Miami Dade College Pharmacology NUR1141
Total Questions : 57
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA toddler ingests a small amount of household cleaning fluid. What is the safest advice for the nurse to provide the caregiver?
Explanation
A. Give the child fluids and proceed to the emergency department.
While giving the child fluids is generally important, proceeding to the emergency department without consulting poison control may not be the most appropriate initial action. Poison control can provide specific guidance based on the substance ingested.
B. Call the poison control center and follow directions.
The safest advice for a toddler who has ingested a small amount of household cleaning fluid is to call the poison control center and follow their directions. Poison control centers are staffed with professionals who can provide specific guidance based on the type and amount of the ingested substance. They can advise on the appropriate steps to take, such as whether immediate medical attention is needed or if monitoring at home is sufficient.
C. Administer syrup of ipecac and monitor for vomiting.
The use of syrup of ipecac is no longer recommended as a routine measure for ingested substances. It can have adverse effects and may not be effective for all substances. Consulting poison control for guidance is considered a more appropriate approach.
D. Have the toddler eat bread to absorb the substance.
The ingestion of certain substances may not be effectively addressed by having the toddler eat bread. The specific advice for management should come from poison control, which can provide evidence-based guidance.
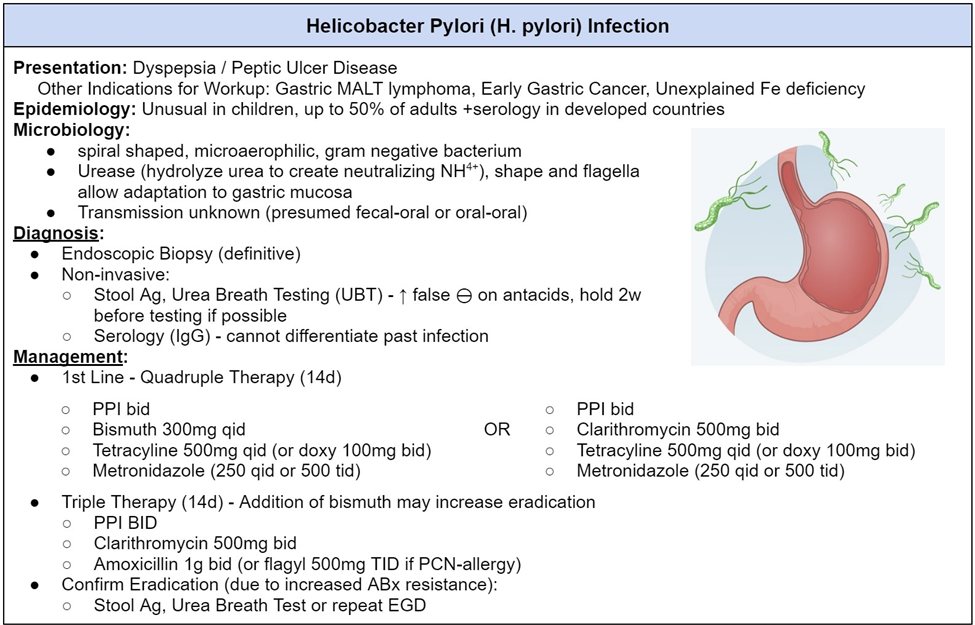
A patient with peptic ulcer disease is noted to have a positive breath test for H. pylori. What will the nurse anticipate the health care provider will order?
Explanation
A. Antacids and narcotics.
Antacids can provide temporary relief of symptoms, but they do not treat the underlying H. pylori infection. Narcotics are not typically used as a standard treatment for peptic ulcer disease related to H. pylori.
B. Pepsin inhibitors and antiemetics.
Pepsin inhibitors and antiemetics may address symptoms but do not target the H. pylori infection directly. The standard treatment involves antibiotics to eradicate the bacteria and proton pump inhibitors to reduce acid production.
C. Proton pump inhibitors and antibiotics.
A positive breath test for H. pylori indicates the presence of Helicobacter pylori bacteria, which is associated with peptic ulcer disease. The standard treatment for H. pylori infection involves a combination of proton pump inhibitors (to reduce stomach acid production) and antibiotics (to eradicate the bacteria).
D. Emetic agents and tranquilizers.
Emetic agents are used to induce vomiting and are not indicated for the treatment of H. pylori infection. Tranquilizers are not part of the standard treatment for peptic ulcer disease associated with H. pylori.

A patient with a gastric ulcer is ordered sucralfate (Carafate). How does this medication works?
Explanation
A. Calm the patient to reduce acid production.
This description is not accurate for sucralfate. Calming the patient to reduce acid production is typically associated with medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 receptor blockers.
B. Block the H2 receptors.
Blocking H2 receptors is the mechanism of action for H2 receptor blockers, such as ranitidine. It is not the mechanism of action for sucralfate.
C. Neutralize the gastric acids.
Neutralizing gastric acids is the mechanism of action for antacids, such as aluminum hydroxide or calcium carbonate. Sucralfate works differently; it forms a protective coating on the gastric lining rather than directly neutralizing acids.
D. Coat the gastric lining.
This is the correct mechanism of action for sucralfate. It forms a protective coating on the gastric lining, adhering to the ulcer site and providing a barrier against gastric acid.
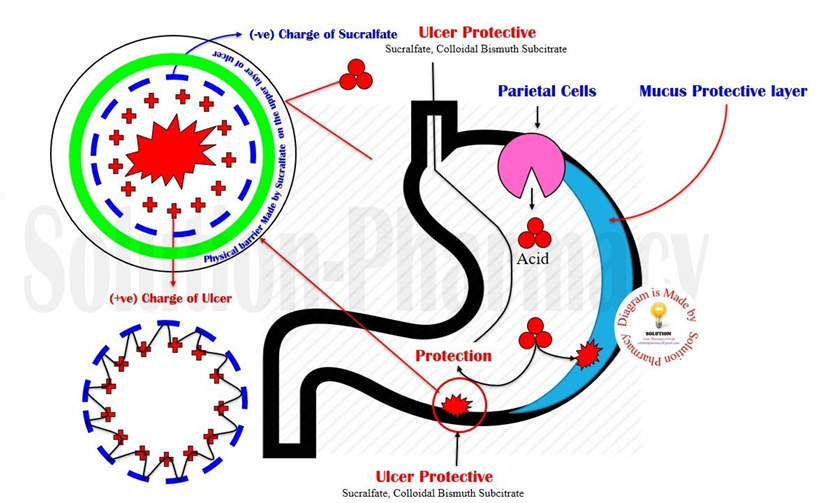
A patient who complains of gastric distress from NSAIDS such as aspirin or indomethacin will most likely benefit from the administration of which medication?
Explanation
A. Misoprostol (Cytotec)
The patient complaining of gastric distress from NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) like aspirin or indomethacin may benefit from the administration of misoprostol (Cytotec). Misoprostol is a prostaglandin analog that helps protect the stomach lining and reduce the risk of NSAID-induced gastric ulcers.
B. Lansoprazole (Prevacid)
Lansoprazole is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that reduces stomach acid production. While PPIs can be used for certain acid-related conditions, they do not directly protect against NSAID-induced gastric distress.
C. Magaldrate (Riopan)
Magaldrate is an antacid that neutralizes stomach acid. It may provide relief from symptoms of indigestion but does not specifically address the gastric distress caused by NSAIDs.
D. Magnesium trisilicate (Gaviscon)
Magnesium trisilicate is an antacid that helps neutralize stomach acid. Like magaldrate, it may alleviate symptoms of indigestion but does not target the underlying issue of NSAID-induced gastric distress.
A patient is suspected to have peptic ulcer disease from H. pylori. The patient asks the nurse what kind of testing will be done to determine the cause of the peptic ulcer. What will the nurse tell the client?
Explanation
A. Blood cultures will need to be drawn.
Blood cultures are not typically used for diagnosing H. pylori infection. Instead, specific blood tests, such as serology or antibody tests, may be employed to detect antibodies against H. pylori.
B. A biopsy of the stomach will be done.
While a biopsy may be taken during an upper endoscopy to examine the stomach lining for ulcers and H. pylori infection, it is not the primary method for detecting the presence of H. pylori. The biopsy may be used for confirming the infection and assessing the severity of damage.
C. A breath test will be performed.
This is the correct choice. The breath test is a common and non-invasive method used to detect the presence of H. pylori. The patient drinks a solution containing a substance that H. pylori can break down, and the detection of carbon dioxide in the patient's breath indicates the presence of the bacteria.
D. Computerized scanning will identify if H. pylori is present.
Computerized scanning, such as computed tomography (CT) scans, is not a primary method for detecting H. pylori. Imaging studies are not typically used for H. pylori diagnosis, and the methods mentioned earlier, like breath tests and endoscopy, are more commonly employed.
A patient is ordered bisacodyl (Dulcolax). Before administering the drug, it is most important for the nurse to assess the patient for what?
Explanation
A. Hypertension
Hypertension is not a specific concern related to the use of bisacodyl. Bisacodyl is a laxative, and high blood pressure is not typically considered a contraindication for its use.
B. Anemia
Anemia is not a specific concern related to the use of bisacodyl. The primary focus before administering bisacodyl is to assess for signs or symptoms of appendicitis, as its use is contraindicated in cases of suspected appendicitis.
C. Allergy to penicillin
Allergy to penicillin is not relevant in the context of administering bisacodyl. These are unrelated medications with different mechanisms of action, and allergy to penicillin does not impact the administration of bisacodyl.
D. Appendicitis
This is the correct choice. Before administering bisacodyl, it is crucial to assess the patient for signs or symptoms of appendicitis. The use of bisacodyl is contraindicated in cases of suspected appendicitis, as it may stimulate bowel activity and worsen the condition.
A patient is ordered a phenothiazine antiemetic for treatment of nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy. The nurse will be evaluating for a positive effect. At what time should the nurse administer the drug?
Explanation
A. As requested by the patient.
Administering the drug only when requested by the patient may not provide adequate prophylaxis against chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. These medications are often prescribed on a schedule to prevent symptoms rather than treating them reactively.
B. 1 hour after chemotherapy administration.
Waiting until 1 hour after chemotherapy administration may not cover the full period during which nausea and vomiting are likely to occur. The administration schedule for antiemetics is often more extended to provide better coverage.
C. The night before the treatment, the day of the treatment, and for 24 hours after the treatment.
This is the correct choice. Administering phenothiazine antiemetics according to this schedule helps ensure continuous coverage during the critical period when chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting are most likely to occur.
D. The day of treatment.
Administering the drug only on the day of treatment may not provide sufficient coverage for the entire duration when chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting can occur. Again, the schedule mentioned in option C is more comprehensive for prevention.
The nurse is instructing a patient who will take psyllium (Metamucil) to treat constipation. What information will the nurse include when teaching the patient?
Explanation
A. The importance of consuming adequate amounts of water
When instructing a patient who will take psyllium (Metamucil) to treat constipation, it is crucial to emphasize the importance of consuming adequate amounts of water. Psyllium is a bulk-forming laxative that works by absorbing water in the intestines, forming a gel-like mass that helps soften stools and promote bowel movements. Without sufficient water intake, psyllium may cause an obstruction or worsen constipation.
B. The need to monitor for systemic side effects.
Psyllium is generally well-tolerated and is not associated with significant systemic side effects. The primary consideration is ensuring proper hydration.
C. The onset of action of 30-60 minutes after administration.
Psyllium is not a fast-acting laxative. It usually takes a longer time to produce its effects, and patients should not expect an immediate response within 30-60 minutes.
D. The need to use the dry form of psyllium to prevent cramping.
Using the dry form of psyllium is not recommended, as it may increase the risk of choking or swallowing difficulties. It is typically recommended to mix psyllium with a sufficient amount of water or other liquids to prevent cramping and ensure proper absorption.
The nurse is deciding on a dosage schedule for methylphenidate (Ritalin). The nurse recognizes that which time is the most appropriate to administer this drug for maximum effectiveness?
Explanation
A. Before breakfast or lunch
Methylphenidate (Ritalin), a stimulant medication commonly used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), is usually administered before breakfast or lunch for maximum effectiveness. This schedule helps align the peak concentration of the medication with the times when increased focus and attention are often needed, such as during school hours.
B. With meals
While it can be administered with meals, the goal is often to have the medication take effect before meals to help with focus and attention during activities like school or work.
C. After dinner
Administering methylphenidate after dinner may interfere with the patient's ability to fall asleep, as the medication can cause insomnia. It is generally recommended to avoid administering it in the late afternoon or evening.
D. At bedtime
Administering methylphenidate at bedtime is not appropriate due to the potential for insomnia. The stimulant effect of the medication is not aligned with the patient's sleep-wake cycle.
How will the parents of a 8 year old child diagnosed with ADHD most typically describe their child's behavior?
Explanation
A. A learning disorder and muscle paralysis
This description does not align with the typical symptoms of ADHD. ADHD is characterized by core symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Muscle paralysis is not a recognized symptom of ADHD.
B. Nervousness and sleeplessness
While some individuals with ADHD may experience difficulties with sleep, nervousness and sleeplessness are not the primary symptoms of ADHD. ADHD is more characterized by difficulties with attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
C. Hyperactivity and decreased attention span
This is the correct choice. Hyperactivity and a decreased attention span are core symptoms of ADHD. Children with ADHD often display impulsive behaviors, have difficulty sustaining attention, and may be overly active.
D. Hyperactivity and nervousness
While hyperactivity is a common symptom of ADHD, nervousness is not typically described as a core symptom. ADHD is more characterized by impulsivity, hyperactivity, and attention difficulties.
A nurse is teaching a client measures to help relieve sleeplessness. Which would be the highest priority teaching point during the instructional session?
Explanation
A. Avoid caffeine-containing beverages before sleep
The highest priority teaching point to help relieve sleeplessness would be to advise the client to avoid caffeine-containing beverages before sleep. Caffeine is a stimulant that can interfere with the ability to fall asleep and maintain a restful sleep.
B. Perform strenuous exercise before bedtime
Strenuous exercise close to bedtime can actually stimulate the body and make it more difficult for the individual to relax and fall asleep. It is generally recommended to engage in exercise earlier in the day.
C. Drink lots of fluids before bedtime
Drinking excessive fluids before bedtime may lead to disrupted sleep as it can increase the need to wake up for bathroom trips during the night. It's advisable to limit fluid intake close to bedtime.
D. Eat a heavy meal before bedtime
Consuming a heavy meal before bedtime can cause discomfort and indigestion, potentially disrupting sleep. It is recommended to have a light, easily digestible meal if eating close to bedtime.
Prescribed is 750 mL of IV fluids to infuse in 10 hours. What rate should the nurse program the IV infusion pump for?
Explanation
To calculate the rate of IV infusion, the nurse should divide the volume of fluid by the time in hours.
In this case, 750 mL divided by 10 hours equals 75 mL per hour.
Therefore, the nurse should program the IV infusion pump for 75 mL per hour.
Prescribed is 80 mg of gentamicin in 50 mL to infuse in 30 minutes. The nurse would program the electronic infusion pump at what rate?
Explanation
To calculate the infusion rate for gentamicin, the nurse needs to use the following formula:
infusion rate (mL/h) = volume (mL) x 60 / time (min).
Plugging in the given values, we get: infusion rate (mL/h) = 50 x 60 / 30 = 100.
Therefore, the nurse would program the electronic infusion pump at 100 mL/h.
A health care provider prescribes 50 mg of a drug. The drug is only available in a 20 mL vial that contains 20 mg/mL of the drug. How much solution must the nurse administer for each dose?
Explanation
To calculate the amount of solution needed for each dose, we need to use the formula:
Amount of solution (mL) = Dose (mg) / Concentration (mg/mL)
Plugging in the given values, we get:
Amount of solution (mL) = 50 mg / 20 mg/mL
Simplifying, we get:
Amount of solution (mL) = 2.5 mL
Therefore, the nurse must administer 2.5 mL of the solution for each dose.
The physician has ordered combination therapy for the client with Helicobacter pylori. The nurse plans to do medication education. What will the best plan by the nurse include?
Explanation
A. Combination therapy has the best outcomes when omeprazole, propranolol, bismuth salicylate are used.
Propranolol is not an antibiotic and is not part of the standard combination therapy for H. pylori. Bismuth subsalicylate may be used in some regimens, but the standard involves a proton pump inhibitor, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin or metronidazole.
B. Combination therapy has the best outcomes when omeprazole, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin are used.
This is the correct choice. The standard combination therapy for H. pylori infection includes a proton pump inhibitor (such as omeprazole), clarithromycin, and amoxicillin or metronidazole.
C. The use of sucralfate along with antibiotics is the best combination therapy for peptic ulcer disease.
Sucralfate is not typically part of the standard antibiotic combination therapy for H. pylori. It is a cytoprotective agent that may be used to treat ulcers but is not a primary component in eradicating H. pylori.
D. Various antibiotics are used to eradicate the bacteria that are responsible for the development of peptic ulcer disease.
While this statement is true, it does not specify the standard combination therapy. The most common antibiotics used in combination therapy for H. pylori include clarithromycin and amoxicillin or metronidazole, along with a proton pump inhibitor.
The nurse prepares to administer benztropine to the patient with Parkinson's Disease. The nurse holds the dose and notifies the physician based on which assessment finding?
Explanation
A. A respiratory rate of 14
A respiratory rate of 14 is within the normal range and is not typically a reason to hold benztropine. Respiratory depression is not a common side effect of this medication.
B. A pulse of 102
A pulse rate of 102 is also within the normal range, and changes in heart rate are generally not a prominent side effect of benztropine. This finding alone is not a typical reason to hold the medication.
C. Blood pressure of 88/60 mmHg
This is the correct choice. Anticholinergic medications, like benztropine, can cause side effects such as a decrease in blood pressure. A blood pressure of 88/60 mmHg may be a concern, and the nurse should hold the dose and notify the physician.
D. A temperature of 100.2°F
An elevated temperature of 100.2°F is not a direct contraindication to benztropine administration. Fever is not a typical side effect of this medication, so an increased temperature alone is not a reason to hold the dose.
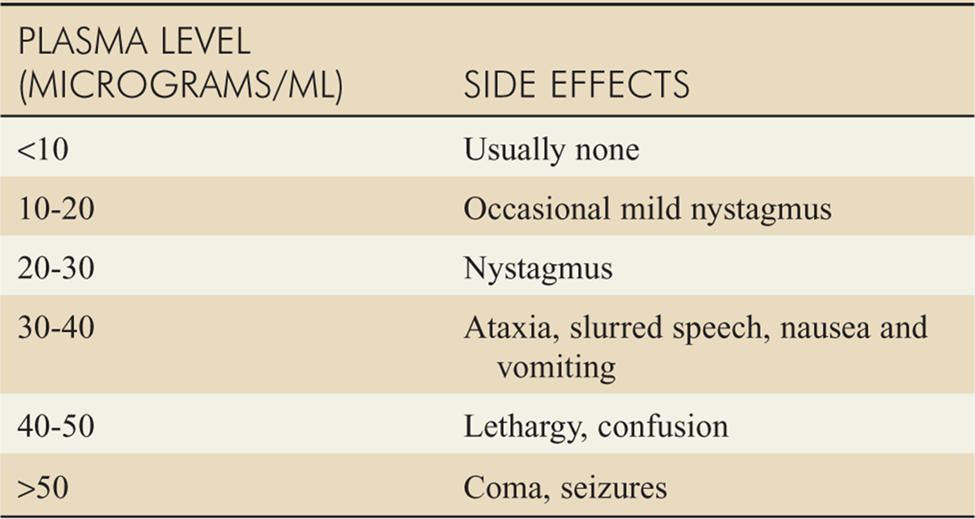
The nurse is preparing to administer phenytoin to a patient who has a seizure disorder. The patient appears drowsy, and the nurse notes that the last random serum drug level was 18 mcg/mL. What action will the nurse take?
Explanation
A. Administer the dose since the patient is not toxic.
This is not the appropriate action. With a drowsy patient and a high serum phenytoin level, there is a concern for toxicity. Administering the next dose could worsen the toxicity.
B. Contact the provider to discuss decreasing the phenytoin dose.
While adjusting the dose may be a consideration, the immediate action should be to withhold the next dose and report the elevated level to the healthcare provider. The provider can then determine the appropriate course of action.
C. Give the drug and monitor closely for adverse effects.
Giving the drug without further intervention is not appropriate when there are signs of potential toxicity, such as drowsiness. Monitoring alone is not sufficient in this case.
D. Report drug toxicity to the providers.
This is the correct choice. With a drowsy patient and a serum phenytoin level of 18 mcg/mL, which is considered high, reporting the drug toxicity to the healthcare provider is the immediate and appropriate action. The provider can then determine the next steps, such as adjusting the dose or ordering additional tests.
The nurse is teaching a patient who has Parkinson's disease about the side effects of carbidopa-levodopa. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
A. "I may experience urinary retention, dry mouth, and constipation."
This statement is accurate. Urinary retention, dry mouth, and constipation are common side effects of carbidopa-levodopa. The patient should be aware of these potential side effects and report them to the healthcare provider if they become problematic.
B. "I may feel dizzy at first, but this side effect will go away with time."
This statement is accurate. Dizziness is a common initial side effect of carbidopa-levodopa, and it often improves with continued use. The patient should be encouraged to report persistent dizziness to the healthcare provider.
C. "I should report nightmares and mental disturbances to my provider."
This statement is accurate. Nightmares and mental disturbances can be side effects of carbidopa-levodopa. The patient should report these symptoms to the healthcare provider for further evaluation and potential adjustments to the medication.
D. "I should take the drug with food to increase absorption."
This statement indicates a need for further teaching. Carbidopa-levodopa is best absorbed when taken on an empty stomach. Taking it with food, especially high-protein meals, can reduce its absorption. The patient should be instructed to take the medication at least 30 minutes before meals or one to two hours after meals for optimal effectiveness.
The nurse is caring for an older adult who is receiving diphenoxylate with atropine to treat severe diarrhea. The nurse will monitor this patient closely for which effect?
Explanation
A. Bradycardia
Bradycardia is not a common side effect of diphenoxylate with atropine. Atropine, which is included in the combination, has anticholinergic effects that can lead to an increased heart rate (tachycardia), not bradycardia.
B. Fluid retention
Fluid retention is not a common side effect of diphenoxylate with atropine. In fact, the medication is used to treat severe diarrhea, and the goal is to decrease fluid loss associated with diarrhea rather than causing fluid retention.
C. Nervousness and tremors
Nervousness and tremors are not common side effects of diphenoxylate with atropine. Atropine's anticholinergic effects may cause nervousness, but these effects are generally not prominent at therapeutic doses.
D. Respiratory depression
This is the correct choice. Respiratory depression is a potential side effect of diphenoxylate with atropine, particularly if the medication is misused or taken in excessive amounts. Atropine is included in the combination to discourage misuse, as it can cause unpleasant anticholinergic effects.
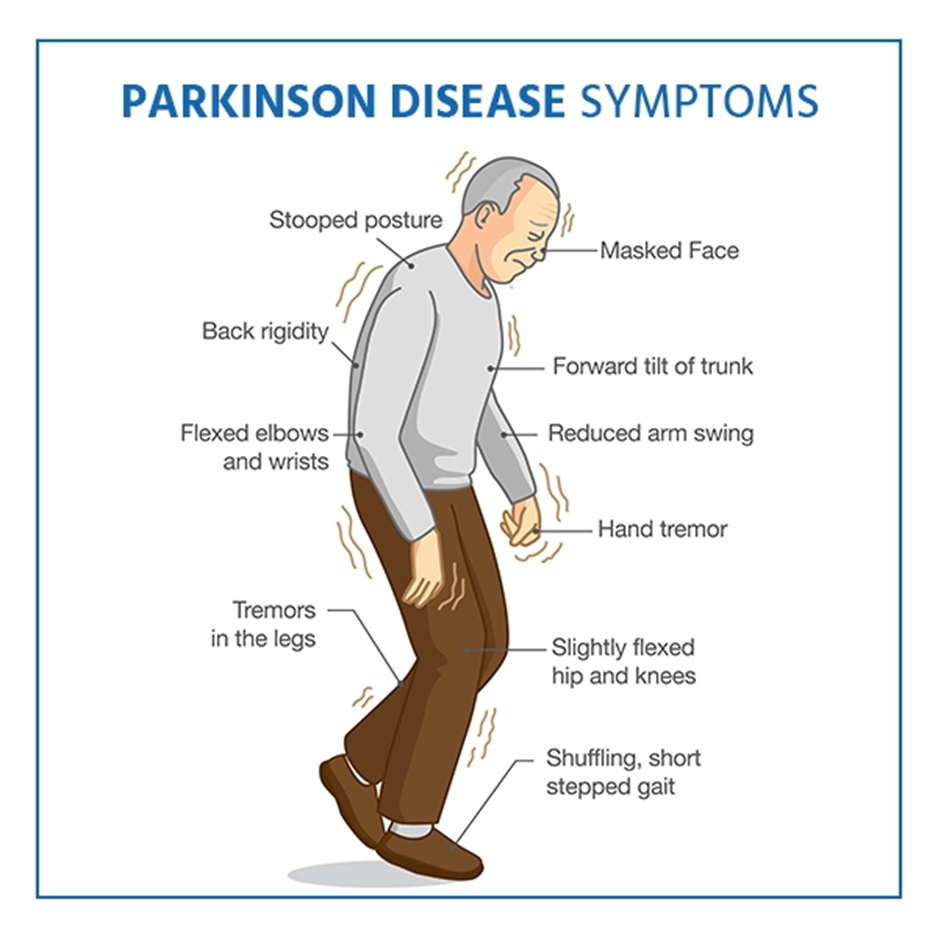
An older patient exhibits a shuffling gait, lack of facial expression, and tremors at rest. The nurse will expect the provider to order which medication for this patient?
Explanation
A. Carbidopa-levodopa
The symptoms described, including a shuffling gait, lack of facial expression, and tremors at rest, are characteristic of Parkinson's disease. Carbidopa-levodopa is a common medication used in the management of Parkinson's disease.
B. Donepezil
Donepezil is used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, a condition characterized by cognitive decline and memory impairment. It is not indicated for Parkinson's disease.
C. Rivastigmine
Rivastigmine is another medication used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, and it is also used in Parkinson's disease dementia. However, it is not the primary medication for the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
D. Tacrine
Tacrine was once used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, but it is no longer commonly prescribed due to safety concerns and the availability of newer, safer medications. It is not indicated for Parkinson's disease.
A patient who recently began having mild symptoms of GERD is reluctant to take medication. What measures will the nurse recommend to minimize this patient's symptoms? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
A. Avoiding hot, spicy foods
Spicy foods can increase the production of stomach acid and may irritate the esophagus, worsening GERD symptoms. Avoiding hot and spicy foods is a dietary measure to minimize the risk of symptom exacerbation.
B. Avoiding tobacco products
Tobacco use is a known risk factor for GERD. Smoking can relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. Advising the patient to quit or avoid tobacco products can contribute to symptom management.
C. Drinking a glass of red wine with dinner
While red wine may have some potential benefits, alcohol, in general, can relax the LES, leading to increased reflux. Therefore, drinking red wine with dinner may not be recommended for someone experiencing GERD symptoms.
D. Eating a snack before bedtime
Eating close to bedtime can increase the likelihood of GERD symptoms, as lying down may allow stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. The nurse may advise against eating a snack right before bedtime to minimize nighttime reflux.
E. Using a small pillow for sleeping
Elevating the head and upper body during sleep can help prevent stomach acid from flowing into the esophagus. Using a small pillow for sleeping is a measure to reduce nighttime reflux and alleviate GERD symptoms.
A patient is receiving a dose of edrophonium. The nurse recognizes that this drug is given to determine the diagnosis of which disease?
Explanation
A. Parkinson's disease
Edrophonium is not used for the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease. Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia. The diagnosis is typically based on clinical symptoms and neurological examination.
B. Alzheimer's disease
Edrophonium is not used for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder affecting cognition. The diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, cognitive assessments, and sometimes imaging studies, but not the use of edrophonium.
C. Myasthenia Gravis
This is the correct choice. Edrophonium is used as a diagnostic tool in Myasthenia Gravis. In individuals with Myasthenia Gravis, the administration of edrophonium can lead to a temporary improvement in muscle strength, helping to confirm the diagnosis.
D. Serotonin Syndrome
Edrophonium is not used for the diagnosis of serotonin syndrome. Serotonin syndrome is a condition caused by an excess of serotonin, often due to the use of certain medications. Diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms and a history of serotonin-affecting medications, not the administration of edrophonium.
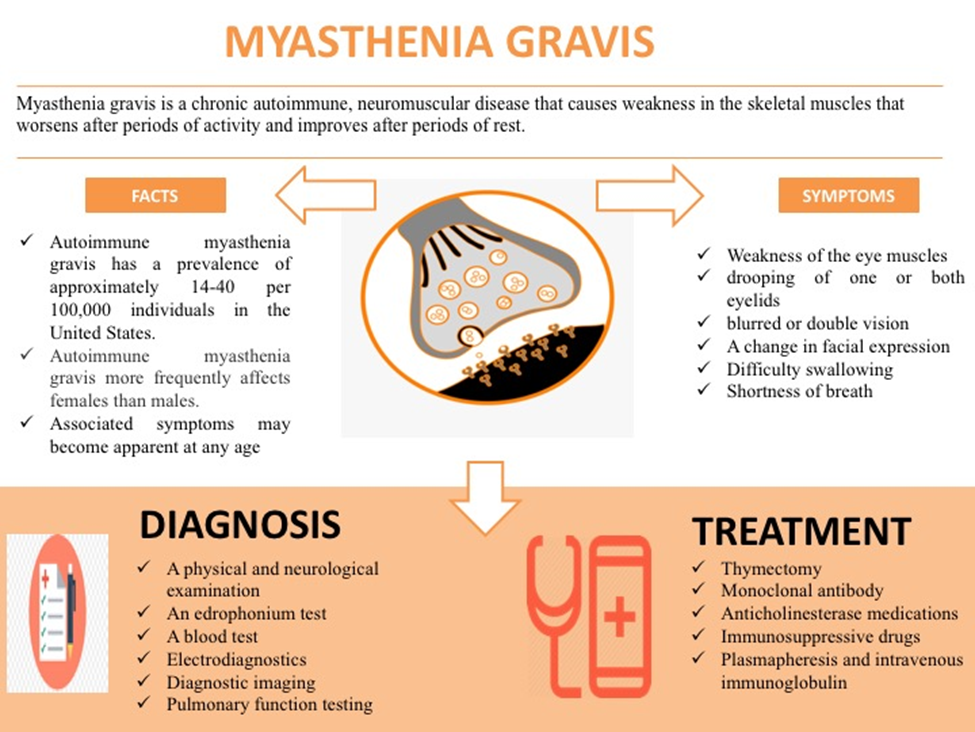
A client with myasthenia gravis is experiencing a cholinergic crisis. Which symptoms are associated with this condition? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
A. Bradycardia
Bradycardia (slow heart rate) is a symptom of cholinergic crisis. Excessive stimulation of acetylcholine receptors can lead to bradycardia.
B. Rash
Rash is not typically associated with cholinergic crisis. Instead, it may be associated with other conditions or drug reactions.
C. Vomiting
Vomiting is a symptom of cholinergic crisis. Excessive stimulation of the gastrointestinal tract by acetylcholine can lead to increased gastrointestinal motility and nausea/vomiting.
D. Fever
Fever is not typically associated with cholinergic crisis. Instead, it may suggest an infection or other inflammatory condition.
E. Drooling
Drooling is a symptom of cholinergic crisis. Excessive stimulation of salivary glands by acetylcholine can lead to increased salivation and drooling.
A patient is experiencing status epilepticus. The nurse prepares to give which drug of choice for the treatment of this condition?
Explanation
A. Diazepam
For the treatment of status epilepticus, the drug of choice is typically a benzodiazepine, and diazepam is commonly used. Diazepam is a fast-acting anticonvulsant that can be administered intravenously to rapidly terminate seizures during status epilepticus.
B. Midazolam
Midazolam is another benzodiazepine that can be used for the treatment of status epilepticus, particularly when intravenous access is difficult. It can be administered intramuscularly or intranasally.
C. Valproic Acid
Valproic acid is an anticonvulsant, but it is not typically the first-line choice for the acute treatment of status epilepticus. It may be considered if benzodiazepines are not effective.
D. Carbamazepine
Carbamazepine is not used for the acute treatment of status epilepticus. It is more commonly used as a maintenance therapy for epilepsy.
A 70-year-old female patient has just been diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease. Which of the following drug is used for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease?
Explanation
A. Bethanechol (Urecholine)
Bethanechol is a cholinergic agonist used to treat urinary retention. It is not indicated for Alzheimer's disease.
B. Albuterol (Proventil)
Albuterol is a bronchodilator used to treat respiratory conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is not indicated for Alzheimer's disease.
C. Rivastigmine
Rivastigmine is a medication commonly used for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. It belongs to a class of drugs called cholinesterase inhibitors, which work by increasing the levels of acetylcholine in the brain. This can help improve cognitive function in individuals with Alzheimer's disease.
D. Edrophonium (Enlon)
Edrophonium is a medication used for the diagnostic evaluation of Myasthenia Gravis. It is not used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 57 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

