infiltration, phlebitis, and nerve damage.
Choice D rationale: The left arm is the safest site to avoid complications such as lymphedema, infection, or thrombosis.
A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving penicillin IV. For which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider as a manifestation of anaphylaxis?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: While increased blood pressure can occur in various conditions, it might not specifically indicate anaphylaxis to penicillin.
Choice B rationale: Hypertonia might not directly correlate with anaphylaxis and could be caused by other factors.
Choice C rationale: Wheezing is a critical sign of anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction to penicillin. Reporting wheezing to the provider is crucial for immediate intervention to prevent further complications associated with anaphylaxis.
Choice D rationale: Urinary retention is not a typical manifestation of anaphylaxis to penicillin and might not be directly linked to the allergic reaction.
A nurse is caring for a client who reports taking propranolol for several years but has recently stopped for financial reasons. The nurse should assess the client for which of the following findings?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: While propranolol withdrawal can have various effects, hyperkalemia isn't typically associated with sudden discontinuation of this medication.
Choice B rationale: Propranolol is a beta-blocker used to treat conditions like hypertension and cardiac arrhythmias. Stopping this medication suddenly can lead to rebound effects, such as an increased heart rate or tachycardia, due to sudden withdrawal of the medication's effects on the heart.
Choice C rationale: Rhinitis is not a typical manifestation of propranolol withdrawal.
Choice D rationale: Bradypnea, or slow breathing, is not commonly associated with the withdrawal effects of propranolol.
A nurse is caring for a client who has major depression and a new prescription for citalopram. Which of the following adverse effects is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Citalopram is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) that increases the level of serotonin in the brain. Serotonin syndrome is a rare but serious adverse effect of SSRIs that can cause confusion, agitation, tremors, seizures, and coma. The nurse should report this finding to the provider immediately, as it can be life-threatening.
Choice B rationale: Insomnia can occur as an adverse effect of citalopram but might not be as immediately concerning as confusion.
Choice C rationale: Bruxism (teeth grinding) can be a side effect of citalopram but might not pose an immediate risk compared to confusion.
Choice D rationale: Weight loss, while a potential side effect, might not be as urgent or immediately concerning as confusion.
A nurse is reviewing the medication list of a client who has erectile dysfunction and is requesting a prescription for sildenafil. The nurse should identify that which of the following medications is a contraindication for receiving this medication?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Furosemide isn't typically contraindicated with sildenafil use.
Choice B rationale: Nitroglycerin and sildenafil both lower blood pressure, and concurrent use can lead to severe hypotension, making nitroglycerin a contraindication for sildenafil use.
Choice C rationale: Indomethacin isn't generally contraindicated with sildenafil use.
Choice D rationale: Albuterol isn't typically contraindicated with sildenafil use.
A nurse is planning to administer a controlled substance to a client who is experiencing pain. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take first?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Before administering controlled substances, ensuring the correct client through proper identification using two identifiers is crucial for patient safety and prevention of medication errors.
Choice B rationale: The fourth step is to document the administration of the medication, which includes recording the date, time, dose, route, site, and client response. This provides evidence of care and helps to monitor the client's pain level and possible side effects.
Choice C rationale: Removing the medication from the cabinet comes after ensuring correct client identification.
Choice D rationale: The third step is to compare the amount of medication available to the inventory record, which shows how much of the medication is in stock and how much has been used. This helps to prevent errors and discrepancies in the medication supply.
A nurse is preparing to administer amphotericin B lipid complex via intermittent IV bolus to a client who has infective endocarditis. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Amphotericin B lipid complex can bind to other solutions, leading to precipitation. Priming the tubing with 0.9% sodium chloride ensures that the medication is not wasted due to precipitation in the tubing.
Choice B rationale: The infusion rate and duration depend on the specific guidelines and conditions but are not directly related to priming the tubing.
Choice C rationale: While the administration method might vary, priming the tubing with a compatible solution is more critical for the initial setup.
Choice D rationale: Color change might not be an accurate indicator of medication integrity or effectiveness in this case.

A nurse is teaching a client who has active pulmonary tuberculosis about the management of medication for the disease. Which of the following statements is appropriate for the nurse to make?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: While monitoring kidney function might be necessary for some medications, it's not a routine monitoring requirement for tuberculosis medication.
Choice B rationale: Treatment for active pulmonary tuberculosis typically involves combination therapy with multiple medications to effectively target the bacteria and prevent resistance.
Choice C rationale: The duration of tuberculosis treatment varies but typically ranges from 6 to 9 months, not 3 years.
Choice D rationale: Tuberculin skin tests are used for diagnosis and not typically for monitoring treatment progress.
A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a gastric ulcer and a new prescription for ranitidine. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: There's no direct contraindication regarding dairy products with ranitidine.
Choice B rationale: Ranitidine, an H2 blocker, requires spacing from antacids to prevent decreased absorption, as antacids can reduce its effectiveness.
Choice C rationale: Aspirin may have interactions or adverse effects when taken concurrently with ranitidine.
Choice D rationale: Fine hand tremors are not an expected side effect of ranitidine.
A nurse is preparing to administer enoxaparin 1 mg/kg subcutaneously every 12 hr. The client's weight is 121 lb. Available is enoxaparin 60 mg/0.6 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer per dose? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Calculation: 1 mg/kg dose x 121 lb (weight) = 55 kg (approximately) 55 kg x 1 mg = 55 mg (dose required) Enoxaparin 60 mg/0.6 mL = 100 mg/mL Therefore, 55 mg / 100 mg/mL =
0.55 mL (rounded to 0.6 mL).
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a client who received a dose of sodium polystyrene sulfonate. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication that the medication has been effective?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Calcium levels might not directly reflect the effectiveness of sodium polystyrene sulfonate.
Choice B rationale: Magnesium levels might not directly reflect the effectiveness of sodium polystyrene sulfonate.
Choice C rationale: Sodium levels might not directly reflect the effectiveness of sodium polystyrene sulfonate.
Choice D rationale: Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is used to lower potassium levels in conditions like hyperkalemia. A decrease in potassium levels (within normal range)
indicates effectiveness.
A nurse is teaching a client about self-administration of enoxaparin. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A rationale: For subcutaneous injections like enoxaparin, the entire length of the needle needs to be inserted to ensure that the medication reaches the fatty tissue under the skin and reduces the risk of bleeding or bruising.
Choice B rationale: The client should not massage the insertion site after injecting the medication, as this may increase the risk of hematoma formation.
Choice C rationale: The client should alternate injection sites between the sides of the abdomen to prevent bruising and irritation.
Choice D rationale: The client should also grasp the skin between the thumb and forefinger while injecting the medication to create a fold of tissue. This ensures that the medication is delivered into the subcutaneous layer and not the muscle.
Choice E rationale: The client should not expel the air bubble from the prefilled syringe, as this helps to seal the medication in the tissue and prevent leakage while ensuring that you receive the full dose of medication.
A nurse is assessing a client who has asthma and a prescription for albuterol. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following adverse effects?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Constipation is not a typical adverse effect associated with albuterol use.
Choice B rationale: Fever is not a commonly reported adverse effect of albuterol.
Choice C rationale: Albuterol, a bronchodilator used in asthma, can lead to increased heart rate or tachycardia as a common adverse effect due to its stimulatory effect on beta-receptors.
Choice D rationale: Albuterol is more likely to cause stimulating effects rather than drowsiness.

A client who has Graves' disease is prescribed methimazole. Which of the following effects should the nurse expect to see after the client has taken the medication for 2 months?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The client's skin temperature will decrease as the thyroid hormone levels decrease and the metabolic rate slows down.
Choice B rationale: The client's heart rate will decrease as the thyroid hormone levels decrease and the cardiac output decreases.
Choice C rationale: The client's sleep pattern will improve as the thyroid hormone levels decrease and the nervous system becomes less stimulated.
Choice D rationale: The client's weight will increase as the thyroid hormone levels decrease and the appetite increases.
A nurse is administering naloxone to a client who has developed an adverse reaction to morphine. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as a therapeutic effect of naloxone.
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Naloxone reverses opioid effects and may lead to decreased pain relief.
Choice B rationale: Naloxone might cause an increase in blood pressure rather than a decrease.
Choice C rationale: Naloxone is an opioid antagonist used to reverse the effects of opioids like morphine. Increased respiratory rate is a therapeutic effect of naloxone, countering the respiratory depression caused by opioids.
Choice D rationale: Naloxone's primary action is to counter opioid-induced respiratory depression, not directly address nausea.
A nurse realizes that they failed to administer a medication that was due 4 hr ago to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Investigating factors that led to the missed medication dose is crucial to identify any system issues, interruptions, or reasons behind the omission, ensuring it's properly addressed and prevented in the future.
Choice B rationale: Assessing for adverse reactions is important but not the initial step when a medication omission is discovered.
Choice C rationale: Investigating the omission's cause precedes reporting it to the provider.
Choice D rationale: Filing an incident report is necessary but should follow a thorough assessment of factors contributing to the missed dosage.
A nurse is monitoring for an infusion reaction for a client who is receiving a dose of IV amphotericin B. Which of the following findings should indicate to the nurse that the client is experiencing an acute infusion reaction?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Hyperglycemia is not typically associated with an acute infusion reaction to amphotericin B.
Choice B rationale: An acute infusion reaction to IV amphotericin B might manifest as fever, among other symptoms like chills, rigors, or headaches, indicating an immediate hypersensitivity reaction.
Choice C rationale: Pedal edema is not a typical manifestation of an acute infusion reaction to amphotericin B.
Choice D rationale: A dry cough is not a common symptom of an acute infusion reaction to amphotericin B.
A nurse is caring for a client who has cancer and reports moderate pain. Which of the following medications should the nurse expect to administer?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Morphine is a potent opioid commonly used to manage moderate to severe cancer-related pain due to its effectiveness in controlling pain intensity.
Choice B rationale: Acetaminophen might not be adequate for managing moderate cancer pain compared to opioids like morphine.
Choice C rationale: Ibuprofen, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), might not be sufficient for moderate to severe cancer-related pain.
Choice D rationale: Aspirin, another NSAID, might not provide adequate pain relief for moderate to severe cancer pain.
A nurse is caring for a client who received neostigmine 1 hr ago and is experiencing a muscarinic response. Which of the following manifestations should the nurse expect?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Myoclonic seizures are not typically associated with neostigmine administration.
Choice B rationale: Fever is not a common adverse effect of neostigmine.
Choice C rationale: Neostigmine, a cholinesterase inhibitor, can lead to excessive muscarinic responses like increased salivation due to its effects on cholinergic receptors.
Choice D rationale: Occipital headaches are not typically reported as a response to neostigmine.
A nurse is preparing to administer heparin subcutaneously to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take to minimize bleeding following the injection?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Massaging the site might increase bleeding or cause irritation after subcutaneous injection.
Choice B rationale: This action might not prevent bleeding and is not a standard technique for subcutaneous injections.
Choice C rationale: Aspiration is not required for subcutaneous injections and might not influence bleeding at the injection site.
Choice D rationale: The Z-track method helps minimize bleeding and ensures medication remains in the muscle by sealing the injection track, decreasing the risk of irritation and bleeding at the injection site.
A nurse is preparing to administer sulfadiazine 150mg/kg PO to divide equally every 6 hr to an adolescent who weighs 88 lb. Available is sulfadiazine 500 mg/tab. How many tablets should the nurse administer per dose? (Round to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
Adolescent weight = 88 lb, 1 kg = 2.2 lb (to convert lb to kg), 88 lb / 2.2 = 40 kg (approx.), 150 mg/kg dose x 40 kg = 6000 mg, Available dose = 500 mg/tab, 6000 mg / 500 mg/tab
= 12 tabs per day, divided equally every 6 hrs = 12 tabs / 4 doses = 3 tabs per dose.
A nurse is planning care for a group of clients. Which of the following client's medications should be monitored by the nurse for hearing loss related to a medication interaction?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Propranolol and raloxifene are not typically associated with causing hearing loss.
Choice B rationale: Furosemide (loop diuretic) and amikacin (aminoglycoside antibiotic) can cause hearing loss, especially when used together, due to their potential ototoxic effects, requiring close monitoring for signs of hearing impairment in clients receiving both medications.
Choice C rationale: Losartan and atorvastatin are not commonly linked to causing hearing loss.
Choice D rationale: While digoxin can cause hearing disturbances, levothyroxine is not typically associated with hearing loss.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 66 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

