PN ADULT MEDICAL SURGICAL 2023
Total Questions : 78
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is reinforcing teaching with a client about breast self-examinations. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
"I will perform breast exams the day my period begins." This statement is incorrect because performing breast exams just before or during your period might not be ideal. Breasts can be more tender or swollen during this time, which could make it harder to detect any abnormalities.
Choice B Reason:
"I will perform breast exams every other month." This statement is incorrect. Regular breast self-exams are important, but doing them every other month might not be frequent enough. It's generally recommended to perform breast self-exams once a month, ideally around the same time each month, to detect any changes or abnormalities early.
Choice C Reason:
"It is common for the skin on my breasts to dimple." This statement is incorrect. Dimpling or puckering of the skin on the breasts can sometimes be a sign of an underlying issue, such as breast cancer. It's not considered a normal or common occurrence, so this statement doesn't indicate an understanding of what to look for during a breast self-exam. If a person notices skin changes like dimpling, it's recommended to seek medical advice.
Choice D Reason:
"It is common for one breast to be larger than the other." This statement reflects an understanding that breast asymmetry, where one breast is slightly larger than the other, is a common and normal occurrence.
A nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription for propranolol for the treatment of atrial fibrillation. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Requesting a dosage increase if the apical heart rate is less than 60/min is not necessary. Propranolol is used to lower heart rate in conditions like atrial fibrillation, so a heart rate below 60/min might be the desired effect of the medication.
Choice B Reason:
Withholding the medication if the systolic blood pressure is less than 90 mm Hg is necessary. Propranolol is a beta-blocker that can lower blood pressure. If the systolic blood pressure drops below 90 mm Hg, withholding the medication is necessary to prevent further lowering of blood pressure, which could lead to adverse effects like dizziness, fainting, or inadequate blood perfusion to vital organs.
Choice C Reason:
Administering the medication with an antacid might interfere with the absorption of propranolol, so they shouldn't be taken together unless instructed by the healthcare provider.
Choice D Reason:
Expecting increased hair growth is not an anticipated effect of propranolol. Hair growth is not a usual side effect associated with this medication.

3 . A nurse is assisting with the plan of care for an older adult client who has a new prescription for transdermal clonidine. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the plan of care?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Informing the client of the adverse effect of diarrhea is less common with clonidine use, especially in comparison to other side effects like dry mouth or skin irritation.
Choice B Reason:
Monitoring for weight loss isn't a primary concern specifically associated with transdermal clonidine use.
Choice C Reason:
Advising the client about increased dry mouth is appropriate. Dry mouth is a common side effect of clonidine, especially when it's administered transdermally (via a patch). Informing the client about this potential side effect helps them anticipate and manage it. Other side effects might include skin irritation or redness at the patch application site, but increased hypopigmentation under the patch is not a recognized or typical side effect of transdermal clonidine.
Choice D Reason:
Checking for increased hypopigmentation under the patch is not a recognized effect of transdermal clonidine.
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory data of a client who is scheduled for a liver biopsy. Which of the following values should the nurse report to the provider?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Bilirubin 1.0 mg/dL (0.3 to 1.0 mg/dL) is incorrect. Bilirubin levels within the normal range typically indicate normal liver function. The value of 1.0 mg/dL falls within the expected range, so it doesn't raise immediate concerns regarding the need for a liver biopsy.
Choice B Reason:
Aspartate aminotransferase 34 units/L (0 to 34 units/L) is incorrect. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is an enzyme found in various tissues, including the liver, heart, muscles, and red blood cells. While a value of 34 units/L is at the upper limit of the normal range, it's still within the expected range and doesn't typically prompt immediate concern for the need for a biopsy.
Choice C Reason:
Ammonia 55 mcg/dL (10 to 80 mcg/dL ) is incorrect. Ammonia levels can rise in cases of liver dysfunction. The level of 55 mcg/dL falls within the reference range, indicating normal or near-normal ammonia levels, which doesn't usually necessitate an urgent liver biopsy.
Choice D Reason:
Platelets 60,000/mm3 (150,000 to 400,000/mm3) is correct. Platelets are crucial for blood clotting. A significantly low platelet count, such as 60,000/mm3, termed thrombocytopenia, can indicate compromised clotting ability, which might pose a risk of bleeding during or after a liver biopsy. In the context of a liver biopsy, a low platelet count warrants attention and consideration before proceeding with the procedure to prevent excessive bleeding or complications.
A nurse is caring for a client who is postoperative following a right radical mastectomy. Which of the following actions should the nurse take to prevent the development of lymphedema?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Keeping both arms below the level of the client's heart doesn't specifically address the prevention of lymphedema and might not be necessary for this purpose.
Choice B Reason:
Limiting range-of-motion exercises with the affected arm could potentially contribute to stiffness and reduced function, but appropriate and gradual range-of-motion exercises are generally recommended to prevent lymphedema.
Choice C Reason:
Using the client's left arm to obtain blood samples is correct. Lymphedema can occur due to the disruption of lymphatic vessels during surgery, leading to the accumulation of lymph fluid. To reduce the risk of lymphedema, medical procedures or blood draws should typically avoid using the affected arm. In this case, after a right radical mastectomy, using the left arm for blood samples can help protect the compromised lymphatic system in the right arm.
Choice D Reason:
Obtaining blood pressure readings using the client's right arm is not directly related to preventing lymphedema. However, excessive pressure or trauma to the affected arm should generally be avoided to reduce the risk of lymphedema.
A nurse is collecting data from an older adult client. Which of the following findings should indicate to the nurse that the client has a bladder infection?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Temperature 37.3°C (99.1°F) is incorrect . While a slightly elevated temperature can sometimes accompany an infection, it's not specific to a bladder infection and might not be present in all cases.
Choice B Reason:
Changed mental status is incorrect. Bladder infections or urinary tract infections (UTIs) in older adults can often present with atypical symptoms, and changes in mental status or acute confusion are common indicators in this population. UTIs can cause subtle but significant alterations in mental function, particularly in the elderly, leading to confusion, agitation, or cognitive impairment.
Choice C Reason:
WBC count 9,000/mm3 (5000 to 10,000/mm3) is incorrect .A WBC count within the normal range doesn't necessarily rule out or confirm a bladder infection. In some cases, UTIs might not significantly elevate the white blood cell count, especially in localized infections.
Choice D Reason:
Diminished reflexes is incorrect . Diminished reflexes are not typically associated with a bladder infection. They might indicate other neurological or muscular issues but are not a common sign of a UTI.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching with a client who has diabetes mellitus about reducing the risk for a stroke. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
"Having a total cholesterol level below 200 mg/dl increases my risk for a stroke." This statement is incorrect. Generally, having a total cholesterol level below 200 mg/dl is considered beneficial for heart health and reducing the risk of stroke.
Choice B Reason:
"My risk for a stroke increases if my HbA1c level is 6 percent or less." This statement is incorrect. An HbA1c level of 6 percent or less is an indicator of good blood sugar control, which usually reduces the risk of stroke. A higher HbA1c level is associated with an increased risk of complications in diabetes, including stroke.
Choice C Reason:
"My provider might prescribe a glucocorticoid regimen to decrease my risk for a stroke." - Glucocorticoids are not typically prescribed to reduce the risk of stroke in individuals with diabetes. These medications may have various uses but are not a standard preventive measure for stroke in this context.
Choice D Reason:
"I can decrease my risk for a stroke by losing excess weight." This statement is appropriate. Maintaining a healthy weight is a significant factor in reducing the risk of stroke, especially for individuals with diabetes. Weight management contributes to better control of blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar, which collectively reduce the risk of stroke.
A nurse is contributing to the plan of care for a client who has developed an infectious wound with foul-smelling drainage. Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Discarding soiled wound care supplies in a trash receptacle outside the client's room is generally a good practice for infection control. However, this action alone might not be sufficient for managing an infectious wound. Proper disposal is essential, but placing the client in isolation is more critical to prevent the spread of infection.
Choice B Reason:
Administering antibiotic therapy before culturing the wound might interfere with accurate culture results. It's generally preferred to obtain wound cultures before starting antibiotic therapy to identify the specific pathogens causing the infection and determine the most effective treatment.
Choice C Reason:
Placing the client in a private room with a private bathroom is correct. Isolating the client in a private room with a private bathroom helps minimize the spread of potential pathogens present in the wound drainage. This measure helps contain the infection and prevents exposure to others.
Choice D Reason:
Instructing visitors to perform hand hygiene for only 5 seconds after leaving the client's room isn't thorough enough for proper infection control. Proper hand hygiene typically involves washing hands with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizer for at least 20 seconds to effectively reduce the spread of infection.
A nurse is contributing to the plan of care for a client who has viral meningitis. Which of the following interventions should the nurse recommend?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Measuring the client's intake and output every 8 hours is a general nursing intervention but might not be specifically pertinent to managing viral meningitis.
Choice B Reason:
Dim the lighting in the client's room is correct. Meningitis often causes sensitivity to light (photophobia) due to the inflammation of the meninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Dimming the lighting in the client's room helps reduce discomfort and sensitivity to light, which is a common symptom of meningitis.
Choice C Reason:
Monitoring the client's temperature every 6 hours is a routine nursing practice, but in viral meningitis, more frequent temperature monitoring might be necessary, especially if the client shows signs of fever or instability.
Choice D Reason:
Initiating contact precautions for viral meningitis is not typically necessary because it's usually transmitted through respiratory secretions. Standard precautions for infection control, including proper hand hygiene, are usually sufficient.
A nurse is initiating the use of a continuous passive motion (CPM) device for a client following a total knee arthroplasty. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Setting the degree of flexion and extension as tolerated by the client is generally appropriate in a CPM device, but this should be done within the prescribed range recommended by the healthcare provider. Simply allowing the client to adjust the degree of flexion and extension without guidance might lead to overextension or inadequate movement, potentially causing discomfort or hindering recovery.
Choice B Reason:
Padding the CPM device with a thick pillow isn't the recommended approach. CPM devices typically come with appropriate padding to ensure comfort and proper positioning. Using a thick pillow might alter the device's mechanics or cause uneven support, affecting the intended movement of the knee.
Choice C Reason:
Placing the client in high-Fowler's position (sitting upright at a 90-degree angle) isn't a standard or necessary position for using a CPM device after a knee arthroplasty. The client can typically use the CPM device while lying in a comfortable and relaxed position, following the healthcare provider's instructions regarding positioning during CPM therapy.
Choice D Reason:
Aligning the client's joints with the joints on the frame is essential for the correct function of the CPM device. This alignment helps in providing the intended range of motion without causing unnecessary stress or strain on the knee joint.

A nurse is preparing to administer warfarin to a client who has chronic atrial fibrillation. Which of the following laboratory values should the nurse monitor prior to administering the medication?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) is incorrect. This is a type of cholesterol and is not specifically monitored in relation to warfarin therapy.
Choice B Reason:
INR (International Normalized Ratio) is correct. Warfarin is an anticoagulant medication, and its dosage needs to be adjusted based on the INR levels. INR monitoring helps assess the clotting tendency of the blood and ensures that the dosage of warfarin is within the therapeutic range to prevent blood clots without causing excessive bleeding.
Choice C Reason:
BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen) is incorrect. This value is primarily used to assess kidney function and is not directly related to monitoring warfarin therapy.
Choice D Reason:
Hct (Hematocrit) is incorrect. This measures the percentage of red blood cells in the blood and is not directly related to monitoring warfarin therapy for atrial fibrillation.
A nurse is reinforcing discharge teaching with a client who has a new permanent pacemaker. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
"I'll make sure I stay away from microwave ovens." This statement is incorrect . While there were concerns about interference in the past, modern pacemakers are generally not affected by household appliances like microwave ovens.
Choice B Reason:
"I should have an MRI, rather than a CAT scan, if necessary." This statement is incorrect. Both MRI and CAT scans have considerations when a person has a pacemaker. An MRI might be contraindicated due to the magnetic field, while a CAT scan might be a safer imaging choice.
Choice C Reason:
"I'll hold my cell phone against the ear on the opposite side of my body." This statement reflects an understanding of the precaution to avoid holding a cell phone directly over the implanted pacemaker. Keeping the phone on the opposite side helps minimize the potential interference with the pacemaker's function.
Choice D Reason:
"I shouldn't travel by plane because of airport security." This statement is incorrect. Airport security systems generally don't affect pacemakers, so traveling by plane is usually safe. However, informing security personnel about the presence of a pacemaker is a good practice.
A nurse is contributing to the plan of care for a client who has AIDS and has malnutrition. Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Encouraging three large meals daily might not be feasible for someone experiencing malnutrition and decreased appetite. Smaller, more frequent meals or snacks throughout the day could be better tolerated and more beneficial.
Choice B Reason:
Administering an antiemetic after each meal assumes that the client will experience nausea or vomiting regularly after eating. This might not be the case for all clients with AIDS and may not be necessary if the primary issue is malnutrition without associated frequent vomiting.
Choice C Reason:
Seasoning foods with spices might improve the taste of food and potentially stimulate appetite, but it's not as direct or comprehensive a measure for addressing malnutrition as providing a high-calorie diet.
Choice D Reason:
Provide a high-calorie diet is correct. Clients with AIDS often experience malnutrition due to various factors such as decreased appetite, difficulty eating, or malabsorption. Offering a high-calorie diet can help address nutritional deficiencies and support the body's increased energy needs.
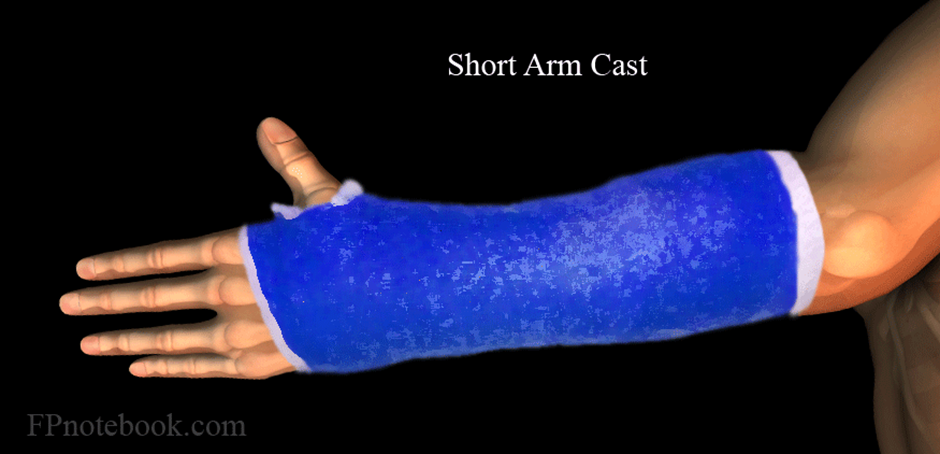
A nurse is caring for a client who has a distal radius fracture with a short arm cast applied. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A Reason
Using a hair dryer to blow hot air into the cast is not recommended. It can cause burns, soften the cast material, or create hot spots, potentially leading to skin damage or discomfort for the client.
Choice B Reason:
Perform neurovascular checks of the affected extremity every 2 hours is correct. Performing neurovascular checks regularly is crucial to assess the circulation, sensation, and movement of the affected extremity. This monitoring helps identify any signs of compromised blood flow or nerve function, which could indicate complications such as compartment syndrome.
Choice C Reason:
Positioning the fractured arm below the level of the client's heart is not advisable. Elevating the injured limb above heart level can help reduce swelling and promote blood flow, aiding in the healing process and preventing complications like swelling-related discomfort or decreased circulation.
Choice D Reason:
Immobilizing the client's fingers using a hand splint might not be necessary with a short arm cast. Typically, a short arm cast provides immobilization of the wrist and forearm while allowing some movement and function of the fingers unless specifically directed by the healthcare provider for individual circumstances.
A nurse is assisting in the plan of care for a client who has thrombocytopenia. Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Checking the client for ecchymosis is appropriate. Thrombocytopenia increases the risk of bleeding and bruising, so monitoring for ecchymosis (bruising) is essential to detect any signs of bleeding. Ecchymosis can occur more easily in individuals with low platelet counts.
Choice B Reason:
Initiating protective isolation for the client is typically unnecessary solely due to thrombocytopenia. Protective isolation is generally for clients with conditions that compromise their immune system or make them more susceptible to infections.
Choice C Reason:
Administering ibuprofen for a mild headache might not be advisable in someone with thrombocytopenia because ibuprofen can affect platelet function and potentially increase the risk of bleeding.
Choice D Reason:
Instructing the client to shave with a disposable razor isn't recommended because using a sharp blade can increase the risk of cuts and bleeding in someone with a low platelet count. Using an electric razor or avoiding shaving might be safer options to prevent injury and bleeding.
A nurse is caring for a client who has a sulfa allergy. Which of the following prescriptions should the nurse clarify with the provider?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Digoxin is a cardiac medication used to treat heart conditions such as heart failure and certain arrhythmias. There's no direct chemical relationship between digoxin and sulfa compounds. Generally, digoxin does not contain sulfa components, so it's less likely to cause an allergic reaction in individuals with sulfa allergies. This medication does not typically require clarification for someone with a sulfa allergy.
Choice B Reason:
Prednisone is a corticosteroid used to treat a variety of conditions, including inflammation, allergies, and autoimmune disorders. It does not contain sulfonamide groups in its structure. As a corticosteroid, prednisone is distinct from sulfonamide drugs and is generally considered safe for individuals with sulfa allergies. There is typically no need to clarify this medication for a sulfa-allergic client.
Choice C Reason:
Celecoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that belongs to the sulfonamide class. While it is not the same as sulfonamide antibiotics, it contains a sulfonamide moiety in its chemical structure. There's a possibility of cross-reactivity or allergic reactions in individuals with sulfa allergies due to the structural similarity, making it essential to clarify this prescription for someone with a sulfa allergy.
Choice D Reason:
Atorvastatin is a statin medication used to lower cholesterol levels. It does not contain a sulfonamide group in its structure. Statins belong to a different drug class and do not typically pose a risk of cross-reactivity in individuals with sulfa allergies. Therefore, atorvastatin is generally considered safe and does not usually require clarification for a sulfa-allergic client.
An occupational health nurse is interpreting the results of a tuberculin skin test for a group of clients who received the test 48 hr ago. Which of the following clients should the nurse identify as having a positive test result?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
A client whose injection site is scabbed is incorrect. Scabbing at the injection site does not provide information about the presence or absence of induration. It doesn't contribute to interpreting the test result directly.
Choice B Reason:
A client whose injection site is firm and measures 3 mm (0.1 in) is incorrect. A measurement of 3 mm of induration is generally considered a negative result for most individuals, including those without any risk factors for tuberculosis (TB).
Choice C Reason:
A client whose injection site has an elevated area measuring 15 mm (0.6 is correct. An area of induration measuring 15 mm or more is considered positive in individuals with no known risk factors for TB.
Choice D Reason:
A client whose injection site is ecchymotic is incorrect. Ecchymosis (bruising) at the injection site is not relevant to the interpretation of the tuberculin skin test. It does not contribute to determining a positive or negative result.
A nurse is caring for a client who has cardiomyopathy and is experiencing sensory overload. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Ensure the blinds in the client's room remain open is not appropriate. Bright light can contribute to sensory overload. It's better to create a subdued and calming environment, so keeping the blinds closed or partially closed might help reduce excess stimuli.
Choice B Reason:
Place the client in a room near the nurses' station is not appropriate. Being near the nurses' station could increase the noise and activity around the client, potentially worsening sensory overload. It's advisable to place the client in a quieter area away from high-traffic zones to minimize auditory and visual stimulation.
Choice C Reason:
Play quiet music in the client's room is incorrect. While soothing music might help some individuals relax, for someone experiencing sensory overload, even low-volume music could add to the stimuli. Silence or minimal ambient noise might be more beneficial.
Choice D Reason:
Break up nursing care into small, frequent sessions is correct. This action is beneficial for managing sensory overload. Breaking up care into smaller sessions allows for adequate rest periods between activities, reducing the overall sensory input at any given time.
A nurse is preparing to perform tracheostomy care for a client. In which order should the nurse take the following steps? (Move the steps into the box on the right, placing them in the order of performance. Use all the steps.)
Explanation
Step D: Explain the procedure to the client. It's crucial to inform the client about the upcoming procedure to promote cooperation, reduce anxiety, and ensure they understand what will happen during the care. This step also allows the client to ask questions and participate in their care if possible.
Step B: Wear clean gloves to remove the tracheostomy dressing:** Wearing clean gloves is essential to maintain the aseptic technique and prevent contamination during the procedure. Removing the dressing allows access to the tracheostomy site for cleaning and assessment.
Step C: Clean the inner cannula using a small brush: Cleaning the inner cannula helps prevent blockages and ensures a patent airway for the client. Regular cleaning of the inner cannula helps remove secretions and debris that could obstruct the airflow through the tracheostomy tube.
Step E: Apply clean tracheostomy ties: Securing the tracheostomy tube in place with clean ties is essential to prevent accidental dislodgement or movement of the tube. Properly securing the tracheostomy ties helps maintain the tube's position and ensures the client's safety.
Step A: Ensure a method to communicate during the procedure:** Communication is crucial during tracheostomy care. Ensuring the client has a method to communicate (such as using a communication board, gestures, or writing) allows them to express any discomfort or concerns during the procedure when verbal communication might be limited due to the care being performed. This step promotes client comfort and safety during the process.
A nurse administered a dose of penicillin to a client 30 min ago. The client reports she has hives and is itching. Which of the following statements by the nurse is the highest priority?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
“I'm going to take your heart rate”. This statement is incorrect. Monitoring vital signs like heart rate is essential in assessing a client's condition. However, in this scenario, the client's report of hives, itching, and a potential allergic reaction is more indicative of an immediate concern for anaphylaxis. While monitoring heart rate is relevant, assessing for signs of anaphylaxis, especially difficulty breathing, takes precedence due to the urgency of potential respiratory distress.
Choice B Reason:
"I need to give you diphenhydramine". This statement is incorrect, administering an antihistamine like diphenhydramine can help alleviate allergic symptoms, including itching and hives. However, confirming the severity of the reaction and ensuring there are no life-threatening symptoms such as breathing difficulties is the immediate priority before administering any medication.
Choice C Reason:
"Are you having difficulty breathing?" This statement is correct. This question directly assesses the client's respiratory status, a crucial indicator of anaphylaxis. If the client is experiencing difficulty breathing, it indicates a severe allergic reaction that requires immediate intervention and emergency medical attention. Recognizing and addressing potential respiratory distress is of utmost importance in managing an allergic reaction to medication.
Choice D Reason:
"Do you have any allergies to medications? This statement is incorrect. Understanding the client's medical history, including allergies, is crucial. However, in this acute situation where the client is already experiencing symptoms of a potential allergic reaction shortly after receiving penicillin, addressing the current symptoms and assessing for signs of anaphylaxis is the most immediate concern.
A nurse is contributing to the plan of care for a client who has influenza. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Having the client wear a surgical mask during transport is recommendable. This intervention aims to prevent the spread of respiratory droplets from the client, potentially reducing the risk of infecting others. It's a preventive measure to contain the transmission of the virus.
Choice B Reason:
Wearing an N95 mask while providing care to the client is not recommended. N95 masks offer a higher level of respiratory protection compared to surgical masks. They are designed to filter out small particles and provide a closer facial fit, primarily protecting the wearer from inhaling airborne particles, including viruses. Healthcare providers may use N95 masks when working closely with infectious patients to reduce the risk of airborne transmission.
Choice C Reason:
Administering an influenza immunization to the client is not recommendable. Influenza immunization is a preventive measure that can protect against specific strains of the influenza virus. However, if the client already has influenza, administering the vaccine won't treat the current infection. Nonetheless, it's essential for prevention in the future, especially for individuals at risk of complications or for herd immunity.
Choice D Reason:
Placing the client in a negative airflow room is not recommendable. Negative airflow rooms are designed to prevent airborne pathogens from spreading to other areas. However, these rooms are typically utilized for airborne infections that require isolation due to their transmission via small particles suspended in the air (such as tuberculosis or measles). Influenza is primarily spread through droplets, and negative airflow rooms may not be routinely used for influenza cases unless there are complications or the client has specific medical conditions necessitating strict isolation.
A nurse is assisting with the care of a client who is receiving peritoneal dialysis. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Chill the dialysate prior to infusion. Generally, the dialysate used in peritoneal dialysis is warmed to body temperature before infusion to enhance comfort and prevent abdominal discomfort. Chilling the dialysate can cause discomfort and is not a standard practice in peritoneal dialysis.
Choice B Reason:
Monitor the client for diarrhea. While gastrointestinal symptoms might occur in some individuals undergoing peritoneal dialysis due to changes in fluid balance, diarrhea is not a typical or expected outcome. However, monitoring for any unusual gastrointestinal symptoms or changes in bowel habits is part of holistic client care.
Choice C Reason:
Weigh the client before and after the treatment. Weighing the client before and after peritoneal dialysis is a critical step to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. The difference in weight helps determine how much fluid was removed during the dialysis process, providing valuable information about the treatment's efficacy and the client's fluid status.
Choice D Reason:
Use clean gloves when handling dialysate bags. Maintaining aseptic technique during peritoneal dialysis is crucial to prevent infections. The use of clean gloves (not sterile gloves, unless otherwise specified) when handling dialysate bags helps minimize the risk of contamination, ensuring the safety of the procedure.
A nurse is assisting with the care of a client who has a seizure disorder. Which of the following supplies should the nurse have at the client's bedside at all times?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Suction equipment is recommended. This is a crucial supply to have at hand. During or after a seizure, the client might have excessive secretions or vomit, which could potentially obstruct their airway. Suction equipment helps clear the airway and maintain breathing, making it an essential item to have bedside.
Choice B Reason:
Padded tongue blades is incorrect. The use of padded tongue blades during a seizure is not recommended. Placing anything inside the mouth during a seizure could cause injury or pose a risk of choking. Keeping the airway clear and ensuring the client's safety is more important than attempting to manipulate the tongue.
Choice C Reason:
Backboard is incorrect.Backboards are typically used for spinal immobilization in cases of suspected spinal injury, not specifically for seizure management. Unless there's a concurrent injury or trauma, a backboard wouldn't be routinely necessary for a client having a seizure.
Choice D Reason:
Wrist restraints is incorrect. Restraints are generally not used for managing seizures. Using restraints during a seizure could potentially cause harm, restrict movement, and increase the risk of injury to the client. Restraints are not considered appropriate or safe for managing seizures.
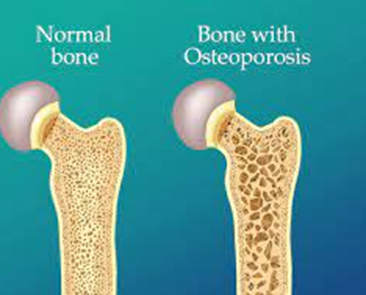
A nurse is reviewing a client's medical history to identify risk factors for osteoporosis. The nurse should identify that which of the following findings is a risk factor for developing osteoporosis?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Age 45 years is incorrect.While age is a significant factor in osteoporosis risk, 45 years old isn't inherently considered a high-risk age for developing osteoporosis. However, bone density tends to decrease gradually with age, and after menopause in women, there's a more significant decline due to hormonal changes.
Choice B Reason:
Regular aerobic exercise is incorrect. Regular exercise, particularly weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening activities, is typically beneficial for bone health. It can help maintain or improve bone density and strength, reducing the risk of osteoporosis. Therefore, regular aerobic exercise is generally considered a protective factor against osteoporosis, rather than a risk factor.
Choice C Reason:
Uses NSAIDs for pain relief is incorrect. While long-term use of certain medications, such as glucocorticoids (steroids), can increase the risk of osteoporosis due to their impact on bone density, the use of NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) for pain relief isn't directly linked to osteoporosis as a significant risk factor. However, chronic use of certain medications might have implications for bone health and should be assessed on an individual basis.
Choice D Reason:
Smoking is a known risk factor for osteoporosis. It can have detrimental effects on bone health by interfering with the body's ability to absorb calcium, decreasing estrogen levels, and impairing bone-forming cells. Consequently, smokers have a higher risk of developing osteoporosis compared to non-smokers.
A nurse is reviewing a client's medical history to identify risk factors for osteoporosis. The nurse should identify that which of the following findings is a risk factor for developing steps
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Age 45 years is incorrect. While age is a significant factor in osteoporosis risk, 45 years old isn't inherently considered a high-risk age for developing osteoporosis. However, bone density tends to decrease gradually with age, and after menopause in women, there's a more significant decline due to hormonal changes.
Choice B Reason:
Regular aerobic exercise is incorrect. Regular exercise, particularly weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening activities, is typically beneficial for bone health. It can help maintain or improve bone density and strength, reducing the risk of osteoporosis. Therefore, regular aerobic exercise is generally considered a protective factor against osteoporosis, rather than a risk factor.
Choice C Reason:
Uses NSAIDs for pain relief is incorrect. While long-term use of certain medications, such as glucocorticoids (steroids), can increase the risk of osteoporosis due to their impact on bone density, the use of NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) for pain relief isn't directly linked to osteoporosis as a significant risk factor. However, chronic use of certain medications might have implications for bone health and should be assessed on an individual basis.
Choice D Reason:
Smoking is a known risk factor for osteoporosis. It can have detrimental effects on bone health by interfering with the body's ability to absorb calcium, decreasing estrogen levels, and impairing bone-forming cells. Consequently, smokers have a higher risk of developing osteoporosis compared to non-smokers.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 78 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

