Fetal Non-Stress Test (NST) > Maternal & Newborn
Exam Review
Comparison with contraction stress test (CST)
Total Questions : 5
Showing 5 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is caring for a client who is undergoing a contraction stress test (CST).
The nurse observes late decelerations in the fetal heart rate (FHR) during three consecutive contractions.
How should the nurse interpret this result?
Explanation
Positive.A positive CST means that there are late decelerations in the FHR during three or more contractions in a 10-minute period.Late decelerations are defined as decelerations that reach their lowest point after the peak of the contraction and that usually persist beyond the end of the contraction.They indicate fetal hypoxia and placental insufficiency.
Negative.A negative CST means that there are no late decelerations in the FHR during at least three contractions in a 10-minute period.A negative CST is reassuring and suggests that the fetus can tolerate labor contractions.
Equivocal.An equivocal CST means that there are late decelerations in the FHR during fewer than half of the contractions or there are variable decelerations with or without other nonreassuring features.An equivocal CST requires further evaluation with a biophysical profile or a repeat CST.
Unsatisfactory.An unsatisfactory CST means that there are fewer than three contractions in a 10-minute period or the tracing is technically inadequate for interpretation.An unsatisfactory CST should be repeated when possible.

A nurse is preparing a client for a nonstress test (NST).
The nurse explains that this test will measure the FHR response to:
Explanation
Fetal movement.This is because a nonstress test (NST) measures the fetal heart rate (FHR) accelerations in response to fetal movement in a defined period of time.A reactive NST is when there are two or more FHR accelerations of at least 15 beats per minute for at least 15 seconds duration in a 20-minute period.
Choice A is wrong because uterine contractions are not the stimulus for FHR accelerations in a NST.Uterine contractions are used in a contraction stress test (CST), which measures the FHR response to uterine contractions induced by oxytocin or nipple stimulation.
Choice C is wrong because oxytocin infusion is not used in a NST.Oxytocin infusion is another way of inducing uterine contractions for a CST.
Choice D is wrong because nipple stimulation is not used in a NST.Nipple stimulation is a natural way of inducing uterine contractions for a CST by releasing endogenous oxytocin.

A nurse is reviewing the results of a nonstress test (NST) for a client at 38 weeks of gestation.
The nurse notes that the baseline FHR is 140 bpm with moderate variability and no decelerations.
There are two episodes of FHR accelerations of at least 15 bpm above the baseline and lasting at least 15 seconds within a 20-minute period.
How should the nurse classify this result?
Explanation
Reactive.This result means that the baby’s heart rate went up to the expected level at least twice during the test, indicating that the baby is getting enough oxygen and is doing well.A nonstress test is a safe, noninvasive test for pregnant women that measures the fetal heart rate as the baby moves in the uterus.
Nonreactive.
This result means that the baby’s heart rate did not go up to the expected level during the test, which may indicate that the baby is not getting enough oxygen or is sleeping.This result does not necessarily mean there is a problem, but it may require further testing or treatment.
Suspicious.
This result is not a standard term for nonstress test interpretation, but it may be used to describe a test that shows some signs of fetal distress, such as decelerations or reduced variability of the fetal heart rate.This result may also require further testing or treatment.
Inconclusive.
This result means that the test did not provide enough information to determine the fetal well-being, either because the baby did not move enough or because of technical problems with the equipment.This result may require repeating the test or using another method of fetal assessment.
A nurse is comparing the advantages and disadvantages of external and internal fetal heart rate (FHR) monitoring.
Which of the following statements is true about external FHR monitoring?
Explanation
It can be used for both antepartum and intrapartum fetal assessment.External fetal heart rate monitoring uses a device to listen to or record the baby’s heartbeat through the mother’s abdomen.It does not require ruptured membranes or cervical dilation for application, unlike internal monitoring.It also does not provide a more accurate and continuous FHR tracing than internal monitoring, nor can it measure the intensity of uterine contractions.
Choice A is wrong because external monitoring is less accurate and consistent than internal monitoring, especially when there is movement or interference.
Choice B is wrong because external monitoring can be done without ruptured membranes or cervical dilation, while internal monitoring requires both.
Choice D is wrong because external monitoring can only measure the frequency and duration of uterine contractions, not the intensity.Internal monitoring can measure the intensity of uterine contractions with a fluid-filled catheter.
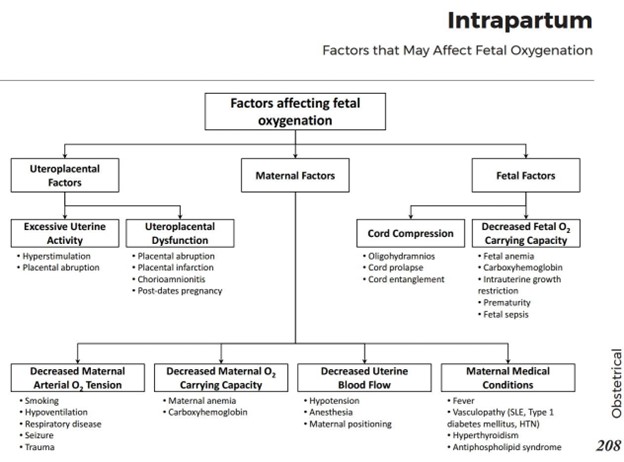
(Select all that apply) A nurse is educating a client about the factors that can affect fetal oxygenation during labor.
The nurse should include which of the following factors in the teaching?
Explanation
These are the factors that can affect fetal oxygenation during labor by decreasing the placental blood flow or the fetal oxygen carrying capacity.
• Choice A is correct because maternal hypotension can reduce the uterine blood flow and cause fetal hypoxia.
• Choice B is correct because maternal fever can increase the maternal and fetal metabolic rate and oxygen demand, as well as cause uteroplacental dysfunction due to chorioamnionitis.
• Choice C is correct because umbilical cord compression can impair the fetal blood flow and oxygen delivery.
• Choice D is wrong because fetal sleep cycles do not affect fetal oxygenation during labor.Fetal sleep cycles are normal variations in the fetal heart rate and variability.
• Choice E is wrong because fetal position does not affect fetal oxygenation during labor.Fetal position may affect the mode of delivery, but not the oxygen supply to the fetus.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 5 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

