RN ATI PHARMACOLOGY 2019 Exam 6 Updated 2024
Total Questions : 65
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is preparing to initiate IV therapy for a client. Which of the following sites should the nurse use to place the peripheral IV catheter?
Explanation
A. Dominant antecubital basilic vein:
While the basilic vein in the antecubital area is a suitable site, the nondominant arm is generally preferred when possible to minimize interference with the client's activities.
B. Nondominant dorsal venous arch:
The dorsal venous arch is not typically used for peripheral IV catheter placement. It is often difficult to secure and can be uncomfortable for the client.
C. Dominant distal dorsal vein:
The dorsal veins are generally not the first choice for peripheral IV catheter placement due to the potential for complications such as infiltration.
D. Nondominant forearm basilic vein:
This is the correct answer. The basilic vein in the nondominant forearm is often a suitable site for peripheral IV catheter placement. The nondominant arm is preferred when feasible to minimize disruption of activities for the client.

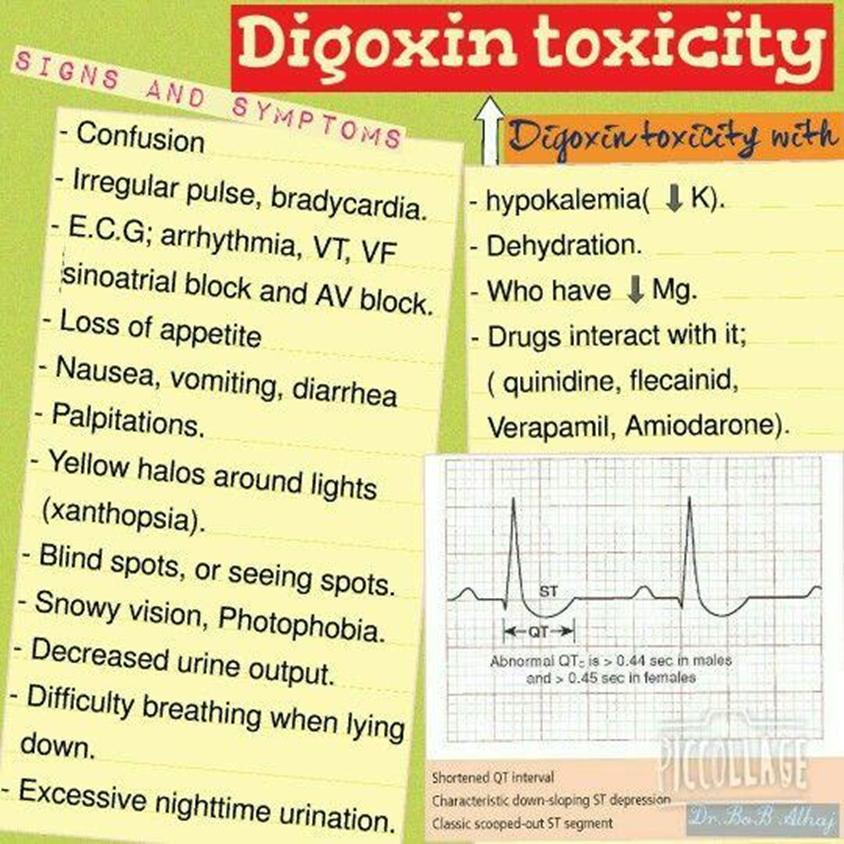
A nurse is assessing a client who has heart failure and is taking digoxin. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication of medication toxicity?
Explanation
A. Visual disturbances:
Visual disturbances, such as blurred or yellow-tinted vision, are common signs of digoxin toxicity. Clients should report any changes in vision promptly.
B. Potassium 4.4 mEq/L:
While electrolyte imbalances, particularly low potassium levels, can increase the risk of digoxin toxicity, a potassium level of 4.4 mEq/L is within the normal range and, by itself, does not indicate digoxin toxicity.
C. Insomnia:
Insomnia is not a typical sign of digoxin toxicity. Symptoms of toxicity are more likely to involve the gastrointestinal and visual systems.
D. Sudden weight gain:
Sudden weight gain can be a symptom of heart failure exacerbation but is not a direct indication of digoxin toxicity. Other signs, such as visual disturbances, are more specific to digoxin toxicity.
A nurse is transcribing a new prescription for a client which states, "Diphenhydramine 50 mg NOW." Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. Inform the client there is a prescription available if needed:
This response does not address the urgency indicated by the prescription stating "NOW." It is essential to take immediate action when the prescription indicates an urgent administration.
B. Notify the pharmacy to send the medication immediately:
While timely medication administration is crucial, contacting the pharmacy directly without clarification from the provider may lead to misinterpretation or errors. It's important to confirm the prescription details first.
C. Administer the medication within 90 minutes:
The prescription indicating "NOW" suggests a need for more immediate administration than within 90 minutes. Waiting for 90 minutes may not be in line with the urgency implied by the prescription.
D. Contact the provider to clarify the prescription:
This is the correct action. The prescription is ambiguous, and the nurse should seek clarification from the provider regarding the urgency of administration, the reason for the medication, and any other pertinent details to ensure safe and appropriate care.

A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving ceftriaxone intravenously. Which of the following manifestations should the nurse identify as an allergic reaction?
Explanation
A. Bradycardia:
Bradycardia is not a typical manifestation of an allergic reaction. Allergic reactions are more likely to involve symptoms such as rash, itching, swelling, and cardiovascular symptoms like tachycardia rather than bradycardia.
B. Hypotension:
This is the correct answer. Hypotension (low blood pressure) can be a sign of an allergic reaction, particularly in severe cases. Anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction, can lead to a rapid drop in blood pressure.
C. Polyuria:
Polyuria, excessive urine production, is not a typical manifestation of an allergic reaction. Allergic reactions are more likely to involve skin, respiratory, and cardiovascular symptoms.
D. Nausea:
Nausea can be a side effect of medications, but it is not a specific manifestation of an allergic reaction. Allergic reactions are more likely to present with symptoms such as skin rash, itching, or respiratory distress.
A nurse in a provider's office is preparing to teach a middle adult client who has a new diagnosis of metabolic syndrome and an HbA1c of 6 Which of the following medications should the nurse plan to teach the client about first?
Explanation
A. Insulin glargine:
Insulin glargine is a long-acting insulin used to control blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. However, it is typically not the first-line choice for a client with a new diagnosis of metabolic syndrome and an HbA1c of 6.
B. Regular insulin:
Regular insulin is a short-acting insulin used to control blood sugar levels, but it is not typically the first choice for initial management of metabolic syndrome. It may be considered in certain situations, but other options are often explored first.
C. Exenatide:
Exenatide is a medication that belongs to the class of incretin mimetics and is used to improve blood sugar control. However, it may not be the first choice for initial treatment.
D. Metformin:
This is the correct answer. Metformin is a first-line medication for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and is commonly used to manage metabolic syndrome. It helps improve insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose production by the liver.
A nurse is reviewing the medication administration record for a client who has cancer and is receiving morphine via a PCA pump. Which of the following prescriptions should the nurse clarify with the provider?
Explanation
A. Acetaminophen: This is a common pain reliever and fever reducer. Acetaminophen is often used alongside other medications, including opioids like morphine, to manage pain more effectively. It's typically safe to use with morphine and is not an immediate concern for clarification.
B. Insulin glargine: Insulin glargine is a long-acting insulin used to control blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes. While it's important to monitor blood sugar levels in patients receiving opioids, especially if they have diabetes, insulin glargine itself doesn't directly interact with morphine or the PCA pump.
C. Ondansetron: Ondansetron is an anti-nausea medication commonly used to prevent nausea and vomiting, particularly associated with chemotherapy or surgery. Patients receiving morphine, especially those with cancer, may also be prone to nausea. Ondansetron helps manage this side effect and does not typically interact adversely with morphine.
D. Naloxone: Naloxone is an opioid antagonist used to rapidly reverse the effects of opioid overdose, including respiratory depression, caused by drugs like morphine. It's administered in emergency situations to counteract the potentially life-threatening effects of opioids. While naloxone is critical for opioid safety, its presence on the medication list requires clear understanding and specific instructions regarding its use, dosage, and administration protocols in case of opioid-related emergencies.
A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving 0.9% sodium chloride solution to treat dehydration. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of the solution?
Explanation
A. Dark amber urine:
Dark amber urine is not typically an adverse effect of receiving 0.9% sodium chloride solution. It may be a sign of concentrated urine, dehydration, or the presence of certain substances, but it is not a direct adverse effect of the solution itself.
B. Decreased skin turgor:
Decreased skin turgor is a clinical manifestation of dehydration and is not an adverse effect of 0.9% sodium chloride solution. The solution is administered to address dehydration and restore fluid balance.
C. Increased bowel sounds:
Increased bowel sounds are not an adverse effect of 0.9% sodium chloride solution. Bowel sounds are influenced by various factors, including the presence of gas and peristalsis, but they are not directly related to the administration of this isotonic solution.
D. Pink, frothy sputum:
This is the correct answer. Pink, frothy sputum is a potential sign of pulmonary edema, which can be associated with fluid overload. Administering 0.9% sodium chloride solution too rapidly or in excessive amounts can lead to fluid overload and pulmonary edema.
A nurse is caring for a client who requires a re-insertion of a short peripheral venous catheter. in which of the following locations should the nurse place the catheter?
Explanation
A. A vein that feels hard to the touch:
A vein that feels hard to the touch may indicate thrombosis or inflammation and is not a suitable site for catheter insertion.
B. A vein in the client's dominant arm:
The choice of arm may depend on the client's preference, but it is not a strict rule. The nurse can choose a suitable vein in either arm based on factors such as accessibility and vein condition.
C. A vein proximal to the previous site:
This is the correct answer. Placing the catheter proximal (above or upstream) to the previous site helps minimize the risk of complications such as infiltration and thrombophlebitis at the new site. It allows for optimal vein health and reduces the likelihood of complications associated with repeated punctures in the same area.
D. A vein on the client's wrist:
Veins on the wrist may be smaller and more prone to complications. It is generally recommended to choose larger, more accessible veins for catheter insertion.
A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetes mellitus and is taking pioglitazone. The nurse should plan to monitor the client for which of the following adverse effects?
Explanation
A. Orthostatic hypotension:
Orthostatic hypotension is not a common adverse effect of pioglitazone. This condition is more associated with medications that affect blood pressure or volume.
B. Tinnitus:
Tinnitus (ringing in the ears) is not typically associated with pioglitazone. Adverse effects of pioglitazone are more related to its impact on glucose metabolism and other metabolic processes.
C. Fluid retention:
This is the correct answer. Fluid retention is a known adverse effect of pioglitazone. It can lead to edema, weight gain, and, in some cases, exacerbation of heart failure. Monitoring for signs of fluid retention is important during treatment with pioglitazone.
D. Insomnia:
Insomnia is not a common adverse effect of pioglitazone. Adverse effects are more related to metabolic processes, and sleep disturbances are not typically associated with this medication.
A nurse realizes that they failed to administer a medication that was due 4 hr ago to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
A. Assess the client for adverse reactions:
While assessing the client for adverse reactions is important, it is not the first action. The nurse should first address the immediate steps related to the missed medication.
B. Determine factors that led to the omission:
This is the correct answer. Understanding the factors that led to the omission is crucial for preventing future errors. The nurse should assess if there were any system failures, distractions, or other factors contributing to the missed dose.
C. File an Incident report:
Filing an incident report is an important step, but it should not be the first action. The nurse needs to address the immediate situation and assess the factors contributing to the omission first.
D. Report the missed dosage to the client's provider:
Reporting the missed dosage to the provider is an important step, but it should not be the first action. The nurse needs to address the immediate situation, assess the client, and determine factors leading to the omission before reporting to the provider.
A nurse in the emergency department is admitting a client who has diabetic ketoacidosis and a blood glucose level of 100 mg/dl. Which of the following interventions should the nurse initiate first?
Explanation
A. Potassium chloride 10 mEq/hr:
While potassium replacement is crucial in DKA, initiating it before fluid resuscitation can lead to further complications. Insulin administration can drive potassium back into cells, potentially causing hypokalemia. Fluid resuscitation helps address dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
B. Bicarbonate by IV infusion:
Bicarbonate therapy is generally reserved for severe cases of acidosis, and its use in DKA is controversial. In this scenario, the blood glucose level is not significantly elevated, and the focus should be on fluid resuscitation and insulin administration.
C. Subcutaneous insulin injections:
While insulin is a critical component of DKA management, it should be administered intravenously for faster and more precise control of blood glucose levels. Subcutaneous insulin injections are not the initial route of administration in DKA.
D. 0.9% sodium chloride 15 mL/kg/hr:
This is the correct answer. The first step in DKA management is fluid resuscitation with isotonic saline (0.9% sodium chloride). The goal is to address dehydration, restore intravascular volume, and improve perfusion. Insulin therapy and other interventions follow fluid resuscitation.
A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetes insipidus and is receiving desmopressin by intermittent IV balus. Which of the fediowing manifestations should indicate to the nurse a therapeutic response to the medication?
Explanation
A. Decrease in urine output:
This is the correct answer. Desmopressin is a synthetic form of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) that works to reduce urine output in individuals with diabetes insipidus. A decrease in urine output indicates a positive response to the medication.
B. Increase in serum glucose:
Desmopressin does not have a direct effect on serum glucose levels. Its primary action is to increase water reabsorption in the kidneys, reducing urine output.
C. Increase in WBC count:
Desmopressin does not have a direct impact on white blood cell (WBC) count. Its main action is on fluid balance and urine concentration.
D. Decrease in blood pressure:
Desmopressin can cause a mild increase in blood pressure, particularly at higher doses. However, blood pressure changes are not the primary therapeutic effect of desmopressin in the context of diabetes insipidus.
A nurse is teaching a client who has active pulmonary tuberculosis about management of medication for the disease. Which of the following statements is appropriate for the nurse to make?
Explanation
A. "You will need to undergo tuberculin skin tests every 6 months while taking medication for your disease."
Tuberculin skin tests are typically used for screening and diagnosis, not for monitoring the effectiveness of tuberculosis treatment. Monitoring for treatment effectiveness involves assessing symptoms, sputum cultures, and other diagnostic tests.
B. "You will need to take two or more medications to treat your disease."
This is the correct answer. Tuberculosis is usually treated with a combination of antibiotics to prevent the development of drug resistance. Multidrug therapy is a standard approach to tuberculosis treatment.
C. "You should anticipate taking medication to treat your disease for at least the next 3 years."
The duration of tuberculosis treatment is generally shorter than 3 years. The standard treatment duration is typically 6 to 9 months, depending on the specific regimen used.
D. "You should report monthly to have your blood drawn to monitor kidney function while taking medication."
Monitoring kidney function is important for some medications, but it is not a standard monthly requirement for tuberculosis treatment. Monitoring typically involves assessing liver function, as certain tuberculosis medications can affect the liver.
A nurse is caring for a client who is in shock and is receiving an infusion of albumin. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect
Explanation
A. Oxygen saturation 96%:
Oxygen saturation at 96% is within the normal range and may not be directly influenced by the infusion of albumin. Albumin administration is more related to improving intravascular volume and blood pressure.
B. PaCO2 30 mm Hg:
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) is a measure of respiratory status. Albumin infusion is not directly associated with changes in PaCO2.
C. Decrease in protein:
Albumin is a protein, and its infusion would not lead to a decrease in protein levels. In fact, albumin administration increases the oncotic pressure in the intravascular space, helping to retain fluid and improve blood volume.
D. Increase in BP:
This is the correct answer. Albumin is a colloid solution that increases oncotic pressure in the bloodstream. By increasing oncotic pressure, albumin helps to draw fluid from the interstitial space into the vascular space, thereby increasing blood volume. This can contribute to an increase in blood pressure, which is a desired effect in the management of shock.
A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving intravenous therapy. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as a manifestation of fluid volume excess?
Explanation
A. Thready pulse:
A thready pulse is more indicative of fluid volume deficit or inadequate cardiac output, not fluid volume excess.
B. Decreased bowel sounds:
Decreased bowel sounds are not a specific sign of fluid volume excess. They may be associated with various gastrointestinal issues but are not directly related to fluid volume status.
C. Bilateral muscle weakness:
Bilateral muscle weakness is not a specific manifestation of fluid volume excess. It may be associated with electrolyte imbalances or other neuromuscular issues.
D. Distended neck veins:
This is the correct answer. Distended neck veins are a classic sign of fluid volume excess or overload. Increased venous pressure from excess fluid can lead to distension of the jugular veins in the neck. This finding is often seen in conditions such as heart failure or renal failure where there is an inability to adequately excrete or distribute fluids.
A nurse is caring for an older adult client who is taking prednisone for long-term treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following adverse effects of this drug?
Explanation
A. Bone loss:
This is the correct answer. Long-term use of corticosteroids, such as prednisone, is associated with an increased risk of osteoporosis and bone loss. This effect is particularly significant in older adults.
B. Hypoglycemia:
Prednisone is more likely to cause hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) rather than hypoglycemia. It can lead to insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism.
C. Liver toxicity:
Liver toxicity is not a common adverse effect of prednisone. Prednisone is metabolized in the liver, but significant liver toxicity is not a typical concern with its use.
D. Hemolytic anemia:
Hemolytic anemia is not a common adverse effect of prednisone. Corticosteroids can affect the immune system, but hemolytic anemia is not a typical manifestation.

A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving intravenous therapy and observes redness and inflammation along the vein. The nurse should identify this finding as which of the following complications of IV therapy?
Explanation
A. Infiltration:
Infiltration refers to the inadvertent administration of a non-vesicant solution into the surrounding tissue. It is characterized by swelling, pallor, and coolness at the infusion site, but redness and inflammation along the vein are not typical signs of infiltration.
B. Extravasation:
Extravasation occurs when a vesicant solution (a substance that can cause tissue damage) infiltrates into the surrounding tissue. It can cause tissue damage and necrosis. While inflammation is a concern with extravasation, it is not the primary sign, and redness may occur later.
C. Venous spasm:
Venous spasm involves the constriction of the blood vessel, leading to decreased blood flow. It is not typically associated with redness and inflammation along the vein.
D. Phlebitis:
This is the correct answer. Phlebitis refers to inflammation of a vein, and it is characterized by redness, warmth, and tenderness along the course of the vein. Phlebitis can be caused by various factors, including irritants in the infused solution, mechanical trauma, or infection.
A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who has a new prescription for furosemide. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
A. This medication should be taken on an empty stomach:
Furosemide can be taken with or without food. Taking it with food can help reduce stomach upset, so there is no requirement to take it on an empty stomach.
B. Increase the amount of potassium in your diet:
This is the correct answer. Furosemide is a loop diuretic that can lead to potassium loss through increased urine output. Supplementing potassium through diet or potassium supplements may be necessary to prevent hypokalemia.
C. Take the medication before going to bed:
Furosemide is often recommended to be taken earlier in the day to avoid disrupting sleep with increased urination during the night. Taking it before going to bed is not a typical recommendation.
D. Weigh yourself on the same day each week:
Regular monitoring of weight is important in clients taking diuretics, but it is typically recommended to weigh daily at the same time each day, not weekly.
A nurse is caring for a group of clients. For which of the following situations should the nurse complete an incident report?
Explanation
A. A client received 0900 medications at 0930:
This situation involves a medication administration error where the medications were administered later than the scheduled time. An incident report should be completed to document the error, investigate the circumstances, and implement measures to prevent recurrence.
B. A client who has asthma was administered tiotropium via inhalation:
Tiotropium is an appropriate medication for asthma. As long as it was administered according to the prescribed guidelines, there is no need for an incident report.
C. A client received a blood transfusion with dextrose 5% in water:
This situation involves a significant medication error, as dextrose 5% in water is not the appropriate solution for a blood transfusion. An incident report should be completed to document the error, investigate the circumstances, and implement measures to prevent recurrence.
D. A client received an infusion of lipids through a central line:
If the infusion of lipids through a central line was ordered and administered appropriately, there is no need for an incident report. Lipid infusions are commonly administered through central lines when indicated.
A nurse is completing a medication reconciliation for a client prior to his transfer to a long-term care facility. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. Omit over-the-counter medications from the at-home medication list:
Over-the-counter medications should be included in the medication reconciliation process to provide a comprehensive overview of all medications the client is taking. These can have interactions or implications for the client's overall health.
B. Include medications the client received in the acute setting but will no longer need after transfer:
Medications that the client will no longer need after transfer should be excluded from the reconciliation list to avoid confusion and unnecessary continuation of those medications.
C. Compare the current list of medications to medications the client will receive after transfer:
This is part of the medication reconciliation process. It is important to ensure continuity of care by comparing the current list of medications with the medications the client will receive after transfer. Any discrepancies or changes should be addressed.
D. Remove duplicate medications of different dosages from the reconciliation list:
This is the correct answer. Duplicate medications with different dosages can lead to confusion and errors. The reconciliation process involves identifying and resolving discrepancies, including duplicates, to ensure accuracy and safety in medication administration
A nurse is preparing to administer nitroglycerin topical ointment to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take?
Explanation
A. Cover the medication on the client's skin with a sterile gauze pad:
Nitroglycerin ointment is typically applied directly to the skin, and covering it with a sterile gauze pad is not a common practice. The ointment is absorbed through the skin.
B. Spread the medication over a 12.7 cm (5 in) area of the client's skin:
This is the correct answer. Nitroglycerin ointment is usually applied to a specific area of the skin, and the recommended area is often around 12.7 cm (5 inches). The nurse should spread the ointment evenly over this specified area.
C. Measure the dosage of medication using the applicator paper:
Nitroglycerin ointment is typically measured using a dosing strip or measuring paper provided with the medication. Using the applicator paper to measure the appropriate dosage is a common practice.
D. Apply the medication to the same site for three consecutive days:
Nitroglycerin ointment is often rotated to different sites to prevent local irritation or tolerance. It is not typically applied to the same site for three consecutive days.
A nurse is reviewing the plan of care with a client who has a new prescription for lovastatin. Which of the following statements by the client should indicate to the nurse a need for further assessment?
Explanation
A. I take metformin for my diabetes:
This statement indicates that the client is aware of taking metformin for diabetes. It is relevant information but doesn't raise immediate concerns about the interaction with lovastatin.
B. "I should avoid drinking grapefruit juice:"
This is a correct statement. Grapefruit juice can interact with lovastatin, potentially increasing the risk of side effects. Advising the client to avoid grapefruit juice is a proper precaution when taking lovastatin.
C. I am trying to decrease my dietary fat intake:
This statement indicates a positive lifestyle change that aligns with the goal of using lovastatin to lower cholesterol. It is a positive and relevant statement.
D. "I was just diagnosed with hepatitis B:"
This is the correct answer. Lovastatin is metabolized by the liver, and liver function is an important consideration. The nurse should assess the severity of hepatitis B, the client's liver function, and whether lovastatin is contraindicated or requires dose adjustment based on the hepatic impairment.
A nurse is caring for a client who is taking azathioprine to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Which of the following laboratory values indicates an adverse effect of this medication?
Explanation
A. BUN 15 mg/dL (Blood Urea Nitrogen):
BUN is a measure of kidney function, and an elevated BUN may suggest impaired kidney function. However, it is not a specific marker for azathioprine adverse effects.
B. WBC 3,000/mm² (White Blood Cell count):
This is the correct answer. Azathioprine can suppress bone marrow function, leading to leukopenia (low white blood cell count). A WBC count of 3,000/mm² indicates a lower-than-normal white blood cell count, which can increase the risk of infection.
C. Hct 45% (Hematocrit):
Hematocrit measures the percentage of red blood cells in the blood. While it can be affected by various factors, it is not a specific marker for azathioprine adverse effects.
D. Platelets 250,000/mm²:
Platelets are involved in blood clotting, and a platelet count of 250,000/mm² is within the normal range. Azathioprine is not typically associated with adverse effects on platelet counts.
A nurse on a medical-surgical unit is preparing to administer an influenza vaccine to a client. The client tells the nurse. "I no longer want to receive this vaccine." Which of the following responses should the nurse make?
Explanation
A. "If I were you, I would get the vaccine to keep my family safe:"
This statement imposes the nurse's personal opinion on the client and may not respect the client's autonomy and decision-making.
B. "Influenza can be very serious to anyone who does not receive the vaccine:"
While this statement conveys the seriousness of influenza, it may be perceived as coercive or fear-inducing. It is important to provide information without pressure.
C. "The influenza vaccine is mandatory for all clients before discharge, so you will need to sign an against medical advice form:"
This statement is not accurate and may create unnecessary tension. Influenza vaccination is generally not mandatory, and clients have the right to decline without being labeled against medical advice for this particular vaccination.
D. "The influenza vaccine is strongly encouraged, but I understand you would like to decline right now:"
This is the correct answer. It acknowledges the client's decision to decline the vaccine while expressing that the vaccine is encouraged. It respects the client's autonomy and allows for open communication about the decision.
A charge nurse is teaching a newly licensed nurse about administering heparin to a client. Which of the following statements by the newly licensed nurse indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
A. I will check the client's INR before administering the heparin:
Checking the International Normalized Ratio (INR) is more relevant for monitoring the effects of warfarin, not heparin. Heparin is typically monitored by activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) or anti-Xa levels.
B. "I will apply pressure for 1 minute after the injection:"
Applying pressure after the injection is not a standard practice for administering heparin. Pressure may be applied after subcutaneous injections to minimize bleeding, but heparin is often given as an intravenous or subcutaneous injection.
C. I will massage the site after injecting the heparin:
Massaging the site after injecting heparin is not recommended. It can increase the risk of hematoma formation. After subcutaneous injection, it is generally advised to avoid massaging the site.
D. I will aspirate before administering the heparin:
This is the correct answer. Aspirating before administering heparin is not necessary. Heparin is typically given without aspiration to avoid causing trauma to the tissues. Aspiration is a technique used with intramuscular injections, not typically with subcutaneous or intravenous administration of heparin.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 65 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

