Rn fundamentals 2019 Exam
Total Questions : 65
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is caring for a client who consumes 3 oz of milk, 2 oz of orange juice, 3 oz of tea, and 4 oz of water over a 4-hr period. The client is also receiving dextrose 5% in 0.45% sodium chloride 30 mL/hr by continuous IV infusion. Calculate the client's intake for that 4-hr period in mL. (Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
1oz= 29.57 mL
Total oral intake= 3+2+3+4= 12oz 12oz x 29.57= 354.84 ml
Total IV 30ml/hr x 4= 120 ml Total= 354.84 +120
= 474.84 ml
= 475 ml (rounded off to the nearest whole number)
A nurse is preparing a sterile field to assist with suturing a client's laceration. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Placing the lid face down on the sterile drape contaminates the sterile field, as the outer surface of the lid is not considered sterile.
Choice B rationale: Applying sterile gloves before opening the bottle of sterile solution is important to maintain asepsis and prevent contamination of the field.
Choice C rationale: Pouring sterile solution with the bottle held 20 cm (8 in) above the sterile bowl helps prevent contamination by minimizing the risk of airborne microorganisms entering the solution.
Choice D rationale: Holding the bottle with the label facing the palm helps prevent drips or spills on the label, maintaining the sterility of the solution.
A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving continuous IV fluids through a peripheral IV. Which of the following findings indicates to the nurse that the client is experiencing fluid overload?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Crackles in the lungs indicate fluid overload, as excess fluid can accumulate in the alveoli, causing crackling sounds during breathing.
Choice B rationale: Bradycardia is not typically associated with fluid overload; tachycardia is a more common sign.
Choice C rationale: Fever is not a direct indicator of fluid overload but may be associated with other conditions.
Choice D rationale: Flattened neck veins are not indicative of fluid overload; distended neck veins are more likely to be seen in this condition.
A visitor reports to a nurse that she slipped and fell in a client's room. The visitor denies any injury, but is walking with a slight limp. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: While risk management may be involved later, the immediate action is to complete an incident report to document the details of the visitor's fall.
Choice B rationale: Administering acetaminophen to the client is not relevant to the visitor's fall and limp.
Choice C rationale: Documenting the occurrence in the client's medical record is important, but completing an incident report is the priority to ensure a thorough investigation and follow-up.
Choice D rationale: Completing an incident report is the priority to ensure a thorough investigation and follow-up. It is crucial for maintaining an accurate record of the event, identifying potential hazards, and implementing preventive measures.
A nurse at an assisted living facility is preparing an in-service for residents about electrical safety. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Cleaning electrical equipment is important for infection control but is not directly related to electrical safety.
Choice B rationale: Disconnecting electrical equipment by grasping the plug is a safe practice, as pulling on the cord can damage the cord and create a safety hazard.
Choice C rationale: Taping electrical cords to the floor can create a tripping hazard and is not recommended for electrical safety.
Choice D rationale: Covering exposed wires with tape is not a recommended practice, as it may not provide adequate protection and can create a fire hazard.
A nurse is preparing to administer several medications to a client. Which of the following data should the nurse plan to use to confirm the client's identity?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The client's admitting diagnosis is not a reliable identifier for confirming the client's identity.
Choice B rationale: The client's telephone number is a unique identifier and can be used to confirm the client's identity before administering medications.
Choice C rationale: The name of the client's next of kin is not a direct identifier of the client and should not be used for confirmation.
Choice D rationale: The client's room number is not a unique identifier and may not accurately confirm the client's identity.
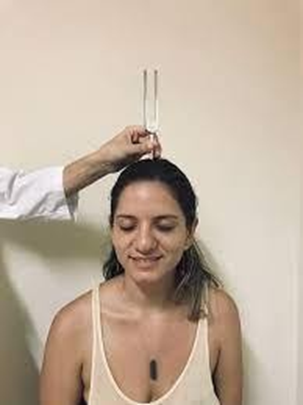
A nurse is testing a client for conduction deafness by performing the Weber's test. Which of the following actions should the nurse take when performing this test?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: To perform the test, the nurse should strike a tuning fork and place its base on the top of the client's head. The client should then report if they hear the sound equally in both ears, or louder in one ear. If the sound is louder in one ear, it indicates that there is either a conductive hearing loss in that ear, or a sensorineural hearing loss in the opposite ear.
Choice B rationale: Placing the base of a vibrating tuning fork on the client's mastoid process is the technique for the Rinne's test and not Weber’s test.
Choice C rationale: Counting how many seconds a client can hear a tuning fork after it has been struck is not a component of the Weber's test.
Choice D rationale: Moving a vibrating tuning fork in front of the client's ear canals one after the other is not the correct procedure for the Weber's test but is instead used in Rinne test.
A nurse is providing preoperative teaching to a client over the phone in preparation for outpatient surgery. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Wearing makeup during surgery is typically discouraged to prevent interference with monitoring equipment and to maintain a sterile environment.
Choice B rationale: Explaining the need to have another adult drive the client home is important due to the potential effects of anesthesia, which can impair the client's ability to drive and make decisions.
Choice C rationale: Showering three times the day before surgery is excessive and not a standard preoperative practice.
Choice D rationale: The client should stop drinking clear liquids 2 hrs before surgery. However, the guidelines for fasting but may vary depending on institutional policies.
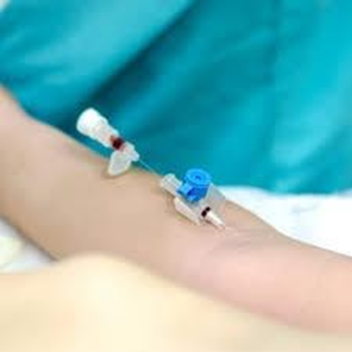
A nurse is preparing to insert a peripheral IV catheter into a client's arm. Which of the following actions should the nurse take to help dilate the vein?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The nurse should instruct the client to relax their arm and keep their hand open, but not to flex their arm, as this can reduce blood flow and make the vein less prominent.
Choice B rationale: Applying a cool compress to the vein for 10 minutes may cause vasoconstriction and make the vein less dilated.
Choice C rationale: Stroking the skin near the vein in an upward direction will increase blood flow and make the vein more visible and palpable.
Choice D rationale: The nurse should avoid dangling the client's arm over the edge of the bed, as this can cause venous pooling and increase the risk of thrombosis.
A nurse is preparing to bathe a client who has dementia. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Using distractions, such as music or gentle conversation, can help make the bathing experience more comfortable for a client with dementia.
Choice B rationale: Giving detailed instructions may be confusing for a client with dementia, as they may have difficulty processing and remembering information.
Choice C rationale: If the client is in distress during the bath, it is essential to modify the approach or consider alternative methods to ensure their comfort and well-being.
Choice D rationale: Allowing the client to select the temperature of the bath water may pose a safety risk, as they may not accurately assess or communicate their preferences.
A nurse is caring for a client who is postoperative and asks the nurse, "When will I get to go home? I'm not sure what happens next." Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Assuring the client that the provider will come to talk to him when she gets the chance may not address the client's immediate concerns and desire for information.
Choice B rationale: Telling the client that the provider will discharge him when she feels he is ready to leave does not provide the client with specific information about their treatment plan and discharge criteria.
Choice C rationale: Explaining that the client should trust the provider because she has an excellent reputation does not address the client's need for information about the next steps in their care.
Choice D rationale: Informing the provider that the client is requesting information about his treatment plan allows for effective communication between the client and the healthcare team, ensuring that the client receives the necessary information and clarification about the postoperative process.
A nurse manager is performing a quality improvement assessment to determine the source of a recurrence of Clostridium difficile on a unit. The nurse manager should identify that which of the following nursing actions is a possible source of the infection?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Wearing gloves when performing perineal care is a standard infection control practice to prevent the spread of infection.
Choice B rationale: Failing to don a mask when entering a client's isolation room may increase the risk of airborne transmission of infections but is not directly related to C. difficile.
Choice C rationale: Putting on a protective gown before entering a client's room is a standard precaution, especially in cases of contact precautions, to prevent the spread of infection.
Choice D rationale: Cleansing visibly fecal-soiled hands with alcohol-based hand rub is not effective for removing fecal material and may contribute to the spread of C. difficile, as alcohol-based hand rubs are not effective against this particular bacterium.
A nurse is preparing to administer a medication to a client. Which of the following should the nurse use as a client identifier?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: A photograph is a visual identifier that helps ensure the nurse administers medications to the correct client. Using physical characteristics, such as a photograph, is a reliable method for verifying a client's identity.
Choice B rationale: Age alone is not a specific enough identifier and may not accurately confirm the identity of the client.
Choice C rationale: Room number is not a reliable individual identifier and may lead to errors, especially in situations where clients are moved or room assignments change.
Choice D rationale: the bed number is not a reliable patient identifier and may result in errors especially when the patient is moved to another bed.
A hospice nurse is visiting a client who has terminal cancer. Which of the following statements by the client's partner should the nurse recognize as an indication of anticipatory grief?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Expressing sadness and missing the person is a common response to grief but does not necessarily indicate anticipatory grief.
Choice B rationale: Feeling angry about the situation is a common response to grief but does not specifically indicate anticipatory grief.
Choice C rationale: Planning a trip for next spring suggests a focus on future plans rather than anticipatory grief.
Choice D rationale: Not discussing funeral arrangements may indicate the partner's difficulty facing the impending loss and is a common sign of anticipatory grief.
A nurse is assessing the visual acuity of a client who wears glasses using a Snellen chart. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The Snellen chart is a tool that measures how well a person can see at a distance of 6 m (20 feet) from the chart.
Choice B rationale: the nurse should document the smallest line the client can read on the chart, as this indicates the level of detail they can discern.
Choice C rationale: the nurse should assess the client's visual acuity with their corrective lenses on, as this reflects their usual vision. The nurse should also test each eye separately and then both eyes together.
Choice D rationale: Instructing the client to begin the assessment with both eyes open is not the standard procedure. The nurse should cover one eye at a time to assess each eye separately. This allows the nurse to detect any differences in vision between the eyes and to assess binocular vision.

A nurse is caring for a client who has a new diagnosis of terminal cancer. Which of the following interventions is the priority?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: While finding a local support group is important, it may not be the immediate priority in caring for a client with a new diagnosis of terminal cancer.
Choice B rationale: the nurse should first assess the client's current level of coping and emotional state before implementing any other interventions. This will help the nurse to tailor the care plan according to the client's needs and preferences.
Choice C rationale: Teaching progressive relaxation techniques is valuable for coping, but it may not be the priority immediately after the diagnosis.
Choice D rationale: Developing a list of goals with the client is the important to address the client's immediate concerns, preferences, and wishes for their care and end-of-life decisions. However, this is not the priority step at this stage.
A nurse is monitoring a client who is receiving continuous IV fluid therapy via a peripheral vein in the left forearm. Which of the following findings indicates that the client has developed phlebitis at the IV site?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Pitting edema at the insertion site is not a typical sign of phlebitis but may indicate fluid overload or other issues.
Choice B rationale: Coolness of the client's left forearm is not a typical sign of phlebitis and may suggest poor peripheral perfusion.
Choice C rationale: Pallor of the client's left forearm is not a typical sign of phlebitis and may indicate decreased blood flow.
Choice D rationale: Erythema (redness) along the path of the vein is a classic sign of phlebitis, indicating inflammation at the IV site.
A nurse is caring for a client who is agitated and threatening to harm others. The nurse places the client in restraints, but does not notify the provider or obtain a prescription for the restraints. This situation represents which of the following torts?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Invasion of privacy involves violating a person's right to keep their personal matters private, not the act of restraining.
Choice B rationale: Negligence involves failure to provide reasonable care and may not be the primary issue in this scenario.
Choice C rationale: Assault involves causing apprehension of harmful or offensive contact, not the act of restraining.
Choice D rationale: False imprisonment occurs when a person is unlawfully restrained or restricted in their freedom of movement, and in this scenario, the nurse is restraining the client without proper authorization.
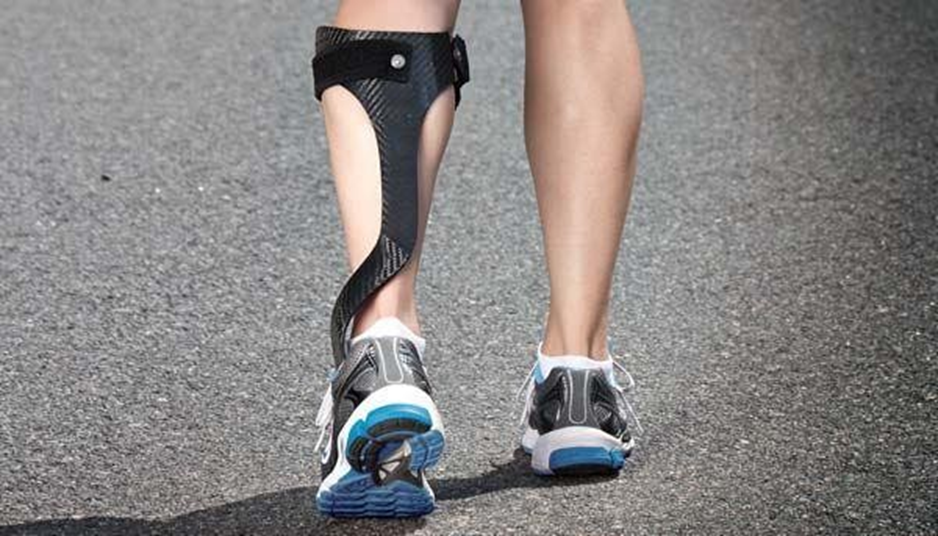
A nurse is caring for a client who has right-sided paralysis following a cerebrovascular accident. Which of the following prescriptions should the nurse anticipate to prevent a plantar flexion contracture of the affected extremity?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Sequential compression devices are used to prevent deep vein thrombosis and are not specifically designed to prevent plantar flexion contractures.
Choice B rationale: Ankle-foot orthotics are devices that help maintain the foot in a dorsiflexed position, preventing plantar flexion contractures in clients with paralysis. \
Choice C rationale: Continuous passive motion machines are typically used for joint mobility exercises and are not specifically designed to prevent plantar flexion contractures.
Choice D rationale: Abduction splints are used to maintain proper alignment and prevent contractures in the hip joint but are not specifically designed for plantar flexion contractures.
A nurse is caring for a client who reports a pain level of 5 on a scale from 0 to 10. The client informs the nurse that pain medications are not an option for managing pain. Which of the following is an appropriate response by the nurse?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Dismissing the client's concerns and insisting that pain medication will work may not be effective and can undermine the client's autonomy.
Choice B rationale: Encouraging the use of herbal remedies from home without proper assessment and approval from the healthcare team may pose risks and is not a recommended approach.
Choice C rationale: Offering a back massage is a non-pharmacological intervention for pain management and respects the client's preferences regarding pain medication.
Choice D rationale: Asking the client why they think pain medication is not going to help is a confrontational approach that may not be helpful in establishing a therapeutic relationship.
A nurse is completing a dressing change on a client who has a surgical wound drain. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Donning clean gloves before cleaning the wound is not sufficient for maintaining asepsis during a dressing change.
Choice B rationale: Cleaning the drain site before the incision may introduce contaminants from the drain site to the incision, increasing the risk of infection.
Choice C rationale: Using a separate, sterile swab for each stroke when cleaning the wound helps prevent the introduction of contaminants and maintains a sterile field during the dressing change.
Choice D rationale: Cutting a 4x4 piece of gauze to place around the drain site is not necessary and does not address the primary concern of maintaining asepsis during the dressing change.
A nurse is caring for a client who has a chest tube following thoracic surgery. Which of the following tasks should the nurse delegate to an assistive personnel?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Evaluating the client's response to pain medication requires nursing judgment and assessment skills and should not be delegated to assistive personnel.
Choice B rationale: Teaching deep breathing and coughing to the client is a nursing responsibility to ensure accurate information and proper technique.
Choice C rationale: Monitoring the characteristics of the client's chest tube drainage involves assessing for potential complications and should not be delegated to assistive personnel.
Choice D rationale: Assisting the client to select food choices from the menu is a non- nursing task that can be delegated to assistive personnel, allowing the nurse to focus on nursing responsibilities. It does not require nursing judgment or skill and can be delegated to an assistive personnel.
A nurse enters a client's room and discovers a smoldering fire in the drapes. After moving clients to a safe location, which of the following actions should the nurse take next?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The first action in the event of a fire is to pull the fire alarm to alert others and initiate the fire response plan.
Choice B rationale: Using an extinguisher to put out the fire is appropriate only if the fire is small and can be safely controlled. The fire alarm should be pulled first to ensure a coordinated response.
Choice C rationale: Turning off electrical equipment in the room is a lower priority than pulling the fire alarm to ensure the safety of everyone in the facility.
Choice D rationale: Closing the doors to client rooms is a measure to contain smoke and fire, but the immediate priority is to pull the fire alarm to initiate the fire response plan.
A nurse is planning care to prevent skin breakdown for a client who is immobile and has urinary incontinence. Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Repositioning the client every 4 hours is important for preventing pressure ulcers but may not be sufficient on its own.
Choice B rationale: Arranging for an alternating pressure mattress helps distribute pressure and reduces the risk of pressure ulcers in immobile clients.
Choice C rationale: Requesting a prescription for an indwelling urinary catheter is not the first-line intervention for preventing skin breakdown and comes with its own set of risks and complications.
Choice D rationale: Applying cornstarch to the client's skin may increase moisture and is not recommended for preventing skin breakdown in the presence of urinary incontinence.
A nurse is preparing to apply a condom catheter for a client who is uncircumcised. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Placing adhesive tape directly on the penis can cause skin irritation and pain when removing the tape hence is not recommended.
Choice B rationale: Allowing 2.5 to 5 cm (1 to 2 in) between the end of the catheter and the tip of the penis helps prevent constriction and ensures proper fit. It also prevents pressure and irritation on the glans penis, which can lead to infection or necrosis.
Choice C rationale: Keeping foreskin in a retracted position after application of the catheter can impair circulation and cause swelling or edema of the foreskin.
Choice D rationale: Changing the condom catheter every 3 days is too infrequent and can increase the risk of urinary tract infection, skin breakdown, and odor. The condom catheter should be changed daily or as per facility policy.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 65 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

