College Exam 2 perfusion euro pm
Total Questions : 49
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreThe nurse is evaluating a client who had a cardiac catheterization with a left antecubital insertion site. Which of the following pulses should the nurse palpate?
Explanation
The brachial pulse in the right arm is the best option to assess because it is contralateral to the insertion site and unaffected by the procedure. The radial pulse in the left arm may be diminished or absent due to arterial occlusion or spasm from the catheterization.
Radial pulse in the left arm is wrong because it may be diminished or absent due to arterial occlusion or spasm from the catheterization.
Radial pulse in the right arm is wrong because it may not reflect the true blood pressure or perfusion status of the client because it is ipsilateral to the heart.
Brachial pulse in the left arm is wrong because it may also be compromised by the insertion site and is not a reliable indicator of circulation.
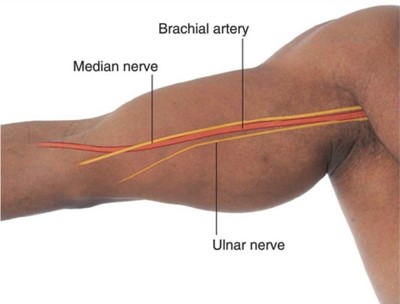
The nurse asks a client who is about to have a cardiac catheterization about any allergies. The client states, "I always get a rash when I eat shellfish." Which of the following is the priority nursing action?
Explanation
The priority nursing action is to notify the provider of the client's allergy because shellfish allergy may indicate an allergy to iodine, which is commonly used as a contrast dye in cardiac catheterization. This could cause a severe allergic reaction or anaphylaxis during the procedure, which could be life-threatening. The provider may need to order a different type of contrast dye or premedicate the client with antihistamines or steroids to prevent an allergic reaction.
a. Ask the client if any other foods cause such a reaction is wrong because it is not the priority action and it does not address the potential risk of iodine allergy.
c. Notify the dietary department of the client's allergy is wrong because it is not relevant to the cardiac catheterization and it does not prevent an allergic reaction during the procedure.
d. Atach a wrist band indicating the client's allergy is wrong because it is not sufficient to alert the provider or the catheterization team of the client's allergy and it does not prevent an allergic reaction during the procedure.
A nurse is preparing to administer total parenteral nutrition (TPN) 1800 mL to infuse over 24 hr. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
To calculate the infusion rate, divide the volume of fluid by the time in hours. In this case, 1800 mL / 24 hr = 75 mL/hr.
Round the answer to the nearest whole number and use a leading zero if it applies.
Do not use a trailing zero because it could be misread as a decimal point. Therefore, the nurse should set the IV pump to deliver 75 mL/hr.

A nurse is caring for a client who has a deep vein thrombosis and is prescribed heparin by continuous IV infusion at 1,200 units/hr. Available is heparin 25,000 units in 500 mL DSW. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth/whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
To calculate the infusion rate, use the formula:
(rate in mL/hr) = (desired dose in units/hr) / (available dose in units/mL)
In this case, the desired dose is 1,200 units/hr and the available dose is 25,000 units / 500 mL = 50 units/mL. Therefore,
(rate in mL/hr) = (1,200 units/hr) / (50 units/mL) = 24 mL/hr
Round the answer to the nearest tenth/whole number and use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero because it could be misread as a decimal point. Therefore, the nurse should set the IV pump to deliver 24 mL/hr.
A nurse is preparing to administer clonazepam 1.5 mg PO in 3 equally divided doses every 8 hr for a client who has seizures. The amount available is clonazepam 0.5 mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer per dose? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
To calculate the number of tablets, divide the total dose by the dose per tablet. In this case, the total dose is 1.5 mg / 3 = 0.5 mg and the dose per tablet is 0.5 mg. Therefore,
(number of tablets) = (0.5 mg) / (0.5 mg) = 1 tablet
Round the answer to the nearest tenth and use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero because it could be misread as a decimal point. Therefore, the nurse should administer 1 tablet per dose.
A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who has peripheral arterial disease (PAD). Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
The nurse should instruct the client to adjust the thermostat so that the environment is warm because cold temperatures can cause vasoconstriction and worsen the symptoms of PAD, such as pain, numbness, and poor wound healing. The client should also avoid exposure to cold weather and wear warm clothing.
- Apply a heating pad on a low setting to help relieve leg pain is wrong because it can cause burns, vasodilation, and increased blood flow to the legs, which can increase the risk of bleeding and edema in PAD.
- Wear antiembolic stockings during the day is wrong because they can impair arterial circulation and cause ischemia and tissue damage in PAD. Antiembolic stockings are used to prevent venous thromboembolism, not arterial disease.
Rest with the legs above heart level is wrong because it can decrease arterial blood flow to the legs and worsen ischemia and pain in PAD. The client should rest with the legs at or below heart level to promote arterial circulation.
A nurse in an outpatient clinic is assessing a middle adult client as part of a routine physical examination. The client's BP is 142/88 mm Hg, his body mass index (BMI) is 31, and he is a current smoker. The nurse should identify that this client has multiple risk factors for which of the following disorders?
Explanation
The nurse should identify that this client has multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease, such as hypertension, obesity, and smoking. These factors can increase the risk of atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease.
Depression is wrong because it is not directly related to the client's physical examination findings. Depression may have other risk factors, such as genetics, stress, trauma, or substance abuse.
Thyroid disease is wrong because it is not directly related to the client's physical examination findings. Thyroid disease may have other risk factors, such as autoimmune disorders, iodine deficiency, or radiation exposure.
Testicular cancer is wrong because it is not directly related to the client's physical examination findings. Testicular cancer may have other risk factors, such as cryptorchidism, family
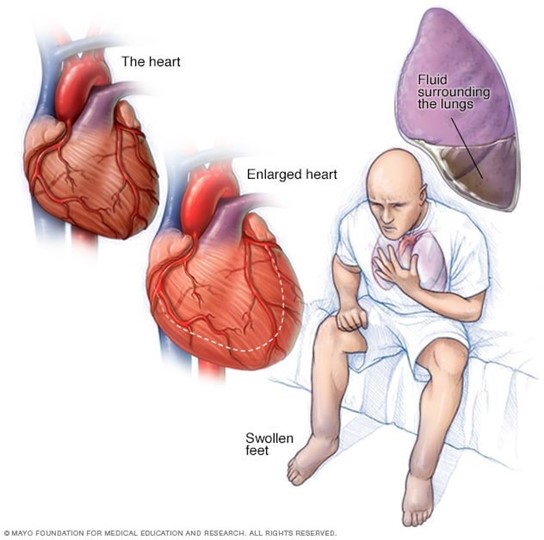
A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who has a new diagnosis of heart failure. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
The nurse should instruct the client to notify the provider of a weight gain of 0.5 kg (1 lb) in a week because it may indicate fluid retention and worsening of heart failure. The client should also monitor daily intake and output, limit sodium and fluid intake, and weigh themselves daily at the same time.
a. Exercise at least three times per week is wrong because it is too vague and may not be appropriate for the client's condition and tolerance. The nurse should advise the client to consult with the provider or a cardiac rehabilitation specialist for an individualized exercise plan that is safe and effective.
c. Take diuretics early in the morning and before bedtime is wrong because it may disrupt the client's sleep patern and cause nocturia. The nurse should advise the client to take diuretics early in the morning and avoid taking them in the evening or at night, unless prescribed otherwise.
d. Take naproxen for generalized discomfort is wrong because naproxen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that can worsen heart failure by causing sodium and water retention, increasing blood pressure, and reducing the effectiveness of diuretics and other heart failure medications. The nurse should advise the client to avoid NSAIDs and use acetaminophen or other alternatives for pain relief, as prescribed by the provider.
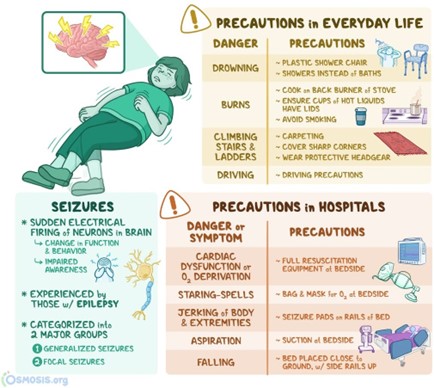
A nurse is caring for a client who is experiencing a seizure. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
The nurse should place a towel under the client's head to protect it from injury during the seizure. The nurse should also loosen any tight clothing, remove any objects that could harm the client, and maintain a patent airway.
Place the client in a prone position is wrong because it can compromise the client's breathing and increase the risk of aspiration. The nurse should place the client in a side-lying position after the seizure to facilitate drainage of oral secretions and prevent aspiration.
Holding the client's arms and legs still is wrong because it can cause injury to the client or the nurse. The nurse should not restrain or interfere with the client's movements during the seizure but rather ensure a safe environment and observe the seizure activity.
Leaving the client to get help is wrong because it can endanger the client's safety and well-being. The nurse should stay with the client during the seizure and call for assistance if needed, but not leave the client alone or unattended.
A nurse enters a client's room and finds him on the floor in the clonic phase of a tonic-clonic seizure. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
- Place a pillow under the client's head.
The nurse should place a pillow under the client's head to protect it from injury during the seizure. The nurse should also loosen any tight clothing, remove any objects that could harm the client, and maintain a patent airway.
- Gently restrain the client's extremities is wrong because it can cause injury to the client or the nurse. The nurse should not restrain or interfere with the client's movements during the seizure, but rather ensure a safe environment and observe the seizure activity.
- Apply a face mask for oxygen administration is wrong because it can be dislodged by the client's movements and pose a choking hazard. The nurse should not atempt to insert anything into the client's mouth or nose during the seizure, but rather provide oxygen by nasal cannula after the seizure if needed.
Insert a padded tongue blade into the client's mouth is wrong because it can damage the client's teeth, gums, or tongue, or cause aspiration or airway obstruction. The nurse should not atempt to insert anything into the client's mouth or nose during the seizure, but rather turn the client to a side-lying position after the
A nurse is in a client's room when the client begins having a tonic-clonic seizure. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
Turn the client's head to the side.
The nurse should turn the client's head to the side first to prevent aspiration of oral secretions and maintain a patent airway. This is the priority action according to the airway, breathing, and circulation (ABC) principle.
Check the client's motor strength is wrong because it is not the priority action and it is not feasible during a seizure. The nurse should check the client's motor strength after the seizure to assess for any neurological deficits or postictal weakness.
Document the time the seizure began is wrong because it is not the priority action and it can be done later. The nurse should document the time, duration, type, and characteristics of the seizure, but only after ensuring the client's safety and well-being.
Loosen the clothing around the client's waist is wrong because it is not the priority action and it may not be necessary. The nurse should loosen any tight clothing that could impair breathing or circulation, but only after securing the airway and protecting the head from injury.
Turn the client's head to the side.
The nurse should turn the client's head to the side first to prevent aspiration of oral secretions and maintain a patent airway. This is the priority action according to the airway, breathing, and circulation (ABC) principle.
Check the client's motor strength is wrong because it is not the priority action and it is not feasible during a seizure. The nurse should check the client's motor strength after the seizure to assess for any neurological deficits or postictal weakness.
Document the time the seizure began is wrong because it is not the priority action and it can be done later. The nurse should document the time, duration, type, and characteristics of the seizure, but only after ensuring the client's safety and well-being.
Loosen the clothing around the client's waist is wrong because it is not the priority action and it may not be necessary. The nurse should loosen any tight clothing that could impair breathing or circulation, but only after securing the airway and protecting the head from injury.
A nurse is caring for a client who has had a myocardial infarction. Upon his first visit to cardiac rehabilitation, he tells the nurse that he doesn't understand why he needs to be there because there is nothing more to do, as the damage is done. Which of the following is the correct nursing response?
Explanation
The nurse should respond with empathy and honesty, and provide factual information about the benefits of cardiac rehabilitation. Cardiac rehabilitation can help the client improve his cardiovascular fitness, reduce his risk factors, prevent further complications, and enhance his quality of life.
"It's not unusual to feel that way at first, but once you learn the routine, you'll enjoy it." is wrong because it is dismissive of the client's feelings and does not address his concern or provide any education.
"Exercise is good for you and good for your heart." is wrong because it is too simplistic and vague, and does not explain how cardiac rehabilitation can help the client specifically.
d. "Your doctor is the expert here, and I'm sure he would only recommend what is best for you." is wrong because it is deferential and does not empower the client or encourage his participation in his own care.

A nurse is caring for a client who has congestive heart failure and is taking digoxin daily. The client refused breakfast and is complaining of nausea and weakness. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
The nurse should check the client's vital signs first because nausea and weakness are signs of digoxin toxicity, which can also cause bradycardia, hypotension, and arrhythmias. The nurse should also assess the client's serum digoxin level, potassium level, and electrocardiogram.
Request a dietitian consult is wrong because it is not the priority action and it does not address the possible cause of the client's symptoms. A dietitian consult may be helpful to provide nutritional education and guidance, but only after ruling out or treating digoxin toxicity.
Suggest that the client rests before eating the meal is wrong because it is not the priority action and it may delay the diagnosis and treatment of digoxin toxicity. The nurse should not assume that the client's symptoms are due to fatigue or lack of appetite, but rather investigate for any underlying problems.
Request an order for an antiemetic is wrong because it is not the priority action and it may mask the symptoms of digoxin toxicity. The nurse should not administer any medications that could interact with digoxin or worsen its effects, but rather notify the provider and follow the protocol for digoxin toxicity management.
A nurse is assessing a client who has chronic venous insufficiency. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
Edema is a common finding in clients who have chronic venous insufficiency, due to the impaired venous return and increased capillary pressure. The edema is usually worse at the end of the day and improves with elevation.
a. Thick, deformed toenails are more likely to be seen in clients who have fungal infections or peripheral arterial disease, not chronic venous insufficiency.
c. Dependent rubor is a sign of peripheral arterial disease, not chronic venous insufficiency. It is a reddish color of the lower extremities that occurs when they are lowered and disappears when they are elevated.
d. Hair loss is another sign of peripheral arterial disease, not chronic venous insufficiency. It is caused by the reduced blood supply to the hair follicles.
A nurse is assessing a client who has right-sided heart failure. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
No explanation
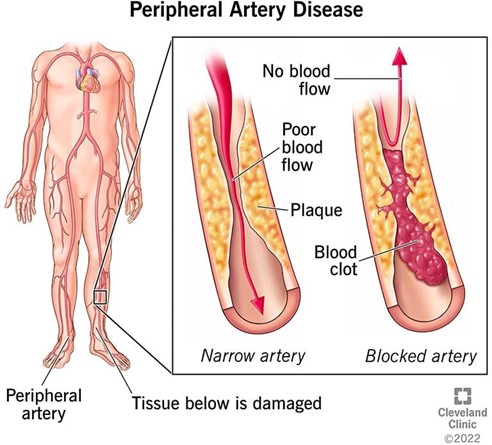
A nurse is caring for a client who has peripheral arterial disease (PAD). Which of the following symptoms should the nurse expect to find in the early stage of the disease?
No explanation
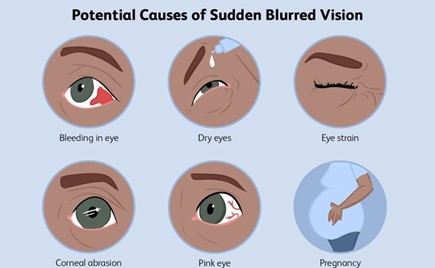
A nurse is caring for a client who has a new diagnosis of essential hypertension. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following findings that is consistent with this diagnosis?
Explanation
Blurred vision is a possible finding in clients who have essential hypertension, due to the damage to the retinal vessels and optic nerve. It may indicate a hypertensive emergency or a target organ damage.
A nurse is assessing a male client who has advanced peripheral artery disease (PAD). Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
feet or toes that occurs at night and is not relieved by rest.
A nurse is performing a cardiac assessment on a client and auscultates an S3 sound. The nurse should recognize that this sound represents which of the following heart conditions?
Explanation
Ventricular gallop is another name for the S3 sound, which is a low-pitched sound heard at the end of diastole, just after the S2 sound. It is caused by the rapid filling of the ventricles and the vibration of the ventricular walls.
Closure of the pulmonic valve is one of the components of the S2 sound, which is a high-pitched sound heard at the end of the systole, just before the S1 sound. It is caused by the closure of the semilunar valves (pulmonic and aortic).
Closure of the mitral valve is one of the components of the S1 sound, which is a high-pitched sound heard at the beginning of systole, just after the S2 sound. It is caused by the closure of the atrioventricular valves (mitral and tricuspid).
d. Atrial gallop is another name for the S4 sound, which is a low-pitched sound heard at the end of diastole, just before the S1 sound. It is caused by atrial contraction and increased resistance to ventricular filling.
A nurse is teaching a client who has angina pectoris about starting therapy with SL nitroglycerin tablets. The nurse should include which of the following instructions regarding how to take the medication?
Explanation
Taking one tablet at the first indication of chest pain is the correct way to use SL nitroglycerin tablets, as they are fast- acting and can relieve anginal symptoms within minutes. The client should place the tablet under the tongue and let it dissolve.
Taking one tablet at the first indication of chest pain is the correct way to use SL nitroglycerin tablets, as they are fast- acting and can relieve anginal symptoms within minutes. The client should place the tablet under the tongue and let it dissolve.
Taking this medication after each meal and at bedtime is not appropriate, as SL nitroglycerin tablets are not meant for routine or prophylactic use, but only for acute episodes of angina.
Taking one tablet every 15 min during an acute attack is not correct, as the client should not exceed three doses in 15 min. If the pain is not relieved after three doses, the client should seek emergency medical attention.
Taking this medication with 8 ounces of water is not necessary, as SL nitroglycerin tablets do not need to be swallowed or washed down with water. They should be dissolved under the tongue for optimal absorption.
A nurse is providing instructions to a client who has a new prescription for sublingual nitroglycerin (Nitrostat) to treat angina pectoris. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
Explanation
A nurse is providing discharge instructions to a client following a cardiac catheterization. Which of the following information should the nurse include?
Explanation
Changing the dressing within 12 hours of the procedure is an important instruction for the client following a cardiac catheterization, as it helps prevent infection and monitor bleeding at the incision site.
a. "You will notice a small hematoma at the incision site." is not correct, as a hematoma is an abnormal finding that indicates bleeding or hematoma formation. The client should report any swelling, bruising, or oozing at the incision site to the provider.
c. "You can resume regular exercise as soon as tomorrow." is not appropriate, as the client should avoid strenuous activity and heavy lifting for at least 24 hours after the procedure, or as directed by the provider.
d. "Pain medication will not be necessary." is not accurate, as the client may experience some mild discomfort or soreness at the incision site, which can be relieved by taking over-the-counter analgesics, unless contraindicated.
A nurse is providing discharge instructions for a client who has congestive heart failure. Which of the following client statements indicates to the nurse that the teaching was effective?
Explanation
Planning to slow down if tired the day after exercising is a statement that indicates the client understands the importance of pacing activities and avoiding overexertion, which can worsen heart failure symptoms.
a. "I should use naproxen to manage discomfort." is not correct, as naproxen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that can cause fluid retention, increase blood pressure, and worsen heart failure. The client should avoid NSAIDs and use other analgesics, such as acetaminophen, unless contraindicated.
c. "I will read food labels and limit my sodium to 4 grams per day." is not appropriate, as 4 grams of sodium per day is too high for a client who has congestive heart failure. The client should limit sodium intake to 2 grams or less per day, as sodium can cause fluid retention and increase the workload of the heart.
d. "I will take my diuretic before sleep and drink fluids during the day." is not advisable, as taking a diuretic before sleep can cause nocturia and disrupt the sleep cycle, which can affect the quality of life and cardiac function. The
A nurse is caring for an older adult client who has left-sided heart failure. Which of the following assessment findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
Frothy sputum is a sign of left-sided heart failure, due to the pulmonary congestion and impaired gas exchange. The sputum may be pink-tinged or blood-streaked, indicating pulmonary edema.
a. Dependent edema is more likely to be seen in clients who have right-sided heart failure, due to the increased venous pressure and fluid retention. The edema is usually symmetrical and affects the lower extremities, abdomen, and sometimes the face.
c. Nocturnal polyuria is not a specific finding of left-sided heart failure, but it may occur in clients who have renal impairment, diabetes mellitus, or diuretic therapy.
d. Jugular distention is another sign of right-sided heart failure, due to the increased central venous pressure and backward flow of blood into the superior vena cava. It is visible as a bulging of the neck veins, especially when the client is in a semi-Fowler's position.
A nurse is teaching a client who has a new diagnosis of venous insufficiency. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
Explanation
Using elastic stockings is an effective way to improve venous return and prevent edema, stasis, and ulceration in clients who have venous insufficiency. The stockings should be applied before getting out of bed and worn throughout the day.
"Apply ice packs to your legs." is not appropriate, as ice packs can cause vasoconstriction and impair blood flow to the legs, worsening the condition.
"Place your legs in a dependent position while in bed." is not advisable, as dependent position can increase venous pressure and fluid accumulation in the legs, leading to edema, pain, and skin breakdown
"Remain on bed rest." is not necessary, as bed rest can reduce muscle contraction and impair venous return. The client should be encouraged to perform regular exercise, such as walking, to enhance circulation and prevent complications.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 49 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

