Smith Chason College Son Los Angeles ADN NURS 146 gero final Exam
Total Questions : 100
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreDiabetes, dementia, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and vitamin B deficiencies may cause neurological damage leading to what condition?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Aphasia is a language disorder that affects the ability to communicate, not the ability to walk or balance.
Choice B reason: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is caused by external forces, such as a blow to the head, not by internal factors, such as diseases or deficiencies.
Choice C reason: Gait disturbances are problems with walking or balance that can result from neurological damage affecting the motor system.
Choice D reason: Postprandial hypotension (PPH) is a drop in blood pressure after eating that can cause dizziness or fainting, but it is not directly related to neurological damage.
Choice E reason: Fallophobia is a fear of falling or heights, not a condition caused by neurological damage.
When assessing an older male client, what are some issues that might put him at risk for dehydration? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A reason: Heart failure can cause fluid retention, which can lead to dehydration if the fluid is not properly balanced.
Choice B reason: Functional impairments can limit the ability to drink or access fluids, which can increase the risk of dehydration.
Choice C reason: Longitudinal furrows on the tongue are a sign of dehydration, as the tongue loses moisture and becomes dry and cracked.
Choice D reason: Hypertension is not directly related to dehydration, although it can be affected by fluid intake and electrolyte balance.
Choice E reason: Diabetes can cause increased urination, which can lead to dehydration if the fluid loss is not replaced.
Which of the following is a true statement concerning suicide among older adults?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Older African American women do not have the highest risk of suicide among older adults. According to the CDC, suicide rates are highest among adults age 75 and older, and highest among males age 75 and older.
Choice B reason: Older adults and younger adults do not manifest suicidal intent in a similar manner. Older adults tend to plan suicide more carefully, use more lethal means, and have fewer warning signs than younger adults.
Choice C reason: A major crisis experienced by the client can contribute to the risk of suicide. Older adults may face various stressors, such as bereavement, loneliness, chronic illness, or loss of independence, that can trigger suicidal thoughts or behavior.
Choice D reason: Ethics do not require that the nurse respects a person’s intent to terminate his or her own life. Nurses have a duty to protect the safety and well-being of their clients, and to intervene if they suspect suicidal risk.
When teaching a client about foods that do not increase blood glucose, which should the nurse include?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Corn is not a food that does not increase blood glucose. Corn is a starchy vegetable that contains carbohydrates, which can raise blood glucose levels.
Choice B reason: White bread is not a food that does not increase blood glucose. White bread is made from refined flour, which has a high glycemic index and can spike blood glucose levels.
Choice C reason: Baked beans are not a food that does not increase blood glucose. Baked beans are high in sugar and carbohydrates, which can affect blood glucose levels.
Choice D reason: Broccoli is a food that does not increase blood glucose. Broccoli is a non-starchy vegetable that is low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, which can help regulate blood glucose levels.
Pressure ulcers are defined as an injury to the skin and/or underlying tissue resulting from pressure or in combination with shear, usually over a bony prominence. As a nurse, what do you know you must do to prevent pressure ulcers? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A reason: Turning immobile clients every 2 hours off bony prominences can reduce the pressure and friction that can cause skin breakdown and ulcer formation.
Choice B reason: Using lift or draw sheets to move clients in bed can prevent dragging or pulling the skin, which can cause shear and damage the underlying tissue.
Choice C reason: Keeping the skin moist is not a correct way to prevent pressure ulcers. Moisture can weaken the skin and make it more prone to injury. The skin should be kept dry and clean, and moisturized if needed.
Choice D reason: Ensuring that your client maintains a healthy nutritional status can promote wound healing and prevent infection. Adequate protein, calories, vitamins, and minerals are essential for skin integrity and tissue repair.
Choice E reason: Applying pressure-relieving devices to vulnerable areas can distribute the pressure and protect the skin from damage. Examples of pressure-relieving devices are foam pads, air mattresses, or cushions.
An older adult client has been admitted to a skilled nursing facility. Which of the following can be caused by physical restraints? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A: Pressure ulcers - Physical restraints can lead to immobility, which increases the risk of pressure ulcers due to prolonged pressure on the skin.
Choice B: Death - Restraints can cause fatal accidents. For example, a person might try to remove the restraint, fall, and suffer a fatal injury.
Choice C: Sepsis - While sepsis is a severe condition often caused by an infection, it's not a direct result of physical restraints. However, if a pressure ulcer (caused by restraints) becomes severely infected, it could potentially lead to sepsis.
Choice D: Decreased circulation/perfusion to the extremities - Restraints can restrict movement, leading to decreased blood flow to the extremities.
Choice E: Fractures - Struggling against restraints can lead to falls and subsequent fractures.
During an assessment, an older adult male client reports that he fell the night before. What should you follow up with? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A reason: Asking about the circumstances behind the fall(s) can help you identify the possible risk factors and causes of the fall(s), such as environmental hazards, medications, chronic conditions, or acute illnesses. Asking about the circumstances can also help you determine the severity and urgency of the situation, and whether the client needs further evaluation or referral.
Choice B reason: Assessing for any injuries the client might have is important, but it is not the first thing you should do after a client reports a fall. You should first ask about the circumstances to rule out any life-threatening or serious injuries that may require immediate attention. Assessing for injuries is part of the comprehensive fall risk assessment that should be done after the initial screening.
Choice C reason: Evaluating the client for gait and balance is also important, but it is not the first thing you should do after a client reports a fall. You should first ask about the circumstances to rule out any underlying medical conditions that may affect the client's gait and balance. Evaluating gait and balance is part of the comprehensive fall risk assessment that should be done after the initial screening.
Choice D reason: Asking about the history or frequency of falls can help you assess the client's fall risk and identify any patterns or trends in the client's fall history. Asking about the history or frequency of falls can also help you tailor the appropriate interventions and prevention strategies for the client.
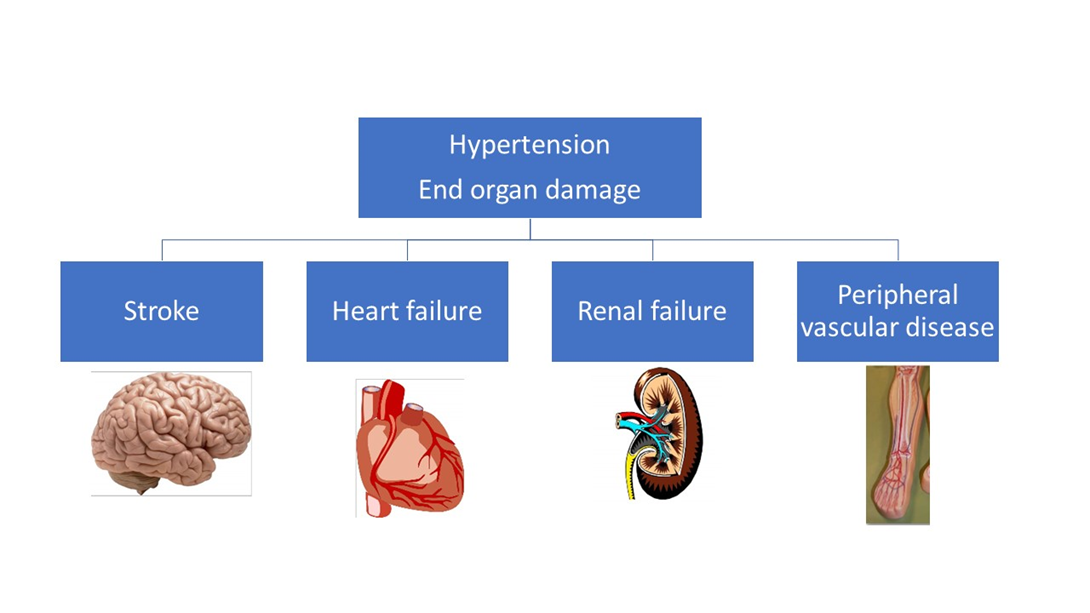
Which are potential results of end-organ damage from chronic hypertension? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A reason: Isolated systolic hypertension is not a result of end-organ damage from chronic hypertension, but rather a risk factor for it. Isolated systolic hypertension is a condition where the systolic blood pressure is elevated (>140 mmHg) while the diastolic blood pressure is normal (<90 mmHg). It is common in older adults due to the stiffening of the arteries, and can increase the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events.
Choice B reason: Atrial fibrillation is a result of end-organ damage from chronic hypertension. Atrial fibrillation is an irregular and often rapid heart rate that can cause poor blood flow and increase the risk of stroke and heart failure. Chronic hypertension can damage the heart muscle and the electrical system of the heart, leading to atrial fibrillation.
Choice C reason: Renal insufficiency is a result of end-organ damage from chronic hypertension. Renal insufficiency is a condition where the kidneys are unable to filter waste and fluid from the blood adequately. Chronic hypertension can damage the blood vessels and the nephrons of the kidneys, leading to renal insufficiency.
Choice D reason: Stroke is a result of end-organ damage from chronic hypertension. Stroke is a sudden interruption of blood supply to the brain, causing brain cell death and neurological deficits. Chronic hypertension can damage the blood vessels in the brain, making them prone to rupture (hemorrhagic stroke) or blockage (ischemic stroke).
Choice E reason: Cardiac disease is a result of end-organ damage from chronic hypertension. Cardiac disease is a broad term that encompasses various disorders of the heart, such as coronary artery disease, heart attack, heart failure, and cardiomyopathy. Chronic hypertension can damage the heart by increasing the workload and the oxygen demand of the heart, causing the heart to enlarge and weaken over time.
When an older female adult client complains of itching and pain and several days later shows you a rash, what do you realize she has?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Scabies is a skin infestation caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin and lay eggs. It causes intense itching and a pimple-like rash, usually in the folds of the skin, such as the armpits, groin, or between the fingers. Scabies is highly contagious and can spread through direct skin contact or shared clothing or bedding.
Choice B reason: Herpes zoster, also known as shingles, is a viral infection that affects the nerves and the skin. It causes a painful, blistering rash that usually appears on one side of the body or face. Herpes zoster is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox, which can reactivate later in life, especially in older adults or people with weakened immune systems.
Choice C reason: Skin cancer is an abnormal growth of skin cells that can be caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. It can appear as a new or changing mole, a sore that does not heal, or a scaly or crusty patch of skin. Skin cancer can vary in appearance, size, shape, and color, depending on the type and stage of the cancer.
Choice D reason: Actinic keratosis is a precancerous skin condition that is caused by chronic sun damage. It appears as rough, scaly, or crusty spots on the skin, usually on the face, ears, scalp, or hands. Actinic keratosis can sometimes develop into squamous cell carcinoma, a type of skin cancer, if left untreated.
You notice that your older adult male client frequently knocks his arm or hand against door frames or chair backs and then develops a purpura. What do you advise your client to do? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A: Protect the skin from trauma. This is a correct answer. Purpura is the discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes due to hemorrhage from small blood vessels¹. It can be caused by various factors, such as blood clotting disorders, medications, infections, or weak blood vessels². Older adults are more prone to develop purpura because their skin becomes thinner and more fragile with age³. Therefore, protecting the skin from trauma, such as knocking against hard surfaces, can help prevent or reduce purpura.
Choice B: Remind the health care personnel to be gentle when handling this client’s skin. This is also a correct answer. Health care personnel should be aware of the risk of purpura in older adults and handle their skin with care. They should avoid applying excessive pressure, friction, or shear forces to the skin, as these can cause damage to the blood vessels and result in purpura. They should also use soft and smooth materials, such as cotton or silk, when dressing or cleaning the skin.
Choice C: Wear a long-sleeved shirt. This is not a correct answer. Wearing a long-sleeved shirt may provide some protection to the skin, but it is not enough to prevent purpura. Moreover, wearing tight or rough clothing can actually worsen the condition by causing irritation or injury to the skin. Therefore, this is not a good advice for the client.
Choice D: Tape a nonadherent dressing over the site of a skin tear. This is another correct answer. A skin tear is a type of wound that occurs when the skin is separated from the underlying tissue, usually due to trauma. Skin tears are common in older adults and can lead to purpura if the blood vessels are damaged. Taping a nonadherent dressing over the site of a skin tear can help protect the wound from infection, promote healing, and prevent further bleeding.
An older adult client had hip replacement surgery 1 day ago, and the nurse thinks that the client is also demonstrating dementia. Which client assessment does the nurse use to determine whether this client is experiencing pain?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Having stable vital signs does not necessarily mean that the client is not experiencing pain. Vital signs can be affected by various factors, such as medications, stress, or emotions, and may not reflect the true level of pain.
Choice B reason: Holding abdomen tightly is a possible sign of pain, especially if the client had abdominal surgery or has a condition that affects the digestive system. The client may be guarding the painful area or trying to relieve the discomfort.
Choice C reason: Not verbalizing is not a reliable indicator of pain, especially for clients with dementia who may have difficulty communicating or expressing their feelings. The nurse should look for other cues, such as facial expressions, body language, or behavioral changes, to assess the client's pain.
Choice D reason: Moving during sleep is not a specific sign of pain, and may be normal for some clients. However, if the client is restless, agitated, or moaning during sleep, it may indicate that the client is in pain and needs intervention.
The gerontological nurse collaborates with the wound care team about an older client who has an ulcer. How is this nurse demonstrating leadership in the care of older people?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Empowering older adults to manage chronic illness is a way of promoting self-care and autonomy, but it is not a specific example of leadership in the care of older people.
Choice B reason: Coordinating members of the health care team is a way of demonstrating leadership in the care of older people, as it involves communication, collaboration, and delegation of tasks among different professionals and disciplines.
Choice C reason: Facilitating access to elder care programs is a way of providing resources and support for older people, but it is not a direct example of leadership in the care of older people.
Choice D reason: Assessing older adults effectively is a way of ensuring quality and safety in the care of older people, but it is not a unique example of leadership in the care of older people.
The nurse identifies which of the following interventions in the treatment of fungal infections? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A: Use an antifungal cleanser daily. This is not a correct answer. Antifungal cleansers are not recommended for treating fungal infections, as they can irritate the skin and disrupt the natural balance of the skin flora¹. Antifungal cleansers may also reduce the effectiveness of other antifungal medications².
Choice B: Eliminate the conditions that created the problem. This is a correct answer. Fungal infections are often caused by factors that create a favorable environment for fungi to grow, such as moisture, warmth, poor hygiene, or weakened immunity³. Eliminating these conditions can help prevent or treat fungal infections by reducing the fungal load and restoring the skin barrier.
Choice C: Thoroughly clean and dry skin daily. This is also a correct answer. Cleaning and drying the skin daily can help remove dirt, sweat, and dead skin cells that can harbor fungi and cause infections. Drying the skin well, especially in the folds and creases, can also prevent moisture buildup that can promote fungal growth.
Choice D: Apply 4x4 dressings to the affected site.This is not a correct answer. Applying dressings to the affected site can trap moisture and heat, which can worsen fungal infections. Dressings may also interfere with the absorption of topical antifungal medications. Dressings are only indicated for fungal infections that cause open wounds or ulcers, and they should be changed frequently and kept clean and dry..
When assessing your client who has a history of falls, you should pay particular attention to which of the following? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A reason: Cognitive disorders are conditions that affect the mental functions, such as memory, reasoning, judgment, or orientation. Cognitive disorders can increase the risk of falls by impairing the awareness, attention, or decision-making of the client.
Choice B reason: Antibiotics are not a factor that requires particular attention when assessing a client who has a history of falls. Antibiotics are medications that treat bacterial infections, and they do not directly affect the risk of falls. However, some antibiotics may have side effects, such as dizziness, nausea, or diarrhea, that can indirectly increase the risk of falls.
Choice C reason: Orthostatic hypotension is a condition where the blood pressure drops significantly when changing position, such as standing up from sitting or lying down. Orthostatic hypotension can cause symptoms, such as lightheadedness, fainting, or blurred vision, that can increase the risk of falls.
Choice D reason: Vision is the sense of sight that allows the perception of the environment and the detection of potential hazards. Vision can decline with age or due to various eye diseases or injuries. Poor vision can increase the risk of falls by affecting the depth perception, contrast sensitivity, or visual field of the client.
Choice E reason: Balance is the ability to maintain the body's center of gravity over its base of support. Balance can be affected by various factors, such as inner ear problems, muscle weakness, joint stiffness, or medication use. Poor balance can increase the risk of falls by impairing the stability and coordination of the client.
An older adult diagnosed with heart failure (HF) reports increasing dyspnea over 2 days. Which of the following should the nurse assess to help determine whether the client has adhered to prescribed therapy? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A reason: Determining coughing frequency is not a reliable way to assess whether the client has adhered to prescribed therapy, as coughing can have various causes and may not be related to heart failure or its treatment.
Choice B reason: Checking for peripheral edema is a useful way to assess whether the client has adhered to prescribed therapy, as peripheral edema is a common sign of fluid retention and worsening heart failure. If the client has been taking diuretics as prescribed, the edema should be reduced or absent.
Choice C reason: Auscultating the lungs bilaterally is a helpful way to assess whether the client has adhered to prescribed therapy, as lung sounds can indicate the presence or absence of pulmonary congestion and crackles, which are signs of fluid overload and worsening heart failure. If the client has been taking medications to improve cardiac function and reduce fluid volume as prescribed, the lungs should be clear or improved.
Choice D reason: Assessing diet over the last 48 hours is a relevant way to assess whether the client has adhered to prescribed therapy, as diet can affect fluid and sodium intake and retention, which can worsen heart failure. If the client has been following a low-sodium and fluid-restricted diet as prescribed, the risk of fluid overload and dyspnea should be lower.
Choice E reason: Comparing current weight to baseline is an important way to assess whether the client has adhered to prescribed therapy, as weight can reflect fluid status and changes in heart failure condition. If the client has been taking medications and following dietary recommendations as prescribed, the weight should be stable or decreased.

When educating a client on the use of an adjuvant medication, which statement best demonstrates the nurse’s understanding of this therapy?
Explanation
Choice A reason: This statement is correct, as adjuvant medications are drugs that are not primarily intended for pain relief, but can enhance the analgesic effect of other pain medications. Examples of adjuvant medications are antidepressants, anticonvulsants, or corticosteroids.
Choice B reason: This statement is false, as adjuvant medications can have significant side effects, depending on the type and dose of the drug. Some common side effects are drowsiness, nausea, dry mouth, or weight gain.
Choice C reason: This statement is misleading, as adjuvant medications are not used instead of opioids, but rather as an adjunct to opioids or other analgesics. Adjuvant medications can help reduce the dose of opioids needed to achieve pain relief, but they do not replace them entirely.
Choice D reason: This statement is inaccurate, as adjuvant medications are not used to eliminate the side effects of opioid medications, but rather to treat the underlying cause or mechanism of pain. Adjuvant medications can target different types of pain, such as neuropathic, inflammatory, or visceral pain.
An older aphasic client has severe osteoarthritis, bilateral contractures of the lower extremities, and a stage IV pressure ulcer. The nurse practitioner prescribes analgesic medications to be administered around-the-clock, with as-needed doses to be administered as appropriate. What observation by the nurse would indicate that the pain regimen is effective? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A: "Client slept throughout the night" - Good sleep can be an indicator of effective pain management. Pain can disrupt sleep, so if the client is sleeping well, it may suggest that their pain is being effectively managed¹.
Choice B: "Client cooperative during AM care" - If the client is cooperative during care, it may suggest that they are not in significant pain. Uncontrolled pain can make people irritable and uncooperative¹.
Choice C: "Client ate 80% of breakfast, 70% of lunch and 100% of dinner" - Pain can affect appetite. If the client is eating well, it may suggest that their pain is under control¹.
Choice D: "Client winces only when turned and repositioned" - If the client only shows signs of discomfort during movement, it may suggest that their pain is generally well-controlled¹.
Choice E: "Client slept during dressing change" - This is not necessarily an indicator of effective pain management. The client could be sleeping due to fatigue, medication effects, or other reasons unrelated to their pain level¹.
Your second older adult female client has been experiencing some problems with urinary incontinence. You suggest that she document which of the following in a “bladder/voiding diary”? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A reason:
It is important for the client to document any difficulty starting or stopping the urinary stream as this can indicate potential issues with bladder function or muscle control.
Choice B reason:
Documenting the character of the urine, such as color and odor, can provide valuable insights into potential underlying health issues, such as dehydration or urinary tract infections.
Choice C reason:
The ability to reach a toilet and use it is crucial information as it helps in understanding the client's mobility and accessibility to restroom facilities, which can impact her urinary patterns.
Choice D reason:
Although not listed, it's essential to note that having a bowel movement at the same time can also provide insights into potential underlying issues and patterns related to urinary incontinence.
Choice E reason:
The amount and timing of fluid intake and urine output are imperative to track as they can reveal patterns and potential triggers for urinary incontinence, aiding in the development of an effective management plan.
According to Healthy People 2020, older adults have been identified as a priority, addressing goals to improve dental health. Identify the correct dental health goals for older adults. (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A: Reduce the proportion of older adults with untreated caries. This is a correct answer because it is one of the Healthy People 2020 oral health objectives for older adults¹. Untreated caries can lead to pain, infection, tooth loss, and reduced quality of life². Reducing the prevalence of untreated caries can improve the oral health and well-being of older adults.
Choice B: Reduce the proportion of adults with untreated dental decay. This is an incorrect answer because it is not specific to older adults. The Healthy People 2020 oral health objectives for adults include reducing the proportion of adults aged 35 to 44 years with untreated dental decay¹. However, this does not address the unique needs and challenges of older adults, such as increased risk of root caries, dry mouth, and periodontal disease².
Choice C: Prevent and control oral and craniofacial diseases, conditions, and injuries. This is a correct answer because it is the overall goal of the Healthy People 2020 oral health objectives¹. Oral and craniofacial diseases, conditions, and injuries can affect the function, appearance, and quality of life of older adults². Preventing and controlling these problems can help older adults maintain their oral health and general health.
Choice D: Improve access to preventive services and dental care. This is a correct answer because it is one of the Healthy People 2020 oral health objectives for older adults¹. Access to preventive services and dental care can help older adults prevent oral diseases, detect problems early, and receive appropriate treatment². However, many older adults face barriers to accessing oral health care, such as lack of dental insurance, transportation, or awareness³. Improving access to oral health care can reduce these disparities and improve the oral health outcomes of older adults.
How is the term “health disparity” best defined?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Health equity is not the definition of health disparity, but rather the opposite of it. Health equity is the state of fair and equal opportunity for everyone to achieve optimal health, regardless of social or economic factors.
Choice B reason: The difference between an expected incidence and prevalence and that which actually occurs in a comparison population group is not the definition of health disparity, but rather a way of measuring it. Incidence and prevalence are epidemiological terms that refer to the number of new and existing cases of a disease or condition in a population, respectively.
Choice C reason: The systematic elimination of the culture of another resulting in decreased wellness is not the definition of health disparity, but rather an example of cultural genocide. Cultural genocide is the deliberate destruction of the identity, heritage, or traditions of a group of people.
Choice D reason: Differences in health outcomes between groups is the definition of health disparity, as it describes the situation where some groups of people experience worse health status or quality of life than others, due to factors such as race, ethnicity, gender, income, education, or geography.
The promotion of an adequate fluid balance which prevents medical complications is defined as?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Overhydration is not the definition of the promotion of an adequate fluid balance, but rather a condition where the body has excess fluid volume, which can cause medical complications, such as edema, hyponatremia, or heart failure.
Choice B reason: Dehydration is not the definition of the promotion of an adequate fluid balance, but rather a condition where the body has insufficient fluid volume, which can cause medical complications, such as hypotension, tachycardia, or kidney failure.
Choice C reason: Hypernatremia is not the definition of the promotion of an adequate fluid balance, but rather a condition where the body has excess sodium concentration in the blood, which can cause medical complications, such as thirst, confusion, or seizures.
Choice D reason: Hydration is the definition of the promotion of an adequate fluid balance, as it refers to the maintenance of the optimal amount and distribution of fluid in the body, which can prevent medical complications, such as dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, or infection.
Which of the following is the most important goal in the nursing plan of care to decrease the frequency of hospitalizations for acute exacerbations of heart failure (HF) in older adults?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Controlling fluid balance is the most important goal in the nursing plan of care to decrease the frequency of hospitalizations for acute exacerbations of HF in older adults, as fluid overload is the main cause of HF worsening and hospital admission. Fluid balance can be controlled by monitoring weight, intake and output, edema, and lung sounds, and by administering diuretics, restricting sodium and fluid intake, and elevating the legs.
Choice B reason: Controlling blood pressure is an important goal in the nursing plan of care to decrease the frequency of hospitalizations for acute exacerbations of HF in older adults, as hypertension is a risk factor and a complication of HF. However, it is not the most important goal, as blood pressure may not always reflect the fluid status or the severity of HF. Blood pressure can be controlled by administering antihypertensive medications, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, beta-blockers, or calcium channel blockers, and by encouraging lifestyle modifications, such as smoking cessation, weight management, and stress reduction.
Choice C reason: Preventing deconditioning is an important goal in the nursing plan of care to decrease the frequency of hospitalizations for acute exacerbations of HF in older adults, as deconditioning is a common problem in HF patients due to reduced physical activity, fatigue, and muscle wasting. However, it is not the most important goal, as deconditioning may not directly affect the fluid balance or the cardiac function. Deconditioning can be prevented by providing exercise training, such as aerobic, resistance, or interval training, and by promoting self-care and adherence to the treatment regimen.
Choice D reason: Maintaining client safety is an important goal in the nursing plan of care to decrease the frequency of hospitalizations for acute exacerbations of HF in older adults, as HF patients are at risk of falls, injuries, infections, or adverse drug reactions. However, it is not the most important goal, as client safety may not specifically address the fluid balance or the cardiac function. Client safety can be maintained by providing a safe environment, such as removing clutter, providing adequate lighting, and using assistive devices, and by preventing complications, such as monitoring for signs of infection, bleeding, or electrolyte imbalance, and by educating the client and the family about the medications, the signs and symptoms of HF worsening, and the emergency measures.
An older client who was recently admitted to the sub-acute setting after having a knee replacement, is very anxious and refuses to get out of bed, stating that it is too painful. Which intervention will the nurse implement?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Allowing the client to remain in bed but sharing that getting up will be required at least twice a day starting the next morning is not an effective intervention, as it does not address the client's current pain or anxiety, and may increase the client's resistance or fear of mobilization.
Choice B reason: Using the Hoyer lift to get her out of bed so that the knee will not experience much movement and so there will be little pain is not an appropriate intervention, as it does not respect the client's autonomy or preference, and may cause more pain or injury to the knee or other joints.
Choice C reason: Sharing with the client that it is important to get out of bed and that there is pain medication available if it does hurt is not a sufficient intervention, as it does not provide the client with adequate pain relief or reassurance, and may imply that the client's pain is not taken seriously or validated.
Choice D reason: Offering pain medication, administering the medication, and waiting 30 minutes before getting her out of bed is the best intervention, as it provides the client with effective pain management, reduces the client's anxiety, and facilitates the client's mobilization and recovery.
The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with hyperthyroidism. Which signs and symptoms indicate hyperthyroidism? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A reason: Sudden onset of symptoms is a sign of hyperthyroidism, as it indicates a rapid increase in thyroid hormone levels that can cause a thyroid storm, a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms of a thyroid storm may include fever, agitation, confusion, sweating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and chest pain.
Choice B reason: Atrial fibrillation is a sign of hyperthyroidism, as it indicates an irregular and fast heartbeat that can result from the excess stimulation of the heart by thyroid hormones. Atrial fibrillation can increase the risk of blood clots, stroke, and heart failure.
Choice C reason: Cold intolerance is not a sign of hyperthyroidism, but rather a sign of hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland produces too little thyroid hormone. Cold intolerance means feeling cold even in warm environments, due to the reduced metabolic rate and heat production.
Choice D reason: Constipation is not a sign of hyperthyroidism, but rather a sign of hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland produces too little thyroid hormone. Constipation means having difficulty passing stools, due to the slowed intestinal motility and digestion.
Choice E reason: Heart failure is not a sign of hyperthyroidism, but rather a complication of hyperthyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. Heart failure means the inability of the heart to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, due to the increased workload and damage to the heart muscle.
A nurse is conducting education on urinary incontinence at a senior center. The nurse is discussing lifestyle changes that are associated with an improvement in urinary incontinence. The nurse includes which of the following interventions? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A: Increase in physical activity
Physical activity can strengthen the muscles that help control urination. Exercises such as Kegels can specifically target these muscles, leading to improvements in urinary incontinence.
Choice B: Blood sugar control
While blood sugar control is important for overall health and can prevent complications from diabetes, it is not directly associated with improvements in urinary incontinence.
Choice C: Smoking cessation
Smoking can lead to coughing which puts pressure on the bladder and can exacerbate symptoms of urinary incontinence. Therefore, smoking cessation can lead to improvements.
Choice D: Weight reduction
Excess weight can put pressure on the bladder and surrounding muscles. Losing weight can reduce this pressure and improve symptoms of urinary incontinence.
There is no Choice E in this case. Each of these interventions can contribute to overall health and may indirectly affect urinary incontinence, but Choices A, C, and D are the most directly related to improvements in this condition.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 100 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

