Hesi Pharmacology exam 2
Total Questions : 36
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreThe nurse is administering the muscle relaxant baclofen by mouth (PO) to a client diagnosed with multiple sclerosis. Which intervention should the nurse implement?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Baclofen is a muscle relaxant used to reduce muscle spasticity in conditions such as multiple sclerosis. One of the common side effects of baclofen is dizziness or orthostatic hypotension, which can increase the risk of falls. Therefore, the nurse should advise the client to move slowly and cautiously when rising and walking to prevent falls and injury.
Choice B rationale: Monitoring intake and output every 8 hours is not directly related to the administration of baclofen.
Choice C rationale: Ensuring the client knows to stop baclofen before using other antispasmodics is not the correct intervention. Baclofen should not be abruptly discontinued without medical advice, and its use should be discussed with the healthcare provider.
Choice D rationale: Evaluating muscle strength every 4 hours may be part of the client's overall care plan, but it is not directly related to the administration of baclofen. Muscle strength evaluation is more pertinent for assessing the progression of multiple sclerosis and its effects on muscle function.
A female client who is a vegetarian has a new prescription for warfarin. The client states she eats leafy green vegetables every day. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: this is not an appropriate response because while it may reduce the intake of vitamin K, suddenly changing the client's diet drastically may not be necessary. It is essential for the healthcare provider to make any necessary adjustments to the medication based on the client's diet.
Choice B rationale: Warfarin is an anticoagulant medication that works by inhibiting the formation of blood clots. It interacts with vitamin K, which plays a crucial role in the blood clotting process. Leafy green vegetables are rich in vitamin K, and their consumption can affect the effectiveness of warfarin. The nurse should advise the client to inform her healthcare provider about her vegetarian diet and the regular consumption of leafy green vegetables. The healthcare provider will then be able to adjust the warfarin dosage accordingly to ensure that the client receives the appropriate and consistent level of anticoagulation.
Choice C rationale: while a vegetarian diet can be healthy, the specific concern here is the potential impact of vitamin K-rich foods on warfarin therapy. It's essential to address this potential interaction rather than focusing solely on the overall healthy lifestyle.
Choice D rationale: Consuming large amounts of leafy green vegetables and vitamin K-rich foods may actually reduce the effectiveness of warfarin, leading to a decreased ability to prevent blood clots. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with the healthcare provider to manage the dosage appropriately.
A client who received a renal transplant three months ago is readmitted to the acute care unit with signs of graft rejection. While taking the client's history, the nurse determines that the client has been self-administering St. John's Wort, an herbal preparation, on the advice of a friend. Which information is most significant about this finding?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Ingestion of Wort can reduce the client's intake of sodium: This information is not directly related to the situation of a renal transplant and graft rejection. It is not the most significant finding regarding the use of St. John's Wort in this context.
Choice B rationale: Adding the herb decreases the need for corticosteroids: There is no evidence or indication that St. John's Wort can decrease the need for corticosteroids, especially in the context of a renal transplant and graft rejection.
Choice C rationale: While St. John's Wort is sometimes used as an herbal remedy for depression, the most significant information, in this case, is its potential to interact with cyclosporine and affect the client's immunosuppressive medication. The focus should be on the drug interaction and the risk it poses to the client's graft health, rather than the reason for using the herb.
Choice D rationale: The most significant information about the finding that the client has been self-administering St. John's Wort is that it can decrease plasma concentrations of cyclosporine. Cyclosporine is an immunosuppressive medication commonly used after a renal transplant to prevent graft rejection. When St. John's Wort is taken concurrently with cyclosporine, it can induce certain liver enzymes responsible for drug metabolism, leading to a decreased concentration of cyclosporine in the bloodstream. This can potentially reduce the effectiveness of cyclosporine in preventing graft rejection, putting the client's transplanted kidney at risk.
A client in the surgical recovery area asks the nurse to bring the largest possible dose of pain medication available. Which action should the nurse implement first?
Explanation
Choice A rationale; When a client requests pain medication, the first action the nurse should take is to assess the client's current pain level. By using a pain scale, the nurse can determine the intensity of the pain and evaluate the need for pain medication appropriately. The pain scale allows the client to express their pain on a standardized scale, helping the nurse to understand the severity of the pain and the most appropriate pain management intervention.
Choice B rationale: While diversional thoughts and non-pharmacological pain management techniques can be useful, the priority is to first assess the pain level and address the client's immediate needs for pain relief.
Choice C rationale: While it's important to consider the client's history of drug use, it is not the first action to take when a client requests pain medication. Assessing the pain level and providing appropriate pain relief should be the initial priority.
Choice D rationale: While it's essential to know the last dose of pain medication the client received, it is not the first action to take when the client is requesting pain medication. Assessing the current pain level and addressing the client's immediate needs should be the first step. The information about the last dose will be relevant for deciding when the next dose can be given.
The nurse is planning care for a client with major depression who is receiving a new prescription for duloxetine. Which information is most important for the nurse to obtain?
Explanation
Choice A rationale; Family history of mental illness is important information to consider when assessing the client's overall mental health history, but it is not directly related to the immediate safety and effectiveness of duloxetine.
Choice B rationale: Weight change in the last month is relevant to monitoring for side effects of duloxetine, but it is not as critical as assessing liver function, which directly impacts the metabolism of the medication.
Choice C rationale: When planning care for a client starting on duloxetine, it is most important for the nurse to obtain liver function laboratory results. Duloxetine is primarily metabolized in the liver, and it is important to assess the client's liver function before starting the medication to ensure that the liver can process the drug effectively and safely. Clients with impaired liver function may require dose adjustments or be at higher risk for adverse effects, so obtaining liver function test results is crucial for safe medication management.
Choice D rationale: Recent use of other antidepressants is essential to avoid potential drug interactions, but it is not the most critical piece of information compared to assessing liver function, which directly affects the client's ability to process duloxetine.
Prior to administering oral doses of calcitriol and calcium carbonate to a client with hypoparathyroidism, the nurse notes that the client's total calcium level is 14 mg/dL (3.5 mmol/L). Which action should the nurse implement?
Reference Range:
Total Calcium [Reference Range: Adult 9 to 10.5 mg\/dL or 2.25 to 2.62 mmol\/L]
Explanation
Choice A rationale: This is not appropriate because the client's elevated calcium level requires immediate attention and further assessment by the healthcare provider before administering any medications that may further raise calcium levels.
Choice B rationale: The client's total calcium level is significantly elevated, which may indicate hypercalcemia. Given the reference range for total calcium in adults is 9 to 10.5 mg/dL (2.25 to 2.62 mmol/L), a calcium level of 14 mg/dL (3.5 mmol/L) is abnormally high. Both calcitriol (active form of vitamin D) and calcium carbonate (calcium supplement) can increase calcium levels in the body. Before administering any medication, the nurse should hold both calcitriol and calcium carbonate and notify the healthcare provider of the elevated calcium level. The healthcare provider will determine the appropriate course of action and may adjust the dosage or temporarily discontinue the medications to prevent further complications related to hypercalcemia.
Choice C rationale: Holding calcium carbonate is a step in the right direction, but given the significant elevation of total calcium, it is best to hold both medications and consult the healthcare provider.
Choice D rationale: Holding calcitriol is a step in the right direction, but both medications should be held to prevent exacerbation of hypercalcemia until further instructions are received from the healthcare provider.
A client with chemotherapy induced nausea receives a prescription for metoclopramide.
Which adverse effect is most important for the nurse to report?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Nausea is the symptom the medication is intended to treat, and it is expected that the client may have some level of nausea while undergoing chemotherapy. It is not the most important adverse effect to report in this scenario.
Choice B rationale: Diarrhea is not a common or significant adverse effect of metoclopramide. While it is essential to monitor for any gastrointestinal side effects, it is not the most important adverse effect to report in this case.
Choice C rationale: Metoclopramide is a medication commonly used to treat nausea and vomiting, particularly related to chemotherapy. One of the significant adverse effects of metoclopramide is the potential to cause extrapyramidal symptoms, including involuntary movements such as dystonia, dyskinesia, and Parkinsonism. These extrapyramidal symptoms can be serious and may require immediate intervention or discontinuation of the medication.
Therefore, it is essential for the nurse to closely monitor the client for any signs of involuntary movements and report them promptly to the healthcare provider for appropriate management.
Choice D rationale: Unusual irritability is not a typical adverse effect associated with metoclopramide. While mood changes can occur with any medication, involuntary movements are a more concerning side effect that requires immediate attention and reporting.
The healthcare provider prescribes the antibiotic tetracycline HCI for an adult client that arrived at an outpatient clinic. Which instruction should the nurse include in the teaching plan for this client?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Tetracycline should generally be taken on an empty stomach, as certain food and beverages, including orange juice, can interfere with its absorption. The nurse should instruct the client to take tetracycline with water and on an empty stomach unless otherwise specified by the healthcare provider.
Choice B rationale: Tetracycline is an antibiotic that can make the skin more sensitive to sunlight, leading to an increased risk of sunburn and photosensitivity reactions. To prevent these adverse effects, the nurse should instruct the client to protect their skin from sunlight while taking the medication. This includes using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding prolonged sun exposure. It is essential to educate the client about this potential side effect to ensure their safety and minimize skin reactions during treatment.
Choice C rationale: Tetracycline does not require routine monitoring of serum drug levels. It is an antibiotic with a well-established dosing regimen, and monitoring drug levels is not necessary for its safe and effective use.
Choice D rationale: While taking tetracycline with milk or antacids may help reduce GI irritation, it can also interfere with the absorption of the medication. Therefore, it is generally recommended to take tetracycline with water and on an empty stomach to ensure optimal absorption and effectiveness.
A client is receiving intravenous (IV) vancomycin and the nurse plans to draw blood for a peak and trough to determine the serum level of the drug. Which collection times provide the best determination of these levels?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Peak and trough levels are essential in monitoring the therapeutic drug levels of certain medications, including vancomycin. The timing of blood collection is crucial to obtain accurate readings. Peak level: The peak level is drawn approximately 30 minutes after the completion of the vancomycin infusion. This is when the drug concentration in the bloodstream is at its highest, allowing the healthcare provider to assess if the dosage is achieving the desired therapeutic effect. Trough level: The trough level is drawn just before the next dose of vancomycin is administered, typically within 30 minutes before the scheduled time. This is when the drug concentration in the bloodstream is at its lowest, ensuring that the levels do not fall below the therapeutic range between doses. By drawing blood samples two hours after the completion of the IV dose and two hours before the next administration, the nurse can accurately determine both the peak and trough levels, providing crucial information for evaluating the client's response to the medication and adjusting the dosage as needed.
Choice B rationale: While this option may provide some information, it does not allow for an accurate determination of both the peak and trough levels. The peak level should be drawn closer to the completion of the infusion (around 30 minutes), and the trough level should be drawn just before the next dose (within 30 minutes).
Choice C rationale: This timing does not allow for accurate peak and trough level determination. The peak level should be drawn closer to the completion of the infusion (around 30 minutes), and the trough level should be drawn just before the next dose (within 30 minutes).
Choice D rationale: Immediately after completion of the IV dose and 30 minutes before the next administration of the medication: Drawing the peak level immediately after the completion of the IV dose may not accurately reflect the highest drug concentration in the bloodstream. The peak level should be drawn around 30 minutes after completion of the infusion for accurate determination. Additionally, the trough level should be drawn within 30 minutes before the next dose, not necessarily 30 minutes before the next administration.
A male client with a history of heart failure (HF) complains of heartburn when he lies down after dinner.
The home health nurse should encourage the client to talk to the healthcare provider about using which over-the-counter medication to relieve this problem?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Heartburn when lying down after dinner can be a symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which is a common concern in individuals with heart failure. Antacids are commonly used to relieve heartburn by neutralizing stomach acid. For patients with heart failure, it is essential to use low sodium antacids because excess sodium intake can worsen fluid retention and lead to increased heart failure symptoms. Low sodium antacids are specifically designed to minimize the sodium content, making them a suitable choice for individuals with heart failure.
Choice B rationale: Diphenhydramine is an antihistamine commonly used for allergy relief and as a sleep aid due to its sedative effects. However, it is not an appropriate choice for relieving heartburn. Diphenhydramine does not have any direct effect on stomach acid, and it is not indicated for GERD or heartburn relief.
Choice C rationale: Low dose aspirin is primarily used as an antiplatelet agent to reduce the risk of blood clots and is commonly prescribed for patients with certain cardiovascular conditions. However, it is not a suitable medication for relieving heartburn. In fact, aspirin can irritate the stomach lining and worsen symptoms of heartburn and gastric irritation.
Choice D rationale: Acetaminophen is a common over-the-counter pain reliever and fever reducer. While it is useful for managing pain and fever, it does not have any effect on stomach acid and is not indicated for heartburn relief. Acetaminophen is not an appropriate choice for addressing heartburn symptoms.
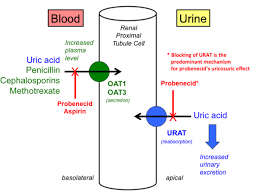
The nurse is providing instructions about a client's new medications. How should the nurse explain the purpose of probenecid, a uricosuric drug?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Probenecid does not prevent kidney stones. Its primary function is to increase the excretion of uric acid in the urine.
Choice B rationale: Probenecid does not affect the strength of the urine stream. Its action is specific to uric acid excretion.
Choice C rationale: Probenecid is not used to alleviate pain and burning during urination. Its main indication is for gout and hyperuricemia.
Choice D rationale: Probenecid is a uricosuric drug used to treat gout and hyperuricemia. It works by inhibiting the reabsorption of uric acid in the kidneys, which promotes its excretion in the urine. By increasing uric acid excretion, probenecid helps to reduce the concentration of uric acid in the blood and prevent gout attacks.
A client receives a new prescription for levothyroxine. Which statement made by client indicates to the nurse the education was effective?
Explanation
The correct answer is D.
Choice A rationale: While iodine is essential for thyroid hormone synthesis, it is not relevant to the administration of levothyroxine. The client does not need to consume foods high in iodine specifically for taking levothyroxine.
Choice B rationale: While iron supplements can interfere with the absorption of levothyroxine, this statement does not indicate that the client understands when to take levothyroxine correctly.
Choice C rationale: Levothyroxine should be taken in the morning, not at bedtime, to avoid interference with sleep and to optimize absorption.
Choice D rationale: Levothyroxine, a thyroid hormone replacement, should be taken on an empty stomach, preferably in the morning, at least 30 minutes before eating. Taking it on an empty stomach maximizes its absorption and ensures optimal therapeutic effects.
The nurse prepares to administer a scheduled dose of labetalol by mouth to a client with hypertension. The client's vital signs are temperature 99° F (37.2° C), heart rate 48 beats/minute, respirations 16 breaths/minute, and blood pressure (B/P) 150/90 mm Hg. Which action should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Administering the dose of labetalol without further assessment may not be appropriate in this situation. The client's heart rate is 48 beats/minute, which is considered bradycardia (heart rate below the normal range of 60-100 beats/minute). Bradycardia can be a potential adverse effect of labetalol, a beta-blocker. Moreover, the client's blood pressure is elevated at 150/90 mm Hg, indicating that the hypertension is not well controlled. Administering the dose without addressing the bradycardia or elevated blood pressure could potentially exacerbate these issues.
Choice B rationale: Withholding the scheduled dose of labetalol is the most appropriate action in this scenario. The client's heart rate of 48 beats/minute is considered bradycardia, which may be a side effect of labetalol or indicative of an underlying issue. Additionally, the client's blood
pressure is elevated, indicating inadequate control of hypertension. Bradycardia can reduce cardiac output and may lead to further complications. Notifying the healthcare provider is essential to obtain further instructions and address the client's bradycardia and hypertension before administering the medication.
Choice C rationale: While telemetry monitoring is appropriate for clients with certain cardiac conditions or when changes in heart rate need close observation, it may not be the most urgent action in this situation. The client's bradycardia and elevated blood pressure are concerning and require immediate attention. Telemetry monitoring may be considered later, but it does not address the immediate need to withhold the medication and seek guidance from the healthcare provider.
Choice D rationale: Orthostatic hypotension refers to a drop in blood pressure when changing positions, such as from lying down to standing up. While orthostatic hypotension is a valid concern for clients taking antihypertensive medications, it is not the primary issue in this scenario. The client's heart rate is 48 beats/minute, indicating bradycardia and the blood pressure is elevated at 150/90 mm Hg, suggesting uncontrolled hypertension. These are the main concerns that require immediate attention and further assessment before administering the labetalol dose.
While assessing a client who takes acetaminophen for chronic pain, the nurse observes that the client's skin looks yellow in color. Which action should the nurse take in response to this finding?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Checking the capillary glucose level is not relevant to the observation of yellow skin color. Jaundice is related to liver function, not glucose levels.
Choice B rationale: Oxygen saturation measurement is not relevant to the observation of yellow skin color. It is used to assess the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood, not liver function.
Choice C rationale: Yellow discoloration of the skin (jaundice) can be indicative of liver dysfunction or damage. Since the client takes acetaminophen for chronic pain, which is metabolized in the liver, the nurse should be concerned about potential hepatotoxicity. Reporting the findings to the healthcare provider is essential for further evaluation and management.
Choice D rationale: Reducing the medication dose is not appropriate without further evaluation and guidance from the healthcare provider. Jaundice may indicate liver dysfunction, and altering the medication without professional assessment could be unsafe.
The nurse is administering sodium polystyrene sulfonate to a client in acute kidney injury (AKI). Which laboratory finding indicates that the medication has been effective?
- Glucose [Reference Range: 74 to 106 mg/dL (4.1 to 5.9 mmol/L)]
- Hemoglobin (Hgb) [Reference Range:12-16 g/dL (120-160 g/L)]
- Potassium (K+) [Reference Range: 3.5 to 5.0 mEq/L (3.5 to 5.0 mmol/L)]
- Ammonia [Reference Range: Adult: 10 to 80 Mcg/dL (6 to 47 Mcmol/dL)]
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Serum ammonia levels are not relevant to the effectiveness of sodium polystyrene sulfonate in treating hyperkalemia.
Choice B rationale: Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is a medication used to treat hyperkalemia (high potassium levels). A serum potassium level of 3.8 mEq/L falls within the normal reference range (3.5 to 5.0 mEq/L), indicating that the medication has been effective in promoting the excretion of potassium and reducing hyperkalemia.
Choice C rationale: Serum glucose levels are not relevant to the effectiveness of sodium polystyrene sulfonate in treating hyperkalemia.
Choice D rationale: Hemoglobin levels are not relevant to the effectiveness of sodium polystyrene sulfonate in treating hyperkalemia.
The nurse is caring for a client who has been taking ibuprofen. Which finding is most important for the nurse report to the healthcare provider?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Hematemesis refers to the vomiting of blood and is a severe and potentially life-threatening adverse effect of ibuprofen. Ibuprofen belongs to the class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can cause gastrointestinal bleeding and ulcerations.
Hematemesis indicates significant gastrointestinal irritation or bleeding, and it requires immediate attention from the healthcare provider to assess and manage the client's condition.
Choice B rationale: Nausea is a common side effect of ibuprofen and other NSAIDs. While it is important to monitor and address any adverse effects experienced by the client, nausea alone is not as urgent or critical as hematemesis, which can indicate a more severe complication.
Choice C rationale: Insomnia is not directly related to the use of ibuprofen. While sleep disturbances can occur as a side effect of some medications, it is not the most important finding to report to the healthcare provider in this context.
Choice D rationale: Dizziness can be a side effect of ibuprofen, but it is not the most concerning finding in this situation. Hematemesis, which indicates potential gastrointestinal bleeding, is a more critical symptom that requires immediate attention and reporting to the healthcare provider.
After taking orlistat for one week, a female client tells the home health nurse that she is experiencing increasingly frequent oily stools and flatus. Which action should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: This option is not appropriate as increasing saturated fat intake would exacerbate the oily stool and flatus symptoms caused by orlistat. Orlistat is specifically designed to reduce fat absorption, and increasing fat intake would be counterproductive and may worsen the side effects.
Choice B rationale: While it is important to assess the client's dietary intake history, it may not provide specific insights into the cause of the oily stools and flatus. These symptoms are well-
known side effects of orlistat, and it is not necessary to gather dietary history information to confirm this. Instead, the focus should be on addressing the side effects and discussing the continuation of the medication with the healthcare provider.
Choice C rationale: The client is experiencing increasingly frequent oily stools and flatus, which are common side effects of orlistat. Orlistat is a medication used to aid weight loss by inhibiting the absorption of dietary fats in the intestines. By blocking the enzyme responsible for breaking down fats, orlistat prevents the absorption of a portion of the dietary fat, leading to increased fat content in the stool.
Choice D rationale: While obtaining a stool specimen for evaluation might be relevant in some situations, it is not the priority in this case. The oily stools and flatus are most likely related to the side effects of orlistat and do not typically require stool testing for confirmation. The more immediate action would be to address the symptoms by advising the client to stop taking the medication and contact her healthcare provider for further guidance.
An older adult with iron deficiency anemia is being discharged with a prescription for ferrous sulfate enteric-coated tablets. To promote best absorption of the medication, which information should the nurse include in the discharge instructions?
Explanation
Choice A rationale; Taking ferrous sulfate at bedtime does not have a significant impact on its absorption. The critical factor is to take it on an empty stomach to maximize absorption, not necessarily at a specific time of day.
Choice B rationale: Enteric-coated tablets are specifically designed to dissolve in the small intestine and not in the stomach. Crushing them would destroy the enteric coating, leading to iron being released in the stomach, which can cause gastric irritation and reduce iron absorption.
Choice C rationale: Iron absorption is influenced by food intake. Taking ferrous sulfate on an empty stomach (at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals) enhances its absorption. When taken with food, especially foods containing calcium, the absorption of iron can be significantly
reduced. Therefore, it is essential to instruct the client to wait at least 2 hours after meals before taking the enteric-coated tablets to optimize iron absorption.
Choice D rationale: Taking ferrous sulfate with a multivitamin may not be ideal for iron absorption. Some multivitamins contain calcium or other minerals that can inhibit iron absorption. To maximize iron absorption, it is best to take ferrous sulfate on an empty stomach, as mentioned in option C.
The nurse initiates an infusion of piperacillin-tazobactam for a client with a urinary tract infection. Five minutes into the infusion, the client reports not feeling well. Which client manifestation should the nurse identify as a reason to stop the infusion?
Explanation
Choice A rationale; A scratchy throat is not a common or significant side effect of piperacillin- tazobactam infusion. While it's essential to monitor for any signs of allergic reactions, a scratchy throat alone is not a definitive reason to stop the infusion.
Choice B rationale: Pupillary constriction is not a known side effect of piperacillin-tazobactam. It is not a significant concern in this context and does not warrant stopping the infusion.
Choice C rationale: Piperacillin-tazobactam is an antibiotic combination used to treat various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections. However, it can cause adverse reactions, and one of the potential side effects is hypertension (high blood pressure). If the client experiences hypertension during the infusion, it could be an indication of an allergic or adverse reaction to the medication, and the infusion should be stopped immediately to prevent further complications.
Choice D rationale: Bradycardia (slow heart rate) is not a common side effect of piperacillin-tazobactam infusion. It is not a typical manifestation of an allergic or adverse reaction to the medication, and stopping the infusion based on bradycardia alone would not be warranted.
A client with anemia secondary to chronic kidney disease (CKD) started a prescription for epoetin alfa two months ago. Which client finding best indicates that the medication is effective?
Reference Range
- Hemoglobin (Hgb) [Reference Range: Male: 14 to 18 g/dL (8.7 to 11.2 mmol/L)]
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Hemoglobin level increased to 12 g/dL (7.45 mmol/L) might be a positive sign, but it is not the best indicator of effectiveness. Improvement in symptoms is a more reliable measure.
Choice B rationale: Epoetin alfa is a synthetic form of erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates the production of red blood cells. In clients with anemia, especially due to CKD, epoetin alfa is given to increase the production of red blood cells and improve hemoglobin levels. The best indicator of its effectiveness is an improvement in anemia-related symptoms, such as increased energy levels and decreased fatigue, which are associated with improved oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
Choice C rationale: A food diary shows that increased consumption of iron-rich foods may be beneficial for a client with anemia, but it is not a direct indicator of the medication's effectiveness.
Choice D rationale: Taking concurrent iron therapy without adverse effects is not a specific indicator of epoetin alfa effectiveness. Iron therapy is usually prescribed to treat iron deficiency anemia, not anemia due to CKD.
The nurse is preparing a discharge teaching plan for a client who is taking ciprofloxacin hydrochloride tablets, which were prescribed because of a suspected anthrax exposure. Which instruction(s) should be included in the teaching plan? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Crushing ciprofloxacin tablets may interfere with their efficacy, and it is generally not recommended to alter the dosage form without consulting a healthcare provider.
Choice B rationale: Ciprofloxacin may cause joint aches and pains, but using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is generally not advised as they can interact with the medication and increase the risk of adverse effects.
Choice C rationale: Ciprofloxacin is associated with the risk of tendonitis and tendon rupture. Therefore, any tendon pain or swelling should be reported immediately to the healthcare provider.
Choice D rationale: Increasing fluid intake while taking ciprofloxacin can help prevent crystalluria, a potential side effect of the medication.
Choice E rationale: Ciprofloxacin can make the skin more sensitive to sunlight, leading to an increased risk of sunburn. Patients should limit exposure to sunlight and avoid tanning beds while taking this medication.
A client with heart failure (HF) develops hyperaldosteronism and spironolactone is prescribed.
Which instruction should the nurse include in this client's plan of care?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: This instruction is not directly related to spironolactone use or hyperaldosteronism. Excessive bruising may be relevant in some situations but not specifically for this scenario.
Choice B rationale: While heart failure patients are often advised to reduce their sodium intake, the use of a salt substitute (potassium-based) would be contraindicated in this case due to the risk of hyperkalemia.
Choice C rationale: This instruction is not directly related to spironolactone use or
hyperaldosteronism. It may be relevant for sun protection, but it is not a priority in this context.
Choice D rationale: Spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic, which means it helps the body retain potassium while excreting sodium and water. Since the client has heart failure (HF), there is a risk of hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) associated with spironolactone use. To prevent this, the nurse should instruct the client to limit their intake of high-potassium foods, such as bananas, oranges, tomatoes, spinach, and other potassium-rich foods.
Find information about a client below.
What should the nurse double-check with a second nurse? Select all that apply.
Explanation
Choice A rationale: This is essential to ensure that the insulin is not discolored or cloudy, as these changes could indicate a problem with the insulin's stability or effectiveness.
Choice B rationale: While it is essential to have a complete history and physical for proper patient care, double-checking this with another nurse is not necessary in the immediate administration of insulin lispro.
Choice C rationale: Double-checking the dose of insulin in the syringe is crucial to avoid medication errors and ensure that the correct amount is being administered to the patient.
Choice D rationale: The sliding scale order is not mentioned in the information provided, and since it is not part of the immediate insulin administration, it does not need to be double-checked in this context.
Choice E rationale: Checking the expiration date is necessary to ensure that the insulin is still within its usable period. Using expired insulin can lead to reduced potency and potentially ineffective blood sugar control.
Choice F rationale: The information provided in the nurse's notes does not indicate that insulin administration is due at a specific site (e.g., subcutaneous injection). Therefore, there is no need for a second nurse to double-check the site at this moment. However, it's important for the administering nurse to choose the appropriate site following the facility's guidelines and rotate injection sites to prevent lipodystrophy.
Choice G rationale: Different types of insulin come in different concentrations (e.g., U-100, U-200). It's important to confirm that the correct concentration is being used to ensure accurate dosing.
Choice H rationale: The nurse should verify that the insulin to be administered is indeed insulin lispro, as indicated in the medication order. Administering the wrong type of insulin can have significant implications for the patient's blood sugar control.
History and Physical Nurses' Notes
The client is a 26-year-old female with acute appendicitis. She has a 12-year history of type 1 diabetes and no other significant medical history. The appendectomy was completed without issue, and the client will be admitted to the surgical floor to recover.
Nurses notes and Laboratory Results
0730
Admitted the client. She is awake and alert. She rates her pain 2/10. Her pulses are equal bilaterally. Heart rate is 76 beats per minute, normal sinus rhythm. Her oxygen saturation is 100% on room air. She has a gauze dressing over her surgical site, which is clean and dry. Her temperature is 98.5° F (37° C). She urinated 50 ml upon arrival in the unit and is stating she is very thirsty. The patient states her last insulin glargine dose was this morning before surgery.
Flow Sheet
0745
2 units insulin lispro given
1800
12 units insulin glargine given
The client ate 45 carbohydrates from her dinner tray. 3 units of insulin lispro given.
Orders
- Admit to the surgical floor
- Dextrose 5% and 0.9% sodium chloride to infuse at 125 mL/hr
- Advance diet as tolerated
- Insulin glargine 12 units subcutaneous every 12 hours
- Ceftriaxone 2 g IV every 24 hours for 3 days, first dose given in surgery
- Insulin lispro 1 unit subcutaneously per 15 carbohydrates
The nurse is preparing the client for discharge and discussing home medications. What home medications may affect the amount of insulin needed by the client? Select all that apply.
Explanation
Choice A rationale: St. John's Wort is an herbal supplement that can interact with various medications, including insulin, and may alter blood glucose levels. It can reduce the effectiveness of insulin, leading to decreased blood glucose control. It is essential for the client to inform the healthcare provider about any use of St. John's Wort to adjust the insulin regimen accordingly.
Choice B rationale: Corticosteroids can increase blood glucose levels by promoting insulin resistance and inhibiting insulin action. Clients with diabetes may require adjustments in their insulin dosage while taking corticosteroids to prevent hyperglycemia.
Choice C rationale: Fluconazole is an antifungal medication that can affect blood glucose levels. It may increase the hypoglycemic effects of insulin, leading to lower blood glucose levels. The
client's insulin regimen may need to be adjusted while taking fluconazole.
Choice D rationale: Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that does not typically have a direct impact on blood glucose levels in people with diabetes.
Choice E rationale: Epinephrine is a hormone that may transiently increase blood glucose levels in response to stress, but it is not a home medication that the client would be taking regularly.
Choice F rationale: Oral contraceptives, specifically combination hormonal contraceptives containing estrogen and progestin, can impact blood glucose levels. They may lead to insulin resistance and, in some cases, increase blood glucose levels. The healthcare provider may need to adjust the insulin dosage for better glycemic control.
Find information about a client below.
The client is in the provider’s office for a physical. He states that he has been monitoring his blood pressure, but it is continuing to go up.
The physician has given the client a prescription for captopril.
Choose the most likely options for the information missing from the statement(s) by selecting from the lists of options provided.
Captopril is a ____________ that works by _________________.
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a different class of
medications commonly used to relieve pain, inflammation, and reduce fever. They are not used
for treating hypertension or acting as ACE inhibitors.
Choice B rationale: Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are another class of
antihypertensive medications that work by blocking the action of angiotensin II, a hormone that
causes blood vessels to constrict. While ARBs are similar in function to ACE inhibitors in
managing blood pressure, captopril specifically belongs to the ACE inhibitor class.
Choice C rationale: Captopril is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. ACE
inhibitors are a class of antihypertensive medications that work by inhibiting the enzyme ACE,
which converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II. By inhibiting this conversion, ACE inhibitors
help relax and dilate blood vessels, leading to decreased blood pressure. They are commonly
used to treat hypertension and other cardiovascular conditions.
Choice D rationale: Aldosterone antagonists are a different class of medications used to block the
action of aldosterone, a hormone that regulates sodium and water balance in the body. They are
used to manage conditions such as heart failure and hypertension but are not synonymous with ACE inhibitors like captopril.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 36 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

