Cesarean delivery > Maternal & Newborn
Exam Review
Complications of Cesarean delivery
Total Questions : 5
Showing 5 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is caring for a client who had a cesarean delivery 24 hours ago.
The nurse notices that the client has a fever of 38.2°C, increased redness and swelling at the incision site, and foul-smelling lochia.
What is the most likely cause of these findings?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Infection.The client’s fever, increased redness and swelling at the incision site, and foul-smelling lochia are all signs of infection, which is a common complication of cesarean delivery.
Choice B. Hemorrhage is wrong because hemorrhage would cause excessive bleeding, low blood pressure, and rapid pulse, which are not mentioned in the question.
Choice C. Deep vein thrombosis is wrong because deep vein thrombosis would cause pain, swelling, and tenderness in the legs, which are not mentioned in the question.
Choice D. Wound dehiscence is wrong because wound dehiscence would cause separation of the incision edges, drainage of serous fluid, and exposure of underlying tissues, which are not mentioned in the question.
Normal ranges for lochia are as follows:
• Lochia rubra: bright red blood and clots that last for 3 to 4 days after delivery
• Lochia serosa: pinkish-brown discharge that lasts for 4 to 10 days after delivery
• Lochia alba: yellowish-white discharge that lasts for 10 to 14 days after delivery
Foul-smelling lochia indicates infection and should be reported to the health care provider.


A nurse is assessing a client who had a cesarean delivery 12 hours ago.
The nurse observes that the client has soaked two perineal pads in one hour, has a heart rate of 120 beats per minute, and has a blood pressure of 90/60 mmHg.
What is the priority intervention for this client?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Apply pressure to the bleeding site.This is because the client is showing signs of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH), which is severe vaginal bleeding after childbirth.PPH can occur up to 12 weeks postpartum, but it is more common within the first 24 hours.PPH can be caused by uterine atony, retained placenta, or trauma to the reproductive organs.
Applying pressure to the bleeding site can help to control the blood loss and prevent shock.
Choice B. Encourage early ambulation is wrong because it can worsen the bleeding and increase the risk of fainting.Early ambulation is beneficial for preventing thromboembolism and promoting recovery, but it should be done after the bleeding is stabilized.
Choice C. Apply sterile dressings to the incision is wrong because it does not address the source of bleeding, which is likely from the vagina or uterus.The incision site may also bleed, but it is usually less than the vaginal bleeding.
Applying sterile dressings to the incision can help to prevent infection, but it is not a priority intervention for PPH.
Choice D. Encourage frequent voiding is wrong because it can cause bladder distension and interfere with uterine contraction.A full bladder can displace the uterus and prevent it from compressing the blood vessels where the placenta was attached.
Encouraging frequent voiding can help to maintain bladder function and reduce discomfort, but it is not a priority intervention for PPH.
Normal ranges for heart rate are 60-100 beats per minute and for blood pressure are 90/60-120/80 mmHg.Normal blood loss after cesarean delivery is less than 1000 mL.
A nurse is teaching a client who had a cesarean delivery about measures to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? (Select all that apply.).
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A, B, C and D. These are all measures to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT) after cesarean delivery.DVT is a blood clot that forms in the deep veins of the legs or arms and can break off and travel to the lungs, causing a life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism (PE).
Choice A is correct because wearing anti-embolism stockings as prescribed can help improve blood flow and reduce swelling in the legs.
Choice B is correct because avoiding crossing your legs when sitting or lying down can prevent pressure on the veins and reduce the risk of blood clots.
Choice C is correct because performing ankle and calf exercises every hour while awake can stimulate blood circulation and prevent blood from pooling in the lower extremities.
Choice D is correct because drinking at least 3 liters of fluid per day can help prevent dehydration, which can thicken the blood and increase the risk of clotting.
Choice E is wrong because elevating your legs above your heart level when resting can impair venous return and increase the risk of DVT.This position is recommended for patients with arterial insufficiency, not venous insufficiency.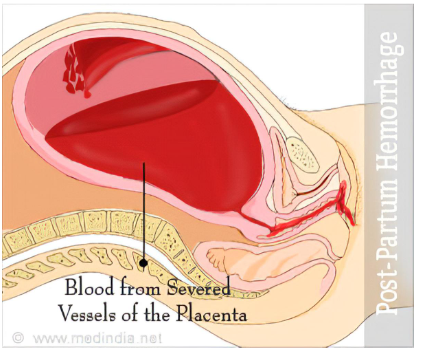
A nurse is assisting a client who had a cesarean delivery to get out of bed for the first time.
The nurse notices that the client’s incision site has opened and there is visible bowel protruding from the wound.
What is the appropriate action for the nurse to take?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. Cover the wound with a sterile, moist dressing and notify the healthcare provider.
This is because the client has a wound dehiscence with evisceration, which is a serious complication that requires immediate medical attention.
The sterile, moist dressing will help prevent infection and keep the bowel tissue moist until surgery can be performed.
Choice A is wrong because pushing the bowel back into the abdomen can cause further damage and increase the risk of infection and peritonitis.
Choice C is wrong because irrigating the wound with normal saline and applying an antibiotic ointment can also introduce bacteria and irritate the bowel tissue.
Choice D is wrong because leaving the wound exposed to air can cause the bowel tissue to dry out and necrose, which can lead to sepsis and shock.
A nurse is evaluating a client who had a cesarean delivery for urinary retention.
Which of the following findings should alert the nurse to this complication?
Explanation
Answer and explanation..
The correct answer is choice D. All of the above.Urinary retention is a common complication after cesarean delivery, and it can be detected by measuring the postvoid residual bladder volume (PVRBV) with an ultrasound scan.A PVRBV of more than 150 mL is considered abnormal and indicative of urinary retention.
The following findings should alert the nurse to this complication:
• Inability to void within 6 hours after delivery: This is a sign of overt urinary retention, which occurs in about 7.4% of women who had a cesarean delivery.It may be caused by factors such as pain, anxiety, anesthesia, or bladder trauma.
• Distended bladder palpable above the symphysis pubis: This is a sign of covert urinary retention, which occurs in about 16.7% of women who had a cesarean delivery.It means that the bladder is overfilled but the woman does not feel the urge to void or has difficulty initiating micturition.
• Urinary output of less than 30 mL per hour: This is a sign of inadequate bladder emptying, which may lead to urinary tract infection, bladder damage, or renal impairment.It may be due to factors such as morphine-related postoperative analgesia, multiple pregnancy, or low body mass index, which are associated with increased risk of urinary retention after cesarean delivery.
Normal ranges for PVRBV and urinary output are:
• PVRBV: less than 150 mL
• Urinary output: more than 30 mL per hour
Sign Up or Login to view all the 5 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

