Fetal Non-Stress Test (NST) > Maternal & Newborn
Exam Review
Introduction
Total Questions : 5
Showing 5 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is caring for a client who is undergoing a fetal non-stress test (NST).
The nurse observes that the fetal heart rate (FHR) accelerates at least 10 bpm for at least 10 seconds with each fetal movement.
The client is 30 weeks pregnant.
How should the nurse interpret this finding?
Explanation
The NST is reactive and normal for gestational age.This means that the fetal heart rate (FHR) accelerates at least 10 bpm for at least 10 seconds with each fetal movement, indicating that the fetus is healthy and getting enough oxygen.A reactive NST is expected for fetuses at 26 to 30 weeks of gestation.
Choice B is wrong because a nonreactive NST means that the FHR does not accelerate with fetal movement, which could indicate fetal distress or hypoxia.A nonreactive NST is abnormal for any gestational age and requires further evaluation.
Choice C is wrong because a reactive NST is not abnormal for gestational age.It is a normal finding that shows the fetus is well-oxygenated and responsive.
Choice D is wrong because a nonreactive NST is not normal for gestational age.It is an abnormal finding that suggests the fetus may be compromised or in need of intervention.
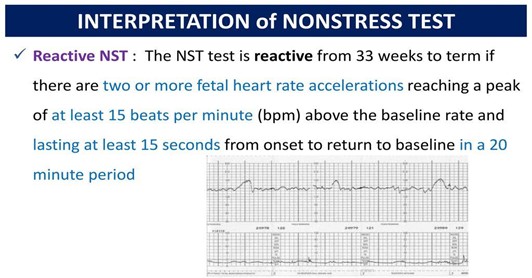
A nurse is preparing a client for a fetal non-stress test (NST).
Which of the following instructions should the nurse give to the client?
Explanation
“You will need to press a button when you feel the baby move.” This is because a non-stress test (NST) is a pregnancy screening that measures fetal heart rate and reaction to movement.The test is performed to make sure the fetus is healthy and getting enough oxygen.By pressing a button when the baby moves, the patient can help the provider record the changes in the fetal heart rate.
Choice A is wrong because the patient does not need to fast for 8 hours before the test.There is no dietary restriction for an NST.
Choice B is wrong because the patient does not need to drink plenty of fluids before the test.However, drinking some fluids may help stimulate fetal movement.
Choice C is wrong because the patient does not need to lie on their back during the test.In fact, lying on the back can compress the blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the fetus.The patient can lie on their side or recline on a chair or exam table.
A nurse is reviewing the results of a fetal non-stress test (NST) for a client who is at 32 weeks of gestation.
The nurse notes that there are no accelerations of the fetal heart rate (FHR) during the 20-minute test.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take next? (Select all that apply.).
Explanation
Perform a biophysical profile (BPP).A BPP is a test that combines a non-stress test (NST) with an ultrasound to evaluate the fetal well-being.A BPP is indicated when an NST is non-reactive, meaning that there are no accelerations of the fetal heart rate (FHR) with fetal movements.A BPP measures five parameters: fetal movement, fetal tone, fetal breathing, amniotic fluid volume and FHR reactivity.
A BPP can help detect fetal hypoxemia or distress and guide further management.
Choice A is wrong because repeating the NST after 24 hours may delay the diagnosis and treatment of fetal compromise.A non-reactive NST requires further evaluation with a BPP or a contraction stress test (CST).
Choice B is wrong because performing a CST may not be safe for a fetus with a non-reactive NST.
A CST involves inducing uterine contractions with oxytocin or nipple stimulation and monitoring the FHR response.A CST can cause fetal distress or placental abruption if the fetus is already hypoxic.
Choice D is wrong because applying an acoustic vibration device to the abdomen may not elicit FHR accelerations if the fetus is hypoxic or asleep.An acoustic stimulation test (AST) is sometimes used to augment an NST, but it is not a substitute for a BPP.
Choice E is wrong because administering oxygen via face mask to the client may not improve the FHR reactivity if the cause of fetal compromise is not maternal hypoxia.Oxygen administration may also have adverse effects on maternal and fetal hemodynamics.
A nurse is teaching a client about the advantages and disadvantages of a fetal non-stress test (NST).
Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
“The NST can be affected by my smoking or medication use.” This statement indicates an understanding of the teaching because smoking and medication use can alter the fetal heart rate response and cause false-negative or false-positive results.
Some possible explanations for the other choices are:
• Choice A is wrong because the NST cannot detect chromosomal abnormalities in the baby.
The NST only measures the fetal heart rate and movement, not the genetic makeup of the baby.To detect chromosomal abnormalities, other tests such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling are needed.
• Choice B is wrong because the NST does not cause contractions or discomfort for the mother or the baby.The NST is a non-invasive and painless procedure that does not put any stress on the fetus.The only discomfort that may occur is from having a belt around the abdomen and a button to press when feeling fetal movement.
• Choice D is wrong because the NST cannot measure the amount of amniotic fluid around the baby.
The NST only monitors the fetal heart rate and movement, not the volume of fluid in the uterus.To measure the amount of amniotic fluid, other tests such as ultrasound or amniotic fluid index are needed.
A nurse is evaluating the results of a fetal non-stress test (NST) for a client who has diabetes mellitus and is at 36 weeks of gestation.
The nurse notes that the fetal heart rate (FHR) baseline is 150 bpm, with occasional increases of 20 bpm that last for 20 seconds.
There are no decelerations of the FHR.
How should the nurse document this finding?
Explanation
Reactive NST.This means that the fetal heart rate (FHR) increases by at least 15 bpm for at least 15 seconds twice in a 20-minute period.This indicates that the fetus is well-oxygenated and not in distress.
Choice B is wrong because a nonreactive NST means that the FHR does not show the expected accelerations, which could indicate fetal hypoxia or other problems.
Choice C is wrong because a positive NST is another term for a contraction stress test (CST), which measures the FHR response to uterine contractions.A positive CST means that the FHR shows late decelerations, which indicate uteroplacental insufficiency.
Choice D is wrong because a negative NST is also another term for a CST, but it means that the FHR does not show late decelerations, which indicate normal fetal oxygenation.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 5 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

