RN Pharmacology 2019 Exam 4 Updated 2024
Total Questions : 58
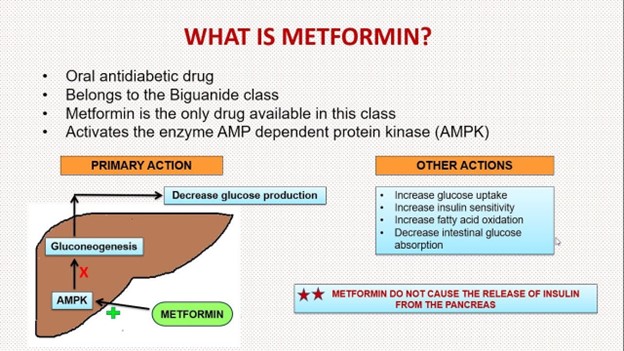
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse accidently administers the medication metformin instead of metoprolol to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. Obtain the client's HDL level.
Explanation: This choice is not relevant to the situation. HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) level is related to cholesterol levels and cardiovascular health, which is not directly affected by the administration of metformin instead of metoprolol.
B. Check the client's glucose level.
Explanation: Correct Choice. Metformin is an oral antidiabetic medication commonly used to lower blood glucose levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. It works by improving insulin sensitivity and decreasing glucose production in the liver. Accidentally administering metformin instead of metoprolol could lead to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or other adverse effects related to glucose levels. Checking the client's glucose level is essential to assess and address any potential issues arising from this medication error.
C. Monitor the client's thyroid function levels.
Explanation: This choice is not directly relevant to the situation. Metformin and metoprolol do not significantly affect thyroid function levels. Thyroid function monitoring would not be the immediate concern in this scenario.
D. Collect the client's uric acid level.
Explanation: This choice is not directly relevant to the situation. Metformin and metoprolol do not have a primary impact on uric acid levels. Collecting the uric acid level would not be a priority in this context.
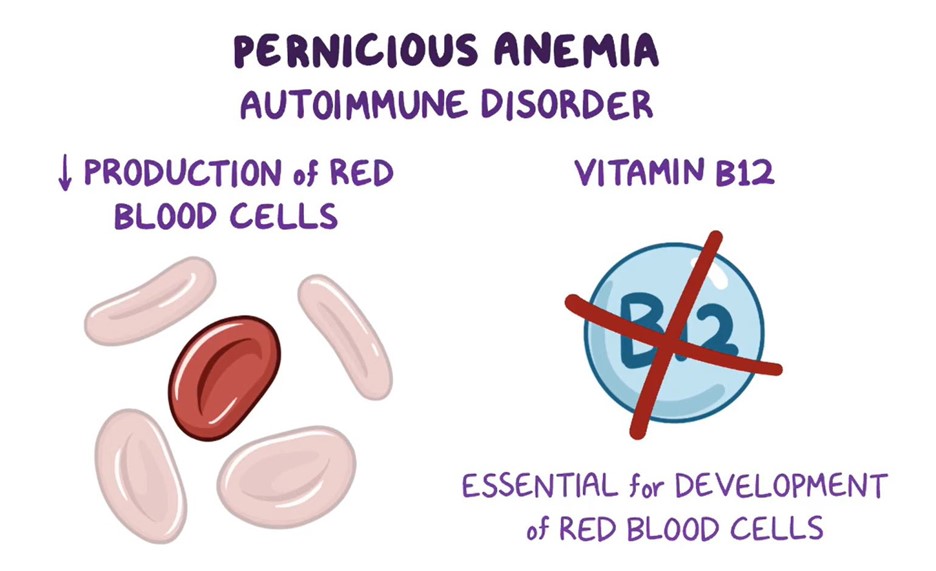
A nurse is teaching a client who has pernicious anemia to self-administer nasal cyanocobalamin. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
A. "Plan to self-administer this medication for the next 6 months": The duration of treatment may vary based on individual circumstances and medical evaluation. It's not appropriate to make a blanket statement about the treatment duration.
B. "Administer the medication into one nostril once per week."
Cyanocobalamin is a form of vitamin B12 that is used to treat pernicious anemia. It can be administered via nasal spray in some cases. The appropriate dosing for nasal cyanocobalamin usually involves administration once a week. The client should be instructed to administer the medication into one nostril as directed by their healthcare provider.
C. "Lie down for 1 hour after administering the medication": There is no need for the client to lie down for an extended period after administering nasal cyanocobalamin.
D. "Use a nasal decongestant 15 minutes before the medication if you have a stuffy nose": This is not a standard recommendation for administering nasal cyanocobalamin. The client should follow the specific instructions provided by their healthcare provider.
A nurse is preparing to administer enoxaparin to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. Administer the medication into the client's muscles.
Explanation: This is incorrect because enoxaparin is usually administered subcutaneously, not into the muscle.
B. Apply firm pressure to the injection site following administration.
Explanation: This is incorrect because while applying gentle pressure after a subcutaneous injection is common practice, it is not specific to enoxaparin.
C. Insert the syringe needle halfway into the client's skin.
Explanation: This is incorrect because the needle should be inserted fully into the subcutaneous tissue, not just halfway, for proper administration of enoxaparin.
D. Expel the air bubble from the syringe prior to injection.
Explanation: This is the correct action. Expelling air bubbles from the syringe prior to injection helps ensure accurate dosing and prevents air from being injected into the subcutaneous tissue.
When administering enoxaparin (low molecular weight heparin) subcutaneously, it's important to expel any air bubbles from the syringe before injection. Air bubbles can cause discomfort and inaccuracies in dosage. The nurse should gently tap the syringe to move air bubbles to the top and then push the plunger slightly to expel the air. The other options are not correct procedures for administering enoxaparin. It is typically injected into the subcutaneous tissue, not a muscle, and firm pressure is not typically applied after administration. The needle is fully inserted into the skin, not halfway.
A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetes mellitus and is taking pioglitazone. The nurse should plan to monitor the client for which of the following adverse effects?
Explanation
A. Orthostatic hypotension: Orthostatic hypotension refers to a drop in blood pressure when changing from a lying to a standing position. This is not a common adverse effect of pioglitazone.
B. Tinnitus: Tinnitus is the perception of ringing or noise in the ears. There is no established link between pioglitazone and tinnitus.
C. Insomnia: Insomnia refers to difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. Pioglitazone is not typically associated with causing insomnia as an adverse effect.
D. Fluid retention
Pioglitazone is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing insulin resistance. One of the potential adverse effects of pioglitazone is fluid retention, which can lead to edema (swelling) in the body. This is because pioglitazone has an impact on sodium and water balance in the body, which can cause fluid accumulation in tissues.
Therefore, the most appropriate adverse effect to monitor for in a client taking pioglitazone is fluid retention.
A nurse is preparing to administer potassium chloride elixir 20 mEq/day PO to divide equally every 12 hr. Available is 6.7 mEq/5 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer per dose? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
To calculate the amount of potassium chloride elixir needed per dose, we can use the following formula:
Amount per dose (mL) = (Desired dose in mEq / Concentration in mEq/mL) * Volume in mL
Given:
Desired dose = 20 mEq/day divided equally every 12 hr = 10 mEq/dose
Concentration = 6.7 mEq/5 mL
Plugging in the values:
Amount per dose (mL) = (10 mEq / 6.7 mEq/5 mL) * 5 mL
Calculating:
Amount per dose (mL) ≈ 7.46 mL
Rounded to the nearest tenth, the nurse should administer approximately 7.5 mL of the potassium chloride elixir per dose.
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory data of a client prior to administering IV tobramycin. Which of the following laboratory values should the nurse report to the provider?
Explanation
A. Hct 43%
Explanation: Hematocrit (Hct) measures the proportion of blood volume that is occupied by red blood cells. A low Hct level could indicate anemia, which might affect the body's ability to deliver sufficient oxygen to tissues.
B. Creatinine 2.5 mg/dL
Explanation: Elevated creatinine levels indicate potential kidney dysfunction. Tobramycin is primarily excreted by the kidneys, so elevated creatinine levels can increase the risk of tobramycin toxicity due to reduced drug clearance.
C. Sodium 137 mEq/L
Explanation: Sodium level within the normal range. It doesn't directly impact the administration of tobramycin.
D. Hgb 15 g/dL
Explanation: Hemoglobin (Hgb) measures the concentration of oxygen-carrying protein in the blood. A normal hemoglobin level is not directly related to the administration of tobramycin.
A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for theophylline, a sustained-release capsule. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
A. "I will need to have blood levels drawn."
Theophylline is a medication used to treat respiratory conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is important to monitor the blood levels of theophylline because it has a narrow therapeutic range – meaning that there is a fine line between a therapeutic dose and a toxic dose. Regular blood tests help to ensure that the client is receiving the appropriate dose for their condition.
B. "I can take my medication in the morning with my coffee." - Theophylline should be taken consistently with meals, so taking it with coffee might not be ideal as it can affect its absorption.
C. "I may sprinkle the medication in applesauce." - Theophylline is usually taken as a sustained-release capsule, which means it is designed to release the medication slowly over time. Crushing or sprinkling the medication can disrupt this mechanism and lead to unintended consequences.
D. "I should limit my fluid intake while on this medication." - There's no requirement to limit fluid intake with theophylline, and in fact, adequate hydration can help prevent some side effects of the medication.
A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for clozapine. Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
A. "Notify your provider if you develop a fever while taking this medication."
Clozapine is an antipsychotic medication used to treat severe mental illnesses like schizophrenia. One of the potentially serious side effects of clozapine is agranulocytosis, which is a significant drop in white blood cell count. This can lead to an increased risk of infection. If the client develops a fever, it could be an early sign of an infection due to the lowered white blood cell count, so it's important for them to notify their provider promptly.
B. "Ringing in the ears is an expected adverse effect of this medication." - Tinnitus (ringing in the ears) is not a commonly reported adverse effect of clozapine.
C. "You might experience weight loss while taking this medication." - Weight gain is actually more commonly associated with clozapine use, rather than weight loss.
D. "Diarrhea is a common adverse effect of this medication." - While gastrointestinal disturbances can occur as side effects of antipsychotic medications, diarrhea is not specifically known as a common adverse effect of clozapine.
A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetes mellitus and is taking pioglitazone. The nurse should plan to monitor the client for which of the following adverse effects?
Explanation
A. Orthostatic hypotension refers to a drop in blood pressure upon standing up quickly. This is not a commonly associated adverse effect of pioglitazone.
B. Tinnitus refers to ringing in the ears and is not typically related to pioglitazone use.
C. Insomnia (difficulty sleeping) is not commonly reported as an adverse effect of pioglitazone.
D. Fluid retention
The nurse should plan to monitor the client for the adverse effects of fluid retention.
Pioglitazone is an oral antidiabetic medication that belongs to the thiazolidinedione class. One of the common adverse effects of pioglitazone is fluid retention or edema. This occurs due to its mechanism of action which can cause fluid buildup in the body's tissues, particularly in the lower extremities. Clients taking pioglitazone should be monitored for signs of edema, such as swelling in the ankles, legs, or feet. Monitoring for weight gain and any signs of worsening heart failure is also important.
A nurse is caring for a client who is taking digoxin to treat heart failure. Which of the following factors predisposes this client to develop digoxin toxicity?
Explanation
A. Taking an HMG CoA reductase inhibitor (commonly known as statins) is not directly associated with digoxin toxicity. Statins are used to lower cholesterol levels.
B. Having a 10-year history of COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) is not directly linked to an increased risk of digoxin toxicity.
C. Having a prolapsed mitral valve is a valvular disorder and is not a primary factor that contributes to digoxin toxicity.
D. Taking a high-ceiling diuretic
The factor that predisposes the client to develop digoxin toxicity is taking a high-ceiling diuretic.
Digoxin toxicity can be influenced by several factors. One important factor is the levels of potassium in the blood. High-ceiling diuretics, also known as loop diuretics (e.g., furosemide), can lead to potassium loss through increased urinary excretion. Low levels of potassium (hypokalemia) can increase the risk of digoxin toxicity, as digoxin has a greater effect on the heart when potassium levels are low.

A nurse is discussing adverse reactions to pain medications in older adult clients with a newly licensed nurse. Which of the following findings should the nurse include as risk factors for an adverse drug reaction? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
A. Multiple health problems: Older adults often have multiple chronic health conditions, which can increase the risk of interactions between medications or exacerbate the effects of certain drugs.
B. Decreased renal function: As people age, their kidney function tends to decrease, which can affect the clearance of drugs from the body. Drugs that are primarily excreted through the kidneys may accumulate in older adults with reduced renal function.
C. Polypharmacy: Older adults are more likely to be taking multiple medications simultaneously. This increases the risk of drug interactions and adverse effects.
D. Decreased percentage of body fat: With age, there is a decrease in lean body mass and an increase in body fat. Fat-soluble drugs can accumulate in body fat, leading to prolonged drug effects and increased risk of toxicity.
E. Increased rate of absorption: Aging can lead to changes in gastrointestinal function, including reduced gastric motility and decreased blood flow to the gastrointestinal tract. These changes may result in delayed drug absorption rather than an increased rate of absorption.
A nurse is monitoring for an infusion reaction for a client who is receiving a dose of IV amphotericin B. Which of the following findings should indicate to the nurse that the client is experiencing an acute infusion reaction?
Explanation
A. Pedal edema
Explanation: Pedal edema (swelling of the feet) is not a typical sign of an acute infusion reaction to IV amphotericin B.
B. Fever
Explanation: Fever is a common sign of an acute infusion reaction, indicating an inflammatory response to the medication.
An acute infusion reaction to IV amphotericin B is most commonly characterized by fever and chills, as well as other flu-like symptoms such as headache, muscle or joint pain, and sometimes a dry cough. Fever is a key indicator of an acute reaction to amphotericin B, and the presence of fever during or after administration should raise concern and prompt the nurse to take appropriate action, including notifying the healthcare provider and discontinuing the infusion.
Pedal edema and hyperglycemia are not typically associated with acute infusion reactions to amphotericin B and are not common manifestations of this type of reaction.
C. Hyperglycemia
Explanation: Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) is not typically associated with an acute infusion reaction to IV amphotericin B.
D. Dry cough
Explanation: A dry cough can be a symptom of an acute infusion reaction, potentially indicating irritation or inflammation of the respiratory tract.

A nurse is reviewing the list of current medications for a client who is to start a new prescription for carbamazepine. The nurse should identify which of the following medications interacts with carbamazepine.
Explanation
A. Estrogen-progestin combination:
Correct Answer: This medication interacts with carbamazepine.
Explanation: Carbamazepine is known to induce certain liver enzymes, including cytochrome P450 enzymes. These enzymes play a role in the metabolism of various medications, including estrogen-containing oral contraceptives (estrogen-progestin combinations). Carbamazepine can increase the metabolism of estrogen-progestin combinations, potentially reducing their effectiveness and increasing the risk of contraceptive failure. Therefore, this interaction can lead to decreased contraceptive efficacy and the potential for unintended pregnancy.
B. Nicotine transdermal system:
Incorrect Explanation: This medication does not interact with carbamazepine.
Explanation: Nicotine replacement therapies, such as nicotine transdermal systems, are not known to have significant interactions with carbamazepine. These therapies are primarily used to aid in smoking cessation and do not share metabolic pathways with carbamazepine.
C. Diphenhydramine:
Incorrect Explanation: This medication does not interact with carbamazepine.
Explanation: Diphenhydramine is an antihistamine used for allergies and as a sleep aid. It does not have a well-established interaction with carbamazepine. However, it's important to note that carbamazepine can have central nervous system (CNS) effects, so caution should be exercised when combining it with other medications that also have CNS effects.
D. Beclomethasone:
Incorrect Explanation: This medication does not interact with carbamazepine.
Explanation: Beclomethasone is a corticosteroid used to manage inflammation associated with conditions like asthma and allergic rhinitis. It is not known to interact with carbamazepine. These two medications have different mechanisms of action and do not share significant metabolic pathways.

A nurse is caring for a client who has major depression and a new prescription for citalopram. Which of the following adverse effects is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider?
Explanation
A. Bruxism:
Correct Answer: This adverse effect is a priority to report to the provider.
Explanation: Bruxism refers to teeth grinding or clenching, often unconsciously during sleep. It can be a potential side effect of citalopram and other selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Bruxism can lead to dental problems, jaw pain, and other discomforts. If this side effect occurs, it should be reported to the provider as it can impact the client's oral health and overall well-being.
B. Confusion:
Incorrect Explanation: While confusion is a concerning adverse effect, it's not typically associated with citalopram use.
Explanation: Confusion is more commonly associated with other medications or medical conditions. If a client experiences confusion, a thorough assessment is warranted, but it may not be directly attributed to citalopram.
C. Weight loss:
Incorrect Explanation: Weight loss can be a side effect of citalopram, but it's not the highest priority in this scenario.
Explanation: Weight loss is a possible side effect of many antidepressants, including citalopram. However, it is generally not as immediately concerning as other adverse effects that can impact a client's health and well-being.
D. Insomnia:
Incorrect Explanation: Insomnia is a common side effect of citalopram and other antidepressants, but it's not the highest priority in this context.
Explanation: Insomnia can be a transient side effect when starting an antidepressant-like citalopram. While it can affect the client's quality of life, it is not as urgent as potential dental issues caused by bruxism.
A nurse is assessing a client who has hypermagnesemia. Which of the following medications should the nurse prepare to administer?
Explanation
A. Calcium gluconate.
Hypermagnesemia refers to an abnormally high level of magnesium in the blood. High levels of magnesium can lead to muscle weakness, decreased reflexes, confusion, and other symptoms. One of the primary treatments for hypermagnesemia is administering calcium gluconate. Calcium gluconate is given intravenously and works by counteracting the effects of excess magnesium on muscles and nerves. It can help restore normal neuromuscular function and decrease symptoms associated with hypermagnesemia.
B. Flumazenil is used to reverse the effects of benzodiazepine overdose or excessive sedation. It has no direct effect on magnesium levels.
C. Acetylcysteine is used to treat acetaminophen (paracetamol) overdose and prevent liver damage. It is not related to treating hypermagnesemia.
D. Protamine sulfate is used to reverse the effects of heparin, a blood-thinning medication. It does not have a role in treating hypermagnesemia.

A nurse is planning care for a client who is receiving morphine via continuous epidural infusion. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following adverse effects?
Explanation
A. Pruritus, which is itching, is a common adverse effect associated with the use of opioids, including morphine. Itching can occur when opioids are administered through various routes, including epidural infusion. The exact mechanism for opioid-induced itching is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to the release of histamines or other chemical mediators.
B. Gastric bleeding is not a common adverse effect of epidurally administered opioids like morphine. Gastric bleeding is more associated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and certain other medications.
C & D. Tachypnea (rapid breathing) and cough are not typical adverse effects of epidurally administered opioids. However, opioids can cause respiratory depression (slow and shallow breathing), so monitoring respiratory status is important when using these medications.
A nurse is caring for a client who is taking lithium and reports starting a new exercise program. The nurse should assess the client for which of the following electrolyte imbalances?
Explanation
A. Hypomagnesemia:
Correct Answer: This electrolyte imbalance is the one the nurse should assess the client for.
Explanation: Lithium is primarily excreted by the kidneys, and its excretion can be influenced by factors that affect renal function, including electrolyte imbalances. Hypomagnesemia (low magnesium levels) can potentially reduce the excretion of lithium, leading to increased lithium levels in the blood. This can increase the risk of lithium toxicity, which can be dangerous. Therefore, monitoring magnesium levels is important in clients taking lithium.
B. Hyponatremia:
Incorrect Explanation: While hyponatremia (low sodium levels) is a potential concern, it is not as directly linked to lithium interaction as hypomagnesemia.
Explanation: Lithium can cause diabetes insipidus, which leads to excessive urination and subsequent loss of water and electrolytes, including sodium. However, hyponatremia is not the immediate electrolyte imbalance that arises due to the interaction with lithium.
C. Hypocalcemia:
Incorrect Explanation: Hypocalcemia (low calcium levels) is not a primary concern in the context of lithium use.
Explanation: Lithium does not have a direct interaction with calcium levels. Hypocalcemia is typically not a result of lithium use or its interaction with other factors.
D. Hypokalemia:
Incorrect Explanation: While electrolyte imbalances like hypokalemia (low potassium levels) can have health implications, it is not the primary electrolyte imbalance to be concerned about with lithium use.
Explanation: Hypokalemia is not a direct consequence of lithium interaction. Monitoring potassium levels is important for overall health, but it's not the primary electrolyte imbalance associated with lithium use and its potential interactions.
A nurse is preparing to administer 4,000 units of heparin subcutaneously to a client who has deep-vein thrombosis. Available in heparin 10,000 units/mL. How many mL of heparin should the nurse administer? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
To calculate the volume of heparin needed, you can use the formula:
Volume (mL) = Desired dose (units) / Concentration (units/mL)
In this case, the desired dose is 4,000 units and the concentration is 10,000 units/mL.
Volume = 4,000 units / 10,000 units/mL = 0.4 mL
So, the nurse should administer 0.4 mL of heparin.
A nurse is planning to administer medications to an older adult client who has dysphagia. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take?
Explanation
A. Place the medications on the back of the client's tongue:
Incorrect Explanation: Placing medications on the back of the tongue can increase the risk of choking and aspiration, especially in individuals with dysphagia.
Explanation: Individuals with dysphagia have difficulty swallowing and are at an increased risk of choking or aspirating (inhaling) substances into the lungs. Placing medications on the back of the tongue can be unsafe and is not recommended.
B. Tilt the client's head back when administering the medications:
Incorrect Explanation: Tipping the head back can worsen swallowing difficulties and increase the risk of choking or aspiration.
Explanation: Tipping the head back can compromise the natural swallowing mechanism and increase the risk of aspiration. It's important to keep the client's head in an upright position to aid safe swallowing.
C. Administer more than one pill to the client at a time:
Incorrect Explanation: Administering multiple pills at once can increase the risk of choking and aspiration, especially in individuals with dysphagia.
Explanation: Administering multiple pills at once can overwhelm the client's ability to swallow safely. This action can increase the risk of choking and aspiration, which is especially dangerous for individuals with dysphagia.
D. Mix the medications with a semisolid food for the client:
Correct Answer: This action is appropriate and safer for administering medications to an older adult client with dysphagia.
Explanation: Mixing medications with semisolid food, such as applesauce or yogurt, can help the client swallow more easily and reduce the risk of choking or aspiration. It's important to check with the healthcare provider or pharmacist to ensure that the medications can be mixed with food and that there are no interactions.
A nurse is preparing to administer the initial dose of penicillin G IM to a client. The nurse should monitor for which of the following as an indication of an allergic reaction following the injection?
Explanation
A. Pallor:
Incorrect Explanation: While pallor (pale skin) can be a sign of an allergic reaction, it is not a specific indication of an allergic reaction to penicillin.
Explanation: Pallor can occur for various reasons, including shock or vasovagal responses, and it is not unique to allergic reactions.
B. Dyspepsia:
Incorrect Explanation: Dyspepsia (indigestion or upset stomach) is not a typical sign of an allergic reaction.
Explanation: Allergic reactions are more commonly associated with skin, respiratory, and cardiovascular symptoms, rather than gastrointestinal symptoms like dyspepsia.
C. Bradycardia:
Incorrect Explanation: Bradycardia (slow heart rate) is not a typical indicator of an allergic reaction.
Explanation: Allergic reactions generally do not directly cause bradycardia. Rapid heart rate (tachycardia) can be a symptom of an allergic reaction in some cases.
D. Urticaria:
Correct Answer: Urticaria (hives) is a common and characteristic sign of an allergic reaction, including to penicillin.
Explanation: Urticaria presents as raised, itchy, and often red welts on the skin. It is a classic manifestation of an allergic response and can occur rapidly after exposure to an allergen, including medications like penicillin.
A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving a peripheral IV infusion and notes infiltration of fluid into the tissues surrounding the insertion site. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. Slow the infusion rate:
Incorrect Explanation: Slowing the infusion rate is not the appropriate action when fluid infiltration has occurred.
Explanation: Fluid infiltration occurs when the IV catheter becomes dislodged from the vein and fluid enters the surrounding tissues. Slowing the infusion rate will not prevent or address this issue.
B. Apply pressure to the IV site:
Correct Answer: Applying pressure to the IV site is an appropriate initial action when fluid infiltration occurs.
Explanation: Applying gentle pressure just above the insertion site can help prevent further fluid from entering the surrounding tissues. This can help minimize the extent of infiltration and reduce potential complications.
C. Elevate the extremity:
Incorrect Explanation: Elevating the extremity is not the primary action to take when fluid infiltration is present.
Explanation: Elevating the extremity might be helpful in reducing swelling and promoting blood flow in general, but it's not the primary action to address fluid infiltration.
D. Flush the IV catheter:
Incorrect Explanation: Flushing the IV catheter is not the appropriate action for addressing fluid infiltration.
Explanation: Flushing the catheter might exacerbate the infiltration by pushing more fluid into the surrounding tissues. It's important to address the issue of infiltration first.
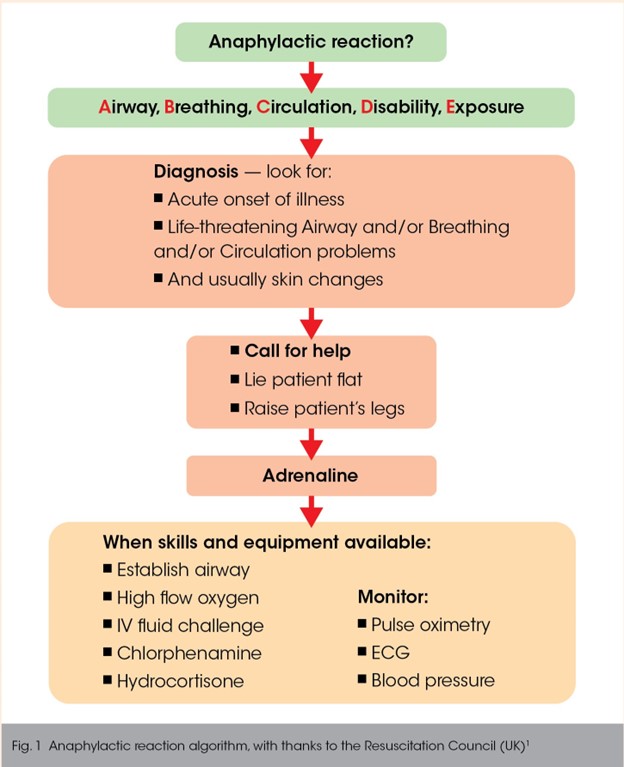
A nurse is caring for a client who develops an anaphylactic reaction to IV antibiotic administration. After assessing the client's respiratory status and stopping the medication infusion, which of the following actions should the nurse take next?
Explanation
A. Replace the infusion with 0.9% sodium chloride:
Incorrect Explanation: While replacing the infusion with a different solution might be considered later, it's not the immediate next step.
Explanation: The primary concern during an anaphylactic reaction is ensuring the client's airway, breathing, and circulation. Addressing the medication infusion should come after stabilizing the client's condition.
B. Give diphenhydramine IM:
Incorrect Explanation: Administering diphenhydramine (an antihistamine) can be beneficial, but it's not the initial priority.
Explanation: Diphenhydramine can help mitigate allergic symptoms, but it's not the first-line treatment for severe anaphylaxis.
C. Elevate the client's legs and feet:
Incorrect Explanation: Elevating the legs and feet is not the appropriate action for managing anaphylaxis.
Explanation: During anaphylaxis, maintaining the airway, ensuring proper circulation, and administering appropriate medications take precedence over elevating the legs.
D. Administer epinephrine IM:
Correct Answer: Administering epinephrine (adrenaline) IM is the appropriate next step in managing anaphylaxis.
Explanation: Epinephrine is the first-line treatment for severe anaphylactic reactions. It helps counteract the symptoms of anaphylaxis by constricting blood vessels, improving circulation, and opening airways. Epinephrine should be administered promptly and followed by seeking emergency medical care.
A nurse recently administered filgrastim intravenously to a client who has cancer and is receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy. For which of the following data, discovered after the medication was administered, should the nurse file an incident report?
Explanation
A. The client's absolute neutrophil count was 2.500/mm³ before the medication was administered:
Incorrect Explanation: This is a normal data point that does not suggest an adverse event or error.
Explanation: An absolute neutrophil count of 2.500/mm³ is within the normal range, and there is no indication of a problem related to the administration of filgrastim based on this information.
B. The nurse flushed the client's IV line with dextrose 5% in water before and after the medication was administered:
Incorrect Explanation: Routine flushing of the IV line with appropriate solutions is a standard practice and not indicative of an incident.
Explanation: Flushing the IV line with dextrose 5% in water before and after medication administration is a routine procedure to maintain line patency and prevent interactions between medications.
C. The client had chemotherapy 12 hours before the medication was administered:
Incorrect Explanation: The timing of chemotherapy does not necessarily indicate an incident.
Explanation: Knowing the timing of chemotherapy is important for overall patient care, but it doesn't necessarily indicate an incident or error related to the administration of filgrastim.
D. The medication vial sat at room temperature for 2 hours before it was administered:
Correct Answer: This is the data point that should lead to filing an incident report.
Explanation: Many medications, including filgrastim, have specific storage requirements to ensure their effectiveness and safety. Allowing a medication vial to sit at room temperature for an extended period can compromise its stability and effectiveness. This situation should be reported as it involves a potential deviation from proper medication storage and handling procedures.
A nurse is reviewing the medical record of an adult client who has a fever and a prescription for acetaminophen. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as a contraindication for receiving this medication?
Explanation
A. Chronic kidney disease:
Correct Answer: This finding is a contraindication for receiving acetaminophen.
Explanation: Acetaminophen is metabolized in the liver, and its active metabolites can potentially be toxic to the liver in excessive amounts. However, if a person has chronic kidney disease, their impaired kidney function can affect the clearance of the drug and its metabolites, increasing the risk of adverse effects. Therefore, acetaminophen is used with caution or avoided in individuals with kidney disease.
B. Alcohol use disorder:
Incorrect Explanation: Alcohol use disorder is a cautionary consideration, but it's not a strict contraindication for acetaminophen use.
Explanation: Chronic excessive alcohol consumption can also affect liver function and the metabolism of acetaminophen. While alcohol use disorder is not a strict contraindication, it's important to consider potential interactions and the cumulative effect on the liver.
C. Hepatitis B vaccine within the last week:
Incorrect Explanation: Receiving the hepatitis B vaccine within the last week is not a contraindication for acetaminophen.
Explanation: Acetaminophen can be used to manage minor discomfort or fever that might be associated with vaccine administration. There is no direct contraindication related to receiving a hepatitis B vaccine within the last week.
D. Diabetes mellitus:
Incorrect Explanation: Diabetes mellitus is not a contraindication for acetaminophen.
Explanation: Diabetes mellitus does not directly impact the use of acetaminophen. However, individuals with diabetes should be mindful of their overall health and potential interactions with other medications they might be taking.
A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for paroxetine. The nurse should instruct the client to monitor for which of the following adverse effects?
Explanation
A. Drowsiness:
Correct Answer: This adverse effect is important for the client to monitor for when taking paroxetine.
Explanation: Paroxetine is an antidepressant medication classified as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). Drowsiness or sedation can be a common side effect of paroxetine and other SSRIs. The client should be advised to monitor their response to the medication and report excessive drowsiness to their healthcare provider.
B. Peripheral edema:
Incorrect Explanation: Peripheral edema is not a typical adverse effect of paroxetine.
Explanation: Peripheral edema is not a common side effect associated with paroxetine use. It's important to monitor for adverse effects, but this specific symptom is not usually associated with this medication.
C. Tinnitus:
Incorrect Explanation: Tinnitus (ringing in the ears) is not commonly associated with paroxetine use.
Explanation: Tinnitus is not a typical side effect of paroxetine. It's important for the client to report any new or unusual symptoms, but tinnitus is not one of the more common adverse effects of this medication.
D. Alopecia:
Incorrect Explanation: Alopecia (hair loss) is not commonly associated with paroxetine use.
Explanation: Alopecia is not a typical side effect of paroxetine. While hair loss can occur with certain medications, it is not a common concern with paroxetine.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 58 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

