Pharmacology for Professional Nursing
Total Questions : 39
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA medication is described as having teratogenic side effects. The nurse understands that teratogenic is defined as which of the following?
Explanation
Teratogenic refers to an agent or factor that causes malformation of an embryo ¹. It is something that can interfere with normal fetal development and cause congenital disabilities ³. Drugs, alcohol, chemicals, and toxic substances are examples of teratogens ³.
Option B is not correct because teratogenic specifically refers to harm caused to a fetus, not kidney damage.
Option C is not correct because teratogenic does not refer to a medication acting in the opposite manner than expected.
Option D is not correct because teratogenic does not refer to a medication causing an additive effect.

What is the nurses best action when a client refuses to take medication?
Explanation
It is important for the nurse to understand why the client is refusing to take the medication. There may be underlying reasons such as side effects, fear, or misunderstanding about the medication. By investigating and addressing these concerns, the nurse can help the client make an informed decision about their treatment.
Option A may not address the underlying reasons for noncompliance and could be perceived as confrontational.
Option C may be appropriate after understanding the reasons for noncompliance and discussing them with the provider.
Option D may also be appropriate in some cases, but it is important to first understand the reasons for noncompliance before involving a social worker.
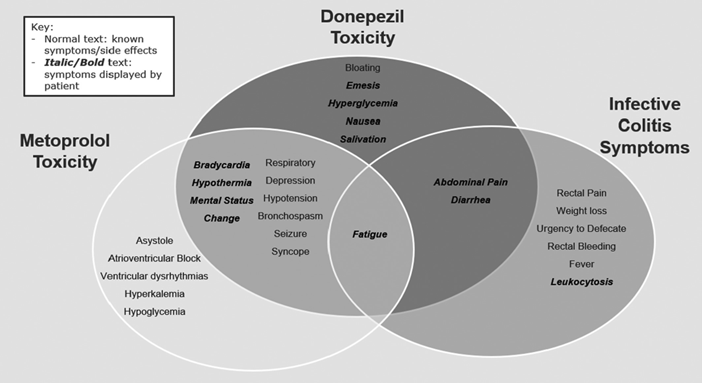
The client diagnosed with Parkinson's disease has been taking carbidopa/levodopa for two years. The client states symptoms are worsening. The health care provider added the prescription donepezil to the client's daily routine. Which information should the nurse teach the client?
Explanation
Donepezil is a medication that can cause side effects such as dizziness and fainting ¹. Therefore, it is important for the client to rise slowly from a lying or sitting position to prevent falls.
Option A is incorrect because donepezil can be taken with or without food.
Option B is incorrect because donepezil does have side effects ¹.
Option C is incorrect because the health care provider added donepezil to the client's daily routine, not to replace carbidopa/levodopa.
Which medication is the medication of choice for the management of absence seizures?
Explanation
Ethosuximide is the medication of choice for the management of absence seizures ³⁵. It is a first-line medication that has been shown to be effective in treating absence seizures ⁵.
Options A and B are incorrect because carbamazepine and phenytoin are not considered first-line medications for absence seizures.
Option D is incorrect because while valproate can be used to treat absence seizures, ethosuximide is preferred due to its effectiveness and safety profile ³.
An agitated, extremely anxious client is brought to the emergency department and the provider orders alprazolam. The nurse understands alprazolam is appropriate to administer in this situation due to which of the following reasons?
Explanation
Alprazolam is a benzodiazepine that is commonly used to treat anxiety disorders and panic disorders ¹². It works by enhancing the activity of certain neurotransmiters in the brain ¹.
Option A is not correct because alprazolam does suppress the central nervous system ¹.
Option B is not correct because alprazolam does not cure generalized anxiety but rather helps manage its symptoms ¹².
Option C is not correct because physical dependence can be a risk when taking alprazolam ¹.

A nurse is aware that an accidental administration of a dose greater than recommended is most likely to result in what negative consequence?
Explanation
An accidental administration of a dose greater than recommended can result in toxicity. This means that the medication reaches harmful levels in the body and can cause damage to organs or other adverse effects.
Option A is incorrect because an overdose is more likely to increase side effects rather than decrease them.
Option B is incorrect because a lowered therapeutic threshold means that a lower dose of medication is needed to achieve the desired effect, which is not related to an overdose.
Option D is incorrect because an overdose can increase the effectiveness of the medication to dangerous levels, rather than decrease it.
A client taking phenytoin suddenly develops hives. The nurse understands which of the following explains this occurrence.
Explanation
The sudden development of hives in a client taking phenytoin is most likely an allergic response to the medication. In this case, the medication should be stopped and the healthcare provider should be notified.
Option A is incorrect because a paradoxical reaction is not related to the development of hives.
Option C is incorrect because an idiosyncratic reaction is unpredictable and can disrupt the treatment plan.
Option D is incorrect because a hypersensitive response would require more than just reducing the dose; the medication should be stopped.
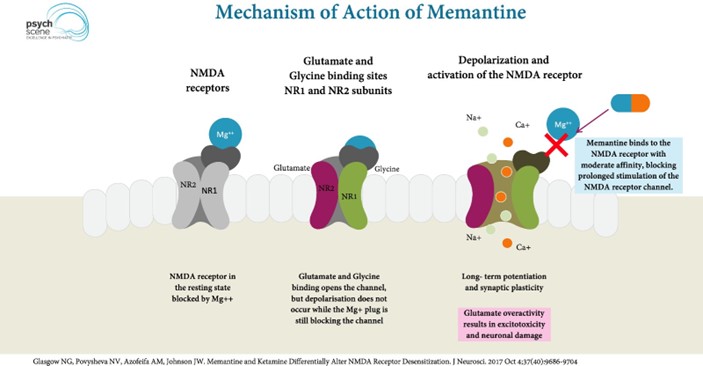
Which statement made by the client's family shows further education is needed regarding the client taking memantine?
Explanation
Memantine is a medication used to treat moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease ¹². It works by reducing the actions of chemicals in the brain that may contribute to the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease ¹. While memantine can help slow the progression of Alzheimer's disease, it is not a cure and may not improve the condition ².
Option A is not correct because constipation is a common side effect of memantine ².
Option B is not correct because memantine is approved for moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease ¹².
Option C is not correct because memantine does regulate the effects of glutamate ³.
Which of the following skeletal muscle relaxants may also be prescribed to manage symptoms of malignant hyperthermia?
Explanation
Dantrolene is a medication that can be used to manage symptoms of malignant hyperthermia ¹. Malignant hyperthermia is a life-threatening reaction to certain medications used during general anesthesia ².
Dantrolene works by inhibiting the release of calcium in the muscles, which helps control the condition and restore normal vital signs ³.
Option A is not correct because baclofen is not used to manage symptoms of malignant hyperthermia.
Option B is not correct because diazepam is not used to manage symptoms of malignant hyperthermia.
Option D is not correct because tizanidine is not used to manage symptoms of malignant hyperthermia.
What anticholinergic side effects are commonly associated with cyclobenzaprine?
Explanation
Cyclobenzaprine is structurally similar to tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) and has similar anticholinergic side effects ³. Common anticholinergic side effects of cyclobenzaprine include dry mouth ¹⁵, constipation ¹⁵, and photophobia ³.
Option A is not correct because bradycardia is not a common side effect of cyclobenzaprine.
Option C is not correct because muscle rigidity, restless movements, and tremors are not common side effects of cyclobenzaprine.
Option D is not correct because flushing, tachycardia, and hives are not common side effects of cyclobenzaprine.

Which medications might increase tremors in a client with Parkinson's disease?
Explanation
Traditional antipsychotics can increase tremors in people with Parkinson's disease ¹. These medications can block dopamine receptors in the brain, which can worsen Parkinson's symptoms ¹.
Option A is not correct because beta-blockers are not known to increase tremors in Parkinson's disease.
Option B is not correct because non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are not known to increase tremors in Parkinson's disease.
Option D is not correct because barbiturates are not known to increase tremors in Parkinson's disease.
A client tells their provider they have had difficulty sleeping for six months. They are requesting a sleep aid to take as needed. Which medication would the nurse anticipate the provider to order?
Explanation
Alprazolam is a benzodiazepine that is commonly used to treat anxiety disorders and panic disorders ¹. It can also be used as a sleep aid due to its sedative effects ³.
Option A is not correct because paroxetine is an antidepressant and is not commonly used as a sleep aid.
Option B is not correct because buspirone is an anti-anxiety medication and is not commonly used as a sleep aid.
Option D is not correct because amitriptyline is an antidepressant and is not commonly used as a sleep aid.
A client currently taking a first-generation antipsychotic (FGA) comes to the clinic for evaluation. The client presents with a shuffling gait and mild tremors. Which order would the nurse expect the provider to give?
Explanation
Anticholinergic medications can be used to treat extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) such as tremors and shuffling gait that can occur as side effects of first-generation antipsychotics ¹².
Option A is not correct because a direct dopamine antagonist would not be used to treat EPS.
Option B is not correct because increasing the dose of the antipsychotic medication could worsen EPS.
Option C is not correct because withholding the medication for two days could lead to a relapse of the underlying condition being treated by the antipsychotic.

An older client may be at higher risk for medication toxicity due to which of the following physiological changes associated with aging?
Explanation
Reduced hepatic blood flow can decrease the metabolism and excretion of many drugs, requiring that doses of some drugs be decreased ². This can increase the risk of medication toxicity in older adults.
Option B is not correct because reduced body fat is not a physiological change associated with aging.
Option C is not correct because the glomerular filtration rate decreases with age ².
Option D is not correct because gastric motility decreases with age ².
A teenager was brought into the emergency room following a lorazepam overdose. What antidote would the nurse expect to administer?
Explanation
Flumazenil is a benzodiazepine antagonist that can be used as an antidote for lorazepam overdose ¹. It works by reversing the effects of benzodiazepines such as lorazepam ¹.
Option A is not correct because naloxone is an opioid antagonist and is not used to treat benzodiazepine overdose.
Option B is not correct because acetylcysteine is used to treat acetaminophen overdose and is not used to treat benzodiazepine overdose.
Option C is not correct because physostigmine is used to treat anticholinergic toxicity and is not used to treat benzodiazepine overdose.
Which statement about food and medication interactions is most accurate?
Explanation
Certain foods can interact with medications by inhibiting or inducing cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, which play a crucial role in drug metabolism ¹. This can alter the way the body processes medications and affect their efficacy and safety ¹.
Option A is not correct because not all medications are best absorbed on an empty stomach. Some medications should be taken with food to improve absorption or reduce side effects ¹.
Option B is not correct because client discomfort is not the only concern when it comes to food and medication interactions.
Option C is not correct because foods can also alter the action of medications ¹.
A 20-year-old client is admitted for treatment of acute schizophrenia and started on risperidone. Which of the following indicates a therapeutic outcome for this medication?
Explanation
Risperidone is an atypical antipsychotic medication used to treat schizophrenia ¹. It works by changing the activity of certain natural substances in the brain ¹. A therapeutic outcome for this medication would be a decrease in symptoms of schizophrenia such as delusional thinking and audiovisual hallucinations ¹.
Option A is not correct because orthostatic hypotension and sedation are side effects of risperidone, not therapeutic outcomes ¹.
Option C is not correct because restful sleep and increased coping abilities are not specific therapeutic outcomes for risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia.
Option D is not correct because decreased anxiety and improved dietary habits are not specific therapeutic outcomes for risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia.
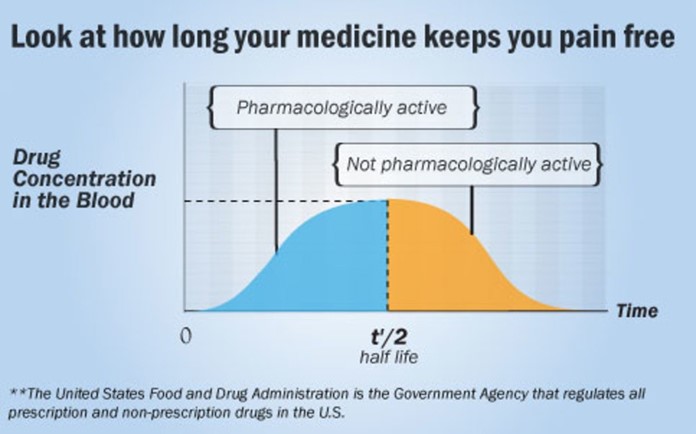
The nurse has given 800mg of a medication that has an 8-hour half-life. How much of the medication will remain in the client's body 24 hours after administration if no additional medication is given?
Explanation
A half-life is the time it takes for the concentration of a drug in the body to decrease by half. In this case, the medication has an 8-hour half-life, so after 8 hours, the concentration of the medication in the client's body would be reduced to 400mg (half of the initial dose of 800mg). After another 8 hours (16 hours total), the concentration would be reduced to 200mg. After another 8 hours (24 hours total), the concentration would be reduced to 100mg.
A client has been taking diazepam for three months. Which of the following statements by the client would indicate the medication is effective?
Explanation
Diazepam is a benzodiazepine medication used to treat anxiety disorders. It works by enhancing the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. A therapeutic outcome for this medication would be a decrease in anxiety and an improved ability to cope with stress.
Option B is not correct because it does not indicate whether the medication is effective or not.
Option C is not correct because it indicates that the client does not see a change in their symptoms.
Option D is not correct because it indicates that the client is self-medicating and increasing their dose without consulting their healthcare provider.

Which of the following information is true when providing education to clients about the use of benzodiazepines?
Explanation
Benzodiazepines are medications that work in the central nervous system and are used for a variety of medical conditions such as anxiety, seizures, and alcohol withdrawal ². They work by blocking excessive activity of nerves in the brain and other areas in the central nervous system ². While benzodiazepines can be effective in treating these conditions, they are not a cure and should be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that may include counseling or other forms of therapy ¹.
Option A is not correct because benzodiazepines do not require frequent blood counts to avoid adverse effects.
Option B is not correct because the decision to stop a medication should be made by a healthcare provider based on an individual's response to treatment.
Option D is not correct because benzodiazepines are not intended for long-term use and should be used for the shortest possible time to achieve therapeutic goals ².
The nurse assessed a client with a toxic level of medication with a half-life of 2 hours. The current toxic level is 40 mEq/dL. The normal range for the medication is 5-10 mEq/L. How many hours will it take for the medication to reach the normal range?
Explanation
The half-life of a medication is the time it takes for the concentration of the medication in the body to decrease by half. In this case, the medication has a half-life of 2 hours and a current toxic level of 40 mEq/dL. After 2 hours, the level will decrease to 20 mEq/dL. After another 2 hours (4 hours total), the level will decrease to 10 mEq/dL, which is within the normal range. However, it will take another 21 half-lives (42 hours) for the level to reach 5 mEq/dL, which is the lower end of the normal range. Therefore, it will take a total of 25 hours (4 + 21) for the medication to reach the normal range.
Option B is incorrect because it would take much longer than 24 hours for the medication to reach the normal range.
Option C is incorrect because it would only take 2 hours for the medication to decrease by half, not reach the normal range.
Option D is incorrect because it would take longer than 4 hours for the medication to reach the normal range.
The older adult client diagnosed with Parkinson's disease (PD) has been prescribed the combination medication carbidopa/levodopa. Which data indicates the medication is effective?
Explanation
Carbidopa/levodopa is a medication used to treat the symptoms of Parkinson's disease, including tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with movement. If the medication is effective, the client should show improvement in their ability to move and perform daily activities. In this case, the client being able to walk upright without stumbling indicates that the medication is effective.
Option B is incorrect because eating 30% to 40% of meals within 1 hour is not related to the effectiveness of carbidopa/levodopa.
Option C is incorrect because displaying emotions when discussing the illness is not related to the effectiveness of carbidopa/levodopa.
Option D is incorrect because cogwheel motion when swinging the arms is a symptom of Parkinson's disease and would indicate that the medication is not effective.
The following order has been written for your client: morphine 1 mg intravenously (IV) every 2 hours as needed for pain. Which of these is true regarding this order?
Explanation
The order states that morphine 1 mg should be given intravenously (IV) every 2 hours as needed for pain. This means that the nurse should assess the client's pain level every 2 hours and determine if 1 mg of morphine IV is needed to manage the pain.
Option A is incorrect because the order specifies that morphine should be given every 2 hours as needed, not every hour.
Option B is incorrect because the order specifies that morphine should be given intravenously (IV), not enterally.
Option D is incorrect because the order specifies that morphine should be given as needed for pain, not automatically every 2 hours.
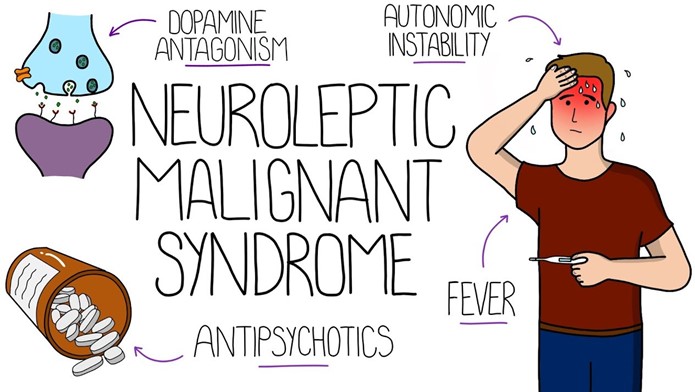
A client with dementia who was taking olanzapine was recently prescribed chlorpromazine for hiccups. The client is currently experiencing high fever, unstable blood pressure, increased confusion, and rigidity. What does the nurse suspect?
Explanation
The client's symptoms of high fever, unstable blood pressure, increased confusion, and rigidity are consistent with neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) ⁴. NMS is a rare but life-threatening reaction that can occur in response to neuroleptic or antipsychotic medication ⁴. In this case, the client was taking olanzapine and was recently prescribed chlorpromazine, both of which are antipsychotic medications that can cause NMS ⁴.
Option A is incorrect because accelerated dementia would not cause the sudden onset of these symptoms.
Option B is incorrect because an infection would not explain the sudden onset of these symptoms after starting a new medication.
Option C is incorrect because aspiration would not cause rigidity or unstable blood pressure.
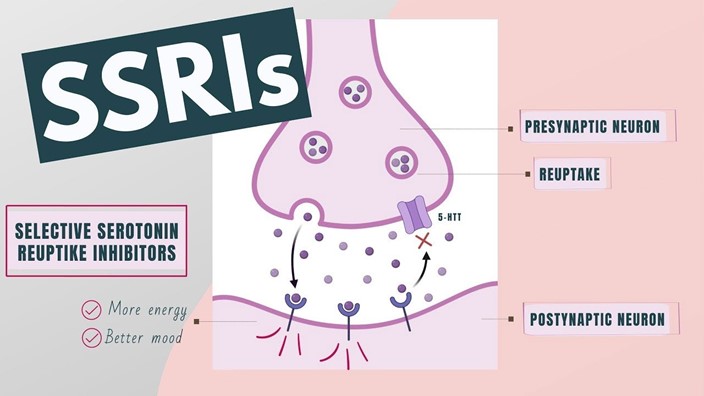
The nurse is caring for a client being treated for depression. The nurse understands that a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) would be chosen as a first-line treatment option over a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) for which of the following reasons?
Explanation
A selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) would be chosen as a first-line treatment option over a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) for several reasons, including reducing the risk of suicide with overdose ³. TCAs have a higher potential for serious or fatal toxicity when taken in large amounts compared to SSRIs ³.
Option A is incorrect because SSRIs can cause sexual dysfunction as a side effect.
Option B is incorrect because both SSRIs and TCAs can cause weight gain and gastrointestinal (GI) effects.
Option C is incorrect because SSRIs can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome when taken with other medications that affect serotonin levels.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 39 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now


