Indiana University OB-Maternal exam 3
Total Questions : 45
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA client in her first trimester of pregnancy is scheduled for an ultrasound.
Which of the following would not be a reason for an ultrasound at this stage?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Fetal position during the first trimester is not definitively determined through ultrasound. While the gestational sac and fetal pole can be visualized, the fetus is still quite small and has ample space to move within the amniotic sac. This makes it challenging to accurately ascertain its position.
Reliable assessment of fetal position typically occurs later in pregnancy, usually between 34 and 36 weeks gestation. At this point, the fetus is larger and less mobile, allowing for a clearer assessment of its position through ultrasound.
The early determination of fetal position in the first trimester is not a primary goal of ultrasound. It is more focused on establishing pregnancy viability, gestational age, and detecting any potential abnormalities.
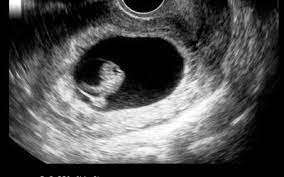
Choice B rationale:
Ultrasound in the first trimester can reliably detect multiple gestations. It can visualize the presence of multiple gestational sacs or fetal poles, clearly indicating whether a woman is carrying twins, triplets, or more.
Early identification of multiple gestations is crucial for optimal pregnancy management. It allows healthcare providers to tailor prenatal care, monitor for potential complications associated with multiple pregnancies, and plan for appropriate delivery. Choice C rationale:
Ultrasound in the first trimester can assist in detecting certain maternal abnormalities that could impact pregnancy. These may include:
Uterine abnormalities, such as fibroids or structural defects
Ovarian cysts
Ectopic pregnancies (where the embryo implants outside the uterus)
Gestational trophoblastic disease (abnormal growth of tissue inside the uterus)
Early identification of these maternal abnormalities allows for timely intervention and management, ensuring the best possible outcomes for both mother and fetus.
Choice D rationale:
Confirming pregnancy is a primary reason for ultrasound in the first trimester. It can visualize the gestational sac, which contains the developing embryo and confirms the presence of a pregnancy.
Ultrasound can also detect the fetal heartbeat, which typically becomes visible between 6 and 8 weeks gestation. This provides further confirmation of a viable pregnancy.
A pregnant client, who is 35 weeks along, comes in for weekly fetal heart monitoring.
After 20 minutes on the monitor, the fetal heart rate tracing shows three accelerations measuring 15 beats by 15 seconds.
How should the nurse report this finding to the provider?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
A positive contraction stress test (CST) indicates a potential problem with the fetal heart's response to uterine contractions, not spontaneous accelerations.
It's not consistent with the findings in this scenario.
Choice C rationale:
A negative CST would show no late decelerations in response to contractions, but it's not relevant here because contractions weren't induced.
Choice D rationale:
A non-reactive NST lacks the required accelerations, which are present in this case.
Choice B rationale:
Definition of reactive NST: A reactive NST is a reassuring fetal heart test that demonstrates a healthy fetal heart rate response to fetal movement. It's characterized by two or more fetal heart rate accelerations of at least 15 beats per minute (bpm) lasting at least 15 seconds within a 20-minute period.
Significance of the findings: The presence of three accelerations measuring 15 bpm by 15 seconds within 20 minutes meets the criteria for a reactive NST. This suggests that the fetal nervous system is functioning well and responding appropriately to stimuli, indicating a healthy fetal heart rate pattern.
Nurse's reporting: The nurse should accurately report this finding to the provider as a "reactive nonstress test (NST)." This information is crucial for clinical decision-making regarding the ongoing management of the pregnancy.
A pregnant client is undergoing a nipple-stimulated contraction stress test (CST). She is experiencing contractions every three minutes.
The fetal heart rate (FHR) baseline is approximately 120 beats/min with no decelerations.
How should the nurse document this test?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Satisfactory is not a standard interpretation for a contraction stress test (CST).
While a normal FHR with no decelerations is generally reassuring, the specific terminology used for a negative CST is "negative."
Using "satisfactory" could lead to potential ambiguity or misunderstanding among healthcare professionals.
Choice B rationale:
Unsatisfactory is used when the CST results are inconclusive or concerning for fetal well-being.
This typically occurs when there are late decelerations in the FHR, suggesting uteroplacental insufficiency and potential fetal hypoxia.
However, in this scenario, there are no decelerations, so "unsatisfactory" is not an appropriate interpretation.
Choice C rationale:
Negative is the correct interpretation for a CST when there are no late decelerations in the FHR, even in the presence of adequate contractions.
A negative CST indicates a reassuring fetal response to stress and suggests that the fetus is likely to tolerate labor without significant compromise.
This is the most accurate and appropriate interpretation for the given findings.
Choice D rationale:
Positive is used when there are late decelerations in the FHR during the CST.
Late decelerations are a sign of uteroplacental insufficiency, which can potentially lead to fetal hypoxia and acidosis.
A positive CST often warrants further evaluation and assessment of fetal well-being, and may even necessitate interventions such as early delivery.
However, in the absence of late decelerations, a positive CST result is not applicable.
A couple is struggling with infertility and wants to know how to maintain their emotional balance.
Which response from the nurse would be most appropriate?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Joining a support group can be beneficial. I can provide some recommendations.
Support groups offer a safe and supportive environment where couples can share their experiences, feelings, and coping strategies with others who understand what they are going through. This can be incredibly helpful in reducing isolation, normalizing their emotions, and promoting a sense of hope. Support groups can also provide valuable information and resources about infertility, treatment options, and coping strategies. Additionally, they can help couples develop a sense of community and belonging, which can be especially important during a challenging time.
I can provide some recommendations for support groups in your area. This demonstrates the nurse's willingness to help the couple find the resources they need and underscores the value of support groups in managing infertility.
Choice B rationale:
Share your situation with friends and family so they can provide support.
While sharing with friends and family can be helpful for some couples, it's important to recognize that not everyone may be able to provide the kind of support that is needed. Some friends and family members may not understand the challenges of infertility or may offer unsolicited advice, which can be hurtful. Additionally, couples may not feel comfortable sharing such personal information with their loved ones. It's important to respect the couple's privacy and preferences in this regard.
Choice C rationale:
Start adoption proceedings immediately as it can be challenging to adopt an infant.
This response is not appropriate as it does not address the couple's immediate concern, which is how to maintain their emotional balance while dealing with infertility. It also assumes that the couple is interested in adoption, which may not be the case. While adoption can be a wonderful option for some families, it's a major decision that requires careful consideration and should not be rushed into.
Choice D rationale:
Speak only with other friends who are dealing with infertility as they can provide the most help.
While connecting with others who are experiencing infertility can be helpful, it's important not to isolate oneself from other sources of support. Friends and family who are not dealing with infertility can still offer valuable support, understanding, and companionship. It's important to have a variety of supportive relationships in one's life.
A 24-year-old woman arrives at the clinic to confirm her pregnancy.
She has a body mass index (BMI) of 17, admits to occasional cocaine use and alcohol consumption, and has a blood pressure of 108/70 mm Hg. Her family history includes diabetes mellitus and cancer, including a sister who recently gave birth to an infant with a neural tube defect (NTD). Which factors place her in a high-risk category?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Drug/alcohol use: While substance abuse during pregnancy can lead to adverse outcomes such as preterm labor, fetal growth restriction, and birth defects, it is not considered a primary factor in determining high-risk status for this patient. The specific substances involved (cocaine and alcohol) are indeed associated with risks, but they are not as significant as other factors in this case.
Age: The patient's age of 24 is not considered a high-risk factor for pregnancy. Advanced maternal age (typically defined as 35 years or older) is associated with increased risks for chromosomal abnormalities and other complications, but this patient falls below that age threshold.
Family history: Family history of diabetes mellitus, cancer, and neural tube defects can be relevant to pregnancy risk, but in this case, other factors outweigh their significance.
Choice B rationale:
Blood pressure: The patient's blood pressure of 108/70 mm Hg is within the normal range and does not contribute to highrisk categorization. High blood pressure (hypertension) during pregnancy can lead to preeclampsia and other complications, but this patient does not present with hypertension.
Age: As explained in Choice A, the patient's age is not a high-risk factor.
BMI: A BMI of 17 is considered underweight, which can increase the risk of certain pregnancy complications such as preterm birth and low birth weight. However, in this case, other factors are more significant in determining high-risk status.
Choice C rationale:
Family history: The patient's family history of a neural tube defect (NTD) in a close relative is a significant risk factor for NTDs in her own pregnancy. NTDs are serious birth defects that affect the brain and spinal cord, and they can have lifelong implications for the child. This factor alone warrants a high-risk categorization.
BMI: The patient's underweight BMI of 17 further contributes to her high-risk status, as it can increase the likelihood of certain complications as mentioned earlier.
Drug/alcohol abuse: The patient's admission of cocaine and alcohol use, even if occasional, is a concerning factor for pregnancy. Cocaine, in particular, is a potent vasoconstrictor that can negatively impact fetal growth and development. Alcohol consumption during pregnancy can lead to fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs), which can cause a range of physical, cognitive, and behavioral problems.
Choice D rationale:
Age: As explained previously, the patient's age is not a high-risk factor.
BMI: The patient's BMI is a contributing factor, but not the most significant one in this case.
Family history: The patient's family history is relevant, but the presence of a neural tube defect in a close relative is the most significant aspect of her family history in terms of pregnancy risk.
During the oliguric phase of acute renal failure, which of the following occurs?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Urine output (UO) does not completely stop during the oliguric phase of acute renal failure. While it is significantly reduced, some urine production still occurs. Complete cessation of urine output is known as anuria, which is a more severe condition and a medical emergency.
Anuria may occur in the most severe cases of acute renal failure, but it is not the defining characteristic of the oliguric phase.
It's crucial to distinguish between oliguria and anuria, as their management approaches differ significantly.
Choice B rationale:
During the oliguric phase of acute renal failure, urine output (UO) is less than 400 mL/24 hours. This is the defining characteristic of this phase.
The decrease in urine output is due to damage to the kidneys' filtering units, known as nephrons. As a result, the kidneys are unable to filter waste products and excess fluids effectively from the blood, leading to their accumulation in the body.
This reduced urine output can lead to various complications, including fluid overload, electrolyte imbalances, and a buildup of waste products in the blood (uremia).
Choice C rationale:
Urine output (UO) is always measured during the oliguric phase of acute renal failure. It is a vital clinical indicator to monitor the severity of kidney dysfunction and guide treatment decisions.
Accurate measurement of urine output is essential for assessing fluid balance, kidney function, and the effectiveness of treatment interventions.
Choice D rationale:
Urine output (UO) is not greater than 500 mL/24 hours during the oliguric phase of acute renal failure. A urine output greater than 500 mL/24 hours would indicate a non-oliguric phase of acute renal failure or a potential recovery phase.
A client, who is 39 weeks pregnant, has been admitted to the hospital for induction.
The doctor has prescribed misoprostol (Cytotec). Which statement by the client indicates a need for further education?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Misoprostol (Cytotec) is a medication used to induce labor.
It is placed in the posterior vaginal fornix.
However, it should not be used if the woman’s water has broken.
If the amniotic sac has ruptured, using Misoprostol can increase the risk of infection for both the mother and the baby.
Therefore, the statement “I can receive the Cytotec as long as my water hasn’t broken yet” indicates a need for further education.
Choice B rationale:
Walking can indeed help to speed up labor by using gravity to help the baby descend.
However, once Misoprostol has been administered, the woman is usually asked to lie on her side for about 30 to 40 minutes to allow the medication to be absorbed.
After that, if the healthcare provider agrees, she may be able to walk around.
Choice C rationale:
Monitoring the baby’s heart rate and the woman’s contraction pattern is a standard procedure during labor and delivery.
This allows the healthcare team to ensure the safety of both the mother and the baby.
It is especially important when medications like Misoprostol are used, as they can cause changes in the frequency and strength of contractions.
Choice D rationale:
Nausea and vomiting are potential side effects of Misoprostol.
However, not all women experience these side effects, and if they do occur, they are usually temporary.
The healthcare provider can offer solutions to manage these side effects if they become bothersome.
A pregnant client is undergoing a quad screen test and inquires about the possible results.
Which of the following responses is most appropriate?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Incorrect. The quad screen test does not examine fetal DNA to determine gender. That is the role of other tests, such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Gender determination is not a primary objective of the quad screen test.
Focusing on gender unnecessarily narrows the scope of the test's potential findings.
Choice B rationale:
Incorrect. The quad screen test does not use fetal tissue. It is a non-invasive blood test that measures levels of four substances in the mother's blood: alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), unconjugated estriol (uE3), and inhibin A.
Fetal tissue sampling is more invasive and carries risks, while the quad screen is a safer alternative.
Clarifying the non-invasive nature of the test is crucial for informed consent and patient understanding.
Choice C rationale:
Incorrect. While AFP levels can be affected by maternal liver function, that is not the primary focus of the quad screen test.
Liver function tests are specifically designed to assess liver health, and they are not part of the quad screen panel.
Distinguishing between liver function assessment and AFP's role in screening for fetal anomalies is essential for accurate interpretation.
Choice D rationale:
Correct. The quad screen test measures levels of AFP, hCG, uE3, and inhibin A in the mother's blood. These substances can provide information about the risk of certain fetal chromosomal abnormalities and neural tube defects.
Elevated AFP levels can indicate an increased risk for neural tube defects such as spina bifida or anencephaly.
Low AFP levels can be associated with Down syndrome or other chromosomal abnormalities.
Understanding the specific disorders that can be indicated by AFP levels is crucial for patient counseling and further testing decisions.
A pregnant client is at the prenatal clinic for a fetal nuchal translucency test.
What does the nurse understand about this test?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Trisomy 21, also known as Down syndrome, is a genetic condition caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21.
The nuchal translucency test (NT) is a non-invasive ultrasound screening test that measures the thickness of the fluid-filled space at the back of a developing baby's neck.
Evidence suggests that fetuses with Down syndrome tend to have increased fluid accumulation in this area, resulting in a larger-than-average nuchal translucency measurement.
Therefore, an increased NT measurement can be a marker for an increased risk of Down syndrome.
It's important to emphasize that the NT test is a screening tool, not a diagnostic test.
This means it can only indicate an increased risk of Down syndrome; it cannot definitively diagnose the condition.
To confirm a diagnosis, further testing, such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis, is required.
Choice B rationale:
Neural tube defects (NTDs) are birth defects that affect the brain, spine, or spinal cord.
The most common NTDs are spina bifida and anencephaly.
The NT test is not a diagnostic test for NTDs, although it might detect some cases of open spina bifida.
However, it's not specifically designed for this purpose, and other tests, such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) screening or detailed ultrasound, are more reliable for diagnosing NTDs.
Choice C rationale:
The NT test is typically performed in the first trimester of pregnancy, between 11 and 14 weeks gestation.
It's not available in the second trimester because the nuchal translucency measurement becomes less reliable after this point in pregnancy.
Choice D rationale:
A nuchal translucency measurement of 3mm or less is generally considered normal.
Measurements greater than 3mm are associated with an increased risk of Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities.
The higher the measurement, the greater the risk.
In addition to oxytocin (Pitocin) administration, what other methods can induce labor?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Prostaglandins:
Mechanism of action: Prostaglandins are hormone-like substances that play a crucial role in labor initiation. They act by softening and ripening the cervix, stimulating uterine contractions, and rupturing the amniotic sac.
Types: Prostaglandins used for labor induction include:
Dinoprostone (Cervidil, Prepidil): Inserted into the vagina as a gel or pessary.
Misoprostol (Cytotec): Administered orally or vaginally.
Effectiveness: Generally effective in initiating labor within 24 hours, with success rates ranging from 60-85%.
Advantages:
Can be used when the cervix is unfavorable (not ripe).
Can be administered in a variety of ways to suit the patient's preferences.
May have a lower risk of uterine hyperstimulation compared to oxytocin.
Disadvantages:
Can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever.
May increase the risk of uterine rupture, especially in women with a history of cesarean delivery.
Choice D rationale:
Amnioinfusion:
Procedure: Involves the infusion of sterile saline solution into the amniotic sac through a small catheter.
Mechanism of action: Not fully understood, but it's thought to work by:
Increasing amniotic fluid volume, which can help to stimulate contractions.
Stretching the uterine walls, which may trigger the release of prostaglandins.
Reducing pressure on the umbilical cord, which can improve fetal oxygenation.
Effectiveness: Usually used in conjunction with other induction methods, such as oxytocin or prostaglandins. Has a success rate of about 50-60% in initiating labor within 24 hours.
Advantages:
May be helpful in cases of low amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios).
Can decrease the risk of umbilical cord compression.
Disadvantages:
Requires the insertion of a catheter into the uterus, which carries a small risk of infection.
May cause discomfort for the mother.
A pregnant client is at the prenatal clinic for a fetal nuchal translucency test.
What does the nurse understand about this test?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Trisomy 21, also known as Down syndrome, is a genetic condition caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21.
The nuchal translucency test (NT) is a non-invasive ultrasound screening test that measures the thickness of the fluid-filled space at the back of a developing baby's neck.
Evidence suggests that fetuses with Down syndrome tend to have increased fluid accumulation in this area, resulting in a larger-than-average nuchal translucency measurement.
Therefore, an increased NT measurement can be a marker for an increased risk of Down syndrome.
It's important to emphasize that the NT test is a screening tool, not a diagnostic test.
This means it can only indicate an increased risk of Down syndrome; it cannot definitively diagnose the condition.
To confirm a diagnosis, further testing, such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis, is required.
Choice B rationale:
Neural tube defects (NTDs) are birth defects that affect the brain, spine, or spinal cord.
The most common NTDs are spina bifida and anencephaly.
The NT test is not a diagnostic test for NTDs, although it might detect some cases of open spina bifida.
However, it's not specifically designed for this purpose, and other tests, such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) screening or detailed ultrasound, are more reliable for diagnosing NTDs.
Choice C rationale:
The NT test is typically performed in the first trimester of pregnancy, between 11 and 14 weeks gestation.
It's not available in the second trimester because the nuchal translucency measurement becomes less reliable after this point in pregnancy.
Choice D rationale:
A nuchal translucency measurement of 3mm or less is generally considered normal.
Measurements greater than 3mm are associated with an increased risk of Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities.
The higher the measurement, the greater the risk.
In addition to oxytocin (Pitocin) administration, what other methods can induce labor?
Explanation
correct answer/s is A and D.
Choice A rationale:
Prostaglandins:
Mechanism of action: Prostaglandins are hormone-like substances that play a crucial role in labor initiation. They act by softening and ripening the cervix, stimulating uterine contractions, and rupturing the amniotic sac.
Types: Prostaglandins used for labor induction include:
Dinoprostone (Cervidil, Prepidil): Inserted into the vagina as a gel or pessary.
Misoprostol (Cytotec): Administered orally or vaginally.
Effectiveness: Generally effective in initiating labor within 24 hours, with success rates ranging from 60-85%.
Advantages:
Can be used when the cervix is unfavorable (not ripe).
Can be administered in a variety of ways to suit the patient's preferences.
May have a lower risk of uterine hyperstimulation compared to oxytocin.
Disadvantages:
Can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever.
May increase the risk of uterine rupture, especially in women with a history of cesarean delivery.
Choice D rationale:
Amnioinfusion:
Procedure: Involves the infusion of sterile saline solution into the amniotic sac through a small catheter.
Mechanism of action: Not fully understood, but it's thought to work by:
Increasing amniotic fluid volume, which can help to stimulate contractions.
Stretching the uterine walls, which may trigger the release of prostaglandins.
Reducing pressure on the umbilical cord, which can improve fetal oxygenation.
Effectiveness: Usually used in conjunction with other induction methods, such as oxytocin or prostaglandins. Has a success rate of about 50-60% in initiating labor within 24 hours.
Advantages:
May be helpful in cases of low amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios).
Can decrease the risk of umbilical cord compression.
Disadvantages:
Requires the insertion of a catheter into the uterus, which carries a small risk of infection.
May cause discomfort for the mother.
In the diuretic phase of renal failure, which of the following happens?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Electrolytes do not consistently improve during the diuretic phase of renal failure. While urine output increases, the kidneys' ability to regulate electrolytes may still be impaired. Electrolyte imbalances, such as hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, and hyperphosphatemia, can persist or even worsen during this phase.
Close monitoring of electrolytes is crucial to guide appropriate interventions, such as electrolyte replacement or restriction.
Choice B rationale:
Urine output (UO) does not remain unchanged during the diuretic phase. It is a defining characteristic of this phase that urine output increases, often significantly. This increase in urine output is a result of the recovering kidney tubules' ability to excrete fluid and waste products.
Choice C rationale:
Urine output (UO) increases in the diuretic phase of renal failure. This is a key feature that distinguishes this phase from the oliguric phase, which is characterized by decreased urine output. The increase in urine output is typically a sign of kidney function recovery. However, it is important to note that the increase in urine output does not necessarily mean that kidney function has fully recovered.
Choice D rationale:
Oxygenation does not typically worsen during the diuretic phase of renal failure. In fact, oxygenation may improve as fluid overload is resolved and pulmonary edema decreases. However, patients with underlying respiratory conditions or those who experience rapid fluid shifts may still require respiratory support.
A pregnant patient has a biophysical profile score of 8. What does this result mean?
Explanation
The correct answer is C. The test results are normal.
Choice A rationale:
A biophysical profile (BPP) score of 8 does not necessarily indicate a need for immediate cesarean delivery.
Cesarean delivery is typically reserved for cases where there is a clear and urgent risk to the health of the mother or fetus, such as severe fetal distress or placental abruption.
A score of 8, while not the highest possible score, is still within the normal range and does not, by itself, constitute a reason for immediate surgical intervention.
Choice B rationale:
Additional tests may be considered in certain cases, such as when the BPP score is borderline or when there are other risk factors present.
However, a score of 8 is generally considered reassuring and does not typically warrant further testing.
It's essential to evaluate the BPP score in the context of the overall clinical picture, including the gestational age, maternal health, and fetal history.
Choice D rationale:
While an obstetric specialist may review the BPP results and discuss delivery options with the patient, this is not typically done within a week for a score of 8.
A score of 8 indicates reassuring fetal well-being, and there is usually no need for such urgent consultation or decision-making.
The timing of delivery discussions would depend on the overall clinical situation and the patient's individual preferences.
Choice C rationale:
A BPP score of 8 is considered normal.
It suggests that the fetus is well-oxygenated and has normal heart rate, breathing movements, muscle tone, and amniotic fluid levels.
This score does not raise immediate concerns about fetal well-being and does not typically require any immediate interventions.
A 37-year-old patient visits her OBGYN office for a routine check-up. She mentions that she and her partner are trying to conceive.
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
This statement suggests that the patient has some awareness of infertility treatments, but it does not necessarily indicate a full understanding of infertility itself.
It's important to consider that a few months of trying to conceive may not be indicative of infertility, as it can take up to a year for healthy couples to achieve pregnancy.
Jumping to fertility treatments without a proper evaluation could lead to unnecessary interventions and potential financial and emotional burdens.
Choice B rationale:
This statement is incorrect. Male factor infertility is a common cause of difficulty conceiving, accounting for about 40% of infertility cases.
It's essential to evaluate both partners when assessing fertility issues.
Choice C rationale:
This statement demonstrates the patient's understanding of the relationship between age and fertility.
Female fertility gradually declines with age, especially after the age of 35, due to a decrease in the number and quality of eggs.
This awareness indicates that the patient is realistic about her chances of conceiving and is prepared to seek appropriate help if needed.
Choice D rationale:
While family history can play a role in infertility, it's not a guarantee that someone will experience the same issues as their relatives.
Each case is unique, and multiple factors can contribute to infertility, including genetics, lifestyle, medical conditions, and environmental factors.
It's important to undergo a thorough evaluation to determine the specific causes of infertility in each individual.
A 40-year-old pregnant patient, currently hospitalized for preterm labor at 34 weeks’ gestation, is discussing potential delivery options with her provider based on the results of a fetal lung maturity test.
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Amniocentesis is the most reliable and direct method to assess fetal lung maturity. It involves the extraction of a small sample of amniotic fluid from the amniotic sac, which surrounds the fetus in the uterus. This fluid contains various substances, including surfactant, which is a crucial substance produced by the fetal lungs that enables them to expand and function properly after birth.
By analyzing the levels of surfactant and other components in the amniotic fluid, clinicians can accurately determine the maturity of the fetal lungs. This information is essential in guiding decisions about potential delivery options, especially in cases of preterm labor or other complications that may necessitate early delivery.
Amniocentesis is generally considered a safe procedure, but it does carry some small risks, such as infection, bleeding, or amniotic fluid leakage. However, these risks are typically outweighed by the benefits of obtaining accurate information about fetal lung maturity when necessary.
Choice B rationale:
Fetal fibronectin (fFN) is a protein that is found in the amniotic fluid and cervicovaginal secretions. Elevated levels of fFN in cervicovaginal secretions between 22 and 34 weeks of gestation can indicate an increased risk of preterm labor.
However, fFN testing is not a direct measure of fetal lung maturity. It is used primarily as a screening tool to assess the risk of preterm birth, not to determine the readiness of the fetal lungs for delivery.
Choice C rationale:
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is a prenatal diagnostic test that involves taking a small sample of chorionic villi, which are tiny finger-like projections of placental tissue. This test is typically performed earlier in pregnancy (between 10 and 13 weeks gestation) to diagnose genetic abnormalities in the fetus.
CVS is not used to assess fetal lung maturity. It does not provide any information about the development of the fetal lungs or their readiness for birth.
Choice D rationale:
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a protein produced by the fetal liver. Elevated levels of AFP in the maternal blood can indicate an increased risk of certain birth defects, such as neural tube defects.
AFP testing is not used to assess fetal lung maturity. It does not provide any information about the development of the fetal lungs or their readiness for birth.
The emergency department nurse notes that a patient with chronic kidney failure has a potassium level of 6.5 mEq/L. Which medications would the nurse expect to administer? Select all that apply.
Explanation
The correct answers are B, C, E, and F.
Rationale for each choice:
- Albuterol
Mechanism of action: Albuterol is a beta-2 agonist that stimulates beta-2 receptors in the cell membranes of skeletal muscle, liver, and adipose tissue. This stimulation causes an increase in intracellular cyclic AMP (cAMP), which activates protein kinase A (PKA). PKA then phosphorylates a number of proteins, including the sodium-potassium ATPase pump. This pump is responsible for transporting potassium ions into cells and out of the bloodstream. By increasing the activity of this pump, albuterol can help to lower serum potassium levels.
Onset of action: Albuterol has a rapid onset of action, typically within 30 minutes.
Duration of action: The duration of action of albuterol is relatively short, usually 4-6 hours.
Dosage: The dosage of albuterol for hyperkalemia is typically 10-20 mg nebulized every 4-6 hours.
Additional considerations: Albuterol can cause tachycardia and tremors. It should be used cautiously in patients with heart disease or hyperthyroidism.
- Kayexalate
Mechanism of action: Kayexalate is a cation exchange resin that binds to potassium ions in the gastrointestinal tract. This prevents the potassium from being absorbed into the bloodstream.
Onset of action: Kayexalate has a relatively slow onset of action, usually 1-2 hours.
Duration of action: The duration of action of Kayexalate is relatively long, usually 4-6 hours.
Dosage: The dosage of Kayexalate for hyperkalemia is typically 15-30 grams orally or rectally every 6 hours.
Additional considerations: Kayexalate can cause constipation and hypocalcemia. It should be used cautiously in patients with bowel obstruction or kidney disease.
- Insulin & dextrose
Mechanism of action: Insulin promotes the movement of potassium into cells, thus lowering serum potassium levels. Dextrose is given along with insulin to prevent hypoglycemia.
Onset of action: Insulin has a rapid onset of action, typically within 30 minutes.
Duration of action: The duration of action of insulin is relatively short, usually 4-6 hours.
Dosage: The dosage of insulin for hyperkalemia is typically 10 units of regular insulin IV push, followed by an infusion of 5-10 units per hour. The dosage of dextrose is typically 50 grams IV push, followed by an infusion of 10% dextrose at 100 mL/hour.
Additional considerations: Insulin can cause hypoglycemia. It should be used cautiously in patients with diabetes mellitus.
A couple has been diagnosed with infertility after trying to conceive for a year.
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Semen analysis is the initial test often performed in the evaluation of infertility. It's a non-invasive, cost-effective, and informative assessment of male fertility. Here's a detailed explanation of its significance:
Assessment of Sperm Quality:
Measures sperm count, motility (movement), and morphology (shape).
Abnormalities in any of these parameters can significantly impact the chances of conception.
Identification of Male Factor Infertility:
Contributes to approximately 40% of infertility cases.
Early identification of male factor infertility guides treatment options and avoids unnecessary testing for the female partner.
Non-Invasive and Cost-Effective:
Simple procedure involving the collection of a semen sample.
Relatively inexpensive compared to other fertility tests.
Informative Results:
Provides valuable insights into sperm health and potential causes of infertility.
Guides further diagnostic evaluation and treatment strategies.
Rationale for other choices:
Choice B: Transvaginal ultrasound
Primarily evaluates female reproductive organs.
Assesses uterine structure, ovarian function, and potential abnormalities like fibroids or cysts.
Not typically the first test in infertility evaluation unless there's a specific female-factor concern. Choice C: Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
Assesses the patency of the fallopian tubes.
Involves X-ray imaging after injecting contrast dye into the uterus.
Often performed after semen analysis if male factor infertility is not identified.
Choice D: Hysteroscopy
A more invasive procedure involving direct visualization of the inside of the uterus.
Used to diagnose and treat uterine abnormalities such as polyps or fibroids.
Not typically a first-line test in infertility evaluation.
A pregnant woman is getting ready for a chorionic villus sampling procedure at 10 weeks.
The nurse has been educating her about the procedure.
Which of the following statements, if made by the client, would indicate that the teaching has been effective?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Fetal lung maturity is not assessed through chorionic villus sampling (CVS). It's primarily evaluated through amniocentesis, a different prenatal diagnostic procedure that involves sampling amniotic fluid.
CVS focuses on placental tissue, not lung development.
It's essential for clients to understand the specific purposes of each prenatal test to make informed decisions and have accurate expectations.
Choice B rationale:
While a non-stress test (NST) might be recommended after CVS in some cases, it's not a routine part of the procedure.
The decision to conduct an NST is based on individual risk factors and assessment by healthcare providers.
It's essential for clients to understand the potential need for additional testing but not assume it's always required.
Choice C rationale:
CVS is considered an invasive procedure, as it involves entering the uterus to collect placental tissue.
Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) methods, which analyze fetal DNA in maternal blood, are available for screening purposes.
It's crucial for clients to differentiate between invasive and non-invasive prenatal testing options to make informed choices based on their preferences and risk factors.
Choice D rationale:
This statement accurately reflects the primary purpose of CVS.
It's a diagnostic procedure that can detect various genetic abnormalities, such as Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis, and TaySachs disease, during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Understanding the ability to detect genetic abnormalities early in pregnancy allows clients to make informed decisions about their pregnancy management and prepare for potential outcomes.
What do nurses understand about the induction of labor?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Bishop score: A tool used to assess the readiness of the cervix for labor induction. It evaluates factors such as cervical dilation, effacement, consistency, position, and station of the fetal presenting part.
Score ranges from 0 to 13: A higher score indicates a more favorable cervix for induction.
Score of 6 or less: Induction is less likely to be successful.
Score of 9 or higher: Induction is more likely to be successful.
Nurses understand: The importance of the Bishop score in predicting the likelihood of successful induction.
Nurses use this information: To counsel patients about the risks and benefits of induction, to prepare for induction, and to monitor progress during induction.
Choice B rationale:
Not always done for medical reasons: Induction can also be elective, meaning it is chosen for non-medical reasons, such as convenience or a desire to avoid a post-term pregnancy.
Examples of medical reasons:
Gestational hypertension or preeclampsia
Fetal growth restriction
Prolonged pregnancy
Chorioamnionitis
Oligohydramnios
Choice C rationale:
Trial of labor (TOL): A term used to describe a vaginal birth attempt after a previous cesarean delivery.
Not synonymous with induction of labor: TOL can occur spontaneously or be induced.
Choice D rationale:
Not always electively done at 37 weeks' gestation: The decision to induce labor at 37 weeks is made on a case-by-case basis.
Factors considered:
Maternal and fetal health
Bishop score
Patient preferences
A pregnant woman comes in for her weekly fetal heart monitoring.
She is 35 weeks’ gestation.
After 20 minutes on the monitor, the fetal heart rate tracing shows 3 accelerations measuring 15 beats by 15 seconds.
How should the nurse report this finding to the provider?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
A positive contraction stress test (CST) indicates that the fetal heart rate decelerates late in response to uterine contractions, suggesting potential uteroplacental insufficiency. However, the scenario does not describe a CST being performed, as it does not mention any assessment of uterine contractions or their relationship to fetal heart rate changes.
Choice C rationale:
A negative contraction stress test (CST) would demonstrate no late decelerations in response to contractions, suggesting adequate placental function. However, as mentioned earlier, a CST is not the test being performed in this scenario.
Choice D rationale:
A non-reactive nonstress test (NST) means that there were not enough fetal heart rate accelerations (at least 2, each lasting at least 15 seconds and peaking at least 15 beats above baseline) within a 20-minute period. This finding sometimes warrants further evaluation of fetal well-being. However, the scenario clearly states that 3 accelerations meeting the criteria for reactivity were observed.
Choice B rationale:
A reactive nonstress test (NST) is considered reassuring and indicates that the fetal heart rate is responding appropriately to fetal movement, suggesting that the fetus is likely healthy and well-oxygenated. The presence of 3 accelerations meeting the criteria for reactivity within a 20-minute period is the hallmark of a reactive NST.
The nurse is examining a female patient in an OB clinic who complains of severe pain during menstruation and intercourse.
The nurse suspects endometriosis.
Which of the following is true?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Infertility is a common issue for women with endometriosis. The endometrial tissue that grows outside the uterus can cause scarring and inflammation, which can block fallopian tubes and prevent eggs from being released or fertilized. Studies have shown that 30-50% of women with endometriosis experience infertility.
It is important to address this potential issue with the patient and discuss options for fertility preservation if desired.
Choice B rationale:
There is no evidence to suggest that women with endometriosis are more likely to have multiples. The likelihood of having multiples is primarily influenced by factors such as genetics, maternal age, and the use of fertility treatments.
Choice C rationale:
Acetaminophen may not be effective for pain relief in women with endometriosis. The pain associated with endometriosis is often severe and can be unresponsive to over-the-counter pain relievers. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen are often more effective in managing endometriosis-related pain.
In some cases, stronger pain medications such as opioids may be necessary.
Choice D rationale:
Oral contraceptives can be helpful for women with endometriosis by:
Suppressing ovulation, which can reduce the amount of endometrial tissue that grows and bleeds each month.
Thinning the uterine lining, which can also reduce pain and bleeding.
Slowing the growth of endometrial tissue.
Oral contraceptives are not a cure for endometriosis, but they can help to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Which of the following practices reflect safe administration of oxytocin (Pitocin)?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Attaching the IV line to the distal port is not a safe practice for oxytocin administration. This is because oxytocin is a high-alert medication that can have serious adverse effects if administered incorrectly. Attaching the IV line to the distal port increases the risk of the medication being infused too quickly, which can lead to uterine hyperstimulation, fetal distress, or even uterine rupture. The safest practice is to attach the IV line to the proximal port, which is closer to the patient's body and allows for slower infusion rates.
Choice B rationale:
Customizing the concentration of oxytocin is not a recommended practice. Oxytocin is available in a premixed solution of 10 units/mL, and this concentration should not be altered. Altering the concentration can lead to dosing errors and increase the risk of adverse effects.
Choice D rationale:
Titrating oxytocin to gravity is not a safe practice. Oxytocin should be administered using an infusion pump that can accurately control the infusion rate. Infusion pumps are necessary to ensure that the medication is administered at the correct dose and rate. Gravity-based infusions are less accurate and can lead to over- or under-infusion of the medication.
Choice C rationale:
Two RN verification is a safe practice for oxytocin administration. This practice involves having two registered nurses independently verify the medication, dose, and infusion rate before administration. This helps to prevent errors and ensure that the medication is administered safely.
A nurse is caring for a patient in labor who is receiving oxytocin (Pitocin) by IV infusion to stimulate uterine contractions.
Which assessment finding would indicate to the nurse that the infusion needs to be discontinued?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Fetal heart rate of 90 beats per minute is a sign of fetal bradycardia, which is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition. It indicates that the fetus is not getting enough oxygen, and it can lead to fetal distress, brain damage, or even death.
Oxytocin can cause uterine hyperstimulation, which can reduce blood flow to the placenta and cause fetal bradycardia. Therefore, if the nurse observes a fetal heart rate of 90 beats per minute, it is essential to discontinue the oxytocin infusion immediately and notify the healthcare provider.
Choice B rationale:
Increased urinary output is not a direct contraindication to oxytocin administration. In fact, oxytocin can sometimes cause a decrease in urinary output due to its antidiuretic effects.
While a significant increase in urinary output could be a sign of fluid overload, it would not necessarily indicate that the oxytocin infusion needs to be discontinued. The nurse would need to assess the patient's overall fluid status and other clinical indicators to make this determination.
Choice C rationale:
Three contractions occurring within a 10-minute period is considered a normal contraction pattern during labor. It is not a sign of uterine hyperstimulation or fetal distress.
In fact, the goal of oxytocin administration is to achieve regular contractions that are occurring every 2-3 minutes and lasting 40-60 seconds. Therefore, this finding would not indicate that the oxytocin infusion needs to be discontinued.
Choice D rationale:
Adequate resting tone of the uterus palpated between contractions is a normal finding during labor. It indicates that the uterus is contracting effectively and is not at risk for uterine atony (lack of muscle tone).
This finding would not be a reason to discontinue the oxytocin infusion.
The nurse is teaching a pregnant client about fetal kick counts.
Which statement made by the client indicates a need for further instruction?
Explanation
Choice C rationale:
It is a misconception that fetal movement decreases as delivery approaches. While the nature of the movements may change— becoming less like kicks and more like rolls or twists due to less space in the uterus—the frequency of movements should remain consistent. In fact, increased fetal movement can be a sign of labor approaching. Therefore, a pregnant client who believes that fetal movements will decrease closer to delivery needs further instruction to ensure they are aware of this important health indicator.
Here's a detailed explanation of why the other choices are correct:
Choice A: This statement is correct. Fetal kick counts can be performed at home, providing a convenient and comfortable way to monitor fetal well-being.
Choice B: This statement is also correct. A decrease in fetal movement, defined as less than 3 kicks in an hour, is a potential concern and warrants contacting a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Choice D: This statement is accurate as well. Daily fetal kick counts are generally recommended to establish a baseline of the baby's usual activity pattern and to detect any significant changes that might indicate a problem.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 45 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

