Ivy Tech Exam 3 Fundamentals
Total Questions : 50
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is reviewing factors that increase the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) with a female client who has recurrent UTIs. Which of the following factors should the nurse include? Select all that apply.
Explanation
A. Frequent catheterization can increase the risk of UTIs due to the introduction of bacteria into the urinary tract.
B. The proximity of the urethra to the anus increases the risk of bacterial contamination from the gastrointestinal tract.
C. Frequent sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urethra, increasing the risk of UTIs.
D. Lowering of testosterone levels is not a significant factor in increasing the risk of UTIs in females.
E. Wiping from front to back helps prevent the introduction of bacteria from the anal area to the urethra.
A nurse is researching dietary options for a patient that includes foods that supply energy to the body. Which are classes of nutrients that supply this energy? Select all that apply.
Explanation
A. Lipids (fats) are a concentrated source of energy for the body.
B. D vitamins are essential for bone health but do not supply energy.
C. Carbohydrates are a primary source of energy for the body.
D. Minerals are essential for various bodily functions but do not supply energy.
E. Proteins are essential for tissue repair and growth but are not a primary source of energy.
A client has an order to take 15 milligrams of liquid prednisone daily for 5 days. The pharmacy has 5mg/5mL concentration available. How many tablespoons will the nurse administer with each dose?
Explanation
1 tablespoon = 15 mL
The available concentration of prednisone available = 5mg/5ml The patient will require a total of 15mls (15 x5/5)
1 tablespoon = 15mls
Therefore, the nurse will administer about 1 tablespoon of prednisone with each dose.
A client is ordered to increase his warfarin to 5mg PO daily. The client has 2mg tablets on hand. How many tablets will the client take daily?
Explanation
To find the answer, we need to divide the ordered dose by the available dose. We can use the following formula:
ordered dose / available dose = number of tablets Substituting the given values, we get:
5 mg / 2 mg = 2.5 tablets
Therefore, the client will take two and a half tablets of warfarin daily.
The physician ordered digoxin (Lanoxin) 0.125 mg IV push every morning. Digoxin is available in a vial labeled 0.5mg/2mL. How many mL with the nurse administer?
Explanation
To find the volume of digoxin needed for each dose, we can use the formula: volume (mL) = dose (mg) / concentration (mg/mL)
Plugging in the given values, we get:
volume (mL) = 0.125 mg / 0.25 mg/mL
volume (mL) = 0.5 mL
So, the nurse will administer 0.5 mL of digoxin with each dose.
A 65 year old client is being seen at the outpatient clinic for a routine physical exam. The abdominal assessment shows distention, firmness, and the client states tenderness throughout the 4 quadrants. Upon further questioning of the client the following is determined; a slight decrease in appetite. consumes 320 mL of water per day along with 320 mL of other fluids such as coffee and soda, snacks frequently on cheese and crackers rather than full meals, and does not get much activity. Client states they have one to two bowel movements per week of hard formed stool. Based on the physical assessment and the answered questions what would be the recommended interventions for this client?
SELECT ALL THAT APPLY.
Explanation
A. Administering an enema may not be the first-line intervention and may have potential risks. Dietary and lifestyle changes are usually recommended first.
B. A high-fiber diet promotes regular bowel movements and helps prevent constipation.
C. Regular exercise, such as walking, can stimulate bowel activity and improve overall health.
D. Well-cooked fruits and vegetables are beneficial, but the emphasis should be on increasing fiber intake.
E. Increasing consumption of eggs, meat, and dairy may not address the constipation issue and might contribute to a low-fiber diet.
Codeine 15 mg IM q4h is ordered. Codeine is available in a vial containing 30 mg/mL. How many mL will the nurse administer?
Explanation
To answer this question, we need to use the formula: D/H x Q = X, where D is the desired dose, H is the dose on hand, Q is the quantity of the drug on hand, and X is the amount to administer. In this case, D is 15 mg, H is 30 mg, Q is 1 mL, and X is unknown. Plugging these values into the formula, we get:
15/30 x 1 = X
0.5 = X
Therefore, the nurse will administer 0.5 mL of codeine to the patient every four hours.
Patients who use supplemental oxygen should follow which safety precautions? SELECT ALL THAT APPLY
Explanation
A. Avoiding synthetic materials helps reduce the risk of static electricity, which could lead to fires.
B. Lit candles pose a fire hazard in the presence of supplemental oxygen.
C. Electric razors can create sparks or flames that can ignite the oxygen and cause a fire or explosion.
D. Storing oxygen away from heat sources reduces the risk of fire.
E. Smoking in the presence of supplemental oxygen is extremely dangerous and should be strictly avoided.
A patient consumed 8oz of coffee and 200mL of water at breakfast, and urinated 300mL. At lunch he consumed a 12oz tea, 60 mL popsicle (frozen ice), and urinated 300mL. After lunch the patient felt nauseated and had 60mL of emesis. Calculate the total output for this patient.
Explanation
To calculate the total output for this patient, we need to add up the amount of fluid that he lost through urination and emesis. Urination is the process of expelling urine from the body, and emesis is the medical term for vomiting. The patient urinated 300mL in the morning and 300mL at lunch, so the total amount of urine output is 600mL. The patient also had 60mL of emesis after lunch, so the total amount of emesis output is 60mL. Therefore, the total output for this patient is 600mL + 60mL = 660mL.
A 60-year-old client is experiencing pain that is caused by distention of the veins in their rectum. What health problem is this client most likely experiencing?
Explanation
A. Laxative usage is more likely to cause diarrhea or loose stools rather than rectal pain from distended veins.
B. Paralytic ileus is characterized by a lack of bowel motility and is not associated with distention of veins in the rectum.
C. Diarrhea is unlikely to cause pain related to distention of rectal veins.
D. Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the rectum and anus, causing pain and discomfort, especially during bowel movements.
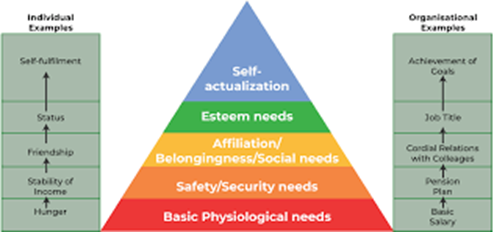
Which of the following are stages recognized by Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory? (Select all that apply).
Explanation
A. Self-Actualization Needs is the highest level in Maslow's hierarchy, representing the fulfillment of personal potential and growth.
B. Physiological Needs is the foundational level, including basic needs like food, water, and shelter.
C. Maslow's hierarchy does not explicitly include spiritual enlightenment as a distinct stage.
D. This stage involves the desire for self-respect, confidence, and recognition.
E. This stage involves the need for interpersonal relationships, love, and a sense of belonging.
A nurse touches a patient's hand to indicate caring and support. What channel of communication is the nurse using within Berlo's Model of Communication?
Explanation
A. Touch is a kinesthetic channel of communication, involving physical contact or body movements.
B. Olfactory relates to the sense of smell and is not relevant to touch.
C. Visual relates to sight and visual cues.
D. Auditory relates to hearing and auditory cues.
A nurse is caring for a client who states "I just don't feel ready to go home." The nurse replies, "you don't feel ready to go home today?" Which type of interviewing technique is the nurse using to enhance communication with the client?
Explanation
A. Directing question involves directing the conversation toward a specific topic or answer.
B. Reflective question involves restating or reflecting the client's words to encourage further communication and exploration of feelings.
C. Sequencing question involves organizing the client's story in chronological order.
D. Disconfirming question involves challenging or denying the client's statements.
A nurse is providing instruction to a client who will be performing a 24 hour urine collection at home. Which of the following instructions will the nurse give the client?
Explanation
A. Keeping the specimen container refrigerated or on ice helps preserve the integrity of the urine sample.
B. Using any type of container may not provide accurate results; a specific collection container is usually recommended.
C. Dating and timing the specimen container at the end of the 24-hour collection period are essential for accurate analysis.
D. Keeping the urine warm is not necessary and may not be practical during the entire collection period.
A client has been prescribed a clear liquid diet. What food or fluid will not be served?
Explanation
A. Apple juice is a clear liquid and is suitable for a clear liquid diet.
B. Chicken broth is a clear liquid and is suitable for a clear liquid diet.
C. Jell-O (gelatin) is a clear liquid and is suitable for a clear liquid diet.
D. Chocolate milk is not a clear liquid; it contains solids and is not appropriate for a clear liquid diet.
A nurse has received an order to suction a patient's endotracheal tube. Which action is most appropriate when performing this intervention?
Explanation
A. Occluding the Y-port during insertion is not a standard practice and may impede proper suctioning.
B. Limiting the application of suction to 20-30 seconds helps prevent hypoxia and tissue damage.
C. Assisting the client into a supine position is not a standard practice for endotracheal tube suctioning.
D. Using sterile saline to moisten the end of the suction catheter may introduce unnecessary moisture into the airway.
A nurse is gathering assessment data on a new patient at the clinic for a yearly physical assessment. The patient is a 55-year-old Hispanic obese male. Patient states his father died at age 52 of a heart attack. During the interview, the patient states they have a desk job and sits all day, eats mostly fast- food, and traditional foods high in fat, and smokes 1 pack of cigarettes per day. The patient states in the evening he mostly enjoys sitting on the couch watching television. The nurse plans to provide education to the patient on modifiable risk factors to prevent coronary artery disease. Which of the following are a modifiable risk factors?
Explanation
A. Race and gender are non-modifiable risk factors.
B. Sedentary lifestyle, diet high in fats, smoking, and obesity are modifiable risk factors.
C. Age and family history are non-modifiable risk factors.
D. Race, age, and gender are non-modifiable risk factors.
A client had his foley catheter removed eight hours ago and is unable to void. The nurse performs a bladder scan to check bladder volume. The bladder scan demonstrates more than 600mL of urine in the bladder. What should the nurse do next?
Explanation
A. Palpating the abdomen may provide additional information but is not the next step in this situation.
B. Documenting the finding as normal volume is not appropriate; a bladder volume of more than 600mL is considered significant.
C. Performing In & Out catheterization is the next step to relieve urinary retention.
D. Rechecking the bladder scan in 6 hours is not appropriate when immediate intervention is needed.
The nurse is assessing a client's stoma after a newly placed ostomy. The nurse understands that which of the following are expected findings of a healthy appearing stoma?
Explanation
A. A healthy stoma is typically dark pink or red in color, indicating good blood supply.
B. Black, purple, or blue colors may indicate poor blood supply and potential ischemia.
C. Black, purple, or blue colors may indicate poor blood supply and potential ischemia.
D. A pale color may indicate poor blood supply and potential ischemia.
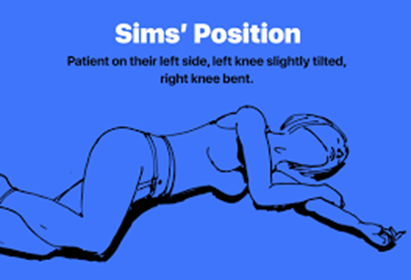
A client is on bedrest, and an enema has been ordered. In what position should the nurse position the client?
Explanation
A. The Sims position (lying on the left side with the upper knee flexed) is commonly used for administering enemas.
B. Trendelenburg (head lower than feet) would increase the risk of aspiration and fluid overload.
C. Fowlers (sitting at a 45-60-degree angle) would decrease the flow of the solution and cause discomfort.
D. Prone (lying on the stomach) position would prevent the insertion of the enema tube and the administration of the solution.
For which of the following clients should the nurse anticipate the need for a pureed diet?
Explanation
A. Hip surgery may not necessarily require a pureed diet.
B. Individuals with difficulty swallowing, as seen in stroke patients, may require a pureed diet to prevent choking and aspiration.
C. Bariatric surgery may involve dietary modifications, but it does not automatically require a pureed diet.
D. Dementia alone may not necessitate a pureed diet; it depends on the individual's ability to chew and swallow safely.
A 73 year old client has been admitted to the hospital for their respiratory disease of COPD. The client states that they have no appetite and eat very little throughout the day due to shortness of breath. The client also states that they have lost significant amounts of weight over the past several months. The nurse caring for the client is concerned that the client may be suffering from malnutrition. Which lab value would the nurse want to check to determine if the client is malnourished?
Explanation
A. Serum albumin level is often used as a marker of nutritional status, and low levels may indicate malnutrition.
B. Cholesterol level is not a specific indicator of malnutrition.
C. White blood cell count is typically associated with immune function rather than nutritional status.
D. Potassium level may be affected by various factors but is not a specific marker for malnutrition.
Age, race, gender, and genetic inheritance are examples of what type of risk factors?
Explanation
A. Intrinsic risk factors are inherent characteristics such as age, race, gender, and genetic inheritance.
B. Extrinsic risk factors are external influences like smoking, diet, and physical activity.
C. Spiritual and emotional factors are not classified as intrinsic risk factors.
D. Emotional factors are not classified as intrinsic risk factors.
The nurse understands that emphysema decreases lung tissue elasticity. How does this affect lung inflation?
Explanation
A. Emphysema is not associated with bronchodilation; it is characterized by the destruction of alveoli.
B. Emphysema does not directly increase oxygen saturation; it impairs gas exchange.
C. Emphysema does not affect systole; it primarily affects lung function.
D. Emphysema decreases lung tissue elasticity, leading to decreased compliance, making it harder for the lungs to inflate and deflate.
The nurse is obtaining morning vital signs and assessing a 64 year old female client who was admitted with community acquired pneumonia over night. The client is sleeping in supine position, however, she is easily arousable, alert and oriented, and reports no complaints at this time. The client's vital signs are: blood pressure 132/68, heart rate 88 beats per minute, respiratory rate 24 breaths per minute. O2 saturation 87% on 2L nasal cannula oxygen. What is the nurse's first priority action?
Explanation
A. Increasing oxygen via face mask may be necessary, but raising the head of the bed is the initial priority to improve oxygenation.
B. Reporting vital signs is important, but immediate intervention is needed to address the low oxygen saturation.
C. Raising the head of the bed helps improve lung expansion and oxygenation in pneumonia patients by reducing pressure on the diaphragm.
D. Administering albuterol may be part of the plan, but improving the client's position is the immediate priority.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 50 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

