Final Exam OB + Community
Total Questions : 60
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreWhat is the highest priority nursing intervention when admitting a pregnant woman who has experienced a bleeding episode in late pregnancy?
Explanation
Assessing fetal heart rate (FHR) and maternal vital signs would be the highest priority nursing intervention when admitting a pregnant woman who has experienced a bleeding episode in late pregnancy. This is because fetal distress or maternal instability may require immediate medical intervention, such as delivery via emergency cesarean section or blood transfusions, respectively.
Therefore, assessing the FHR and maternal vital signs will help to determine the urgency of the situation and guide the next steps in the management of the patient. Once the patient's condition has stabilized, performing venipuncture for hemoglobin and hematocrit levels, monitoring uterine contractions, and placing clean disposable pads to collect any drainage can be done as appropriate.
A patient arrives at OB triage with a complaint of vaginal bleeding. The nurse would prioritize all of the following questions during the assessment except:
Explanation
The question that the nurse would prioritize the least during the assessment is "Do you plan to have a vaginal or cesarean delivery?" This is because the priority at this point is to determine the urgency of the situation and assess the patient's current condition. The patient's delivery plan can be addressed later after the initial assessment is completed and the patient's stability has been established.
The other questions are all important in determining the cause and severity of the bleeding and the appropriate course of action. The question about the number of weeks is important to determine the gestational age and potential causes of bleeding, as some causes are more common in certain stages of pregnancy. The question about pain can help to determine the possible causes of bleeding and the patient's comfort level. The question about the last ultrasound is important to determine the location of the placenta and whether there are any abnormalities or potential complications.
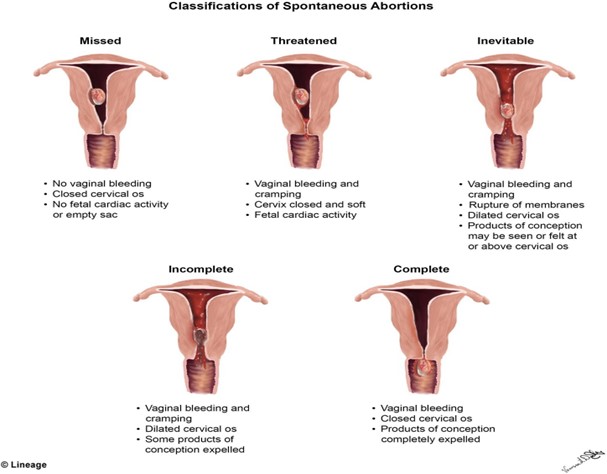
A woman presents to the emergency department complaining of bleeding and cramping. The initial history is significant for a last menstrual period 6 weeks ago. On sterile speculum examination, the care provider finds that the cervix is closed. The anticipated plan of care for this woman would be based on a probable diagnosis of which type of spontaneous abortion?
Explanation
Based on the provided information, the probable diagnosis for the spontaneous abortion in this woman would be a threatened abortion, since the cervix is closed and there is no evidence of expulsion of fetal or placental tissue. A threatened abortion is defined as vaginal bleeding occurring before the 20th week of gestation, with a closed cervical os, and no expulsion of fetal or placental tissue.
The other types of spontaneous abortion are defined as follows:
B. Inevitable abortion: vaginal bleeding and cramping with an open cervical os, with or without expulsion of fetal or placental tissue
C. Missed abortion: fetal demise without expulsion of fetal tissue, and may be associated with a closed cervical os and absence of uterine contractions
D. Incomplete abortion: partial expulsion of fetal or placental tissue, with or without vaginal bleeding, and may be associated with an open cervical os and uterine contractions
A pregnant woman is being discharged from the hospital after the placement of a cervical cerclage because of a history of recurrent pregnancy loss, secondary to an incompetent cervix. Which information regarding postprocedural care should the nurse emphasize in the discharge teaching?
Explanation
The information that the nurse should emphasize in the discharge teaching for a pregnant woman who has undergone a cervical cerclage due to an incompetent cervix is that the presence of any contractions, rupture of membranes (ROM), or severe perineal pressure should be reported to her healthcare provider immediately. This is because these symptoms could indicate cervical dilation or premature labor, which can lead to pregnancy loss or other complications.
Reporting any vaginal discharge is important, but it is not the most critical symptom to monitor for after cervical cerclage placement. Vaginal discharge is common after cervical cerclage and can occur for several weeks without posing a significant risk to the pregnancy.
A cesarean birth may or may not be necessary depending on the patient's individual circumstances and the course of the pregnancy. It is not a given that all women with cervical cerclage require a cesarean delivery.
While some activity restrictions may be necessary after cervical cerclage placement, it is not necessary for the patient to arrange for care at home. Many women are able to manage their daily activities with appropriate precautions and guidance from their healthcare provider.
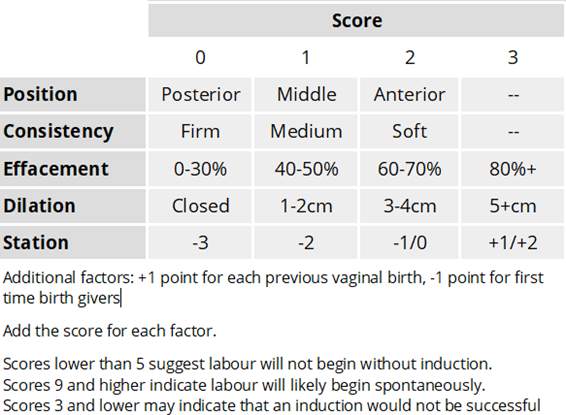
Readiness for induction of labor is assessed by determining the:
Explanation
The readiness for induction of labor is assessed by determining the Bishop score. The Bishop score is a system used to evaluate the cervix for induction of labor readiness. It is based on the assessment of five factors: cervical dilation, cervical effacement, cervical consistency, cervical position, and fetal station. Each factor is scored on a scale of 0 to 3, with a maximum possible score of 15.
The higher the Bishop score, the more favorable the cervix is for induction of labor, and the higher the likelihood of a successful vaginal delivery. A Bishop score of 8 or higher is considered favorable for induction of labor. A low Bishop score may indicate that the cervix is not yet ripe and may need further cervical ripening before induction can be attempted.
The Apgar score is a test used to evaluate a newborn's physical condition at birth, based on five factors: appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiration.
The biophysical profile is a prenatal ultrasound evaluation that assesses fetal well-being by evaluating fetal breathing, fetal movement, fetal tone, amniotic fluid volume, and fetal heart rate. Fetal position is an important consideration during labor, as it can impact the progression and outcome of labor, but it is not used to assess readiness for induction of labor.
During labor a fetus with an average heart rate of 135 beats/min over a 10-minute period would be considered to have:
Explanation
The baseline fetal heart rate is the average heart rate over a 10-minute period, excluding accelerations and decelerations, and is an important indicator of fetal well-being during labor.
A baseline fetal heart rate of 110-160 beats/min is considered normal. A baseline heart rate of less than 110 beats/min is considered bradycardia, which can be a sign of fetal distress or hypoxia. A baseline heart rate greater than 160 beats/min is considered tachycardia, which can also be a sign of fetal distress or hypoxia.
Cervidil (dinoprostone) has been ordered for a pregnant woman at 42 weeks of gestation. The nurse recognizes that this medication will be administered to:
Explanation
Cervidil (dinoprostone) is a medication used to ripen the cervix in preparation for labor induction in women who are at or near term.
Cervidil contains a synthetic form of prostaglandin E2, which helps to soften and thin the cervix, making it easier to dilate and efface during labor. The medication is usually administered vaginally, in the form of a small, flat, rectangular-shaped insert that is placed near the cervix.
The medication is released slowly over time, helping to ripen the cervix gradually.
Cervidil is not used to stimulate the amniotic membranes to rupture, enhance uteroplacental perfusion in an aging placenta, or increase amniotic fluid volume.
Fetal well-being during labor is assessed by:
Explanation
Fetal well-being during labor is assessed by the response of the fetal heart rate (FHR) to uterine contractions (UCs). During labor, the fetal heart rate is monitored to assess the well-being of the fetus. The fetal heart rate should increase in response to fetal movement and contractions, which indicates that the fetus is receiving adequate oxygenation and blood flow. This response is called an "acceleration" in the FHR. However, accelerations alone are not enough to assess fetal well-being during labor. It is the combination of the FHR pattern with the uterine contractions pattern that provides the most information.
In addition to the FHR response to UCs, other factors that may be used to assess fetal well-being during labor include fetal scalp blood sampling, fetal pulse oximetry, and fetal ultrasound. Maternal pain control may help to decrease maternal stress and anxiety during labor, but it is not directly related to fetal well-being. An FHR above 110 beats/min is within the normal range for a fetal baseline heart rate, but it is not enough to assess fetal well-being during labor.
A woman in labor has just received an epidural black. The most important nursing intervention is to:
Explanation
Epidural blocks are commonly used during labor to provide pain relief. However, they can also cause a sudden drop in blood pressure, known as epidural-induced hypotension, which can affect fetal oxygenation and fetal heart rate. Therefore, it is important to monitor maternal blood pressure frequently after an epidural block is administered.
While monitoring the maternal pulse is also important, hypotension is the most common complication of epidural anesthesia and can lead to decreased blood flow to the fetus. Therefore, monitoring maternal blood pressure is the priority.
Monitoring the fetus is also important, but it is not the most important intervention after an epidural block. Limiting parenteral fluids may be necessary in some cases to help prevent or treat hypotension, but it is not always necessary and should be done based on the individual situation.
The nurse recognizes that a nonstress test (NST) in which two or more fetal heart rate (FHR) accelerations of 15 beats/min or more occur with fetal movement in a 20-minute period is:
Explanation
The nurse recognizes that a nonstress test (NST) in which two or more fetal heart rate (FHR) accelerations of 15 beats/min or more occur with fetal movement in a 20-minute period is considered reactive. A reactive NST is a reassuring sign of fetal well-being and indicates that the fetal nervous system and cardiovascular system are intact and functioning appropriately. If a reactive NST is not obtained, further testing or evaluation may be necessary to assess fetal well-being.
A 41-week pregnant multigravida presents in the labor and delivery unit after a nonstress test indicated that her fetus could be experiencing some difficulties in utero. Which diagnostic tool would yield more detailed information about the fetus?
Explanation
The biophysical profile (BPP) would yield more detailed information about the fetus in this scenario. The BPP is a prenatal ultrasound evaluation that assesses fetal well-being by evaluating five biophysical variables: fetal breathing movements, fetal movements, fetal tone, amniotic fluid volume, and fetal heart rate. The BPP is a more detailed assessment of fetal well-being compared to a nonstress test and can provide valuable information about the fetus's overall health and well-being, including any potential issues or difficulties.
MSAFP screening is a blood test that can detect certain fetal abnormalities, but it does not provide detailed information about fetal well-being.
Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (PLBS) is an invasive test that is used to obtain a sample of fetal blood for testing in cases of suspected fetal anemia or other blood disorders. Ultrasound for fetal anomalies is a diagnostic tool used to detect structural abnormalities or defects in the fetus. While it can provide some information about fetal well-being, it is not as comprehensive as the BPP in evaluating fetal health and wellness.
The nurse is assessing the knowledge of new parents with a child born with maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). This is an autosomal recessive inherited disorder, which means that:
Explanation
Both genes of a pair must be abnormal for the disorder to be expressed. In autosomal recessive inheritance, the gene for the disorder is located on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome) and a person must inherit two copies of the abnormal gene (one from each parent) in order for the disorder to be expressed. If a person inherits only one copy of the abnormal gene, they are a carrier of the disorder but do not typically show symptoms.
A man smokes two packs of cigarettes a day. He wants to know if smoking is contributing to the difficulty he and his wife are having getting pregnant. The nurse's most appropriate response is:
Explanation
Smoking has been linked to a variety of health issues, including decreased fertility in both men and women. It can cause damage to sperm DNA and reduce sperm motility, which can make it more difficult for sperm to reach and fertilize an egg. Therefore, smoking can contribute to infertility issues. It's important for the man to quit smoking or at least reduce his cigarette consumption to increase his chances of conception with his wife.
During this phase of a disaster, evaluation of the disaster plan and cleanup of the area are hallmark activities.
Explanation
The recovery phase of a disaster is the period when the immediate danger has passed, and the focus shifts to restoring the affected area to its pre-disaster state. The hallmark activities during this phase include the evaluation of the disaster plan, as well as cleanup and rebuilding efforts to help affected individuals and communities recover from the disaster's effects. The recovery phase can last for weeks, months, or even years, depending on the severity and extent of the damage caused by the disaster.
Excessive blood loss after childbirth can have several causes; the most common is:
Explanation
The most common cause of excessive blood loss after childbirth is the failure of the uterine muscle to contract firmly, which is also known as uterine atony. If the uterus does not contract effectively after delivery, it cannot properly close off the blood vessels that were connected to the placenta, leading to heavy bleeding. Uterine atony can occur due to various factors, such as prolonged labor, multiple births, or the use of certain medications during labor.
Other causes of excessive blood loss after childbirth include retained placental fragments, vaginal or vulvar hematomas, or unrepaired lacerations of the vagina or cervix, but these are less common than uterine atony.

On examining a woman who gave birth 5 hours ago, the nurse finds that the woman has completely saturated a perineal pad within 15 minutes. The nurse's first action is to:
Explanation
The nurse's first action should be to massage the woman's fundus. A completely saturated perineal pad within 15 minutes after giving birth indicates excessive bleeding, which is also known as postpartum hemorrhage (PPH). Massaging the uterus (fundus) can help it to contract, reduce bleeding, and prevent further blood loss. Once the fundus has been massaged, the nurse should assess the woman's vital signs and continue to monitor her for signs of continued bleeding. If bleeding persists despite massage, the nurse should begin an intravenous (IV) infusion of Ringer's lactate solution and call the woman's primary healthcare provider.
A bioterrorism attack occurred locally in which people were exposed to anthrax. As the nurse, you understand the main priority would be:
Explanation
In the case of a bioterrorism attack involving anthrax, the main priority for the nurse is to administer antibiotics within 48 hours of exposure using the Strategic National Stockpile. Anthrax is a serious bacterial infection that can be used as a bioterrorism weapon. Antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, and penicillin, can be used to prevent anthrax from developing in people who have been exposed.
There is currently no vaccine available for anthrax exposure. Also, symptom support alone is not enough in cases of anthrax exposure, as anthrax can progress rapidly and lead to serious complications. Placing everyone who was exposed in quarantine may not be necessary in all situations, and should be determined on a case-by-case basis depending on the extent and severity of the exposure.
A public health nurse in a large city is planning and developing strategies to disseminate information to residents about infant safe sleep practices. Which of the following best exhibits the nurse's understanding of effective health communication in the community?
Explanation
Effective health communication requires that messages be designed with the audience's needs and characteristics in mind, and pretesting is an important part of this process. Pretesting materials for feedback about comprehension helps to ensure that the messages are clear, understandable, and culturally appropriate for the target audience. This also allows the nurse to make any necessary revisions to improve the materials' effectiveness.
The nurse's target audience should be specific to those who have infants or who are expecting an infant, rather than including all residents, as this is too broad and may not effectively reach the intended audience. Additionally, the use of radio advertisements developed in English only may not be effective for reaching all members of the community, particularly those who do not speak English as their primary language. Lastly, materials written at a high school reading level may not be appropriate for all members of the community, particularly those with lower levels of literacy.
Which client is displaying health literacy at the basic functional level?
Explanation
Health literacy is defined as the degree to which an individual can obtain, process, and
understand basic health information and services needed to make appropriate health decisions. Basic functional health literacy refers to an individual's ability to read and understand simple health information and instructions.
While all the clients mentioned may be demonstrating health literacy, the ability to read and understand discharge instructions after routine surgery is a basic functional health literacy skill. This client is able to comprehend written health information and follow simple instructions, which is an important aspect of managing their own health care.
The other clients mentioned may be displaying a higher level of health literacy, such as the client who is teaching a class about cancer survival or the client with Type II Diabetes who is using nutritional information to make a grocery list. These individuals may have a greater ability to understand and apply complex health information and navigate the healthcare system.
Which of the following outcomes best describes the effect environmental health has had in our community?
Explanation
Environmental health is concerned with the impact of environmental factors on human health, including physical, chemical, biological, and social factors. By improving environmental health in a community, we can decrease exposure to environmental hazards and reduce the incidence of environmentally related diseases, resulting in improved health outcomes.
One of the most important outcomes of environmental health interventions is increased life expectancy for the community. By reducing exposure to environmental hazards, such as air pollution, water pollution, and toxic chemicals, we can decrease the incidence of environmentally related diseases, such as respiratory disease, cancer, and neurological disorders. This, in turn, can increase life expectancy and improve the overall health of the community.
The public health nurse wants to assess potential environmental health issues within a particular district. Which of the following would the nurse include in the assessment?
Explanation
When assessing potential environmental health issues in a district, the public health nurse would consider a range of factors that may impact the health and well-being of the community. These factors may include the built environment (e.g. housing, transportation, urban planning), workplace hazards, food safety, and a range of other environmental exposures that could potentially harm human health.
By considering all of these factors, the public health nurse can gain a more comprehensive understanding of potential environmental health issues in the district and develop appropriate strategies for addressing these issues to improve the health and well-being of the community.
A nurse is developing goals for a community education program. Which of the following methods should be used?
Explanation
One of the most important principles of effective health education is to involve the target audience in the planning process. By involving the target audience in the planning process, the nurse can gain a better understanding of their needs, priorities, and concerns related to health and wellness. This, in turn, can help the nurse develop education goals that are relevant, engaging, and effective at improving health outcomes.
Asking the formal leadership of a community what the learning needs are, using the expertise of professional nurses who are skilled at assessing needs, or interviewing physicians to determine the highest need based on diagnoses can all be useful strategies for gathering information about community health needs. However, none of these strategies are as effective at identifying the specific needs and priorities of the target audience as asking the target audience directly.
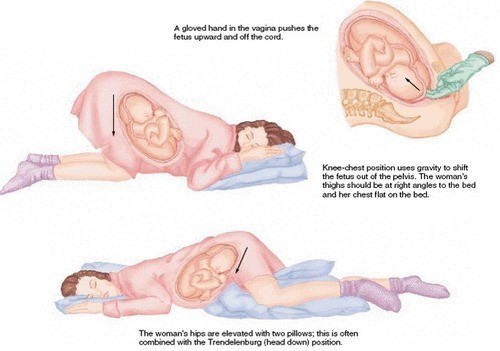
A pregnant woman's amniotic membranes rupture and a prolapsed umbilical cord is found. What intervention would be the first priority?
Explanation
In the case of a prolapsed umbilical cord, the first priority intervention is to relieve pressure on the cord. Placing the woman in the knee-chest position or Trendelenburg position with the hips elevated is the best way to achieve this. This position helps to reduce the compression of the cord and improve fetal oxygenation.
Option B is incorrect because while oxygen may be necessary, relieving pressure on the cord is the priority.
Option C is incorrect because a vaginal birth should not proceed with a prolapsed umbilical cord, as it can cause cord compression and fetal distress.
Option D is incorrect because covering the cord in sterile gauze soaked in saline is not a priority intervention and may not be effective in relieving pressure on the cord.
Which of the following complications is not associated with cesarean births?
Explanation
Perineal hematoma is a complication that can occur after vaginal births, typically due to trauma or injury to the perineum during delivery. Wound dehiscence, UTIs, and DVTs are all possible complications associated with cesarean births. Wound dehiscence is a separation of the layers of the surgical incision, UTIs can occur due to catheterization during the surgery, and DVTs can occur due to immobility during the recovery period.
A cesarean section would be most appropriate for which of the following clients?
Explanation
A history of cesarean section for fetal distress is an indication for a repeat cesarean section in subsequent pregnancies, as the risk of recurrence of fetal distress is higher. A trial of labor after cesarean (TOLAC) may be attempted in some cases, but a planned cesarean section is often recommended.
Option B is incorrect because fear of natural childbirth is not a medical indication for a cesarean section.
Option C is incorrect because gestational diabetes does not typically require a cesarean section unless other complications arise, such as fetal macrosomia or failed induction of labor.
Option D is incorrect because a history of cephalopelvic disproportion with the first pregnancy may not necessarily require a cesarean section in subsequent pregnancies. A trial of labor may be attempted, depending on the circumstances.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 60 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

