Cesarean delivery > Maternal & Newborn
Exam Review
Patient Education
Total Questions : 14
Showing 14 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is providing discharge instructions to a client who had a cesarean delivery.
Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.“I will avoid lifting anything heavier than my baby for the next 6 weeks.” This statement indicates that the client understands the importance of limiting physical activity and protecting the incision site from strain or injury.Lifting heavy objects can increase the risk of bleeding, infection, or wound dehiscence.
Choice B is wrong because resuming regular exercise routine as soon as getting home is not advisable after a C-section.The client should gradually increase activity levels and avoid strenuous exercises until cleared by the healthcare provider.
Choice C is wrong because ibuprofen may not be sufficient for pain relief after a C-section.The client may need stronger pain medications prescribed by the healthcare provider and should follow the instructions on how to take them safely.
Choice D is wrong because removing the dressing from the incision site tomorrow is too soon.The client should keep the incision site clean and dry and follow the healthcare provider’s instructions on when and how to change the dressing.Removing the dressing too early can increase the risk of infection or wound dehiscence.
A nurse is monitoring a client who had a cesarean delivery for signs of thromboembolism.
Which of the following findings should alert the nurse to this complication?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Shortness of breath and chest pain are signs of pulmonary embolism (PE), which is a life-threatening complication of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).DVT is a type of blood clot that can occur in the legs or arms, especially during pregnancy and postpartum.PE happens when a blood clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, blocking blood flow.
Choice B is wrong because nausea and vomiting are not specific signs of thromboembolism.
They can be caused by many other conditions, such as morning sickness, food poisoning, or medication side effects.
Choice C is wrong because headache and blurred vision are not typical signs of thromboembolism.
They can be associated with other pregnancy complications, such as preeclampsia or eclampsia.
Choice D is wrong because fever and chills are not common signs of thromboembolism.
They can indicate an infection or inflammation, such as mastitis or endometritis.
Pregnant women have a higher risk of developing DVT and PE because of hormonal changes, increased blood clotting factors, reduced blood flow to the legs, and other factors.The risk is even higher after a cesarean delivery.
Therefore, it is important to know the signs and symptoms of thromboembolism and seek immediate medical attention if they occur.Thromboembolism can be prevented and treated with anticoagulant medications, compression stockings, and physical activity.
A nurse is evaluating the bonding between a client who had a cesarean delivery and her newborn.
Which of the following behaviors by the client indicates effective bonding? (Select all that apply.).
Explanation
The correct answer is choices A, B, C and E. These behaviors by the client indicate effective bonding because they show affection, attention, communication and comfort to the newborn.
Holding the newborn close to her chest promotes skin-to-skin contact and warmth.
Making eye contact with the newborn fosters visual recognition and attachment.
Talking to the newborn in a soft voice stimulates auditory development and soothes the newborn.
Stroking the newborn’s hair and skin enhances tactile stimulation and bonding.
Choice D is wrong because handing the newborn to a family member when crying does not indicate effective bonding.
It shows that the client is unable or unwilling to cope with the newborn’s needs and emotions.
It may also interfere with the establishment of breastfeeding and maternal-infant attachment.
The client should try to calm the newborn by holding, rocking, feeding or changing him or her.
A client is scheduled for a cesarean section (C-section).
Which nursing intervention should be included in preoperative care?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C) Encouraging coughing and deep breathing exercises.
This is because coughing and deep breathing exercises can help prevent atelectasis and pneumonia, which are common postoperative complications of C-section.
Coughing and deep breathing exercises also promote oxygenation and circulation.
Choice A) Administering an opioid analgesic is wrong because opioids can cause respiratory depression and sedation, which are not desirable before surgery.
Opioids can also cross the placenta and affect the fetus.
Choice B) Assessing for signs of deep vein thrombosis is wrong because this is not a priority intervention before surgery.
Deep vein thrombosis is more likely to occur after surgery due to immobility and venous stasis.
Choice D) Providing a high-carbohydrate meal is wrong because this can increase the risk of aspiration during surgery.
The client should be kept NPO (nothing by mouth) for at least 6 hours before surgery.
Which nursing intervention is most important for preventing respiratory complications such as pneumonia and atelectasis in a postoperative client?
Explanation
The correct answer is choiceD) Use of incentive spirometry.Incentive spirometry is a device that helps patients take slow, deep breaths to expand their lungs and prevent respiratory complications such as pneumonia and atelectasis.Incentive spirometry also helps clear mucus and fluids from the lungs and improves ventilation.
Choice A is wrong because controlling anxiety and agitation may not directly prevent respiratory complications, although it may help patients breathe more comfortably.
Choice B is wrong because adequate nutrition and fluids are important for general health and recovery, but they do not specifically prevent respiratory complications.
Choice C is wrong because adequate pain control may help patients breathe more deeply and cough more effectively, but it is not enough to prevent respiratory complications by itself.
Choice E is wrong because early ambulation may improve blood circulation and reduce the risk of thromboembolism, but it does not directly prevent respiratory complications.
Which nursing intervention is most important for preventing surgical site infections in clients undergoing surgery?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A) Administering prophylactic antibiotics as ordered.According to the WHO guidelines for the prevention of surgical site infection (SSI), prophylactic antibiotics should be given within 60 minutes before skin incision and discontinued within 24 hours after surgery.
This reduces the risk of SSI by preventing bacterial colonization of the surgical site.
Choice B) Encouraging coughing and deep breathing exercises is wrong because this intervention is mainly for preventing respiratory complications, not SSI.Coughing and deep breathing exercises help to clear secretions and prevent atelectasis and pneumonia.
Choice C) Providing adequate pain control is wrong because this intervention is mainly for improving patient comfort and recovery, not SSI.Pain control may reduce stress and inflammation, but it does not directly affect the risk of SSI.
Choice D) Assessing for signs of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is wrong because this intervention is mainly for preventing venous thromboembolism (VTE), not SSI.
DVT is a condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs.
It can cause pain, swelling, and redness.If the clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism (PE), which can be life-threatening.
Some other intraoperative interventions for preventing SSI include using an alcohol-based skin prep, maintaining body temperature, using impervious wound protectors, and performing SSI surveillance.
A nurse is caring for a client who had an unscheduled cesarean delivery due to fetal distress.
Which of the following interventions should the nurse implement in the immediate postoperative period?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice D. All of the above interventions should be implemented in the immediate postoperative period after a cesarean delivery.
Choice A is correct because assessing the client’s fundus for firmness and position is important to prevent postpartum hemorrhage and monitor uterine involution.The fundus should be firm and at the level of the umbilicus one hour after delivery and descend into the pelvis at a rate of approximately 1 cm per day.
Choice B is correct because encouraging early ambulation can prevent thromboembolism, which is a potential complication of cesarean delivery.Early mobilization can also reduce pain, ileus, and urinary retention.
Choice C is correct because monitoring the client’s intake and output can help detect fluid imbalance, dehydration, or urinary tract infection.
Fluid intake should be adequate to maintain hydration and support lactation.Urinary output should be at least 30 mL per hour.
Therefore, choice D is correct because all of the above interventions are appropriate for postoperative care after a cesarean delivery.
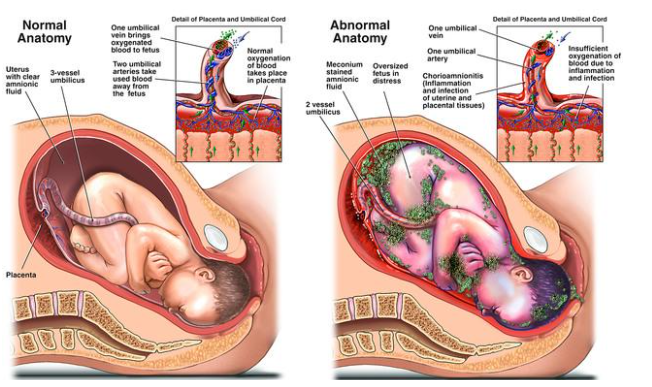
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a client who is scheduled for a cesarean delivery.
Which of the following values should the nurse report to the provider?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. The client can use patient-controlled analgesia to self-administer opioids.This is a form of multimodal analgesia, which is the core principle for cesarean delivery pain management.
Patient-controlled analgesia allows the client to have control over their pain relief and adjust the dose according to their needs.
Choice A is wrong because the client may experience delays in receiving analgesics if they have to request them from the nurse, which can lead to inadequate pain relief and increased opioid consumption.
Choice C is wrong because ice packs are not recommended for cesarean delivery pain management, as they may interfere with wound healing and increase the risk of infection.
Choice D is wrong because deep breathing and relaxation exercises are not sufficient to manage acute postoperative pain, although they may be helpful as adjuncts to pharmacologic methods.
A nurse is monitoring a patient who had a cesarean delivery for signs of infection.
Which of the following findings should alert the nurse to a possible infection? (Select all that apply.).
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A and B.A temperature of 38°C (100.4°F) or higher and foul-smelling lochia or increased lochia are signs of infection after a C-section.A C-section is a major surgery that involves making incisions in the abdomen and uterus, which can get infected by bacteria.An infection can also affect the lining of the uterus (endometritis) or the urinary tract.
Choice C is wrong because tenderness or hardness in the lower abdomen is normal after a C-section and does not indicate an infection.
Choice D is wrong because a decreased white blood cell count is not a sign of infection.In fact, an increased white blood cell count is more likely to occur with an infection.
Choice E is wrong because increased thirst or dry mouth is not a sign of infection.It could be due to dehydration, medication, or hormonal changes.
A nurse is providing discharge instructions to a patient who had a cesarean delivery.
Which of the following statements by the patient indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
“I can take ibuprofen or acetaminophen for pain relief.” This is because these are safe and effective medications for pain management after a C-section.
Choice A is wrong because driving is not recommended until the incision is healed and the pain is gone, which can take 4 to 6 weeks.
Choice B is wrong because lifting anything heavier than the baby can strain the incision and cause bleeding or infection.
Choice C is wrong because sexual intercourse should be avoided until the vaginal bleeding stops and the incision is healed, which can take 4 to 6 weeks or longer.
A nurse is evaluating the bonding between a patient who had a cesarean delivery and her newborn.
Which of the following behaviors by the patient indicates positive bonding?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Holding the baby close to her chest and stroking his hair indicates positive bonding between the mother and the newborn.This behavior shows that the mother is attentive, affectionate, and responsive to her baby’s needs.
Choice B is wrong because looking away from the baby and talking to the visitors suggests that the mother is not interested in or attached to her baby.She may be distracted, overwhelmed, or depressed.
Choice C is wrong because handing the baby to the nurse whenever he cries implies that the mother is not willing or able to comfort her baby.She may be avoiding contact or feeling helpless.
Choice D is wrong because feeding the baby with a bottle and avoiding eye contact indicates that the mother is not engaging with her baby.She may be missing an opportunity to bond through eye contact, touch, and voice.
The health care team member is providing preoperative education to a patient who is having a planned cesarean delivery.
The patient asks, “When will I be able to see my baby?” The health care team member is aware that promoting maternal bonding during the recovery period is especially important for postcesarean patients.
Why is this true?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. Mothers may be at increased risk for poor bonding with the newborn.This is because cesarean delivery can interfere with the natural hormonal and physiological processes that facilitate maternal-infant attachment, such as skin-to-skin contact, breastfeeding initiation, and oxytocin release.Cesarean delivery can also cause more pain, stress, and anxiety for the mother, which can affect her emotional availability and responsiveness to the newborn.
Choice A is wrong because mothers do not necessarily have more problems with parenting skills after cesarean delivery.
Parenting skills depend on many factors, such as education, support, personality, and motivation.
Cesarean delivery may pose some challenges for postpartum recovery and care, but it does not imply that mothers are less competent or capable of parenting.
Choice C is wrong because mothers can breastfeed right away after cesarean delivery, unless there are medical contraindications or complications.
Breastfeeding is beneficial for both the mother and the newborn, as it provides nutrition, immunity, comfort, and bonding.However, breastfeeding after cesarean delivery may require more assistance and support from health care providers and family members, as well as alternative positions and techniques to avoid pain and discomfort.
Choice D is wrong because mothers do not necessarily resent the health care team member for keeping the newborn in the nursery.
Mothers may appreciate the help and care that the health care team member provides for them and their newborns.
However, keeping the newborn in the nursery may delay or reduce the opportunities for maternal-infant interaction and bonding.
Therefore, it is recommended to promote early and frequent contact between the mother and the newborn after cesarean delivery, as long as it is safe
As a patient is arriving in the recovery area following a cesarean delivery, the health care team member receives a hand-off report from the anesthesia provider.
Which information should be included in this report? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
The correct answer is choices A, B, C and D. The type of anesthesia used, the estimated blood loss during surgery, the vital signs and oxygen saturation, and the allergies and medications given are all important information to be included in the hand-off report from the anesthesia provider to the recovery area staff.
These information help to assess the patient’s condition, monitor for complications, and plan for appropriate interventions.
Choice E is wrong because the Apgar scores of the newborn are not relevant to the patient’s recovery from cesarean delivery.
The Apgar scores are used to evaluate the newborn’s physical condition at birth and are usually reported by the neonatal team.
The recovery area staff should focus on the patient’s postoperative care and pain management.
The following statement(s) is/are true about the risks of Cesarean section:.
Explanation
The correct answer is choiceD.A planned Cesarean section increases the rate of unexplained stillbirths at or after 34 weeks in future pregnancies.This is because a prior Cesarean section can cause placental abnormalities such as placenta previa and placenta accreta, which are associated with increased risk of stillbirth.
Choice A is wrong because the evidence comparing the risks of planned Cesarean section and vaginal delivery is mainly low or moderate quality.There are many confounding factors that can affect the outcomes of different modes of delivery, and most studies are observational and not randomized.
Choice B is wrong because the immediate maternal risks from a planned Cesarean section are not significantly higher than those of a planned vaginal delivery.However, a planned Cesarean section is associated with higher risks of infection, thromboembolism, wound complications, and longer hospital stay than a planned vaginal delivery.
Choice C is wrong because a vaginal birth is not associated with a comparable or higher maternal mortality rate than planned Cesarean section.The maternal mortality rate for planned Cesarean section is 0.01% and for planned vaginal delivery is 0.02%, which means there is no significant difference between the two modes of delivery.
Choice E is wrong because there is no evidence that an association exists between a prior Cesarean section and subsequent preterm birth, fetal growth restriction and spontaneous miscarriage.
These outcomes are more likely to be influenced by other factors such as maternal age, medical conditions,
Sign Up or Login to view all the 14 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

