Exam Review
Hesi PN Exit Exam Three
Total Questions : 150
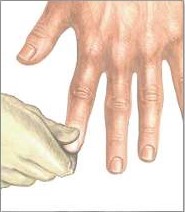
Showing 10 questions, Sign in for moreThe practical nurse (PN) applies and then releases pressure to a client's fingernail as seen in the photo. Normal nail color returns in 2 seconds. Which action should the PN take?
Explanation
- Capillary refill time is a test that measures how quickly the blood returns to the tissues after pressure is applied and released on a nailbed or a fingertip. It is an indicator of peripheral circulation and tissue perfusion.
- To perform the capillary refill test, the examiner should press firmly on the nailbed or fingertip for a few seconds, then release the pressure and observe how long it takes for the normal color to return. The normal capillary refill time is less than 2 seconds .
- In the photo, the practical nurse (PN) applies and then releases pressure to a client's fingernail. Normal nail color returns in 2 seconds, which indicates a normal capillary refill time and adequate peripheral circulation. This is a normal and expected finding that does not require any further action, except for documentation.
- Therefore, option D is the correct answer, as it reflects the appropriate and standard nursing practice of documenting any assessment findings in the client's chart. Option D also implies that the PN does not need to report, observe, or repeat anything else related to the capillary refill test, as it was done correctly and yielded normal results.
- Options A, B, and C are incorrect answers, as they do not reflect the appropriate or necessary actions for the PN to take after performing a normal capillary refill test.
A client who had a knee replacement surgery and received a prescription for enoxaparin 30 mg subcutaneously every 12 hours for 10 days. The medication is available in 30 mg per 0.3 mL pre-filled syringes. How many mL should the practical nurse (PN) administer each day? (Enter numerical value only.)
Explanation
To calculate how many milliliters (mL) the practical nurse (PN) should administer each day, we can first determine the total daily dosage of enoxaparin.
The prescribed dosage is 30 mg every 12 hours, so the total daily dosage is:
30 mg + 30 mg = 60 mg
Next, we can calculate the number of milliliters (mL) needed to deliver the total daily dosage. Since the medication is available in a concentration of 30 mg per 0.3 mL, we can set up a proportion to find the equivalent mL for 60 mg:
30 mg / 0.3 mL = 60 mg / x mL
Cross-multiplying, we get:
30 mg * x mL = 60 mg * 0.3 mL
30x = 18
Dividing both sides by 30, we find:
x = 0.6 mL
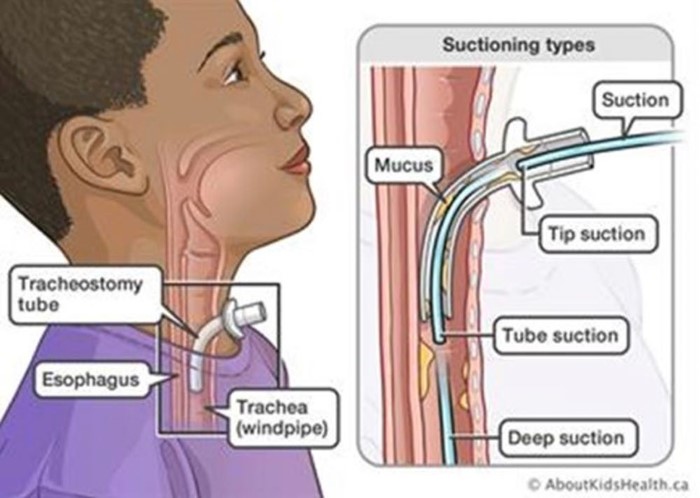
In caring for a client who requires seizure precautions, the practical nurse (PN) should ensure the ready availability of equipment to perform which procedure?
Explanation
- Seizure precautions are measures taken to protect a client who is at risk of having a seizure, which is a sudden and abnormal electrical activity in the brain that can cause changes in behavior, movement, sensation, or consciousness. Seizure precautions include providing a safe environment, monitoring the client's vital signs and neurological status, administering anticonvulsant medications, and documenting the onset, duration, and characteristics of any seizure activity.
- One of the potential complications of a seizure is aspiration, which is the inhalation of foreign material into the lungs, such as saliva, vomit, or food. Aspiration can cause choking, pneumonia, or respiratory distress. To prevent or treat aspiration, the practical nurse (PN) should ensure the ready availability of equipment to perform suctioning of the trachea, which is the tube that connects the mouth and nose to the lungs. Suctioning of the trachea involves inserting a catheter through the nose or mouth into the trachea and applying negative pressure to remove any secretions or debris from the airway.
- Therefore, option A is the correct answer, while options B, C, and D are incorrect.
The practical nurse (PN) is told that she keeps her 2-year-old child in a playpen so he will not get dirty. Which statement should the PN use in responding to this concern about using a playpen?
Explanation
- A playpen is a portable enclosure that provides a confined space for a child to play in. It can be useful for keeping a child safe and supervised when the caregiver is busy or needs a break, but it should not be used as a substitute for active play or interaction with the caregiver or others.
- A 2-year-old child is in the developmental stage of toddlerhood, which is characterized by rapid physical, cognitive, social, and emotional growth. Toddlers are curious and eager to learn about the world around them, and they need opportunities to explore, experiment, and manipulate objects and materials. They also need stimulation, guidance, and feedback from their caregivers and peers to develop their language, problem-solving, and social skills.
- Keeping a 2-year-old child in a playpen for long periods of time or to prevent them from getting dirty can have negative effects on their development and well-being. It can limit their physical activity, creativity, and independence, and it can cause boredom, frustration, or resentment . It can also interfere with their attachment and bonding with their caregiver, as well as their self-esteem and self-image.
- Therefore, the practical nurse (PN) should use the statement "Children need time to actively explore their environment" in responding to this concern about using a playpen. This statement reflects the developmental needs and rights of the child, and it encourages the caregiver to provide a more stimulating and supportive environment for the child. It also implies that getting dirty is not a problem, but rather a natural and healthy part of play and learning.
- Therefore, option D is the correct answer, while options A, B, and C are incorrect. Option A is incorrect because it is judgmental and may offend or discourage the caregiver.

At the first dressing change, the practical nurse (PN) tells the client that her mastectomy incision is healing well, but the client refuses to look at the incision and refuses to talk about it. Which response by the PN to the client's silence is best?
Explanation
- A mastectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of all or part of the breast, usually to treat breast cancer. A mastectomy can have a significant impact on a woman's physical, emotional, and psychological well-being, as it may affect her body image, self-esteem, sexuality, and identity.
- A mastectomy incision is the wound that results from the surgery, which may vary in size, shape, and location depending on the type and extent of the mastectomy. The incision may be closed with stitches, staples, or glue, and covered with a dressing or bandage.
- The first dressing change is usually done within 24 to 48 hours after the surgery, and it involves removing the old dressing, inspecting the incision for any signs of infection or complications, cleaning the wound, applying a new dressing, and educating the client about wound care .
- When the practical nurse (PN) tells the client that her mastectomy incision is healing well, but the client refuses to look at the incision and refuses to talk about it, this may indicate that the client is experiencing denial, fear, anger, grief, or depression due to the loss of her breast. These are normal and common reactions that may occur at different stages of the recovery process.
- The best response by the PN to the client's silence is to acknowledge and respect the client's feelings, provide support and reassurance, and offer assistance when needed. This will help to establish trust and rapport with the client, as well as promote her coping and adjustment.
- Therefore, option A is the best answer, as it shows empathy and respect for the client's feelings, while also informing the client that the PN will be available when she is ready to look or talk about the mastectomy. Option A also implies that the PN will not pressure or force the client to do something that she is not comfortable with.
- Options B, C, and D are incorrect answers, as they do not show empathy or respect for the client's feelings, and they may cause more harm than good.
Prior to giving digoxin, the practical nurse (PN) assesses that a 2-month-old infant's heart rate is 120 beats/minute. Based on this finding, what action should the PN take?
Explanation
This is the correct answer. Holding the medication allows for further evaluation of the heart rate after some time. Rechecking the heart rate in 1 hour helps to assess if the heart rate has returned to a normal range.
This allows for safer medication administration and appropriate management based on the reevaluation of the heart rate.
Digoxin is a medication used to treat certain heart conditions, and it affects the heart rate. In infants, the normal heart rate range is generally higher than in adults. However, a heart rate of 120 beats per minute in a 2-month-old infant is considered high. Before administering digoxin, it is important for the practical nurse (PN) to assess the infant's heart rate and determine if it falls within the expected range.
In this scenario, since the heart rate of the infant is 120 beats per minute, which is elevated, the appropriate action for the PN is to hold the medication. This means that the PN should not administer the digoxin at that time. Instead, the PN should document the cardiac assessment, which includes noting the heart rate of 120 beats per minute.
Furthermore, it is necessary to recheck the infant's heart rate in 1 hour. This is important because the heart rate can fluctuate, and it is essential to ensure that the heart rate has returned to an appropriate range before administering any medication that affects cardiac function, such as digoxin. Based on the reevaluation of the heart rate after 1 hour, further actions can be determined, such as administering the medication if the heart rate has returned to an acceptable range or consulting with the charge nurse for further guidance.

Which information should the practical nurse (PN) collect during the admission assessment of a terminally ill client to an acute care facility?
Explanation
- A terminally ill client is a client who has a progressive and incurable disease or condition that is expected to result in death within a short period of time, such as months or weeks. A terminally ill client may require palliative care, which is the care that focuses on relieving pain and suffering and improving the quality of life for the client and their family.
- An admission assessment is the process of collecting information about a client's health status, needs, preferences, and goals when they are admitted to a health care facility, such as a hospital, nursing home, or hospice. An admission assessment helps to establish a baseline for the client's condition, plan and implement appropriate interventions, and evaluate the outcomes of care.
- A health care proxy is a legal document that allows a client to appoint another person, such as a family member or a friend, to make health care decisions for them if they become unable to do so themselves. A health care proxy may also include specific instructions or preferences about the type and extent of care that the client wishes to receive or refuse, such as life-sustaining treatments, resuscitation, or organ donation.
- Health care proxy documentation is important information that the practical nurse (PN) should collect during the admission assessment of a terminally ill client to an acute care facility, as it reflects the client's autonomy, dignity, and wishes regarding their end-of-life care. It also helps to ensure that the client's healthcare decisions are respected and followed by the healthcare team and the facility.
- Therefore, option A is the correct answer, while options B, C, and D are incorrect.
The practical nurse (PN) learns that a client who is receiving chemotherapy has developed stomatitis. Which information should the PN obtain from the client during a focused assessment?
Explanation
Stomatitis refers to the inflammation of the mouth and oral mucosa, which can cause pain and difficulty swallowing. In the context of a client receiving chemotherapy, stomatitis is a common side effect that can occur due to the effects of chemotherapy on rapidly dividing cells, including those in the oral cavity. When a client develops stomatitis, it is important for the practical nurse (PN) to obtain information about the client's ability to swallow during a focused assessment. This is because stomatitis can significantly impact a client's ability to eat and drink comfortably, which can lead to dehydration and malnutrition. Assessing the client's ability to swallow helps determine the extent of the issue and guides appropriate interventions and support.
A male client tells the practical nurse (PN) that the pill he has been taking at home is a different color and size than the one the PN is trying to give him now. How should the PN respond?
Explanation
- Medication administration is a process that involves prescribing, dispensing, and giving medications to patients. It is a critical and complex task that requires accuracy, safety, and adherence to the rights of medication administration, such as the right patient, right drug, right dose, right route, right time, right documentation, and right response.
- When a male client tells the practical nurse (PN) that the pill he has been taking at home is a different color and size than the one the PN is trying to give him now, this may indicate a potential medication error
or discrepancy. A medication error is any preventable event that may cause or lead to inappropriate medication use or patient harm. A medication discrepancy is any difference between the current and previous medication regimens of a patient.
- The PN should respond to the client's concern by telling him that the PN will verify that the dispensed medication is a valid prescription. This means that the PN will check the medication label, the medication order, and the medication administration record (MAR) to confirm that the medication given to the client matches the one prescribed by the healthcare provider. The PN will also compare the dispensed medication with a drug reference guide or a picture of the medication to ensure that it is the correct drug and dosage form. The PN will also report any suspected errors or discrepancies to the healthcare provider or the pharmacy for clarification or correction.
- Options A, B, and D are incorrect answers, as they do not reflect the appropriate or responsible actions for the PN to take when faced with a possible medication error or discrepancy.
A client reports experiencing numbness and tingling in the extremities. Which of the client's serum laboratory values should the practical nurse (PN) prioritize reporting to the healthcare provider?
Explanation
When a client reports experiencing numbness and tingling in the extremities, it is crucial for the practical nurse (PN) to prioritize reporting the client's electrolyte levels to the healthcare provider. Electrolytes are essential minerals that help maintain the balance of fluids in the body and enable proper nerve and muscle function. Imbalances in electrolyte levels can lead to neurological symptoms, including numbness and tingling.
Options a, b, and d are not the correct priorities to report in this situation:

Sign Up or Login to view all the 150 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

