Hesi Dosage Calculations Care
Total Questions : 41
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA client with dehydration is prescribed a potassium chloride infusion at 10 mEq/hr. Potassium chloride 80 mEq is mixed with 1 liter of normal saline. The nurse should regulate the infusion pump to deliver how many mL/hour? (Enter numeric value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest whole number.)
Explanation
To calculate the infusion rate, we can use the following formula:
Infusion rate = (Total volume of solution x dose of potassium chloride) / time in hours
In this case, the total volume of solution is 1 liter or 1000 mL. The dose of potassium chloride is 10 mEq/hr. Since 80 mEq is mixed with 1 liter of normal saline, we can calculate the dose of potassium chloride in mL/hr as follows:
80 mEq / 1000 mL = 0.08 mEq/mL
10 mEq/hr x 0.08 mEq/mL = 0.8 mL/hr
Therefore, the infusion pump should be regulated to deliver 83 mL/hour.
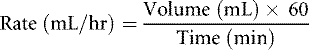
The nurse is preparing to administer enoxaparin 90 mg subcutaneously daily to a client admitted with a pulmonary embolism. The pharmacy provides a prefilled syringe labeled "Enoxaparin 100 mg/1 mL." How many milliliters should the nurse administer? (Enter numeric value only.)
Explanation
To calculate the number of milliliters the nurse should administer, we can use the following formula: Dose to administer = Ordered dose / Available dose
In this case, the ordered dose is 90 mg and the available dose is 100 mg/1 mL. We can calculate the dose to administer as follows:
90 mg / 100 mg/1 mL = 0.9 mL.
The health care provider prescribes streptomycin 300 mg IM q12 hours for a client with tuberculosis. The available vial is labeled "Streptomycin 1 gram/2.5 mL." How many milliliters should the nurse administer? (Enter the numerical value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest tenth.)
Explanation
To calculate the number of milliliters the nurse should administer, we can use the following formula:
Dose to administer = Ordered dose / Available dose
In this case, the ordered dose is 300 mg and the available dose is 1 g/2.5 mL. We can calculate the dose to administer as follows:
300 mg / 1000 mg/2.5 mL = 0.75 mL.
The nurse is preparing a change of shift report for a client who has a 1000 mL infusion of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP that was started 5 hours ago at a rate of 125 mL/hour via an infusion pump. The nurse should report how many mL remain to be infused to the oncoming nurse? (Enter numeric value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest whole number.)
Explanation
To calculate the number of milliliters that remain to be infused, we can use the following formula: Volume remaining = Total volume - Volume infused
In this case, the total volume is 1000 mL and the volume infused is:
125 mL/hour x 5 hours = 625 mL So the volume remaining is:
1000 mL - 625 mL = 375 mL.
The nurse is caring for a client with an oral temperature of 36.5°C. What temperature in Fahrenheit should the nurse document in the medical record? (Enter numerical value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest tenth.)
Explanation
To convert Celsius to Fahrenheit, we can use the following formula:
°F = (°C x 1.8) + 32
In this case, the oral temperature is 36.5°C. We can calculate the temperature in Fahrenheit as follows: (36.5 x 1.8) + 32 = 97.7°F.
The healthcare provider prescribes a slow continuous infusion of labetalol to be administered at 2mg/minute. Labetalol HCI Injection, USP 200 mg/40 mL is added to 160 mL of 5% Dextrose Injection, USP for a total volume of 200 mL. How many mL/hour should the nurse program the infusion pump? (Enter numerical value only.)
Explanation
To calculate the infusion rate in mL/hour, we can use the following formula:
Infusion rate (mL/hour) = Dose (mg/minute) x 60 / Concentration (mg/mL) In this case, the dose is 2 mg/minute and the concentration is:
200 mg/40 mL = 5 mg/mL
We can calculate the infusion rate as follows:
2 mg/minute x 60 / 5 mg/mL = 24 mL/hour
However, the total volume of the solution is 200 mL. Therefore, we need to adjust the infusion rate to ensure that the medication is infused over the correct time period. If we divide the total volume by the infusion time, we can calculate the infusion rate required to deliver the medication over that time period:
200 mL / (120 minutes) = 100 mL/hour
So we need to adjust our initial calculation to ensure that we are infusing at a rate of 100 mL/hour. We can do this by using a proportion:
2 mg/minute x 60 / 5 mg/mL = X mL/hour x 1 Solving for X gives us:
X = (2 x 60 x 1) / 5 = 24 mL/hour
So we should program the infusion pump to deliver 6 mL/hour.
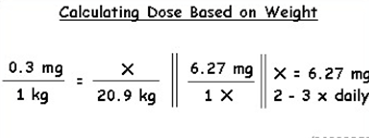
The healthcare provider prescribes a single dose of filgrastim 5 mcg/kg subcutaneously for a client who weighs 59 kg. The medication is available in a 300 mcg/mL vial. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Enter numerical value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest tenth.)
Explanation
To calculate the volume of medication to administer, we can use the following formula: Volume = Dose / Concentration
In this case, the dose is 5 mcg/kg and the client weighs 59 kg. We can calculate the total dose as follows: 5 mcg/kg x 59 kg = 295 mcg
The medication is available in a 300 mcg/mL vial. We can calculate the volume required as follows: 295 mcg / 300 mcg/mL = 0.9833 mL
We should round this value to the nearest tenth of a milliliter, which gives us 0.1 mL.
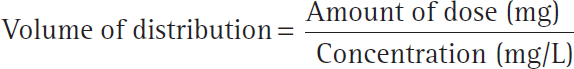
The healthcare provider prescribes 1 liter of 0.9% Sodium chloride, USP intravenously to be infused over 12 hours for a client. How many mL/hr should the nurse program the infusion pump to deliver? (Enter numerical value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest whole number.)
Explanation
To calculate the infusion rate in mL/hour, we can use the following formula Infusion rate (mL/hour) = Volume (mL) / Time (hours)
In this case, the volume is 1000 mL and the time is 12 hours. We can calculate the infusion rate as follows: 1000 mL / 12 hours = 83.3 mL/hour
We should round this value to the nearest whole number, which gives us 83 mL/hour.
The healthcare provider prescribes hydroxyzine 35 mg IM for a client who is vomiting. The available drug is labeled 50 mg/mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Enter numerical value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest tenth.)
Explanation
To calculate the volume of medication to administer, we can use the following formula: Volume = Dose / Concentration
In this case, the dose is 35 mg and the concentration is 50 mg/mL. We can calculate the volume required as follows: 35 mg / 50 mg/mL = 0.7 mL
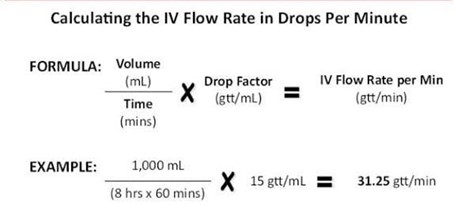
A client receives a prescription for 2 liters of lactated Ringer's intravenously (IV) to be infused over 12 hours. The IV administration set delivers 20 gtt/mL. How many gtt/min should the nurse regulate the infusion? (Enter numerical value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest whole number.)
Explanation
To calculate the infusion rate in drops per minute (gtt/min), we can use the following formula: Infusion rate (gtt/min) = Volume (mL) x Drop factor / Time (minutes)
In this case, the volume is 2000 mL, the drop factor is 20 gtt/mL, and the time is 720 minutes (12 hours x 60 minutes/hour). We can calculate the infusion rate as follows:
2000 mL x 20 gtt/mL / 720 minutes = 55.56 gtt/min
We should round this value to the nearest whole number, which gives us 33 gtt/min.

A client receives a prescription for vancomycin 1 gram intravenously (IV) every 12 hours, which is to be infused over 2 hours. The IV bag contains vancomycin 1 gram in 250 mL of dextrose 5% in water (D,W). The nurse should program the infusion pump to deliver how many mL/hour? (Enter numerical value only.)
Explanation
To calculate the infusion rate in mL/hour, we can use the following formula:
Infusion rate (mL/hour) = Volume (mL) / Time (hours)
In this case, the volume is 250 mL and the time is 2 hours. We can calculate the infusion rate as follows: 250 mL / 2 hours = 125 mL/hour
The healthcare provider prescribes epoetin alfa 75 Units/kg subcutaneously for a client who weighs 80 kg. The available vial is labeled Epoetin Alfa 10,000 Units/mL. How many milliliters should the nurse administer to the client for a safe single dose? (Enter numerical value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest tenth.)
Explanation
To calculate the volume of medication to administer, we can use the following formula: Volume = Dose / Concentration
In this case, the dose is 75 Units/kg and the client weighs 80 kg. We can calculate the total dose as follows: 75 Units/kg x 80 kg = 6000 Units
The medication is available in a 10,000 Units/mL vial. We can calculate the volume required as follows: 6000 Units / 10,000 Units/mL = 0.6 mL
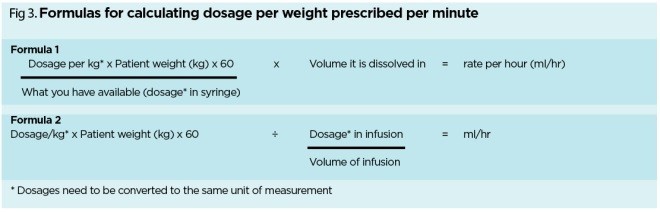
The nurse is preparing to administer enoxaparin 135 mg subcutaneously. The medication is available in a cartridge labeled 150 mg/mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? (Enter numeric value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest tenth.)
Explanation
To calculate the volume of medication to administer, we can use the following formula: Volume = Dose / Concentration
In this case, the dose is 135 mg and the concentration is 150 mg/mL. We can calculate the volume required as follows: 135 mg / 150 mg/mL = 0.9 mL
A client with peptic ulcer disease receives a prescription for dicyclomine 20 mg PO four times daily. The medication is available in 10 mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer in a 24-hour period? (Enter numeric value only.)
Explanation
The total daily dose is 80 mg (20 mg x 4). Since the medication is available in 10 mg tablets, we can calculate the number of tablets required as follows:
80 mg / 10 mg per tablet = 8 tablets
A client receives a prescription for an intravenous (IV) infusion of 5% Dextrose Injection, USP in 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP at 55 mL/hour. The IV administration set delivers 10 gtt/mL. The nurse should regulate the drop rate to deliver how many gtts/minute? (Enter numerical value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest whole number.)
Explanation
To calculate the drop rate in gtts/minute, we can use the following formula:
Drop rate (gtts/minute) = (Volume (mL) x Drop factor) / Time (minutes)
In this case, the volume is 55 mL, the drop factor is 10 gtt/mL, and the time is 60 minutes. We can calculate the drop rate as follows:
(55 mL x 10 gtt/mL) / 60 minutes = 9.17 gtts/minute
We can round this value to the nearest whole number to get 92 gtts/min
The healthcare provider prescribes epinephrine 0.01 mg/kg intramuscularly for a child with asthma who weighs 55 pounds. The available medication is labeled 1 mg/mL. Based on the child's weight, how many mL should the nurse administer? (Enter numerical value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest hundredth.)
Explanation
The child weighs 55 pounds which is equivalent to 24.95 kg (1 kg = 2.20462 pounds).
The healthcare provider prescribes epinephrine 0.01 mg/kg, so the child should receive 0.2495 mg of epinephrine (0.01 mg/kg 24.95 kg).
The available medication is labeled 1 mg/mL, so the nurse should administer 0.25 mL of medication (0.2495 mg / 1 mg/mL).
A client who weighs 172 pounds receives a prescription for levothyroxine 1.6 mcg/kg/day by mouth. The medication is available in 50 mcg scored tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer? (Enter numerical value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest tenth.)
Explanation
The client weighs 172 pounds which is equivalent to 78.02 kg (1 kg = 2.20462 pounds).
The prescription for levothyroxine is 1.6 mcg/kg/day, so the client should receive 124.83 mcg of levothyroxine per day (1.6 mcg/kg/day * 78.02 kg).
The medication is available in 50 mcg scored tablets, so the nurse should administer 2.5 tablets per day (124.83 mcg / 50 mcg/tablet).
A client receives a prescription for digoxin 125 mcg by mouth daily. The medication is available in 0.0625 mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer? (Enter numerical value only.)
Explanation
The client receives a prescription for digoxin 125 mcg by mouth daily. Since 1 mg is equivalent to 1000 mcg, 125 mcg is equivalent to 0.125 mg.
The medication is available in 0.0625 mg tablets, so the nurse should administer 2 tablets (0.125 mg / 0.0625 mg/tablet).
A child weighing 52.5 pounds receives a prescription for asparaginase 4,780 IU IV. The vial is labeled, "Asparaginase 10,000 IU single-use vial. For IM use, reconstitute in 2 mL sterile sodium chloride, and for IV use, reconstitute in 5 mL". How many mL should the nurse administer? (Enter the numeric value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest tenth.)
Explanation
The child receives a prescription for asparaginase 4,780 IU IV.
The vial is labeled "Asparaginase 10,000 IU single-use vial" and for IV use, it should be reconstituted in 5 mL.
Since the child needs 4,780 IU of asparaginase and the vial contains 10,000 IU, the nurse should administer 2.39 mL of medication (4,780 IU / 10,000 IU * 5 mL).
A client who is experiencing indigestion receives a prescription for magnesium hydroxide 1200 mg by mouth every 6 hours. The bottle is labeled "Magnesium Hydroxide, USP 400 mg per 5 mL." How many ounces should the nurse instruct the client to take with each dose? (Enter numerical value only.)
Explanation
The client receives a prescription for magnesium hydroxide 1200 mg by mouth every 6 hours.
The bottle is labeled "Magnesium Hydroxide, USP 400 mg per 5 mL", so the client should take 15 mL of medication with each dose (1200 mg / 400 mg/5 mL * 5 mL).
Since 1 ounce is equivalent to 29.5735 mL, the client should take 0.51 ounces of medication with each dose (15 mL / 29.5735 mL/ounce).
The healthcare provider prescribes regular insulin 8 units/hour intravenously (IV). The IV solution contains 100 units of regular insulin in 100 mL of 0.9% normal saline. How many mL/hour should the nurse program the infusion pump? (Enter numerical value only.)
Explanation
The healthcare provider prescribes regular insulin 8 units/hour intravenously (IV).
The IV solution contains 100 units of regular insulin in 100 mL of 0.9% normal saline, so the concentration of insulin in the IV solution is 1 unit/mL (100 units / 100 mL).
Since the healthcare provider prescribes 8 units/hour of insulin, the nurse should program the infusion pump to deliver 8 mL/hour of the IV solution (8 units/hour / 1 unit/

A client has a prescription for clonidine for hypertension. The available medication is labeled, clonidine 0.3 mg per tablet. The client reports taking two tablets, twice daily. What total daily medication dose, in mg, is the client taking? (Enter numerical value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest tenth.)
Explanation
The client has a prescription for clonidine for hypertension and the available medication is labeled clonidine 0.3 mg per tablet.
The client reports taking two tablets, twice daily, so the total daily medication dose is 1.2 mg (2 tablets * 0.3 mg/tablet * 2 times/day).
A client with pneumonia is receiving a secondary infusion of azithromycin 500 mg in 250 mL of normal saline (NS) to be infused in 90 minutes. How many mL/hour should the nurse program the infusion pump? (Enter numerical value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest whole number.)
Explanation
The client with pneumonia is receiving a secondary infusion of azithromycin 500 mg in 250 mL of normal saline (NS) to be infused in 90 minutes.
To calculate the infusion rate in mL/hour, we need to divide the total volume of the infusion (250 mL) by the infusion time in hours (90 minutes / 60 minutes/hour = 1.5 hours).
The nurse should program the infusion pump to deliver 167 mL/hour (250 mL / 1.5 hours).
The healthcare provider prescribes interferon beta-1b 0.1875 mg every other day for a client with multiple sclerosis. The nurse reconstitutes the single-use vial of powder labeled 0.3 mg with 1.2 mL of sterile water. How many ml should the nurse administer to the client? (Enter the numerical value only. If rounding is required round to the nearest hundredth)
Explanation
The healthcare provider prescribes interferon beta-1b 0.1875 mg every other day for a client with multiple sclerosis.
The nurse reconstitutes the single-use vial of powder labeled 0.3 mg with 1.2 mL of sterile water, so the concentration of interferon beta-1b in the solution is 0.25 mg/mL (0.3 mg / 1.2 mL).
Since the healthcare provider prescribes 0.1875 mg of interferon beta-1b, the nurse should administer 0.75 mL of medication (0.1875 mg / 0.25 mg/mL).
A client is receiving a prescription for penicillin 1.2 million units IM. The available vial is labeled, "600,000 units/2 mL". How many mL should the nurse administer? (Enter numeric value only)
Explanation
The client is receiving a prescription for penicillin 1.2 million units IM.
The available vial is labeled "600,000 units/2 mL", so the concentration of penicillin in the solution is 300,000 units/mL (600,000 units / 2 mL).
Since the healthcare provider prescribes 1.2 million units of penicillin, the nurse should administer 4 mL of medication (1.2 million units / 300,000 units/mL).

Sign Up or Login to view all the 41 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

