Samuel Merrit University Paediatric Exam
Total Questions : 44
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreParents tell the nurse that their two-year-old son often sleeps with them. They seem unconcerned about this. The nurse's response should be based on which of the following?
Explanation
A. Separation from parents should be completed by this age
This statement is not accurate. The age at which a child separates from their parents can vary widely and is influenced by cultural, familial, and individual factors. There is no strict rule that separation should be completed by a specific age, and it can vary from one family to another.
B. Daytime attention should be increased
This statement does not directly address the issue of co-sleeping. It suggests increasing daytime attention but does not provide guidance or understanding about the parents' choice to have their child sleep with them.
C. This is a common practice, especially in some cultural groups
This statement recognizes the cultural diversity in child-rearing practices. Co-sleeping is indeed a common practice in many cultures, and acknowledging this fact helps to avoid making value judgments based on one's own cultural perspective.
D. It is illegal for parents to sleep with their children, and this is reportable abuse
This statement is not accurate. Co-sleeping itself is not illegal, and it is not considered abuse. The appropriateness of co-sleeping can depend on various factors, but it is not inherently illegal or abusive.
A six-year-old complains of pain at the surgical site, one hour after the nurse gave IV morphine, which is ordered every four hours prn pain. What is the nurse's best next step?
Explanation
A. Ask the patient to wait a little longer for the medicine to work.
This option may not be appropriate, especially if the child is experiencing significant pain. It's essential to address the child's pain promptly rather than asking them to wait, as adequate pain management is crucial for the child's well-being.
B. Review whether the morphine dose is therapeutic for his weight.
While reviewing the dose for the child's weight is important, it may not be the immediate next step in this situation. If the child is experiencing pain that persists after one hour, the priority is to address the immediate pain concern. The nurse can later review the medication orders and dosages in collaboration with the healthcare provider.
C. Call the physician immediately.
This is the most appropriate next step in this scenario. If the child is experiencing pain despite having received morphine one hour ago, contacting the physician is important to discuss the current situation, assess the need for additional pain management, and potentially make adjustments to the treatment plan.
D. Encourage the child to use television as a form of distraction.
Distraction can be a helpful complementary measure for managing pain, but it may not be sufficient in this case if the pain persists. The primary focus should be on addressing the pain through appropriate medical interventions, and calling the physician is a more urgent step.
Which assessment indicates to a nurse that a school-age child is in need of pain medication?
Explanation
A. The child's current vital signs are consistent with vital signs over the past 4 hours.
Vital signs alone may not be sufficient to assess pain in a child. Children may experience pain without significant changes in vital signs. Behavioral cues and self-reporting are important indicators of pain in pediatric patients.
B. The child becomes quiet when held and cuddled.
While seeking comfort through cuddling may be a sign of distress or discomfort, it is not specific enough to determine the need for pain medication. Additional assessment is required to understand the underlying cause of the child's change in behavior.
C. The child has a temperature of 38.5°C.
Fever alone does not necessarily indicate the need for pain medication. It may suggest an infection or illness, but the specific assessment of pain requires consideration of the child's behavior, verbal expressions, and any other cues related to pain.
D. The child is lying stiffly in bed, not moving, and refusing to get up.
In this scenario, the child's behavior of lying stiffly in bed, not moving, and refusing to get up is indicative of potential pain. Children may express pain in various ways, and behavioral cues such as changes in activity, refusal to move, or guarding certain body parts can suggest discomfort. It is important for the nurse to assess and address the child's pain promptly.
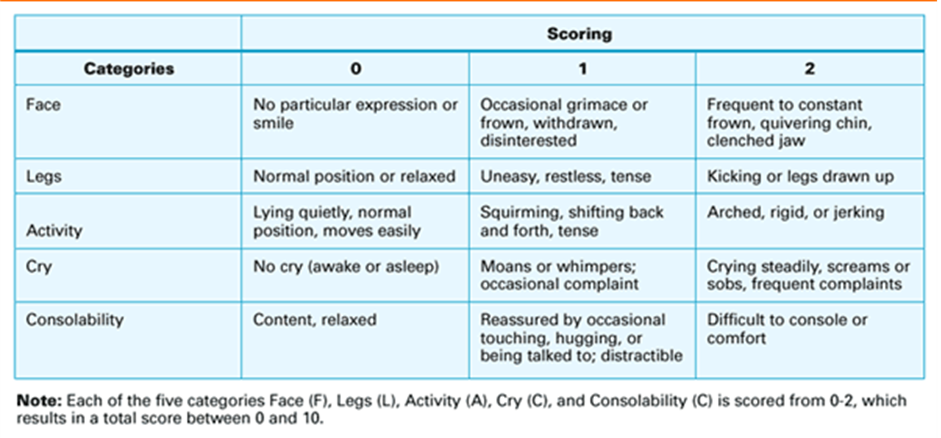
The nurse is using the FLACC scale to evaluate pain in a preverbal child. The nurse makes the following assessment: Face:occasional grimace; Leg: relaxed; Activity: squirming, tense; Cry: no cry; Consolability: content, relaxed. The nurse records patient's pain using the FLACC assessment as:
Explanation
The FLACC (Face, Legs, Activity, Cry, Consolability) scale is commonly used to assess pain in preverbal children. Each category is scored on a scale from 0 to 2, and the total scores range from 0 to 10. Let's assess the given observations:
Face: occasional grimace (score 1)
Leg: relaxed (score 0)
Activity: squirming, tense (score 2)
Cry: no cry (score 0)
Consolability: content, relaxed (score 0)
Now add the scores together: 1 (Face) + 0 (Leg) + 2 (Activity) + 0 (Cry) + 0 (Consolability) = 3
Therefore, the FLACC score for this preverbal child is 3. This score indicates a moderate level of pain.
When assessing a child's pain, the best approach is for the nurse to:
Explanation
A. Use self/parent report, behavioral, and physiological factors
This choice emphasizes a comprehensive approach to pain assessment, considering self-report if the child can communicate, parent report for younger children or those unable to express themselves verbally, and a combination of behavioral and physiological factors. This approach recognizes the multidimensional nature of pain and aims to gather information from various sources for a more accurate assessment.
B. Ask the parents for a pain rating
While parents' input is valuable, relying solely on parental perception may not capture the full picture of the child's pain experience. It's important to consider other aspects, including the child's self-report (if possible) and behavioral and physiological factors.
C. Look for behavioral clues for pain such as crying
Behavioral observation is a crucial component of pain assessment. However, relying solely on crying may overlook subtle cues or variations in how different children express pain. A more comprehensive approach involves considering various behavioral indicators.
D. Use measures of heart rate and respiratory rate
Physiological measures, such as heart rate and respiratory rate, can provide additional information but should not be used in isolation. Physiological responses can vary, and other dimensions of pain assessment, including self-report and behavioral observations, should be considered for a more complete understanding.
While caring for a 4 year old, the nurse uses which tool to assess pain?
Explanation
A. FACES
The FACES scale, often depicted with a series of faces displaying different expressions, is commonly used for children who can understand and respond to a scale of faces indicating different levels of pain. It is suitable for older children who can articulate their feelings.
B. FLACC
The FLACC (Face, Legs, Activity, Cry, Consolability) scale is commonly used to assess pain in preverbal and non-verbal children, such as a 4-year-old. It evaluates the child's facial expression, leg movement, activity level, cry, and ease of consolability to determine the level of pain.
C. APPT
There is no widely recognized pain assessment tool referred to as "APPT." It may be a term specific to a certain context or institution.
D. Numeric
Numeric pain scales involve asking individuals to rate their pain on a numerical scale, usually ranging from 0 to 10. These scales are often used with older children and adults who can understand and communicate numerical values to describe their pain intensity.
To enhance the effectiveness of the pharmacological pain intervention administered to a 4-year old child with an injured knee, the nurse plans to add a nonpharmacological intervention. Which of the following actions would be appropriate for the nurse to perform? (select all that apply)
Explanation
A. Perform passive range of motion on the injured knee.
While passive range of motion exercises can be beneficial in some situations, it's important to exercise caution, especially with an injured knee. Without detailed information about the nature and extent of the injury, manipulating the injured area could potentially worsen the pain or cause harm. It is advisable to consult with the healthcare provider before implementing passive range of motion exercises.
B. Put an ice pack on the child's knee.
Applying an ice pack is a nonpharmacological intervention that can help reduce inflammation and provide pain relief for certain types of injuries. It is commonly used in the management of acute injuries to minimize swelling and alleviate discomfort.
C. Have the child watch a favorite program on television.
Distraction is an effective nonpharmacological approach to pain management, especially in children. Allowing the child to engage in a favorite activity, such as watching a program on television, can divert their attention from the pain and contribute to their overall well-being.
D. Read a book to the child.
Reading a book is a comforting and distracting activity. It creates a positive and calming environment, and it can help shift the child's focus away from the pain. This nonpharmacological intervention promotes a sense of comfort and reassurance.
A fifteen-year-old has been injured during football practice and has been taken to the hospital via ambulance. Providers have been unable to speak to parents despite several attempts to contact them. The youth needs emergency surgery, and understand the risks and benefits of the surgery. Which action is most appropriate at this time?
Explanation
A. Wait for parents to obtain consent
Waiting for parents to obtain consent might not be appropriate in emergency situations where immediate intervention is necessary. Delays could impact the outcome, and the healthcare team needs to prioritize the well-being of the patient.
B. Give pain medications until consent can be obtained
Administering pain medications alone might provide temporary relief but does not address the underlying issue requiring emergency surgery. It's important to address the root cause promptly, especially if surgery is deemed necessary.
C. Have the youth give assent, and proceed with surgery
This option is appropriate when dealing with a mature minor who can understand the nature, risks, and benefits of the surgery. Assent from the youth is sought in conjunction with attempts to contact parents. It is an ethical and legal approach in emergency situations.
D. Attempt to contact another relative
Attempting to contact another relative might be a consideration, but it could introduce additional delays. If the situation is urgent and the youth can provide informed assent, proceeding with surgery while continuing efforts to contact parents is a reasonable approach.
A 5-month-old infant presents to the ED with right upper arm swelling, and a fracture is suspected. The mother told the triage nurse that the infant rolled off the changing table during a diaper change, and later said the infant rolled off the couch when the doorbell rang. What knowledge guides the nurse in planning the next steps?
Explanation
A. Parents don't remember details when they are under stress
While stress can impact memory, inconsistencies in the provided explanations may raise concerns beyond the impact of stress. It's important to consider the possibility of child maltreatment and further investigate.
B. The focus should be on the injury, not how it occurred
In cases of pediatric injuries, understanding how the injury occurred is crucial for making appropriate clinical decisions. The circumstances surrounding the injury can provide important information about its cause, including the possibility of non-accidental trauma.
C. Infant bones are prone to fractures
While it is true that infants can sustain fractures more easily than older children, the nurse still needs to consider the consistency of the provided information about how the injury occurred. Inconsistent explanations may raise concerns about the accuracy of the reported events.
D. Inconsistencies in how the injury occurred may indicate child maltreatment
In cases where there are inconsistencies in the explanation of how an injury occurred, healthcare providers need to consider the possibility of child maltreatment. This is particularly important in pediatric cases where non-accidental trauma, such as child abuse, may be a concern. The nurse should be alert to the possibility of abuse, especially when the given explanations for the injury are inconsistent or change.
Which situation would be appropriate to refer to the hospital ethics committee?
Explanation
A. Parents are shocked when their child is diagnosed with a malignant bone tumor. The orthopedic surgeon discusses the options of limb amputation and a limb-salvage procedure. The parents are asked to consider each option.
This situation involves a difficult medical decision, but it does not describe a conflict or ethical dilemma that necessitates immediate involvement of the ethics committee. The parents are being informed about treatment options, and their input is sought in making a decision for their child's care.
B. The physician recommends that a young child be taken off the ventilator. The parents, who are divorced and have joint custody of the child, have differing views about whether to discontinue the ventilator.
This scenario presents a clear ethical dilemma involving the withdrawal of life-sustaining treatment. The differing views of the divorced parents with joint custody may require the involvement of the hospital ethics committee to provide guidance and facilitate resolution.
C. A child in end-stage renal failure is placed on the renal transplant list. The parents are asked to sign permission for surgery after a cadaver kidney is located. One parent is out of town and gives telephone consent.
While organ transplantation involves ethical considerations, the described situation does not present an immediate conflict or dilemma that requires the ethics committee's urgent involvement. The scenario seems to involve a common process of obtaining consent for surgery.
D. After initial therapies have failed, a child with leukemia is evaluated for a new cancer protocol. The child, age 8 years, gives assent for the new treatment, and his parents give their consent.
This scenario involves a child participating in the decision-making process through assent, and the parents providing consent. While significant, it does not describe a conflict or ethical dilemma that requires immediate ethics committee involvement. The situation seems to involve standard procedures for obtaining informed assent and consent for medical treatment.
The father of a hospitalized child tells the nurse, "He can't have meat. We are Buddhist and vegetarians." The nurse's best intervention is to:
Explanation
A. Ask a Buddhist priest to visit.
While spiritual and cultural support can be beneficial, the immediate concern raised by the father is related to dietary preferences. Requesting a visit from a Buddhist priest may not directly address the issue of providing a suitable diet for the child.
B. Explain that hospital patients are exempt from dietary rules.
This approach may not be well-received, as it could be perceived as dismissive of the family's cultural and religious beliefs. It's important to respect and accommodate the family's dietary preferences whenever possible.
C. Help the parent understand that meat provides protein needed for healing.
While nutritional education is valuable, it should be presented in a way that respects the family's beliefs. It's important to acknowledge and accommodate the family's vegetarian preferences while exploring alternative sources of protein.
D. Order the child a meatless tray.
This is the most appropriate intervention in this situation. Ordering a meatless tray respects the family's dietary preferences and ensures that the child's nutritional needs are met within the context of their cultural and religious beliefs.
Staff members working with school-aged children believe it is important for each child to understand and agree to medical treatment, even though they are a minor. The term for this process is:
Explanation
A. Informed consent
Informed consent refers to the process of obtaining permission from a person who has the legal capacity to make decisions for themselves. It involves providing comprehensive information about the nature, risks, benefits, and alternatives of a medical intervention to enable the individual to make an informed decision.
B. Emancipation
Emancipation is a legal process that grants minors the status of being free from the control of their parents or guardians. It is usually granted based on factors such as maturity, financial independence, or special circumstances. Emancipated minors may have legal capacities similar to those of adults.
C. Assent
Assent is the process of obtaining a child's agreement or approval for medical treatment. It recognizes the child's developing capacity to understand the nature of the treatment, and it allows the child to express their willingness to participate in the decision-making process regarding their healthcare. Assent is sought in addition to the informed consent of the parents or legal guardians.
D. Confidentiality
Confidentiality involves keeping private information secure and not disclosing it without proper authorization. While confidentiality is an important aspect of healthcare, it is not specifically related to the process of obtaining a child's agreement to medical treatment.
The nurse discovers welts on the back of a child whose parents identify as 1st generation Vietnamese. The mother states she rubbed the edge of a coin on her child's oiled back because he had back pain. The nurse should recognize that this is:
Explanation
A. Child Abuse
While the presence of welts might be concerning, it is essential for the nurse to consider cultural practices before labeling the situation as child abuse. In this case, the coin rubbing is described as a cultural practice rather than an abusive act.
B. A cultural practice to rid the body of disease.
This is the correct choice. Coin rubbing, or "coining," is a cultural practice in some traditions, including Vietnamese culture. It is believed to have therapeutic benefits and is used to address health concerns.
C. A child discipline measure common in Asian cultures.
The scenario does not provide evidence that the coin rubbing is a form of discipline. It seems to be described as a traditional health practice rather than a disciplinary measure.
D. A cultural practice to treat temper tantrums.
The scenario does not indicate that the coin rubbing is related to treating temper tantrums. It appears to be described as a health-related cultural practice rather than a disciplinary measure.
Shortly before a child's elective surgery, the parent tells the nurse, "I am having second thoughts about my child undergoing this surgery." The nurse respects the parent's concern and calls the surgeon. What ethical/moral principle is represented by this situation?
Explanation
A. Autonomy.
The ethical/moral principle represented in this situation is autonomy. Autonomy refers to the respect for an individual's right to make their own decisions and choices about their own life and well-being. In this case, the parent expressing second thoughts about the child's surgery reflects a reconsideration of the decision, and the nurse's action of calling the surgeon respects the parent's autonomy by seeking further discussion and clarification.
B. Fidelity
Fidelity refers to the principle of faithfulness, loyalty, and keeping promises. While it is important in the healthcare context, the scenario does not involve a breach of fidelity.
C. Equality
Equality relates to the fair and just treatment of individuals. In this scenario, the primary focus is on the parent's autonomy and the reconsideration of the elective surgery, rather than issues of equality.
D. Justice
Justice involves the fair distribution of benefits and burdens in society. The scenario does not directly relate to justice but is more aligned with the principle of autonomy as the parent reconsiders the decision about the child's surgery.
Which statement by the nurse is most appropriate to a 15 year old whose friend has mentioned suicide?
Explanation
A. "This is common for teens to threaten suicide when they want attention."
This statement is dismissive and could contribute to a lack of appropriate intervention. It is essential not to trivialize or assume that all suicide threats are attention-seeking, as they may indicate underlying distress and a need for support.
B. "Your friend's threat needs to be taken seriously and immediate help for your friend is important."
This is the most appropriate response. It acknowledges the seriousness of the situation, emphasizes the need for immediate help, and reflects a responsible and caring approach to addressing a friend's mention of suicide.
C. "If your friend mentions suicide a second time, you will want to get your friend some help."
Waiting for a second mention is not appropriate, as any mention of suicide should be treated seriously. Delaying intervention until a second mention could be dangerous, as the friend may be in immediate distress.
D. "You need to gather details about your friend's suicide plan."
While gathering information about a friend's thoughts and plans is important for a comprehensive assessment, it is not the primary concern in the immediate response to a suicide mention. The immediate focus should be on ensuring the friend's safety and involving appropriate professionals for help.
Which information could be given to the parents of a 12-month-old child regarding appropriate play activities for this age?
Explanation
A. Provide a coloring book so they can color within the lines.
Coloring within the lines is a fine motor skill that is not typically developed at 12 months. Fine motor activities like coloring may become more suitable as the child grows, but at this age, the emphasis is generally on gross motor skills.
B. Provide a stick horse to develop gross motor coordination.
While a stick horse may be a fun toy, it may not be the most appropriate choice for a 12-month-old who is still working on basic motor skills. Gross motor coordination can be better encouraged with toys that support standing, walking, and pushing.
C. Place a cradle gym across the crib to facilitate fine motor skills.
A cradle gym can be appropriate for visual and sensory stimulation, but it is more related to visual tracking and reaching than fine motor skills. Fine motor skills typically involve more intricate hand movements, which may not be fully developed at 12 months.
D. Give large push-pull toys for kinesthetic stimulation.
For a 12-month-old child, appropriate play activities should focus on promoting gross motor skills, coordination, and exploration. Giving large push-pull toys encourages the development of kinesthetic skills, allowing the child to practice standing, walking, and moving. It also supports the development of coordination and balance.
What intervention should the nurse implement when a 4 year old asks for a band-aid after an injection?
Explanation
A. Show them that the bleeding has stopped.
While showing that the bleeding has stopped is informative, it might not address the child's emotional response or desire for comfort. Applying a band-aid can provide a tangible and comforting solution.
B. Ask why they want a band-aid.
While understanding the child's reasons is important, in this situation, a direct question might not be necessary. The child's request for a band-aid is likely a common response to the perception of an injury or discomfort.
C. Apply a band-aid.
This is the most appropriate intervention in this situation. Applying a band-aid responds to the child's request, provides a tangible form of comfort, and can make the overall experience more positive.
D. Explain that a band-aid is not needed.
While it's true that a band-aid may not be medically necessary, providing one is a simple and kind gesture that can help ease the child's anxiety and contribute to a positive experience.
The nurse is discussing safety with the father of a four-year old child. Critical teaching points should include the following except:
Explanation
A. "You should always hold your child's hand when crossing the street."
This is a critical teaching point. Holding a child's hand while crossing the street is an important safety measure to prevent accidents and ensure the child's safety.
B. "Swim lessons would be important now to ensure your child is safe around a pool."
This is also a critical teaching point. Swim lessons can be essential for water safety, especially if there is a pool in the vicinity.
C. "Medications with childproof tops are safe to keep on the counter so you remember to take them."
This statement is incorrect. Medications, even with childproof tops, should be stored out of reach of children to prevent accidental ingestion. It's important to emphasize proper medication storage.
D. "All small objects should be kept out of your child's view since he may aspirate them."
This is a valid teaching point. Small objects can pose a choking hazard, and keeping them out of a child's reach is crucial for safety.
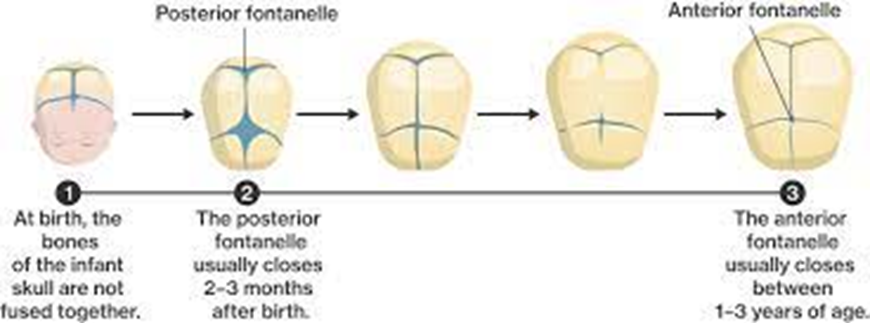
The nurse is doing a routine assessment on a 19-month-old infant and notes that the anterior fontanel is closed. This should be interpreted as:
Explanation
A. An abnormal finding-indicates the need for developmental assessment.
This is not accurate. The closure of the anterior fontanel within the expected age range does not indicate an abnormal finding or the need for additional developmental assessment.
B. A normal finding.
This is the correct interpretation. The anterior fontanel normally closes between 12 to 18 months, and closure by 19 months is within the expected developmental range.
C. An abnormal finding-indicates the need for immediate referral to a practitioner.
This is not necessary based on the information provided. The closure of the anterior fontanel within the expected timeframe is a normal finding.
D. A questionable finding-the infant should be rechecked in 1 month.
There's no need for rechecking in 1 month. The closure of the anterior fontanel at 19 months is considered normal.
The nurse is observing parents playing with their 10 month old daughter. What should the nurse recognize as evidence that the child is developing object permanence?
Explanation
A. She returns the blocks to the same spot on the table.
This behavior is more related to a sense of order or routine rather than object permanence. It doesn't directly demonstrate understanding object permanence.
B. She looks for the toy the parents hide under the blanket.
This behavior is consistent with the concept of object permanence. If the child searches for a hidden toy, it indicates an understanding that the object still exists even when out of sight.
C. She bangs two cubes held in her hands.
Banging cubes is not directly related to object permanence. It might demonstrate exploration or cause-and-effect understanding, but it doesn't specifically indicate object permanence.
D. She recognizes that a ball of clay is the same when flattened out.
This behavior demonstrates an understanding of conservation, which is different from object permanence. Conservation involves recognizing that the quantity of a substance remains the same despite changes in shape.
A previously "potty-trained" 30 month old child had reverted to wearing diapers while hospitalized. The nurse should recognize:
Explanation
A. Developmental delays occur because of hospitalizations.
This statement implies that the hospitalization itself causes developmental delays, which is not accurate. Hospitalization might disrupt routines, but it does not directly cause developmental delays.
B. The child is too young to be potty trained.
The child was previously "potty-trained," so age is not the primary factor. Regression in toilet training can occur for various reasons.
C. Regression is sometimes seen during hospitalization.
This statement is correct. Regression, including reverting to behaviors like wearing diapers, can occur in response to stress, illness, or changes in routine, such as hospitalization.
D. The child is experiencing urinary urgency as a result of the hospitalization.
While urinary urgency can be a possibility, the given scenario emphasizes the regression to wearing diapers, which is more indicative of behavioral regression rather than a physical issue like urgency.
The nurse observes some children in the playroom. Which play situation exhibits the characteristics of parallel play?
Explanation
A. Brian playing with his truck next to Kristina playing with her truck
This scenario describes parallel play. In parallel play, children play near each other but engage in their own activities without direct interaction.
B. Adam playing a board game with Kyle, Steven, and Erich
This scenario describes interactive or cooperative play, where children play together, sharing an activity and interacting.
C. Danielle playing with a music box on her mother's lap
This scenario represents a form of one-on-one play with a parent, which is not parallel play.
D. Kimberly and Amanda sharing clay to each make things
This scenario describes interactive or cooperative play, as the children are sharing materials and engaging in a joint activity.
The nurse is caring for a hospitalized four-year-old boy. His parents tell the nurse that they will be back to visit at six in the evening. When he asks the nurse when his parents are coming, the nurse's best response would be which of the following?
Explanation
A. "They will come around dinner time."
This response uses the term "dinner time," which might be too abstract for a young child. It doesn't provide a specific visual reference.
B. "It won't be much longer."
This response is somewhat vague and may not offer a clear understanding of when the parents will arrive. Young children may not grasp the concept of "much longer."
C. "They will be here soon."
Similar to choice B, this response is somewhat vague and relies on the child's interpretation of "soon," which can vary.
D. "Let me show you where 6 o'clock is on the clock."
This response is the most concrete and provides a visual reference by using the clock. It helps the child understand the passage of time in a more tangible way.
A nurse planning care for a 10 year old child should take into account that which thought process is seen at this age?
Explanation
A. Magical thinking
Magical thinking is a cognitive characteristic commonly observed in preschool-aged children. It involves believing that one's thoughts, wishes, or actions can influence events, even when there is no logical or causal connection. For example, a preschooler might believe that simply thinking about a toy can make it appear.
B. Thoughts are all-powerful
The belief that thoughts have omnipotent power is often seen in the preoperational stage of cognitive development, which occurs in early childhood. Children in this stage may think that their thoughts alone can cause significant changes or events.
C. Ability to conserve
Conservation is a cognitive skill associated with the concrete operational stage of development, typically occurring around 7 to 11 years of age. Children at this stage understand that certain properties of objects remain the same despite changes in appearance. For example, they recognize that the amount of liquid stays the same when poured into a differently shaped container.
D. Animism
Animism is a concept observed in the preoperational stage, where children attribute life-like qualities to inanimate objects. For instance, a child might believe that a stuffed animal has feelings or thoughts.
The nurse needs to take a B/P on a 3 year old who is in the playroom. What is the best intervention?
Explanation
A. Document B/P not obtained because the child was in the playroom.
This is not the best option. The nurse should attempt to obtain the blood pressure as part of routine monitoring.
B. Take the child back to their room, take their B/P and then take them back to the playroom.
This may disrupt the child's play and is not the most efficient approach for routine blood pressure monitoring.
C. Take the child to the treatment room.
This might be unnecessary for a routine blood pressure check and could cause unnecessary anxiety for the child.
D. Take the B/P in the playroom.
This is the best intervention. If possible, taking the blood pressure in the playroom allows the child to remain in a familiar and comfortable environment, reducing anxiety and promoting cooperation.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 44 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

