Nursing 110 fundamental
Total Questions : 76
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreWhich of the following is the best example of a measurable client goal? The client will:
Explanation
The correct answer is choice D. Identify the five major drug side effects before discharge tomorrow. This is a measurable goal as it has a specific action, which is to identify five major drug side effects, and a specific time frame, which is before discharge tomorrow. The goal is also realistic and achievable within the given time frame. Option A, sitting out of bed in the chair, is not specific enough and lacks a time frame. Option B, verbalizing feelings about surgery at some point, is too vague and lacks a specific action and time frame. Option C, eating low-sodium food, is specific but lacks a time frame and may not be realistic given the client's condition.
Which of the following scenarios would represent proper delegation as applies to delegating care to the right professional?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice D. Asking LPN to pass morning PO blood pressure med to client. This is an appropriate task for an LPN to complete as it falls within their scope of practice and does not require the skills or knowledge of a registered nurse or a physician. Option A, letting the certified nursing assistant change a sterile wound dressing, is not appropriate as it requires sterile technique and should be performed by a licensed nurse. Option B, having the LPN complete the initial admission assessment, is not appropriate as this is a nursing assessment that requires the skills and knowledge of a registered nurse. Option C, allowing the certified nursing assistant to place an IV, is not appropriate as it requires specialized skills and knowledge that are within the scope of practice of a licensed
nurse.
A nurse is performing a head to toe assessment on a client. Which of the following assessment findings would the nurse recognize as requiring an immediate action and would be the first priority when addressing a patient health problem?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. Cyanosis. Cyanosis is a medical emergency and requires immediate action by the nurse. It indicates that the client is not receiving adequate oxygenation and can lead to respiratory failure if not addressed promptly. Pallor (Option A) and erythema (Option D) are concerning but are not immediate priorities compared to cyanosis. Jaundice (Option B) may indicate liver dysfunction but is not an immediate priority unless it is associated with other symptoms such as severe abdominal pain or altered mental status.
The home health nurse notes the client has gained 5 pounds overnight and has increased edema in the lower extremities. The nurse is calling the physician to obtain an order over the phone for furosemide medication. The physician gives an order and the nurse enters the order in the client's medical record. What will the nurse do next after writing down the order?
Explanation
Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is choice C, Read back the order to the physician.
After obtaining the physician's order over the phone, the nurse should read back the order to the physician to confirm accuracy and prevent medication errors.
This process ensures that the order is correctly transcribed and the right medication, dose, and route are given to the patient. Calling the pharmacy to check medication availability is not the nurse's responsibility, and initiating the prescription and administering the medication is inappropriate without confirming the order with the physician. Drawing up the medication into an appropriately labeled syringe before confirming the order with the physician is also inappropriate and can lead to medication errors. Therefore, reading back the order to the physician is the most appropriate action for the nurse to take.
The nurse is teaching a patient with a new ostomy about skin care to preserve tissue integrity. What teaching will the nurse provide about cleansing the ostomy area?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B, Use water and mild soap.
When teaching a patient about ostomy care, the nurse should instruct the patient to clean the area around the ostomy with water and mild soap. Using a whirlpool bath, alcohol-based sanitizer, or chlorhexidine or HCG is not recommended as they can irritate the skin and damage the stoma. Cleansing the ostomy area with water and mild soap is the best way to maintain the skin's integrity and prevent irritation and infection.
Which statement by a nurse would be the most therapeutic response to a patient who cannot decide if they want to receive recommended chemotherapy treatment?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C, "Can you tell me more about why you are undecided?"
When a patient is undecided about receiving recommended chemotherapy treatment, the most therapeutic response from the nurse would be to ask the patient to tell more about why they are undecided. This approach allows the patient to express their feelings and concerns about the treatment, which may help them come to a decision. The nurse should not tell the patient what they should do or criticize them for taking time to decide. The decision to undergo chemotherapy is a significant one, and the patient needs to feel that they have support and guidance from their healthcare provider to make an informed decision.
The nurse is caring for a patient who is confused and agitated. The patient continues to get out of bed without assistance and is at high risk for falls. The nurse is considering alternatives to implement prior to applying restraints.
Of the following, which would the nurse NOT consider in the plan of care as an alternative to restraints?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C, Place all 4 side rails up to prevent the patient from getting out of bed and falling.
When considering alternatives to restraints for a confused and agitated patient who is at high risk for falls, placing all 4 side rails up to prevent the patient from getting out of bed and falling is not an appropriate alternative. This action can be considered as restraint use and can increase the patient's agitation and risk for injury. Instead, the nurse should provide the patient with activities to do while in bed, play music or video selections of the patient's choice, and reduce stimulation noise and light to calm the patient.
A nurse is teaching a preoperative patient how to use an incentive spirometer. Which instruction should be included in the education to the patient?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. Instruct the patient to inhale slowly and as deeply as possible through the mouthpiece without using the nose. Preoperative teaching on how to use an incentive spirometer is important to prevent postoperative respiratory complications such as atelectasis and pneumonia. Inhaling slowly and as deeply as possible through the mouthpiece without using the nose helps to open up the alveoli, promoting oxygen exchange in the lungs. The patient should be instructed to hold their breath for 3-5 seconds before exhaling slowly through the mouthpiece. The procedure should be repeated 10 times every hour while awake.
A client has just had abdominal surgery, and the nurse is consulting with him about his diet now that he is allowed to eat. Which nutrient is most important for wound healing?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. Protein is most important for wound healing. After abdominal surgery, the client requires adequate protein to promote wound healing and tissue repair. Protein is essential for collagen synthesis, a protein that is responsible for the tensile strength of the wound. The recommended daily allowance for protein for an adult is 0.8 g/kg of body weight. Foods high in protein include meat, fish, poultry, dairy products, beans, and nuts.
While caring for a female patient with advanced multiple sclerosis, the nurse is discussing the difference between hospice and palliative care. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the difference between hospice care and palliative care?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. "I will need palliative care to assist with treating my symptoms so that I can have quality of life across the span of my illness." Palliative care aims to improve the quality of life of patients and their families facing life-threatening illnesses. The goal of palliative care is to provide symptom management, pain relief, and support to patients and families throughout the course of their illness. Hospice care is a type of palliative care for patients with a life expectancy of six months or less, where the focus of care is comfort rather than curative treatment.
Which of the following is the best example of a measurable client goal? The client will:
Explanation
The correct answer is choice D. Identify the five major drug side effects before discharge tomorrow. A measurable client goal should be specific, observable, and
measurable. It should describe a behavior or outcome that the client can achieve. Identifying the five major drug side effects is specific and measurable. Sitting out of bed in a chair is too general, while verbalizing feelings about surgery at some point is not observable and not time-bound. Eating low sodium food is specific but not measurable.
A nurse is implementing interventions to prevent a patient from developing Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in the legs by applying a pneumatic or sequential compression device (SCD's). Which explanation would the nurse give the patient in regards to how this device works?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice D. The nurse would explain to the patient that SCDs work by filling with air and applying intermittent or sequential pressure to the legs to enhance blood flow and venous return. This can help prevent blood clots, such as DVT, from forming in the legs. SCDs are often used for patients who are immobile, such as those who have undergone surgery or who are hospitalized for a medical condition. The device is comfortable to wear and can be adjusted to fit the patient's size and shape. The nurse would also explain the importance of wearing the device as prescribed, and how to properly use and care for it. By using SCDs as directed, the patient can significantly reduce their risk of developing a potentially life-threatening blood clot.
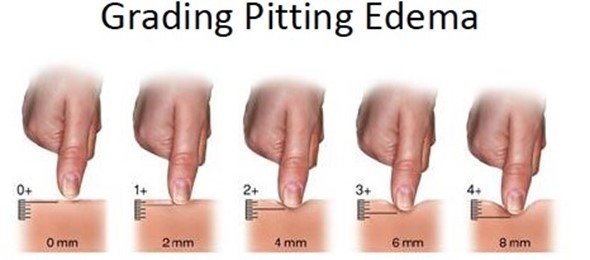
A nurse is performing a physical assessment of a patient who is experiencing fluid volume excess. Upon examination of the patient's legs, the nurse documents: Pitting edema; 8-mm pit. Pit remained for 4 minutes after pressing. What grade of edema has this nurse documented?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B, 3+ Pitting Edema. The nurse has documented pitting edema, which means that when pressure is applied to the skin, an indentation or pit remains after the pressure is released. The grade of pitting edema is determined by the depth of the indentation and how long it takes for the skin to return to its normal state. A 1+ pitting edema is barely detectable with a 2 mm depth, while a 4+ pitting edema has a very deep indentation that can last for more than 30 seconds. In this case, the nurse has documented an 8 mm pit that remained for 4 minutes, which is characteristic of 3+ pitting edema.
The nurse performed an assessment on a patient's upper extremities. All findings were within normal limits. Which reflects the most accurate and complete terminology used when documenting these normal results?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. When documenting normal findings of a patient's upper extremities, it is important to include the skin color, temperature, moisture and integrity, as well as the capillary refill time, the strength and equality of the radial pulses, and the strength and equality of the grips. In this case, the skin was pink, warm, dry, and intact. Capillary refill was less than 5 seconds in all fingers. Radial pulses were +4 and equal bilaterally. Grips were strong 10 out of 10 and equal bilaterally. These findings indicate normal circulation, sensation, and muscle strength in the upper extremities. The nurse must document these findings accurately and thoroughly to ensure continuity of care and to provide a baseline for future assessments.
A nurse is beginning a complete bed bath for a client. After preparing the client by removing the client's gown and placing a bath blanket over him, which of the following areas should the nurse wash first?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C, face. When beginning a complete bed bath, the nurse should first wash the client's face, followed by the arms, chest, abdomen, legs, perineal area, back, and then feet. Washing the face first is important to promote client comfort and hygiene, and also sets a positive tone for the rest of the bath. Additionally, washing the face before the perineal area helps to prevent cross-contamination of bacteria from the perineal area to the face.
The nurse is assisting with the insertion of a nasogastric tube into a client. The nurse should place the client in which position for insertion?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B, High Fowler's position. The High Fowler's position is the optimal position for nasogastric tube insertion as it allows for easy visualization and access to the nasal cavity, pharynx, and esophagus. The client should be in a semi-sitting position with the head of the bed elevated to at least 45-60 degrees. This position allows for better visualization and easier passage of the nasogastric tube through the nasal passages and into the esophagus. The other positions listed do not provide the optimal positioning for nasogastric tube insertion.
A nurse is caring for a client with a wound on the lower extremity. What findings would the nurse observe that would indicate a wound infection?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. Signs of a wound infection include redness, warmth, and tenderness around the wound, as well as fever, chills, and malaise. The wound base may appear yellow, indicating the presence of pus, and may have a foul odor. Serous drainage is typically clear and does not indicate infection, while serosanguineous drainage may indicate a mild infection or normal healing process. An oral temperature of 101.5°F is elevated and may indicate an infection.
A home care nurse is caring for a comatose patient who requires total care. A visitor stops by the house identifying as a family friend and inquires about the patient's condition and if there is anything they can do to help the family. How should the nurse respond to maintain HIPAA compliance?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. The nurse should maintain HIPAA compliance by not sharing any patient information with a non-designated person, even if they identify as a family friend. The nurse should inform the visitor that they cannot share any patient information and suggest that they talk to the patient's family directly if they wish to offer assistance. It is important to protect patient privacy and confidentiality and to only share information with authorized individuals who have a legitimate need to know.
A nurse is caring for a client who has a history of falling at their assisted living facility. The client is oriented
to person, place, and time and can follow directions. Which of the following actions should the nurse take to decrease the risk of another fall?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice D. To decrease the risk of falls, the nurse should educate the patient on using the call light and make sure the call light is within reach. Restraints should only be used as a last resort and can increase the risk of injury and agitation in the patient. Side rails should be used with caution and only as appropriate, as they can also increase the risk of injury in the patient. A belt restraint may not be necessary and can lead to unnecessary restrictions and limitations for the client. It is important to promote the client's independence while ensuring their safety.
A nurse is teaching a home care client and the family about using prescribed oxygen. What is a critical factor in regard to safety that must be included in teaching?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B, safety measures necessary to prevent a fire. When teaching a home care client and their family about using prescribed oxygen, safety measures are critical. Oxygen supports combustion, so it is important to follow safety measures to prevent a fire. These safety measures include avoiding smoking, using electric razors instead of a blade, and avoiding flammable products such as oils, aerosol sprays, and alcohol-based hand sanitizers near the oxygen source. The oxygen should be kept away from heat sources and the tubing should be free from kinks or damage. The healthcare provider's phone number should also be readily available in case of any questions or emergencies.
A nurse is caring for a client who is being treated for bladder infection. The client reports to the nurse that he has been having painful burning with urination. How should the nurse document the client's condition?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B: Dysuria. Dysuria refers to painful or difficult urination. This can be a symptom of a bladder infection, also known as a urinary tract infection (UTI). When documenting a client's condition, it is important to use accurate terminology to communicate effectively with other healthcare professionals. Other terms such as anuria, oliguria, and polyuria refer to different conditions related to urine output and should not be used to describe the symptom of painful urination.
A nurse is assisting a patient who is 2 days postoperative from an abdominal surgery to sit in a chair. After assisting the patient to the side of the bed and to stand up, the patient tells the nurse she feels faint. What should be the nurse's immediate action to keep the patient safe?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Lower the patient back to the side of the bed, pivot her back into the bed, and assess the patient's vital signs. When a patient reports feeling faint while attempting to stand, it is important to take immediate action to prevent a fall and ensure patient safety. Lowering the patient back to the bed will help prevent injury in case of a fall. Then, the nurse should pivot the patient back into the bed slowly and safely. Once the patient is lying down, assess the vital signs, particularly the blood pressure and heart rate, to ensure that the patient is stable. This information can help the nurse determine if the patient is experiencing postural hypotension or other complications from surgery. After assessing the vital signs, the nurse can report the findings to the healthcare provider and implement appropriate interventions to help prevent future episodes of fainting.
The nurse is caring for a client with moderate vision loss. Which intervention would be most appropriate for this client?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. Ensuring the client has access to all corrective eyewear is the most appropriate intervention for a client with moderate vision loss. The nurse should encourage the client to wear any corrective lenses that they have and ensure they have access to their glasses or contact lenses. The nurse should also ensure that the client is in a well-lit environment and that any written materials are provided in a large font size or in an audio format. It is important for the nurse to speak clearly and directly to the client, but not necessarily in a loud voice. Placing the client close to the nurse's station may not be the most appropriate intervention if the client requires privacy or if it is noisy in that area.
A client comes to the emergency department complaining of abdominal cramping and severe persistent diarrhea. The client has recently traveled outside of the United States to an area that may be prone to water contamination. The physician has written several orders. Which assessment and diagnostic physician order would be the first priority for the nurse to complete based on the patient's symptoms?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B: Bowel sounds and obtain a stool specimen.
When a client presents with abdominal cramping and persistent diarrhea, obtaining a stool specimen is the first priority to determine the cause of the diarrhea. The stool specimen can be sent to the laboratory for analysis to check for the presence of bacteria, viruses, or parasites. The nurse should also assess bowel sounds as part of the client's abdominal assessment to monitor for any changes in bowel motility. The other options listed are not the first priority in this situation and may be ordered after the cause of the diarrhea has been determined.
A nurse asks a client the current level of pain using a scale of 0 to 10 after administering pain medications 30 minutes ago. Which of the following steps of the nursing process is the nurse performing?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice D, Evaluation.
Evaluation is the step of the nursing process where the nurse assesses the client's response to interventions that were implemented during the implementation step. In this scenario, the nurse administered pain medication and is now evaluating its effectiveness by asking the client to rate their current level of pain on a scale of 0 to 10. Based on the client's response, the nurse can determine whether the intervention was successful or whether adjustments to the plan of care are necessary.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 76 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

