Exam 4 Gastrointestinal disorders
Total Questions : 40
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreThere is an order to administer a large volume, cleansing enema to an adult patient. The enema bag is filled with how many milliliters of fluid for this procedure?
Explanation
ChoiceA: This volume might be insufficient for a large volume, cleansing enema, as it may not effectively cleanse the colon.
Choice: This range is the appropriate volume for a large volume, cleansing enema, as it provides enough fluid to cleanse the colon effectively without causing excessive distension.
Choice C: This volume is too low for a large volume, cleansing enema, and it may not be enough to achieve the desired effect.
Choice D: This volume is too low for a large volume, cleansing enema, and it may not effectively cleanse the colon.
A nurse is monitoring bowel elimination of a patient who has a history of constipation. The nurse implements measures to assist with bowel elimination if the patient has not had a bowel movement what would be the BEST option to try first?
Explanation
Choice A: A stool softener is the best option to try first for a patient with constipation as it helps to soften the stool, making it easier to pass.
Choice B: Soap suds enemas are used to promote bowel movements, but they are more invasive and can cause discomfort. Stool softeners should be tried before resorting to enemas.
Choice C : Suppositories can also help with constipation, but they are generally not the first option to try. Stool softeners are milder and more suitable initially.
Choice D: While mineral oil enemas can provide lubrication to facilitate bowel movements, stool softeners are generally preferred for their milder action.
A nurse performs an abdominal assessment on 4 patients. Which of the following would be considered a normal abdominal assessment?
Explanation
Choice A This is considered a normal abdominal assessment. The abdomen is soft and not distended, and bowel sounds are present and normal in all four quadrants.
Choice B Abdominal distension and firmness may indicate possible bowel obstruction or other gastrointestinal issues. Hypoactive bowel sounds suggest reduced motility, which is not normal.
Choice C Abdominal distension with hyperactive bowel sounds may indicate gastrointestinal irritation or increased motility, which is not normal.
Choice D A firm abdomen with hypoactive bowel sounds is not typical of a normal abdominal assessment.
A nurse is preparing her patient to receive a Fleet enema. What position is best for the procedure?
Explanation
Choice A The supine position (lying flat on the back) is not suitable for administering an enema as it does not facilitate proper flow and retention of the solution.
Choice B High Fowler's position (sitting upright at a 90degree angle) is not appropriate for enema administration, as it might cause discomfort and hinder proper administration.
Choice C Semi Fowler's position (sitting at a semiupright angle) is also not the best option for enema administration, as it may not allow the solution to flow effectively.
Choice D The Sims position, with the patient lying on the left side with the right knee flexed, allows the enema solution to flow downward by gravity and improves retention. It is the best position for enema administration.
A patient who is constipated has just received a mineral oilretention enema. The nurse encourages this patient to hold this enema for a minimum of how long?
Explanation
Choice A: Holding the enema for only 5 minutes may not provide enough time for the mineral oil to soften the stool and facilitate a bowel movement.
Choice B Holding the enema for 60 minutes is unnecessary and can lead to discomfort and difficulty for the patient.
Choice C Holding the enema for only 1 minute is too short for the mineral oil to be effective in softening the stool.
Choice D Encouraging the patient to hold the mineral oil enema for a minimum of 15 minutes allows sufficient time for the oil to work on the stool and improve the chances of a successful bowel movement.
A nurse is digitally removing stool that is impacted from a patient. The nurse should stop the procedure immediately and take corrective action if the patient's:
Explanation
Choice A This change in blood pressure is not alarming and does not require immediate cessation of the procedure.
Choice B A slight increase in temperature is within a normal range and does not indicate an urgent issue related to the stool removal procedure.
Choice C A significant decrease in pulse rate suggests bradycardia, which can be a serious sign and might be caused by the stimulation of the vagus nerve during the procedure. The nurse should stop immediately and take corrective action.
Choice D An increase in respiratory rate may indicate increased anxiety or discomfort, but it is not an immediate cause for stopping the procedure.
A nurse is preparing her patient to receive a Fleet enema. What position is best for the procedure?
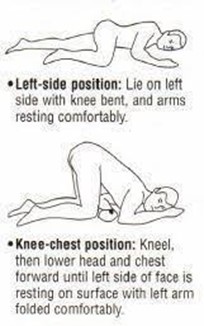
Explanation
Choice A The supine position is not suitable for administering an enema as it does not facilitate proper flow and retention of the solution.
Choice B High Fowler's position is not the best option for enema administration, as it might cause discomfort and hinder proper administration.
Choice C Semi Fowler's position is also not the best option for enema administration, as it may not allow the solution to flow effectively.
Choice D The Sims position, with the patient lying on the left side with the right knee flexed, allows the enema solution to flow downward by gravity and improves retention. It is the best position for enema administration.
A patient with a colostomy asks how often the faceplate (wafer) of the ostomy appliance should be changed. The most appropriate response by the nurse is that it is usually changed every
Explanation
Choice A Changing the faceplate every 3 to 5 days might be necessary for some individuals with specific needs, but it is not the typical frequency for most colostomy patients.
Choice B Changing the faceplate every 1 to 3 days is too frequent for most colostomy patients and might lead to unnecessary waste and discomfort.
Choice C Changing the faceplate every 2 to 3 days is still relatively frequent and might not be necessary for most colostomy patients.
Choice D Changing the faceplate every 4 to 7 days is the usual recommendation for colostomy patients, as it allows for sufficient wear time while minimizing the frequency of changes.
A nurse is preparing a cleansing enema for an adult patient who is constipated and has not responded to laxative use. Before giving the enema, the nurse should
Explanation
Choice A Using a cool solution might cause discomfort and could lead to cramping, which is not ideal for an enema administration.
Choice B Boiling the solution is unnecessary and might be unsafe, as it could cause burns or damage the components of the enema.
Choice C Warming the solution to body temperature (around 98.6°F or 37°C) is the appropriate approach, as it ensures patient comfort and reduces the risk of cramping or discomfort.
Choice D Microwaving the solution might lead to uneven heating and could potentially create hot spots, which could cause burns or discomfort for the patient.
The nurse would expect the least formed stool to be present in which portion of the digestive tract?
Explanation
Choice A The sigmoid colon is the final portion of the large intestine before the rectum, and it is where stool is most likely to be compacted and least formed as water continues to be reabsorbed, resulting in a more solid consistency.
Choice B The ascending colon is the initial part of the large intestine where undigested food enters. Stool in this region is still relatively liquid and not yet fully formed.
Choice C The descending colon follows the transverse colon and is responsible for further water absorption. Stool in this region is becoming more formed but is not as solid as in the sigmoid colon.
Choice D The transverse colon is located between the ascending and descending colon, and stool in this region is becoming more formed as water absorption continues.
A patient expresses concerns over having bright red stool. Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
Explanation
Choice A: Bright red stool can be caused by various factors, including the consumption of certain foods, medications, or gastrointestinal bleeding. Stress can lead to changes in bowel movements and might cause bright red stool due to increased gastrointestinal motility.
Choice B: While it's essential to reassure the patient, dismissing their concern without further assessment is not appropriate. The nurse should still investigate the potential causes of bright red stool.
Choice C: Jumping to conclusions and ordering immediate tests without further assessment is not the best approach. Before taking any action, the nurse should gather more information and assess other possible causes.
Choice D: Suggesting a colonoscopy as the first step is not necessary for every case of bright red stool. Further assessment is needed to determine the cause before resorting to such an invasive procedure.
A nurse is caring for a patient with a colostomy. The ostomy drainage bag should be emptied whenever it is
Explanation
Choice A The ostomy drainage bag should be emptied when it is full to prevent leakage and discomfort for the patient. A full bag can cause the seal to break and may lead to skin irritation or infection around the stoma.
Choice B Waiting until the bag is half full might result in leakage and discomfort for the patient. It is best to empty the bag before it becomes too full.
Choice C Emptying the bag when it is only onequarter full is unnecessary and may lead to frequent bag changes, increasing the workload for the patient and the nurse.
Choice D Waiting until the bag is threequarters full might lead to discomfort for the patient and could increase the risk of leakage. It is best to empty the bag before it reaches this level of fullness.
The most formed stool occurs in which portion of the colon?
Explanation
Choice A : The descending colon is the portion of the colon where stool becomes more formed as water is absorbed, leading to the gradual solidification of stool.
Choice B The transverse colon is responsible for further water absorption, but stool is still relatively less formed compared to the descending colon.
Choice C There is no segment called "oblique colon." It might be a typographical error.
Choice D The ascending colon is the initial part of the colon where undigested food enters, and stool is relatively less formed compared to the descending colon.
A patient is having trouble defecating into a bedpan while lying in bed. Which action by the nurse would assist the patient in having a successful bowel movement?
Explanation
Choice A Laxatives might be an option, but they should not be the first intervention. Other noninvasive measures should be tried first.
Choice B Administering a cleansing enema is not the first intervention for a patient having
trouble defecating into a bedpan. It is an invasive procedure and should be considered after less invasive measures have been tried.
Choice C Withholding pain medication might lead to unnecessary discomfort for the patient and is not the best approach to promote bowel movements.
Choice D Raising the head of the bed will help the patient assume a more upright position, which can facilitate bowel movement and defecation into the bedpan more effectively.
The nurse knows that a bowel training schedule would be most beneficial in the plan of care for which patient?
Explanation
Choice A A bowel training schedule is not typically required for patients with an ileostomy, as they have a surgically created opening (stoma) for stool to pass directly out of the body.
Choice B Bowel training can be beneficial for patients with incontinence, as it involves establishing a regular toileting routine to help regain bowel control and prevent accidental bowel movements.
Choice C C. difficile is an infectious condition that affects the gastrointestinal tract, and bowel training may not be the primary intervention for this patient.
Choice D Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease, and while bowel training may be helpful for some Crohn's patients, it is not the most common intervention for this condition.
A nurse is educating a patient on how to irrigate an ostomy bag. Which statement by the patient indicates the need for further instruction?
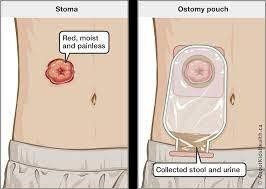
Explanation
Choice A This statement is correct, as patients should never attempt to insert anything into the stoma to remove fecal material.
Choice B This statement is also correct, as using warm water for irrigation can help reduce discomfort and cramping during the procedure.
Choice C This statement is incorrect. Patients should use only the irrigation solution recommended by their healthcare provider, as using the wrong solution can lead to complications or damage to the stoma.
Choice D This statement is correct, as sitting on the toilet allows the ostomy bag and irrigation solution to drain directly into the toilet, making the procedure more convenient.
The nurse is emptying an ileostomy pouch for a patient. Which assessment finding would the nurse report immediately?
Explanation
Choice A For an ileostomy, liquid consistency of stool is expected as the output, and it is not an immediate concern.
Choice B Foul odor from the stool is common with ileostomy output, and while it can be unpleasant, it is not an immediate concern.
Choice C This finding should be reported immediately, as it could indicate bleeding from the stoma or intestinal mucosa, which requires prompt evaluation and intervention.
Choice D Continuous output from an ileostomy is normal and expected, so it is not a cause for immediate concern.
What foods would increase colostomy odors?
Explanation
Choice A Turnips are known to increase colostomy odors, as certain sulfurcontaining compounds present in turnips can produce a strong odor in the stool.
Choice B Beets may cause the stool to have a reddish appearance, but they are not specifically associated with increased colostomy odors.
Choice C Buttermilk is not typically associated with increased colostomy odors. Choice D Yogurt is not typically associated with increased colostomy odors.
The nurse knows that the best way to clean around a colostomy stoma is to use the following
Explanation
Choice A Alcohol swabs may be too harsh and irritating for the delicate skin around the stoma. Mild soap and water are preferred for cleaning.
Choice B Tap water alone may not be sufficient for removing debris and ensuring proper cleanliness around the stoma. Mild soap and water are preferred for cleaning.
Choice C Iodine may be too harsh and irritating for the peristomal skin. Mild soap and water are preferred for cleaning.
Choice D Mild soap and water are the best choice for cleaning around the colostomy stoma as they effectively remove debris and cleanse the area without being overly harsh on the skin.
After an initial assessment, a nurse documents that a patient, admitted for abdominal pain, has hyperactive bowel sounds. As a result, the nurse could expect the patient's bowel movements to be
Explanation
Choice A This range of bowel sounds is considered normal. Hyperactive bowel sounds refer to an increased frequency and intensity of bowel sounds, exceeding the upper limit of the normal range.
Choice B Bowel sounds less than the normal range might indicate decreased bowel motility but are not associated with hyperactive bowel sounds.
Choice C Absent bowel sounds would be concerning and may indicate an ileus or other gastrointestinal issue, but it is not associated with hyperactive bowel sounds.
Choice D Hyperactive bowel sounds are characterized by an increased frequency and intensity of bowel sounds, exceeding the normal range, and are likely to be documented in a patient with abdominal pain.
A patient has stools that are foulsmelling and that float on water. The nurse documents that this patient is having
Explanation
Choice A Rhinorrhea refers to a runny or stuffy nose and is not related to the described stool characteristics.
Choice B Amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation and is not related to the described stool characteristics.
Choice C Steatorrhea is the presence of bulky, foulsmelling, floating stools that contain a high amount of undigested fat. It is often associated with malabsorption disorders or pancreatic
insufficiency.
Choice D Diarrhea is characterized by loose or watery stools and is not related to the described stool characteristics.
The nurse is caring for an anxious patient who is scheduled for surgery for colostomy placement. While the nurse is talking to the patient, the patient states, "I am so scared." It is a priority for the nurse to focus on addressing the
Explanation
Choice A Addressing the cause of the patient's anxiety and fear is the priority to provide
emotional support and comfort. The nurse should actively listen to the patient's concerns and offer appropriate reassurance and information.
Choice B While assessing the patient's bowel sounds and gas is important for the overall care, it is not the priority at this moment when the patient is expressing fear and anxiety.
Choice C Addressing the family's questions is important, but the patient's emotional wellbeing should be the immediate focus.
Choice D Respiratory assessment is essential but is not the priority when the patient is expressing fear and anxiety about the upcoming surgery.
The nurse is caring for a patient with complaints of constant diarrhea for 3 days. The patient is exhibiting signs and symptoms of dehydration. The best fluid source for this patient to drink small amounts of is
Explanation
Choice A: KoolAid is not an ideal choice for rehydration as it is high in sugar and may exacerbate diarrhea and dehydration.
Choice B : Gatorade is a suitable option for rehydration because it contains electrolytes (sodium, potassium, and chloride) that help replace those lost through diarrhea. It can help maintain
electrolyte balance and improve hydration.
Choice C Orange juice is not recommended during active diarrhea as it is acidic and may irritate the gastrointestinal tract, potentially worsening diarrhea.
Choice D Cola beverages are not recommended for rehydration as they contain caffeine, sugar, and carbonation, which can further contribute to dehydration.
A nurse is caring for 4 patients each patient has a colostomy bag. Which patient should be seen first and made a priority?
Explanation
Choice A A pale blue stoma may indicate a lack of blood supply (ischemia) to the stoma, which is concerning but not as immediately critical as fecal contamination.
Choice B A continuous draining stoma is normal, and there is no indication of an urgent issue in this scenario.
Choice C This patient should be seen first and made a priority as fecal contamination of the stoma can lead to skin irritation, infection, and complications. Immediate cleaning and appropriate care are necessary.
Choice D A beefy red, moist stoma is a healthy stoma appearance and does not indicate an urgent issue.
Your patient is supposed to get a tap water enema. What medical diagnosis would NOT qualify him for this procedure?
Explanation
Choice A Pneumonia is not a contraindication for a tap water enema.
Choice B A tap water enema is not recommended for patients with edema or excess fluid volume due to the risk of further fluid overload.
Choice C Hypertension is not a contraindication for a tap water enema unless the patient has other cardiovascular conditions that could be exacerbated by the procedure.
Choice D Diabetes mellitus is not a contraindication for a tap water enema. However, patients with diabetes may need careful monitoring during the procedure due to potential glucose
fluctuations.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 40 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

