Smith Chason Los Angeles ATI Med Surg Exam 2
Total Questions : 57
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for moreA nurse is teaching a client who has a new diagnosis of aplastic anemia. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
A. Aplastic anemia results in an inability to absorb vitamin B12: This statement is incorrect. Aplastic anemia is not related to the absorption of vitamin B12. It primarily involves a decrease in the production of blood cells by the bone marrow.
B. Aplastic anemia results from decreased bone marrow production of RBCs: This is the correct information. Aplastic anemia is a condition characterized by the failure of the bone marrow to produce an adequate number of blood cells, including red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets.
C. Aplastic anemia results in an increased rate of RBC destruction: This statement is incorrect. Aplastic anemia is not associated with an increased rate of RBC destruction. Instead, it is characterized by a reduction in the number of blood cells produced by the bone marrow.
D. Aplastic anemia is associated with a decreased intake of iron: This statement is incorrect. Aplastic anemia is not related to a decreased intake of iron. It is primarily a disorder of bone marrow function leading to insufficient production of blood cells.
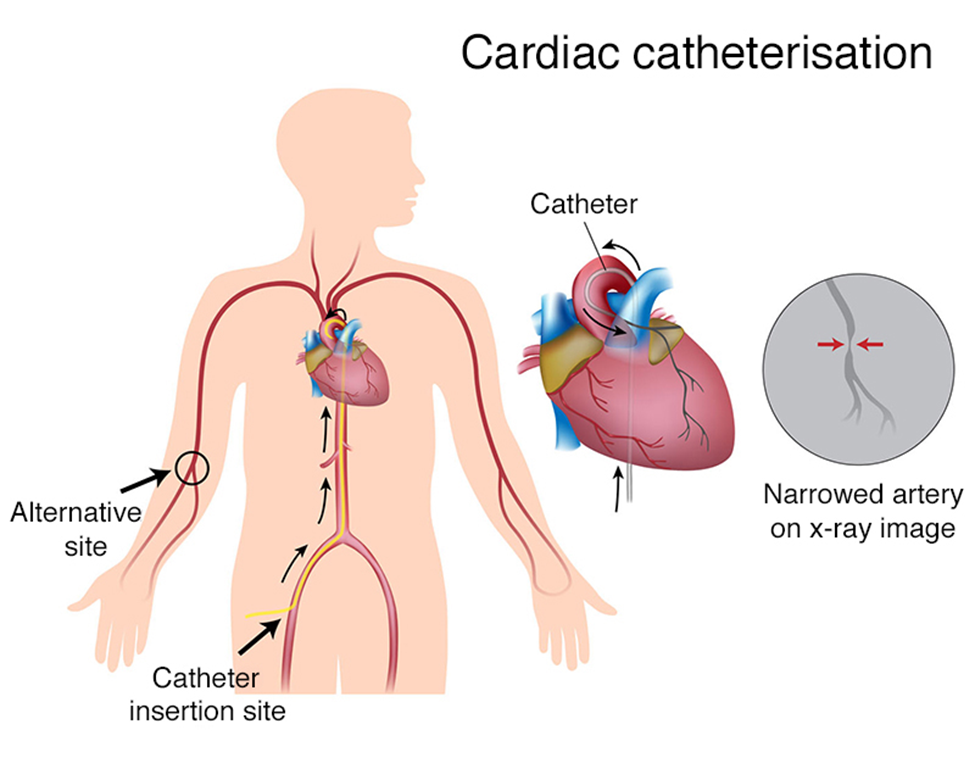
A nurse is caring for a client 4 hr following a cardiac catheterization. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. Elevate the head of the bed 45": After a cardiac catheterization, it is generally recommended to keep the head of the bed flat or in a slightly elevated position. This helps prevent stress on the insertion site.
B. Keep the affected leg slightly flexed: This is the correct action. After a cardiac catheterization, the affected leg (the one with the catheter insertion site) should be kept straight or slightly flexed at the knee to avoid stress on the femoral artery puncture site. This position helps prevent bleeding and hematoma formation.
C. Keep the client NPO for 4 hr: There is typically no need to keep the client NPO for an extended period after a cardiac catheterization. However, individual protocols may vary, and the nurse should follow the specific instructions provided by the healthcare provider.
D. Have the client lie flat in bed: While it's generally recommended to keep the head of the bed flat or slightly elevated, lying flat may put additional stress on the femoral artery puncture site. The preferred position is often with the head of the bed flat or slightly elevated and the affected leg kept straight or slightly flexed.
A nurse on a medical-surgical unit is caring for four clients who are 24 to 36 hr postoperative. Which of the following surgical procedures places the client at risk for deep-vein thrombosis?
Explanation
A. Myringotomy: Myringotomy is a procedure involving the insertion of tubes into the eardrum to treat conditions such as chronic ear infections. This procedure is not associated with a significant risk of deep-vein thrombosis.
B. Hip arthroplasty: Hip arthroplasty, or hip replacement surgery, is associated with an increased risk of deep-vein thrombosis due to factors such as immobility, surgical trauma, and alterations in blood flow. Prophylactic measures, such as anticoagulant medications and early ambulation, are often employed to reduce this risk.
C. Cataract extraction: Cataract extraction is a procedure to remove a cloudy lens from the eye. This surgery is not typically associated with a high risk of deep-vein thrombosis.
D. Laparoscopic appendectomy: Laparoscopic appendectomy, a minimally invasive procedure to remove the appendix, is generally associated with a lower risk of deep-vein thrombosis compared to major orthopedic surgeries like hip arthroplasty.
A nurse is caring for a client who is in the immediate postoperative period following a partial laryngectomy. Which of the following parameters should the nurse assess first?
Explanation
A. Tissue integrity: While assessing tissue integrity is important, ensuring airway patency takes precedence in the immediate postoperative period, especially following a procedure involving the larynx. Maintaining a patent airway is a critical priority.
B. Pain severity: Pain assessment is important, but it is not the primary concern immediately postoperatively in the context of a partial laryngectomy. Airway patency is of higher priority.
C. Airway patency: This is the correct answer. Following a partial laryngectomy, there may be concerns related to airway compromise due to the surgical procedure. The nurse should assess the airway first to ensure there are no obstructions or complications affecting the client's ability to breathe.
D. Wound drainage: While assessing wound drainage is important for monitoring surgical sites, it is not the first priority in the immediate postoperative period following a partial laryngectomy. Airway patency is a more critical concern.
A nurse is giving a presentation at a community center about chronic bronchitis. Which of the following information should the nurse include as effective for preventing this disorder?
Explanation
A. Smoking cessation: Chronic bronchitis is often associated with smoking and exposure to tobacco smoke. The most effective preventive measure for chronic bronchitis is to quit smoking and avoid exposure to secondhand smoke. Smoking cessation not only prevents chronic bronchitis but also improves overall respiratory health.
B. Regular moderate exercise: While regular exercise is beneficial for overall health, it is not specifically cited as a primary preventive measure for chronic bronchitis. However, exercise can contribute to overall respiratory health and well-being.
C. Maintenance of ideal weight: Maintaining an ideal weight is important for overall health, but it is not identified as a specific preventive measure for chronic bronchitis.
D. Annual influenza immunization: Influenza immunization is important for preventing influenza (flu) and its complications. While individuals with chronic bronchitis may be at increased risk for respiratory infections, annual influenza immunization is not a direct preventive measure for chronic bronchitis itself.
A nurse is assessing a client who has postoperative atelectasis and is hypoxic. Which of the following manifestations should the nurse expert?
Explanation
A. Bradypnea: Bradypnea refers to abnormally slow breathing. In the context of postoperative atelectasis and hypoxia, the client is more likely to exhibit tachypnea (rapid breathing) as the body attempts to compensate for reduced oxygen levels.
B. Bradycardia: Bradycardia is an abnormally slow heart rate. While hypoxia can lead to changes in heart rate, it is more common to observe tachycardia (increased heart rate) as a compensatory response to decreased oxygen levels.
C. Intercostal retractions: Intercostal retractions occur when the muscles between the ribs pull inward during inspiration. In a client with atelectasis and hypoxia, increased respiratory effort may result in intercostal retractions as the body tries to enhance airflow and improve oxygenation.
D. Lethargy: Lethargy refers to a state of drowsiness or fatigue. While hypoxia can lead to lethargy, it is not a specific respiratory manifestation. Other respiratory signs, such as increased respiratory rate and retractions, are more likely to be observed.
A nurse is reviewing the PT, aPTT, and INR laboratory values for a client who is experiencing an acute episode of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Which of the following laboratory results should the nurse expect?
Explanation
A. The laboratory values are the same as the previous test values: This is unlikely in DIC. In an acute episode of DIC, there is usually a significant disturbance in coagulation values due to the consumption of clotting factors and the development of clotting abnormalities.
B. The laboratory values are within the expected reference range: In DIC, the coagulation values are usually not within the expected reference range. Instead, they are prolonged, reflecting the imbalance in the coagulation system.
C. The laboratory values are prolonged: This is the correct answer. In DIC, the PT, aPTT, and INR are prolonged because the coagulation factors are being consumed in the process of widespread clot formation.
D. The laboratory values are decreased: This is not typical for DIC. In DIC, the issue is not a decrease in clotting factors but rather their consumption, leading to an overall imbalance in the coagulation system.
A nurse is teaching a client who has tuberculosis and is to start combination drug therapy. Which of the following medications should the nurse plan to administer? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
A. Montelukast: Montelukast is a leukotriene receptor antagonist commonly used in the management of asthma and allergic rhinitis. It is not part of the standard tuberculosis treatment regimen.
B. Rifampin: Rifampin is a key component of tuberculosis treatment and is effective against both active and latent tuberculosis.
C. Acyclovir is an antiviral medication primarily used for herpes simplex virus infections and is not part of the standard treatment for tuberculosis.
D. Isoniazid: Isoniazid is another essential drug in the treatment of tuberculosis, particularly for the prevention of latent tuberculosis progression to active disease.
E. Pyrazinamide: Pyrazinamide is part of the standard combination therapy for tuberculosis.
A nurse is caring for a client who has a central venous catheter and suddenly develops chest pain, dyspnea, dizziness, and tachycardia. The nurse suspects air embolism and clamps the catheter immediately. What other action should the nurse take at this time?
Explanation
A. Remove the catheter: Removing the catheter may not be the immediate priority. The nurse should focus on preventing further air entry into the circulation and addressing the symptoms.
B. Replace the infusion system: While ensuring that the infusion system is intact is important, it is not the primary action needed to manage an air embolism.
C. Prepare for chest tube insertion: Chest tube insertion is not the primary intervention for an air embolism. The focus should be on preventing the progression of the embolism and providing supportive care.
D. Place the client on his left side in Trendelenburg position: This is the correct answer. Placing the client on the left side in Trendelenburg position is a maneuver used to trap air in the right atrium, preventing it from traveling to the pulmonary artery. The left side position helps to prevent the air from traveling to the right ventricle and into the pulmonary artery, reducing the risk of further complications.
A nurse is auscultating a client's heart sounds and hears an extra heart sound before what should be considered the first heart sound S1. The nurse should document this finding as which of the following heart sounds?
Explanation
A. A friction rub: A friction rub is a high-pitched, scratchy sound heard during the cardiac cycle, typically indicative of inflammation of the pericardial sac. It is not an extra heart sound but rather an abnormal sound associated with inflammation.
B. A split second heart sound (S₂): The split second heart sound refers to the splitting of the second heart sound (S₂) into two components, usually associated with changes in the closure of the aortic and pulmonic valves. It is not an extra heart sound occurring before S₁.
C. The third heart sound (S₃): This is the correct answer. The third heart sound (S₃) is an extra heart sound occurring early in diastole, often associated with heart failure or volume overload. It is heard after S₂ and before S₁.
D. The fourth heart sound (S₄): The fourth heart sound (S₄) is another extra heart sound that occurs late in diastole. It is associated with conditions that result in decreased ventricular compliance.
A nurse is providing discharge instructions to a client who developed deep-vein thrombosis (DVT) postoperatively and is prescribed anticoagulant therapy. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
Explanation
A. Wearing loose, non-constricting stockings: This instruction is not recommended for a client with DVT. Compression stockings, which are snug-fitting, may be prescribed to prevent DVT, but loose stockings would not provide the necessary compression.
B. Applying cool compresses to her legs: Cool compresses are not typically recommended for DVT. Warm compresses may be used to improve blood circulation, but cold compresses may not be suitable.
C. Taking an NSAID tablet daily: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are not typically recommended for individuals with DVT, especially when on anticoagulant therapy, as they may increase the risk of bleeding.
D. Flexing her knees and feet frequently: This is the correct answer. Encouraging the client to flex her knees and feet frequently helps promote blood circulation and reduces the risk of venous stasis, which can contribute to the formation of blood clots. It is a beneficial measure for clients with DVT.
A nurse is planning care for a client following a cardiac catheterization accessed through his femoral artery. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take?
Explanation
A. Restrict the client's fluid intake: There is typically no need to restrict fluid intake after a cardiac catheterization. Adequate hydration is important for preventing complications and promoting recovery.
B. Ambulate the client 1 hr following the procedure: While early ambulation is encouraged in many cases, the timing may vary based on the specific protocols of the healthcare provider. It is important to follow the healthcare provider's orders regarding post-catheterization ambulation.
C. Instruct the client to perform range-of-motion exercises to his lower extremities: Range-of-motion exercises are beneficial to prevent complications such as venous stasis and deep vein thrombosis. However, the specific exercises and timing may vary. It is important to follow the healthcare provider's instructions.
D. Perform neurovascular checks with vital signs: This is the correct answer. After a cardiac catheterization accessed through the femoral artery, it is crucial to monitor neurovascular status in the affected extremity. Assessing peripheral pulses, skin color, temperature, and capillary refill, along with monitoring vital signs, helps detect any signs of complications such as bleeding or vascular compromise.
A nurse is caring for a client who is postoperative and whose respirations are shallow and 9/min. Which of the following acid-based imbalances should the nurse identify the client as being at risk for developing initially?
Explanation
A. Respiratory alkalosis: Respiratory alkalosis is characterized by a decrease in carbonic acid (CO2) due to hyperventilation, leading to an increased pH. Shallow respirations would not typically cause respiratory alkalosis.
B. Respiratory acidosis: This is the correct answer. Shallow respirations result in inadequate elimination of CO2, leading to an excess of carbonic acid and the development of respiratory acidosis.
C. Metabolic acidosis: Metabolic acidosis is characterized by a decrease in bicarbonate (HCO3-), not carbonic acid (CO2). Shallow respirations would not directly contribute to metabolic acidosis.
D. Metabolic alkalosis: Metabolic alkalosis is characterized by an increase in bicarbonate (HCO3-). Shallow respirations would not typically cause metabolic alkalosis.
The nurse is caring for a client who has heart failure and a history of asthma. The nurse reviews the provider's orders and recognizes that clarification is needed for which of the following medications?
Explanation
A. Carvedilol: Carvedilol is a beta-blocker with additional alpha-blocking properties commonly used in heart failure management. It may be beneficial in heart failure, but caution is needed in patients with asthma as beta-blockers can potentially exacerbate bronchospasm.
B. Captopril: Captopril is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor used in heart failure. It can be part of heart failure management, and its use is generally appropriate.
C. Isosorbide dinitrate: Isosorbide dinitrate is a nitrate used for the management of heart failure and angina. It can be beneficial in dilating blood vessels and reducing the workload on the heart.
D. Fluticasone: Fluticasone is an inhaled corticosteroid commonly used in asthma management. In this context, considering the client's history of asthma and heart failure, there might be concern about the use of inhaled corticosteroids due to potential effects on fluid retention and exacerbation of heart failure symptoms. Therefore, the nurse should seek clarification about the use of fluticasone in this particular client.
A client is admitted to the emergency room with a respiratory rate of 7/min. Arterial blood gases (ABG) reveal the following values. Which of the following is an appropriate analysis of the ABGs?
pH 7.22
PaCO2 68 mm Hg
Base excess -2
PaO2 78 mm Hg
Saturation 80%
Bicarbonate 26 mEq/L
Explanation
pH 7.22: Indicates acidosis (normal range: 7.35-7.45).
PaCO2 68 mm Hg: Elevated partial pressure of carbon dioxide, suggesting respiratory acidosis (normal range: 35-45 mm Hg).
Base excess -2: Indicates a mild metabolic acidosis.
PaO2 78 mm Hg: Within the normal range (80-100 mm Hg), indicating adequate oxygenation.
Saturation 80%: Below the normal range (95-100%), suggesting some degree of hypoxemia.
Bicarbonate 26 mEq/L: Elevated bicarbonate levels, suggesting metabolic compensation for the respiratory acidosis.
Therefore, the client is experiencing respiratory acidosis with partial metabolic compensation (mild metabolic acidosis).
A nurse is assessing a client for hypoxemia during an asthma attack. Which of the following manifestations should the nurse expect?
Explanation
A. Nausea: While respiratory distress can lead to various symptoms, nausea is not a typical manifestation of hypoxemia during an asthma attack.
B. Dysphagia: Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) is not a direct manifestation of hypoxemia during an asthma attack. Asthma primarily affects the airways and respiratory function.
C. Hypotension: Hypotension (low blood pressure) is not typically associated with hypoxemia during an asthma attack. In fact, increased respiratory effort and stress can lead to increased heart rate and, in some cases, increased blood pressure.
D. Agitation: This is the correct answer. Hypoxemia, which occurs when there is an inadequate amount of oxygen in the blood, can lead to increased restlessness, anxiety, and agitation. Agitation is a common manifestation of the body's response to insufficient oxygenation.
A nurse is reviewing a client's laboratory results and finds the hemoglobin is 10 g/dL. and the hematocrit is 30%. The nurse recognizes that the client is at risk for which of the following?
Explanation
A. Cellular hypoxia: Hemoglobin carries oxygen to the body's tissues. A low hemoglobin level, as well as a low hematocrit, indicates a reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood, putting the client at risk for cellular hypoxia. Symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
B. Prolonged bleeding: Hemoglobin and hematocrit levels are not directly indicative of a risk of prolonged bleeding. Prolonged bleeding is more related to platelet function and clotting factors.
C. Impaired immunity: Hemoglobin and hematocrit levels are not directly indicative of impaired immunity. Immune function is more closely associated with white blood cell count and function.
D. Fluid retention: Hemoglobin and hematocrit levels are not directly associated with fluid retention. Fluid retention is more related to factors such as sodium balance and kidney function.
A college health nurse interprets the peak expiratory flow rate for a student who has asthma and finds that the student is in the yellow zone of his asthma action plan. The nurse should base her actions on which of the following information? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Asthma action plans often use a color-coded system to guide management based on peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) measurements. The zones are typically green (80-100% of personal best), yellow (50-79% of personal best), and red (less than 50% of personal best).
A. The student needs to go to the hospital.
This is not necessarily true for the yellow zone. Going to the hospital is usually indicated in the red zone, which indicates severe impairment.
B. The nurse should obtain a second expiratory flow rate.
While obtaining a second measurement can be helpful for confirming accuracy, immediate action is often recommended in the yellow zone to prevent worsening.
C. The student should use his quick-relief inhaler.
In the yellow zone, indicating moderate impairment, the use of a quick-relief (rescue) inhaler is often recommended to relieve symptoms and prevent progression to the red zone.
D. The student's peak flow is 50% to 80% of his best peak flow.
This is the correct range for the yellow zone, indicating moderate impairment. Action is needed to prevent worsening.
E. The student's asthma is not well controlled.
The yellow zone suggests that the student's asthma is not well controlled at that moment, and intervention is needed to prevent further deterioration.
A nurse is caring for a client who has COPD.
Medication
Indacaterol 75 mcg, one inhalation daily
Acetylcysteine 20% solution 3 to 5 ml nebulizer every 6 to 8 hr while awake
Select the 5 findings that require follow-up.
Explanation
A. Disorientation:
This may indicate a neurological or cognitive issue and requires further assessment.
B. Barrel-shaped chest:
This is a characteristic finding in COPD, but any change or worsening may need evaluation.
C. Yellow sputum:
Yellow or greenish sputum may indicate an infection, and follow-up is needed.
D. Nebulizer use:
Nebulizer use is part of the prescribed treatment.
E. Ankle edema:
Edema can be a sign of heart failure or other cardiovascular issues and should be investigated.
F. SaO2 92%:
Oxygen saturation of 92% is below the normal range. It may indicate respiratory compromise and needs attention.
G. Clubbing of fingers:
While clubbing can be associated with chronic respiratory conditions, it is not an immediate concern.
H. Lives alone:
Living alone may impact the client's support system but does not require immediate medical attention.
A nurse is caring for a client who is postoperative and is at risk for developing venous thromboembolism (VTE). The nurse should instruct the client to avoid which of the following unsafe actions?
Explanation
A. Flexing her ankles: Ankle flexion exercises and periodic ankle flexion are encouraged to promote blood circulation and prevent venous stasis, which can contribute to the development of venous thromboembolism (VTE).
B. Elevating her feet: Elevating the feet can also help prevent venous stasis and promote blood circulation. It is a recommended action to reduce the risk of VTE.
C. Massaging her legs: This is the correct answer. Massage of the legs, particularly deep tissue massage, can dislodge blood clots and increase the risk of embolization, including the risk of venous thromboembolism.
D. Ambulating soon after surgery: Early ambulation is an important preventive measure for VTE. It helps stimulate blood flow and prevents venous stasis. Encouraging the client to ambulate as soon as possible after surgery is a recommended practice.
A nurse is providing instructions to a client who has a new prescription for sublingual nitroglycerin (Nitrostat) to treat angina pectoris. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
Explanation
A. "The medication can take up to 15 minutes to take effect." - This statement is not accurate, sublingual nitroglycerin works rapidly and often provides relief within a few minutes.
B. Sublingual nitroglycerin is administered by placing the tablet under the tongue, and it should be allowed to dissolve or be absorbed directly into the bloodstream through the mucous membranes. It is not swallowed or chewed. The small sip of water can help facilitate the dissolving process.
C. "Avoid taking the medication prior to exercising." - This statement is not accurate. Nitroglycerin can be taken before anticipated exertion or activities that may trigger angina to prevent anginal episodes during physical activity.
D. "Stop taking the medication and notify your provider if you develop a headache." - While headaches are a common side effect of nitroglycerin, they are generally transient and not a reason to stop taking the medication. Persistent or severe headaches should be reported to the healthcare provider.
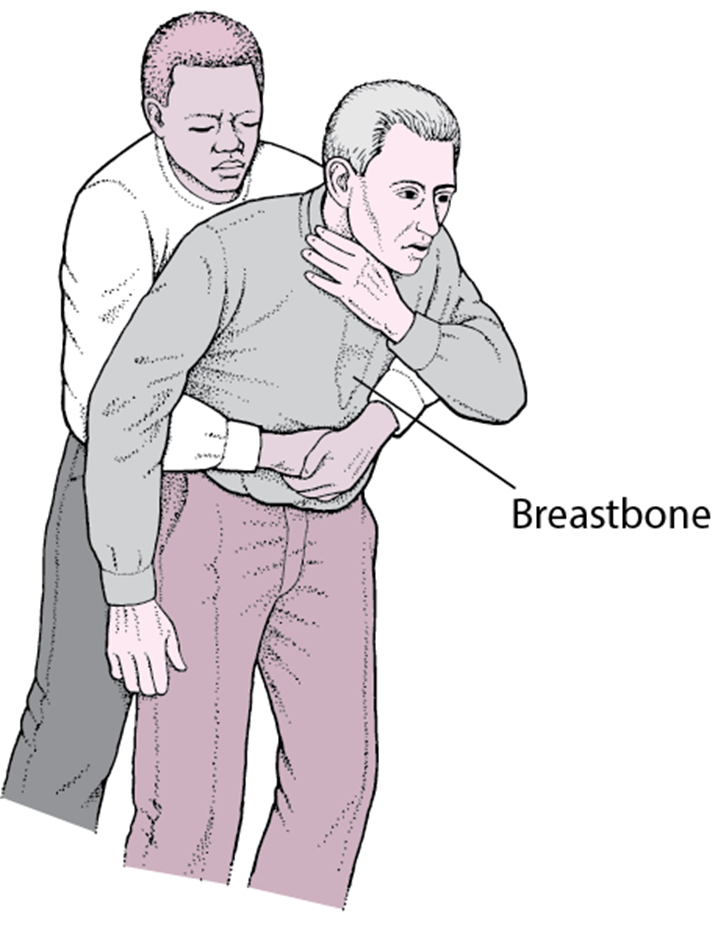
A nurse is dining at a restaurant when a woman begins to scream that her partner is choking. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. Instruct the woman to call 911: This is a correct action, but it should be the second step after the nurse initiates first aid measures. Directing someone to call for emergency assistance is crucial, but immediate intervention to relieve the choking takes precedence.
B. The Heimlich maneuver involves abdominal thrusts and is the recommended technique for relieving choking in a conscious person. It is essential to act quickly and decisively to clear the airway.
C. Ask the partner if he can speak: If the person is unable to speak, cough, or breathe, it may indicate complete airway obstruction. The nurse should not delay intervention by asking if the person can speak but should immediately proceed with measures to relieve the choking.
D. Perform chest compressions: Chest compressions are not indicated for a conscious choking victim. Chest compressions are performed in the context of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) for an unconscious person with no pulse.
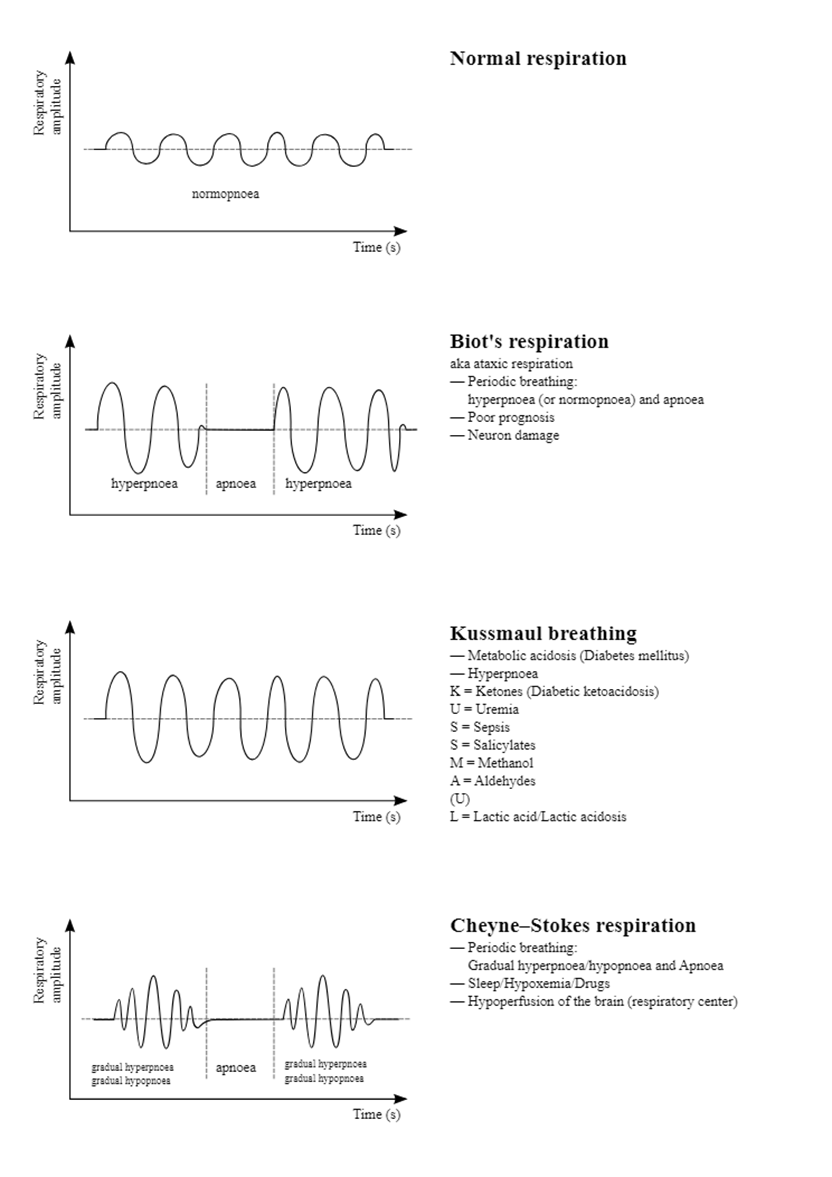
A nurse is caring for a client who is unconscious and has a breathing pattern characterized by alternating periods of hyperventilation and apnea. The nurse should document that the client has which of the following respiratory alterations?
Explanation
A. Cheyne-Stokes respirations: Cheyne-Stokes respirations are characterized by alternating periods of hyperventilation followed by apnea. This respiratory pattern is often observed in clients with conditions affecting the central nervous system, such as brain injury or stroke.
B. Apneustic respirations: Apneustic respirations are characterized by prolonged, gasping inhalations followed by extremely short, ineffective exhalations. This pattern is associated with damage to the pons, a part of the brainstem.
C. Stridor: Stridor is a high-pitched, noisy breathing sound caused by turbulent airflow through a partially obstructed airway. It is not related to the described alternating pattern of hyperventilation and apnea.
D. Kussmaul respirations: Kussmaul respirations are deep, rapid respirations often seen in metabolic acidosis. They are not characterized by the alternating pattern described in the scenario.
A nurse is caring for a client who has active pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) and a new prescription for IV rifampin. The nurse should instruct the client that they should expect to experience which of the following manifestations while taking this medication?
Explanation
A. Red-colored urine: Rifampin, when taken orally or intravenously, can cause red discoloration of bodily fluids, including urine, sweat, saliva, and tears. This is a common and harmless side effect of the medication. Clients should be informed about this potential discoloration to avoid unnecessary concern.
B. Black-colored stools: Black-colored stools are not an expected side effect of rifampin.
C. Staining of teeth: While rifampin can cause staining of contact lenses, it is not associated with tooth discoloration.
D. Constipation: Constipation is not a common side effect of rifampin. Gastrointestinal side effects may include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
A nurse is admitting a client who has active tuberculosis to a room on a medical-surgical unit. Which of the following room assignments should the nurse make for the client?
Explanation
A. A room that is within view of the nurses' station: While visibility to the nurses' station is advantageous for monitoring the client, it is not the most critical consideration for a client with active tuberculosis. The priority is to prevent the spread of infectious droplets to other clients and healthcare workers.
B. A room in the ICU: Placing a client with active tuberculosis in the ICU may not be necessary unless there are specific medical reasons requiring intensive care. However, the room assignment should prioritize infection control measures.
C. A room with another nonsurgical client: It is not advisable to place a client with active tuberculosis in a room with another nonsurgical client due to the risk of spreading the infection to a potentially vulnerable individual.
D. A room with air exhaust directly to the outdoor environment: This is the correct answer. The preferred room assignment for a client with active tuberculosis is one with proper ventilation that allows air to be exhausted directly to the outdoor environment. Negative pressure rooms with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration are often used to minimize the risk of airborne transmission.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 57 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

