RN Ati fundamental of nursing
Total Questions : 68
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is preparing to administer a cleansing enema to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
The correct answer is B. Hold the container of solution 15 cm (6 in) above the anus, then lower it 15 cm below the anus.
A. This height is too high and can lead to uncomfortable or rapid administration of the enema.
B. This technique allows for a slow, controlled flow of the enema solution and promotes client comfort.
C. Holding the container at the client's upper hip would not provide the appropriate angle for administering the enema.
D. This choice does not provide specific guidance on the height or angle for administering the enema, which is crucial for the procedure's effectiveness.

A nurse is assisting with transferring a client from the bed to a wheelchair. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. Elevating the bed for the comfort of the nurse does not address the safety and comfort of the client during the transfer.
B. While it's important to have assistance if needed, using several people to lift the client may not always be necessary or appropriate.
C. This positioningis not optimal, as it makes it harder for the client to pivot and sit on the wheelchair.
D. Ensuring the wheels of both the bed and the wheelchair are locked helps maintain stability and safety during the transfer process, reducing the risk of accidental movement and potential falls.
A nurse in a long-term care facility is caring for an older adult client who has dementia and begins to have frequent episodes of urinary incontinence. After the provider determines no medical cause for the client's incontinence, which of the following interventions should the nurse initiate to manage this behavior?
Explanation
A. Using an indwelling urinary catheter should be avoided unless absolutely necessary due to the associated risks of infection and other complications. It's not the first-line intervention for managing urinary incontinence.
B. Frequent toileting, also known as scheduled toileting or prompted voiding, is an effective intervention for managing urinary incontinence in older adults with dementia. It helps prevent accidents by ensuring the client has regular opportunities to use the
bathroom.
C. Reminding the client to tell the nurse when they need to urinate can be helpful, but it may not be sufficient on its own, especially for individuals with dementia who may have difficulty recognizing or communicating their needs.
D. Using adult diapers should be considered a last resort, as it does not address the underlying issue and may not promote the client's independence or dignity.
A nurse is assessing a client's peripheral circulation. In which of the following locations should the nurse palpate to assess the posterior tibial pulse? (Selectable areas, or "Hot Spots," are outlined in the artwork below. Select only the outlined area that corresponds to your answer.)
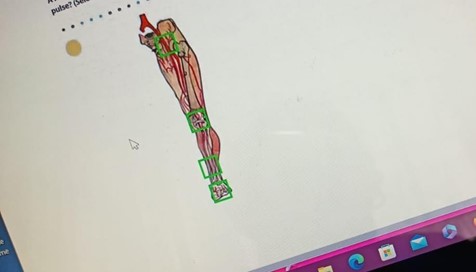
Explanation
A. Inguinal canal is not the correct location for assessing the posterior tibial pulse. This area is associated with the femoral pulse.
B. The knee is not the correct location for assessing the posterior tibial pulse. This area is not directly related to the posterior tibial pulse.
C. The lower third of the tibia, anterior aspect is the correct location for palpating the posterior tibial pulse. This pulse can be found on the inside of the ankle, slightly below and behind the medial malleolus.
D. Dorsal aspect of the foot is where the dorsalis pedis pulse is located, not the posterior tibial pulse.
A nurse is assessing a client's cranial nerves as part of a neurological examination. Which of the following actions should the nurse take to assess cranial nerve III?
Explanation
A. Cranial nerve III, also known as the oculomotor nerve, controls the muscles that move the eye and regulates the size of the pupil. Assessing the pupillary response to light helps evaluate the function of this nerve.
B. Eliciting the gag reflex is associated with cranial nerves IX (glossopharyngeal) and X (vagus), not cranial nerve III.
C. Testing visual acuity is primarily associated with cranial nerve II (optic nerve), not cranial nerve III.
D. Observing facial symmetry is important for assessing cranial nerve VII (facial nerve), not cranial nerve III.
A nurse is caring for a client who requires isolation for active pulmonary tuberculosis. Which of the following precautions should the nurse include when creating a sign to post outside of the client's room? (Select all that apply.)
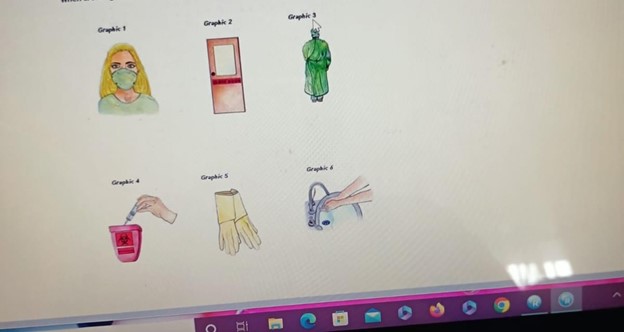
Explanation
A. Wearing a mask helps protect against the transmission of airborne particles, which is important for preventing the spread of tuberculosis.
B. Wearing a gown can provide an additional barrier to prevent the transmission of infectious material.
C. Disposing sharps here is not directly related to tuberculosis precautions. This statement is more relevant for a sharps disposal container.
D. Wearing gloves is important to prevent direct contact with potentially contaminated surfaces.
E. Hand hygiene is crucial for infection control and should be emphasized for anyone entering or exiting the room of a client in isolation.
F. "Radiation inside" is not applicable to the isolation precautions for tuberculosis. This statement is unrelated to tuberculosis precautions and may cause confusion.
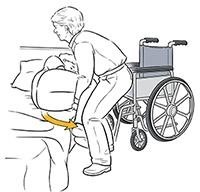
A nurse is assisting with transferring a client from the bed to a wheelchair. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. Elevating the bed for the nurse's comfort is not a priority. The focus should be on ensuring the safety and comfort of the client during the transfer.
B. While it's important to have enough help when transferring a client, acquiring the help of several people to lift the client may not always be necessary. It depends on the client's mobility and the specific transfer technique being used.
C. Positioning the wheelchair at a 90° angle to the bed allows for a safe and efficient transfer. This position provides a clear path for the client to move from the bed to the wheelchair.
D. Locking the wheels of both the bed and the wheelchair is important, but it should be done after the client is safely positioned in the wheelchair. This helps to prevent any unintended movement during the transfer.
A nurse is reviewing information about the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) with a newly licensed nurse. Which of the following statements by the newly licensed nurse indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
A. This statement is incorrect. While HIPAA allows for certain disclosures to family members, it is important to follow specific guidelines and obtain appropriate consent or authorization from the client when sharing their health information. There are also circumstances where a client may request that information be withheld from certain family members.
B. This statement is correct. HIPAA is a federal law that establishes privacy standards for protected health information.
C. This statement is correct. A client's address is considered personally identifiable information under HIPAA.
D. The statement appears to be cut off. However, it is important to note that HIPAA does indeed establish regulations for protecting individually identifiable health information in various forms, including verbal, electronic, and written.
A nurse removes an indwelling urinary catheter that an older adult client has had in place for 2 days. The nurse should assess the client for which of the following expected outcomes after catheter removal?
Explanation
A. After removal of an indwelling urinary catheter, it is common for a client to experience urinary frequency for a few days. This is due to the bladder readjusting to its normal function.
B. Blood-tinged urine may occur after catheter removal, but it is not an expected outcome. It should be assessed and reported if it occurs.
C. Highly concentrated urine is not typically an expected outcome after catheter removal.
It may indicate dehydration or another issue that should be addressed.
D. Temporary urinary retention can occur after catheter removal, especially in older adults. This is why it's important to monitor the client for signs of retention, such as discomfort, restlessness, or a palpable bladder.
A nurse is caring for a client who has a wound infection. Which of the following actions should the nurse take when obtaining a wound-drainage specimen for culture?
Explanation
A. Irrigating the wound with an antiseptic prior to obtaining the specimen can introduce substances that may interfere with the accuracy of the culture results. Sterile saline is the preferred solution for wound irrigation.
B. Intact skin at the wound edges should not be included in the culture. The specimen should be obtained directly from the wound bed or drainage.
C. Swabbing an area of skin away from the wound to identify the usual flora is not appropriate for obtaining a wound drainage specimen. The culture should be taken directly from the wound site.
D. Before obtaining a wound-drainage specimen for culture, it is important to cleanse the wound with a sterile solution, such as 0.9% sodium chloride saline irrigation. This helps remove debris and contaminants from the wound site, providing a more accurate specimen for culture.
A nurse is caring for a client who has impaired mobility. Which of the following support devices should the nurse plan to use to prevent the client from developing plantar flexion contractures?
Explanation
A. A sheepskin heel pad is primarily used for pressure ulcer prevention, not for preventing plantar flexion contractures.
B. A footboard helps maintain the feet in a dorsiflexed position, preventing plantar flexion contractures in clients with impaired mobility. This device provides support and alignment to the lower extremities.
C. A trochanter roll is used to prevent external rotation of the hips and to maintain proper alignment. It is not specifically designed to prevent plantar flexion contractures.
D. An abduction pillow is used to maintain hip alignment and prevent hip adduction. It is not designed to address plantar flexion contractures.
A nurse is preparing to administer a cleansing enema to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. When administering a cleansing enema, it is important to hold the container of solution about 30 cm (12 in) above the anus. This provides enough gravitational force for the solution to flow gently into the rectum.
B. This action involves unnecessary movement of the container and is not a standard technique for administering a cleansing enema.
C. Holding the container level with the client's upper hip does not provide sufficient height for the gravitational force needed to administer the enema effectively.
D. Keeping the container at a level to maintain client comfort is not specific guidance for administering a cleansing enema. The height of the container above the anus is a critical factor in ensuring the enema flows properly.
A nurse is having difficulty caring for a client due to variables affecting the communication process. Which of the following should the nurse identify as an interpersonal variable? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
A. Education may influence the communication process to some extent, but it is not typically considered an interpersonal variable. It falls more under the category of contextual or environmental factors.
B. Time can affect communication in terms of available time for interaction, but it is not specifically related to interpersonal variables.
C. Perception refers to how individuals interpret and make sense of information. It is a key interpersonal variable that can influence how a message is received and understood.
D. Gender can be an interpersonal variable that affects communication. Different genders may have different communication styles and preferences.
E. Feedback is an important component of effective communication. It involves providing a response or reaction to the message, which can help clarify understanding and promote further interaction.
A nurse is preparing to move a client who is only partially able to assist up in bed. Which of the following methods should the nurse plan to use?
Explanation
A. Having one nurse lift as the client pushes with his feet may not provide enough support and could potentially lead to an unsafe transfer, especially if the client is only partially able to assist.
B. Lifting the client under the shoulders with the assistance of another nurse may be appropriate for a different type of transfer, such as a sit-to-stand transfer, but it may not be the most suitable method for moving the client up in bed.
C. When a client is only partially able to assist, using a friction-reducing device, such as a slide or transfer board, is an effective and safe method. This device helps reduce the
friction between the client and the bed, making it easier to move the client up in bed.
D. Using a trapeze bar requires the client to have a certain level of strength and mobility, and may not be suitable for a client who is only partially able to assist.
A home health nurse is conducting a home safety assessment for an older adult client. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as a safety risk for the client? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
A. Water heater temperature set at 54.4°C (130°F) is considered a safe temperature for preventing scalds. This is not a safety risk.
B. Throw rugs can be a tripping hazard for older adults, especially if they are not secured properly.
C. Electric cords behind the furniture can pose a tripping hazard and may also be a fire risk if they are not managed safely.
D. Raised toilet seats are generally considered a safety aid for older adults, as they can make it easier to sit down and stand up. This is not a safety risk.
E. A bathtub with rails is a safety feature that can assist the client in getting in and out of the bathtub safely. This is not a safety risk.
A nurse is removing personal protective equipment (PPE) after giving direct care to a client who requires isolation. Which of the following PPE items should the nurse remove first?
Explanation
A. Gloves should be removed first. This is because the gloves are the items most likely to be contaminated. To remove gloves, grasp the outside edge near the wrist and peel them off, turning them inside out as you go.
B. The gown should be removed next. The gown protects the nurse's clothing from contamination. Untie or unfasten the gown, and then carefully remove it, taking care to avoid touching the outside of the gown.
C. Face shields or goggles should be removed next if used. This helps protect the eyes and face. Handle the shield or goggles by the headband or earpieces and remove them without touching the front.
D. Mask should be removed last. The mask helps protect the respiratory system. Untie or unhook the mask from behind the ears or head and discard it.
A nurse is caring for a client.
Nurses' Notes
Day 1:
1300:
Client has a 2.5 cm (1 in) x 2.5 cm (1 in) stage 2 pressure injury to dorsal lateral aspect of left heal; wound bed red, moist, approximated edges; surrounding skin inflamed, red,, non-tender to palpation. Client reports pain score of 0 on 0 to 10 pain scale. Pedal pulse left foot 1+, unable to assess capillary refill due to toe fungus bilaterally, Pedal pulse right foot 2+. Wound care as prescribed; heel floated on pillow.
Medical History
Day 1:
Diabetes mellitus Hyperlipidemia
Labs
Day 1
Hct 38% (37% to 47%)
Hgb 13 (12 g/dL to 16 g/dL)
WBC 11,500/mm3 (5000 to 10,000/mm3)
Potassium 3.6 mEq/L (3.5 mEq/L to 5 mEq/L)
Pre-albumin level 10 mg/dL (15 to 36 mg/dL)
Albumin: 3.0 g/dL (3.5 to 5 g/dL)
Fingerstick blood glucose, fasting 186 mg/dL (74 to 106 mg/dL)
Select the 5 findings that can cause delayed wound healing.
Explanation
A. Potassium level is incorrect because it is within the normal range and does not affect wound healing directly.
B. Prealbumin level is correct because it is low, indicating malnutrition and poor protein intake, which are essential for tissue repair and immune function.
C. History of diabetes mellitus is correct because it causes impaired blood flow, increased risk of infection, and delayed inflammatory response, which all hinder wound healing.
D. History of hyperlipidemia is correct because it causes atherosclerosis and reduced blood supply to the affected area, which limits oxygen and nutrient delivery to the wound.
E. Wound infection is correct because it increases inflammation, tissue damage, and metabolic demands, which prolong the healing process and may lead to complications.
F. Decreased pedal perfusion is correct because it indicates poor circulation to the lower extremities, which impairs wound healing by reducing oxygen and nutrient delivery to
the wound.
G. Fasting blood glucose is incorrect because it is not a direct cause of delayed wound healing, but rather a reflection of the client's diabetes management. However, high blood glucose levels can impair wound healing by affecting blood flow, immune function, and collagen synthesis.
A nurse is planning care for a client who requires airborne precautions. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. Standing 1.8 m (6 feet) away from the client is not sufficient for airborne precautions.
Proper respiratory protection is required, such as an N95 mask.
B. Allowing the client to ambulate in the hall is not a specific action related to airborne precautions. If the client needs to leave their room, they should wear a mask to prevent the spread of airborne particles.
C. A positive-pressure airflow room is not typically required for airborne precautions.
However, ensuring proper ventilation in the room is important.
D. Airborne precautions are required for clients with illnesses that spread via small droplets or dust particles that can remain in the air for extended periods. This includes diseases like tuberculosis, chickenpox, and measles. The nurse should wear an N95 respirator mask to provide protection against inhaling these particles.

A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for an elective surgical procedure. Which of the following actions should the nurse take regarding informed consent?
Explanation
A. Obtaining the client's consent is a crucial step in the informed consent process. The client must voluntarily agree to undergo the procedure after being provided with adequate information.
B. Explaining the risks and benefits of the procedure is part of the informed consent process.
The client needs to be informed about potential risks, benefits, and alternatives before giving consent.
C. Witnessing the client's signature is an important part of the informed consent process to verify that the signature is voluntary and genuine.
D. Explaining the procedure to the client if they do not understand is essential for ensuring that the client has sufficient information to make an informed decision. This should be done in a clear and understandable manner.
A nurse is teaching a class of older adults about the expected physiologic changes of aging. Which of the following changes should the nurse include in the discussion? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
A. More difficulty seeing due to a greater sensitivity to glare is a common age-related change in vision.
B. Dehydration of intervertebral discs can occur with aging, leading to decreased flexibility and potentially contributing to back pain.
C. While systolic blood pressure may increase with age, decreased systolic blood pressure is not a typical age-related change.
D. Decreased cough reflex is an expected change, which can lead to an increased risk of respiratory infections in older adults.
E. Decreased bladder capacity is an expected age-related change due to changes in the bladder muscles and elasticity of the tissues. This can contribute to increased frequency of urination in older adults.
A nurse finds an open vial of morphine lying on top of the cabinet in a client's room. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. Independently disposing of the remaining medication may not be in compliance with facility policies and could potentially interfere with an investigation into how the medication was left unattended.
B. Returning the medication to the unit's stock for future use is not appropriate, as the vial is already open and its integrity may be compromised.
C. Administering the medication to other clients is absolutely not an option. This could lead to serious harm or even fatal consequences for the other clients involved.
D. When a nurse discovers an open vial of medication left unattended, it is a serious safety concern. The nurse should report the discrepancy immediately to the appropriate personnel or supervisor. This ensures that the situation is addressed promptly and that necessary actions are taken to prevent potential harm to clients.
A nurse is planning care for a client who has a decreased level of consciousness. The client is receiving continuous enteral feedings via a gastrostomy tube due to an inability to swallow. Which of the following is the priority action by the nurse?
Explanation
A. When caring for a client with a decreased level of consciousness who is receiving continuous enteral feedings, the top priority is to ensure the client's airway and respiratory status are maintained. This is because a decreased level of consciousness can increase the risk of aspiration, which can lead to respiratory distress or compromise.
B. Monitoring intake and output every 8 hours is important for overall fluid balance, but it is not the top priority in this situation.
C. Elevating the head of the client's bed to 30° to 45° helps reduce the risk of aspiration during feeding and is an important action, but it is not the highest priority in this scenario.
D. Checking residual volume every 4 to 6 hours is a part of enteral feeding care, but it is not the top priority. Monitoring respiratory status takes precedence due to the potential risk of aspiration.
A nurse is caring for four clients who have drainage tubes. Which of the following clients should the nurse recognize as being at risk for hypokalemia?
Explanation
A. A chest tube to water seal is used to remove air or fluid from the pleural space. This does not directly impact the client's potassium levels.
B. A tracheostomy tube attached to humidified oxygen delivers oxygen directly to the client's airway and does not have a direct effect on potassium levels.
C. An indwelling urinary catheter to gravity drainage does not typically cause significant potassium loss. Urinary catheters primarily collect urine, which contains waste products, rather than electrolytes like potassium.
D. A client with an NG tube to suction may experience loss of gastric contents, which can lead to the loss of electrolytes, including potassium. This places the client at risk for hypokalemia.
A nurse is documenting information in a computerized health record. Which of the following nursing actions jeopardizes client confidentiality?
Explanation
A. Using a computer terminal in a non-public area is appropriate and helps maintain client confidentiality.
B. Sharing computer passwords with coworkers is a serious breach of client confidentiality and security. Each individual should have their own unique login credentials to ensure accountability and protect sensitive information.
C. Logging out of the computer before leaving a terminal is a standard practice to protect client information from unauthorized access.
D. Preventing an unidentified healthcare worker from viewing a health record on the computer screen is a responsible action to protect client confidentiality.
A nurse accidentally sticks her hand with a syringe needle after administering an IM injection to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
A. Reporting the incident to the charge nurse is an important step, but it should come after the immediate action of washing the affected area.
B. Washing the area of the puncture thoroughly with soap and water is the initial step in managing a needlestick injury to minimize the risk of infection.
C. Going to employee health services is important for further assessment and follow-up, but it should be done after washing the area of the puncture.
D. Completing an incident report is an essential part of documenting the needlestick injury, but it is a secondary step that should be taken after the initial action of washing the area.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 68 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

