RN Adult Medical Surgical 2019 Exam 4 Updated 2024
Total Questions : 63
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is planning care for a client who is receiving heparin IV to treat a pulmonary embolism. Which of the following medications should the nurse plan to have at the bedside?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Acetylcysteine is not the antidote for heparin. Acetylcysteine is used to treat acetaminophen (paracetamol) overdose.
Choice B rationale: Protamine sulfate is the antidote for heparin, working to reverse its anticoagulant effects. In case of excessive bleeding or overdose, administering protamine sulfate can rapidly neutralize heparin.
Choice C rationale: Vitamin K is not the antidote for heparin. Vitamin K is used to reverse the effects of warfarin, a different type of anticoagulant.
Choice D rationale: Fumazenil is not the antidote for heparin. Fumazenil is used to reverse the effects of benzodiazepines, not anticoagulants like heparin.
A nurse is teaching the family of a client who has Alzheimer's disease about caring for the client at home. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Placing a large-face clock in the client's bedroom helps the individual with Alzheimer's disease maintain orientation to time, promoting a sense of familiarity and reducing confusion.
Choice B rationale: While a monthly calendar could be helpful, a large-face clock is a more direct and immediate way to help the client understand the current time and reduce disorientation.
Choice C rationale: Covering electrical outlets is important for safety but may not directly address the client's cognitive needs associated with Alzheimer's disease.
Choice D rationale: Keeping the client's bedroom dark at night might contribute to increased confusion and disorientation for someone with Alzheimer's disease.
A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who is to undergo open heart surgery. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider as a contraindication to receiving heparin?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Thrombocytopenia (a low platelet count) is a contraindication to heparin therapy because heparin can further increase the risk of bleeding in individuals with reduced platelet levels.
Choice B rationale: Rheumatoid arthritis is not a contraindication to heparin therapy. It is an autoimmune condition affecting the joints.
Choice C rationale: COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) is not a contraindication to heparin therapy. Heparin primarily affects the circulatory system.
Choice D rationale: Thalassemia is not a contraindication to heparin therapy.
Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder affecting hemoglobin production.
A nurse is caring for a client who understands a prescribed surgical procedure, but cannot read or write. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: According to the American Nurses Association (ANA) Code of Ethics, the nurse should respect the client's right to self-determination and autonomy. The nurse should also provide the client with adequate information and ensure that the client understands the risks and benefits of the procedure. If the client is unable to read or write, the nurse should witness the client's mark on the consent form and document it in the medical record.
Choice B rationale: Contacting the client's power of attorney may be necessary in certain situations, but involving a family member directly for consent is generally more immediate and practical.
Choice C rationale: Notifying the surgical team about the client's inability to sign the consent is important, but the more immediate action is to involve a family member in the consent process.
Choice D rationale: This violates the client’s right to autonomy, unless the client requests or authorizes it.
A nurse is planning care for a client who is 1 day postoperative following an open cholecystectomy. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care?
Explanation
Choice Arationale: Placing pillows under the client's knees may help with comfort but does not directly address the prevention of postoperative complications like venous thromboembolism.
Choice B rationale: Avoiding the use of anticoagulants without a specific medical reason may increase the risk of blood clot formation.
Choice C rationale: Encouraging leg exercises is important for preventing complications such as deep vein thrombosis, and discouraging them may increase the risk of immobility-related issues.
Choice Drationale: Applying compression stockings helps prevent venous thromboembolism in postoperative clients by improving circulation and reducing the risk of blood clots in the lower extremities.
A nurse is assessing a client who is preoperative and reports an allergy to bananas. The nurse should recognize that the client is at risk for an allergic cross-reactivity to which of the following substances?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The client reporting an allergy to bananas may indicate a latex allergy, as individuals with a latex allergy may also react to certain fruits, including bananas.
Choice B rationale: Adhesive tape is not typically associated with cross-reactivity in individuals with a banana allergy.
Choice C rationale: Povidone-iodine is not typically associated with cross-reactivity in individuals with a banana allergy.
Choice D rationale: Anesthetics, in general, are not typically associated with cross- reactivity in individuals with a banana allergy.
A nurse is assessing for early signs of compartment syndrome for a client who has a short-leg fiberglass cast. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Bounding distal pulses are not indicative of compartment syndrome; diminished pulses are more likely.
Choice B rationale: Erythema of the toes is not typically an early sign of compartment syndrome.
Choice C rationale: Capillary refill less than 2 seconds is a normal finding and is not indicative of compartment syndrome.
Choice D rationale: Intense pain with movement is an early sign of compartment syndrome. Other findings include pallor, cool skin, and decreased pulse.
A nurse is caring for a client who has a newly inserted chest tube. The nurse should clarify which of the following prescriptions with the provider?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Administering morphine for pain control is appropriate and does not require clarification.
Choice B rationale: Notifying the provider when tidaling (fluctuation of fluid in the water seal chamber) ceases is appropriate, as it could indicate a problem with the chest tube.
Choice C rationale: Vigorously stripping the chest tube is an outdated and potentially harmful practice. The nurse should clarify this prescription with the provider.
Choice D rationale: Assisting the client out of bed three times daily is a routine activity and does not require clarification.
A nurse is caring for a client who has been receiving total parenteral nutrition (TPN) for 1 week. For which of the following findings should the nurse notify the provider?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: A calcium level of 11.5 mg/dl is elevated and should be reported to the provider, as it may indicate hypercalcemia.
Choice B rationale: Output 200 mL more than intake over the past 12 hr may require monitoring but does not necessitate immediate notification.
Choice C rationale: A serum albumin level of 3.9 g/dl is within the normal range and does not require immediate notification.
Choice D rationale: A fasting blood glucose level of 105 mg/dl is within the normal range and does not require immediate notification.
A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving valsartan to treat heart failure. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an Indication that the medication is effective?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Increased heart rate is not an expected effect of valsartan and may indicate other issues.
Choice B rationale: Decreased urinary output is not a specific indicator of the effectiveness of valsartan in treating heart failure.
Choice C rationale: Valsartan, an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), is used to treat heart failure by vasodilating blood vessels and reducing blood pressure. Therefore, a decrease in blood pressure is an indication that the medication is effective.
Choice D rationale: Increased potassium level is a potential side effect of ARBs but is not the primary indicator of the medication's effectiveness in treating heart failure.
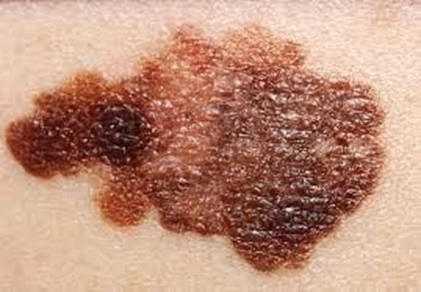
A nurse is performing skin cancer screening on a group of clients. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication of melanoma?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: One of the signs of melanoma is a change in an existing mole or the appearance of a new mole that has an asymmetrical shape, an irregular or jagged border, a variation in color, a diameter larger than 6 mm, or an evolving appearance over time.
Choice B rationale: A raised lesion with a rolled border is more likely to be a basal cell carcinoma, another type of skin cancer that originates from the basal layer of the epidermis.
Choice C rationale: A scaly lesion with a crusted appearance is more likely to be a squamous cell carcinoma, another type of skin cancer that originates from the squamous cells of the epidermis.
Choice D rationale: A reddened lesion with dilated blood vessels is more likely to be a cherry angioma, a benign growth of blood vessels that can occur anywhere on the skin.
A nurse is assessing a client who has acute pancreatitis and has been receiving total parenteral nutrition for the past 72 hr. Which of the following findings requires the nurse to intervene?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Right upper quadrant pain is expected in acute pancreatitis and should be managed, but it does not necessarily indicate an immediate need for intervention.
Choice B rationale: Crackles in bilateral lower lobes indicate potential fluid overload and may require intervention, such as adjusting the rate of TPN or administering diuretics.
Choice C rationale: An elevated capillary blood glucose level is a common finding in patients receiving TPN and may be managed with insulin, but it does not require immediate intervention.
Choice D rationale: An elevated WBC count is expected in acute pancreatitis and may not require immediate intervention unless other signs of infection are present.
A nurse is caring for a client who has tuberculosis and is taking rifampin. The client reports that her saliva has turned red-orange in color. Which of the following responses should the nurse make?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Red-orange discoloration of body fluids, including saliva, is an expected adverse effect of rifampin and is not harmful. It is important for the nurse to educate the client about this side effect.
Choice B rationale: The discoloration is not an indication for changing the medication regimen, as it is a known and expected side effect of rifampin.
Choice C rationale: The red-orange discoloration is not a sign of medication toxicity, but rather a benign side effect of rifampin.
Choice D rationale: Increasing fluid intake will not resolve the discoloration, as it is caused by the medication and is not a sign of dehydration.
A nurse is checking a client's ventilator settings. The nurse should understand that positive end-expiratory pressure has which of the following purposes?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: PEEP does not control the rate of ventilations; it is a setting that affects the pressure in the airways at the end of expiration.
Choice B rationale: Tidal volume is a separate setting on the ventilator that determines the amount of air delivered with each breath.
Choice C rationale: Positive airway pressure during inspiration is more related to the inspiratory pressure setting on the ventilator, not PEEP.
Choice D rationale: Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) is used to prevent alveolar collapse during expiration, improving oxygenation and preventing atelectasis.
A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who has chronic urinary tract infections. The client has a prescription for ciprofloxacin 250 mg PO twice daily. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Drinking 2 to 3 L of fluids daily is important to maintain adequate hydration and help flush bacteria from the urinary tract, reducing the risk of urinary tract infections.
Choice B rationale: Taking an antacid 30 minutes before ciprofloxacin is not recommended, as it can interfere with the absorption of the medication. Ciprofloxacin should be taken with a full glass of water.
Choice C rationale: Monitoring heart rate is not directly related to ciprofloxacin therapy for urinary tract infections.
Choice D rationale: Taking a laxative is not necessary for preventing constipation related to ciprofloxacin use for urinary tract infections.
A PACU nurse is monitoring the drainage from a client's NG tube following abdominal surgery. Which of the following findings in the first postoperative hour should the nurse report to the provider?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: 150 mL of serosanguineous drainage is an expected finding in the first postoperative hour and does not necessarily require immediate reporting.
Choice B rationale: 200 mL of brown drainage may be related to old blood and may not be an immediate concern.
Choice C rationale: 100 mL of red drainage from the NG tube in the first postoperative hour may indicate active bleeding and should be reported to the provider as it could be a sign of a complication following abdominal surgery.
Choice D rationale: 75 mL of greenish-yellow drainage may be related to bile and is not necessarily an immediate concern unless accompanied by other symptoms.
A nurse is caring for a client who has developed a heart rate of 38/min and reports tremors and feeling faint. Which of the following medications should the nurse anticipate administering?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Digoxin is not typically used for acute management of bradycardia; it is more commonly used for heart failure.
Choice B rationale: Diltiazem is a calcium channel blocker and may further reduce heart rate, making it inappropriate for this situation.
Choice C rationale: Magnesium sulfate is used for certain cardiac arrhythmias but is not the first-line treatment for symptomatic bradycardia.
Choice D rationale: A heart rate of 38/min with symptoms of tremors and feeling faint suggests symptomatic bradycardia. Atropine sulfate is commonly used to increase heart rate in bradycardia.
A nurse is preparing to administer a unit of packed RBCs to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: A 21-gauge needle is too small for blood administration and can cause hemolysis.
Choice B rationale: This is because the Y tubing allows the nurse to flush the blood tubing with normal saline before and after the transfusion, and to stop the transfusion quickly if a reaction occurs.
Choice C rationale: The client's first set of vital signs should be obtained before initiating the transfusion and then every 15 minutes for the first hour.
Choice D rationale: Administering the unit of packed RBCs over 1 hr is too rapid and may lead to adverse reactions. Packed RBCs are usually administered over 2 to 4 hours.
A nurse is caring for a client who had a total hip arthroplasty. Which of the following actions should the nurse take to prevent hip dislocation?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Leaning forward when attempting to stand is not a preventive measure for hip dislocation.
Choice B rationale: Elevating the knees higher than the hips when sitting can increase the risk of hip dislocation and should be avoided.
Choice C rationale: The wedge device is typically used to maintain proper hip alignment, and removing it when turning is not recommended.
Choice D rationale: Placing two bed pillows between the legs when in bed helps maintain proper hip alignment and prevents hip dislocation after a total hip arthroplasty.
A nurse on a medical unit is planning care for a group of clients. Which of the following clients should the nurse attend to first?
Explanation
Choice Arationale: A client with thrombocytopenia reporting a nosebleed may need intervention, but it is not an immediate concern unless severe bleeding is present.
Choice Brationale: A client with left-sided paralysis and slurred speech from a prior stroke may need attention, but their airway and oxygenation should take precedence.
Choice C rationale: A client with multiple sclerosis reporting ataxia and vertigo may need assessment and care, but their symptoms are not indicative of an immediate life-threatening situation.
Choice D rationale: A client with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and an oxygen saturation of 89% requires immediate attention, as this indicates potential respiratory distress and hypoxemia.
A nurse is caring for a client following a below-the-knee amputation. The client states, "My life is over." Which of the following responses should the nurse make?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: While acknowledging the client's upset feelings is important, postponing the conversation may not address the immediate emotional needs of the client.
Choice B rationale: Asking the client "Why do you think your life is over?" encourages the client to express their feelings and concerns, facilitating open communication and understanding.
Choice C rationale: While stating that most people can adjust following the surgery is true, it may minimize the client's feelings and not address the individual's unique emotional experience.
Choice D rationale: Offering to connect the client with another amputee may be helpful, but it does not directly address the client's expressed feelings of despair.
A nurse is reviewing laboratory results for four clients who are scheduled for surgery.
Which of the following laboratory values should the nurse report to the surgeon?.
Explanation
Choice A rationale: A platelet count of 95,000/mm³ is below the normal range (150,000 to 450,000/mm³) and may increase the risk of bleeding during surgery. The nurse should report this finding to the surgeon.
Choice B rationale: An INR of 1.6 is within the normal range for most surgical procedures.
Choice C rationale: An Hct of 42% is within the normal range and does not require immediate reporting.
Choice D rationale: A WBC count of 8,000/mm³ is within the normal range and does not require immediate reporting.
A nurse is caring for a client who was admitted with nausea, vomiting, and a possible bowel obstruction. An NG tube is placed and set to low intermittent suction. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The client's abdomen becoming distended and firm may indicate increased pressure and potential complications, such as a worsening bowel obstruction. This can lead to bowel ischemia, perforation, and peritonitis, which are life-threatening complications.
Choice B rationale: The gradual decrease in drainage from the NG tube may be expected as the condition improves and is not an immediate concern.
Choice C rationale: Bright green drainage with brown fecal material is consistent with bilious content, which is expected in the setting of a bowel obstruction.
Choice D rationale: The client reporting thirst and a sore throat may be related to the NG tube, but it does not require immediate reporting unless it persists or worsens.
A nurse is preparing to discontinue long-term total parenteral nutrition (TPN) therapy for a client. The nurse should plan to discontinue the TPN gradually to reduce the risk of which of the following adverse effects?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Diarrhea is not a common adverse effect associated with discontinuing TPN.
Choice B rationale: Constipation is not a common adverse effect associated with discontinuing TPN.
Choice C rationale: TPN provides a high amount of glucose, which stimulates the pancreas to produce insulin. If TPN is stopped abruptly, the insulin level may remain high while the glucose level drops, resulting in hypoglycemia. To prevent this, the nurse should taper off the TPN infusion gradually and monitor the client's blood glucose levels closely.
Choice D rationale: Gradually discontinuing TPN reduces the risk of hypoglycemia and not hyperglycemia.

A nurse in a long-term care facility is caring for a bedridden client. Which of the following findings should alert the nurse to a potential complication of the client's immobility?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Blurred vision is not typically associated with immobility but may have other causes such as ocular issues.
Choice B rationale: Polyuria is not typically associated with immobility but may have other causes such as diabetes or fluid intake.
Choice C rationale: Diarrhea is not typically associated with immobility but may have other causes such as gastrointestinal issues or infections.
Choice D rationale: Confusion can be a potential complication of immobility, and it may be related to factors such as decreased sensory input, social isolation, or other effects of prolonged bedrest.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 63 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

