Fetal Non-Stress Test (NST) > Maternal & Newborn
Exam Review
Procedure and equipment
Total Questions : 5
Showing 5 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is preparing to perform a nonstress test (NST) for a pregnant client at 38 weeks of gestation.
What equipment should the nurse gather for this procedure? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
A nonstress test (NST) is a non-invasive test used to evaluate a baby’s well-being by monitoring fetal heartbeat and movements.The equipment needed for this procedure includes a belt with two transducers and a paper strip or a computer screen.The belt with two transducers is used to measure the fetal heart rate and uterine contractions, while the paper strip or computer screen displays the results.
Choice A is wrong because a reclining chair or bed is not necessary for an NST.The test can be done while the pregnant person is seated comfortably in a chair or resting in a reclined position on a table.
Choice D is wrong because a button for the client to press is not required for an NST.The test does not depend on the client’s perception of fetal movement, but rather on the objective measurement of fetal heart rate and uterine activity.
Choice E is wrong because an acoustic stimulator is not part of the standard equipment for an NST.
An acoustic stimulator is a device that produces a loud noise to stimulate the fetus and elicit a heart rate response.It may be used in some cases when the NST results are nonreactive, but it is not routinely used.
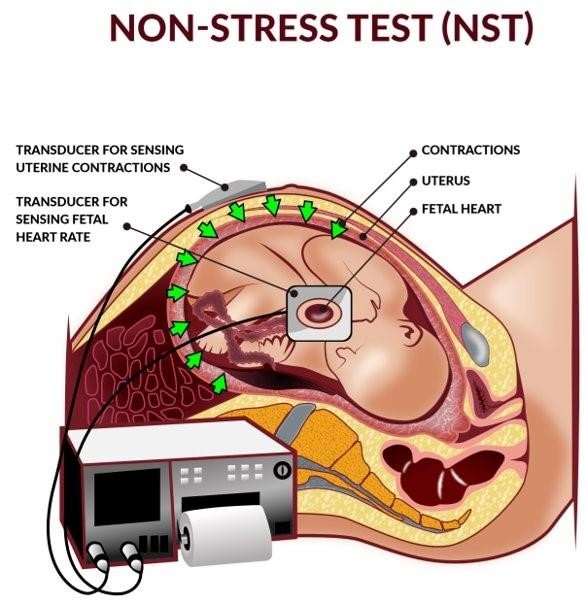
A nurse is reviewing the results of a nonstress test (NST) for a pregnant client at 32 weeks of gestation.
The nurse notes that the fetal heart rate (FHR) baseline is 140 bpm with moderate variability and two accelerations of 15 bpm lasting 15 seconds each in a 20-minute period.
How should the nurse interpret these findings?
Explanation
The NST is reactive, indicating fetal well-being.A reactive NST means that the fetal heart rate increases by at least15 bpmfor at least15 secondstwice or more in a20-minuteperiod.This shows that the fetus is healthy and getting enough oxygen.
Choice B is wrong because a nonreactive NST means that the fetal heart rate does not show the expected accelerations in a 40-minute period, which may indicate fetal compromise.
Choice C is wrong because an inconclusive NST means that the test results are unclear or not enough data was collected, which may require further testing.
Choice D is wrong because an invalid NST means that the test was not performed correctly or there was interference with the fetal heart rate monitoring, which may require a repeat test.
Normal ranges for fetal heart rate are110 to 160 bpmwith moderate variability (5 to 25 bpm) and no decelerations.

A nurse is performing a nonstress test (NST) for a pregnant client at 36 weeks of gestation who reports decreased fetal movement.
The nurse observes that the fetal heart rate (FHR) baseline is 120 bpm with minimal variability and no accelerations in a 20-minute period.
What should the nurse do next?
Explanation
Offer the client a snack or juice to stimulate fetal activity.
A nonstress test (NST) is a pregnancy screening that measures fetal heart rate and reaction to movement.It is performed to make sure the fetus is healthy and getting enough oxygen.A reactive NST means that the fetal heart rate increases by at least 15 beats per minute for at least 15 seconds twice in a 20-minute period.A nonreactive NST means that this criteria is not met.
Choice B is wrong because applying an acoustic stimulator to elicit fetal movement is not recommended as a routine practice and may cause fetal distress.
Choice C is wrong because stopping the test and notifying the provider immediately is not necessary unless there are signs of fetal compromise, such as severe variable or late decelerations, or a nonreassuring fetal heart rate pattern.
Choice D is wrong because extending the test for another 20 minutes may not change the result and may prolong the discomfort of the client.A nonreactive NST does not mean there is a problem, but it may require further testing, such as a biophysical profile or a contraction stress test.
A nurse is teaching a pregnant client about the purpose and procedure of a nonstress test (NST).
Which of the following statements by the client indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
The test will require me to lie on my back for the duration of the test.This statement indicates a need for further teaching because lying on the back can compress the inferior vena cava and reduce blood flow to the baby.The test can be done in a reclining chair or on an exam table with a wedge under one hip to avoid this problem.
Choice A is correct because the test will measure how the baby’s heart rate changes when he moves.In most healthy babies, the heart rate increases during movement.
Choice B is correct because the test will take at least 20 minutes, but it may take longer if the baby is not active or moving during that time period.
Choice C is correct because the test will involve placing two belts around the abdomen.One will measure the baby’s heartbeat and the other will record contractions.
A nurse is evaluating the results of a nonstress test (NST) for a pregnant client at 34 weeks of gestation who has gestational diabetes mellitus.
The nurse notes that the fetal heart rate (FHR) baseline is 150 bpm with moderate variability and three accelerations of 20 bpm lasting 20 seconds each in a 10-minute period.
How should the nurse document these findings?
Explanation
Reactive NST.This means that the fetal heart rate increased by at least 15 beats per minute (bpm) for at least 15 seconds twice or more in a 20-minute period.This indicates that the baby is getting enough oxygen and is doing well.
Nonreactive NST is wrong because it means that the fetal heart rate did not meet the criteria for a reactive NST.This could mean that the baby is not getting enough oxygen, is asleep, or has a problem with the nervous system.
Positive NST is wrong because it is not a term used to describe the results of a nonstress test.It is a term used to describe the results of a contraction stress test (CST), which is a different test that measures how the fetal heart rate responds to uterine contractions.
Negative NST is wrong because it is also not a term used to describe the results of a nonstress test.It is another term used to describe the results of a contraction stress test (CST), which means that the fetal heart rate did not show any signs of distress during contractions.
The normal range for fetal heart rate is 110 to 160 bpm, with moderate variability.
Variability refers to how much the heart rate changes from beat to beat.Moderate variability means that the heart rate changes by 6 to 25 bpm.Accelerations are brief increases in the heart rate that are usually caused by fetal movement.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 5 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

