Cesarean delivery > Maternal & Newborn
Exam Review
Introduction
Total Questions : 10
Showing 10 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is reviewing the medical records of four pregnant clients who are scheduled for cesarean delivery.
Which client has the highest risk of developing a postoperative infection?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.A client with gestational diabetes mellitus has a higher risk of developing a postoperative infection after cesarean section because diabetes impairs wound healing and increases susceptibility to infection.
Choice B is wrong because active herpes virus infection does not increase the risk of surgical site infection after cesarean section.
Choice C is wrong because placenta previa is not a risk factor for postoperative infection after cesarean section.
Choice D is wrong because fetal breech presentation does not increase the risk of surgical site infection after cesarean section.
Some of the other risk factors for postoperative infection after cesarean section are high body mass index, intrapartum fever, prolonged rupture of membranes, prolonged labor, chorioamnionitis, anemia, and vertical skin incision.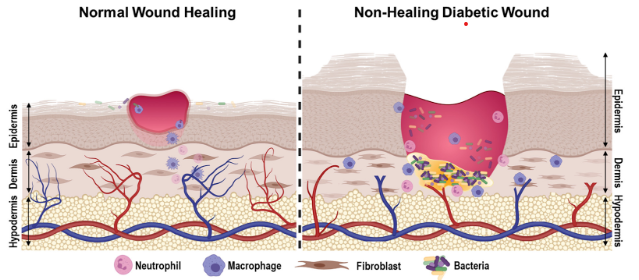
A nurse is caring for a client who had an emergency cesarean delivery due to fetal distress.
The nurse notices that the client has a large amount of bright red blood on her perineal pad.
What is the nurse’s priority action?
Explanation
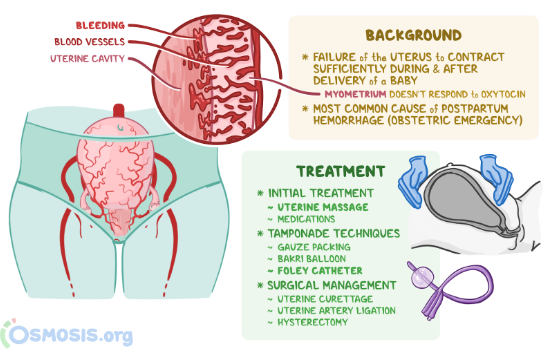
The correct answer is choice B. Massage the client’s fundus and check for firmness.This is because the most common cause of postpartum hemorrhage is uterine atony, which is a lack of contraction of the uterus after delivery.Massaging the fundus stimulates the uterus to contract and reduces bleeding from the placental site.Checking for firmness ensures that the uterus is not distended by blood clots or retained placental fragments, which can also cause hemorrhage.
Choice A is wrong because assessing the client’s vital signs and level of consciousness is not a priority action.
These are important indicators of blood loss and shock, but they do not address the source of bleeding.The nurse should first try to stop the bleeding by massaging the fundus and then assess the client’s status.
Choice C is wrong because notifying the provider and preparing for a blood transfusion are not priority actions.
These are interventions that may be needed if the bleeding does not stop with fundal massage or if the client develops signs of severe hemorrhage or shock.However, they are not the first steps to take in managing postpartum hemorrhage.
Choice D is wrong because administering oxytocin as prescribed to stimulate uterine contractions is not a priority action.Oxytocin is a uterotonic medication that can help prevent and treat postpartum hemorrhage by causing sustained uterine contractions.
However, it is not the first intervention to try in case of bleeding.The nurse should first massage the fundus and check for firmness, and then administer oxytocin if ordered by the provider.
Normal ranges for blood loss after delivery are less than 500 mL for vaginal birth and less than 1000 mL for cesarean birth.Normal ranges for vital signs and level of consciousness vary depending on the individual client, but some signs of hypovolemia and shock include tachycardia, hypotension, tachypnea, pallor, cold clammy skin, oliguria, anxiety, confusion, and loss of consciousness.Normal range for uterine firmness is a well-contracted uterus that feels like a hard ball at or below the umbilicus.
A nurse is teaching a prenatal class about the indications for cesarean delivery.
The nurse should include that which of the following conditions can lead to a cesarean delivery? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A, C, D and E. These are all conditions that can lead to a cesarean delivery.
Choice A is correct because cephalopelvic disproportion (CPD) means that the baby’s head or body is too large to fit through the mother’s pelvis.This can cause prolonged or obstructed labor and fetal distress.
Choice B is wrong because gestational hypertension (high blood pressure during pregnancy) is not a direct indication for a cesarean delivery.However, it can be associated with other complications such as preeclampsia, placental abruption or fetal growth restriction that might require a cesarean delivery.
Choice C is correct because fetal malposition means that the baby is not in the optimal position for vaginal delivery.
This includes breech (feet or buttocks first), transverse (sideways) or oblique (diagonal) presentations.These can increase the risk of cord prolapse, fetal injury or uterine rupture.
Choice D is correct because placenta abruption means that the placenta separates from the uterine wall before delivery.
This can cause severe bleeding, fetal hypoxia or stillbirth.A cesarean delivery is usually performed to save the mother and the baby.
Choice E is correct because cord prolapse means that the umbilical cord slips through the cervix ahead of the baby.
This can compress the cord and cut off the blood supply to the baby.A cesarean delivery is usually performed as an emergency to prevent fetal death.
A nurse is preparing a client for a planned cesarean delivery.
The nurse should explain that which of the following types of anesthesia is most commonly used for this procedure?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B.Spinal anesthesia is the most commonly used type of anesthesia for cesarean delivery.It is administered around the spinal cord using a needle and it numbs the lower body for three to four hours.It has the advantages of being fast-acting, providing good operating conditions, and having minimal effects on the fetus.
Choice A is wrong because general anesthesia is rarely used for cesarean delivery unless there is an emergency or a contraindication for regional anesthesia.It involves putting the mother to sleep with drugs that can cross the placenta and affect the fetus.
Choice C is wrong because epidural anesthesia is not as commonly used as spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery.It is administered around the nerves in the lower back and it requires a larger dose and a longer time to work than spinal anesthesia.
Choice D is wrong because local anesthesia is rarely used for cesarean delivery and only for minor procedures such as repairing a wound or removing stitches.It involves injecting a drug into the skin or tissue to numb a small area.
A nurse is assessing a client who had a cesarean delivery 24 hours ago.
The nurse should identify that which of the following findings is a potential complication of this procedure?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.Urinary output of 40 mL/hr is a potential complication of cesarean delivery because it indicates inadequate fluid intake, blood loss, or urinary tract injury.The normal range of urinary output is 30 to 60 mL/hr.
Choice B is wrong because incision site with serous drainage is a normal finding after cesarean delivery and does not indicate infection or bleeding.
Choice C is wrong because abdominal pain relieved by analgesics is also a normal finding after cesarean delivery and does not indicate any complication.
Choice D is wrong because uterus palpable at the umbilicus is an expected finding after cesarean delivery and indicates that the uterus is contracting and returning to its pre-pregnancy size.
A nurse is assessing a patient’s medical history before Cesarean delivery.
What should the nurse assess?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. The patient’s allergies.
The nurse should assess the patient’s allergies before Cesarean delivery to prevent any adverse reactions to medications, anesthesia, or latex products that may be used during the procedure.
Allergies can cause serious complications such as anaphylaxis, which can be life-threatening for both the mother and the baby.
Choice B is wrong because the patient’s age is not a relevant factor for Cesarean delivery.
Age does not affect the surgical technique or the outcome of the operation.
Choice C is wrong because the patient’s height is not a relevant factor for Cesarean delivery.
Height does not affect the size of the incision or the amount of blood loss during the surgery.
Choice D is wrong because the patient’s weight is not a relevant factor for Cesarean delivery.
Weight does not affect the type of anesthesia or the risk of infection after the surgery.
Normal ranges for vital signs and laboratory values are not applicable for this question.
A client is scheduled for Cesarean delivery.
What should the nurse do to support the client emotionally?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. Address any concerns or anxieties the client may have regarding the procedure.Emotional support is a critical aspect of quality care throughout pregnancy and childbirth.Women who have a cesarean section may experience a range of emotions, such as depression, regret, or lower self-esteem.
The nurse should provide emotional support by listening to the client’s feelings, answering their questions, and reassuring them about the procedure.
Choice A is wrong because educating the client about the surgical procedure is not enough to support them emotionally.
The client may still have fears or worries that need to be addressed.
Choice B is wrong because administering prescribed medications as ordered by the healthcare provider is not directly related to emotional support.
Medications may help with pain relief or infection prevention, but they do not address the client’s psychological needs.
Choice D is wrong because ensuring that informed consent has been obtained from the client is a legal and ethical requirement, but it does not necessarily imply emotional support.
The client may still feel coerced, uninformed, or unhappy about the procedure.
A nurse is performing a physical examination on a patient before Cesarean delivery.
What should the nurse pay special attention to?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. The patient’s abdomen and pelvic area.
The nurse should pay special attention to the patient’s abdomen and pelvic area before Cesarean delivery because this is where the surgery will take place.
The nurse should assess the size and position of the uterus, the fetal heart rate and movement, and any signs of infection or bleeding in the abdominal and pelvic area.
The nurse should also prepare the patient for the surgery by shaving the pubic hair, inserting a urinary catheter, and administering prophylactic antibiotics if ordered.
Choice A is wrong because the patient’s medical history is not as relevant as the current physical examination before Cesarean delivery.
The nurse should review the medical history for any risk factors or complications, but this is not the main focus of the examination.
Choice B is wrong because the patient’s allergies are not as important as the patient’s abdomen and pelvic area before Cesarean delivery.
The nurse should ask about any allergies to medications, latex, or iodine, but this is not the primary concern of the examination.
Choice D is wrong because the patient’s height is not as significant as the patient’s abdomen and pelvic area before Cesarean delivery.
The nurse should measure the patient’s height and weight to calculate the body mass index (BMI), but this is not the main objective of the examination.
A nurse is administering prescribed medications before Cesarean delivery.
What medication should the nurse administer?
Explanation
Prophylactic antibiotics and antacids are commonly given before a Cesarean delivery to prevent infection and reduce the risk of aspiration.Antibiotics can reduce the incidence of postoperative endometritis and wound infection.Antacids can neutralize the stomach acid and lower the pH, which can minimize the lung injury if aspiration occurs.
Choice B is wrong because painkillers and sedatives are not routinely given before a Cesarean delivery.Painkillers are usually given after the surgery or during the surgery if regional anesthesia is used.Sedatives are not recommended because they can cause respiratory depression and cross the placenta to affect the baby.
Choice C is wrong because antidepressants and antipsychotics are not indicated for a Cesarean delivery unless the woman has a psychiatric condition that requires them.These medications can have adverse effects on the mother and the baby, such as bleeding, hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, sedation, withdrawal symptoms, and neurobehavioral changes.
Choice D is wrong because antihistamines and decongestants are not relevant for a Cesarean delivery.Antihistamines can cause sedation, dry mouth, and urinary retention, and decongestants can cause hypertension, tachycardia, and insomnia.These medications can also cross the placenta and affect the baby’s health.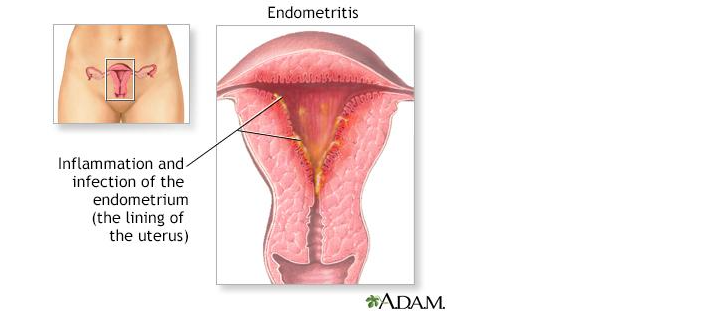
A nurse is educating a patient about Cesarean delivery before surgery.
What should the nurse educate the patient about?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice D. All of the above.
The nurse should educate the patient about the risks, benefits and expected outcomes of Cesarean delivery before surgery.
Choice A is wrong because it is not enough to inform the patient only about the risks of surgery, such as infection, bleeding, injury to organs or anesthesia complications.
The patient also needs to know the benefits and expected outcomes of surgery.
Choice B is wrong because it is not enough to inform the patient only about the benefits of surgery, such as avoiding labor complications, delivering a healthy baby or having a planned date of birth.
The patient also needs to know the risks and expected outcomes of surgery.
Choice C is wrong because it is not enough to inform the patient only about the expected outcomes of surgery, such as the length of hospital stay, the recovery process or the wound care.
The patient also needs to know the risks and benefits of surgery.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 10 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

