Kaplan fundamentals ngn
Total Questions : 29
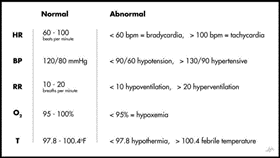
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreThe nurse is caring for a senior adult client with three diagnoses of Parkinson's disease and an exacerbation of COPD. The nurse observes the unlicensed assistant personnel (UAP) providing morning care and obtaining vital signs by using a portable electronic blood pressure cuff and clip-on pulse oximetry sensor.
Nurse's Notes: Vital Sign # 0715: Client sitting up in bed with oxygen 2.1 per nasal cannula (NC) on. Clear pink skin and warm and dry lungs with scattered wheezes throughout. The client complains of shortness of breath and states, "I feel so much better than I did a couple of days ago." Mild tremors were noted. The client states, "My hands shake all the time."
1140: Client is still in bed with oxygen 2.1 per NC on, scattered wheezes throughout, and coarse rhonchi, which are clear with coughing. Cough is productive of yellow phlegm. Skin cool and dry. The client complains of shortness of breath or discomfort and states, "I like to keep it chilly in my room to help me breathe."
1140: The UAP reports to the nurse that the client's SpO2 is decreased.
Q1. After assessing the patient and reviewing the vital signs, which nursing action is appropriate to address the decreased SpO2?
(Select all that apply.)
Explanation
The nurse should verify the pulse oximeter is intact and properly applied and verify the supplemental oxygen is turned on and functioning. The nurse should also correlate the apical pulse rate with the pulse rate on the oximeter to ensure accuracy.
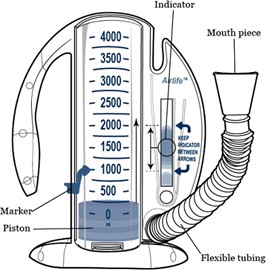
The nurse instructs the client on the use of an incentive spirometer. Which observation indicates to the nurse that additional teaching is required?
Explanation
An incentive spirometer is used to help improve lung function by encouraging deep breathing. The user should inhale through the mouthpiece, not through the nose. This observation indicates that additional teaching is required.
The nurse provides care for a client with a poor appetite. Which action does the nurse take to enhance the client's nutritional intake?
Explanation
This action can help enhance the client's nutritional intake by ensuring that the client has enough time to eat without interruptions. It is important for the nurse to prioritize the client's mealtimes and make sure that they are not disrupted by other procedures or activities.
The emergency department (ED) triage nurse receives a report from emergency medical services (EMS) on an older adult client being brought to the ED via EMS. After receiving the report, the nurse reviews the client's electronic medical record (EMR) for history and the most recent medication list.
1635: Most recent entry from a visit to primary care provider 5 days ago. Vital signs were BP 164/90, HR 96, RR 20, T 96.7°F (35.9°C), and SpO2 96% on room air. Past Medical History (PMH) positive for osteoporosis, a history of ovarian cancer treated with a hysterectomy and chemotherapy 16 years ago, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertension being managed with diet and exercise. During this recent visit, the client was started on hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) 12.5 mg, 1 tablet PO every AM. No Known Drug Allergies (NKDA). Additional home medications include:
- Atorvastatin 20 mg PO, 1 tablet every PM
- Calcium 1000 mg, 1 tablet PO BID
- multi-vitamin, 1 capsule PO every AM
The nurse obtained the bloodwork, started the IV, and administered morphine IV push.
> Complete the following sentence:
The nurse's highest priority is planning care knowing that the client is at risk for seizures due to ______ and _______.
Explanation
The nurse's highest priority is planning care knowing that the client is at risk for seizures due to hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) and chemotherapy.
The nurse's highest priority is planning care knowing that the client is at risk for seizures due to the recent initiation of hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), which can cause electrolyte imbalances such as hyponatremia, and the history of chemotherapy for ovarian cancer, which may increase the risk of seizure activity.
The emergency department (ED) triage nurse receives a report from emergency medical services (EMS) on an older adult client being brought to the ED via EMS. After receiving the report, the nurse reviews the client's electronic medical record (EMR) for history and the most recent medication list.
The client was transferred to ED Bed 5 via stretcher. The client’s spouse is at the bedside. The client states "I feel so much better now except my wrist. It's really hurting." Advised to assess and then check with ED physician about something for the pain. VS BP 112/68 HR 99 RR 20. T 98.4° F (36.9° C). SpO2 96% on room air. The client is alert and oriented (A&O x 4), pleasant, and cooperative. PERRLA, skin intact with no bruising except for dorsal left forearm and wrist which is ecchymotic and edematous. Radial pulses are strong and equal (+3). Fingers warm with capillary refill - 3 sec. Lungs clear Abdomen soft with bowel sounds x 4 quadrants. Pedal pulse + x 4 and no pedal edema.
The client is being prepped for an open reduction internal fixation of the left wrist on the morning of day 2.
> Which three findings indicate that the client’s hemodynamic status has improved?
Explanation
An increase in blood pressure (BP) from 112/68 mm Hg to 122/80 mm Hg indicates an improvement in hemodynamic status, as it shows that the client's blood vessels are constricting to maintain BP and tissue perfusion. f) An increase in urine output from 18 mL/hour to 45 mL/hour indicates an improvement in renal function and fluid balance, which is important for maintaining hemodynamic stability. c) An increase in serum potassium level from 5 mEq/L (5 mmol/L) to 5.4 mEq/L (5.4 mmol/L) indicates an improvement in electrolyte balance, which is important for maintaining proper cardiac function and hemodynamic stability.
Option b) Serum sodium decreased from 146 mEq/L (146 mmol/L) to 138 mEq/L (138 mmol/L) is not a finding that indicates improvement in hemodynamic status. Hyponatremia or low serum sodium levels can cause fluid shifts in the body leading to altered mental status, seizures, and cerebral edema, among other complications. However, the given information does not suggest that the client has hyponatremia or that their hyponatremia has improved.
Option d) Urine output averaging 18 mL/hour is not an improvement, and it may indicate renal insufficiency or failure, which can lead to fluid overload and hemodynamic instability.
Option e) Bowel sounds in all four quadrants indicate normal bowel motility, which is important for proper digestion and absorption of nutrients but does not directly indicate an improvement in hemodynamic status.
The nurse provides care for a client recovering from a motor vehicle crash. For which sign of fluid volume overload does the nurse measure the client's intake and output? (Select all that apply)
Explanation
These are all signs of fluid volume overload. Measuring the client's intake and output can help the nurse monitor the client's fluid balance and detect any imbalances. A productive cough may indicate fluid accumulation in the lungs.
Weight gain and edema are also signs of fluid retention.
The nurse provides care for a client having an incisional biopsy of a skin lesion. Which teaching about the care of the site does the nurse provide to the client?
Explanation
After an incisional biopsy of a skin lesion, the client should be instructed to keep the suture area covered with gauze to protect it from irritation and infection. The area should be kept clean and dry, but cleansing with hydrogen peroxide is not necessary and may actually delay healing. The use of hydrocortisone cream is not recommended as it may interfere with wound healing. The area should not be left open to air as this may increase the risk of infection. The client should also be instructed to avoid strenuous activity and lifting heavy objects until the site has fully healed.
The nurse provides care for a child with an abdominal wound. The wound edges are approximated. Which does the nurse include when rendering the prescribed wound care to this child? (Select all that apply)
Explanation
These are all important steps in rendering prescribed wound care for a child with an abdominal wound. Measuring the size of the wound helps to track healing progress. Working outward from the incision and wiping from a clean area to a less clean area helps to prevent infection.

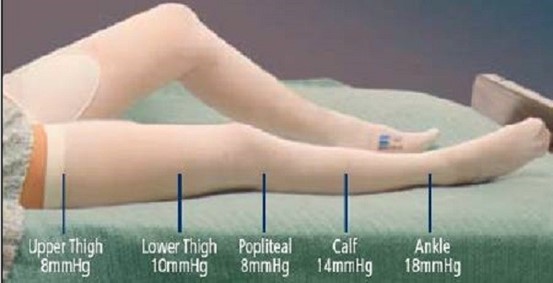
A client recovering from surgery sits in a chair for breakfast. Which action does the nurse take before applying newly prescribed anti-embolism stockings to the client's lower extremities?
Explanation
Before applying anti-embolism stockings, the nurse should ask the client to lie supine in bed for 15 minutes. This is because anti-embolism stockings should be applied with the client in a supine position ¹. This helps to promote blood return to the heart and decrease the risk of blood clots ¹.
A client receives a clear liquid diet. The nurse removes which item from the client's tray? (Select all that apply)
Explanation
A clear liquid diet consists of clear liquids that are easily digestible and leave no undigested residue in the intestinal tract. This includes items such as clear juices, broths, and popsicles. Coffee with cream and sugar and gelatin with applesauce are not considered clear liquids and should be removed from the client's tray.

An infant client has a tracheostomy. The nurse prepares to suction the tracheostomy. Which most important principle does the nurse use to plan care?
Explanation
It is important to use the appropriate suction pressure, time, and catheter size when suctioning a tracheostomy to prevent injury and ensure effective removal of secretions.
The nurse omits to document an assessment finding that resulted in a significant client injury. For which legal issue does the nurse need to prepare?
Explanation
Malpractice refers to professional negligence or failure to provide the appropriate level of care that results in harm to a patient. In this case, the nurse's omission of documenting an assessment finding that resulted in a significant client injury could be considered malpractice.
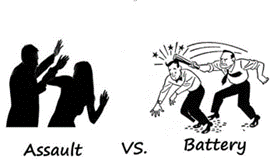
A family member tells the nurse, "I overheard a caregiver threaten my uncle." The family member said the caregiver remarked, "If you don't learn to calm down, I will have to restrain you." Based on this information, which criminal offense does the nurse communicate to the nurse manager?
Explanation
Assault is an intentional act that causes another person to be in fear of immediate harm ¹. In this case, the caregiver's threat to restrain the uncle if he doesn't calm down can be considered an assault because it puts the uncle in fear of immediate harm.
The battery is defined as an intentional offensive or harmful touching of another person that is done without his or her consent ³. Malpractice refers to professional negligence by a healthcare provider that causes injury or harm to a patient. Negligence refers to a failure to exercise reasonable care that results in harm to another person. In this scenario, there is no evidence of batery, malpractice, or negligence.
A client receives a diagnosis of right-sided paralysis. Which action does the nurse take when assisting the client in transferring from the bed to the wheelchair?
Explanation
This is because the client has right-sided paralysis and will not be able to bear weight on their right leg. By standing on their left leg and pivoting to the chair, the client can safely transfer from the bed to the wheelchair with the assistance of the nurse.
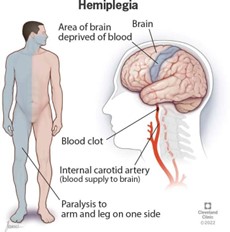
The nurse delegated vital signs for a group of patients to the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). Which client condition would prohibit having a rectal temperature taken by the UAP?
Explanation
A rectal temperature should not be taken if the client has bradycardia because stimulation of the vagus nerve during the insertion of the rectal thermometer can result in a further decrease in heart rate. Hypertension, tachypnea, and pyrexia are not contraindications for taking a rectal temperature.
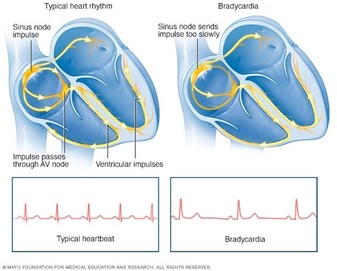
The nurse evaluates a client's plan of care. The client has an outcome of 'Client will learn self-glucose testing before discharge'. When evidence best allows the nurse to meet the outcome of the plan?
Explanation
This is because the outcome of the plan is for the client to learn self-glucose testing, which implies that the client can perform the testing correctly on their own. Option A shows that the client has successfully learned and can perform the skill independently, which is the ultimate goal of the plan.
Option B, "Client says 'I can do the testing now'," and option C, "Client explains the testing process to the nurse," may show that the client has some understanding of the testing process, but they do not demonstrate that the client can perform the skill independently.
Option D, "Client observes the nurse test glucose 5 times," is not an appropriate method for evaluating the client's ability to perform self-glucose testing. Observing the nurse perform the skill does not demonstrate that the client has learned the skill themselves.
The nurse plans care for a client who reports avoiding people because of having scabies and difficulty walking. Which statement does the nurse document as the client's greatest concern?
Explanation
The client's statement of avoiding people because of having scabies and difficulty walking indicates that the client may be experiencing social isolation and loneliness. Loneliness is a significant concern for clients as it can lead to depression, anxiety, and other negative health outcomes. The other options, such as the potential for falls, injury, and self-neglect, may also be concerns for the client but are not indicated as the greatest concern in this scenario based on the information provided. Therefore, the nurse should document the client's greatest concern as the potential for loneliness.
A young adult client has a partner and no children. The client has a hysterectomy because of endometrial cancer. The client has an IV and an indwelling urinary catheter. The client is crying asking for their partner. Which action does the nurse take first?
Explanation
The client is likely feeling scared, vulnerable, and alone. By calling the partner to come and visit, the nurse can provide the client with emotional support and comfort during this difficult time. This can also help to alleviate the client's distress and promote a sense of security and familiarity.
Assessing the IV site for inflammation (a) and measuring the urine output for the day (b) are important aspects of the client's care, but they are not the priority in this situation. Asking the client if pain medication is required (d) is also important, but it can wait until the client's emotional needs have been addressed.
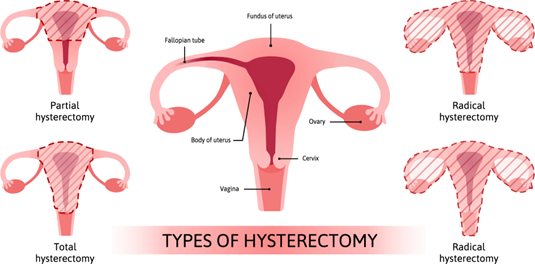
The nurse provides care for a client who is severely malnourished. A central venous access device (CVAD) is placed to administer total parenteral nutrition (TPN). Which laboratory result does the nurse closely monitor?
Explanation
Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) is a form of nutrition that is administered intravenously when a client is unable to eat or absorb nutrients orally or enterally. TPN solutions contain a high concentration of glucose, which provides the body with energy. Therefore, the nurse must closely monitor the client's glucose levels, as TPN can cause hyperglycemia (high blood sugar levels).
Frequent monitoring of blood glucose levels is necessary to ensure that the client's blood sugar stays within an acceptable range. Hyperglycemia can lead to a variety of complications, including dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and damage to organs such as the kidneys and eyes. If the client's blood glucose levels are consistently high, adjustments to the TPN solution may be necessary, or insulin may need to be administered to help regulate blood sugar levels.
Therefore, glucose is the laboratory result that the nurse must closely monitor when a client is receiving TPN via a central venous access device (CVAD).
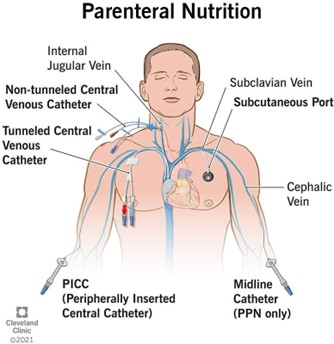
In which situation is the nurse determined to be negligent?
Explanation
Negligence is a failure to act in a reasonable and prudent manner that results in harm or injury to another person. In option c), the nurse did not exercise reasonable care in ensuring that the medication was given to the correct patient, which resulted in harm to the wrong patient.
The other options (a, b, and d) do not involve a failure to act in a reasonable and prudent manner that caused harm or injury to the client. In option a), the nurse provided written and verbal instructions, but the client did not follow them, which is beyond the nurse's control.
In option b), the nurse made an error in documenting the fluid count, which is a documentation error, not negligence. In option d), the nurse acted appropriately by calling the healthcare provider to change the client's behavior, and the situation does not involve negligence.
The nurse provides care for a client diagnosed with pneumonia. The client is unable to expectorate respiratory secretions. The nurse suctions the client's nasopharyngeal airway. When is suctioning technique correct?
Explanation
When suctioning a client's nasopharyngeal airway, the nurse should moisten the catheter with sterile saline or water-soluble lubricant prior to insertion. This helps to decrease discomfort and trauma to the client's nasal mucosa.
Advancing the catheter 2-3 inches (5 to 7.6 cm) (a) is not correct because it can cause injury to the client's airway or trachea. The catheter should only be inserted to a distance equal to the distance from the nose to the earlobe (about 6 to 8 inches or 15 to 20 cm).
Applying suction intermittently for 20 seconds (b) is not correct because it can cause hypoxia and trauma to the client's airway. The suction should be applied continuously while withdrawing the catheter, for no more than 10 seconds.
Using the non-dominant hand to manipulate the catheter (d) is not correct because it can cause the catheter to become contaminated with the nurse's non-sterile hand. The dominant hand should be used to manipulate the catheter while maintaining sterile technique.
While the nurse prepares an injection for a client, the needle cap falls on the floor. Which action indicates that the injection will be sterile?
Explanation
Dropping the needle cap on the floor contaminates it, and any attempt to clean it with alcohol will not make it sterile again. Therefore, the only way to ensure that the injection will be sterile is to use a new sterile syringe and needle.
Holding the syringe upright or cleansing the contaminated needle cap with alcohol is not enough to ensure sterility and can put the patient at risk for infection.
The nurse provides care for a patient with an infected surgical wound. The nurse assesses the wound and changes the dressing. Which does the nurse include in the documentation? Select all that apply.
Explanation
a. Presence of exudate: The presence and amount of exudate can indicate the severity of the infection and the effectiveness of treatment.
c. Approximation of edges: This refers to how well the edges of the wound are coming together and healing, which is important in evaluating the progress of healing.
e. Color of wound bed: The color of the wound bed can also indicate the severity of infection and the effectiveness of treatment.
Therefore, the correct answers are a, c, and e.
The number of sutures and the time of the last antibiotic are important information for the nurse to know, but they do not need to be included in the documentation of the wound assessment and dressing change.
The nurse provides care to a toddler-age client and prescribed catheterization to obtain a urine specimen. Which procedure does the nurse implement? (Select all that apply)
Explanation
It is important to explain the procedure in detail before beginning to help the child understand what is happening and reduce anxiety. Having the child blow on a pinwheel during insertion can help distract them and reduce discomfort. A size 10 Fr catheter is appropriate for a toddler-age child ¹². Inserting 2% lidocaine lubricant into the meatus can help reduce discomfort during the procedure.
On the other hand, inserting the catheter about 5 cm may not be appropriate as the depth of insertion varies depending on the child's anatomy. Using firm pressure if resistance is met is not recommended as it can cause injury to the urethra.
A bed-bound chart has a prescription for routine urinalysis. In which way does the nurse obtain the urine sample for the laboratory?
Explanation
This is known as a clean-catch urine sample. The nurse cleanses the urinary meatus to reduce the chance of contamination from bacteria on the skin. The patient then collects a urine sample in a sterile container while voiding.

Sign Up or Login to view all the 29 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

